Highlights
What are the main findings?
- PS-InSAR accurately captured millimeter-scale settlements along the Honam High-Speed Railway embankments, showing strong agreement with leveling survey results (MAE = 1.7–4.2 mm).
- Quantitative regression analysis demonstrated that land-cover composition—particularly the balance between vegetation and high-reflectivity surfaces—explains a significant portion of the variability in PS-InSAR accuracy and persistent scatterer density.
What is the implication of the main finding?
- The study transforms the well-known limitation of vegetation-induced decorrelation into a predictive framework by statistically modeling its influence on PS-InSAR performance.
- The proposed regression-based approach provides practical guidance for selecting monitoring zones and determining when complementary ground-based surveys are required, thereby improving the reliability of satellite-based settlement monitoring strategies for railway infrastructure management.
Abstract
Accurate monitoring of settlement in high-speed railway embankments is critical for operational safety and long-term serviceability. This study investigates the applicability of Persistent Scatterer Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar (PS-InSAR) for quantifying millimeter-scale deformations and emphasizes how surrounding environmental factors influence measurement accuracy. Using 29 TerraSAR-X images acquired between 2016 and 2018, PS-InSAR-derived settlements were compared with precise leveling survey data across twelve representative embankment sections of the Honam High-Speed Railway in South Korea. Temporal and spatial discrepancies between the two datasets were harmonized through preprocessing, allowing robust accuracy assessment using mean absolute error (MAE) and standard deviation (SD). Results demonstrate that PS-InSAR reliably captures settlement trends, with MAE ranging from 1.7 to 4.2 mm across different scenes. However, significant variability in accuracy was observed depending on local land-cover composition. Correlation analysis revealed that vegetation-dominated areas, such as agricultural and forest land, reduce persistent scatterer density and increase measurement variability, whereas high-reflectivity surfaces, including transportation facilities and buildings, enhance measurement stability and precision. These findings confirm that environmental conditions are decisive factors in determining the performance of PS-InSAR. The study highlights the necessity of integrating site-specific land-cover information when designing and interpreting satellite-based monitoring strategies for railway infrastructure management.
1. Introduction
High-speed railway construction has rapidly expanded worldwide over the past two decades, driven by the demand for greater transportation capacity, improved network availability, and reduced environmental impact. In particular, in countries with extensive high-speed rail networks, stringent standards are applied to control post-construction settlement, as excessive or uneven settlement can compromise passenger comfort, ride quality, and operational safety for trains operating at speeds exceeding 200 km/h [1]. Settlement monitoring in railway infrastructure typically involves two complementary approaches: continuous monitoring through the installation of settlement plates and extensometers, and periodic monitoring through optical surveying methods, such as total station measurements. While these conventional methods are widely adopted, they present limitations. Direct-contact sensors can be damaged, lost, or suffer data interruptions, while optical surveys—though highly accurate—are costly for continuous, long-term deployment and are constrained in terms of spatial coverage and accessibility.
In recent decades, remote sensing technologies, particularly Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar (InSAR), have been extensively developed and established as powerful tools for large-scale, long-term deformation monitoring. InSAR operates by transmitting microwave signals from a satellite, receiving the reflected signals, and using the phase difference between successive acquisitions to measure surface displacement with millimeter-level accuracy. Unlike optical imaging, InSAR measurements are largely unaffected by cloud cover or weather conditions and can be obtained repeatedly over broad areas [2,3]. Depending on data acquisition and processing methods, InSAR techniques are often classified into Differential InSAR (D-InSAR) and Persistent Scatterer InSAR (PS-InSAR). Carnec et al. first demonstrated the feasibility of D-InSAR for measuring small-scale ground deformation in mining areas [4]. Since then, researchers have widely applied InSAR to mining subsidence detection and deformation analysis [3,5,6].
Among InSAR techniques, PS-InSAR offers notable advantages for infrastructure monitoring. By analyzing a stack of 25 or more SAR images acquired over the same area, PS-InSAR enables time-series displacement estimation while mitigating atmospheric delays, DEM errors, and orbital inaccuracies. This capability makes PS-InSAR particularly suitable for urban environments and critical infrastructure where high accuracy is required. Applications have included building collapse risk mapping [7], tunnel construction monitoring [8], and post-earthquake deformation mapping and fault modeling [9,10,11,12,13]. Furthermore, Hu et al. demonstrated the benefits of integrating InSAR with LiDAR to overcome geolocation limitations and enhance the detection of railway system deformations [14]. In recent years, PS-InSAR and related time-series InSAR methods have been increasingly adopted for deformation monitoring of linear infrastructures, including bridges, pavements, and transport corridors. For example, Tonelli et al. (2023) [15] applied multi-temporal InSAR to a road bridge and interpreted displacement responses in relation to temperature and water-level changes. Farneti et al. (2023) [16] proposed a method to extract 2D displacement fields of multispan bridges from InSAR data with quantified uncertainty bounds. Biondi et al. (2020) [17] reviewed the potential of SAR-based structural health monitoring (SHM) for bridges, highlighting opportunities and challenges in applying PS techniques. Wu et al. (2023) [18] examined radar interferometry for urban infrastructure stability, showing how urban geometry and scattering conditions influence coherence and deformation detection. Meanwhile, Jiang & Yu (2025) [19] demonstrated seasonal pavement elevation monitoring in a cold-climate setting using PS-InSAR to detect frost heave and thaw settlement cycles. More recently, Lee et al. (2025) [20] conducted a comprehensive PS-InSAR investigation of the Honam High-Speed Railway in South Korea, successfully mapping ground deformation patterns and demonstrating the capability of high-resolution InSAR data for long-term monitoring of high-speed rail infrastructure. Their work represents an important advancement in satellite-based railway deformation analysis and clearly established the potential of InSAR for high-precision track-bed monitoring under Korean site conditions.
Despite these advancements, relatively few studies have investigated how environmental conditions—such as terrain, vegetation, land use, and cadastral characteristics—affect the spatial distribution and accuracy of PS points. For linear infrastructures like railway embankments, the radar backscatter properties of the surrounding land cover can substantially influence PS point density and the reliability of displacement measurements. Vegetated areas may reduce PS density due to temporal decorrelation, whereas urbanized areas with hard, reflective surfaces tend to improve measurement stability. However, a quantitative understanding of these effects remains limited, hindering the optimization of PS-InSAR monitoring strategies for site-specific conditions. Especially, while Lee et al. (2025) [20] effectively visualized deformation trends, their study focused primarily on detecting and characterizing displacement and did not explicitly quantify how environmental or land-cover conditions influence the accuracy of PS-InSAR measurements. Because radar backscatter and temporal coherence are strongly dependent on surface characteristics, a deeper statistical understanding of these relationships is essential for improving the reliability of satellite-based deformation monitoring.
In this study, we build upon the foundation established by Lee et al. (2025) [20] by performing a detailed quantitative assessment of how surrounding land-cover composition affects PS-InSAR accuracy in high-speed railway embankments. Using twelve representative sections of the Honam HSR, PS-InSAR results were compared with leveling survey data, and statistical regression models were developed to describe the relationship between accuracy indicators—such as mean absolute error (MAE) and standard deviation (SD)—and land-cover parameters. This approach provides a new quantitative framework for evaluating environmental influences on PS-InSAR performance and offers practical insights for optimizing satellite-based monitoring strategies for linear infrastructures.
2. PS-InSAR-Based Assessment of Concrete Track Settlement Measurement Accuracy
2.1. Study Area
The study area is located along the Honam High-Speed Railway (HSR) in South Korea, a major trunk line designed to enhance national transport capacity and regional connectivity. The Honam HSR was inaugurated in April 2015, linking the capital region near Osong to the city of Gwangju and ultimately extending to Mokpo. The total length of the line is approximately 230 km, constructed predominantly on embankments and railway bridges to accommodate train speeds up to 300 km/h. The line was developed to alleviate congestion on the existing Honam conventional line and to reduce travel time between the Seoul metropolitan area and the southwest of the Korean Peninsula.
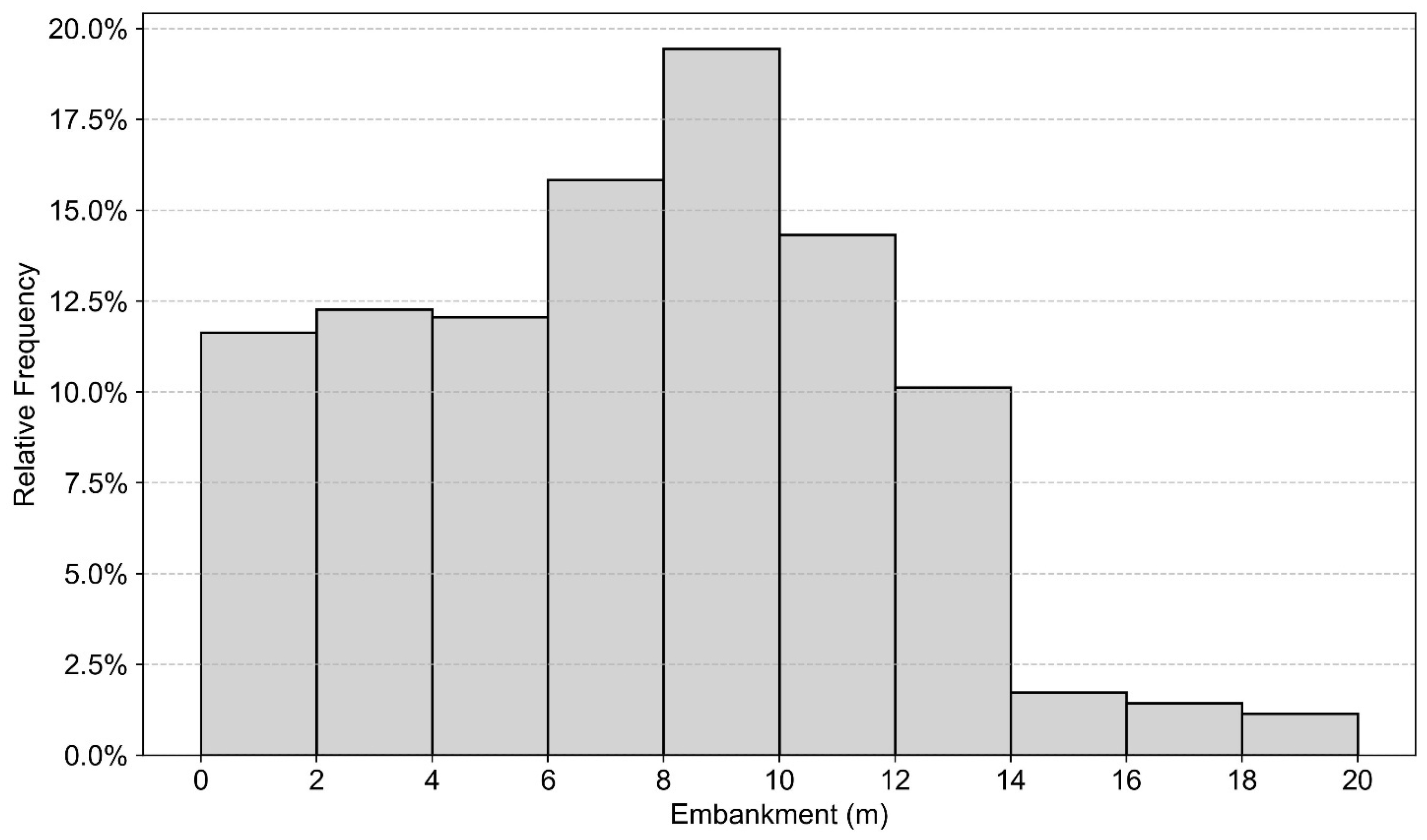
From a geotechnical perspective, the Honam HSR traverses a wide range of soil conditions, including soft alluvial deposits in floodplain areas and weathered residual soils in inland regions. In addition, many embankment sections have considerable height, raising concerns about significant settlement; the embankments have an average height of 7.0 m, with a maximum of 19.5 m, and the most frequent height observed is 9.0 m. Analysis by height categories shows that 38.9% of the embankments are less than 6.0 m high, 38.0% are between 6.0 m and 10.0 m, and 23.1% exceed 10.0 m (Figure 1). Settlement control of the railway substructure is therefore of critical importance, as uneven or excessive post-construction settlement can degrade track alignment, ride quality, and operational safety of high-speed trains. To mitigate such risks, the Honam HSR has been the subject of extensive geotechnical monitoring and instrumentation programs, including settlement plates, extensometers, and periodic leveling surveys conducted along representative embankment sections. These ground-based data provide valuable references against which satellite-based monitoring techniques, such as PS-InSAR, can be evaluated.
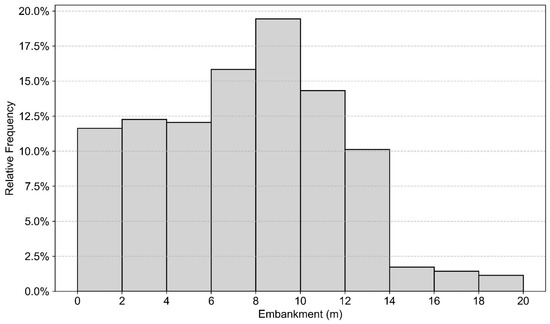
Figure 1.
Embankment Height Distribution of Honam HSR.
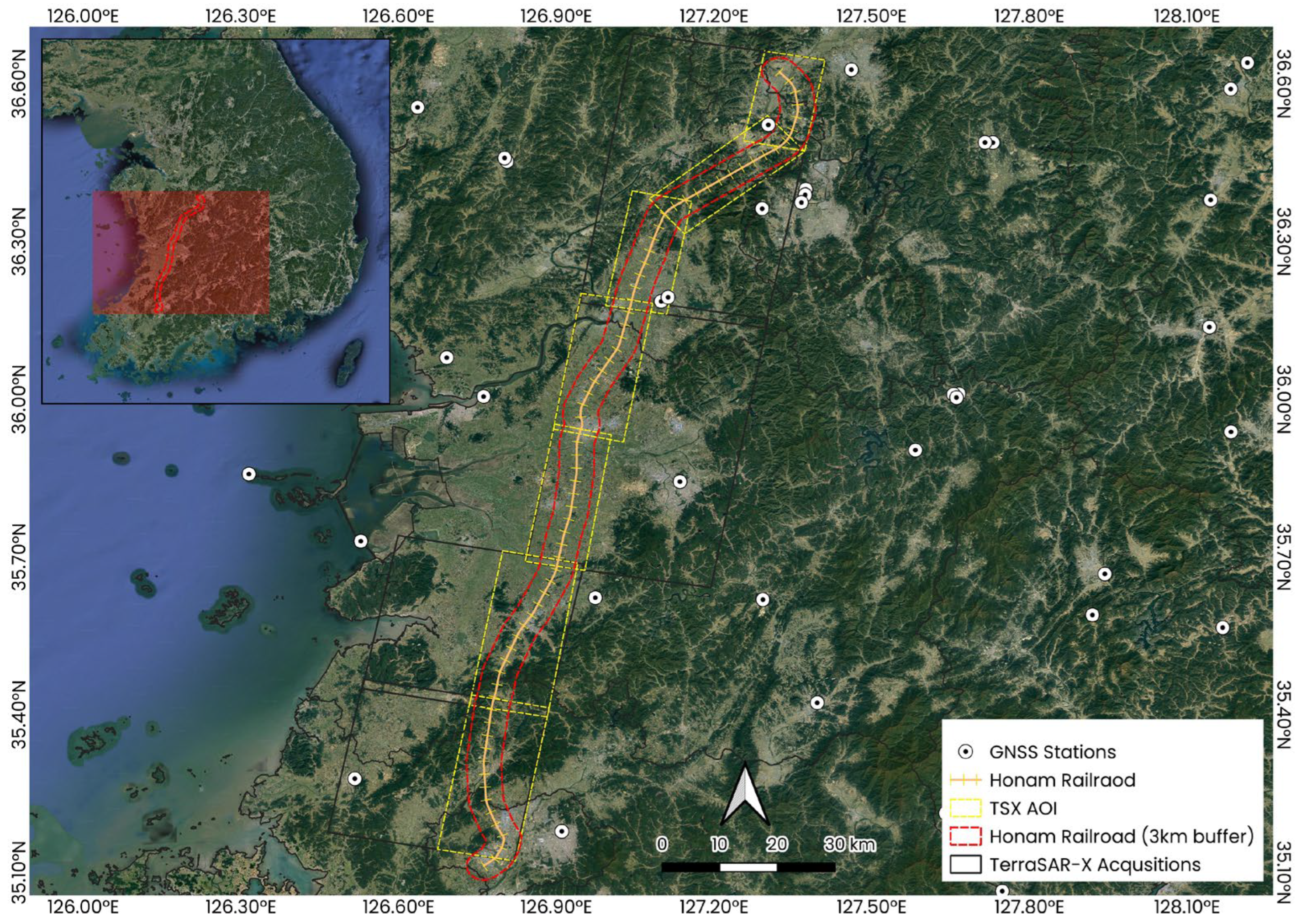
Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) images are generated by measuring the electromagnetic waves emitted and subsequently reflected from the Earth’s surface. Consequently, the characteristics of these reflected waves significantly influence image interpretation, with accuracy varying depending on whether areas exhibit high or low reflectivity. Generally, high radar intensity signifies an excellent reflected signal. Rigid structures and steel frameworks typically exhibit very high reflection intensities, whereas flat terrains, vegetated zones, and water bodies such as rivers tend to show relatively low reflection intensities due to specular reflection and low coherence. In this study, twelve representative embankment sections along the Honam HSR were selected for detailed analysis, also taking into account the availability of leveling survey data. These sections cover diverse land-cover environments—ranging from agricultural fields and forested zones to urbanized corridors—thus allowing for a systematic assessment of how surrounding environmental factors influence PS-InSAR measurement density and accuracy. As illustrated in Figure 2, the selected embankment sections are distributed across diverse land-cover environments, which provides a representative dataset for evaluating how surrounding conditions affect PS-InSAR accuracy.
Figure 2.
Study area with selected embankment sections for analysis.
Settlement measurement of concrete slab tracks using leveling surveys is performed using settlement pins installed at the center of the track gauge (for both up and down directions). The settlement pins were installed at 5 m intervals in sections where settlement is a concern, such as at bridge-embankment and tunnel-embankment transition zones and soft soil areas, and at 10 m intervals in standard embankment sections [21]. The pins are secured by drilling a hole with a hammer drill, injecting an adhesive (e.g., epoxy), and inserting the pin. They are positioned at the center of the track to minimize measurement errors during the process.
The accuracy of the leveling survey must be maintained within ±1 mm, and measured values are recorded to the nearest 0.1 mm. Measurements are performed by closing a loop with round-trip readings for each benchmark, with the closing error required to be within 1.5√S mm (where S is the observation distance in km). For locations where settlement has not converged, the measurement frequency is increased, and continuous monitoring is conducted until the annual settlement is below 2 mm. Depending on the rate of settlement, measurements are performed two to four times a year. In this study, to allow for more comparisons with the PS-InSAR results, sections with a relatively high rate of settlement, where four annual leveling surveys are conducted, were selected.
2.2. Methodology: Settlement Evaluation Using PS-InSAR
PS-InSAR is a multi-temporal InSAR technique designed to measure ground deformation with millimeter-level precision by analyzing radar phase changes from stable reflectors over time [22]. Unlike traditional differential InSAR, which suffers from coherence loss in vegetated areas and atmospheric phase artifacts, PS-InSAR overcomes these limitations by focusing on highly stable scatterers—such as rails and built infrastructure—well-suited for railway monitoring [14].
TerraSAR-X X-band images were employed due to their high spatial resolution and short wavelength, which are advantageous for detecting subtle deformations along steel-based railway structures. The satellite operates with an 11-day revisit cycle, and in this study, StripMap mode data with approximately 22-day intervals were utilized between August 2016 and September 2018. The StripMap mode was selected to accommodate the long and narrow geometry of the high-speed railway corridor, allowing consistent observation coverage with adequate spatial resolution for PS-InSAR processing. The X-band configuration offers enhanced sensitivity to surface features and is therefore well suited for infrastructure monitoring where reflective metallic and concrete components are dominant.
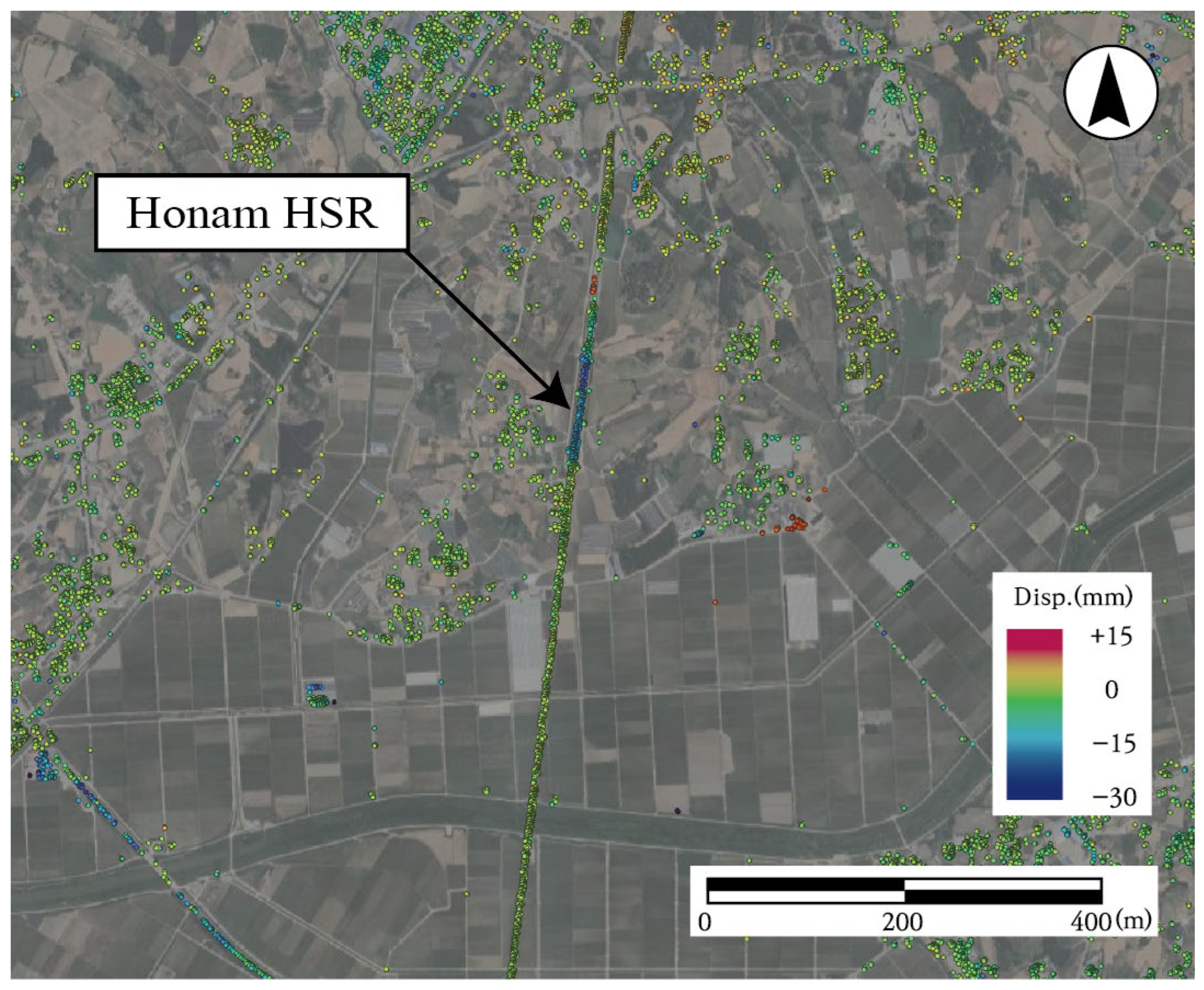
The PS-InSAR analysis in this study was conducted using ENVI SARScape 5.6.0, a commercial platform that implements the standard PS-InSAR processing workflow. The overall workflow included co-registration of SAR images, interferogram generation, selection of stable pixels, estimation of the atmospheric phase screen (APS), and phase unwrapping. First, SAR image stacks were co-registered with DEM support to eliminate flat-earth and topographic phase contributions. Differential interferograms were then formed using a single-master strategy, with coherence maps guiding stable candidate selection [23]. Persistent scatterer candidates were identified using the Amplitude Dispersion Index (, where and denote the standard deviation and mean amplitude, respectively) typically with thresholds below 0.25–0.4 to preserve phase reliability. After correcting for orbital and DEM-related phase errors, low-pass spatial and high-pass temporal filtering were applied to separate deformation signals from long-wavelength atmospheric artifacts [24]. Finally, the unwrapped phases were inverted into displacement time series relative to a stable reference point, and the results were geocoded for spatial interpretation. This process yielded deformation rates and time-series information for each PS point, which were used for comparison with ground-based leveling data and subsequently integrated into GIS for identifying vulnerable railway segments (e.g., embankments, tunnel approaches) [25]. As shown in Figure 3, the resulting LOS deformation map visualizes the spatial distribution of PS points and the corresponding deformation patterns along the Honam HSR embankment section.
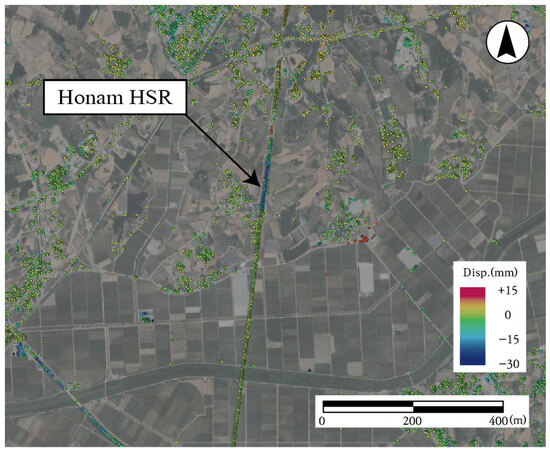
Figure 3.
An example of line-of-sight deformation map of the Honam High-Speed Railway derived from PS-InSAR analysis (positive is uplift, negative is settlement).
To enhance the accuracy of the PS-InSAR analysis, this study adopted optimized processing parameters previously validated through a systematic parametric analysis presented in Kim et al. (2024) [26]. That study comprehensively evaluated the influence of key parameters—such as coherence threshold, sub-area overlap, and spatial/temporal filter sizes—on the stability and precision of TerraSAR-X–derived displacement results for the same Honam HSR corridor. The findings confirmed that variations within the optimized parameter ranges (e.g., coherence threshold 0.6–0.9, overlap ±5%, spatial filter 300–1200 m, and temporal filter 180–782 days) demonstrating the robustness of the adopted configuration. Accordingly, this study applied these validated parameters to ensure methodological consistency and reliable comparison with ground-based leveling data. The final set of parameters employed in the present analysis is summarized in Table 1. Although a minor adjustment of the temporal filter could increase the deformation amplitude, the optimized configuration validated in Kim et al. (2024) [26] was retained to ensure consistent coherence stability across all embankment sections.

Table 1.
Optimized Parameter Set for PS-InSAR Analysis [26].
2.3. Results and Accuracy Assessment
The inherent differences between the leveling survey and PS-InSAR dataset—specifically, their distinct observation frequency and spatial sampling densities—necessitated a dedicated preprocessing workflow before a reliable comparison could be made. While the PS-InSAR dataset consisted of images acquired at an average interval of 22 days, leveling surveys were performed approximately every three months. To enable direct comparison, PS-InSAR-derived settlements were extracted from SAR images acquired within ±10 days of each leveling survey date, a tolerance window commonly adopted in previous validation studies. Based on this criterion, a total of 12 matching epochs were identified between late August 2016 and September 2018, which formed the basis of the comparative analysis.
Spatial discrepancies were also addressed prior to comparison. While leveling surveys were performed at intervals of 5 m or 10 m along the alignment, PS-InSAR measurements do not originate from fixed points but rather from radar backscattering centers, which can vary across acquisitions. In addition, multiple scatterers can be detected near a single leveling station. To harmonize these differences, PS-InSAR measurements located within a 2.5 m radius around each leveling benchmark were extracted and averaged, yielding a representative displacement value at each station. This spatial aggregation ensured that the InSAR results could be directly compared with ground-truth leveling data.
Finally, the accuracy and precision of the PS-InSAR-derived settlements were evaluated by comparing them defined under the assumption that the leveling survey results represent the reference truth. Accuracy was quantified using the Mean Absolute Error (MAE), which provides a straightforward measure of the average difference between the two datasets. Precision was assessed by the Standard Deviation (SD) of the error, which quantifies the consistency of the displacement errors.
The formulas for these metrics are as follows:
where is the total number of leveling survey stations used for comparison, is the averaged PS-InSAR settlement value for the ith leveling station, is the ground truth settlement value from the leveling survey at the ith station, is the mean of the differences between the averaged PS-InSAR values and the leveling survey values. These values were calculated individually for each embankment section, providing a detailed and comprehensive assessment of the technique’s reliability at the local scale.
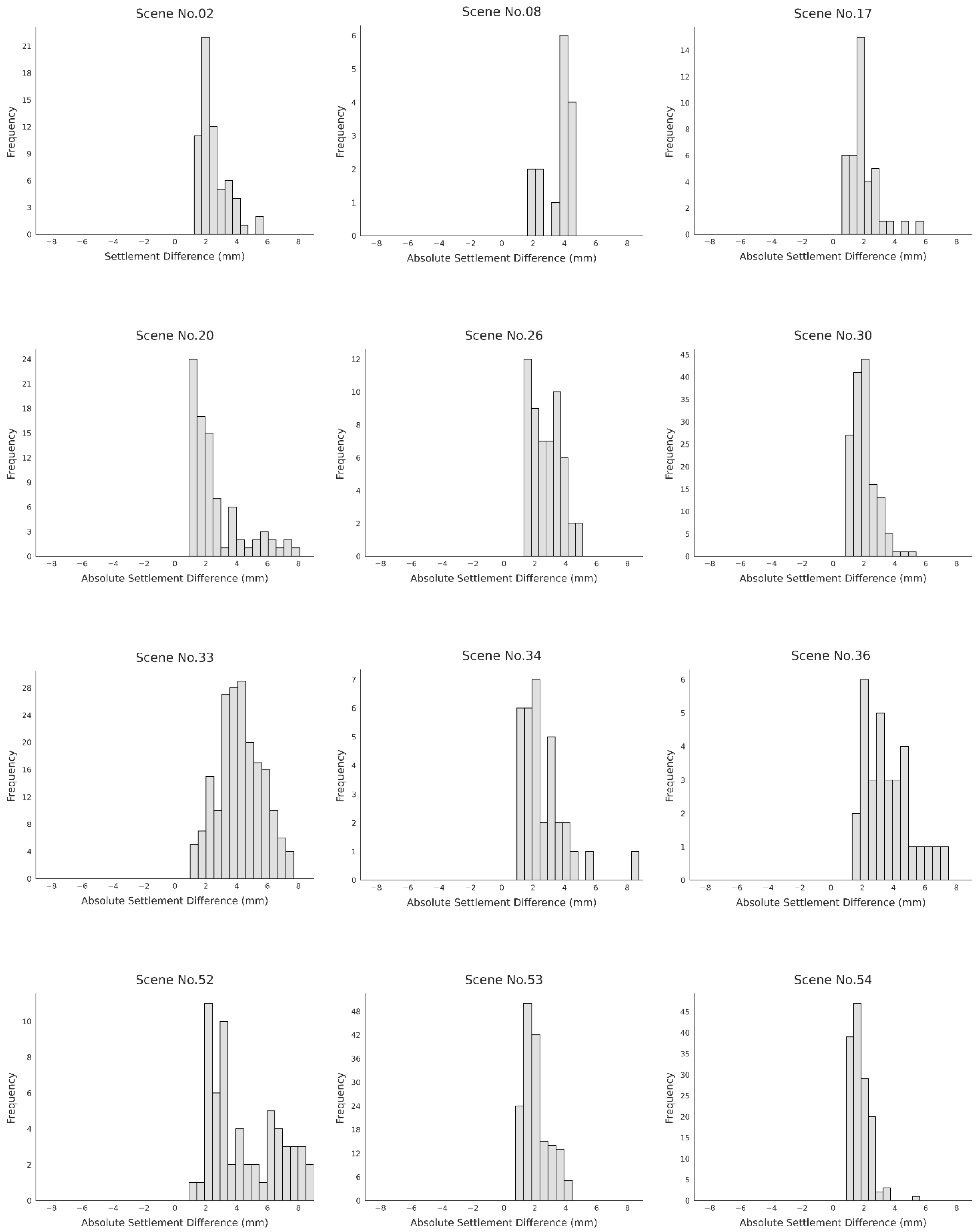
The histograms in Figure 4 and Table 2 illustrate the absolute settlement differences between the two measurement methods: leveling and PS-InSAR. The x-axis represents the magnitude of the difference in millimeters, while the y-axis shows the frequency of data points for each range. Although a high degree of agreement is observed between the two techniques, the distributions are notably centered around a mean difference of 1.7 to 4.2 mm, indicating a consistent, albeit small, discrepancy. A key observation is that the magnitude of this difference varies across different scenes. This variation suggests that the accuracy of PS-InSAR is not uniform and may be influenced by specific site conditions. To investigate this further, a correlation analysis will be performed in Section 3, Correlation Analysis Between Land-Cover Characteristics and PS-InSAR Settlement Measurement Accuracy, to examine how land-cover types and other environmental conditions contribute to these observed differences. This approach will provide a deeper understanding of the factors affecting the accuracy of PS-InSAR measurements in different railway sections. These variations suggest that measurement discrepancies are not random but are systematically related to local site conditions, motivating the subsequent correlation analysis with land-cover characteristics.
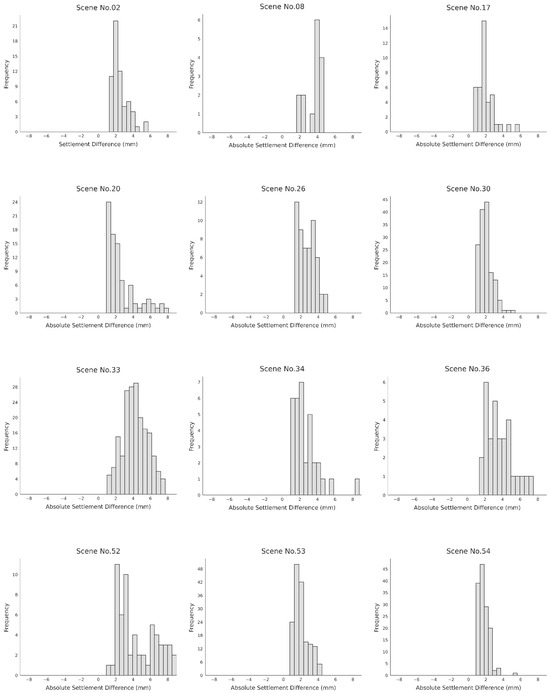
Figure 4.
Absolute settlement differences between the two measurement methods.

Table 2.
Accuracy Assessment Results of the Selected Twelve Embankment Section.
3. Correlation Analysis Between Land-Cover Characteristics and PS-InSAR Settlement Measurement Accuracy
3.1. Environmental Parameter Analysis Method
To quantitatively evaluate the influence of environmental factors on the accuracy of PS-InSAR-based settlement measurements for railway embankment sections, twelve representative scenes were selected for analysis. For each scene, the analysis area was defined by centering on the monitored railway embankment segment and expanding equally in all four directions by the segment length, resulting in a square-shaped boundary. Within this defined area, the most recent cadastral map data were obtained, and the area and proportion of each land-cover category were calculated using a GIS platform. The Korean cadastral classification system comprises 18 categories [27], which are summarized in Table 3.

Table 3.
Korean cadastral land-cover classification system.
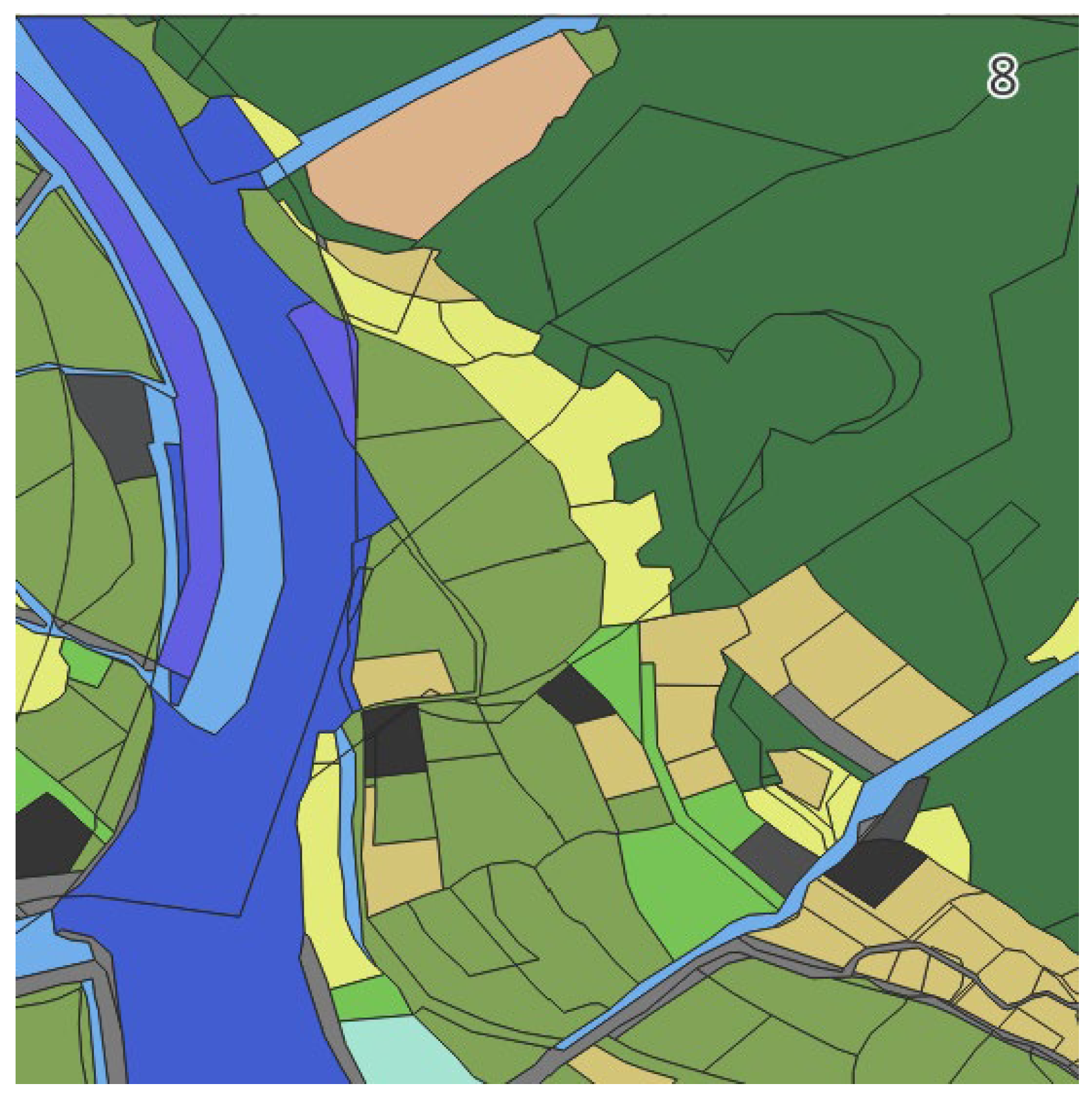
As an example, for Scene 8, the analysis boundary was set according to this procedure, as illustrated in Figure 5. The cadastral map data for this area were processed to calculate the area and proportion of each category, and the results are presented in Table 4. The analysis revealed a diverse composition of agricultural land, forest, water bodies, buildings, and other categories, providing a representative case for the subsequent aggregation process.
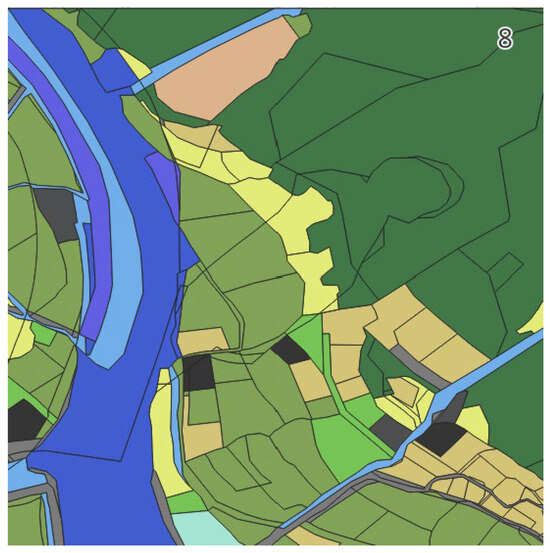
Figure 5.
Example of analysis boundary setting for surrounding land-cover evaluation (Scene 8).

Table 4.
Area proportion by cadastral category (Scene 8).
However, directly using the full set of cadastral categories in correlation analysis presents limitations, as the diversity of categories across scenes increases variance and complicates interpretation. To address this, similar land-cover types were consolidated into broader classifications. Agricultural land included ‘fields’, ‘paddies’, ‘orchards’, and ‘pasture’; forest land comprised ‘woodlands’ and ‘mountains’; water bodies included ‘rivers/streams’; transportation facilities included ‘railways’ and ‘roads’; buildings encompassed ‘residential’, ‘commercial’, and ‘industrial’ areas as well as ‘warehouses’ and ‘public buildings’; and all remaining categories were grouped under ‘others’.
This reclassification standardized the surrounding land-cover information for each scene into six major categories—agricultural land, forest land, water bodies, transportation facilities, buildings, and others—the results of which are summarized in Table 5. The analysis indicated that, for most sections of the Korean railway network, agricultural and forest land occupy a substantial proportion of the surrounding area. However, in certain urban sections, the combined proportion of transportation facilities and buildings reached up to 25%. Such differences are considered potential factors influencing the precision of PS-InSAR measurements, and in this study, they were examined through quantitative correlation analysis.

Table 5.
Surrounding land-cover composition after reclassification.
3.2. Correlation Analysis Between Environmental Parameters and PS-InSAR Precision
The relationship between surrounding land-cover characteristics and the precision of PS-InSAR-based settlement measurements was examined by integrating the reclassified land-cover data for each scene with corresponding measurement accuracy indicators, namely the mean absolute error (MAE) and the standard deviation (SD) of the error distribution. In addition to the six primary land-cover classes, two composite indices were derived to better capture scattering characteristics. The first represents vegetation-dominated areas, obtained by combining the proportions of agricultural land and forest land, which are generally associated with reduced persistent scatterer (PS) density. The second represents high-reflectivity surfaces, obtained by combining the proportions of transportation facilities and buildings, which typically enhance PS density.
The integrated dataset used for this analysis is provided in Table 6. Correlation strength was interpreted according to established thresholds: coefficients above 0.8 indicate a very strong correlation, 0.6–0.8 a strong correlation, 0.4–0.6 a moderate correlation, 0.2–0.4 a weak correlation, and below 0.2 a very weak or negligible correlation.

Table 6.
Integrated dataset for correlation analysis (environmental parameters and PS-InSAR precision).
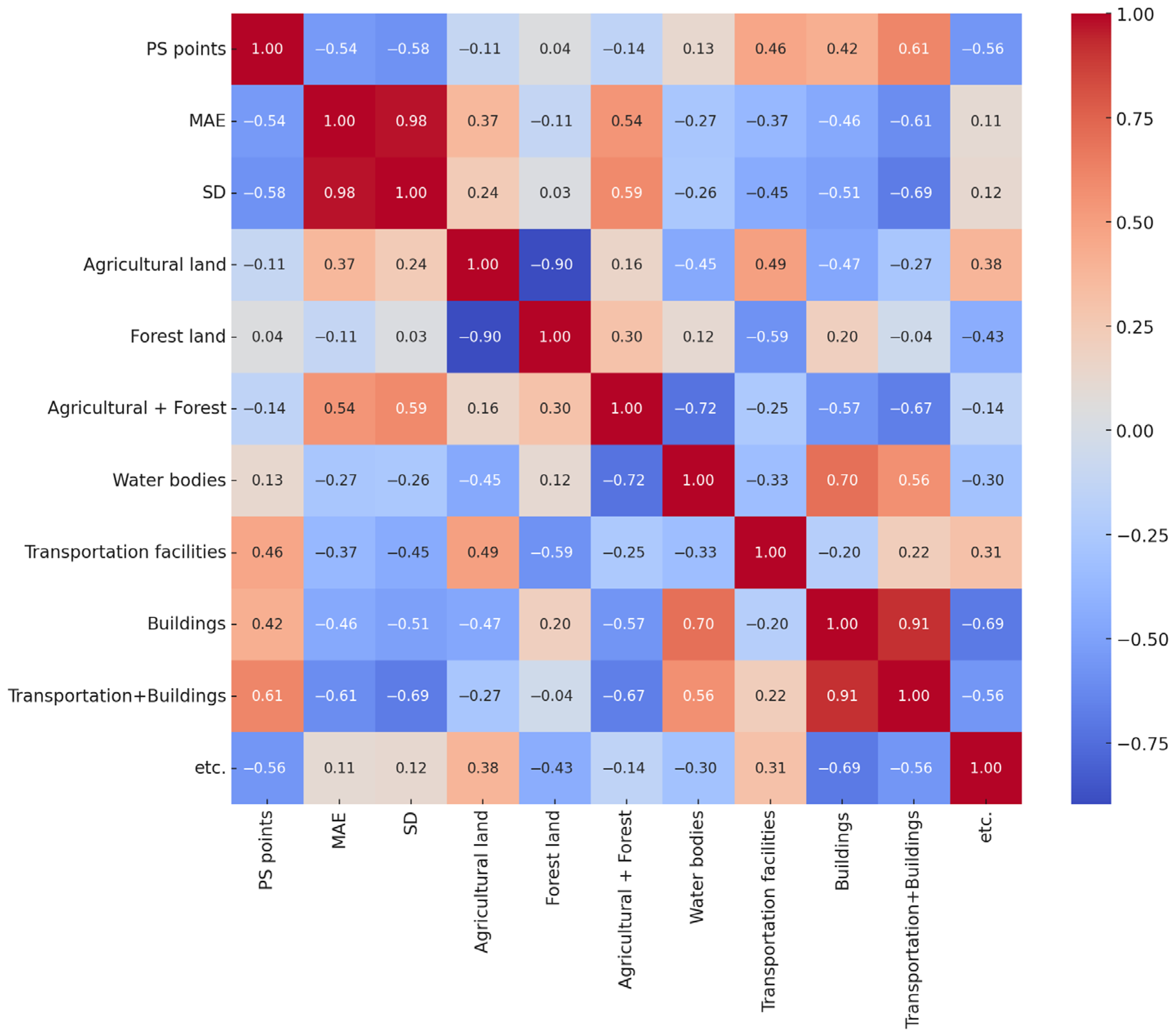
Figure 6 presents the correlation matrix heatmap derived from the multivariate analysis. The results show that MAE exhibited a moderate negative correlation with PS density (r = −0.54), a moderate positive correlation with vegetation-dominated surfaces (r = 0.54), and a moderately strong negative correlation with the proportion of high-reflectivity surfaces (r = −0.61), suggesting that an increase in transportation facilities and building coverage generally reduces the average measurement error. The SD, which is more directly related to PS-InSAR network precision, demonstrated a moderate negative correlation with PS density (r = −0.58), a moderate positive correlation with vegetation-dominated surfaces (r = 0.59), and a moderately strong negative correlation with high-reflectivity surfaces (r = −0.69). These patterns indicate that areas dominated by vegetation tend to show greater variability in PS-InSAR measurements, whereas urbanized areas with a higher proportion of transportation and building infrastructure yield more stable and precise results. These patterns provide quantitative evidence that land-cover composition systematically influences the reliability of PS-InSAR settlement measurements. The observed correlations can be explained by the radar backscattering characteristics of each land-cover type. In vegetation-dominated areas such as agricultural and forest land, temporal changes in canopy structure and moisture content lead to phase decorrelation, reducing persistent scatterer density and measurement stability. In contrast, urbanized and transportation areas composed of concrete, steel, and asphalt maintain strong radar coherence and stable reflections, resulting in higher PS density and improved accuracy. Water surfaces, with very low backscatter, contribute little to reliable PS detection. These mechanisms clarify how surface conditions physically control PS-InSAR performance and support the statistical relationships identified in this study. In particular, the negative correlations between high-reflectivity surfaces (transportation facilities and buildings) and both MAE and SD suggest that urbanized environments enhance the stability of radar backscattering, leading to denser PS points and more consistent displacement estimations. Conversely, the positive correlation between vegetation-dominated areas and SD highlights the susceptibility of agricultural and forested zones to temporal decorrelation, which reduces scatterer persistence and increases variability in measurement precision. From a practical perspective, these findings imply that PS-InSAR-based settlement monitoring should be carefully interpreted in regions dominated by vegetation, where supplementary ground-based surveys may still be necessary to ensure reliability. In contrast, for urbanized railway sections with a high proportion of reflective surfaces, PS-InSAR alone can provide sufficient accuracy for operational monitoring, thereby reducing the need for frequent leveling surveys. Consequently, the integration of site-specific land-cover information is not only useful for interpreting error sources but also essential for optimizing monitoring strategies and resource allocation in railway infrastructure management. These insights could be extended to develop predictive models that incorporate land-cover parameters into PS-InSAR processing workflows, enabling proactive identification of sections where measurement errors are likely to occur. A novel aspect of this study is that it moves beyond site-specific accuracy assessments and demonstrates, with statistical evidence, that land-cover composition systematically governs PS-InSAR performance. This contribution fills a gap in the existing literature, where environmental determinants of PS-InSAR accuracy have rarely been quantified in the context of railway infrastructure monitoring.
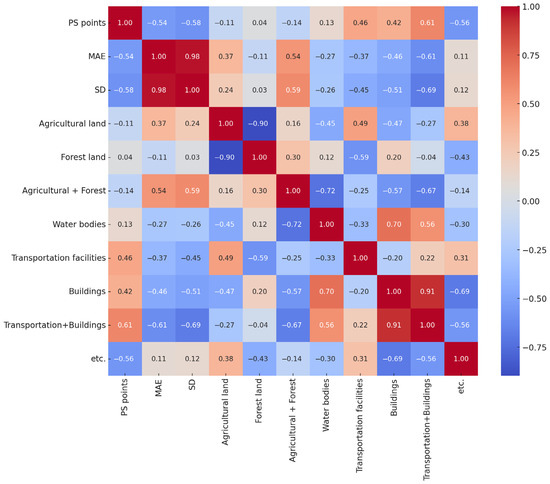
Figure 6.
Correlation matrix heatmap between environmental parameters and PS-InSAR precision.
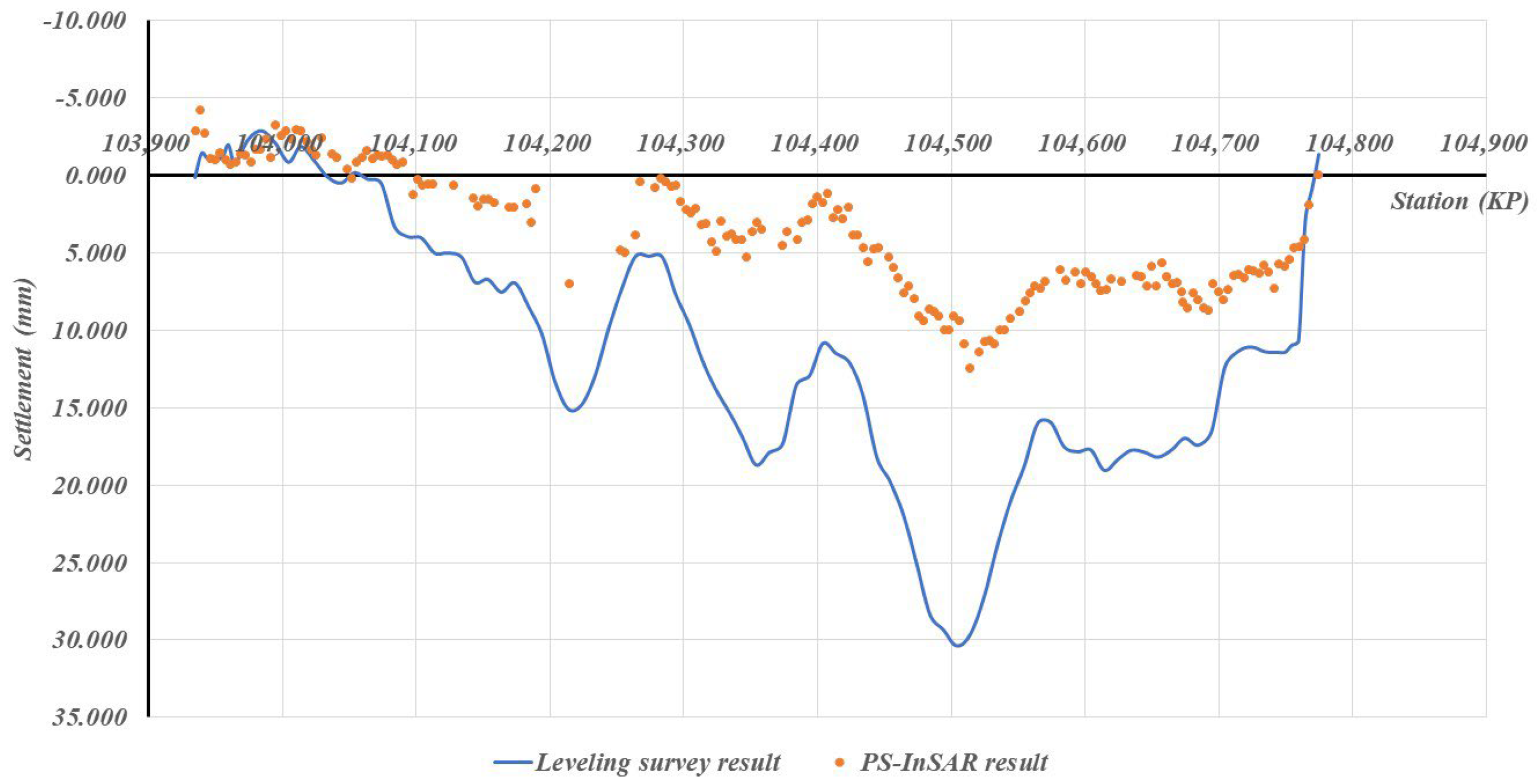
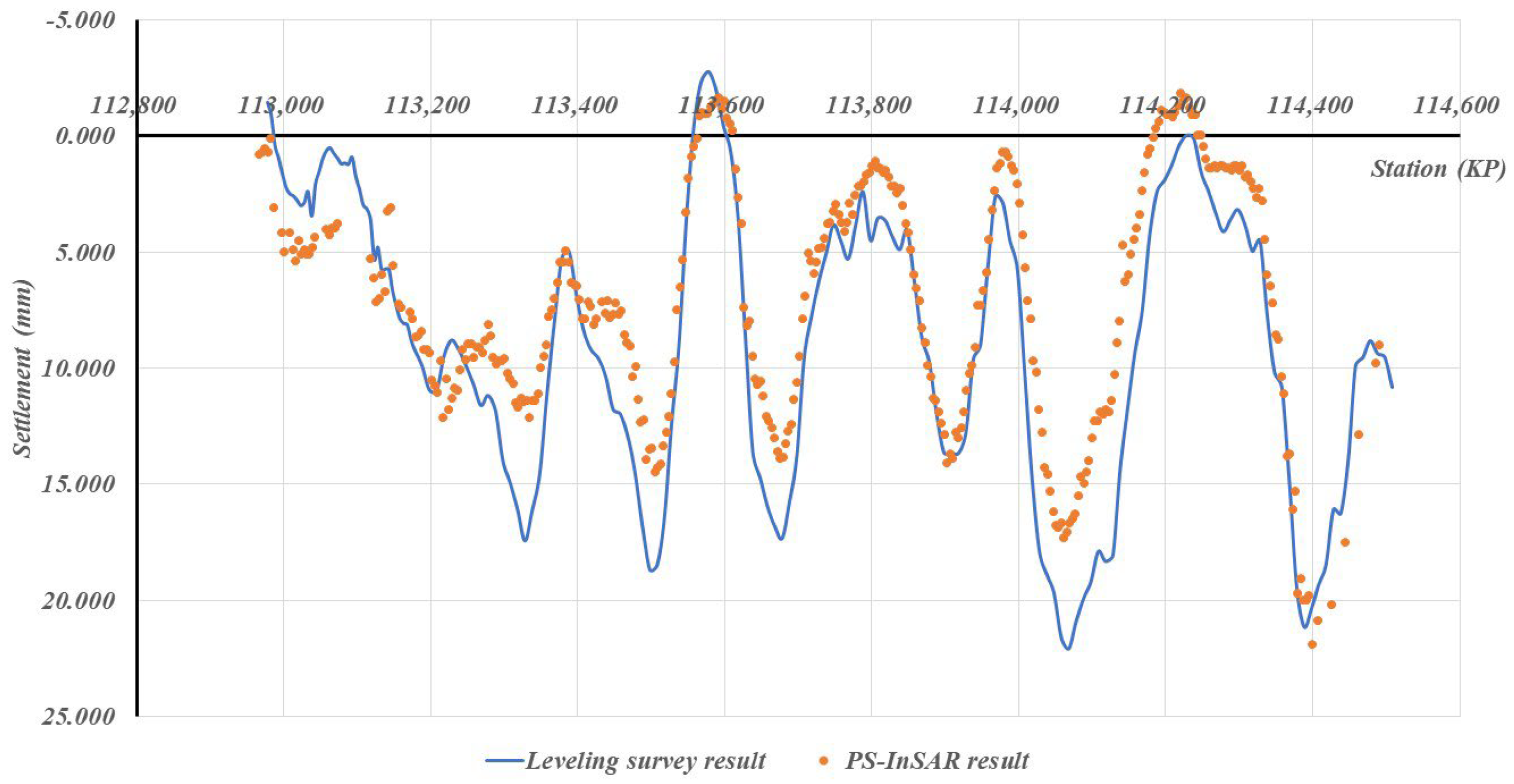
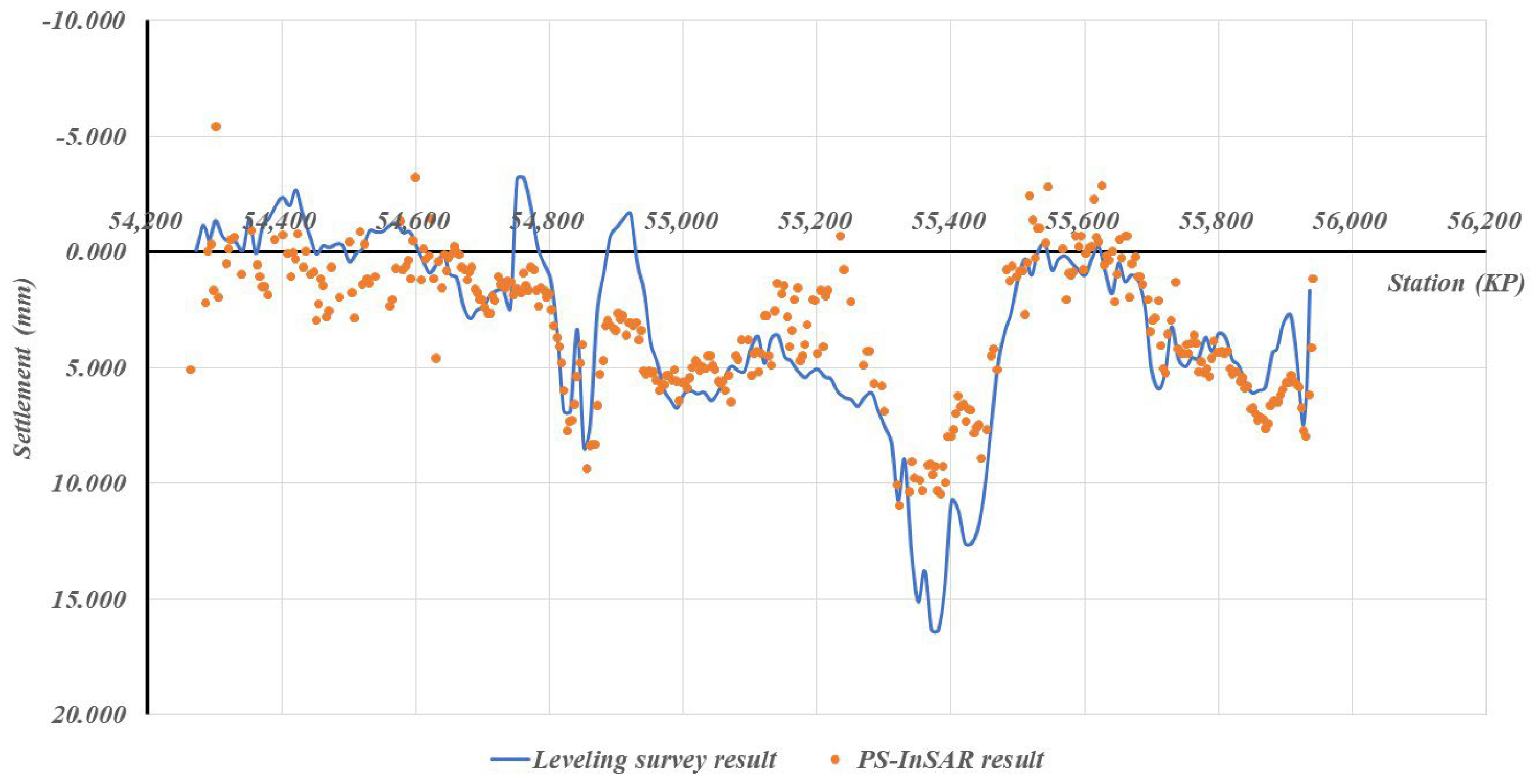
Case-specific observations further reinforce these statistical findings. As shown in Figure 7, Scene 52, where vegetation-dominated surfaces account for 86% of the surrounding area and high-reflectivity surfaces only 8.4%, exhibited the largest measurement errors (MAE = 6.013 mm, SD = 3.892 mm). This clearly reflects the adverse impact of temporal decorrelation in agricultural and forested landscapes, which lowers scatterer persistence and increases error variability. In contrast, Figure 8 and Figure 9 illustrate Scenes 54 and 30, respectively, where high-reflectivity surfaces comprise nearly 20% of the surrounding land cover. These sections recorded much smaller discrepancies between PS-InSAR and field survey results (MAE ≈ 2.0 mm, SD ≤ 0.764 mm), confirming that reflective man-made structures contribute to stable backscattering and higher PS density.
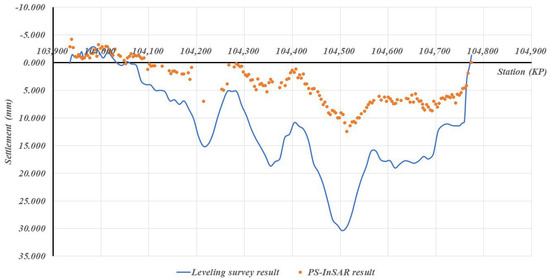
Figure 7.
Field survey vs. PS-InSAR results for Scene 52.
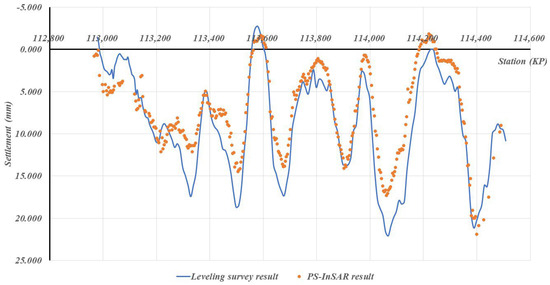
Figure 8.
Field survey vs. PS-InSAR results for Scene 54.
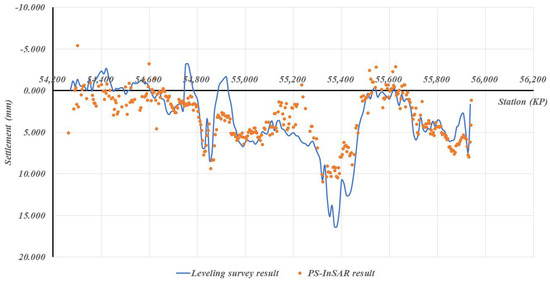
Figure 9.
Field survey vs. PS-InSAR results for Scene 30.
Collectively, these examples visually demonstrate how surrounding land-cover conditions translate into measurable differences in monitoring precision. The strong contrast between Scene 52 and Scenes 54 and 30 provides direct empirical evidence that vegetation-dominated areas remain the most challenging environments for PS-InSAR monitoring, whereas urbanized or infrastructure-rich corridors offer conditions favorable for achieving millimeter-level accuracy.
3.3. Suggestion of Correlation Equations Between Environmental Parameter and PS-InSAR Accuracy Indices
To deepen the statistical analysis and develop a predictive understanding of how surrounding land-cover composition affects PS-InSAR measurement reliability, linear regression models were constructed for the two key accuracy indicators: the Mean Absolute Error (MAE) and the Standard Deviation (SD) of the displacement difference between PS-InSAR and leveling surveys. These indicators, respectively, represent the overall bias and dispersion of satellite-based settlement measurements compared to field data.
The regression models were established using the combined proportion of vegetation-dominated surfaces (agricultural and forest land) and high-reflectivity surfaces (transportation facilities and buildings) as explanatory variables, since the correlation analysis in Section 3.2 indicated that these composite parameters exhibit the strongest relationship with PS-InSAR precision. The derived equations are expressed as follows:
where the independent variables represent the fractional proportions expressed as decimals of the surrounding land-cover categories within each analysis area. Specifically, “Agricultural” and “Forest” denote the proportion of agricultural and forest land, respectively, while “Transportation” and “Buildings” indicate the proportion of transportation facilities and building areas.
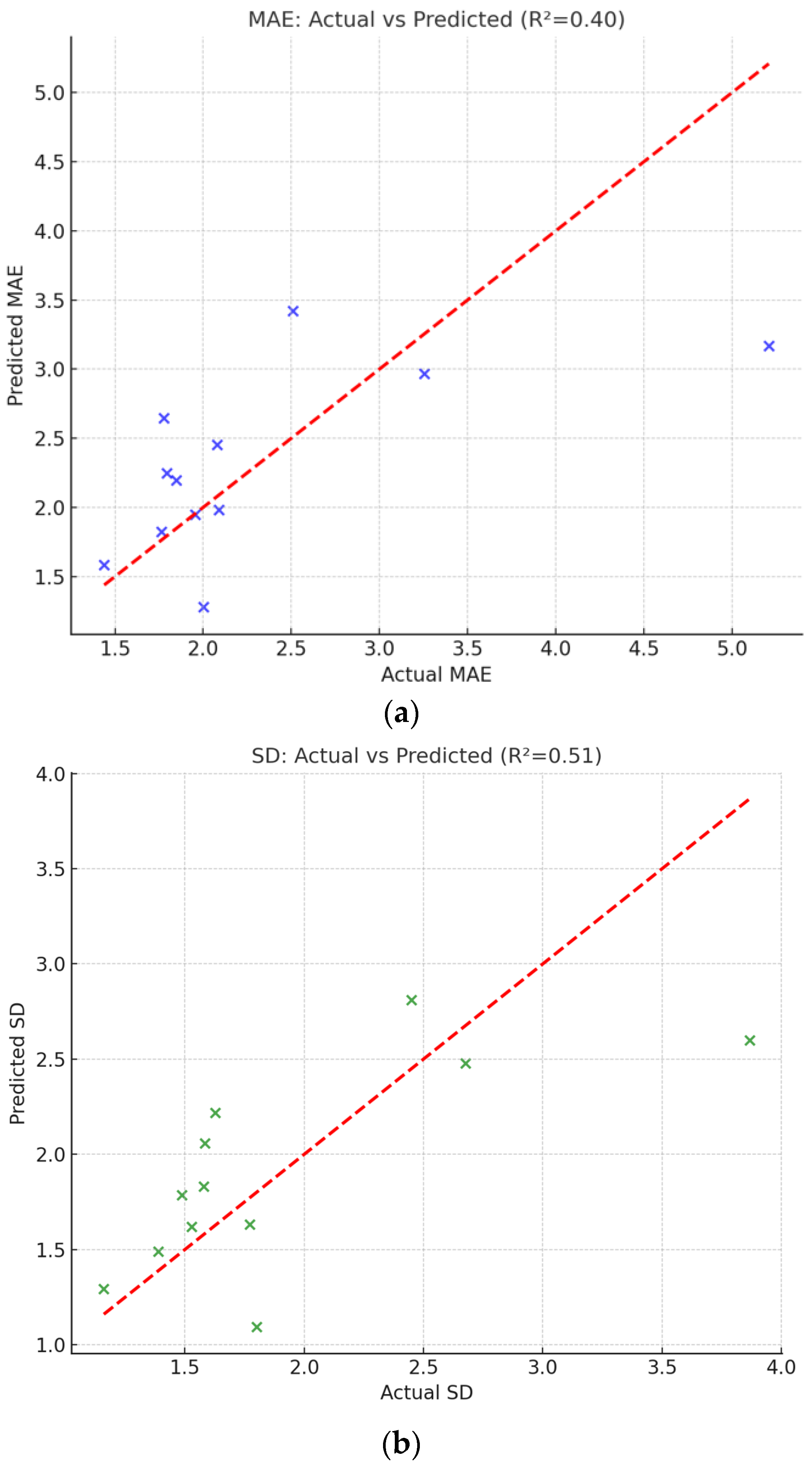
The regression models indicate that the surrounding land-cover composition can explain a substantial portion of the variability in PS-InSAR accuracy across different embankment sections. The fitted results, illustrated in Figure 10, show that most data points cluster closely along the 1:1 line, suggesting that the predicted and observed accuracy indices are in reasonable agreement. Although residual scatter exists due to other unmodeled factors (e.g., atmospheric artifacts, local terrain geometry, or temporal decorrelation), the models successfully capture the dominant physical trend—namely, that PS-InSAR performance systematically degrades in vegetation-rich environments and improves in infrastructure-dense regions.
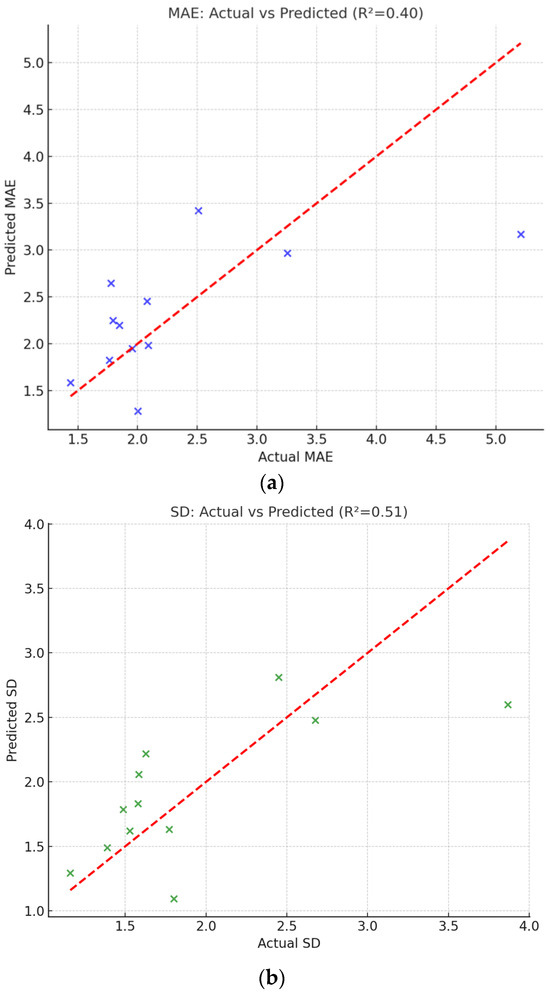
Figure 10.
Comparison between actual and predicted accuracy indices from regression analysis. (a) Relationship between actual and predicted Mean Absolute Error (MAE). (b) Relationship between actual and predicted Standard Deviation (SD).
This finding quantitatively supports the earlier correlation analysis and provides a predictive framework for estimating the potential reliability of PS-InSAR monitoring in future applications. From a practical perspective, these models allow engineers and researchers to anticipate the achievable accuracy of PS-InSAR measurements at new sites based on simple land-cover statistics derived from GIS or remote sensing data. Such an approach can assist in selecting optimal monitoring zones or in planning complementary ground-based measurements in areas expected to yield low radar coherence.
Figure 10 presents the comparison between actual and predicted values of MAE and SD. In both cases, the data points align well with the 1:1 reference line (red dashed), demonstrating that the regression models capture the dominant variability in PS-InSAR accuracy as a function of surrounding land-cover composition. Overall, the regression results provide statistical evidence that the surface environment exerts a quantifiable influence on PS-InSAR accuracy, reinforcing the need to consider local land-cover composition in the design and interpretation of satellite-based deformation monitoring programs.
This finding is consistent with the theoretical foundations of radar coherence and backscattering established by Zebker and Villasenor (1992) [28] and Fornaro et al. (2012) [29], who demonstrated that vegetation and surface roughness induce temporal decorrelation, whereas rigid and urban surfaces maintain stronger radar coherence. The present study extends these established principles by quantitatively modeling how such environmental factors statistically influence PS-InSAR accuracy for high-speed railway monitoring.
4. Conclusions
This study demonstrated the feasibility of applying Persistent Scatterer Interferometry (PS-InSAR) to assess settlement behavior in railway embankments and examined how surrounding land-cover conditions affect measurement accuracy. Twelve representative scenes were analyzed using cadastral data, reclassified into six consolidated land-cover categories, and correlated with accuracy indicators such as PS density, mean absolute error, and standard deviation. The results showed that PS-InSAR can capture millimeter-scale settlements with reasonable accuracy, while also revealing systematic variations in performance across different land-cover environments. These findings not only provide new insights into environmental factors influencing InSAR monitoring, but also offer practical guidelines for designing more reliable satellite-based monitoring strategies in railway infrastructure management.
1. The PS-InSAR analysis successfully captured the settlement behavior of the Honam HSR embankments and showed strong consistency with leveling survey results, confirming the capability of satellite-based deformation monitoring for long-term infrastructure observation.
2. Land-cover composition significantly affected PS-InSAR accuracy and PS density. Vegetation-dominated areas exhibited larger measurement errors and lower PS density, whereas high-reflectivity surfaces, such as transportation facilities and buildings, improved coherence and measurement stability.
3. To deepen the statistical interpretation, regression models were developed to quantitatively evaluate the relationship between land-cover characteristics and PS-InSAR accuracy indices (MAE and SD). The models indicated that environmental parameters explain a substantial portion of the spatial variability in PS-InSAR precision, providing a predictive basis for assessing accuracy under varying surface conditions.
4. These findings extend previous studies by transforming the well-known limitation of vegetation-induced decorrelation into a quantitative and predictive framework. The regression-based approach enables objective estimation of PS-InSAR accuracy using simple land-cover information derived from GIS or remote-sensing datasets.
5. Future studies should aim to validate these findings across other high-speed railway corridors and explore the integration of PS-InSAR with complementary ground-based monitoring systems to further enhance reliability. The novelty of this work lies in quantifying, in this context, the impact of land-cover conditions on PS-InSAR accuracy in railway settlement monitoring, thereby providing a predictive framework for designing more robust satellite-based monitoring strategies.
Author Contributions
B.-k.K.: Writing—Original Draft, Review & editing, Methodology, J.K.: Writing—Original Draft, Review & editing, Methodology, J.P.: Investigation, Validation, I.L.: Visualization, Resources., M.Y.: Writing—review and editing, Methodology, supervision. The authors confirm that this work has not been published before, and its publication has been approved by all co-authors. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study supported by the Korea Railroad Research Institute through the Development of Railway Infrastructure Monitoring Technology Using Multi-Satellite Data (PK2501B4), for which we express our deep appreciation.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Zhou, S.; Wang, B.; Shan, Y. Review of research on high-speed railway subgrade settlement in soft soil area. Railw. Eng. Sci. 2020, 28, 129–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Soldato, M.; Confuorto, P.; Bianchini, S.; Sbarra, P.; Casagli, N. Review of Works Combining GNSS and InSAR in Europe. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Deng, K.; Zheng, M. Research on ground deformation monitoring method in mining areas using the probability integral model fusion D-InSAR, sub-band InSAR and offset-tracking. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2020, 85, 101981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carnec, C.; Massonnet, D.; King, C. Two examples of the use of SAR interferometry on displacement fields of small spatial extent. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1996, 23, 3579–3582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Wu, L.; Chen, B. The application research on subsidence monitoring of coal mining area with d-InSAR. In Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS’05), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 25–29 July 2005; pp. 5216–5218. [Google Scholar]
- Samsonov, S.; d’Oreye, N.; Smets, B. Ground deformation associated with post-mining activity at the French-German border revealed by novel InSAR time series method. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2013, 23, 142–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamadi, B.; Balz, T.; Younes, A. Towards a PS-InSAR Based Prediction Model for Building Collapse: Spatiotemporal Patterns of Vertical Surface Motion in Collapsed Building Areas—Case Study of Alexandria, Egypt. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez, R.A.; Lee, G.; Choi, S.; Kwon, T.; Kim, T.; Ryu, H.; Kim, S.; Bae, B.; Hyun, C. Monitoring of construction-induced urban ground deformation using Sentinel-1 PS-InSAR: The case study of tunneling in Dangjin, Korea. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2022, 108, 102721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Chen, T.; Wang, M.; Li, Y. Multi-Segment Rupture Model of the 2016 Kumamoto Earthquake Revealed by InSAR and GPS Data. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Novellis, V.; Reale, D.; Adinolfi, G.M.; Sansosti, E.; Convertito, V. Geodetic Model of the March 2021 Thessaly Seismic Sequence Inferred from Seismological and InSAR Data. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Hu, J.; Li, Z.; Ma, Z.; Shi, J.; Xu, W.; Sun, Q. Three-Dimensional Surface Displacements of the 8 January 2022 Mw6.7 Menyuan Earthquake, China from Sentinel-1 and ALOS-2 SAR Observations. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smail, T.; Abed, M.; Mebarki, A.; Lazecky, M. Earthquake-induced landslide monitoring and survey by means of InSAR. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2022, 22, 1609–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, Y.; Park, S.; Kim, H. Observation of spatial and temporal patterns of seasonal ground deformation in central Yakutia using time series InSAR data in the freezing season. Remote Sens. Environ. 2023, 293, 113615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, F.; van Leijen, F.J.; Chang, L.; Wu, J.; Hanssen, R.F. Monitoring deformation along railway systems combining multi-temporal InSAR and LiDAR data. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonelli, D.; Caspani, V.F.; Valentini, A.; Rocca, A.; Torboli, R.; Vitti, A.; Zonta, D. Interpretation of Bridge Health Monitoring Data from Satellite InSAR Technology. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 5242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farneti, E.; Gentile, C.; Giannico, G.; Ruccolo, A.; Mariani, M.; Fedele, R. A Method for Structural Monitoring of Multispan Bridges Using InSAR Data. Struct. Health Monit. 2023, 22, 1215–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biondi, F.; Addabbo, P.; Ullo, S.L.; Clemente, C.; Orlando, D. Perspectives on the Structural Health Monitoring of Bridges by Synthetic Aperture Radar. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, C.; Chen, F.; Li, Y. Radar Interferometry for Urban Infrastructure Stability. Sustainability 2023, 15, 14654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Yu, X. Space-Based Long-Term Condition Monitoring of Cold-Region Pavement with PS-InSAR. J. Infrastruct. Preserv. Resil. 2025, 6, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.J.; Yun, H.S.; Kim, T.Y. Monitoring of High-Speed Railway Ground Deformation Using Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar Image Analysis. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 4318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korea National Railway. Guideline for Track Maintenance; Korea National Railway: Daejeon, Republic of Korea, 2018. (In Korean) [Google Scholar]
- Ferretti, A.; Prati, C.; Rocca, F. Permanent scatterers in SAR interferometry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2001, 39, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooper, A.; Zebker, H.; Segall, P.; Kampes, B. A new method for measuring deformation on volcanoes and other natural terrains using InSAR persistent scatterers. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004, 31, L23611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, R.; Lau, A.; Mossefin, M.E.; Kong, G.; Nordal, S.; Pan, Y. Monitoring of ground displacement-induced railway anomalies using PS-InSAR techniques. Measurement 2025, 248, 116863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kizilirmak, G.; Cakir, Z. Application of PS-InSAR and Diagnostic Train Measurement Techniques for Monitoring Subsidence in High-Speed Railway in Konya, Türkiye. Infrastructures 2024, 9, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.K.; Kim, W.; Lee, C.; Yoo, M.; Lee, I. Validating railway infrastructure deformation monitoring: A comparative analysis of field data and TerraSAR-X PS-InSAR results. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2024, 28, 1777–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, W.; Lim, Y.; Park, K.-H. Deep learning based Land Cover Classification Using Convolutional Neural Network: A case study of Korea. J. Korean Geogr. Soc. 2019, 54, 1–16. (In Korean) [Google Scholar]
- Zebker, H.A.; Villasenor, J. Decorrelation in Interferometric Radar Echoes. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1992, 30, 950–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fornaro, G.; Reale, D.; Verde, S. Potential of SAR for Monitoring Transportation Infrastructures: An Analysis with the Multi-Dimensional Imaging Technique. J. Geophys. Eng. 2012, 9, S1–S9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).