Study on Lithospheric Tectonic Features of Tianshan and Adjacent Regions and the Genesis Mechanism of the Wushi Ms7.1 Earthquake
Abstract
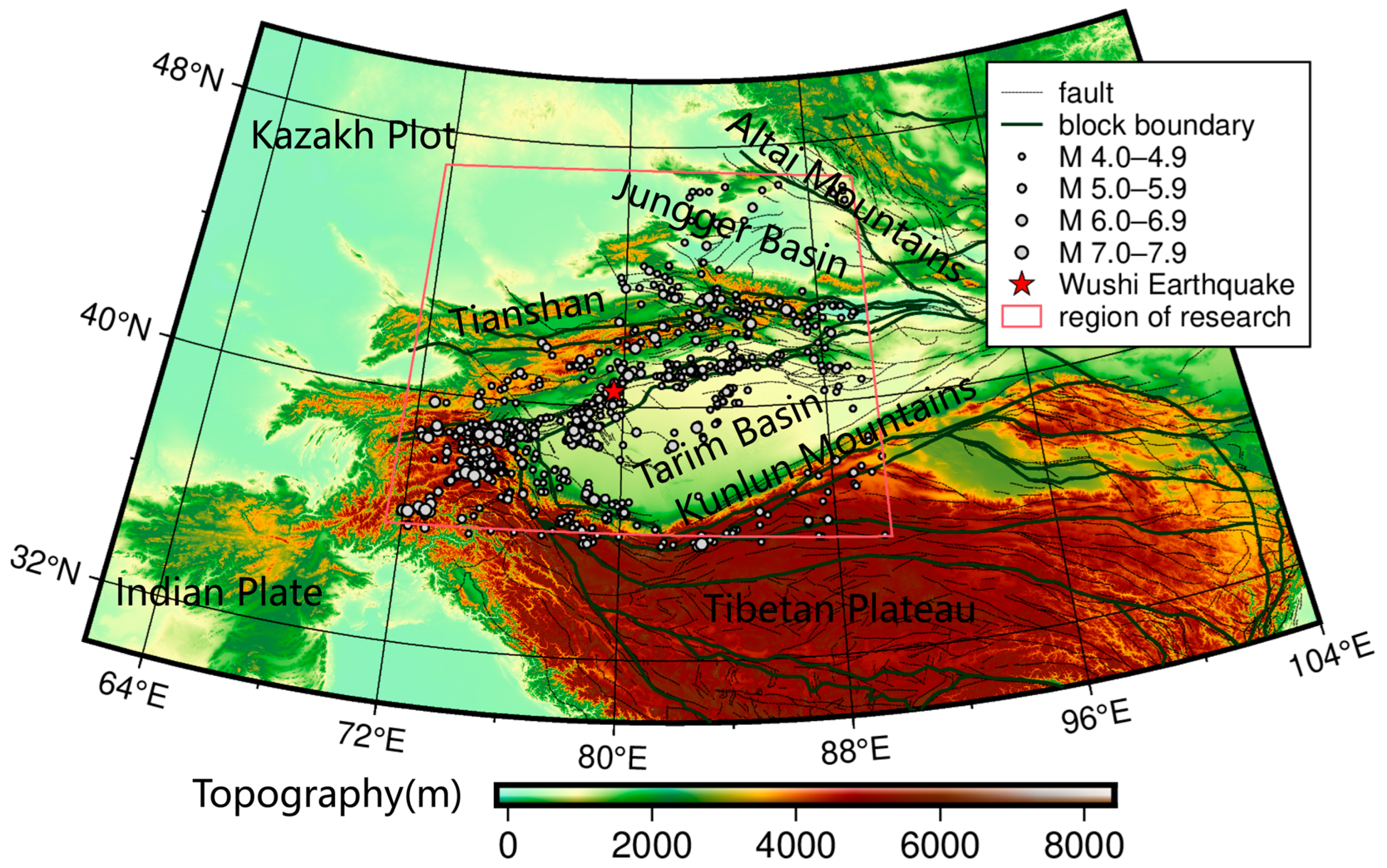
1. Introduction
2. Geotectonic Background
3. Effective Elastic Thickness
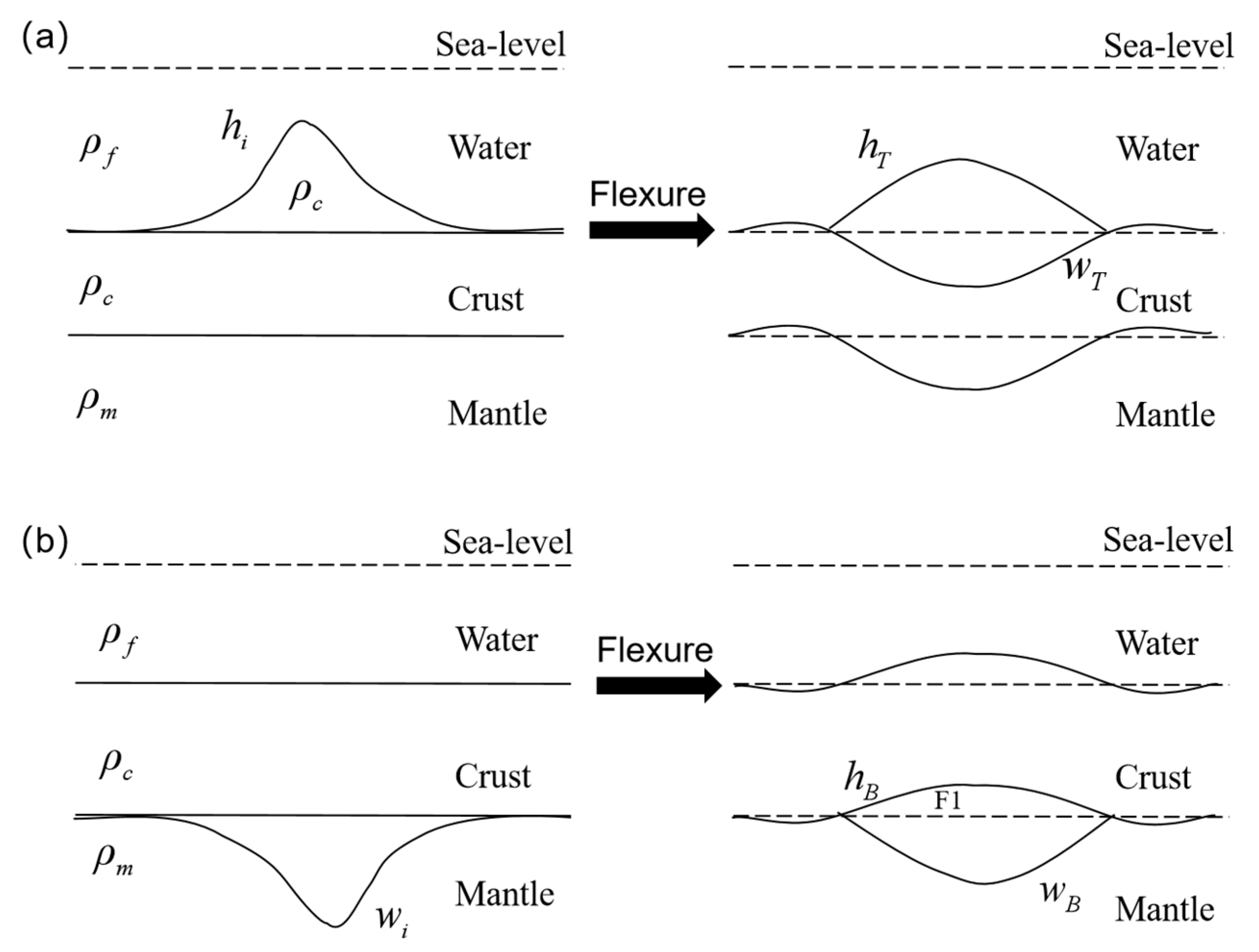
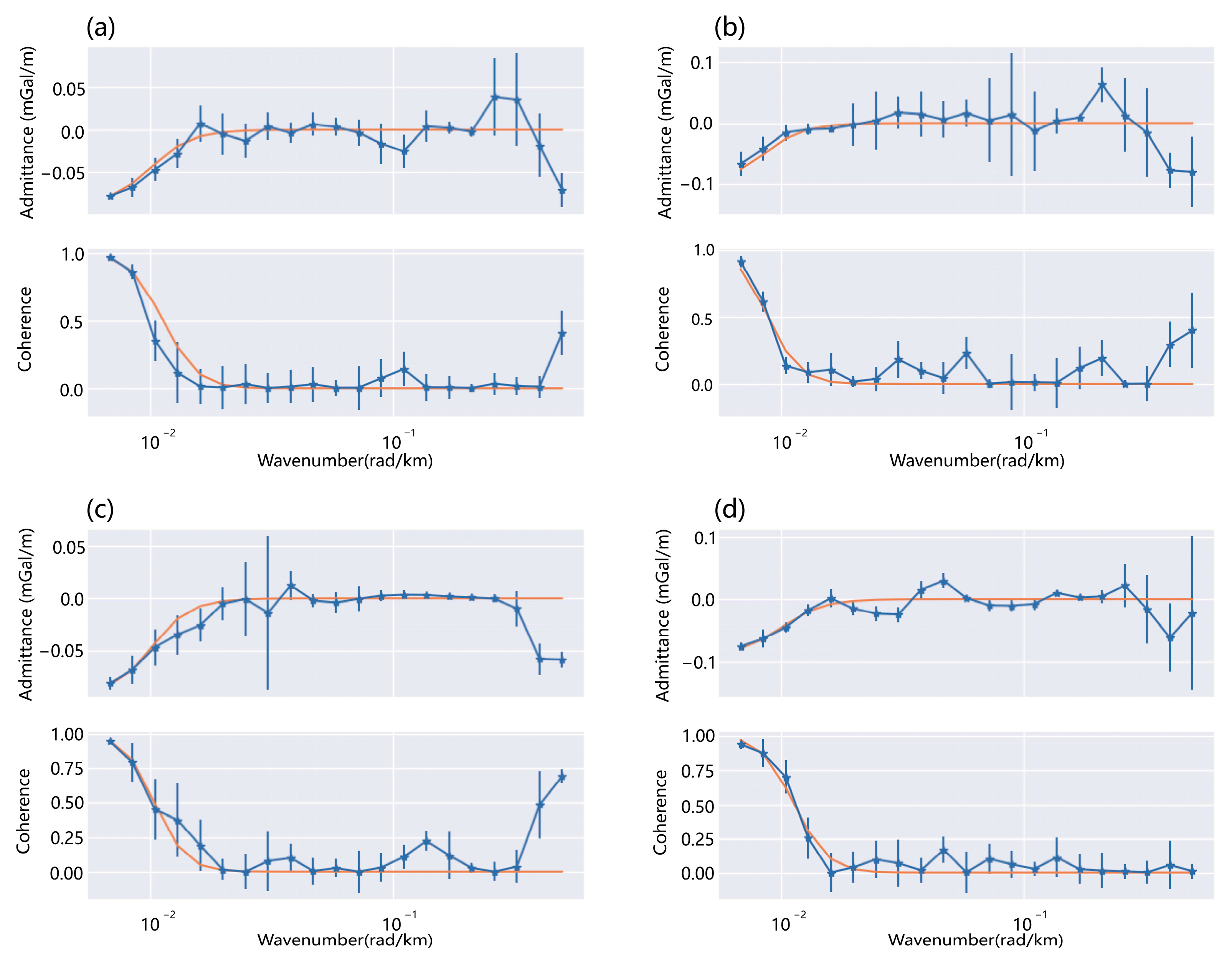
3.1. Methods and Principles
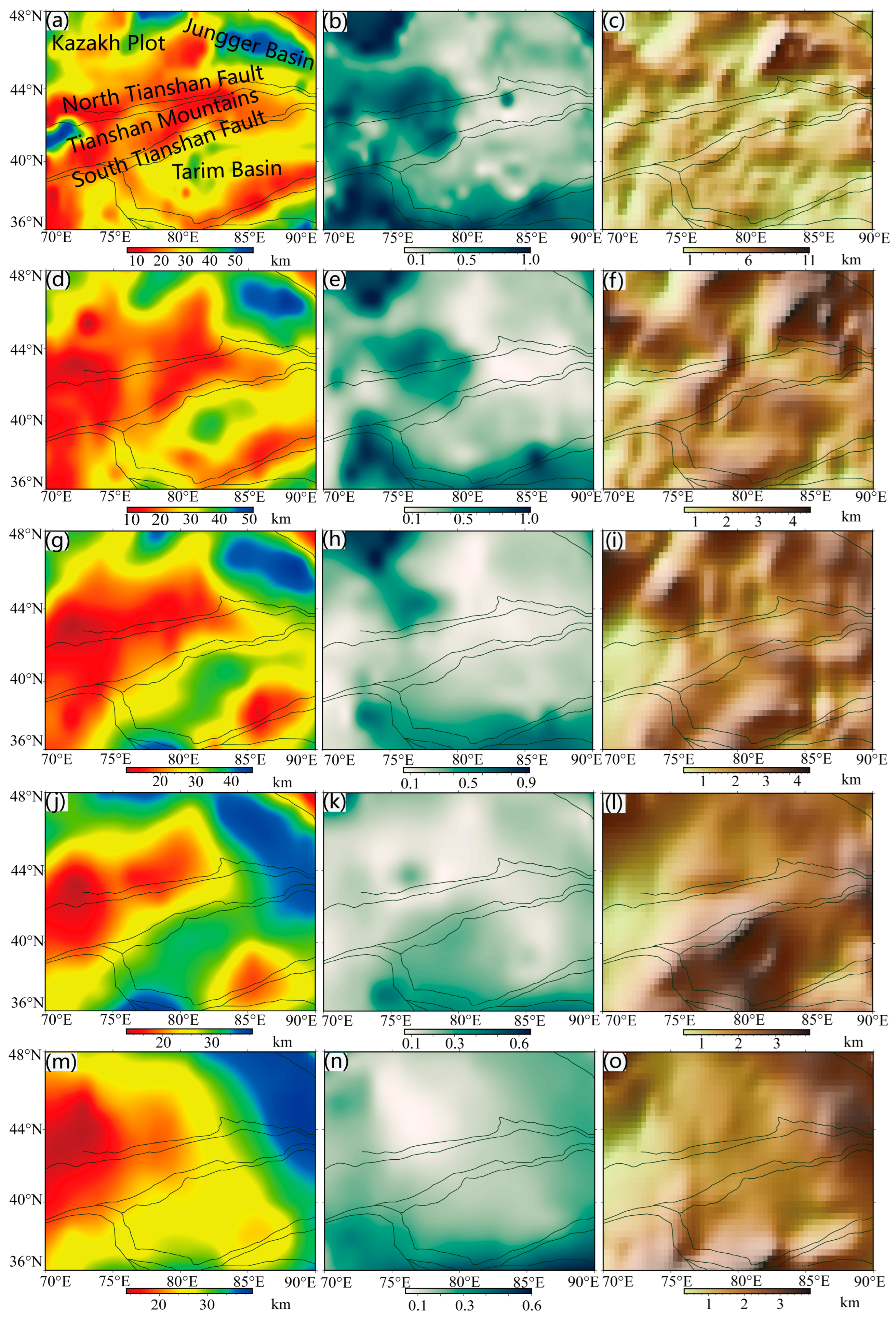
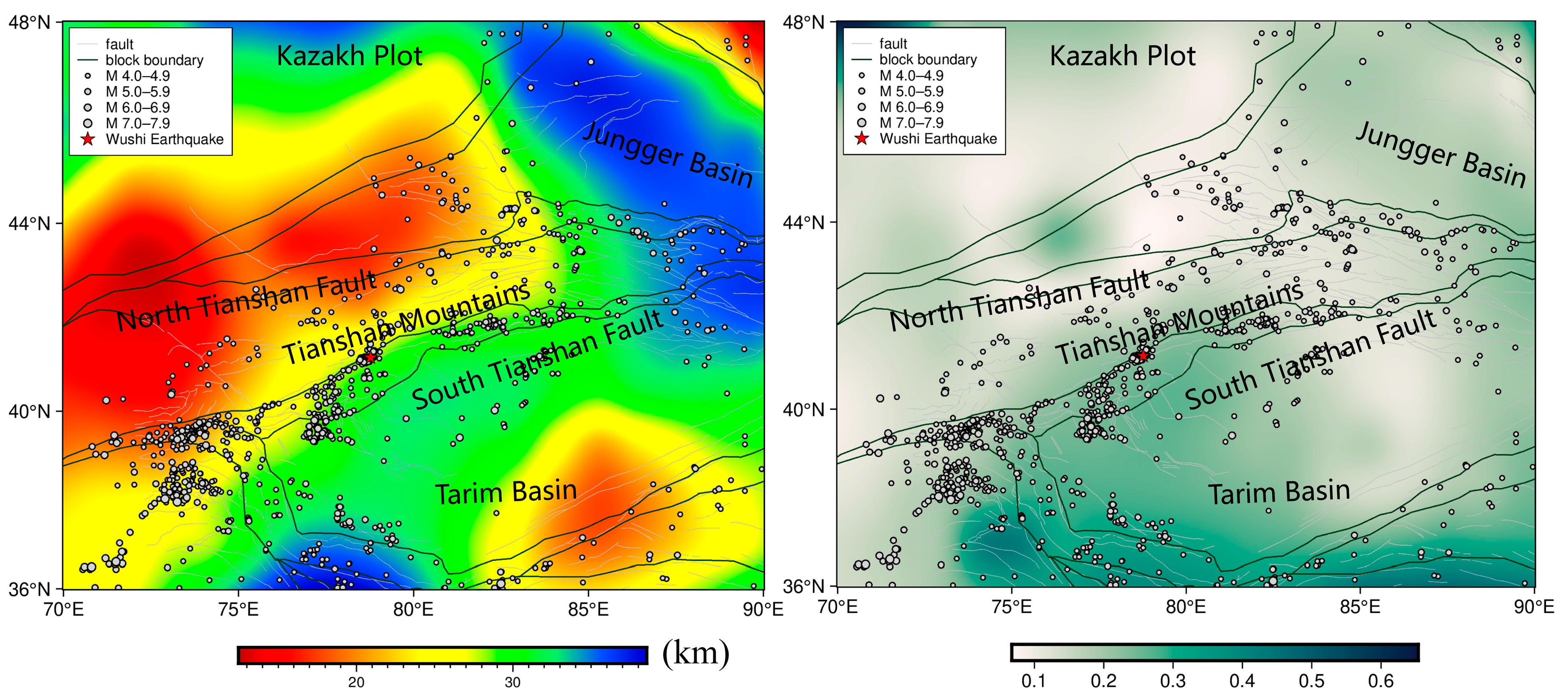
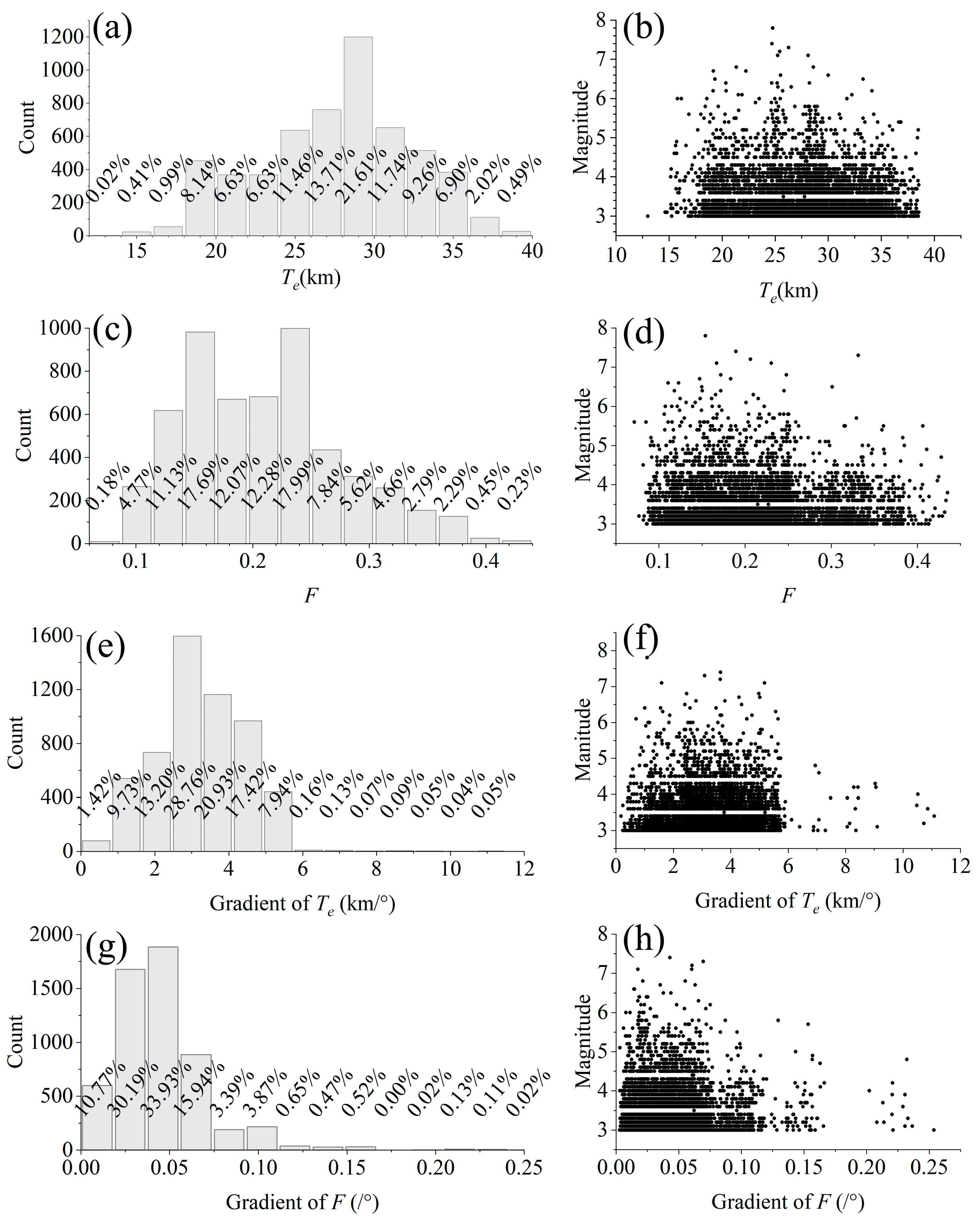
3.2. Data and Calculations
3.3. Analysis of the Relationship with Earthquakes
4. Gravity Field and Apparent Density Variation Characteristics
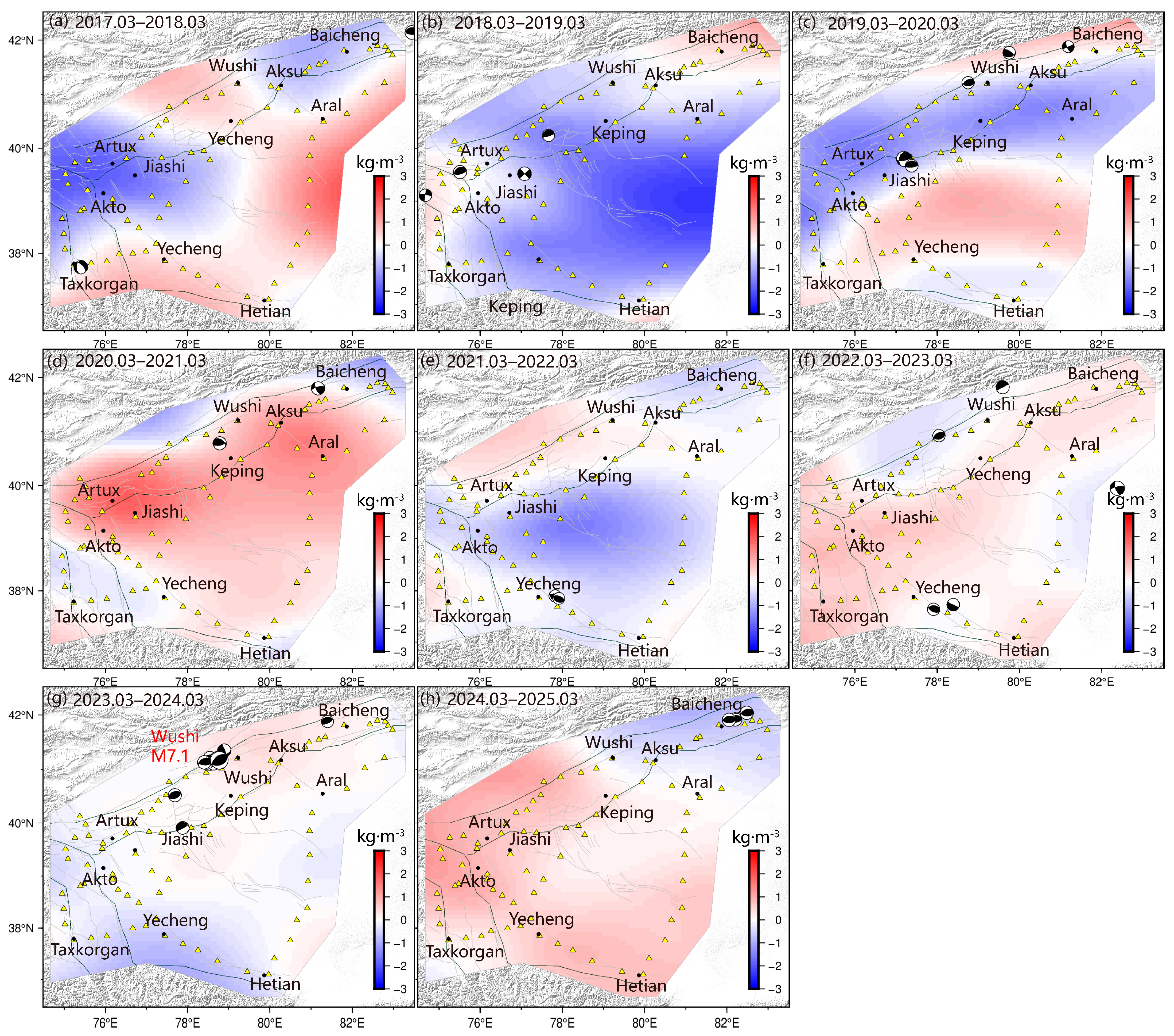
4.1. Analysis of One-Year Scale Gravity Field Variations
4.2. Field Source Apparent Density Variation Analysis
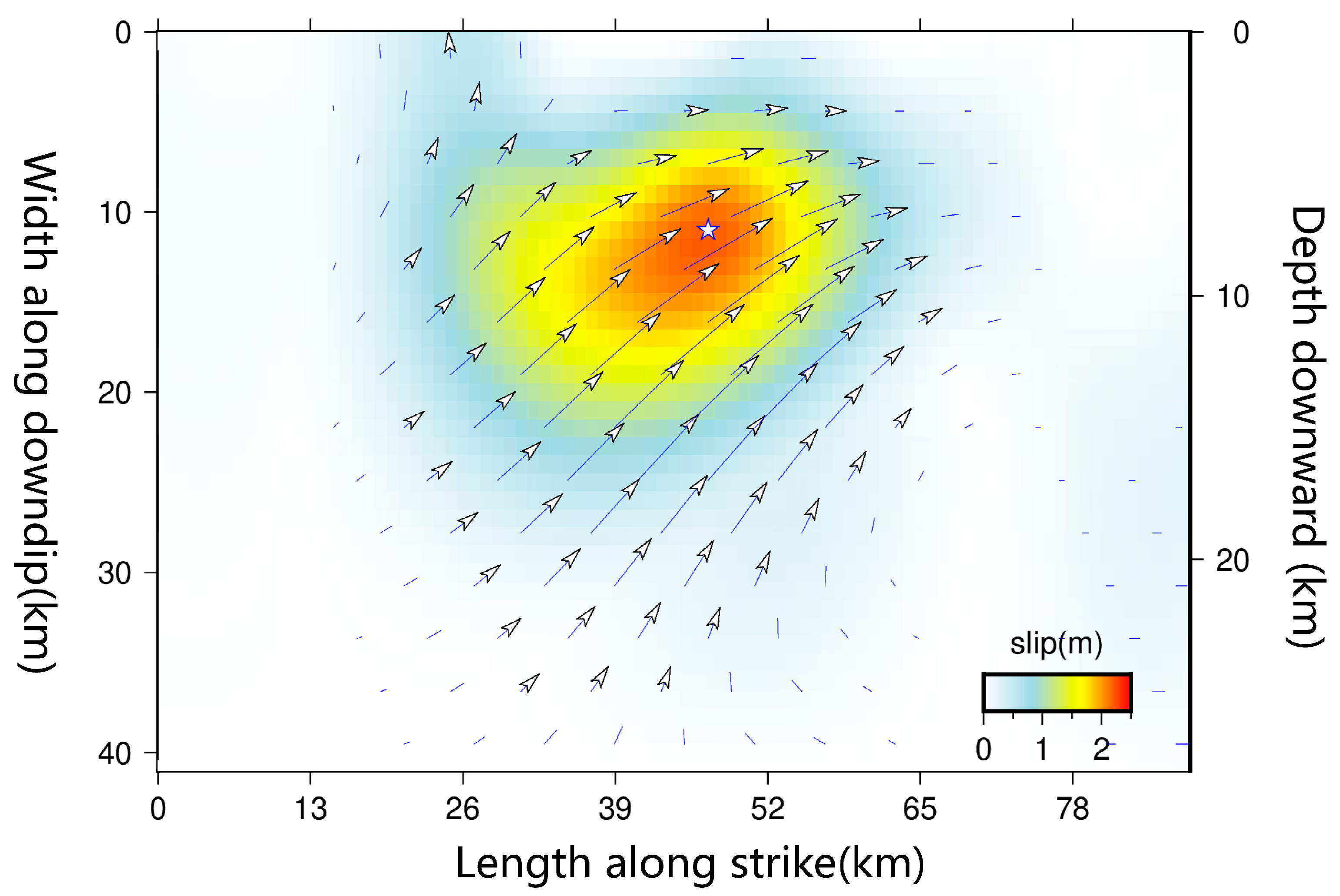
5. InSAR Coseismic Deformation Monitoring
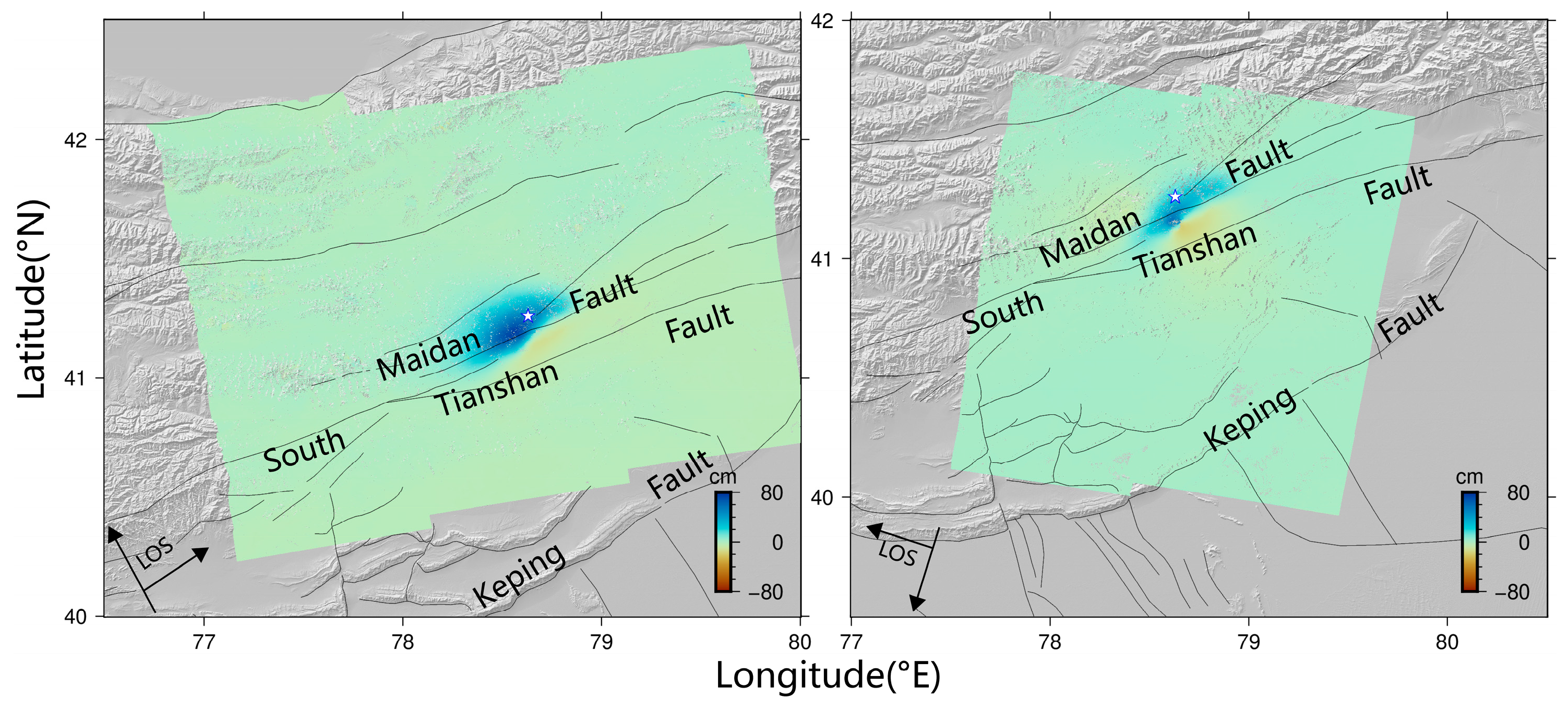
5.1. Data and Processing Methods
5.2. Coseismic Deformation Field and Fault Slip Modeling
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lowry, A.R.; Smith, R.B. Strength and rheology of the western US Cordillera. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 1995, 100, 17947–17963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cloetingh, S.; Ziegler, P.A.; Beekman, F.; Andriessen, P.A.M.; Matenco, L.; Dèzes, P.; Sokoutis, D. Lithospheric memory, state of stress and rheology: Neotectonic controls on Europe’s intraplate continental topography. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2005, 24, 241–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handy, M.R.; Brun, J.P. Seismicity, structure and strength of the continental lithosphere. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2004, 223, 427–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maggi, A.; Jackson, J.A.; Mckenzie, D.; Priestley, K. Earthquake focal depths, effective elastic thickness, and the strength of the continental lithosphere. Geology 2000, 28, 495–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenzie, D.; Fairhead, D. Estimates of the effective elastic thickness of the continental lithosphere from Bouguer and free air gravity anomalies. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 1997, 102, 27523–27552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Che, C.; Kaban, M.K.; Du, J.; Liang, Q.; Thomas, M. Variations of the effective elastic thickness over China and surroundings and their relation to the lithosphere dynamics. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2013, 363, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, D.F. Gravity changes during the Alaska earthquake. J. Geophys. Res. 1966, 71, 451–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.T.; Gu, H.D.; Lu, Z.X. Variations of gravity before and after the Haicheng earthquake, 1975, and the Tangshan earthquake, 1976. Phys. Earth Planet. Inter. 1979, 18, 330–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heki, K.; Matsuo, K. Coseismic gravity changes of the 2010 earthquake in central Chile from satellite gravimetry. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2010, 37, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Liu, G.; Lu, Z.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, G. Lithospheric structure and dynamic processes of the Tianshan orogenic belt and the Junggar basin. Tectonophysics 2003, 376, 199–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Song, F.; Ni, X. Paleozoic accretionary orogenesis and major transitional tectonicevents of the Tianshan orogcn. Acta Geol. Sin. 2022, 96, 3514–3540. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Li, C.; Pak, N.; Ivleva, E.; Yu, X.; Zhou, G.; Xiao, W.; Han, S.; Halilov, Z.; Takenov, N.; et al. Tectonic division and Paleozoic ocean- continent transition in Western Tianshan Orogen. Geol. China 2017, 4, 623–641, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Zou, H.; Li, H. Tectonic framework and evolution of the Tarim Block in NW China. Gondwana Res. 2013, 23, 1306–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, S.A.; Hendrix, M.S.; Wang, L. Collisional successor basins of western China: Impact of tectonic inheritance on sand composition. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 1993, 105, 323–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, A.; Nie, S.; Craig, P. Late Cenozoic tectonic evolution of the southern Chinese Tian Shan. Tectonics 1998, 17, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, J.; Zhao, D. Teleseismic P-wave tomography and the upper mantle structure of the central Tien Shan orogenic belt. Phys. Earth Planet. Inter. 2007, 162, 165–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hapaer, T.; Tang, Q.; Sun, W. Opposite facing dipping structure in the uppermost mantle beneath the central Tien Shan from Pn traveltime tomography. Int. J. Earth Sci. 2022, 111, 2571–2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laske, G.; Masters, G.; Ma, Z. Update on CRUST1. 0—A 1-degree global model of Earth’s crust. Geophys. Res. Abstr. 2013, 15, 2658. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Chen, S.; Zhang, B. Analysis of the Variation of Gravity Field Source Before the 2013 Lushan Ms 7.0 Earthquake. Earthquake 2021, 41, 78–92. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, R.; Diao, F.; Hoechner, A. SDM-A geodetic inversion code incorporating with layered crust structure and curved fault geometry. In Proceedings of the EGU General Assembly, Vienna, Austria, 7 April 2013. Conference Abstracts EGU2013-2411. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, D.; Zhao, L.; Yuan, H. Receiver function mapping of the mantle transition zone beneath the Tian Shan orogenic belt. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2022, 127, e2022JB024635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.; Zhu, J.; Luo, Z.; Xu, Y. Petrogenesis and geological implications of the Late Carboniferous Baiyanggouvolcanic rocks. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2018, 34, 126–142. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.; Rocker, S.W.; Wei, R.-P.; Zhang, W.-L.; Wei, B. Analysis of seismic activity in the crust from earthquake relocation in the Central Tian Shan. Chin. J. Geophys 2005, 48, 1308–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.; Li, L.; Zhang, Z.; Shi, Y.; Li, Q.; Xue, Z.; Wang, F.; Wu, L. Paleozoic tectonic of evolution of Tianshanorogen: In the view from a structure analysis of the HP-UHP metamorphic belt of SW Chinese Tianshan. Acta Petrol. 2015, 31, 2115–2128. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, H.; Li, Y. Deformation characteristics of the active backslope belt in the northern foothills of the Tianshan Mountains. Quat. Sci. 2010, 30, 1003–1011. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, C. Characteristics of Late Quaternary activity and role in the tectonic deformation of the NED-trending faults in the southwestern Tien Shan. Prog. Earthq. Sci. 2017, 09, 46–48. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, Y. Bayesian Estimation of the Effective Elastic Thickness of the Lithosphere and Application to Typical Continental Regions. Ph.D. Thesis, Institute of Geophysics, China Earthquake Administration (CEA), Beijing, China, June 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Dorman, L.M.; Lewis, B.T. Experimental isostasy: 1. Theory of the determination of the Earth’s isostatic response to a concentrated load. J. Geophys. Res. 1970, 75, 3357–3365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenzie, D.; Bowin, C. The relationship between bathymetry and gravity in the Atlantic Ocean. J. Geophys. Res. 1976, 81, 1903–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, R.L. The rapid calculation of potential anomalies. Geophys. J. Int. 1973, 31, 447–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirby, J.F.; Swain, C.J. A reassessment of spectral Te estimation in continental interiors: The case of North America. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2009, 114, B08401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonvalot, S.; Balmino, G.; Briais, A. World Gravity Map: Commission for the Geological Map of the World; 25 April 2012; BGI–CGMW-CNES-IRD: Paris, France, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z. Theory and Methods for Determining the Earth’s Gravity Field from Satellite Tracking Satellite Measurements. Ph.D. Thesis, Wuhan University, Wuhan, China, December 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, F.; Yn, J.; Zhang, C. The Effective Elastic Thickness of Lithosphere and Its Tectonic Implications in the South China Block. Acta Geosci. Sin. 2022, 43, 771–784. [Google Scholar]
- Kirby, J.F.; Swain, C.J. Improving the spatial resolution of effective elastic thickness estimation with the fan wavelet transform. Comput. Geosci. 2011, 37, 1345–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Liu, J.; Chen, C. Elastic thickness of the Himalayan–Tibetan orogen estimated from the fan wavelet coherence method, and its implications for lithospheric structure. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2015, 409, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Chen, S.; Han, J. Effective elastic thickness of lithosphere and mechanical characteristics of strong seismic tectonic zones in mainland China. Earthquake 2021, 41, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, D. Studies on the Lithospheric Structure and Seismodynamic Environment of Tianshan and Neighboring Areas. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Science and Technology of China (USTC), Hefei, China, September 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Zuo, Y.; Li, J.; Li, W. Mesozoic and Cenozoic ”thermal” Lithospheric thickness evolution in the Tarim basin. Prog. Geophys. 2015, 30, 1608–1615. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J.; Huang, Y.; Ma, Z. Discussion on the basement structure and property of northern Junggar basin. Chin. J. Geop. Hys. 2008, 51, 767–1775. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H.; Teng, J.; Wang, Q. Numerical simulation study of sufficient and necessary conditions for material flow in the lower crust of the Tibetan Plateau. In Proceedings of the 27th Annual Meeting of the Chinese Geophysical Society, Chengdu, China, 17 October 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, J.; Liu, M.; Liu, Y. Present-day temperature-pressure field and its controlling factors of the lower composite reservoir in the southern margin of Junggar Basin. Chin. J. Geol. 2021, 56, 28–43. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Li, C.; Shi, Y. Characterization of geodetic heat flow density distribution in the Tarim Basin. ACTA Geophys. A Sin. 1995, 06, 855–856. [Google Scholar]
- Han, K.; Liu, D.; Ailixiati, Y. InSAR Coseismic Deformation and Slip Distribution Characteristics of the Jishishan MS6.2 Earthquake in 2023. J. Geod. Geodyn. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Deng, Q.; Zhang, Z. Active faults, earthquake hazards and associated geodynamic processes in continental China. Sci. Sin. Terrae 2013, 43, 1607–1620. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Teng, J. Crustal equilibrium anomalies and their relation to earthquake distribution in the eastern part of Sichuan and Tibet. Chin. J. Geophys. 2010, 53, 2631–2638. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, G.; Sheng, C.; Li, Z. Gravity equilibrium and effective elastic thickness of the lithosphere in the eastern part of the Ba Yan Ka La Massif and neighboring areas. Chin. J. Geophys. 2020, 63, 956–968. [Google Scholar]
- Su, Z.; Lu, B.; Li, B. Effective elastic thickness of the lithosphere along the northeastern margin of the Tibetan Plateau in relation to seismic distribution. Chin. J. Geophys. 2024, 67, 520–533. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, S. Spectral Correlation Method to Calculate the Effective Elastic Thickness of South China Sea. Ph.D. Thesis, China University of Geosciences, Beijing, China, May 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, M.; Jin, T.; Hao, H. Effective elastic thickness of the lithosphere at the southeastern margin of the Tibetan Plateau and its tectonic significance. Chin. J. Geophys. 2020, 63, 969–987. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, X.; Liu, F.; Zhang, G.; Zhao, Y.; Wei, S.; Mao, J.; Zhang, S. Progress of time-varying gravity in seismic research. Rev. Geophys. Planet. Phys. 2022, 53, 278–291. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, D.; Chen, S.; Wang, X. The apparent density variation of the focal area before and after Jiashi MS 6.4 earthquake and its tectonic significance. Seismol. Geol. 2021, 43, 311–328. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, S.; Huang, J.; Zheng, Q. Reconstruction of strong pre-seismic gravity change data and inversion of apparent density–An example of the 2021 Yangbi 6.4 magnitude earthquake. J. Seismol. Res. 2025, 48, 631–640. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.; Shen, C.; Zhang, G. Rethinking the development of mobile gravity monitoring and forecasting in China. J. Geod. Geodyn. 2018, 38, 441–446. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, M.; Hao, H.; Li, H. Analysis of Gravity Change Anomaly Indicators for Seismic Analysis and Forecasting. Earthq. Res. China 2019, 35, 417–430. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, M.; Hao, H.; Han, Y. Gravity flexura lisostasy background of the 2021 Madoi (Qinghai) Ms 7.4 earthquake and gravity change before the earthquake. Chin. J. Geophys. 2021, 64, 3135–3149. [Google Scholar]
- Farr, T.G.; Rosen, P.A.; Caro, E. The shuttle radar topography mission. Rev. Geophys. 2007, 45, RG2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, R.M.; Werner, C.L. Radar interferogram filtering for geophysical applications. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1998, 25, 4035–4038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costantini, M.A. novel phase unwrap method based on network programming. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1998, 36, 813–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Z.; Chuan, W.; Jian, M. Earthquake sequence relocation and seismogenic structure of the 2024 Ms7.1 Wushi earthquake on January 23, 2024, Xinjiang. Seismol. Geol. 2025, 47, 488–506. [Google Scholar]
- Jiu, Y.; Yang, W.; Cai, X. Coseismic deformation and slip distribution of the January 2024 Xinjiang WushiMS7.1 earthquake revealed by InSAR observations. Chin. J. Geophys. 2025, 68, 2532–2543. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, X.; Guo, L.; Chen, Z. A method for gravity anomaly separation based on preferential continuation and its application. Appl. Geophys. 2009, 6, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, X.; Liu, D.; Ailixiati, Y. Study on the characteristics of gravity field and apparent density in Urumqi and its surrounding areas. Seismol. Geol. 2024, 46, 1123–1150. [Google Scholar]



| Spatial Resolution | Orbit | Master Image | Secondary Image | Time Baseline | Spatial Baseline | Polarization | Beam Mode | Incidence | Azimuth |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 × 20 m | As056 | 14 January 2024 | 26 January 2024 | 12 d | −19.65 m | VV | IW | 39.66° | 13.57° |
| Des136 | 20 January 2024 | 25 February 2024 | 36 d | 109.54 m | 39.64° | 166.40° |
| Location/(°E, °N) | Strike/° | Dip/° | Rake/° | Depth/km | Magnitude/Mw | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| USGS | 78.66, 41.26 | 235 | 45 | 42 | 13.0 | 7.0 |
| GFZ | 78.73, 41.28 | 251 | 38 | 73 | 15.0 | 7.0 |
| GCMT | 78.56, 41.19 | 235 | 46 | 44 | 16.1 | 7.1 |
| This Paper | 78.61, 41.22 | 232 | 48 | 80 | 11.9 | 7.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, K.; Liu, D.; Yushan, A.; Shi, W.; Li, J.; Kong, X.; He, H. Study on Lithospheric Tectonic Features of Tianshan and Adjacent Regions and the Genesis Mechanism of the Wushi Ms7.1 Earthquake. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 2655. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17152655
Han K, Liu D, Yushan A, Shi W, Li J, Kong X, He H. Study on Lithospheric Tectonic Features of Tianshan and Adjacent Regions and the Genesis Mechanism of the Wushi Ms7.1 Earthquake. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(15):2655. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17152655
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Kai, Daiqin Liu, Ailixiati Yushan, Wen Shi, Jie Li, Xiangkui Kong, and Hao He. 2025. "Study on Lithospheric Tectonic Features of Tianshan and Adjacent Regions and the Genesis Mechanism of the Wushi Ms7.1 Earthquake" Remote Sensing 17, no. 15: 2655. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17152655
APA StyleHan, K., Liu, D., Yushan, A., Shi, W., Li, J., Kong, X., & He, H. (2025). Study on Lithospheric Tectonic Features of Tianshan and Adjacent Regions and the Genesis Mechanism of the Wushi Ms7.1 Earthquake. Remote Sensing, 17(15), 2655. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17152655







