InSAR Inversion of the Source Mechanism of the 23 January 2024 Xinjiang Wushi Mw7.0 Earthquake
Abstract
1. Introduction
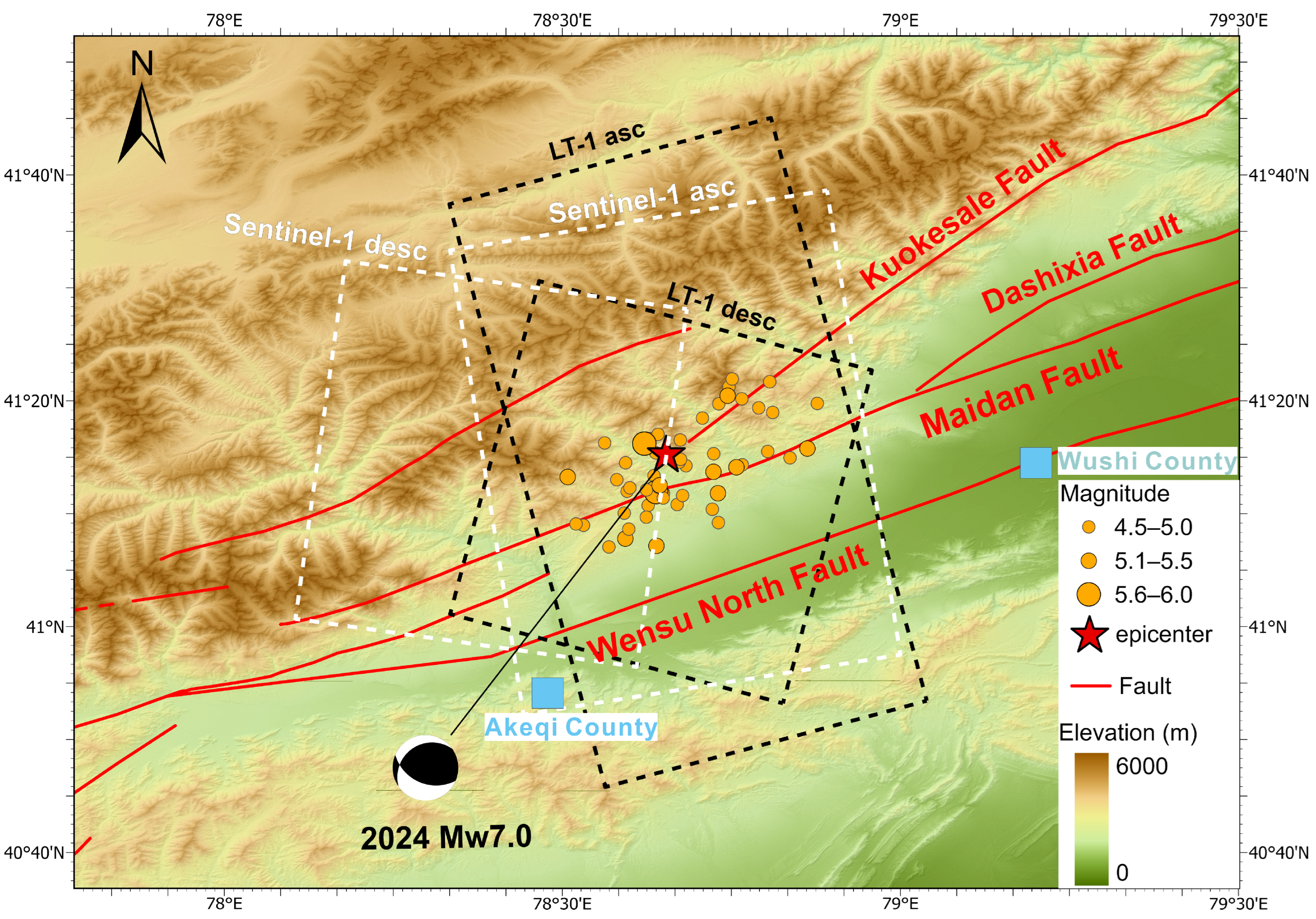
2. Tectonic Background
3. InSAR Coseismic Deformation
3.1. InSAR Data and Methodology
3.2. Characterization of the Coseismic Deformation
4. Rupture Parameter Inversion and Coulomb Stress Calculation
4.1. Coseismic Inversion
4.2. Coseismic Inversion Results
4.3. Aftershock Deformation and Inversion
4.4. Coseismic Coulomb Stress Changes in the Wushi Earthquake
5. Discussion
5.1. Stability Analysis of Coulomb Stress Changes
5.2. Relationship Between the Mainshock and the 30 January Aftershock
5.3. The Wushi Earthquake and Tianshan Tectonics
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, Z.; Fang, L.H.; Chen, K.; Liu, R.F.; Wang, Y.Z.; Guo, X.Y. Quick Output Parameters Related to the 23 January 2024 MS7.1 Wushi Earthquake in the Aksu Region of Xinjiang. Prog. Earthq. Sci. 2024, 54, 221–228. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B.X.; Qian, L.; Li, T.; Chen, J.; Xu, J.H.; Yao, Y.; Fang, L.H.; Xie, C.; Chen, J.B.; Liu, G.H.; et al. Geological Disasters and Surface Ruptures of January 23, 2024 MS7.1 Wushi Earthquake, Xinjiang, China. Seismol. Geol. 2024, 46, 220–234. [Google Scholar]
- Nai, Y.H.; Han, B.Q.; Liu, Z.J.; Li, Z.H.; Song, C.; Yu, C.; Li, S.J.; Peng, J.B. Coseismic Surface Displacements and Source Model of the 2024 Mw7.0 Wushi (Xinjiang, China) Earthquake Revealed by InSAR Observations. Geomat. Inf. Sci. Wuhan Univ. 2024, 50, 368–376. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, L.; Chen, Z.D.; Xie, L.; Zhu, Z.; Xu, W. Coseismic deformation and slip model of the 2024 MW7.0 Wushi earthquake obtained from InSAR observation. Rev. Geophys. Planet. Phys. 2024, 55, 453–460. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, S.Y.; Li, Z.J.; Zhao, P.; Luo, J.J. Source Parameters and Seismogenic Fault Model of the 2024 Mw7.0 Wushi (Xinjiang, China) Earthquake Revealed by InSAR Observations. Pure Appl. Geophys. 2024, 182, 1149–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.R.; Liu, X.; Dai, X.F.; Yin, G.Y.; Yang, Y.; Guo, J.Y. D-InSAR-Based Analysis of Slip Distribution and Coulomb Stress Implications from the 2024 Mw7.01 Wushi Earthquake. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 4319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Famiglietti, N.A.; Cheloni, D.; Caputo, R.; Vicari, A. Geodetic model of the 2024 January 22 Mw 7.0 Wushi (northwestern China) earthquake and Mw 5.7 aftershock from inversion of InSAR data. Geophys. J. Int. 2025, 241, 941–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Tang, X.M.; Li, T.; Zhao, H. Turkey-Syria Mw 7.8 Earthquake Deformation Monitoring Using Lutan-1 SAR Data. In Proceedings of the Photonics Electromagnetics Research Symposium (PIERS), Chengdu, China, 15 January 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.S.; Li, Q.; Jiao, Q.S.; Jiang, W.L.; LI, B.Q.; Zhang, J.F.; Luo, Y. Application of Lutan-1 SAR Satellite Constellation to Earthquake Industry and Its Prospect. Geomat. Inf. Sci. Wuhan Univ. 2024, 49, 1741–1752. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, C.Y. Late Quaternary Activity of the East-Northeastern Trending Faults in the Southwestern Tianshan and Their Role in the Tectonic Deformation of the Tianshan Mountains. Ph.D. Thesis, Institute of Geology, China Earthquake Administration, Beijing, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Hendrix, M.S.; Dumitru, T.A.; Graham, S.A. Late Oligocene-Early Miocene Unroofing in the Chinese Tian Shan: An Early Effect of the India-Asia Collision. Geology 1994, 22, 487–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, A.; Nie, S.; Craig, P.; Harrison, T.M.; Ryerson, F.J.; Qian, X.L.; Yang, G. Late Cenozoic Tectonic Evolution of the Southern Chinese Tian Shan. Tectonics 1998, 17, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.P.; Ran, Y.K.; Cheng, J.W.; Chen, L.C.; Xu, X.W. Measurement of Terrace Deformation and Crustal Shortening of Some Renascent Fold Zones within Kalpin Nappe Structure. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2007, 50, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.T.; Cheng, H.H.; Dong, P.Y.; Pang, Y.J.; Zhang, H.; Shi, Y.L. Numerical Analysis of Seismogenic Stress Field and Fault Activity Characteristics of Tianshan Orogen and Its Adjacent Areas. Chin. J. Geophys. 2020, 63, 4037–4049. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, B.; Chen, C.Y. Study on the Relationship Between GNSS Deformation Characteristics and Earthquakes in Xinjiang and Its Adjacent Regions. J. Seismol. Res. 2024, 47, 419–429. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, L.X.; Li, T.; Chen, Z.X.; Jobe, J.T.; Fang, L.H. Active Structural Geometries and Their Correlation with Moderate (M 5.5–7.0) Earthquakes in the Jiashi-Keping Region, Tian Shan Southwestern Front. Tectonics 2021, 40, 12. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, C.Y.; Alimujiang, D.X.; Dai, X.Y.; Wu, G.D.; Chen, J.B. Discovery of the Late Quaternary Activity Along the Eastern Segment of Maidan Fault in Southwest Tianshan and Its Tectonic Implication. Seismol. Geol. 2014, 36, 976–990. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, Q.C.; Wu, C.Y.; Shen, J.; Wu, G.D.; Ren, P. Evidence of Left-Lateral Strike-Slip Along the Akqi Segment of Maidan Fault in Southwest Tianshan Mountains, China and Its Latest Activity. China Earthq. Eng. J. 2015, 37, 222–227. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Q.; Wen, Y.; Xu, C.; Zhao, X. Present-day tectonic activities of transverse faults in the Keping region, southwest Tianshan. Seismol. Res. Lett. 2024, 96, 1901–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NASA/METI/AIST/Japan Space systems and U.S./Japan ASTER Science Team. ASTER Global Digital Elevation Model V003; NASA: Washington, DC, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.W.; Zebker, H.A. Network Approaches to Two-Dimensional Phase Unwrapping: Intractability and Two New Algorithms. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 2000, 17, 401–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Penna, N.T.; Li, Z. Generation of Real-Time Mode High-Resolution Water Vapor Fields from GPS Observations. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2017, 122, 2008–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Li, Z.; Penna, N.T. Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar Atmospheric Correction Using a GPS-Based Iterative Tropospheric Decomposition Model. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 204, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finkel, R.A.; Bentley, J.L. Quad trees a data structure for retrieval on composite keys. Acta Inform. 1974, 4, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jónsson, S. Fault Slip Distribution of the 1999 Mw 7.1 Hector Mine, California, Earthquake, Estimated from Satellite Radar and GPS Measurements. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 2002, 92, 1377–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, W.P.; Li, Z.H. A Novel Hybrid PSO/Simplex Algorithm for Determining Earthquake Source Parameters Using InSAR Data. Prog. Geophys. 2010, 25, 1189–1196. [Google Scholar]
- Okada, Y. Surface Deformation Due to Shear and Tensile Faults in a Half-Space. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 1985, 75, 1135–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, R.A.; Segall, P. Detection of a Locked Zone at Depth on the Parkfield, California, Segment of the San Andreas Fault. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 1987, 92, 7945–7962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akaike, H. Likelihood and the Bayes Procedure. In Bayesian Statistics; Bernardo, J.M., DeGroot, M.H., Lindley, D.V., Smith, A.F.M., Eds.; University Press: Valencia, Spain, 1980; pp. 143–166. [Google Scholar]
- Fukahata, Y.; Wright, T.J. A non-linear geodetic data inversion using ABIC for slip distribution on a fault with an unknown dip angle. Geophys. J. Int. 2008, 173, 353–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, G.C.P.; Stein, R.S.; Lin, J. Static Stress Changes and the Triggering of Earthquakes. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 1994, 84, 935–953. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, R.; Lorenzo-Martín, F.; Roth, F. PSGRN/PSCMP—A New Code for Calculating Co- and Post-Seismic Deformation, Geoid and Gravity Changes Based on the Viscoelastic-Gravitational Dislocation Theory. Comput. Geosci. 2006, 32, 527–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, X.; Shan, B.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, R.J. Stress Transfer and Its Implication for Earthquake Hazard on the Kunlun Fault, Tibet. Tectonophysics 2010, 491, 216–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, X.; Luo, G.; Zheng, L.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, C. Early Post-Seismic Deformation Revealed After the Wushi (China) Earthquake (Mw = 7.1) Occurred on 22 January 2024. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.; Sun, J.; Ji, L. The 2024 Mw 7.1 Wushi Earthquake: A Thrust and Strike-Slip Event Unveiling the Seismic Mechanisms of the South Tian Shan’s Thick-Skin Tectonics. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 2937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










| Source | Locations | Depth (km) | Focal Mechanisms | Fault Dimensions | Magnitude (MW) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lon (°) | Lat (°) | Strike (°) | Dip (°) | Rake (°) | Length (km) | Width (km) | |||
| USGS | 78.65 | 41.27 | 13 | 235 | 45 | 42 | — | — | 7.0 |
| GCMT | 78.57 | 41.19 | 14 | 236 | 48 | 47 | — | — | 7.0 |
| Nai [3] | 78.64 | 41.23 | 6.6 | 230.27 | 55 | 42 | 34.7 | 10.5 | 7.05 |
| Zhao [4] | 78.60 | 41.19 | 13 | 228 | 67 | 60 | 34 | 14.2 | 7.0 |
| Yu [5] | 78.65 | 41.22 | 15 | 229 | 62.8 | 49.8 | 35 | 6 | 7.02 |
| Ding [6] | 78.66 | 41.23 | 13 | 228.34 | 61.88 | 42 | 34.8 | 15.8 | 7.02 |
| Famiglietti [7] | 78.67 | 41.21 | 7.4 | 229.7 | 61.6 | 47.2 | 36.3 | 12.1 | 7.01 |
| This study | 78.69 | 41.22 | 7 | 229.38 | 64.64 | 45 | 34.9 | 7.74 | 7.1 |
| Effective Friction Coefficient | 0.2 | 0.4 | 0.6 | 0.8 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coulomb Stress Change | 0.3391 × 106 Pa | 0.4251 × 106 Pa | 0.5110 × 106 Pa | 0.5969 × 106 Pa |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jin, M.; Li, Y.; Li, Y. InSAR Inversion of the Source Mechanism of the 23 January 2024 Xinjiang Wushi Mw7.0 Earthquake. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 2435. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17142435
Jin M, Li Y, Li Y. InSAR Inversion of the Source Mechanism of the 23 January 2024 Xinjiang Wushi Mw7.0 Earthquake. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(14):2435. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17142435
Chicago/Turabian StyleJin, Mingyang, Yongsheng Li, and Yujiang Li. 2025. "InSAR Inversion of the Source Mechanism of the 23 January 2024 Xinjiang Wushi Mw7.0 Earthquake" Remote Sensing 17, no. 14: 2435. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17142435
APA StyleJin, M., Li, Y., & Li, Y. (2025). InSAR Inversion of the Source Mechanism of the 23 January 2024 Xinjiang Wushi Mw7.0 Earthquake. Remote Sensing, 17(14), 2435. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17142435







