Quantifying the Drivers of the Spatial Distribution of Urban Surfaces in Bangladesh: A Multi-Method Geospatial Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
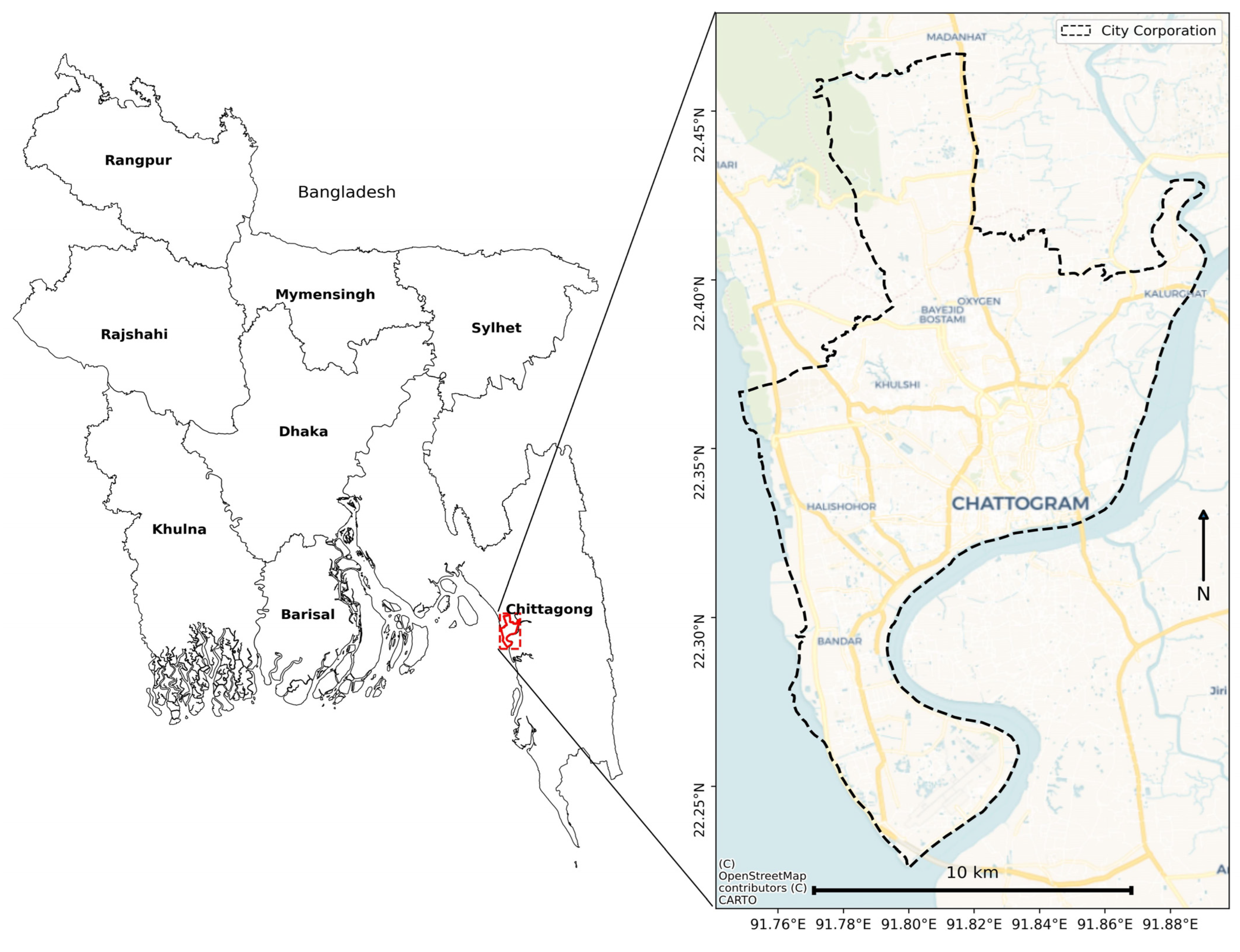
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Characteristics
2.3. Methods
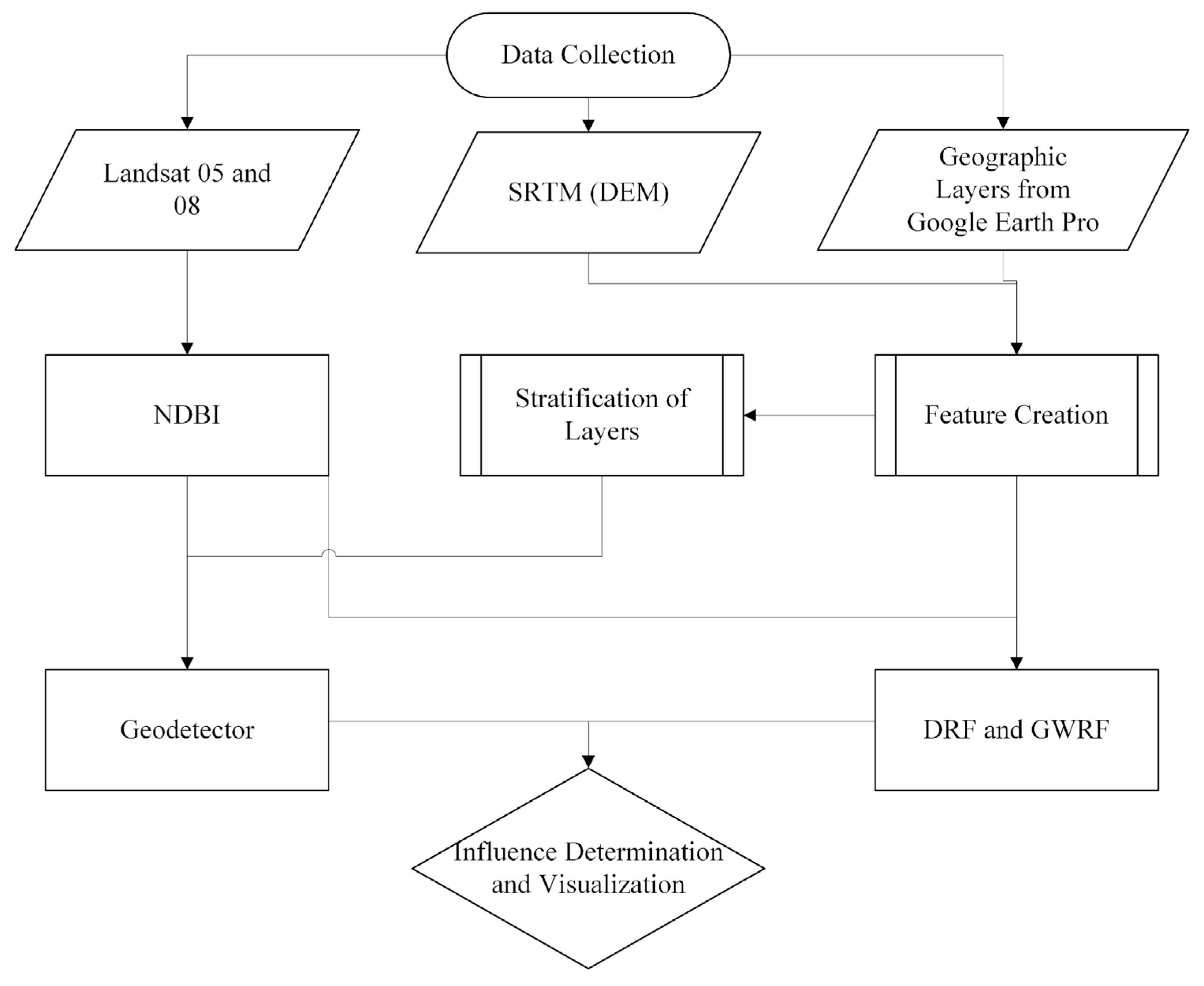
2.3.1. Data Processing
2.3.2. Index-Based Urban Surface Determination
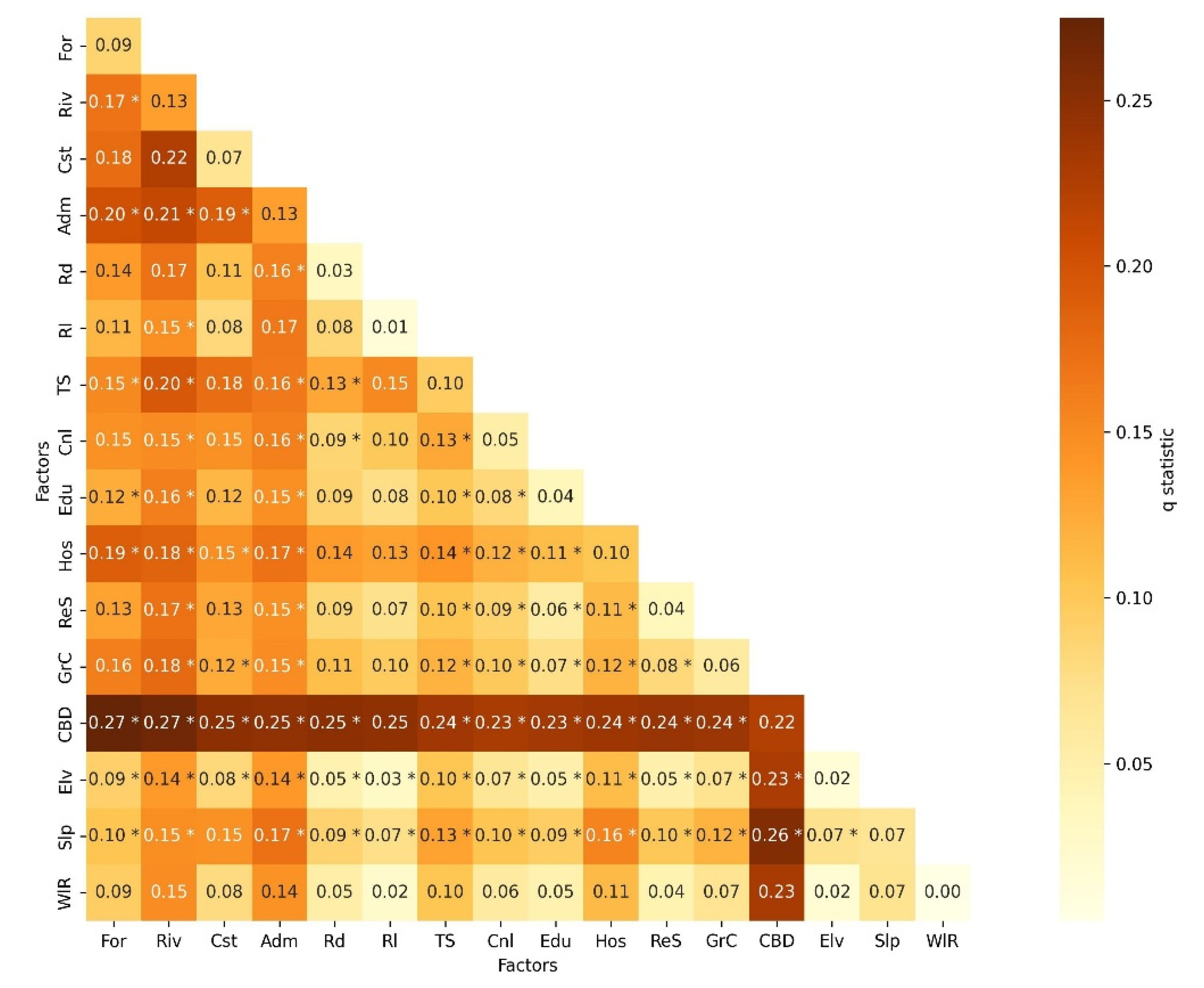
2.3.3. Geodetector
2.3.4. Distributional Random Forest (DRF)
2.3.5. Geographically Weighted Random Forest (GWRF)
3. Results
3.1. Validation of the Results
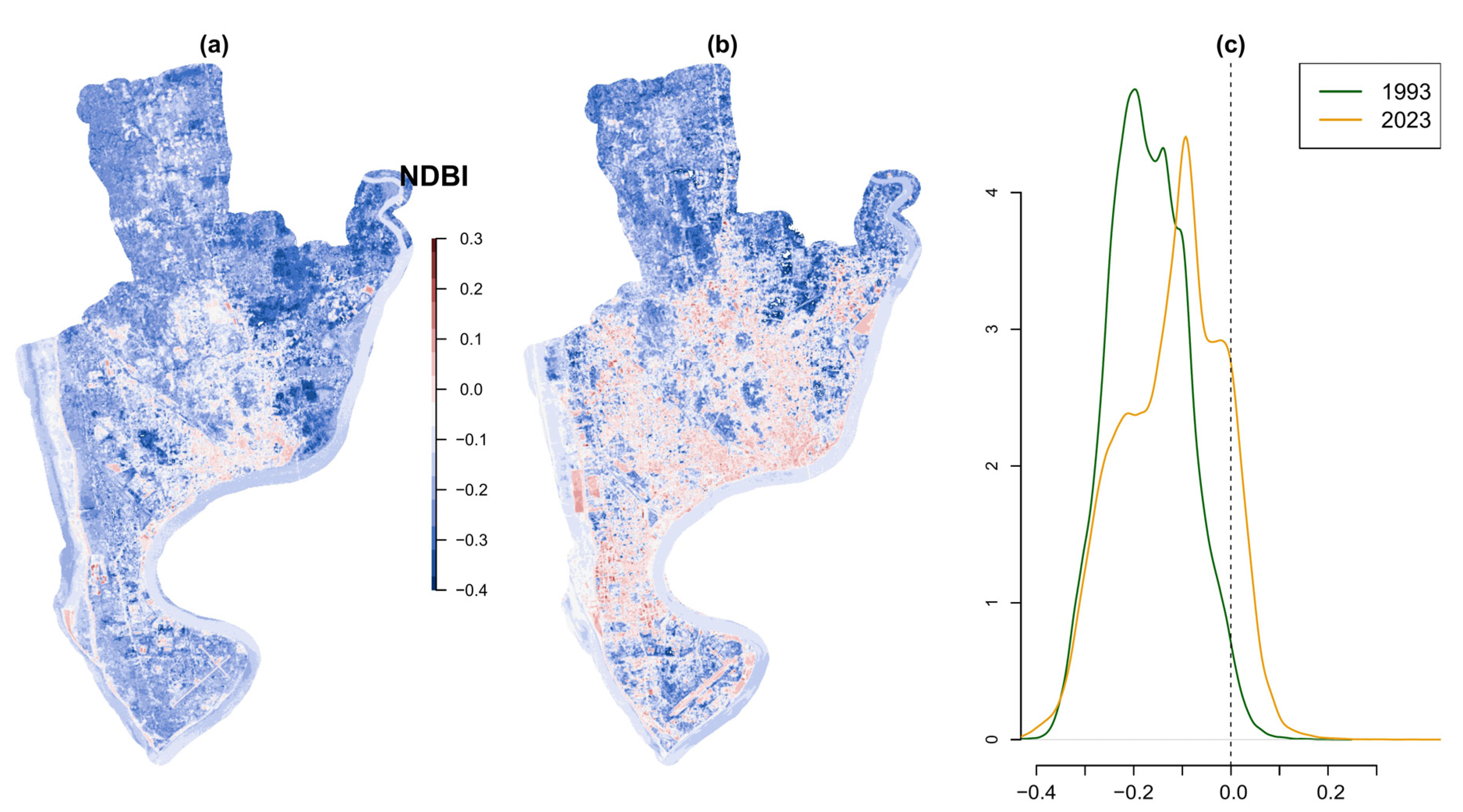
3.2. Spatial Distribution of Urban Surface and Temporal Change
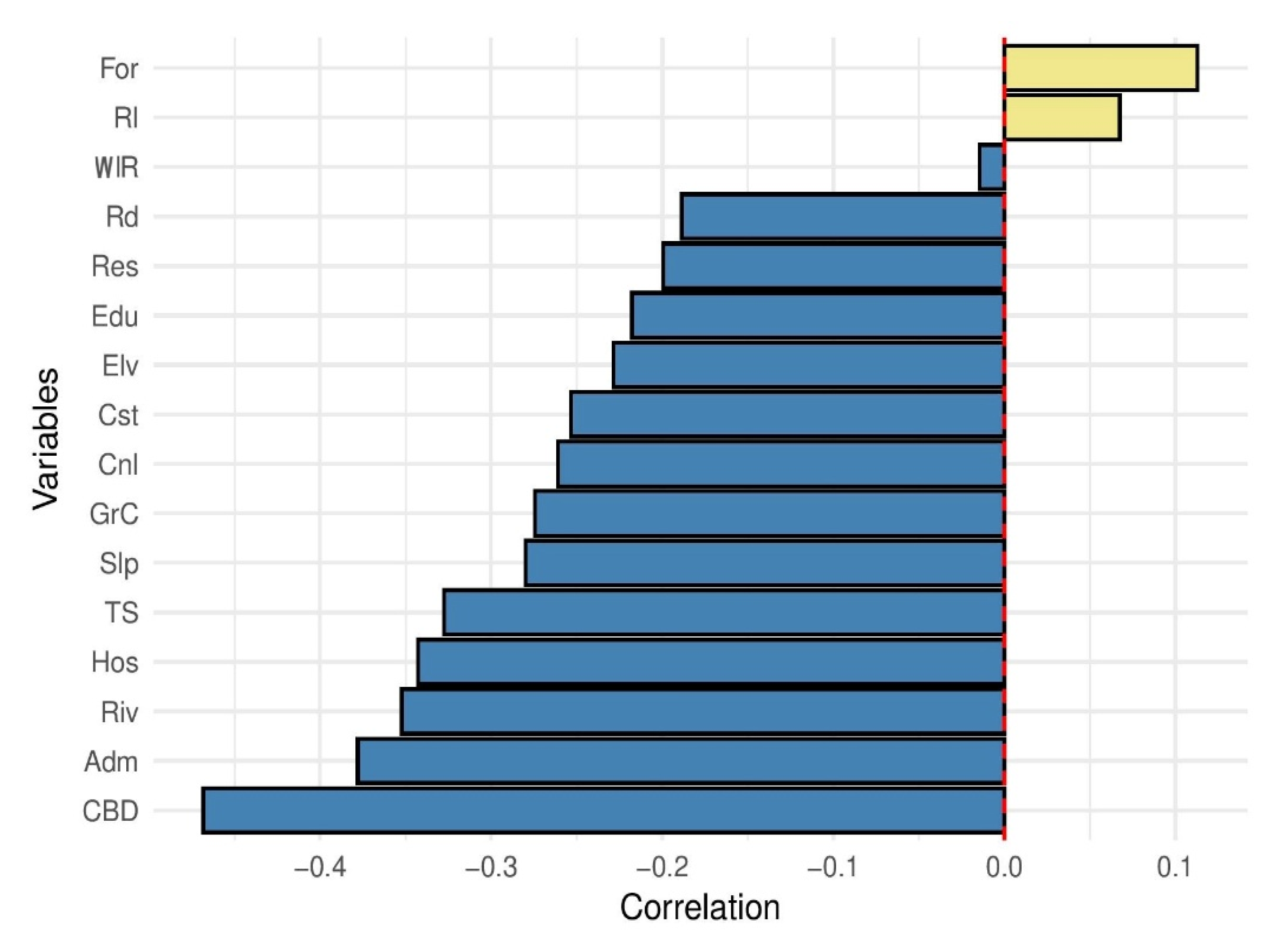
3.3. The Influence and Direction of Individual Factors
3.4. Combined Influence of Factors
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BBS | Bangladesh Bureau of Statistics |
| CBD | Central Business District |
| DEM | Digital Elevation Model |
| DRF | Distributed Random Forest |
| GIS | Geographic Information Systems |
| GWRF | Geographically Weighted Random Forest |
| LULC | Land Use and Land Cover |
| ML | Machine Learning |
| NDBI | Normalized Difference Built-up Index |
| OOB | Out-of-Bag |
| RF | Random Forest |
| RMSE | Root Mean Square Error |
| RS | Remote Sensing |
| SDUS | Spatial Distribution of Urban Surfaces |
| SSH | Spatial Stratified Heterogeneity |
| UHI | Urban Heat Island |
Appendix A
| Variable | Equal | Quantile | Fisher-Jenks | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | CBD | 0.22 | 0.22 | 0.22 |
| 2 | Riv | 0.15 | 0.15 | 0.14 |
| 3 | Adm | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.13 |
| 4 | Hos | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.11 |
| 5 | TS | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 |
| 6 | Elv | 0.07 | 0.08 | 0.08 |
| 7 | Slp | 0.07 | 0.07 | 0.08 |
| 8 | Cst | 0.07 | 0.07 | 0.07 |
| 9 | GrC | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.07 |
| 10 | Cnl | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.06 |
| 11 | Edu | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.05 |
| 12 | ReS | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.04 |
| 13 | Road | 0.03 | 0.04 | 0.04 |
| 14 | For | 0.09 | 0.03 | 0.03 |
| 15 | Rail | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 |
| Model | RMSE | MAE | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| DRF | 0.622 | 0.473 | 0.612 |
| Global GWRF | 0.640 | — | 0.59 |
| Local GWRF | 0.686 | — | 0.529 |
References
- Evers, D.; Katurić, I.; Van Der Wouden, R. Understanding Urbanization. In Urbanization in Europe; Sustainable Urban Futures; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 1–14. ISBN 978-3-031-62260-1. [Google Scholar]
- Rashid, K.J.; Akter, T.; Imrul Kayes, A.S.M.; Yachin Islam, M. Exploring the Spatio-Temporal Patterns and Driving Forces of Urban Growth in Dhaka Megacity from 1990 to 2020. In Urban Commons, Future Smart Cities and Sustainability; Chatterjee, U., Bandyopadhyay, N., Setiawati, M.D., Sarkar, S., Eds.; Springer Geography; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 375–400. ISBN 978-3-031-24766-8. [Google Scholar]
- Yeh, C.-T.; Huang, S.-L. Global Urbanization and Demand for Natural Resources. In Carbon Sequestration in Urban Ecosystems; Lal, R., Augustin, B., Eds.; Springer Netherlands: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2012; pp. 355–371. ISBN 978-94-007-2365-8. [Google Scholar]
- Henderson, J.V.; Turner, M.A. Urbanization in the Developing World: Too Early or Too Slow? J. Econ. Perspect. 2020, 34, 150–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewan, A.M.; Yamaguchi, Y. Land Use and Land Cover Change in Greater Dhaka, Bangladesh: Using Remote Sensing to Promote Sustainable Urbanization. Appl. Geogr. 2009, 29, 390–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, W.; Yang, M. Urbanization, Economic Growth and Environmental Pollution: Evidence from China. Sustain. Comput. Inform. Syst. 2019, 21, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalaby, A.; Tateishi, R. Remote Sensing and GIS for Mapping and Monitoring Land Cover and Land-Use Changes in the Northwestern Coastal Zone of Egypt. Appl. Geogr. 2007, 27, 28–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuli, R.D.; Rashid, K.J.; Islam, M.M.; Sobhan, M.; Islam, S.T.; Mondal, K.P.; Talukder, B.; Mondal, A.M. Impact of Climatic Parameters on Spatiotemporal Variation of Air Pollutants across Bangladesh. Urban Clim. 2025, 59, 102263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodman, D. Environment and Urbanization. In International Encyclopedia of Geography; Richardson, D., Castree, N., Goodchild, M.F., Kobayashi, A., Liu, W., Marston, R.A., Eds.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 1–9. ISBN 978-0-470-65963-2. [Google Scholar]
- Estache, A.; Fay, M. Current Debates on Infrastructure Policy 2007; World Bank Publications: Washington, DC, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- BBS. Statistical yearbook Bangladesh 2022; Statistics & Informatics Division (SID), Ministry of Planning Government of The People’s Republic of Bangladesh: Dhaka, Bangladesh, 2023; p. 589. [Google Scholar]
- Murayama, Y.; Simwanda, M.; Ranagalage, M. Spatiotemporal Analysis of Urbanization Using GIS and Remote Sensing in Developing Countries. Sustainability 2021, 13, 3681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Seto, K.C.; Stokes, E.C.; Deng, C.; Pickett, S.T.A.; Taubenböck, H. Understanding an Urbanizing Planet: Strategic Directions for Remote Sensing. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 228, 164–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javed, A.; Cheng, Q.; Peng, H.; Altan, O.; Li, Y.; Ara, I.; Huq, E.; Ali, Y.; Saleem, N. Review of Spectral Indices for Urban Remote Sensing. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2021, 87, 513–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, D.K.; Mandal, A.C.; Majumder, R.; Patra, P.; Bhunia, G.S. Analysis for Mapping of Built-Up Area Using Remotely Sensed Indices—A Case Study of Rajarhat Block in Barasat Sadar Sub-Division in West Bengal (India). J. Landsc. Ecol. 2018, 11, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kebede, T.A.; Hailu, B.T.; Suryabhagavan, K.V. Evaluation of Spectral Built-up Indices for Impervious Surface Extraction Using Sentinel-2A MSI Imageries: A Case of Addis Ababa City, Ethiopia. Environ. Chall. 2022, 8, 100568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H. A New Index for Delineating Built-up Land Features in Satellite Imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2008, 29, 4269–4276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Abuduwaili, J.; Liu, W.; Feng, S.; Saparov, G.; Ma, L. Application of Geographical Detector and Geographically Weighted Regression for Assessing Landscape Ecological Risk in the Irtysh River Basin, Central Asia. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 158, 111540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.-F.; Zhang, T.-L.; Fu, B.-J. A Measure of Spatial Stratified Heterogeneity. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 67, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, X.; Christakos, G.; Liao, Y.; Zhang, T.; Gu, X.; Zheng, X. Geographical Detectors-Based Health Risk Assessment and Its Application in the Neural Tube Defects Study of the Heshun Region, China. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2010, 24, 107–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, K.F.; Chesson, P.; Harrison, S.; Inouye, B.D.; Melbourne, B.A.; Rice, K.J. Spatial Heterogeneity Explains the Scale Dependence of the Native–Exotic Diversity Relationship. Ecology 2005, 86, 1602–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anselin, L. Local Indicators of Spatial Association—LISA. Geogr. Anal. 1995, 27, 93–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwanghart, W.; Beck, J.; Kuhn, N. Measuring Population Densities in a Heterogeneous World. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2008, 17, 566–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Xu, C. Knowledge Diffusion of Geodetector: A Perspective of the Literature Review and Geotree. Heliyon 2023, 9, e19651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, K.J.; Tuli, R.D.; Nasher, N.M.R.; Akter, T.; Karim, K.H.R.; Hasan, M.M.; Talha, M.; Chowdhury, S.I.A.; Musharrat, M. Greening and Browning Trend with Physio-Climatic Drivers in Chattogram Division, Bangladesh. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L. Random Forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- H2O.ai. H2o: R Interface for H2O. R Package Version 3.42.0.2. Available online: https://github.com/h2oai/h2o-3 (accessed on 7 February 2025).
- Fotheringham, A.; Brunsdon, C.; Charlton, M. Geographically Weighted Regression: The Analysis of Spatially Varying Relationships; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2002; Volume 13. [Google Scholar]
- Georganos, S.; Grippa, T.; Gadiaga, A.; Linard, C.; Lennert, M.; Vanhuysse, S.; Mboga, N.; Wolff, E.; Kalogirou, S. Geographical Random Forests: A Spatial Extension of the Random Forest Algorithm to Address Spatial Heterogeneity in Remote Sensing and Population Modelling. Geocarto Int. 2019, 36, 121–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, B. Landslide Susceptibility Mapping Using Multi-Criteria Evaluation Techniques in Chittagong Metropolitan Area, Bangladesh. Landslides 2015, 12, 1077–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazi, M.Y.; Rahman, M.Z.; Uddin, M.M.; Rahman, F.M.A. Spatio-Temporal Dynamic Land Cover Changes and Their Impacts on the Urban Thermal Environment in the Chittagong Metropolitan Area, Bangladesh. GeoJournal 2021, 86, 2119–2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.M.; Islam, R.; Rahman, M.S.; Ibrahim, M.; Shamsuzzoha, M.; Khanam, R.; Zaman, A.K.M.M. Analysis of Land Use and Land Cover Changing Patterns of Bangladesh Using Remote Sensing Technology. Am. J. Environ. Sci. 2021, 17, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, M.M.; Nazem, M.N.I. Examination of Land Use/Land Cover Changes, Urban Growth Dynamics, and Environmental Sustainability in Chittagong City, Bangladesh. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2016, 18, 697–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imran, H.M.; Hossain, A.; Shammas, M.I.; Das, M.K.; Islam, M.R.; Rahman, K.; Almazroui, M. Land Surface Temperature and Human Thermal Comfort Responses to Land Use Dynamics in Chittagong City of Bangladesh. Geomat. Nat. Hazards Risk 2022, 13, 2283–2312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.S. New-Build Gentrification in Chittagong, Bangladesh: A Case Study from Asian Gentrification Perspective. Master’s Thesis, University of Helsinki, Helsinki, Finland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Rai, R.; Zhang, Y.; Paudel, B.; Li, S.; Khanal, N. A Synthesis of Studies on Land Use and Land Cover Dynamics during 1930–2015 in Bangladesh. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Pandit, S.; Eva, E.A.; Bagmar, M.S.H.; Papia, M.; Banik, L.; Dube, T.; Rahman, F.; Razi, M.A. Examining the Nexus between Land Surface Temperature and Urban Growth in Chattogram Metropolitan Area of Bangladesh Using Long Term Landsat Series Data. Urban. Clim. 2020, 32, 100593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samad, M.R.B.; Chisty, K.U.; Rahman, A. Urbanization and Urban Growth Dynamics: A Study on Chittagong City. J. Bangladesh Inst. Plan. 2015, 8, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CCC At a Glance of Chattogram City Corporation. Available online: https://ccc.gov.bd/site/page/68a6b4b6-426a-49eb-89fb-842eb7d91922/- (accessed on 2 February 2025).
- Mia, M.A.; Nasrin, S.; Zhang, M.; Rasiah, R. City profile: Chittagong, Bangladesh. Cities 2015, 48, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zannat, K.E.; Ashraful Islam, K.M.; Sunny, D.S.; Moury, T.; Tuli, R.D.; Dewan, A.; Adnan, M.S.G. Nonmotorized Commuting Behavior of Middle-Income Working Adults in a Developing Country. J. Urban. Plan. Dev. 2021, 147, 05021011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.S. Sea-Level Changes in Bangladesh: The Last Ten Thousand Years, 1st ed.; Asiatic Society of Bangladesh: Dhaka, Bangladesh, 2001; ISBN 978-984-31-1443-3. [Google Scholar]
- Khatun, M.A.; Rashid, M.B.; Hygen, H.O. Climate of Bangladesh; Bangladesh Meteorological Department and MET Norway: Dhaka, Bangladesh, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Islam, M.R.; Raja, D.R. Waterlogging Risk Assessment: An Undervalued Disaster Risk in Coastal Urban Community of Chattogram, Bangladesh. Earth 2021, 2, 151–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, Y.; Gao, J.; Ni, S. Use of Normalized Difference Built-up Index in Automatically Mapping Urban Areas from TM Imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2003, 24, 583–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Xu, C. Geodetector: Principle and Prospective. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2017, 72, 116–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Wang, J.; Ge, Y.; Xu, C. An Optimal Parameters-Based Geographical Detector Model Enhances Geographic Characteristics of Explanatory Variables for Spatial Heterogeneity Analysis: Cases with Different Types of Spatial Data. GISci. Remote Sens. 2020, 57, 593–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhou, Y.; Yu, Y.; Li, F.; Zhang, R.; Li, W. Using the Geodetector Method to Characterize the Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Vegetation and Its Interaction with Environmental Factors in the Qinba Mountains, China. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Z.; Zhang, X.; Xu, X.; Zhang, H.; Wu, Z.; Pang, J. Quantifying Influences of Physiographic Factors on Temperate Dryland Vegetation, Northwest China. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 40092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rey, S.J.; Stephens, P.; Laura, J. An Evaluation of Sampling and Full Enumeration Strategies for Fisher Jenks Classification in Big Data Settings. Trans. GIS 2017, 21, 796–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Probst, P.; Wright, M.N.; Boulesteix, A. Hyperparameters and Tuning Strategies for Random Forest. WIREs Data Min. Knowl. 2019, 9, e1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenwell, B.M.; Boehmke, B.C. Variable Importance Plots—An Introduction to the Vip Package. R J. 2020, 12, 343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalogirou, S.; Georganos, S. SpatialML: Spatial Machine Learning, R Package Version 0.1.7; CRAN: Vienna, Austria, 2024; Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=SpatialML (accessed on 14 April 2025).
- Li, X.; Zhou, W.; Ouyang, Z. Forty Years of Urban Expansion in Beijing: What Is the Relative Importance of Physical, Socioeconomic, and Neighborhood Factors? Appl. Geogr. 2013, 38, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Liu, D.; Zhang, C.; Yu, L.; Yang, B.; Qiao, S.; Wang, X. Research on Spatial–Temporal Characteristics and Driving Factors of Urban Development Intensity for Pearl River Delta Region Based on Geodetector. Land 2023, 12, 1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, W. Location and Land Use: Toward a General Theory of Land Rent; Harvard University Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1964; ISBN 978-0-674-72956-8. [Google Scholar]
- Samad, R.B.; Das, T.; Mitra, A.; Nowshin, I. Assessment of Job-Housing Scenario and Its Impacts on the Dwellers of Chittagong City. J. Hous. Res. 2018, 27, 183–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, G.A. Central Business District. In International Encyclopedia of Human Geography; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2009; pp. 18–25. ISBN 978-0-08-044910-4. [Google Scholar]
- CCC Social Management Plan (SMP) for South Agrabad, Chittagong City Corporation; Bangladesh Municipal Development Fund (BMDF): Dhak, Bangladesh, 2017.
- Hasan, S.M.; Haider, M.A. Green Infrastructure Development for a Sustainable Urban Environment in Chittagong City, Bangladesh. J. Archit./Plan. Res. Stud. (JARS) 2023, 20, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panday, P.K. Central-Local Relations, Inter-Organisational Coordination, and Policy Implementation in Urban Bangladesh. Asia Pac. J. Public. Adm. 2006, 28, 41–58. [Google Scholar]
- Sakaki, S. Chittagong Strategic Urban Transport Master Plan (Vol. 1 of 2): Main Report; World Bank Group: Washington, DC, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Seto, K.C.; Güneralp, B.; Hutyra, L.R. Global Forecasts of Urban Expansion to 2030 and Direct Impacts on Biodiversity and Carbon Pools. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 16083–16088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angel, S.; Parent, J.; Civco, D.L.; Blei, A.M. The Persistent Decline in Urban Densities: Global and Historical Evidence of Sprawl; Lincoln Institute of Land Policy Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Belenok, V.; Hebryn-Baidy, L.; Bielousova, N.; Gladilin, V.; Kryachok, S.; Tereshchenko, A.; Alpert, S.; Bodnar, S. Machine Learning Based Combinatorial Analysis for Land Use and Land Cover Assessment in Kyiv City (Ukraine). J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2023, 17, 014506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Data | Source | Collection Date | Resolution |
|---|---|---|---|
| Landsat 05 (TM)/LT51360451993104BKT01 | USGS | 14 April 1993 | 30 m |
| Landsat 09 (OLI-2)/LC91360452023115LGN00 | USGS | 25 April 2023 | 30 m |
| SRTM (DEM) | USGS | 11 February 2000 | 1-ARC |
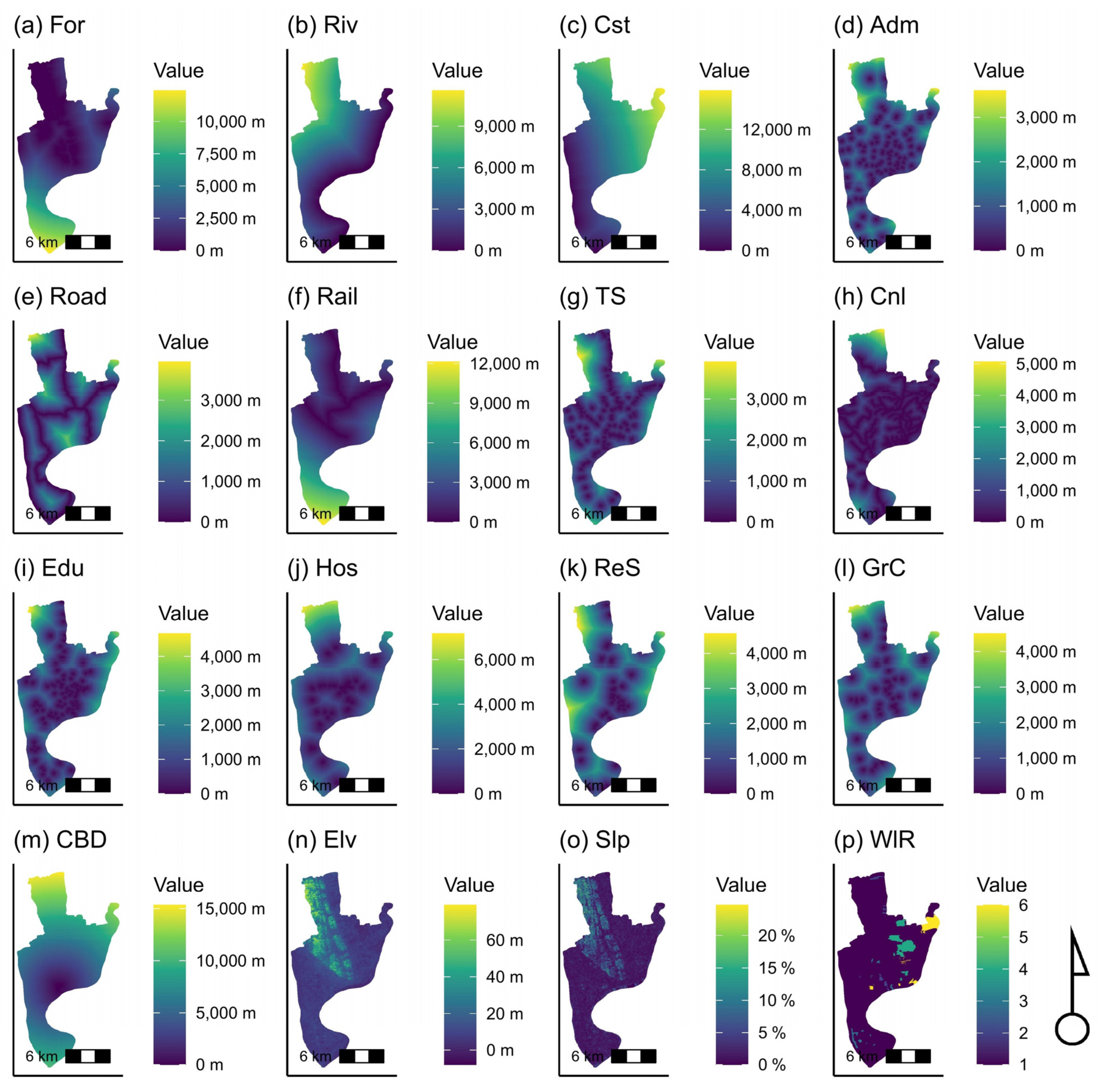
| Forest (For), Major Roads (Rd), Railways (Rl), Major Canals (Cnl), Administrative Buildings (Adm), Growth Centers (GrC), Sea Coast (Cst), Rivers (Riv), Transportation Stations (TS), Educational Institutions (Edu), Hospitals (Hos), Recreation Sites (ReS), Central Business District (CBD) | Prepared by the authors from the Google Earth Pro (GIS layers from Worldview) | 2022 | - |
| Waterlogging Risk (WlR) | [44] | 2019 | - |
| Geodetector | Global GWRF | Local GWRF | DRF | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rank | Variable | q Statistic | Variable | Importance | Variable | Importance | Variable | Importance |
| 1 | CBD | 0.22 | CBD | 1846.28 | For | 26.34 | CBD | 0.57 |
| 2 | Riv | 0.14 | For | 1522.42 | Riv | 22.83 | Cst | 0.35 |
| 3 | Adm | 0.13 | Riv | 1135.10 | Cst | 22.16 | Riv | 0.35 |
| 4 | Hos | 0.11 | Cst | 1021.35 | GrC | 21.86 | For | 0.34 |
| 5 | TS | 0.1 | Adm | 998.64 | CBD | 21.18 | Adm | 0.31 |
| 6 | Elv | 0.08 | Hos | 924.58 | Rd | 20.84 | RS | 0.30 |
| 7 | Slp | 0.08 | TS | 812.77 | Hos | 20.79 | Elv | 0.28 |
| 8 | Cst | 0.07 | Rl | 753.76 | RS | 20.68 | Hos | 0.23 |
| 9 | GrC | 0.07 | RS | 733.09 | Rl | 20.28 | Rd | 0.22 |
| 10 | Cnl | 0.06 | Elv | 730.83 | Adm | 20.25 | GrC | 0.21 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rashid, K.J.; Tuli, R.D.; Liu, W.; Mesev, V. Quantifying the Drivers of the Spatial Distribution of Urban Surfaces in Bangladesh: A Multi-Method Geospatial Analysis. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 2050. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17122050
Rashid KJ, Tuli RD, Liu W, Mesev V. Quantifying the Drivers of the Spatial Distribution of Urban Surfaces in Bangladesh: A Multi-Method Geospatial Analysis. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(12):2050. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17122050
Chicago/Turabian StyleRashid, Kazi Jihadur, Rajsree Das Tuli, Weibo Liu, and Victor Mesev. 2025. "Quantifying the Drivers of the Spatial Distribution of Urban Surfaces in Bangladesh: A Multi-Method Geospatial Analysis" Remote Sensing 17, no. 12: 2050. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17122050
APA StyleRashid, K. J., Tuli, R. D., Liu, W., & Mesev, V. (2025). Quantifying the Drivers of the Spatial Distribution of Urban Surfaces in Bangladesh: A Multi-Method Geospatial Analysis. Remote Sensing, 17(12), 2050. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17122050







