TIAR-SAR: An Oriented SAR Ship Detector Combining a Task Interaction Head Architecture with Composite Angle Regression
Abstract
1. Introduction
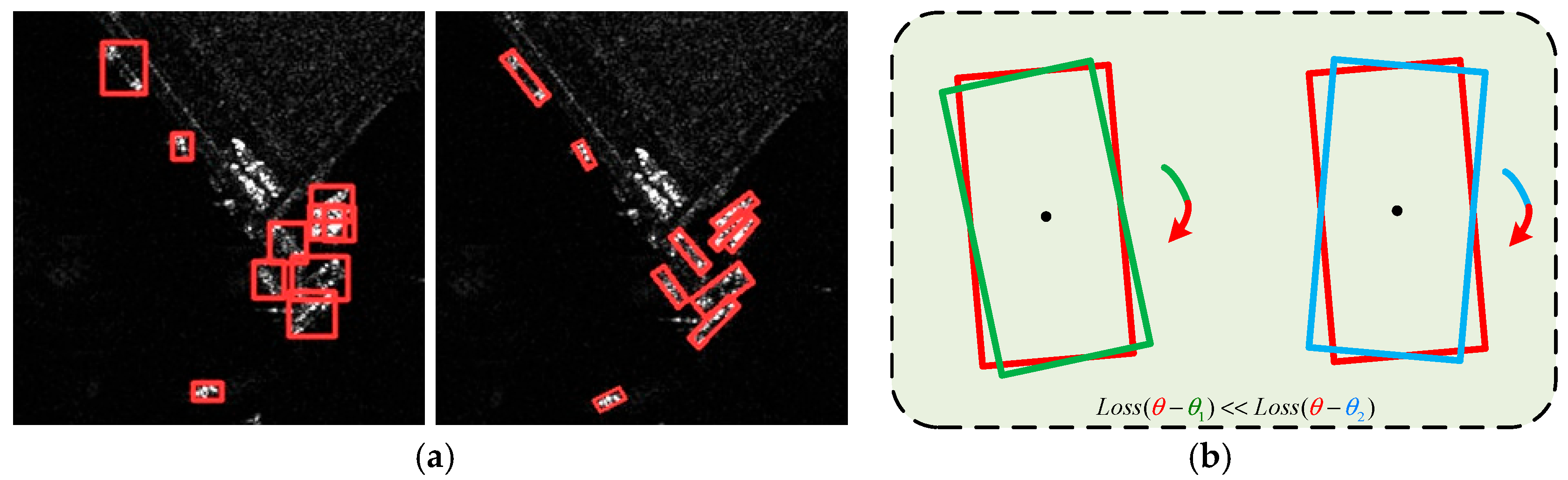
- (1)
- To improve ship detection performance under complex maritime scenarios, an oriented object detector named TIAR-SAR, which is based on task interaction and angle regression, is designed. TIAR-SAR mainly includes two core parts: the Tihead and JARM.
- (2)
- To enhance the consistency of predictions in regression and classification tasks, the Tihead adopts task decomposition to strengthen feature convergence and promote the flow of feature information between different tasks through task interaction, ultimately improving feature alignment.
- (3)
- To improve the estimation accuracy of ship angle, JARM combines CARL with a BACM to alleviate the BDP in oriented object detection. It enhances the accuracy of angle estimation without additional computational burden.
- (4)
- Experimental results derived from using the SRSDD and HRSID datasets show that our proposed methods achieve advanced detection performance with fewer model parameters compared to most existing methods. Experiments on the DOTAv1 dataset further verify its generality and robustness.
2. Related Work
2.1. SAR Ship Detection
2.2. Multi-Task Detection Head Network
2.3. Oriented Object Detection and Loss Function
3. Methodology
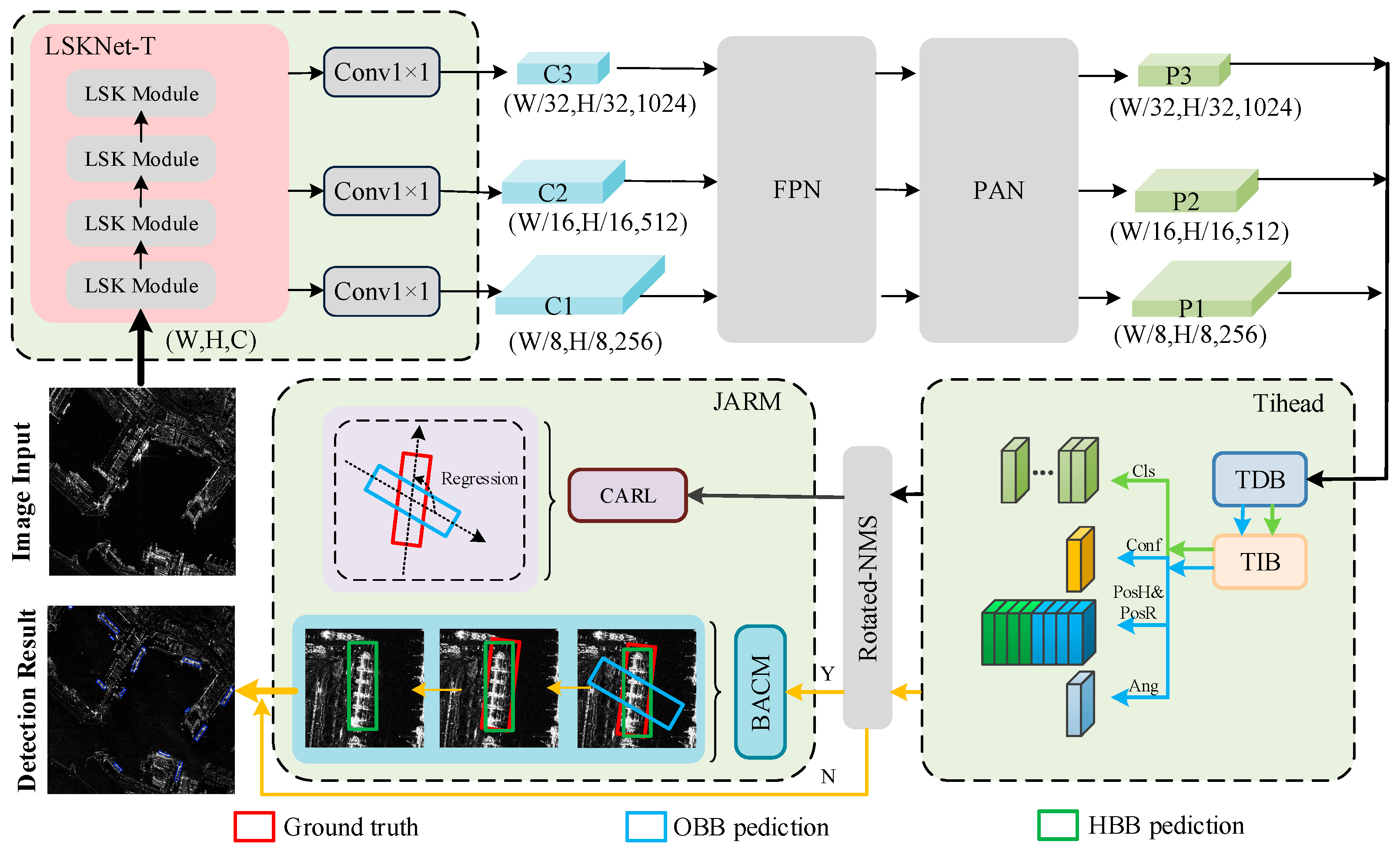
3.1. The Proposed TIAR-SAR Model
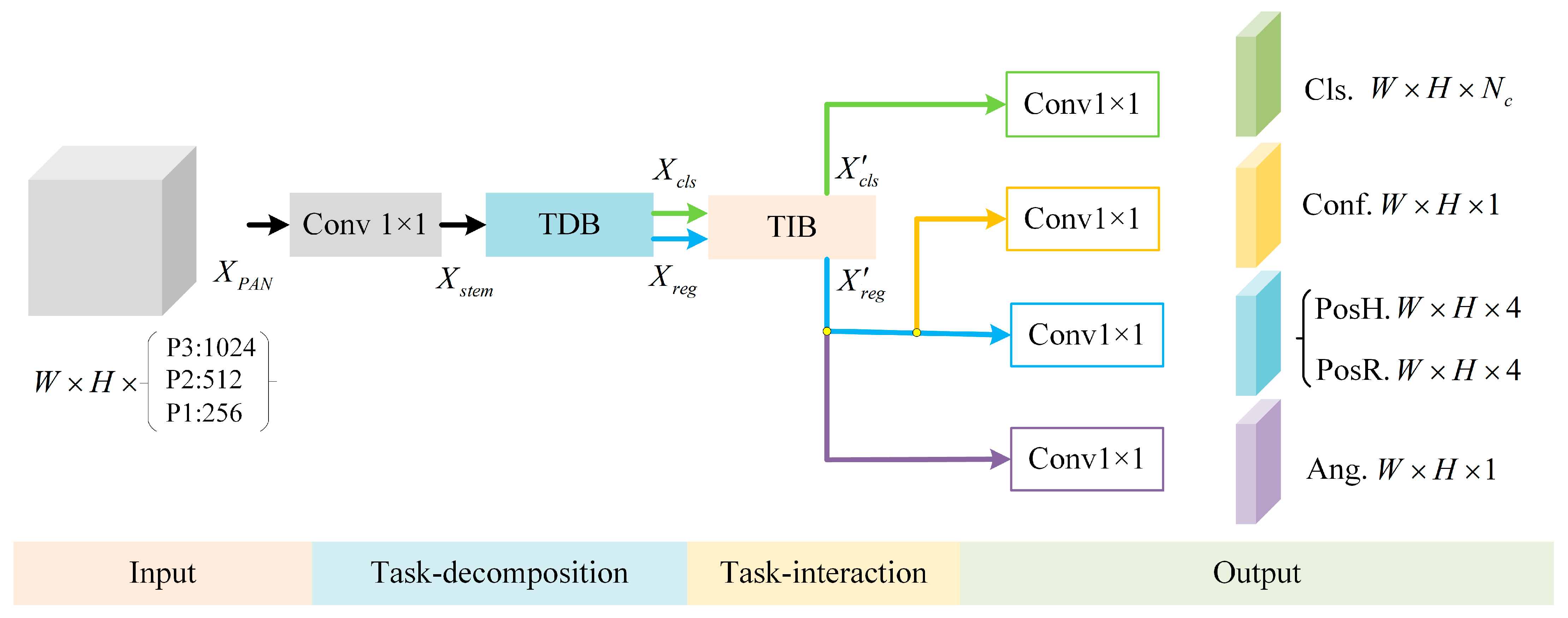
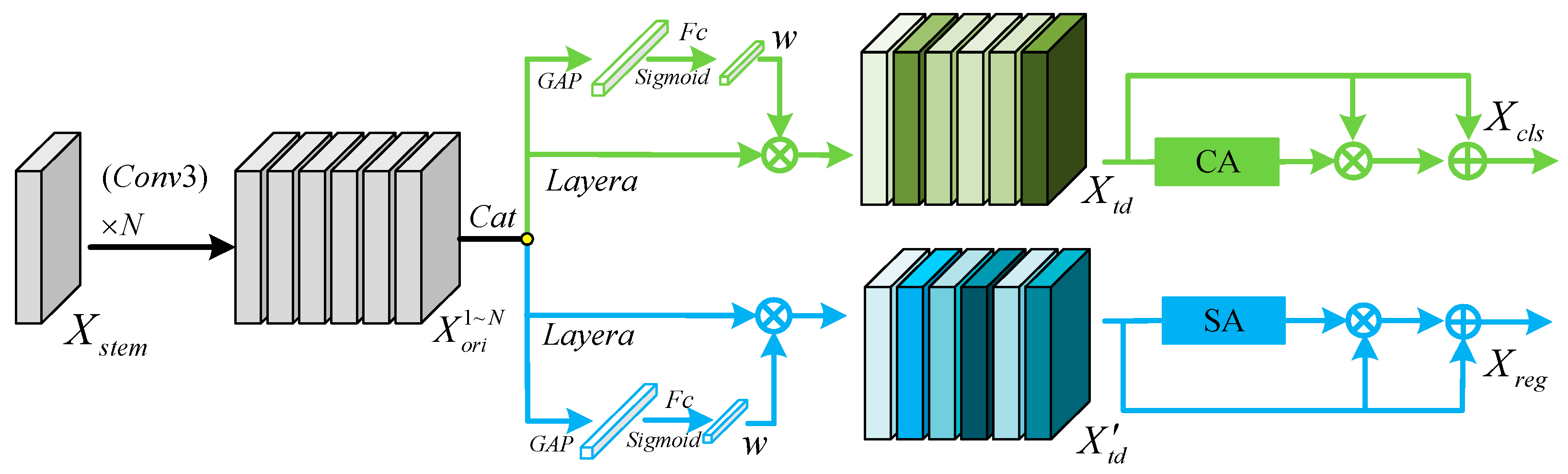
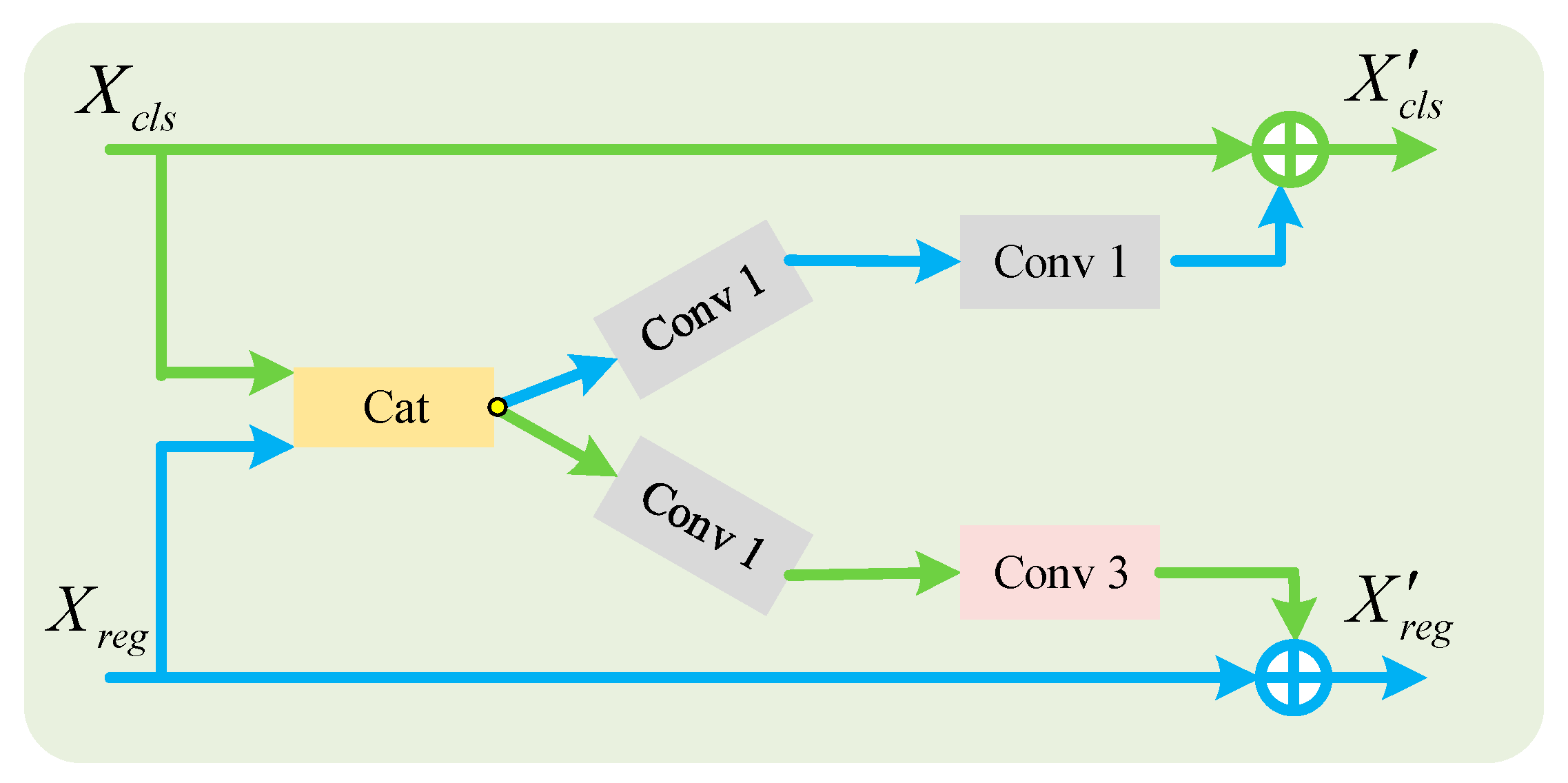
3.2. Task Interaction Detection Head
3.3. Joint Angle Refinement Mechanism
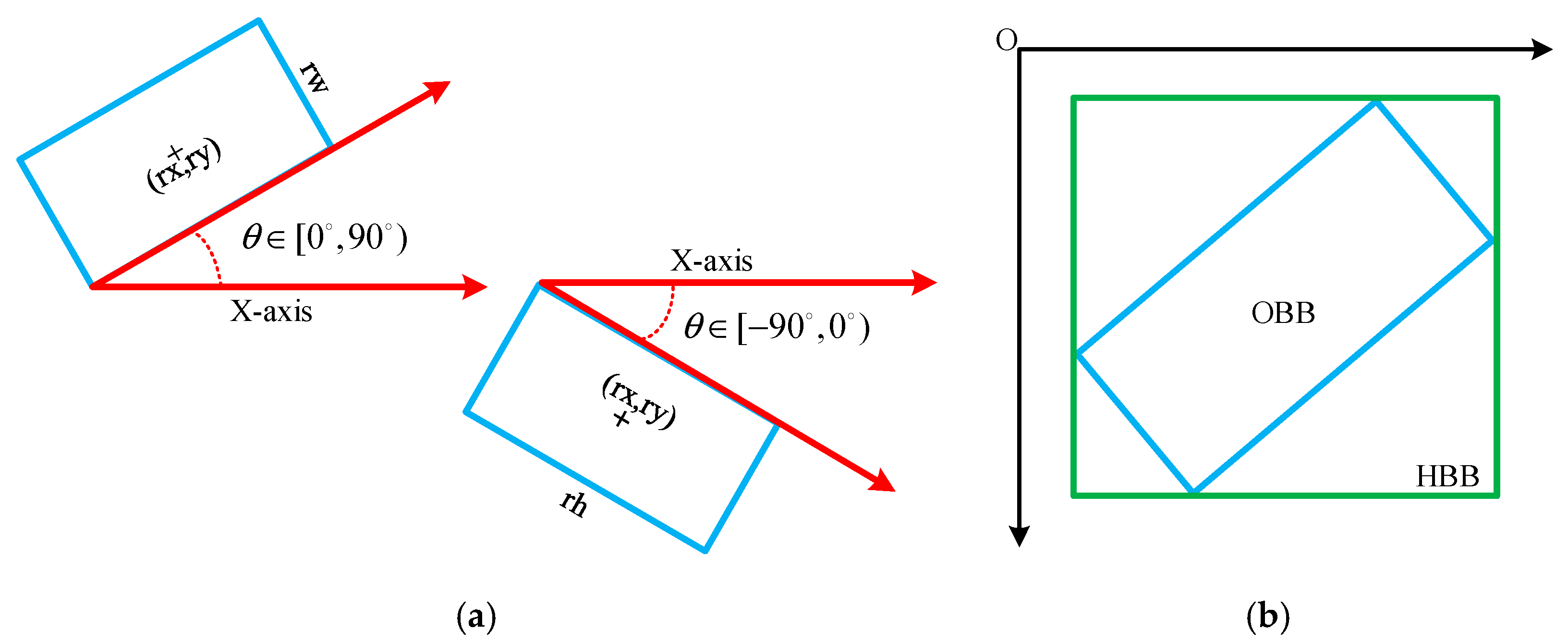
3.3.1. Composite Angle Regression Loss Function Based on HBBs and OBBs
- (1)
- Direct regression loss: .
- (2)
- Indirect regression loss: .
3.3.2. Boundary Angle Correction Mechanism
4. Results
4.1. Datasets
- (1)
- SRSDD: The SRSDD dataset is used for multi-category SAR ship-oriented object detection. All images in the dataset have a resolution of 1 m and 1024 × 1024 pixels per image. The dataset includes six fine-grained ship categories—oil tanker (C1), bulk carrier (C2), fishing boat (C3), law enforcement vessel (C4), dredger (C5), and container ship (C6)—with a total of 2884 ship instances. Among all dataset images, data from nearshore scenarios account for 63.1%, with complex maritime backgrounds and numerous interferences. The training set consists of 532 images, and the test set comprises 134 images.
- (2)
- HRSID: The OBB labels of the HRSID dataset are obtained from the minimum bounding rectangles through instance segmentation annotations. This SAR ship dataset consists of 5604 images, covering 16,951 ship objects and including various offshore and nearshore scenarios. The image resolutions vary from 1 m to 5 m. The training set and test set have 3623 images and 1955 images, respectively.
- (3)
- DOTAv1: The DOTAv1 dataset [59] collects 2806 aerial images from multiple platforms. The objects in DOTAv1 exhibit a wide range of scales, orientations, and shapes. This dataset includes 15 categories: baseball diamonds (BDs), planes (PLs), bridges (BRs), ground tracks fields (GTFs), ships (SHs), small vehicles (SVs), large vehicles (LVs), tennis courts (TCs), basketball courts (BCs), storage tanks (STs), harbors (HBs), soccer ball fields (SBFs), roundabouts (RAs), swimming pools (SPs), and helicopters (HCs). The number of images in the training set, validation set, and test set is 1411, 458, and 937, respectively.
4.2. Evaluation Metric and Experimental Settings
4.3. Ablation Experiments
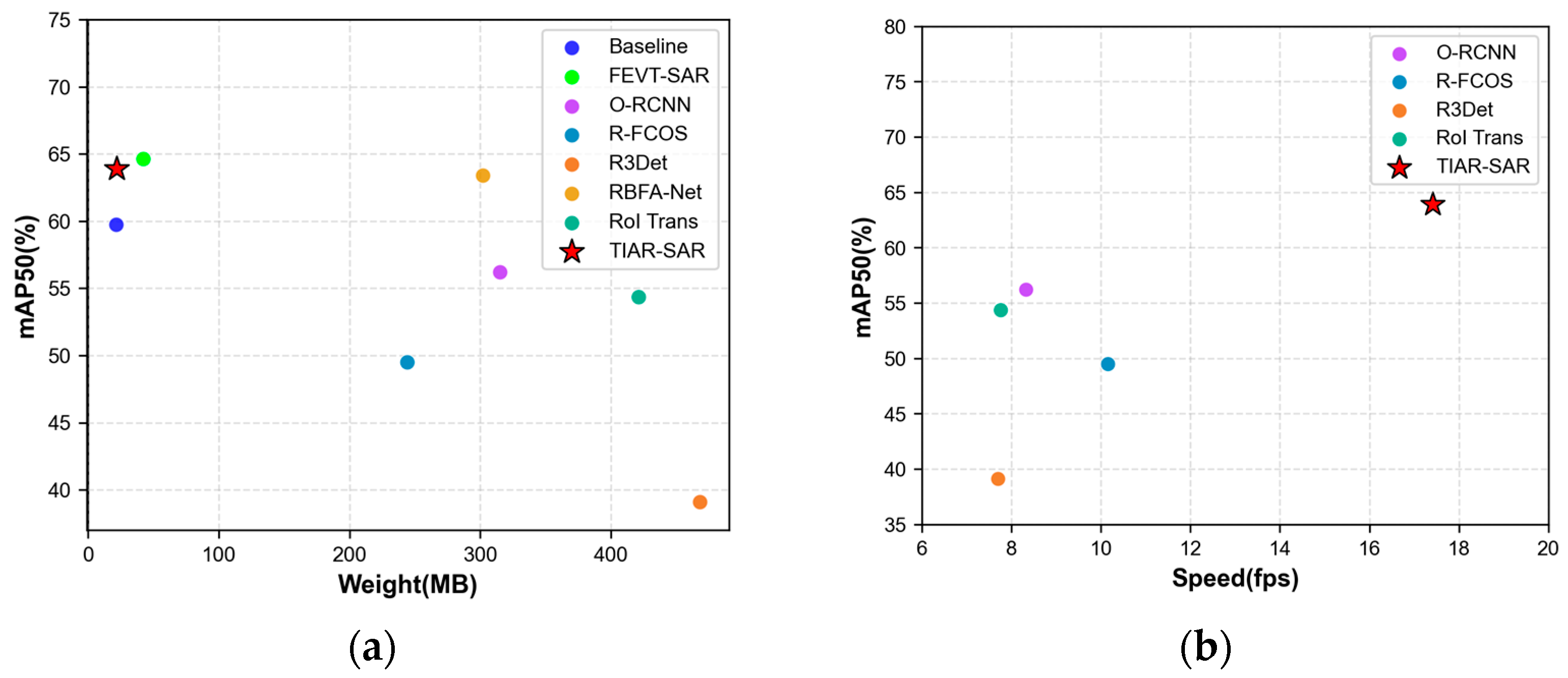
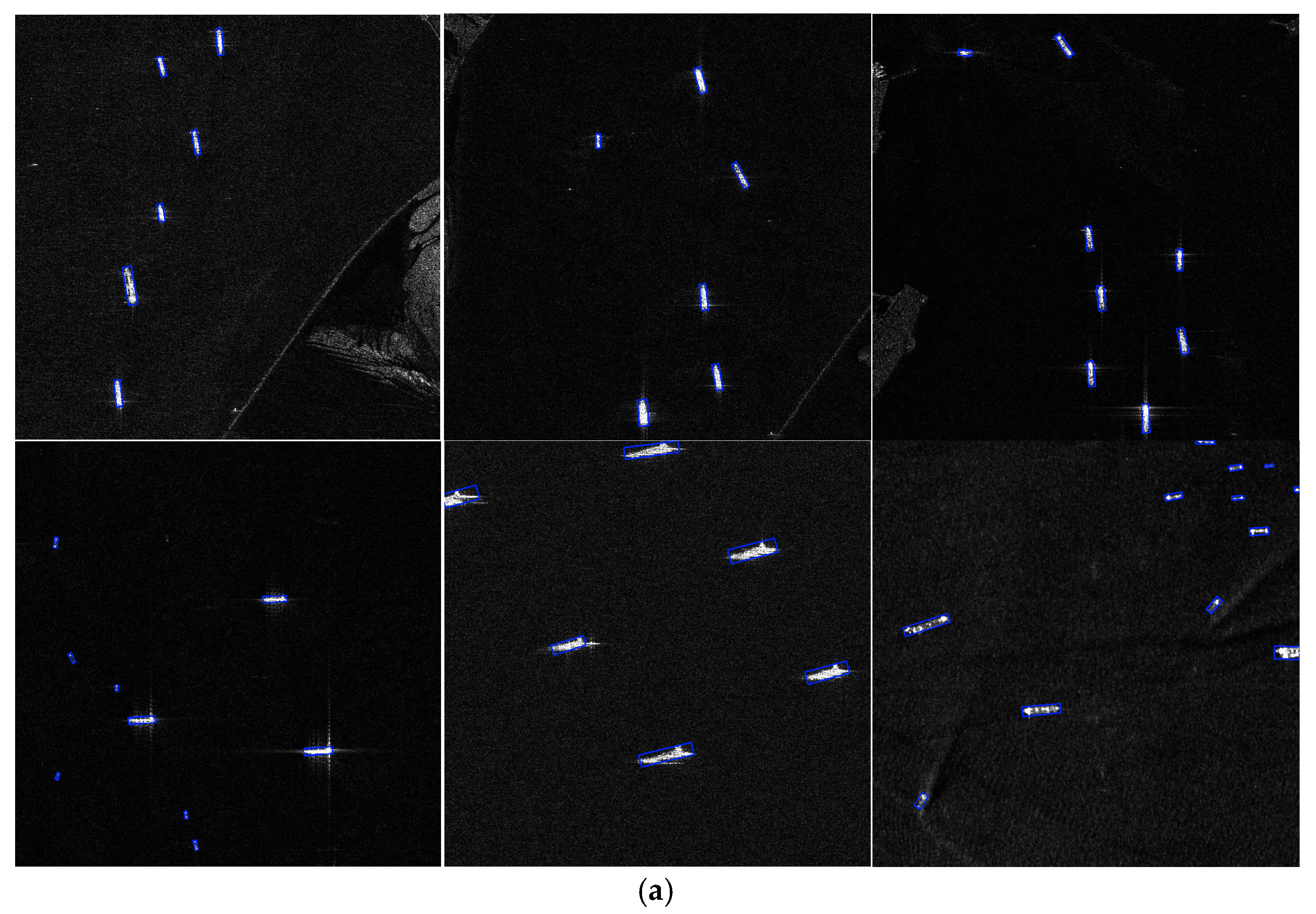
4.4. Comparison with Several State-of-the-Art Methods
4.5. Generalization Ability
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Deng, Y.; Tang, S.; Chang, S.; Zhang, H.; Liu, D.; Wang, W. A novel scheme for range ambiguity suppression of spaceborne SAR based on underdetermined blind source separation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2025, 63, 5207915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Zou, H.; Deng, Z.; Li, M.; Cao, X.; Ma, Q. Oriented inshore ship detection and classification based on cascade RCNN. Syst. Eng. Electron. 2020, 42, 1903–1910. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, Q.; Zang, F. Ship detection for visual maritime surveillance from non-stationary platforms. Ocean Eng. 2017, 141, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, S.; Sun, Z.; Liu, C.; Sun, Y.; Ji, K.; Kuang, G. Cross-sensor SAR image target detection based on dynamic feature discrimination and center-aware calibration. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2025, 63, 5209417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, T.; Chang, S.; Deng, Y.; Xue, F.; Wang, C.; Jia, X. Oriented SAR Ship Detection Based on Edge Deformable Convolution and Point Set Representation. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Leng, X.; Lei, Y.; Xiong, B.; Ji, K.; Kuang, G. BiFA-YOLO: A novel YOLO-based method for arbitrary-oriented ship detection in high-resolution SAR images. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Yang, Z.; Yang, J.; Gao, G. CFAR Ship Detection Methods Using Compact Polarimetric SAR in a K-Wishart Distribution. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2019, 12, 3737–3745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, Y.; Ma, Y.; Jiang, H. Survey on object detection in tilting box for remote sensing images. Nat. Remote Sens. Bull. 2022, 26, 1723–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, D.; Gao, X.; Dai, W.; Fu, J.; Wang, Z.; Sun, X.; Wu, Y. SRT-Net: Scattering Region Topology Network for Oriented Ship Detection in Large-Scale SAR Images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2024, 62, 5202318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Sun, X.; Wang, Z.; Fu, K. Oriented Ship Detection Based on Strong Scattering Points Network in Large-Scale SAR Images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 5218018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, B.; Zhang, Q.; Tong, M.; He, C. Oriented ship detector for remote sensing imagery based on pairwise branch detection head and SAR feature enhancement. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Z.; Liu, S.; Wang, F.; Li, Z.; Sun, J. Yolox: Exceeding yolo series in 2021. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2107.08430. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, X.; Chen, Y.; Xiao, B.; Chen, D.; Liu, M.; Yuan, L.; Zhang, L. Dynamic head: Unifying object detection heads with attentions. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Virtual, 20–25 July 2021; pp. 7373–7382. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Yuan, L.; Liu, Z.; Wang, L.; Li, H.; Fu, Y. Rethinking classification and localization for object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 10186–10195. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, C.; Zhong, Y.; Gao, Y.; Scott, M.R.; Huang, W. TOOD: Task-Aligned One-Stage Object Detection. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 3490–3499. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, H.; Yang, R.; Zhang, Y.; Duan, H.; Huang, Y.; Hu, R.; Li, X.; Zheng, Y. Unihead: Unifying multi-perception for detection heads. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2024, 36, 9565–9576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Yan, J.; He, T. Arbitrary-Oriented Object Detection with Circular Smooth Label. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; pp. 677–694. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; Hou, L.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, W.; Yan, J. Dense label encoding for boundary discontinuity free rotation detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 19–25 June 2021; pp. 15819–15829. [Google Scholar]
- Girshick, R. Fast r-cnn. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 11–18 December 2015; pp. 1440–1448. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Xu, C.; Su, H.; Gao, L.; Wang, T. Deep Learning for SAR Ship Detection: Past, Present and Future. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, S.; Lu, D.; Qiu, X.; Ding, C. SRSDD-v1.0: A High-Resolution SAR Rotation Ship Detection Dataset. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 5104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.; Zeng, X.; Qu, Q.; Wang, M.; Su, H.; Shi, J. HRSID: A high-resolution SAR images dataset for ship detection and instance segmentation. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 120234–120254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Zhang, X.; Ke, X.; Zhan, X.; Shi, J.; Wei, S.; Pan, D.; Li, J.; Su, H.; Zhou, Y.; et al. LS-SSDD-v1.0: A Deep Learning Dataset Dedicated to Small Ship Detection from Large-Scale Sentinel-1 SAR Images. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suo, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, S.; Hu, Y. BoxPaste: An Effective Data Augmentation Method for SAR Ship Detection. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, M.; Gu, Y.; Peng, D. FEVT-SAR: Multi-category Oriented SAR Ship Detection Based on Feature Enhancement VisionTransformer. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2024, 18, 2704–2717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Leng, X.; Zhang, X.; Xiong, B.; Ji, K.; Kuang, G. Ship Recognition for Complex SAR Images via Dual-Branch Transformer Fusion Network. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2024, 21, 4009905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Jiang, X.; Xu, G.; Yang, X.; Liu, X.; Li, Z. PVT-SAR: An Arbitrarily Oriented SAR Ship Detector with Pyramid Vision Transformer. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2023, 16, 291–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Feng, S.; Zhao, C.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, S.; Ji, K. MGSFA-Net: Multiscale Global Scattering Feature Association Network for SARShip Target Recognition. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Observ. Remote Sens. 2024, 17, 4611–4625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, K.; Zhang, M.; Zhao, H.; Tang, R.; Lin, S.; Cheng, X.; Wang, H. Arbitrary-Oriented Ellipse Detector for Ship Detection in Remote Sensing Images. IEEE J. Sel. Topics Appl. Earth Observ. Remote Sens. 2023, 16, 7151–7162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Z.; Zhang, X. A high accuracy detection network for rotated multi-class SAR ship detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Pasadena, CA, USA, 16–21 July 2023; pp. 4954–4957. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, Z.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, T.; Xu, X.; Zeng, T. RBFA-Net: A Rotated Balanced Feature-Aligned Network for Rotated SAR Ship Detection and Classification. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Leng, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, Z.; Xiong, B.; Ji, K.; Kuang, G. Arbitrary-direction SAR ship detection method for multi-scale imbalance. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2025, 63, 5208921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Liu, Y.; Qu, L.; Cai, J.; Fang, J. A Spatial Cross-Scale Attention Network and Global Average Accuracy Loss for SAR Ship Detection. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Li, J.; Lin, W.; See, J.; Wang, J.; Duan, L.; Chen, Z.; He, C.; Zou, J. Towards Accurate One-Stage Object Detection with AP-Loss. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 5119–5127. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, T.Y.; Goyal, P.; Girshick, R.; He, K.; Dollár, P. Focal loss for dense object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2980–2988. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Z.; Gao, R.; Huang, K.; Xu, Q. Triangle Distance IoU Loss, Attention-Weighted Feature Pyramid Network, and Rotated-SAR Ship Dataset for Arbitrary-Oriented SAR Ship Detection. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Wu, T.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, W. An Efficient Lightweight SAR Ship Target Detection Network with Improved Regression Loss Function and Enhanced Feature Information Expression. Sensors 2022, 22, 3447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, T.; Chang, S.; Wang, C.; Jia, X. SAR Small Ship Detection Based on Enhanced YOLO Network. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Z.; Shen, C.; Chen, H.; He, T. Fcos: Fully convolutional one-stage object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 9627–9636. [Google Scholar]
- Zhuang, J.; Qin, Z.; Yu, H.; Chen, X. Task-Specific Context Decoupling for Object Detection. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2303.01047. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Y.; Zhu, X.; Wang, X.; Yang, S.; Li, W.; Wang, H.; Fu, P.; Luo, Z. R2CNN: Rotational region CNN for orientation robust scene text detection. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1706.09579. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.; Fu, M.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Chen, K.; Xia, G.-S.; Bai, X. Gliding vertex on the horizontal bounding box for multi-oriented object detection. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2020, 43, 1452–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, J.; Xue, N.; Long, Y.; Xia, G.S.; Lu, Q. Learning RoI transformer for oriented object detection in aerial images. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–21 June 2019; pp. 2849–2858. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, X.; Cheng, G.; Wang, J.; Yao, X.; Han, J. Oriented R-CNN for object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, BC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 3520–3529. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; Yan, J.; Feng, Z.; He, T. R3det: Refined single-stage detector with feature refinement for rotating object. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 2–9 February 2021; pp. 3163–3171. [Google Scholar]
- Han, J.; Ding, J.; Li, J.; Xia, G.-S. Align deep features for oriented object detection. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 60, 5602511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Chen, K.; Lin, W.; See, J.; Yu, H.; Ke, Y.; Yang, C. Piou loss: Towards accurate oriented object detection in complex environments. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; pp. 195–211. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, G.; Yang, J.; Wang, W.; Yan, J.; Zhang, X.; Tian, Q. The KFIoU loss for rotated object detection. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2201.12558. [Google Scholar]
- Murrugarra-Llerena, J.; Kirsten, L.N.; Zeni, L.F.; Jung, C.R. Probabilistic Intersection-Over-Union for Training and Evaluation of Oriented Object Detectors. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2024, 33, 671–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Yang, X.; Yang, J.; Ming, Q.; Wang, W.; Tian, Q.; Yan, J. Learning high-precision bounding box for rotated object detection via kullback-leibler divergence. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2021, 34, 18381–18394. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; Yan, J.; Ming, Q.; Wang, W.; Zhang, X.; Tian, Q. Rethinking rotated object detection with gaussian wasserstein distance loss. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Vienna, Austria, 18–24 July 2021; pp. 11830–11841. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; Yang, J.; Yan, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, T.; Guo, Z.; Sun, X.; Fu, K. Scrdet: Towards more robust detection for small, cluttered and rotated objects. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 8232–8241. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, W.; Yang, X.; Peng, S.; Yan, J.; Guo, Y. Learning modulated loss for rotated object detection. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Online, 2–9 February 2021; pp. 2458–2466. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Huang, Z.; Chen, Z.; Song, Y.; Li, W. Multigrained angle representation for remote-sensing object detection. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Gu, Y.; Peng, D.; Liu, J.; Chen, H. An Improved YOLOv3 Model for Arbitrary Direction Ship Detection in Synthetic Aperture Radar Images. J. Mil. Eng. 2021, 42, 1698–1707. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; Yan, J.; He, T. On the Arbitrary-Oriented Object Detection: Classification based Approaches Revisited. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2022, 130, 1340–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, X.; Dai, Y.; Hou, Q.; Liu, L.; Liu, Y.; Cheng, M.M.; Yang, J. LSKNet: A Foundation Lightweight Backbone for Remote Sensing. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Paris, France, 2–6 October 2023; pp. 1–22. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.-F.; Ren, W.; Zhang, Z.; Jia, Z.; Wang, L.; Tan, T. Focal and efficient IOU loss for accurate bounding box regression. Neurocomputing 2022, 506, 146–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, G.S.; Bai, X.; Ding, J.; Zhu, Z.; Belongie, S.; Luo, J.; Datcu, M.; Pelillo, M.; Zhang, L. DOTA: A Large-Scale Dataset for Object Detection in Aerial Images. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 3974–3983. [Google Scholar]
- Everingham, M.; Eslami, S.M.A.; Van Gool, L.; Williams, C.K.I.; Winn, J.; Zisserman, A. The Pascal Visual Object Classes Challenge: A Retrospective. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2014, 111, 98–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everingham, M.; Van Gool, L.; Williams, C.K.I.; Winn, J.; Zisserman, A. The Pascal Visual Object Classes (VOC) Challenge. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2010, 88, 303–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Hu, G.; Zhou, H.; Wang, S.; Feng, Z.; Yue, S. A Ship Detection Method via Redesigned FCOS in Large-Scale SAR Images. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.; Lai, Q.; Wang, Y.; Wang, W.; Sun, Z.; Yao, Y. Poly kernel inception network for remote sensing detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 16–22 June 2024; pp. 27706–27716. [Google Scholar]

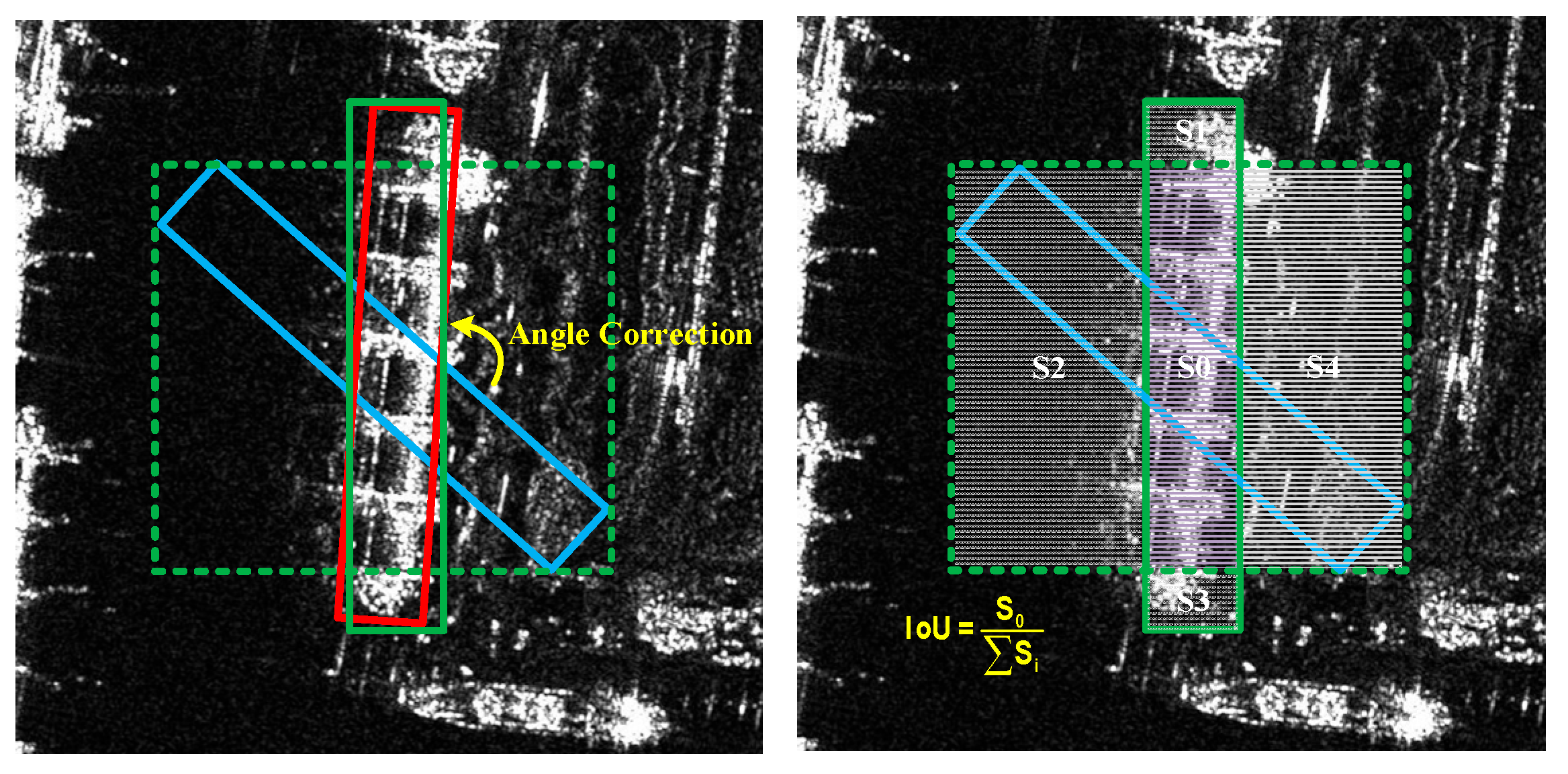

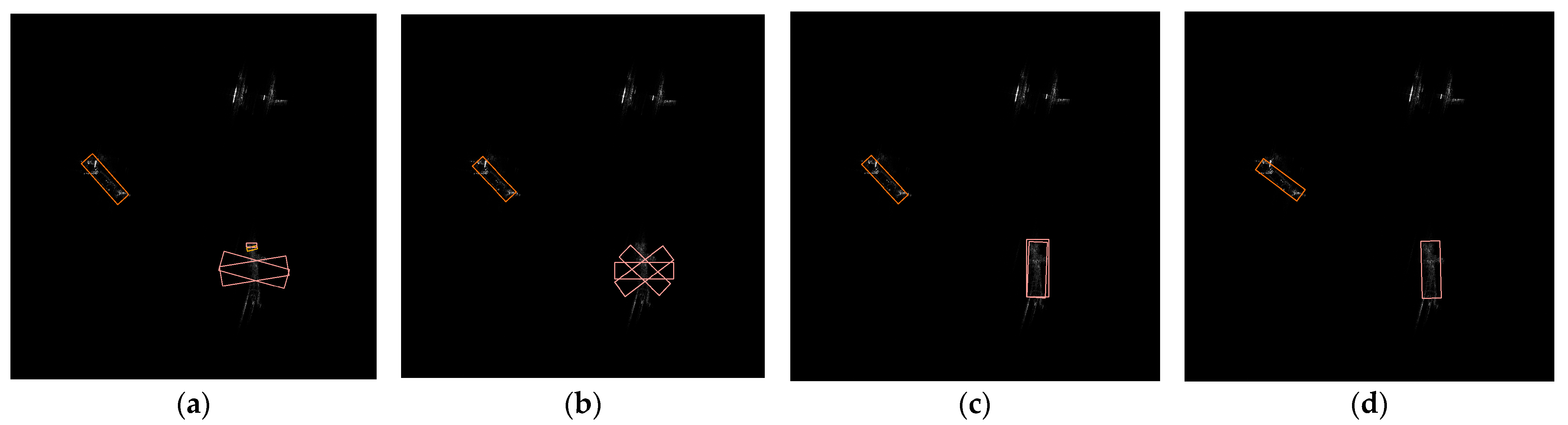


| The correction process of BACM |
| , OBB prediction |
| to do then 7: else 9: end if 10: end for 11: |
| Datasets | Resolution | Image Size | Images | Categories | Polarization |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SRSDD | 1 m | 1024 × 1024 | 666 | 6 | HH, VV |
| HRSID | 0.5 m, 1 m, 3 m | 800 × 800 | 5604 | 1 | HH, VV, HV, VH |
| DOTAv1 | 0.1 m~2 m | 800~4000 | 2806 | 15 | - |
| Datasets | Epoch | Batch Size | Input Size (Train/Test) |
|---|---|---|---|
| SRSDD | 300 | 4 | 1024 × 1024 |
| HRSID | 150 | 8 | 800 × 800 |
| DOTAv1 | 60 | 4 | 1024 × 1024 |
| Head Type | C1 | C2 | C3 | C4 | C5 | C6 | mAP50 (%) | Model Size (MB) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coupled head | 41.76 | 54.61 | 14.50 | 76.00 | 68.84 | 37.16 | 48.81 | 16.04 |
| Parallel head | 48.99 | 72.43 | 23.82 | 100 | 67.10 | 46.09 | 59.74 | 21.39 |
| T-head | 52.51 | 64.69 | 32.50 | 100 | 70.71 | 42.40 | 60.47 | 23.95 |
| Unihead | 50.61 | 63.18 | 35.84 | 94.29 | 69.70 | 51.59 | 60.87 | 21.22 |
| Tihead (ours) | 52.98 | 57.54 | 36.30 | 100 | 72.19 | 47.31 | 61.05 | 21.91 |
| Methods | Category | mAP50 (%) | AAE (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Smooth L1 | Regression | 59.74 | 8.41 |
| CSL | Classification | 56.23 | 9.43 |
| GCL | Classification | 60.14 | 11.76 |
| JARM (ours) | Regression | 61.68 | 6.74 |
| Tihead | JARM | P | R | mAP50 (%) | F1 (%) | Weights (MB) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 61.10 | 60.72 | 59.74 | 60.91 | 21.39 | ||
| 2 | √ | 65.52 | 59.79 | 61.05 | 62.52 | 21.91 | |
| 3 | √ | 64.54 | 63.23 | 61.68 | 63.87 | 21.40 | |
| 4 | √ | √ | 69.13 | 63.07 | 63.91 | 65.96 | 21.92 |
| Methods | C1 | C2 | C3 | C4 | C5 | C6 | mAP50 (%) | Weights (MB) | Speed (fps) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R-FCOS [21,62] | 54.88 | 47.36 | 25.12 | 5.45 | 83.00 | 81.11 | 49.49 | 244 | 10.15 |
| R3Det [21,45] | 44.61 | 42.98 | 18.32 | 1.09 | 54.27 | 73.48 | 39.12 | 468 | 7.69 |
| RoI Trans * [21,43] | 61.43 | 48.89 | 32.89 | 27.27 | 79.41 | 76.41 | 54.38 | 421 | 7.75 |
| O-RCNN * [21,44] | 63.55 | 57.56 | 35.35 | 27.27 | 77.50 | 76.14 | 56.23 | 315 | 8.32 |
| RMCD-Net [30] | 56.51 | 62.28 | 36.73 | 54.52 | 81.71 | 78.00 | 61.62 | - | - |
| RBFA-Net [31] | 59.39 | 57.36 | 41.51 | 73.48 | 77.17 | 71.62 | 63.42 | 302 | - |
| FEVT-SAR [25] | 48.11 | 55.77 | 35.21 | 100 | 77.27 | 71.39 | 64.63 | 42.17 | - |
| TIAR-SAR (ours) | 55.70 | 69.26 | 33.10 | 100 | 70.84 | 54.54 | 63.91 | 21.92 | 17.42 |
| Methods | Metric Type | Inshore (mAP50) | Offshore (mAP50) | All (mAP50) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RetinaNet-O [29,35] | VOC07 | 49.8 | 90.0 | 75.9 |
| S2ANet [29,46] | VOC07 | 66.6 | 90.8 | 80.6 |
| RoI Trans * [29,43] | VOC07 | 65.7 | 90.8 | 80.3 |
| Gliding Vertex * [29,42] | VOC07 | 57.5 | 90.6 | 78.6 |
| O-RCNN * [29,44] | VOC07 | 41.6 | 90.2 | 62.7 |
| AEDet [29] | VOC07 | 76.5 | 90.8 | 88.2 |
| FEVT-SAR [25] | VOC12 | 78.6 | - | 89.6 |
| YOLOv8m-OBB | VOC07 | 74.8 | 90.7 | 86.6 |
| VOC12 | 75.7 | 97.1 | 87.9 | |
| TIAR-SAR (ours) | VOC07 | 77.2 | 90.6 | 88.6 |
| VOC12 | 80.5 | 97.4 | 90.3 |
| Methods | PL | BD | BR | GTF | SV | LV | SH | TC | BC | ST | SBF | RA | HA | SP | HC | mAP50 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SASM | 86.4 | 79.0 | 52.5 | 69.8 | 77.3 | 76.0 | 86.7 | 90.9 | 82.6 | 85.7 | 60.1 | 68.2 | 74.0 | 72.2 | 62.4 | 74.9 |
| O-RepPoint | 87.0 | 83.2 | 54.1 | 71.2 | 80.2 | 78.4 | 87.3 | 90.9 | 86.0 | 86.3 | 59.9 | 70.5 | 73.5 | 72.3 | 59.0 | 76.0 |
| R3Det | 89.6 | 82.4 | 49.8 | 71.7 | 80.0 | 81.4 | 87.8 | 90.9 | 84.2 | 86.1 | 61.1 | 66.6 | 73.1 | 73.9 | 60.0 | 75.9 |
| S2ANet | 89.7 | 84.2 | 51.9 | 71.9 | 80.8 | 83.5 | 88.3 | 90.8 | 87.0 | 86.9 | 65.0 | 69.5 | 75.8 | 80.2 | 61.9 | 77.8 |
| Redet * | 88.8 | 82.6 | 54.0 | 74.0 | 78.1 | 84.1 | 88.0 | 90.9 | 87.8 | 85.8 | 61.8 | 60.4 | 76.0 | 68.1 | 63.6 | 76.3 |
| RoI Trans * | 89.3 | 85.6 | 55.8 | 74.7 | 74.7 | 79.1 | 88.1 | 90.9 | 87.4 | 86.9 | 61.7 | 64.3 | 77.8 | 75.4 | 66.1 | 77.2 |
| O-RCNN * | 89.7 | 84.2 | 55.8 | 77.6 | 80.3 | 84.5 | 88.1 | 90.9 | 87.6 | 86.1 | 66.9 | 70.2 | 77.5 | 73.6 | 62.9 | 78.4 |
| TIAR-SAR (ours) | 89.3 | 83.5 | 52.9 | 79.7 | 81.1 | 84.8 | 88.3 | 90.8 | 87.1 | 88.1 | 62.0 | 69.2 | 75.7 | 80.7 | 72.5 | 79.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gu, Y.; Fang, M.; Peng, D. TIAR-SAR: An Oriented SAR Ship Detector Combining a Task Interaction Head Architecture with Composite Angle Regression. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 2049. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17122049
Gu Y, Fang M, Peng D. TIAR-SAR: An Oriented SAR Ship Detector Combining a Task Interaction Head Architecture with Composite Angle Regression. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(12):2049. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17122049
Chicago/Turabian StyleGu, Yu, Minding Fang, and Dongliang Peng. 2025. "TIAR-SAR: An Oriented SAR Ship Detector Combining a Task Interaction Head Architecture with Composite Angle Regression" Remote Sensing 17, no. 12: 2049. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17122049
APA StyleGu, Y., Fang, M., & Peng, D. (2025). TIAR-SAR: An Oriented SAR Ship Detector Combining a Task Interaction Head Architecture with Composite Angle Regression. Remote Sensing, 17(12), 2049. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17122049






