Application of WRF-LES on the Simulation of Seasonal Characteristics of Atmospheric Boundary Layer Structure in Taklamakan Desert
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. In-Site Observation and Reanalysis Data
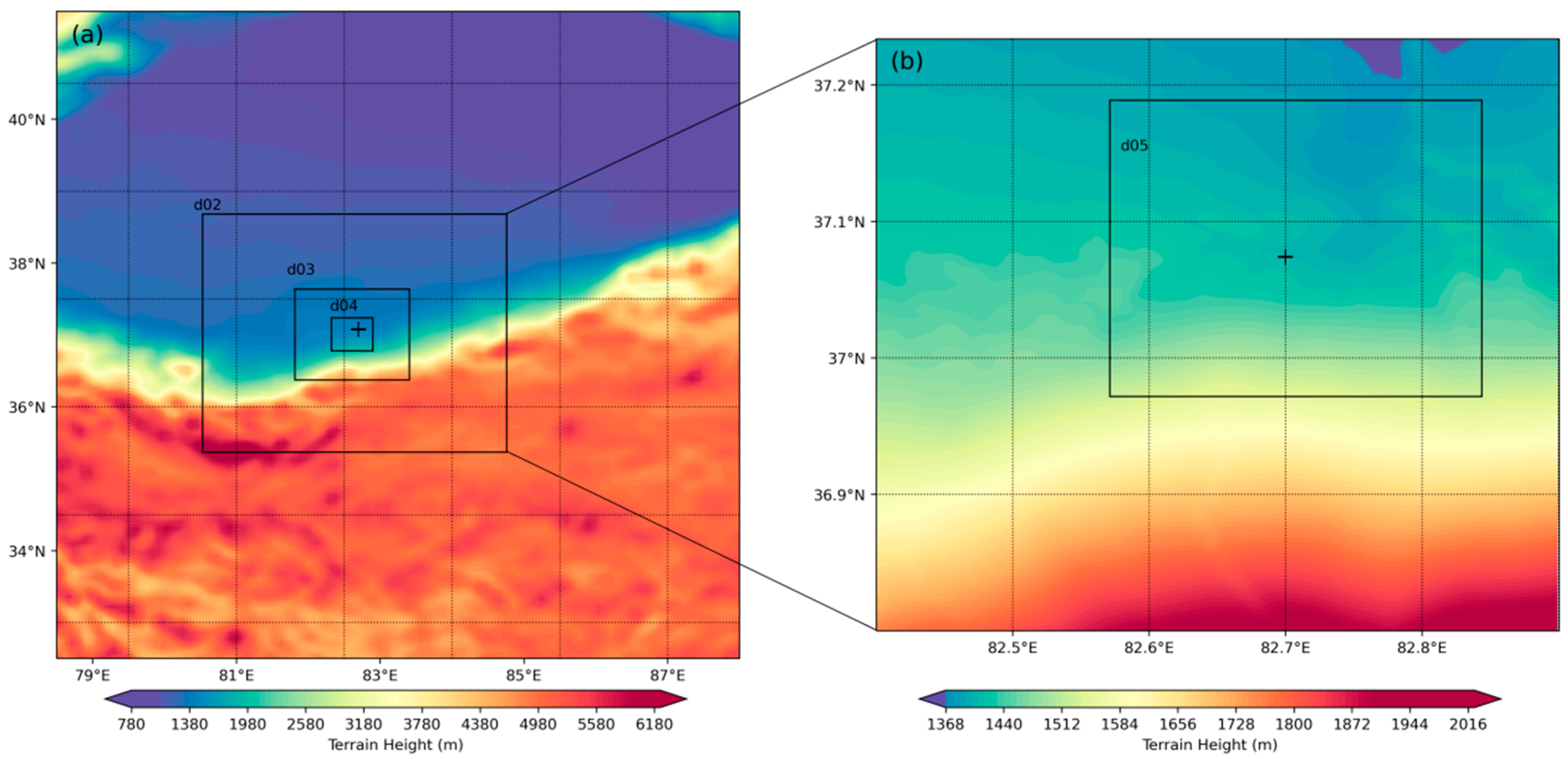
2.2. Model Configurations
2.3. Turbulence Extracting Method
3. Results
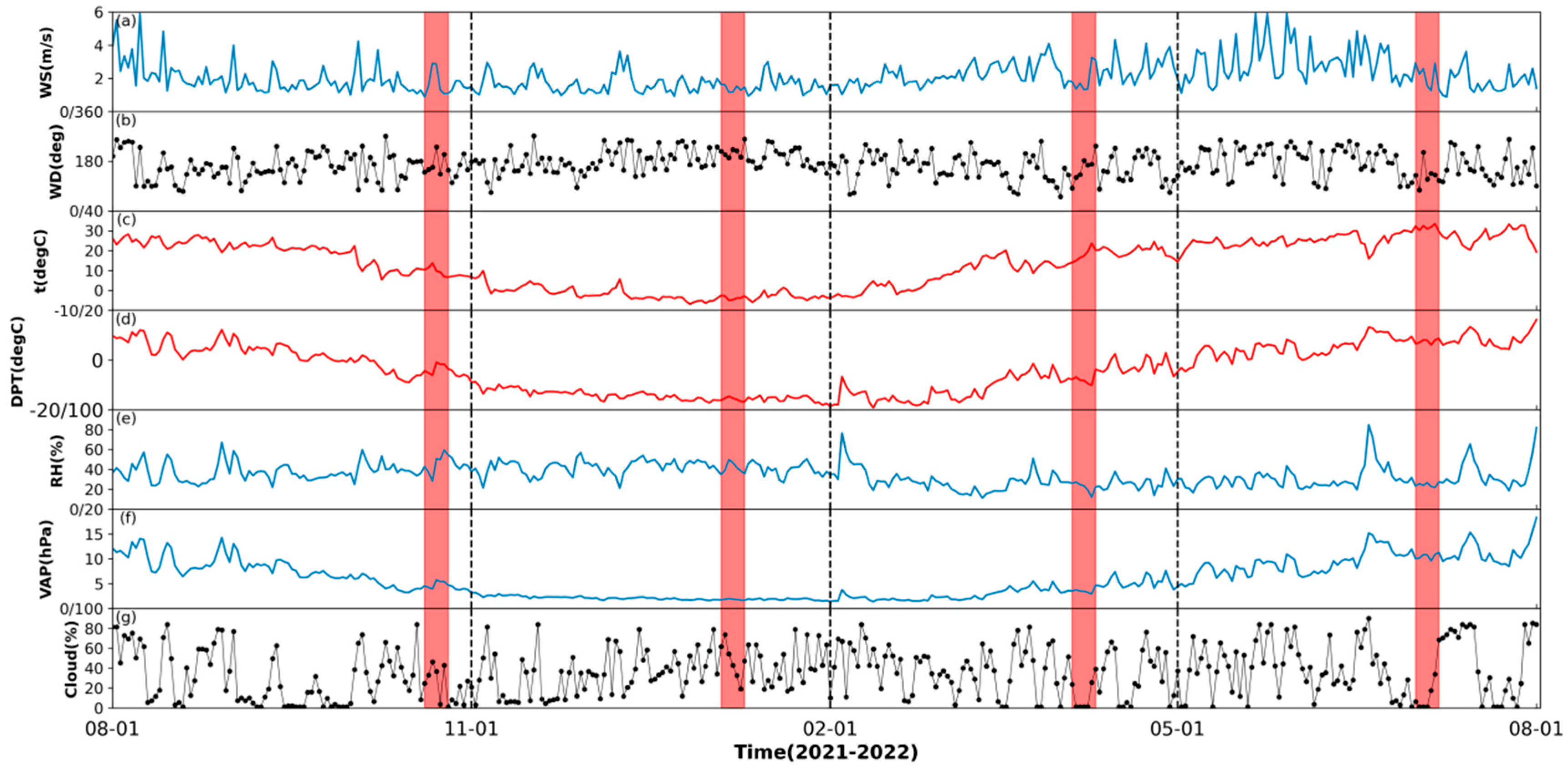
3.1. Surface Meteorological Elements
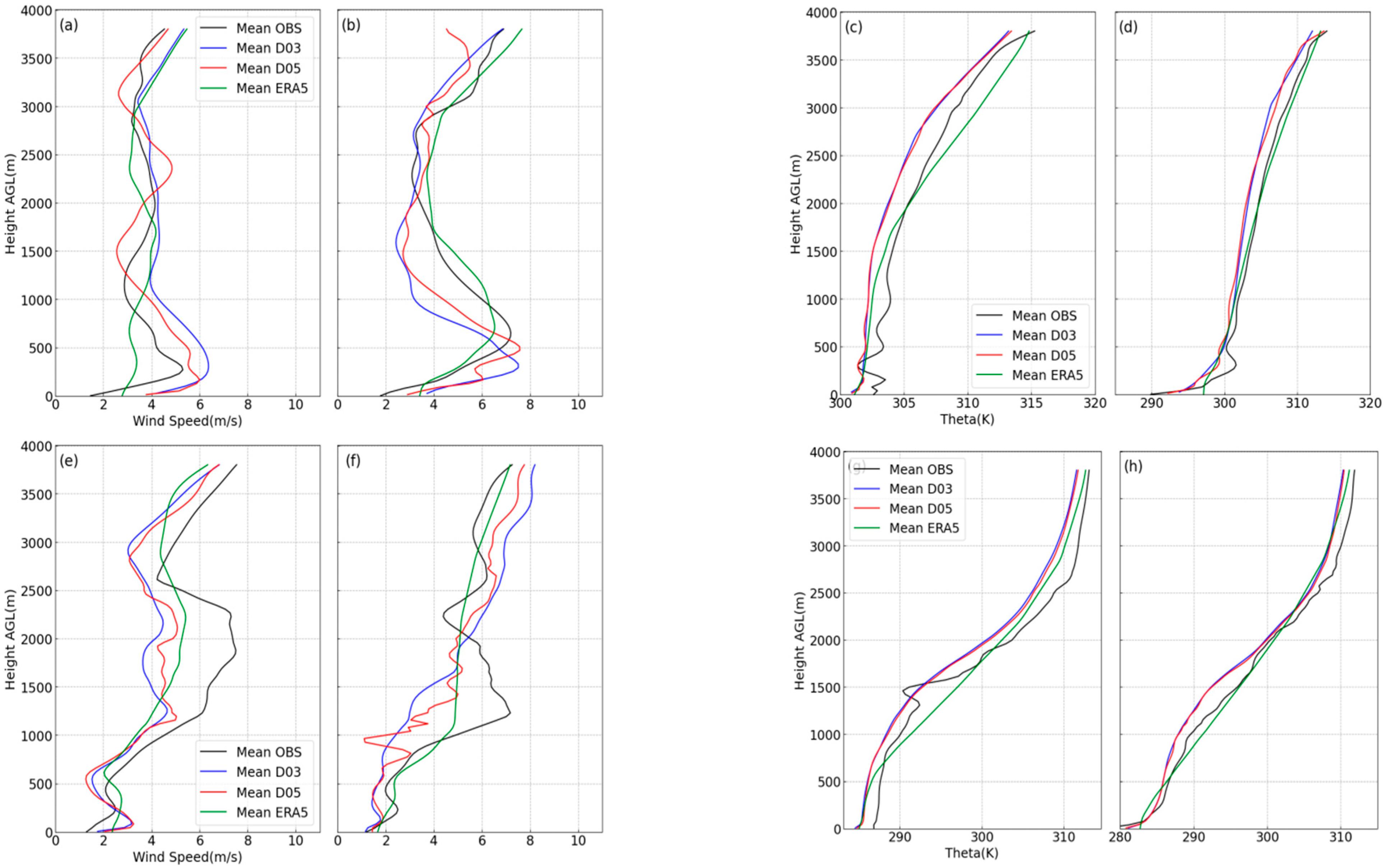
3.2. Sounding Profiles
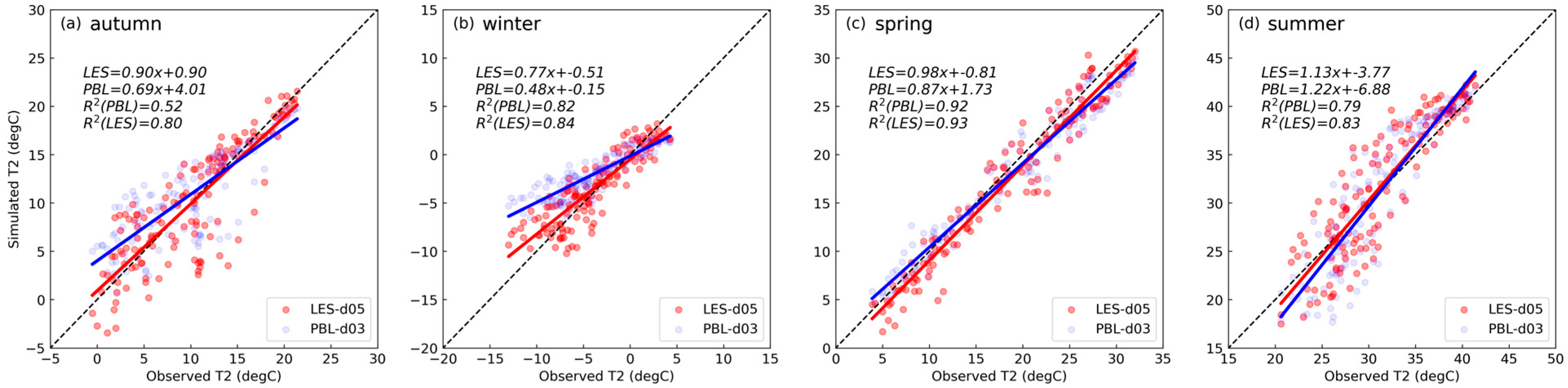
3.3. Simulation Error
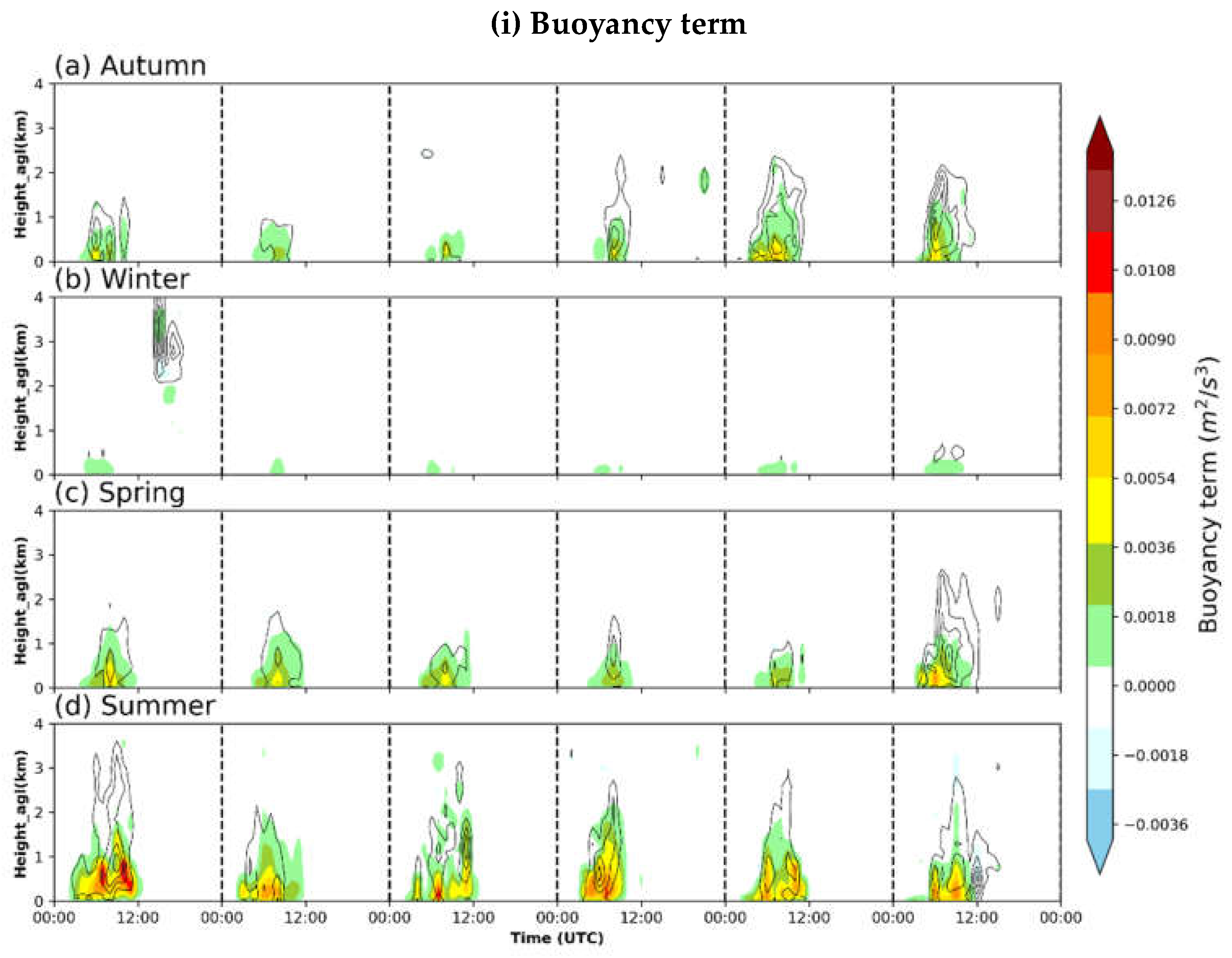
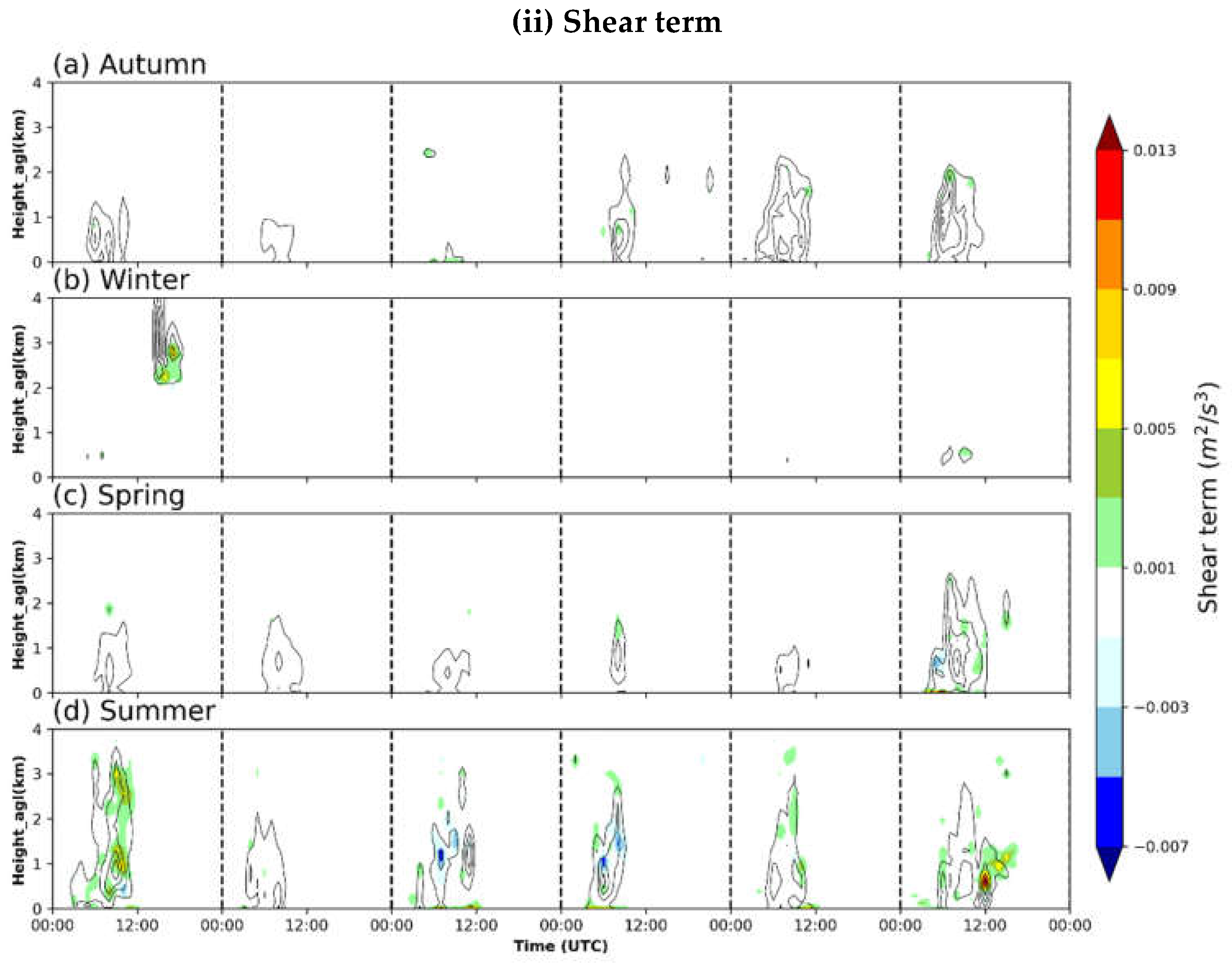
3.4. Mechanism of Improved Simulation in LES
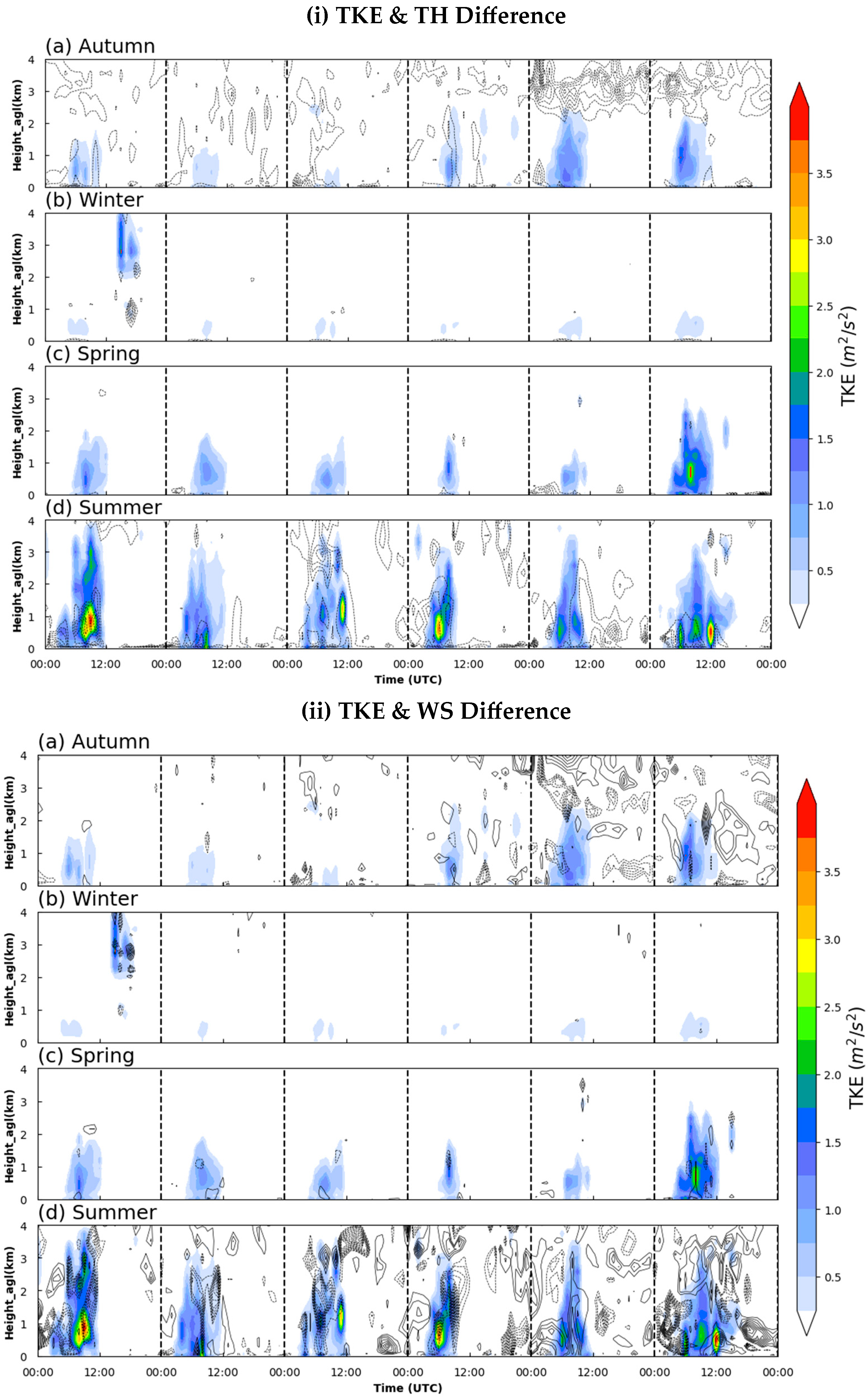
3.4.1. TKE
3.4.2. Cloud
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, M.; Wei, W.; He, Q.; Yang, Y.; Fan, L.; Zhang, J. Summer atmospheric boundary layer structure in the hinterland of Taklimakan Desert, China. J. Arid. Land 2016, 8, 846–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Xu, H.; Wang, Y.; Wang, M. The performance of a scale-aware nonlocal PBL scheme for the subkilometer simulation of a deep CBL over the Taklimakan desert. Adv. Meteorol. 2018, 2018, 8759594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Wang, T.; Wang, W.; Li, Z.; Yan, H. Climate effects of dust aerosols over East Asian arid and semiarid regions. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 11–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Huang, J.; Zhou, C.; Yang, X.; Ali, M.; Li, C.; Pan, H.; Huo, W.; Yu, H.; Liu, X. Taklimakan desert carbon-sink decreases under climate change. Sci. Bull. 2020, 65, 431–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, J.; Yue, X.; Sun, Q.; Wang, S. Case study of dust event sources from the Gobi and Taklamakan deserts: An investigation of the horizontal evolution and topographical effect using numerical modeling and remote sensing. J. Environ. Sci. 2017, 56, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, L.; Yang, X.; Zhao, T.; He, Q.; Lu, H.; Mamtimin, A.; Huo, W.; Yang, F.; Liu, C. Modeling study on three-dimensional distribution of dust aerosols during a dust storm over the Tarim Basin, Northwest China. Atmos. Res. 2019, 218, 285–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lothon, M.; Lohou, F.; Pino, D.; Couvreux, F.; Pardyjak, E.; Reuder, J.; Vilà-Guerau de Arellano, J.; Durand, P.; Hartogensis, O.; Legain, D. The BLLAST field experiment: Boundary-layer late afternoon and sunset turbulence. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 10931–10960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiangang, L.; Yinhuan, A.; Zhaoguo, L.; Mamtimin, A. Characteristics of atmospheric boundary layer over the Badain Jaran desert in summer. J. Desert Res. 2014, 34, 488–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takemi, T. Structure and evolution of a severe squall line over the arid region in northwest China. Mon. Weather Rev. 1999, 127, 1301–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Liu, W.; Long, X.-E.; Chen, Y.; Huang, T.; Huo, J.; Duan, L.; Wang, X. Effects of nitrogen addition on C: N: P stoichiometry in moss crust-soil continuum in the N-limited Gurbantünggüt Desert, Northwest China. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2020, 98, 103174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.-Y.; Pan, H.-L. Nonlocal boundary layer vertical diffusion in a medium-range forecast model. Mon. Weather Rev. 1996, 124, 2322–2339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mellor, G.L.; Yamada, T. Development of a turbulence closure model for geophysical fluid problems. Rev. Geophys. 1982, 20, 851–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, H.H.; Dudhia, J. Evaluation of PBL parameterizations in WRF at subkilometer grid spacings: Turbulence statistics in the dry convective boundary layer. Mon. Weather Rev. 2016, 144, 1161–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, W.; Zhang, X. The role of the planetary boundary layer parameterization schemes on the meteorological and aerosol pollution simulations: A review. Atmos. Res. 2020, 239, 104890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letzel, M.O.; Krane, M.; Raasch, S. High resolution urban large-eddy simulation studies from street canyon to neighbourhood scale. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 8770–8784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, H.; Schumann, U. Coherent structure of the convective boundary layer derived from large-eddy simulations. J. Fluid Mech. 1989, 200, 511–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heath, N.K.; Fuelberg, H.E.; Tanelli, S.; Turk, F.J.; Lawson, R.P.; Woods, S.; Freeman, S. WRF nested large-eddy simulations of deep convection during SEAC4RS. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2017, 122, 3953–3974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Liu, Q.; Li, Y. Tornado-scale vortices in the tropical cyclone boundary layer: Numerical simulation with the WRF–LES framework. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 2477–2487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryan, G.H.; Wyngaard, J.C.; Fritsch, J.M. Resolution requirements for the simulation of deep moist convection. Mon. Weather Rev. 2003, 131, 2394–2416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-W.; Park, S.-U. Coherent structures near the surface in a strongly sheared convective boundary layer generated by large-eddy simulation. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 2003, 106, 35–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moeng, C.; Dudhia, J.; Klemp, J.; Sullivan, P. Examining two-way grid nesting for large eddy simulation of the PBL using the WRF model. Mon. Weather Rev. 2007, 135, 2295–2311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talbot, C.; Bou-Zeid, E.; Smith, J. Nested mesoscale large-eddy simulations with WRF: Performance in real test cases. J. Hydrometeorol. 2012, 13, 1421–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Warner, T.; Liu, Y.; Vincent, C.; Wu, W.; Mahoney, B.; Swerdlin, S.; Parks, K.; Boehnert, J. Simultaneous nested modeling from the synoptic scale to the LES scale for wind energy applications. J. Wind. Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 2011, 99, 308–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, B.W.; Zhang, F. Numerical simulations of h urricane k atrina (2005) in the turbulent gray zone. J. Adv. Model. Earth Syst. 2015, 7, 142–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; He, D.; Zhang, G.; Zhu, S.; Dai, R.; Jin, X.; Fu, W.; Shen, W.; Chen, J.; Fan, Y. Comparison of horizontal wind observed by wind profiler radars with ERA5 reanalysis data in Anhui, China. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2022, 150, 1745–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.; Guo, J.; Li, J.; Cao, L.; Chen, T.; Wang, D.; Chen, D.; Han, Y.; Guo, X.; Xu, H. Spatiotemporal characteristics of atmospheric turbulence over China estimated using operational high-resolution soundings. Environ. Res. Lett. 2021, 16, 054050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Y.; Liu, S.; Guo, J.; Huang, S.; Yan, Y.; Lou, M. Unraveling the relationships between boundary layer height and PM2.5 pollution in China based on four-year radiosonde measurements. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 243, 1186–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hersbach, H.; Bell, B.; Berrisford, P.; Biavati, G.; Horányi, A.; Muñoz Sabater, J.; Nicolas, J.; Peubey, C.; Radu, R.; Rozum, I.; et al. ERA5 Hourly Data on Pressure Levels from 1940 to Present. Copernicus Climate Change Service (C3S) Climate Data Store (CDS). 2023. Available online: https://doi.org/10.24381/cds.bd0915c6 (accessed on 30 August 2023).
- Pleim, J.E. A combined local and nonlocal closure model for the atmospheric boundary layer. Part I: Model description and testing. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2007, 46, 1383–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Sayit, H.; Mamtimin, A.; Zhu, J.; Zhou, C.; Huo, W.; Yang, F.; Yang, X.; Gao, J.; Zhao, X. Evaluation of five planetary boundary layer schemes in WRF over China’s largest semi-fixed desert. Atmos. Res. 2021, 256, 105567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, L.; Zhao, T.; Yang, X.; Liu, C.; He, Q.; Duan, J.X. An assessment of atmospheric boundary layer schemes over the Taklimakan Desert hinterland. J. Meteorol. Sci. 2018, 38, 157–166. [Google Scholar]
- Wyngaard, J.C. Toward numerical modeling in the “Terra Incognita”. J. Atmos. Sci. 2004, 61, 1816–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Bao, J.-W.; Chen, B.; Grell, E.D. A three-dimensional scale-adaptive turbulent kinetic energy scheme in the WRF-ARW model. Mon. Weather Rev. 2018, 146, 2023–2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudhia, J. Numerical study of convection observed during the winter monsoon experiment using a mesoscale two-dimensional model. J. Atmos. Sci. 1989, 46, 3077–3107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mlawer, E.J.; Taubman, S.J.; Brown, P.D.; Iacono, M.J.; Clough, S.A. Radiative transfer for inhomogeneous atmospheres: RRTM, a validated correlated-k model for the longwave. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1997, 102, 16663–16682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.-Y.; Lim, J.-O.J. The WRF single-moment 6-class microphysics scheme (WSM6). Asia-Pac. J. Atmos. Sci. 2006, 42, 129–151. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, F.; Dudhia, J. Coupling an advanced land surface–hydrology model with the Penn State–NCAR MM5 modeling system. Part I: Model implementation and sensitivity. Mon. Weather Rev. 2001, 129, 569–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez, P.A.; Dudhia, J.; González-Rouco, J.F.; Navarro, J.; Montávez, J.P.; García-Bustamante, E. A revised scheme for the WRF surface layer formulation. Mon. Weather Rev. 2012, 140, 898–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedl, M.A.; McIver, D.K.; Hodges, J.C.; Zhang, X.Y.; Muchoney, D.; Strahler, A.H.; Woodcock, C.E.; Gopal, S.; Schneider, A.; Cooper, A. Global land cover mapping from MODIS: Algorithms and early results. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 83, 287–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Pu, Z. Vertical eddy diffusivity parameterization based on a large-eddy simulation and its impact on prediction of hurricane landfall. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2021, 48, e2020GL090703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stull, R.B. An Introduction to Boundary Layer Meteorology; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1988; Volume 13. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Muñoz-Esparza, D.; Hu, F.; Yan, C.; Miao, S. Simulation of flow fields in complex terrain with WRF-LES: Sensitivity assessment of different PBL treatments. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2020, 59, 1481–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lujun, X.U.; Huizhi, L.I.U.; Xiangde, X.U.; Qun, D.; Lei, W. Evaluation of the WRF model to simulate atmospheric boundary layer over Nagqu area in the Tibetan Plateau. Acta Meteorol. Sin. 2018, 76, 955–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, C.; Bao, Y.; Yuan, C.; Li, Z.; Zong, C. Comparison of the performances between the WRF and WRF-LES models in radiation fog—A case study. Atmos. Res. 2019, 226, 76–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Pu, Z. Turbulence Effects on the Formation of Cold Fog over Complex Terrain with Large-Eddy Simulation. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2022, 49, e2022GL098792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| D01 | D02 | D03 | D04 | D05 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grids | 119 × 119 | 120 × 120 | 138 × 138 | 150 × 150 | 213 × 213 |
| ∆x(m) | 9000 | 3000 | 1000 | 333 | 111 |
| Z_vert | 81 | 81 | 81 | 81 | 81 |
| Time_step | 9 | 3 | 1 | 1/3 | 1/9 |
| Bl_pbl | ACM2 | ACM2 | ACM2 | None | None |
| SGS | None | None | None | SMS-3D-TKE | SMS-3D-TKE |
| Microphysics | WSM6 | WSM6 | WSM6 | WSM6 | WSM6 |
| Ra_lw | RRTM | RRTM | RRTM | RRTM | RRTM |
| Ra_sw | Duhia | Duhia | Duhia | Duhia | Duhia |
| Cu_physics | Kain-Fritsch | None | None | None | None |
| Surface layer | Revised_MM5 | Revised_MM5 | Revised_MM5 | Revised_MM5 | Revised_MM5 |
| Land surface | Noah | Noah | Noah | Noah | Noah |
| Autumn | Winter | Spring | Summer | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LES | −1.69 | −0.36 | −1.46 | −1.97 |
| PBL | −1.97 | −0.52 | −1.76 | −2.71 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, X.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, Z.; Sun, J. Application of WRF-LES on the Simulation of Seasonal Characteristics of Atmospheric Boundary Layer Structure in Taklamakan Desert. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 558. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16030558
Xu X, Li X, Zhang Y, Gao Z, Sun J. Application of WRF-LES on the Simulation of Seasonal Characteristics of Atmospheric Boundary Layer Structure in Taklamakan Desert. Remote Sensing. 2024; 16(3):558. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16030558
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Xiaoyi, Xin Li, Yuanjie Zhang, Zhiqiu Gao, and Jingxi Sun. 2024. "Application of WRF-LES on the Simulation of Seasonal Characteristics of Atmospheric Boundary Layer Structure in Taklamakan Desert" Remote Sensing 16, no. 3: 558. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16030558
APA StyleXu, X., Li, X., Zhang, Y., Gao, Z., & Sun, J. (2024). Application of WRF-LES on the Simulation of Seasonal Characteristics of Atmospheric Boundary Layer Structure in Taklamakan Desert. Remote Sensing, 16(3), 558. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16030558






