Abstract
This paper analyzes low-Earth-orbit (LEO) satellite downlinks when an airborne interference source moves parallel to the satellite trajectory by considering the relative angle differences between the satellites and the interference sources. To make the experimental interference situations more like actual environments, the LEO trajectories are obtained from two-line element set (TLE) data. Airborne interference sources with various altitudes move parallel to the LEO trajectories, and a jamming to signal (J/S) ratio is calculated based on the relative angle differences between the ground station, the LEO satellite, and the interference source. To accurately calculate the J/S ratio, we should apply the sidelobe gain from which the interference signal enters to the ground station antenna. In order to calculate the relative angle difference ψ, the coordinates of the satellite and the interference source are converted from the World Geodetic System 1984 (WGS84) to the ground station-centered east–north-up (ENU) system. The resulting J/S ratio demonstrates that the distance and the relative angle difference ψ between the ground stations, LEO satellite, and airborne interference source appear to be important factors causing changes in the J/S ratio. Among them, the relative angle difference ψ, which determines the sidelobe gain of the ground station antenna, is the most significant factor affecting the J/S ratio variation.
1. Introduction
Low-Earth-orbit (LEO) satellites have been widely used to perform various Earth observation missions, such as resource monitoring, weather surveillance, and military reconnaissance, while circling the Earth along a trajectory below 2000 km in altitude [1,2]. To perform these missions effectively, the satellites often employ synthetic aperture radars to capture high-resolution images of the Earth’s surface, and the image data are then transmitted at a high speed to ground stations using X-band downlinks. The period of data communication between LEO satellites and ground stations is limited to a maximum of 10 min, though this varies slightly depending on the satellite trajectory. In order to predict whether or not image data can be received within such a short period of time, a link budget analysis that considers various environmental factors is essential. A link budget analysis considering natural earth environment, such as atmospheric impact [3,4,5] and Doppler shift [6,7,8], has been previously conducted. In addition, studies on link budget in interference environments where ground station antennas are exposed to intentional electromagnetic (EM) interference sources have also been investigated [9,10,11]. Although some research has been conducted in various interference situations, there is a lack of studies analyzing real LEO satellite trajectories and airborne interference sources. In particular, the airborne interference sources have a much greater impact on the satellite downlink compared to ground-based interference sources. Since ground stations should receive data within 10 min, the downlink can be significantly affected by the speed or path of the airborne interference source. Additionally, more in-depth research is required to accurately derive link budgets by considering the sidelobe gain of the ground station antenna based on the relative angle difference between the LEO satellite and the airborne interference source. The sidelobe gain of the ground station antenna is important because it has a critical impact on the J/S ratio, and the sidelobe gain is determined by the relative difference in angle between the LEO satellite and the airborne interference source.
In this paper, we analyze LEO satellite downlinks under interference situations when airborne interference sources move parallel to the satellite trajectory by considering the relative angle differences between the satellites and the interference sources. To make interference situations more like actual environments, we use the two-line element set (TLE) data of LEO satellite trajectory information, including geodetic coordinates provided by the Joint Space Operations Center at Vandenberg Air Force Base. Airborne interference sources with various altitudes (3 km, 6 km, 9 km, and 12 km) move parallel to the trajectories of the LEO satellites, and the jamming to signal (J/S) ratio is calculated based on the relative angle differences between the ground station, satellite, and interference source. In this study, only the simplest path, traveling parallel to the satellite, is observed. In order to express the positions of these three elements, the World Geodetic System 1984 (WGS84) coordinates are converted to the ground station-centered east–north-up (ENU) system [12,13]. Based on the ENU coordinates, the relative angle difference between the satellite and the interference source is calculated, and the sidelobe gain of the ground station antenna to the direction where interference electromagnetic (EM) waves are incoming. The radiation pattern of the ground station antenna is obtained using geometrical optics (GO) and physical optics (PO) [14], and the sidelobe gain is then obtained and applied to the J/S ratio calculation. We investigate the link budget under interference situations in which airborne interference sources move at a minimum distance of 100 km (Path 1), 200 km (Path 2), and 300 km (Path 3) from the ground station. For each path, the elevation angle and slant distance between the interference source and ground station are calculated during the data communication period according to the altitudes of the airborne interference source. In all scenarios, the period of data communication between the LEO satellite and the ground station is assumed to be approximately 600 s. We examine the J/S ratio results according to satellite trajectories, with maximum elevation angles of 86.8° (Trajectory 1), 62.7° (Trajectory 2), and 37.3° (Trajectory 3). The trends in relative angle difference and J/S ratio according to the paths and altitudes of the interference source are observed, and the results confirm that the J/S ratio increases as the relative angle difference decreases. These results show that although the distances between ground station, LEO satellite, and interference source are important from a J/S ratio perspective, the relative angle difference between the interference source and satellite is an even more critical factor.
2. Scenario of Interference Source Moving along the Satellite Trajectory
2.1. LEO Satellite Downlink Scenario and J/S Ratio Calculation
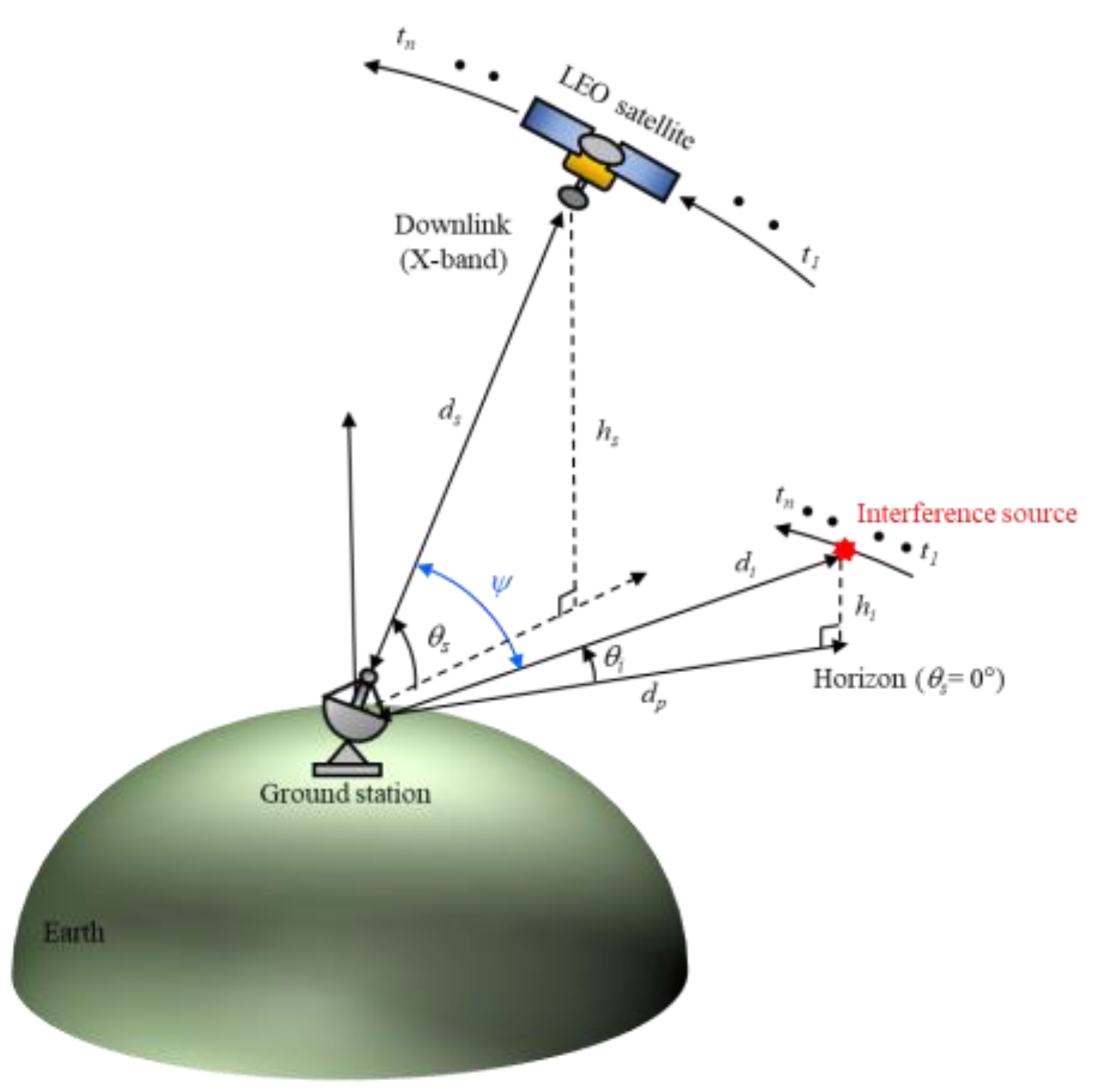
Figure 1 shows a conceptual figure of an LEO satellite downlink scenario in an interference situation where the ground station is exposed to strong EM waves incoming from an airborne source that moves along a path parallel to the LEO satellite trajectory. The LEO satellite moves along a trajectory with an altitude of hs and transmits image data to the ground station through an X-band downlink. When the ground station is assumed to be the center of the coordinates, θs is the elevation angle between the LEO satellite and the Earth’s surface, and ds is the slant distance from the ground station to the satellite. As the satellite transmits image data to the ground station, the airborne interference source moves parallel to the trajectory of the LEO satellite at a distance dp from the ground station. The elevation angle between the interference source and the Earth’s surface is θi, and the slant distance to the interference source is di. The satellite transmits image data between t1 and tn to the ground station located at a specific latitude and longitude on the Earth’ surface. The ideal data communication time is about 600 s, during which the relative angle difference between the LEO satellite and the airborne interference source is ψ. To analyze the link budget under these conditions, the J/S ratio can be calculated using Equation (1):
where S is the power received by the ground station from the LEO satellite. is the transmission power from the satellite, and is the bore-sight gain of the data transmission antenna in the satellite. (ξ) is the gain pattern of the ground station antenna according to the steering angle ξ, and (ξ = 0°) is the bore-sight gain of the ground station antenna. Here, it is assumed that the ground station antenna is precisely tracking in the direction of the satellite, and thus the ground station’s movements toward the satellite are always (ξ = 0°). is the path loss between the LEO satellite and the ground station, calculated assuming free space. J is the power received at the ground station from the airborne interference source and is calculated in a similar way to S. is the transmission power from the airborne interference source, and is the bore-sight gain of the airborne interference source antenna. (ξ = ψ) is the sidelobe gain of the ground station antenna to the direction where the ground station is exposed to strong incoming EM interference waves. is the path loss from the airborne interference source to the ground station.
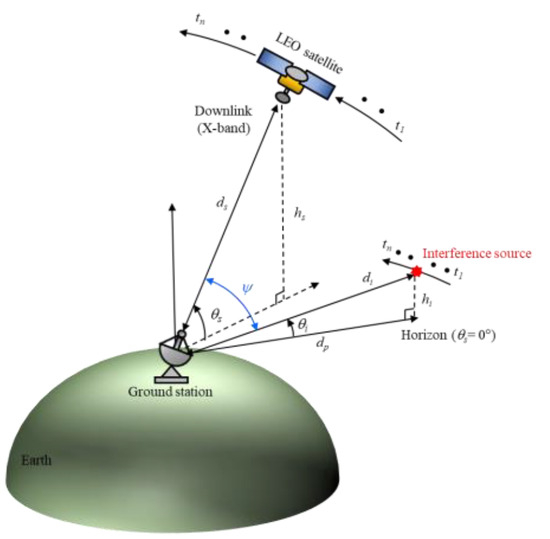
Figure 1.
Conceptual figure of the LEO satellite downlink scenario under interference situations.
2.2. Derivation of Relative Angle Difference ψ with Sidelobe Gain
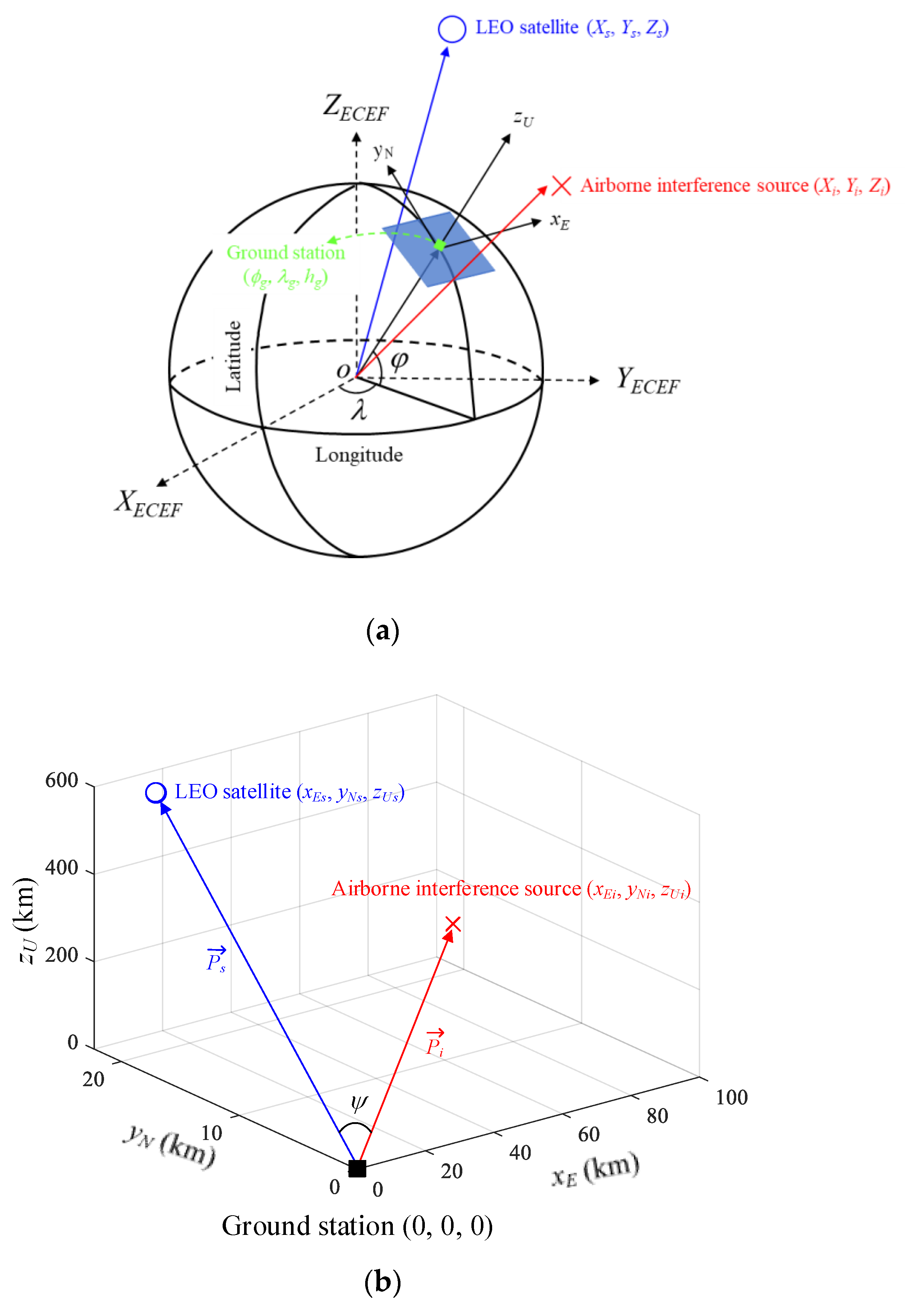
For the J/S ratio in Equation (1), Ls can be obtained using the LEO satellite’s TLE data. The TLE data consist of two lines of trajectory information, including epoch times, eccentricities, and inclination angles. Based on these data, location information, such as latitude, longitude, and altitude, is obtained to predict the trajectory. ds is calculated by applying the free-space Friis equation with the slant distance between the satellite and ground station. J is then calculated from the path loss and the sidelobe gain of the ground station antenna toward the interference source, and thus the sidelobe gain is determined by the location of the interference source. To calculate the sidelobe gain toward the interference source, the relative angle difference ψ is defined. ψ is the angle between the LEO satellite and the airborne interference source when the ground station antenna is set as the origin of the coordinate system. Latitude, longitude, and altitude coordinates are generally referred to using WGS84. For example, the latitude ϕg, longitude λg, and altitude hg of the ground station according to WGS84 are indicated by the green square marker in Figure 2a. To calculate the relative angle difference ψ, the WGS84 coordinates of the LEO satellite, ground station, and airborne interference source are converted into ENU coordinates. The ENU system uses Cartesian coordinates relative to a specific Earth location as its origin. Here, the location of the ground station is the origin for the ENU system. Converting coordinates from WGS84 to ENU requires two steps: conversion from WGS84 to Earth-centered Earth-fixed (ECEF), and then conversion from ECEF to ENU. To convert to the ECEF coordinate system, the Earth’s radius R is calculated at latitude ϕ by Equation (2), where a (= 6378.137 km for WGS84) is the ellipsoidal equatorial radius and e is the eccentricity of the ellipsoid (e2 = 0.00669437999 for WGS84). The ECEF system has the center of the Earth as the origin (0, 0, 0), which allows us to calculate XECEF, YECEF, and ZECEF from latitude ϕ, longitude λ, and altitude h using Equations (3)–(5):
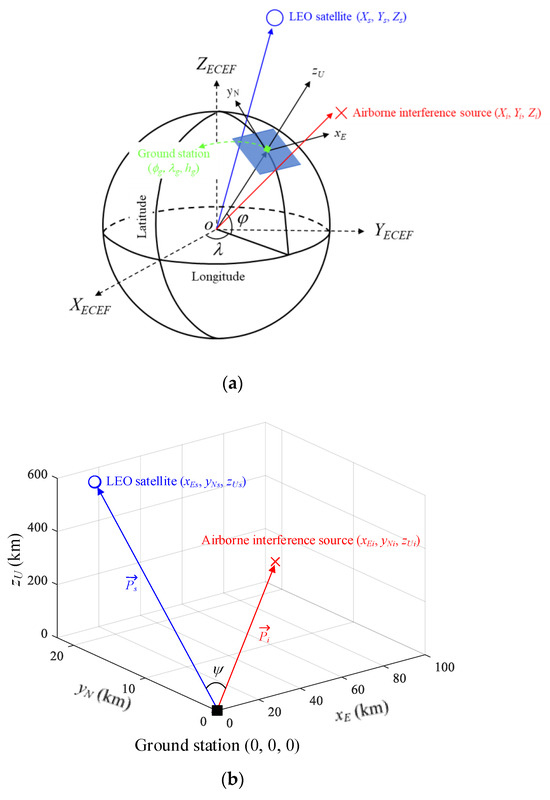
Figure 2.
Schematic diagram for the conversion of the coordinate systems for the ground station, LEO satellite, and interference source: (a) conversion from WGS84 to the ECEF; (b) transformation from ECEF to ENU.
Now, the locations of the ground station, LEO satellite, and airborne interference source are converted from WGS84 to ECEF, and the transformation matrices (6) and (7) can be used to obtain the ENU coordinates where the ground station is the origin. and are the position vectors of the satellite and interference source, respectively. The relative angle difference ψ can be derived by calculating the dot product of the two vectors using Equation (8).
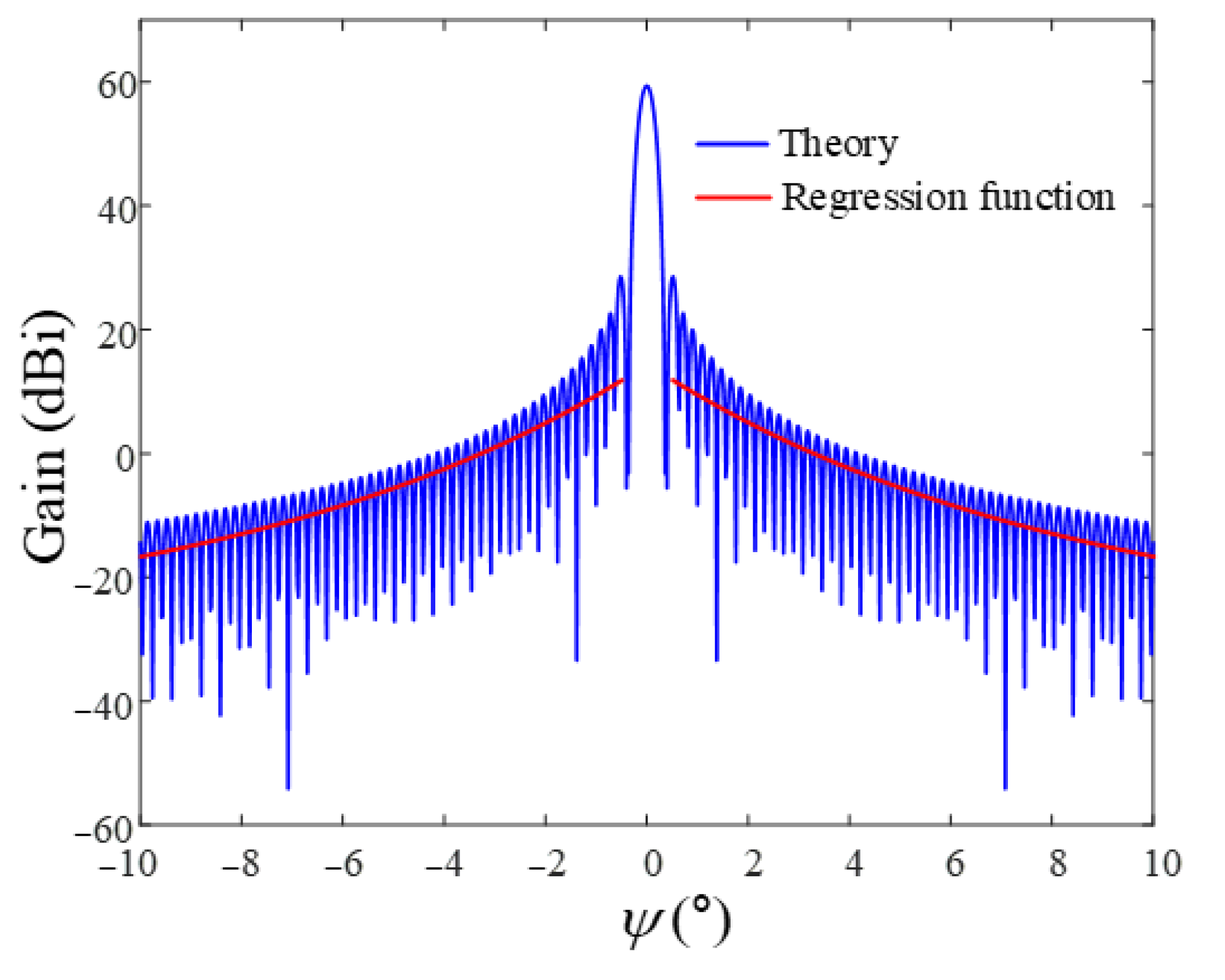
Figure 3 shows the radiation pattern of a ground station antenna with a parabolic reflector and rectangular feed horn. The bore-sight gain (ξ = 0°) of the antenna is 59 dBi at 8 GHz. The blue solid line indicates the radiation pattern obtained using the GO and PO methods. The GO method is used to model the antenna, focusing inside the reflector, and the PO method is used to calculate the scattering on the reflector surface by considering the current distribution on the surface [15,16,17,18,19,20]. By combining these two methods, the ground station antenna radiation pattern can be calculated. The parabolic diameter of the ground station antenna is 11.3 m, and a feed horn antenna with rectangular aperture is employed. Since sidelobe gains exhibit large fluctuations according to angle, we apply a regression model in order to more easily observe the tendency of the J/S ratio. The regression model is based on the exponential Equation (9):
where a1 (= −31.5817), a2 (= 36.7337), b 1(= 0.0046), and b2 (= −0.0682) are the coefficients that best fit the point, shown as the red solid line. To determine the sidelobe gain, we apply the ψ obtained from Equation (8) to Equation (9). All scenarios for downlink with airborne interference sources are simulated using Equations (1)–(5). Detailed simulation parameters are given in Table 1.
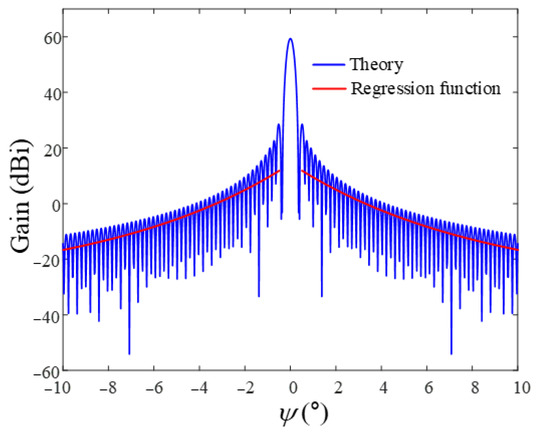
Figure 3.
Radiation pattern of the ground station antenna with regression model.

Table 1.
Parameters for the downlink simulation.
3. Analysis of the LEO Satellite Downlinks in Interference Situations
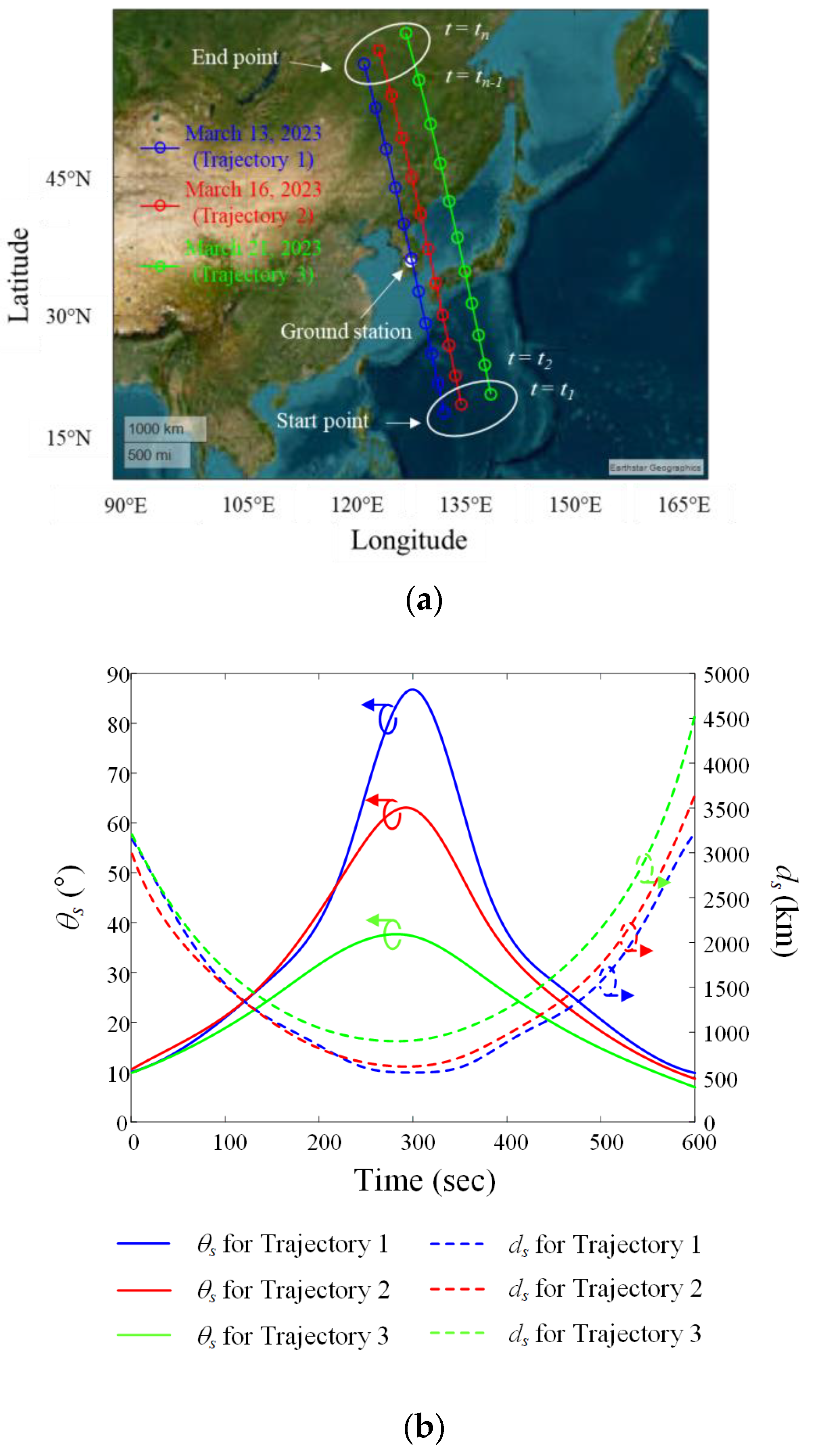
Figure 4a shows the satellite trajectories obtained from the TLE data. The blue, red, and green solid lines with circle markers represent the trajectories of the LEO satellite for 13 March (Trajectory 1), 16 March (Trajectory 2), and 21 March (Trajectory 3), 2023, respectively. The ground station is located at latitude 36.33° and longitude 127.26°. The time at which communication between this ground station and the LEO satellite begins is defined as t1, and the time when communication ends is defined as tn. In general, the data communication time is less than 600 s, so t1 and tn are defined as 0 and 600 s, respectively, in this scenario. Figure 4b shows the slant distance ds and elevation angle θs between the ground station and the LEO satellite for each trajectory. The maximum elevation angles of Trajectory 1, Trajectory 2, and Trajectory 3 are 86.8°, 62.7°, and 37.3°, respectively, and the slant distances from the ground station to the satellite at the maximum elevation angle of each trajectory are 550.9 km, 618.6 km, and 908.1 km, respectively.
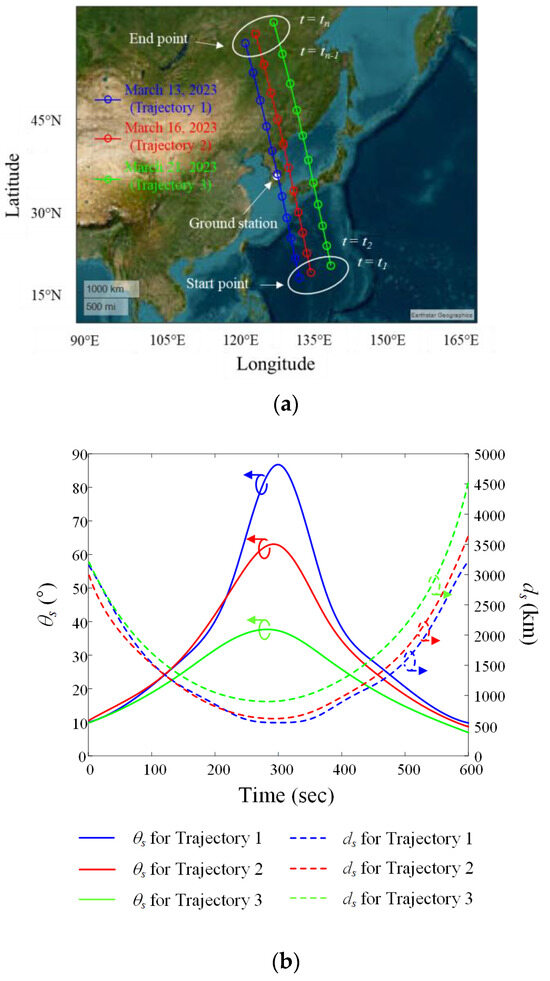
Figure 4.
Location information for LEO satellite trajectories during the data communication period: (a) trajectories on a map based on the WGS84 geodetic data; (b) elevation angle θs and slant distance ds for each trajectory using the ENU coordinate system.
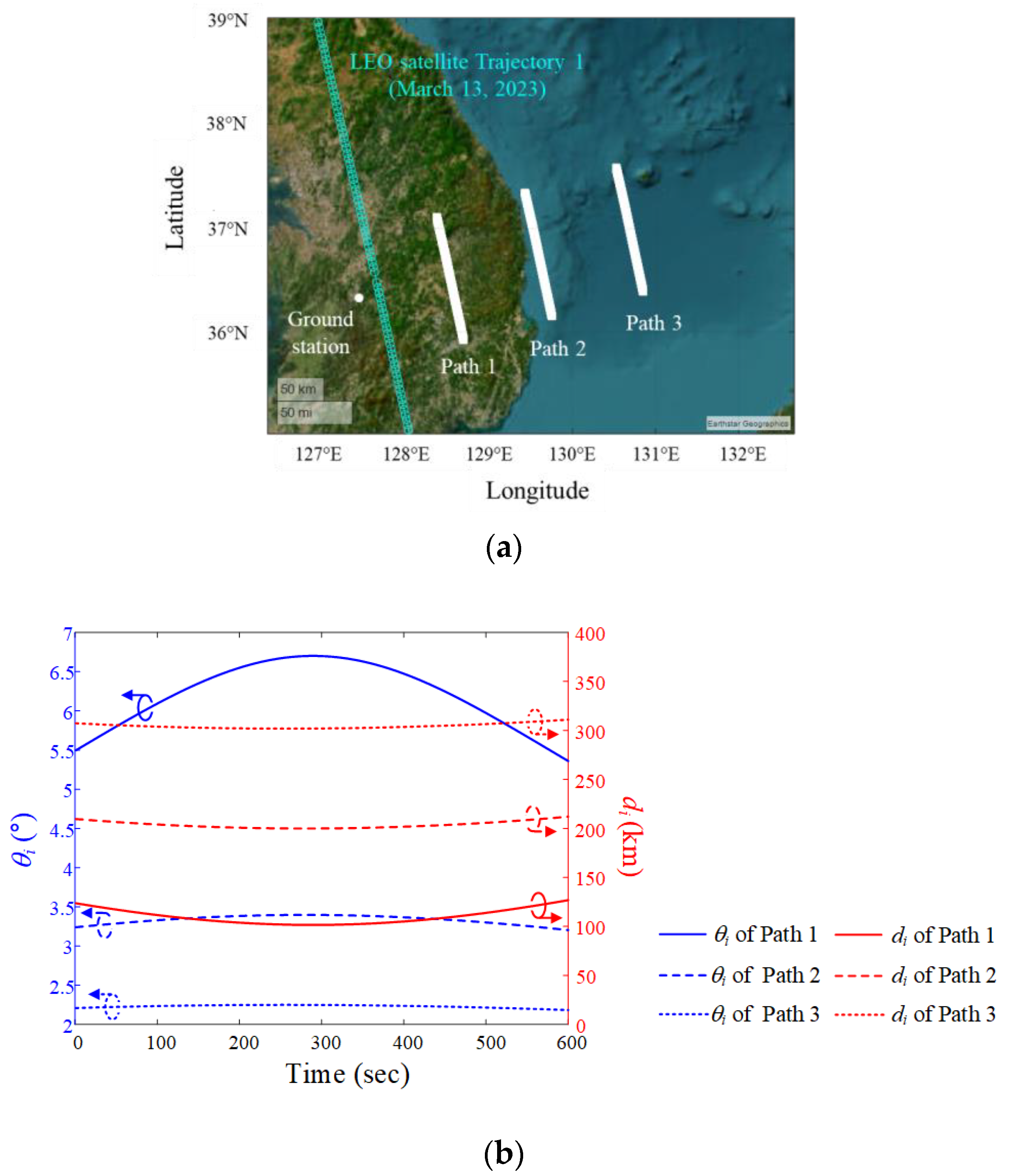
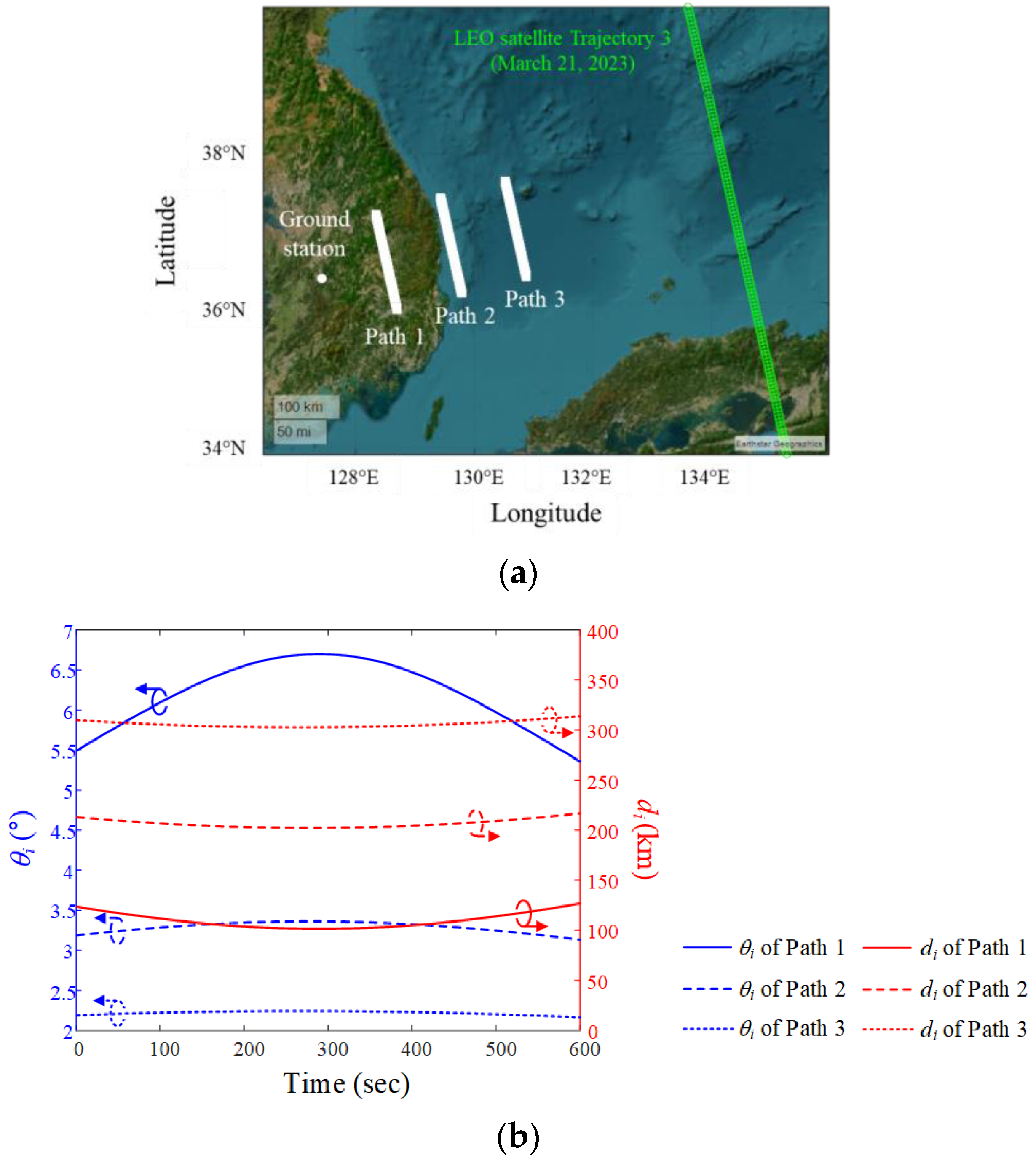
Figure 5a,b show the airborne interference source paths during the data communication period on 13 March 2023. dp is the distance between the ground station and the interference source, and the minimum dp for paths 1, 2, and 3 is 100 km, 200 km, and 300 km, respectively, with the paths parallel to the LEO satellite using Trajectory 1. The ground paths of the interference source and satellite, and the ground station location, are illustrated on a map (Mercator projection) based on the WGS84 geodetic data. To observe the movement of the interference source from the perspective of the ground station, its elevation angle θi and slant distance di are derived using ENU coordinates, with the ground station as the origin location. When the altitude of the interference source is fixed at 12 km, the maximum elevation angles are 6.7° (Path 1), 3.4° (Path 2), and 2.2° (Path 3). The minimum slant distances are 101.6 km (Path 1), 201.7 km (Path 2), and 301.9 km (Path 3).
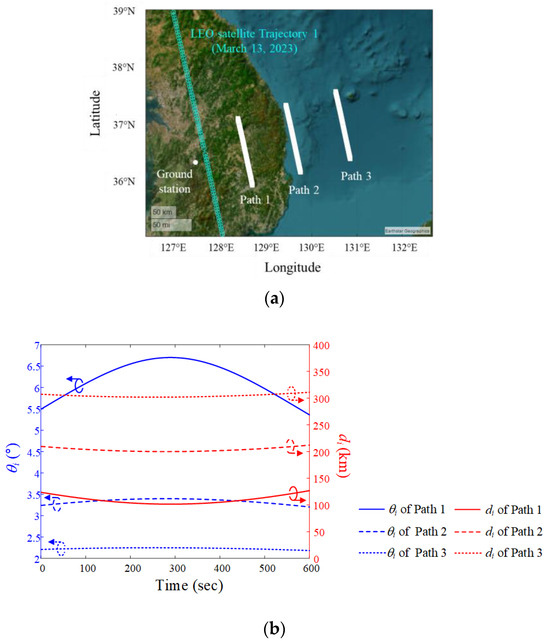
Figure 5.
Airborne interference source paths during the data communication period when the LEO satellite moves along Trajectory 1: (a) paths on a map based on the WGS84 geodetic data; (b) elevation angle θi and slant distance di for each path.
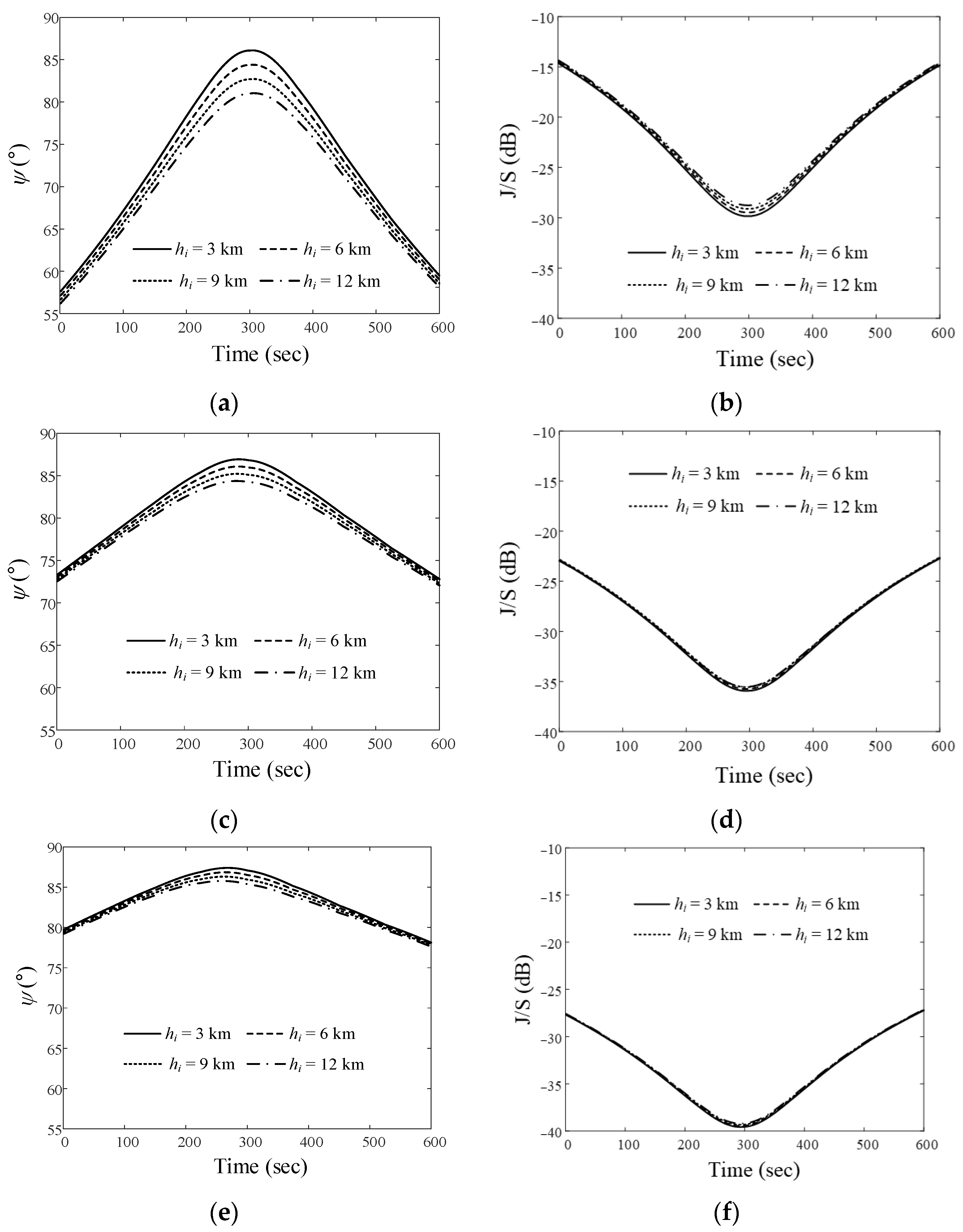
Figure 6 shows the relative angle difference ψ and J/S ratio results obtained by varying the altitude of the airborne interference when the LEO satellite moves along Trajectory 1. In order to more easily observe the trends according to the path and altitude during the data communication period (n = 1, N = 600), the average ψ and J/S ratio are obtained using Equations (10) and (11):
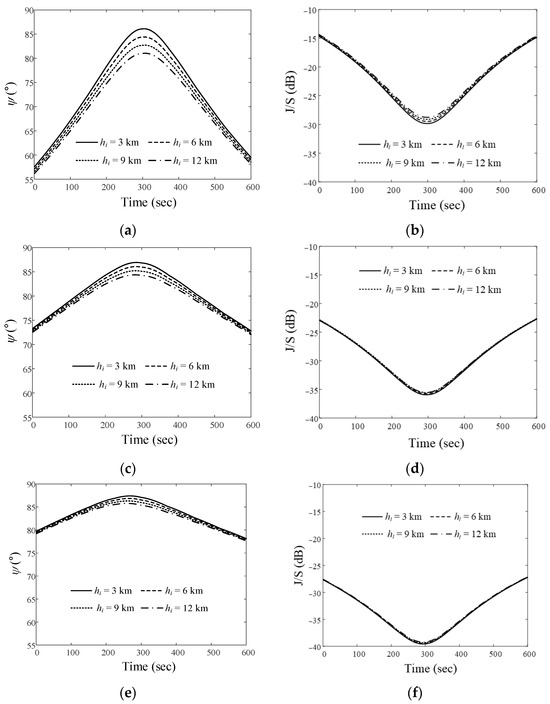
Figure 6.
Relative angle differences ψ and J/S ratios of the airborne interference source at different altitudes when the LEO satellite moves along Trajectory 1: (a) ψ for Path 1; (b) J/S ratio for Path 1; (c) ψ for Path 2; (d) J/S ratio for Path 2; (e) ψ for Path 3; (f) J/S ratio for Path 3.
Figure 6a,b show ψ and the J/S ratio when the altitudes of the interference source in Path 1 are 3 km, 6 km, 9 km, and 12 km. The ψave values according to these altitudes are 73.2°, 72.2°, 71.2°, and 70.2°, respectively. The Jave/Save ratios for these altitudes are −22.3 dB, −22.1 dB, −21.9 dB, and −21.7 dB, respectively. Figure 6c,d present the ψ and J/S ratio according to altitude when the interference source moves along Path 2. For each altitude, the ψave values are 80.8°, 80.3°, 79.8°, and 79.3°, respectively. The Jave/Save ratios are −29.5 dB, −29.4 dB, −29.2 dB, and −29.1 dB, respectively. The ψ and J/S ratio when the interference source moves along Path 3 are illustrated in Figure 6e,f.
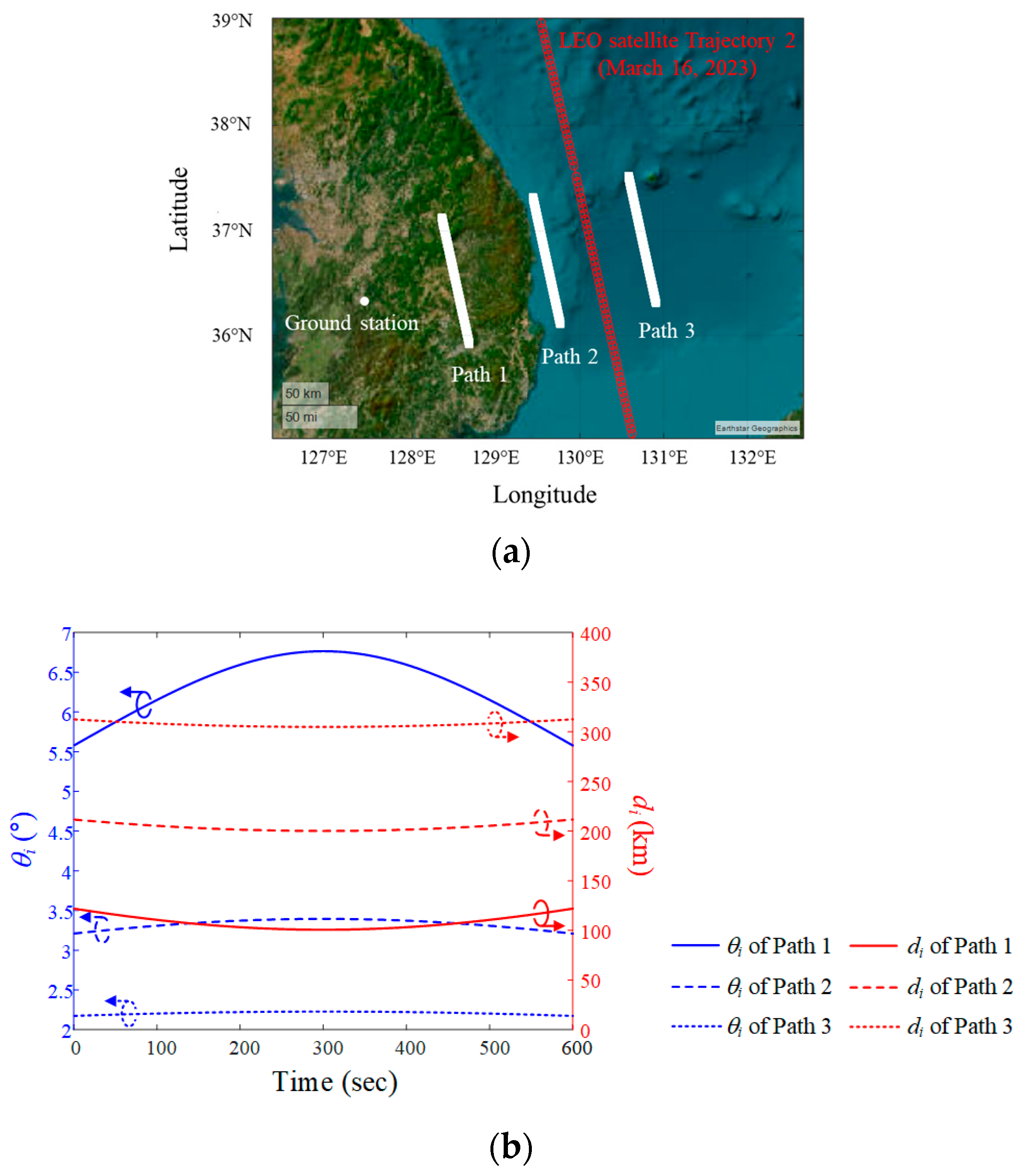
Figure 7a shows the ground paths of the airborne interference source and LEO Trajectory 2 for 16 March 2023. The minimum dp for paths 1, 2, and 3 is 100 km, 200 km, and 300 km, respectively, and the paths are parallel to LEO satellite Trajectory 2. Figure 7b shows the elevation angle θi and slant distance di for when the interference source moves along Paths 1, 2, and 3 at an altitude of 12 km. The maximum elevation angles are 6.7° (Path 1), 3.4° (Path 2), and 2.2° (Path 3). When the interference source is located at the maximum elevation, the slant distances are 101.2 km (Path 1), 201.5 km (Path 2), and 301.2 km (Path 3).
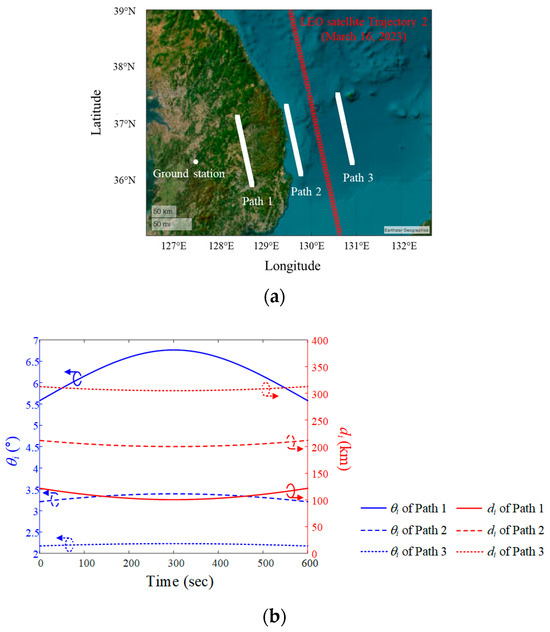
Figure 7.
Airborne interference source paths during the data communication period when the LEO satellite moves along Trajectory 2: (a) paths on a map based on the WGS84 geodetic data; (b) elevation angle θI and slant distance di for each path.
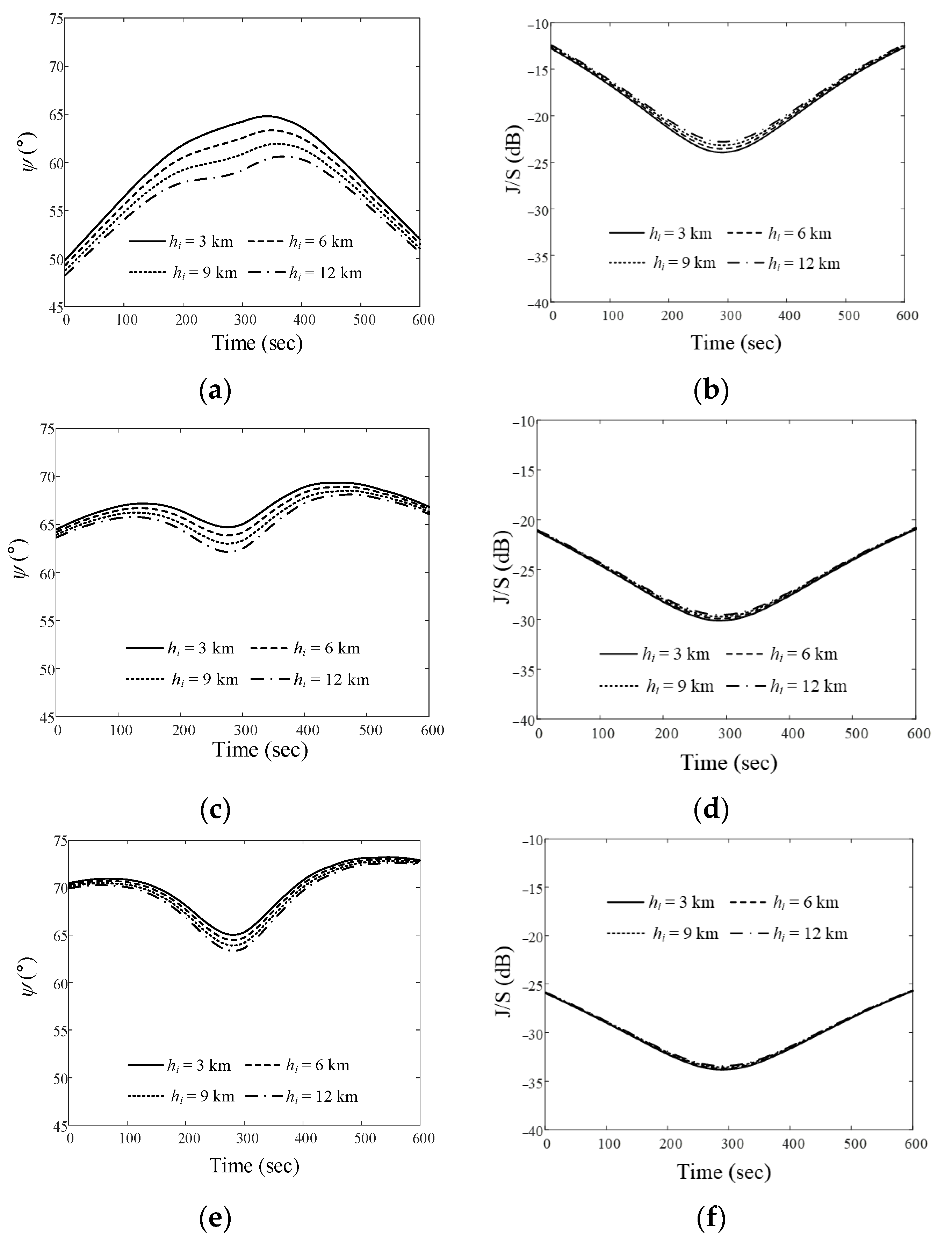
Figure 8a,b show ψ and the J/S ratio according to the different altitudes of the airborne interference source. When the source moves along Path 1 at altitudes of 3 km, 6 km, 9 km, and 12 km, the ψave values are 59.4°, 58.4°, 57.3°, and 56.3°, respectively, and the Jave/Save ratios are −18.7 dB, −18.4 dB, −18.2 dB, and −17.9 dB, respectively. Figure 8c,d show the results of ψ and J/S depending on altitude when the interference source moves along Path 2. The ψave values at these altitudes are 67.1°, 66.6°, 66°, and 65.5°, respectively. The Jave/Save ratios are –26 dB, –25.9 dB, –25.8 dB, and –29.1 dB, respectively. Figure 8e,f present the ψ and J/S ratios when the interference source moves along Path 3. Ψave values are 70°, 69.7°, 69.3°, and 68.9°, and Jave/Save ratios are −30.3 dB, −30.2 dB, −30.1 dB, and −30.1 dB, respectively.
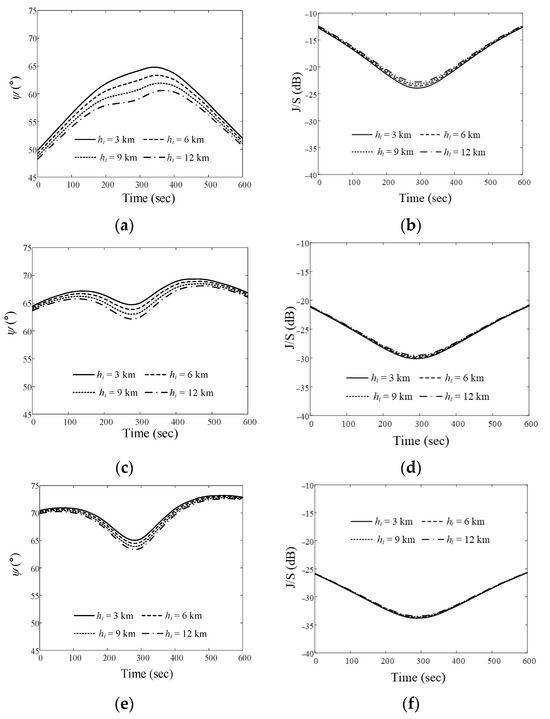
Figure 8.
Relative angle differences ψ and J/S ratios of the airborne interference source at different altitudes when the LEO satellite moves along Trajectory 2: (a) ψ for Path 1; (b) J/S ratio for Path 1; (c) ψ for Path 2; (d) J/S ratio for Path 2; (e) ψ for Path 3; (f) J/S ratio for Path 3.
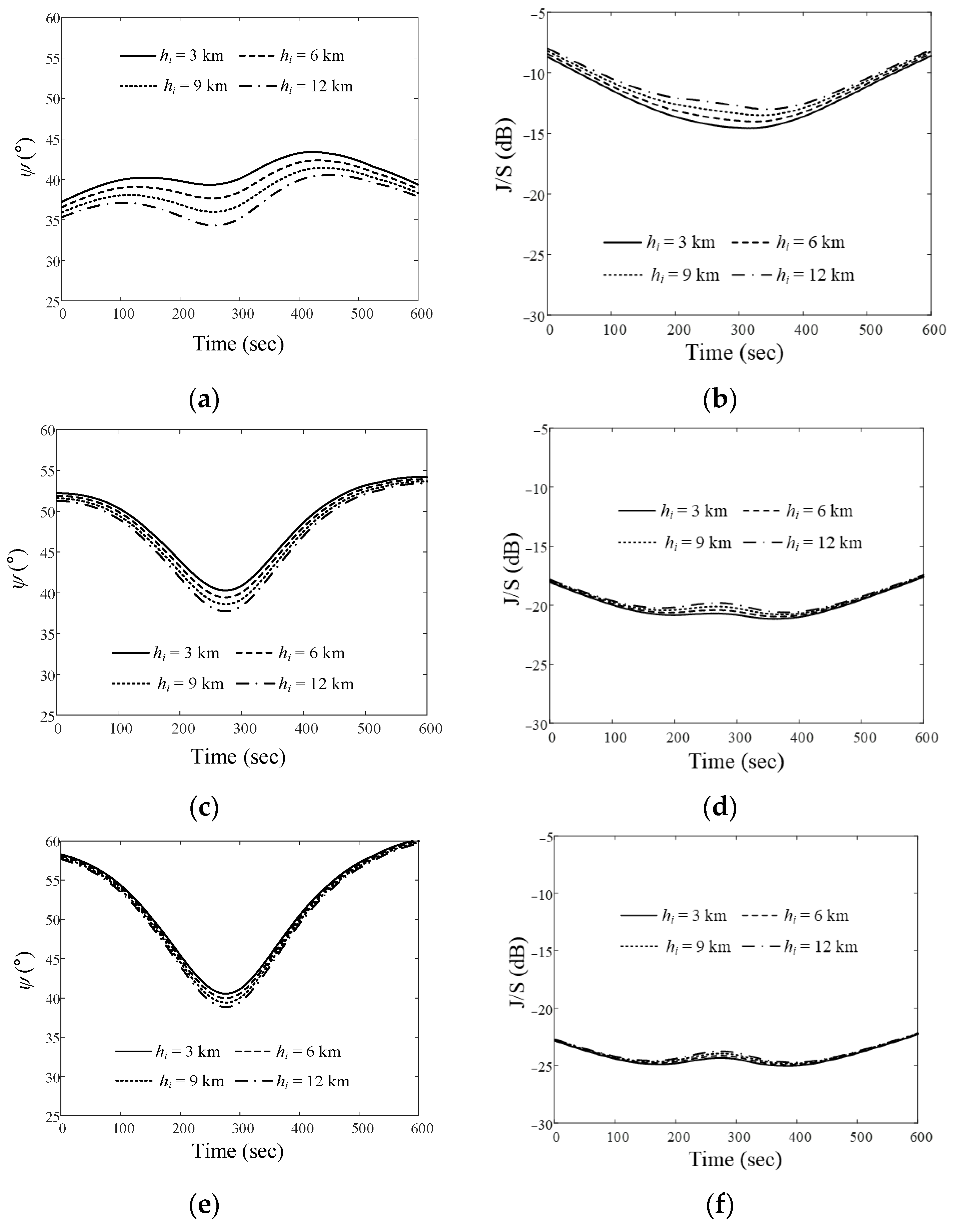
Figure 9a is for the case of Trajectory 3 (21 March 2023). The maximum elevation angles for Paths 1, 2, and 3 are 6.7°, 3.4°, and 2.2°, respectively, and the slant distances are 101.6 km, 201.7 km, and 301.9 km, respectively.
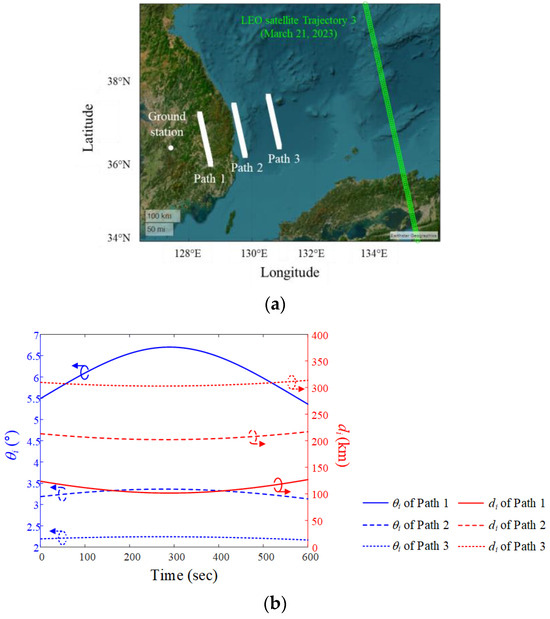
Figure 9.
Airborne interference source paths during the data communication period when the LEO satellite moves along Trajectory 3: (a) paths on a map based on the WGS84 geodetic data; (b) elevation angle θi and slant distance di for each path.
Figure 10a,b show the ψ and J/S ratios when the airborne interference source moves along Path 1. For altitudes of 3 km, 6 km, 9 km, and 12 km of the airborne interference source, the ψave values are 40.7°, 39.6°, 38.5°, and 37.5°, respectively. The Jave/Save ratios are −12.2 dB, −11.9 dB, −11.5 dB, and −11.1 dB, respectively. Figure 10c,d present the ψ and J/S ratios for Path 2. The ψave values are 48.4°, 47.8°, 47.3°, and 46.8°, and the Jave/Save ratios are −20.1 dB, −19.9 dB, −19.7 dB, and −19.6 dB, respectively.
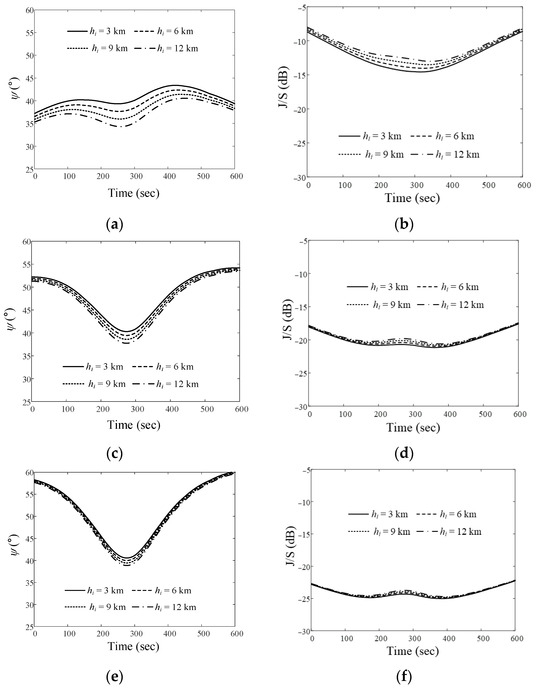
Figure 10.
Relative angle difference ψ and J/S ratio results obtained by varying the altitude of the airborne interference source when the LEO satellite moves along Trajectory 3: (a) ψ for Path 1; (b) J/S ratio for Path 1; (c) ψ for Path 2; (d) J/S ratio for Path 2; (e) ψ for Path 3; (f) J/S ratio for Path 3.
Figure 10e,f illustrate the ψ and J/S ratios when the interference source moves along Path 3. The ψave values are 51.3°, 69.7°, 69.3°, and 68.9°, with the Jave/Save ratios of −30.3 dB, −30.2 dB, −30.1 dB, and −30.1 dB, respectively.
In Table 2, ψave values and Jave/Save ratios are summarized. As can be seen from these results, for satellite Trajectory 1, the highest ψave value (83.6°) is observed when the interference source moves along Path 3 at an altitude of 3 km. In this case, the Jave/Save ratio is also the lowest at −33.6 dB. When the satellite moves along Trajectory 3 with Path 1 (an altitude of 12 km), the lowest ψave value (37.5°) and the highest Jave/Save ratio (−11.1 dB) are observed. For Trajectory 1 (with Path 1), the ψave at an altitude of 12 km is about 3° lower than that at an altitude of 3 km. On the other hand, the Jave/Save ratio at 12 km is 0.6 dB higher than at 3 km. As altitude hi increases, ψave decreases and the Jave/Save ratio increases slightly. These results show that the relative angle difference ψ between the LEO satellite and interference source is a critical factor for the J/S ratio.

Table 2.
Summary of ψave and Jave/Save ratio results for all scenarios.
4. Conclusions
We analyzed LEO satellite downlinks under interference situations when airborne interference sources move parallel to the LEO satellite trajectory by considering relative angle differences between satellites and interference sources. To make interference situations more like actual environments, the LEO trajectories were obtained from TLE data. Airborne interference sources with various altitudes moved parallel to the satellite trajectories, and the J/S ratio was calculated according to the relative angle differences between the ground station, satellite, and interference source. In order to calculate the relative angle difference ψ, the satellite and interference source coordinates were converted from the WGS84 to the ENU coordinate system. By applying the relative angle difference ψ, we obtained the sidelobe gain of the ground station antenna in the direction of the interference from the ground station antenna. Through a comprehensive link budget analysis, the J/S ratio was found to be 22.5 dB higher in Trajectory 3, where the relative angle difference ψ was small compared to the other trajectories. These results showed that the relative angle difference ψ is more important in the J/S ratio than the distance between the ground station and the interference source or satellite.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, H.C. and E.K.; methodology, E.K., J.K. and H.C.; software, E.K.; validation, E.K., J.K. and H.C.; formal analysis, E.K. and H.C.; investigation, E.K.; resources, E.K. and H.C.; data curation, E.K. and H.C.; writing—original draft preparation, E.K.; writing—review and editing, E.K., J.K., Y.P. and H.C.; visualization, E.K. and H.C.; supervision, H.C.; project administration, Y.P.; funding acquisition, H.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Agency for Defense Development (UI210013YD).
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Kim, M.J.; Lim, S.; Shin, D.C. Analysis method for determining optimal synthetic aperture time using estimated range and doppler cone angle at the center of synthetic aperture length. J. Electromagn. Eng. Sci. 2023, 23, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.G.; Kim, C.K.; Park, S.O. Ocean image formation algorithm using altimeter data for next generation satellite SAR. J. Electromagn. Eng. Sci. 2022, 22, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewark, U.J.; Antes, J.; Walheim, J.; Timmermann, J.; Zwick, T.; Kallfass, I. Link budget analysis for future E-band gigabit satellite communication links (71–76 and 81–84 Ghz). CEAS Space J. 2013, 4, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cakaj, S.; Malarić, K. Rigorous analysis on performance of LEO satellite ground station in urban environment. Int. J. Satell. Commun. Netw. 2007, 25, 619–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.Y.; Liu, C.H. Modeling the effects of ionospheric scintillations on LEO satellite communications. Int. J. Satell. Commun. Netw. 2004, 8, 147–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilcoyne, D.K.; Rowe, S.A.; Headley, W.C.; Mortensen, D.J.; McGwier, R.W.; Leffke, Z.J.; Reinhart, R.C. Link adaptation for mitigating earth-to-space propagation effects on the NASA scan testbed. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Aerospace Conference, Big Sky, MT, USA, 5–12 March 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Barbarić, D.; Vuković, J.; Babic, D. Link budget analysis for a proposed Cubesat Earth observation mission. In Proceedings of the 2018 41st International Convention on Information and Communication Technology, Opatija, Croatia, 21–25 May 2018; pp. 133–138. [Google Scholar]
- Reiten, K.; Schlanbusch, R.; Kristiansen, R.; Vedal, F.; Nicklasson, P.J.; Berntsen, P.C. Link and doppler analysis for space-based AIS reception. In Proceedings of the 2007 3rd International Conference on Recent Advances in Space Technologies, Istanbul, Turkey, 14–16 June 2007; pp. 556–561. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, H.; Zhang, J.; Sun, Z.; Yang, H. Event-based wireless tracking control for a wheeled mobile robot against reactive jamming Attacks. IEEE Trans. Control Netw. Syst. 2023, 10, 1925–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lineswala, P.L.; Shah, S.N.; Shah, R. Different categorization for jammer: The enemy of satellite navigation. In Proceedings of the 2017 2nd International Conference for Convergence in Technology (I2CT), Mumbai, India, 7–9 April 2017; pp. 282–287. [Google Scholar]
- Sathaye, H.; Noubir, G.; Ranganathan, A. On the implications of spoofing and jamming aviation datalink applications. In Proceedings of the 38th Annual Computer Security Applications Conference, Austin, TX, USA, 5–9 December 2022; pp. 548–560. [Google Scholar]
- Senapati, M.; Anand, B.; Barsaiyan, V.; Rajalakshmi, P. Geo-referencing system for locating objects globally in LiDAR point cloud. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 6th World Forum on Internet of Things (WF-IoT), New Orleans, LA, USA, 2–16 June 2020; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Huynh, G.; Williamson, C. Integration of Google Maps/Earth with microscale meteorology models and data visualization. Comput. Geosci. 2013, 61, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merabtine, N.; Boualleg, A.; Benslama, M. Analysis of radiation patterns and feed illumination of the reflector antenna using the physical and geometrical optics. Semicond. Phys. Quant. 2006, 9, 53–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piu, H.; Rahmat Samii, Y. Analysis and characterization of multilayered reflector antennas: Rain/snow accumulation and deployable membrane. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propagat. 1998, 46, 1593–1605. [Google Scholar]
- Hung, C.; Mittra, R. Secondary pattern and focal region distribution of reflector antennas under wide-angle scaning. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propagat. 1983, 31, 756–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusch, W. The current state of the reflector antenna art. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propagat. 1984, 32, 313–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, F.J.; Prata, A. Generalized classical axially symmetric dual-reflector antennas. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propagat. 2001, 49, 547–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, D.W.; Rahmat-Samii, Y. A generalized diffraction synthesis technique for high performance reflector antennas. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propagat. 1995, 43, 27–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoferer, R.A.; Rahmat-Samii, Y. Subreflector shaping for antenna distortion compensation: An efficient Fourier-Jacobi expansion with GO/PO analysis. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propagat. 2002, 50, 1676–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).