PolSAR Image Classification Based on Multi-Modal Contrastive Fully Convolutional Network
Abstract
1. Introduction
- A pixel-level semantic segmentation method is proposed that can effectively reduce the impact of speckle noise and improve the regional consistency of classification results for the PolSAR image classification task.
- Combining contrastive learning and semantic segmentation methods, a multi-modal contrastive fully convolutional network is proposed, which can achieve better terrain classification with limited labeled samples.
- To further enhance the classification accuracy and boost network stability, a classification strategy with overlapping pixels in the neighborhood window is introduced. Experimental findings demonstrate the effectiveness of this strategy in significantly improving the classification accuracy of the proposed method.
2. Proposed Classification Framework
2.1. PolSAR Features
2.2. Fully Convolutional Network
2.3. Multi-Modal Contrastive Fully Convolutional Network (MCFCN)
2.4. Procedure of the MCFCN
| Algorithm 1 The Whole Process of the MCFCN. |
| Training process: |
| Input: Randomly select the labeled PolSAR dataset. |
| 1: Extraction of multi-modal features from polarimetric coherency matrix by polarimetric target decomposition methods. |
| 2: The whole-view PolSAR image is segmented into a number M of size w × w pixels and a multi-modal positive and negative sample set U is constructed. |
| 3: Combining contrastive learning with FCN to construct a multi-modal contrastive fully convolutional network (MCFCN). |
| 4: The MCFCN model constructed in step 3 is trained in a self-supervised manner using the positive and negative sample set U, and the parameters of the model are saved. |
| 5: The labeled data are used to fine-tune the network model trained in step 4 to obtain the final network model. |
| Testing process: |
| 1: Multiple differentially PolSAR image datasets to be classified are obtained in a sliding window manner. |
| 2: The data obtained in the previous step are classified using the network trained in the training process to obtain multiple classification results. |
| 3: A majority voting method is used on the multiple classification results obtained to determine the final label. |
| Output: Final label map. |
3. Experimental Design
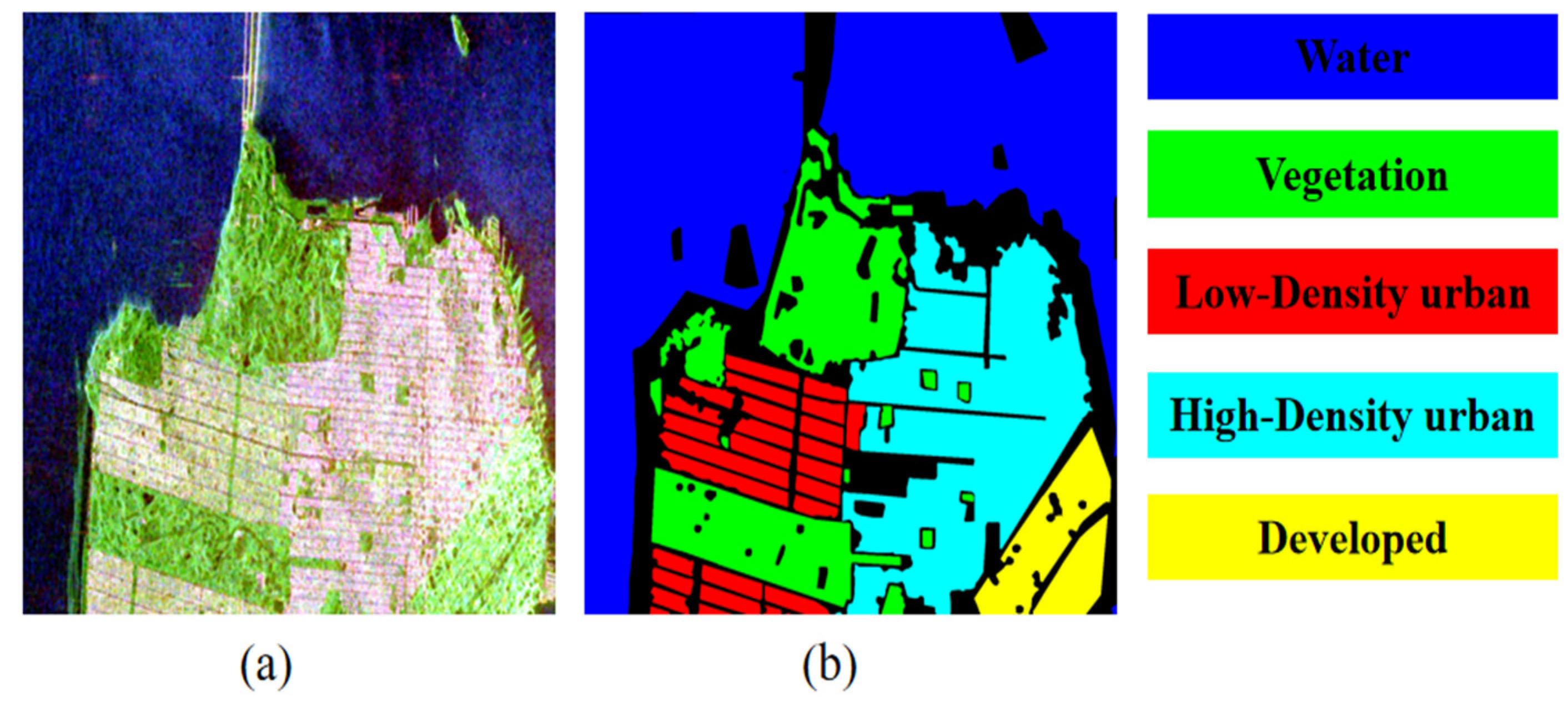
3.1. Experimental Data
3.2. Experimental Design
3.3. Parameter Analysis
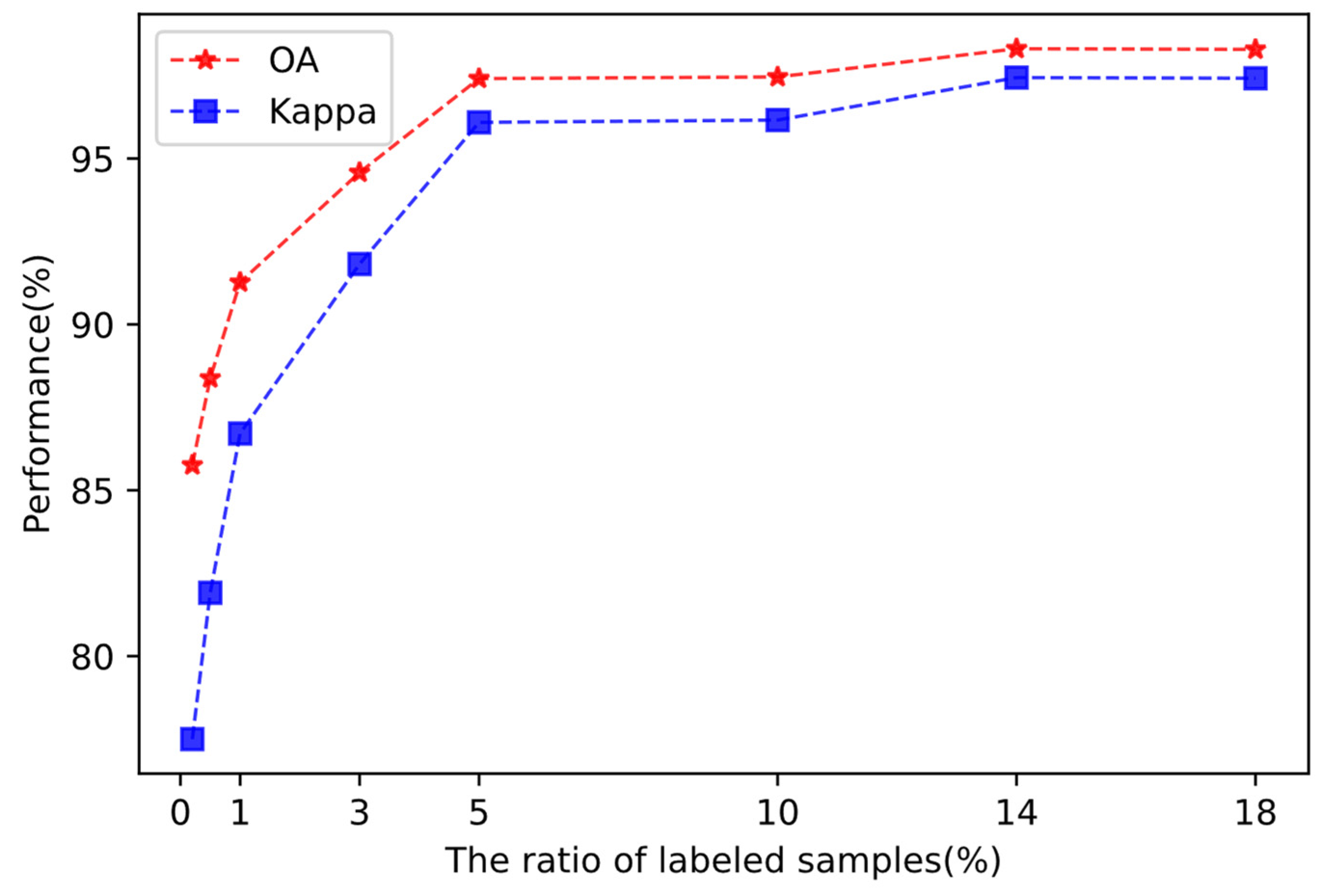
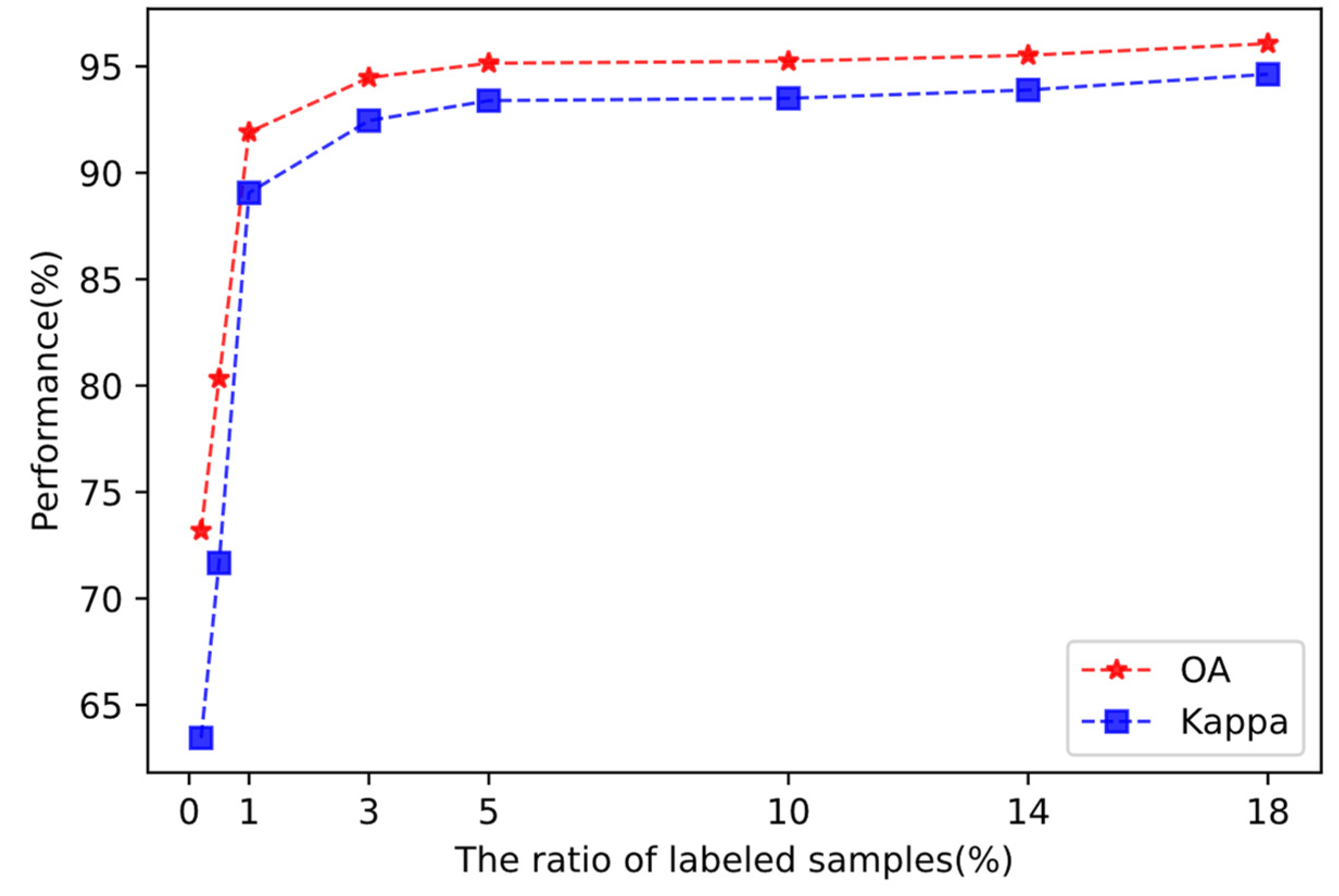
3.3.1. Effect of the Number of Labeled Samples
3.3.2. Effect of the Size of Sliding Window
3.3.3. Effect of the Batch Size
4. Experimental Results
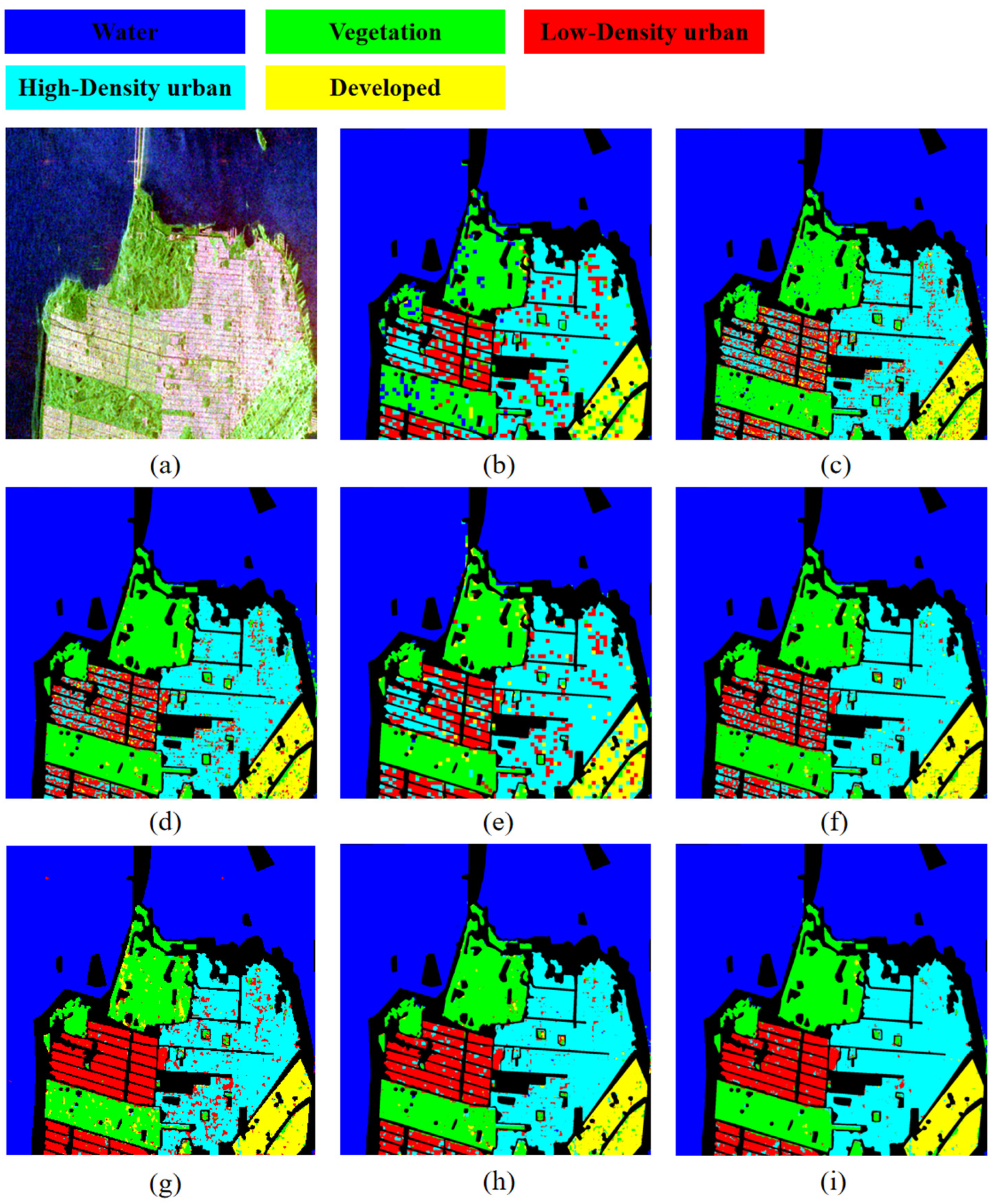
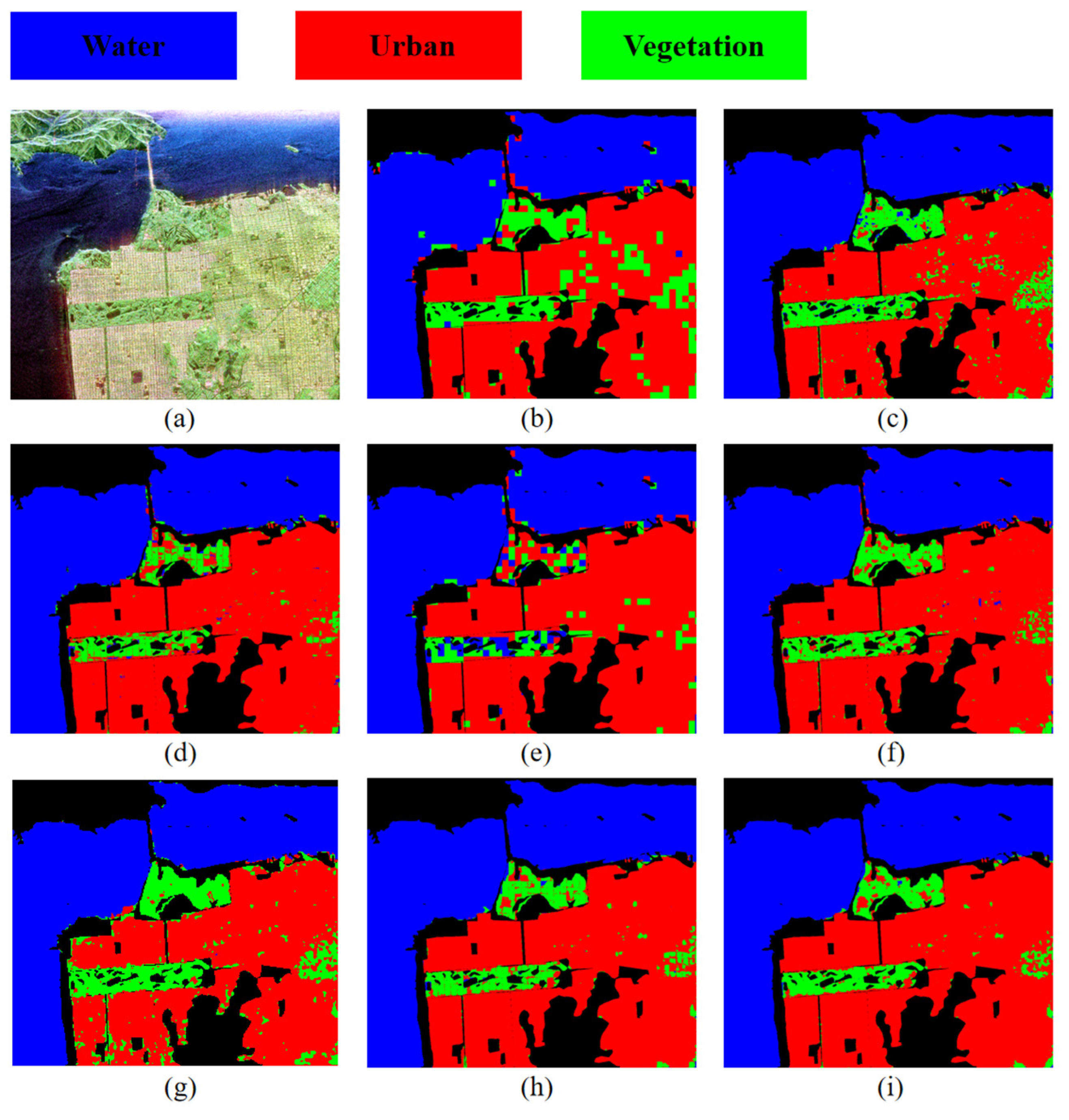
4.1. Classification Results of the San Francisco I Dataset
4.2. Classification Results of the Rs2-Fleveoland Dataset
4.3. Classification Results of San Francisco II Dataset
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, J.; Li, M.; Yu, H.; Xing, M. Full-Aperture Processing of Airborne Microwave Photonic SAR Raw Data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 5218812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zeng, X.; Yan, Z.; Kang, J.; Sun, X. AIR-PolSAR-Seg: A Large-Scale Data Set for Terrain Segmentation in Complex-Scene PolSAR Images. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2022, 15, 3830–3841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, B.; Guan, J.; Wu, Q.; Jiao, L. Semisupervised Classification of PolSAR Image Incorporating Labels’ Semantic Priors. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2020, 17, 1737–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, H.; Sun, J.; Xu, Z. A Graph-Based Semisupervised Deep Learning Model for PolSAR Image Classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 2116–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, D.; Wang, W.; Tang, T.; Guan, D.; Quan, S.; Liu, T.; Su, Y. Adaptive Statistical Superpixel Merging with Edge Penalty for PolSAR Image Segmentation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 58, 2412–2429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadhiya, T.; Roy, A.K. Superpixel-Driven Optimized Wishart Network for Fast PolSAR Image Classification Using Global k-Means Algorithm. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 58, 97–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, R.; Zhu, K.; Feng, J.; Wang, C.; Jiao, L.; Xu, S. Reg-Superpixel Guided Convolutional Neural Network of PolSAR Image Classification Based on Feature Selection and Receptive Field Reconstruction. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2023, 16, 4312–4327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samat, A.; Li, E.; Du, P.; Liu, S.; Miao, Z.; Zhang, W. CatBoost for RS Image Classification with Pseudo Label Support from Neighbor Patches-Based Clustering. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2022, 19, 8004105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Wang, H.; Xu, F.; Jin, Y.Q. Polarimetric SAR Image Classification Using Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2016, 13, 1935–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.; Xie, Z.; Zhao, F.; Ren, B. POLSAR Image Classification via Clustering-WAE Classification Model. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 40041–40049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ersahin, K.; Cumming, I.G.; Ward, R.K. Segmentation and Classification of Polarimetric SAR Data Using Spectral Graph Partitioning. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2010, 48, 164–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, M.; Zhou, F.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Z. Tensorial Independent Component Analysis-Based Feature Extraction for Polarimetric SAR Data Classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2015, 53, 2481–2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lardeux, C.; Frison, P.L.; Tison, C.; Souyris, J.C.; Stoll, B.; Fruneau, B.; Rudant, J.P. Support Vector Machine for Multifrequency SAR Polarimetric Data Classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2009, 47, 4143–4152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, P.; Singh, D. A Statistical-Measure-Based Adaptive Land Cover Classification Algorithm by Efficient Utilization of Polarimetric SAR Observables. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 2889–2900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, Y.; Guo, J.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, Y.; Lei, B.; Qiu, X.; Ding, C. Winner Takes All: A Superpixel Aided Voting Algorithm for Training Unsupervised PolSAR CNN Classifiers. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 1002519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullissa, A.G.; Persello, C.; Stein, A. PolSARNet: A Deep Fully Convolutional Network for Polarimetric SAR Image Classification. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2019, 12, 5300–5309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.; Li, M.; Zhang, P.; Wu, Y.; Song, W. Complex-Valued 3-D Convolutional Neural Network for PolSAR Image Classification. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2020, 17, 1022–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Zhang, F.; Xiang, D.; Yin, Q.; Zhou, Y. PolSAR Image Classification with Multiscale Superpixel-Based Graph Convolutional Network. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 5209314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Zou, B.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, S. Automatic Design of CNNs via Differentiable Neural Architecture Search for PolSAR Image Classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 58, 6362–6375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.W.; Tao, C.S. PolSAR Image Classification Using Polarimetric-Feature-Driven Deep Convolutional Neural Network. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2018, 15, 627–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Cheng, J.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, F.; Yin, Q. A Multichannel Fusion Convolutional Neural Network Based on Scattering Mechanism for PolSAR Image Classification. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2022, 19, 4007805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; He, C.; He, B.; Tong, M. Learning Scattering Similarity and Texture-Based Attention with Convolutional Neural Networks for PolSAR Image Classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 5207419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shelhamer, E.; Long, J.; Darrell, T. Fully Convolutional Networks for Semantic Segmentation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 39, 640–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Interventions, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, L.; Zeng, Z.; Liu, A.; Xie, X.; Wang, H.; Xu, F.; Hong, W. A Lightweight Complex-Valued DeepLabv3+ for Semantic Segmentation of PolSAR Image. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2022, 15, 930–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.C.; Papandreou, G.; Kokkinos, I.; Murphy, K.; Yuille, A.L. DeepLab: Semantic Image Segmentation with Deep Convolutional Nets, Atrous Convolution, and Fully Connected CRFs. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2018, 40, 834–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, L.; Shao, Q.; Guo, Y.; Xie, X.; Liang, M.; Hong, W. Complex-Valued U-Net with Capsule Embedded for Semantic Segmentation of PolSAR Image. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchi, F.M.; Grahn, J.; Eckerstorfer, M.; Malnes, E.; Vickers, H. Snow Avalanche Segmentation in SAR Images with Fully Convolutional Neural Networks. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2021, 14, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Li, H.; Li, X.; Guo, H.; Zhang, L. PolSAR Image Semantic Segmentation Based on Deep Transfer Learning—Realizing Smooth Classification with Small Training Sets. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2019, 16, 977–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahzad, M.; Maurer, M.; Fraundorfer, F.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, X.X. Buildings Detection in VHR SAR Images Using Fully Convolution Neural Networks. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 1100–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, C.; Azimi, S.M.; Merkle, N. Road Segmentation in SAR Satellite Images with Deep Fully Convolutional Neural Networks. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2018, 15, 1867–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, J.; Zhang, F.; Ma, F.; Yin, Q.; Xiang, D. Random Region Matting for the High-Resolution PolSAR Image Semantic Segmentation. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2021, 14, 3040–3051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, H.; Wang, Z.; Sun, X.; Xiao, D.; Fu, K. PSRN: Polarimetric Space Reconstruction Network for PolSAR Image Semantic Segmentation. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2021, 14, 10716–10732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Tian, M.; Xie, W.; Liu, H. A New Parallel Dual-Channel Fully Convolutional Network via Semi-Supervised FCM for PolSAR Image Classification. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2020, 13, 4493–4505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Pan, Z.; Hu, Y. Exploring PolSAR Images Representation via Self-Supervised Learning and Its Application on Few-Shot Classification. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2022, 19, 4512605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Hou, B.; Ren, B.; Wu, Q.; Jiao, L. An Improved Neural Network Classification Algorithm by Expanding Training Samples for Polarimetric SAR Application. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 5214216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Li, M.; Zhang, P.; Tan, X.; Song, W. Unsupervised Complex-Valued Sparse Feature Learning for PolSAR Image Classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 5230516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, L.; Tian, Y. Self-Supervised Visual Feature Learning with Deep Neural Networks: A Survey. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2021, 43, 4037–4058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le-Khac, P.H.; Healy, G.; Smeaton, A.F. Contrastive Representation Learning: A Framework and Review. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 193907–193934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cloude, S.R.; Pottier, E. A review of target decomposition theorems in radar polarimetry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1996, 34, 498–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cloude, S.R.; Pottier, E. An entropy based classification scheme for land applications of polarimetric SAR. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1997, 35, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, A.; Durden, S.L. A three-component scattering model for polarimetric SAR data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1998, 36, 963–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhu, J.; Yan, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Li, H. LaST: Label-Free Self-Distillation Contrastive Learning with Transformer Architecture for Remote Sensing Image Scene Classification. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2022, 19, 6512205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamali, A.; Mahdianpari, M.; Mohammadimanesh, F.; Bhattacharya, A.; Homayouni, S. PolSAR Image Classification Based on Deep Convolutional Neural Networks Using Wavelet Transformation. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2022, 19, 4510105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Features | Description | |
|---|---|---|
| Anchor | T11, T22, T33, Re(T12), Im(T12), Re(T13), Im(T13), Re(T23), Im(T23) | Extracted from the coherency matrix |
| |a|2, |b|2, |c|2 | Pauli decomposition | |
| Positive sample | Phs, Phd, Phv | Freeman decomposition |
| H, A, α | H/A/α decomposition |
| Method | CNN | U-Net | FCN | CL-CNN | CL-FCN | WT | MCFCN* | MCFCN | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Class | |||||||||
| Water | 99.95 | 99.87 | 99.74 | 99.73 | 99.86 | 99.94 | 99.93 | 99.90 | |
| Vegetation | 83.93 | 93.18 | 95.48 | 90.45 | 93.10 | 89.04 | 92.20 | 96.06 | |
| Low-Density urban | 58.00 | 55.06 | 62.92 | 59.65 | 65.44 | 98.44 | 93.45 | 95.74 | |
| High-Density urban | 85.46 | 90.52 | 90.18 | 87.97 | 97.50 | 88.49 | 97.54 | 98.95 | |
| Developed | 78.87 | 78.35 | 85.15 | 75.22 | 90.04 | 93.94 | 92.93 | 94.30 | |
| OA | 90.06 | 92.16 | 93.35 | 91.39 | 95.01 | 96.47 | 97.41 | 98.52 | |
| Kappa | 84.82 | 88.10 | 89.94 | 86.97 | 92.44 | 95.28 | 96.09 | 97.76 | |
| Method | CNN | U-Net | FCN | CL-CNN | CL-FCN | WT | MCFCN* | MCFCN | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Class | |||||||||
| Water | 96.68 | 98.93 | 98.22 | 96.37 | 97.40 | 98.40 | 97.95 | 98.97 | |
| Forest | 89.48 | 94.47 | 92.68 | 87.51 | 94.88 | 94.26 | 92.65 | 95.16 | |
| Building | 73.32 | 63.37 | 83.30 | 82.11 | 84.88 | 92.65 | 94.46 | 96.58 | |
| Farmland | 89.55 | 87.03 | 93.00 | 90.86 | 95.44 | 84.36 | 95.27 | 95.85 | |
| OA | 89.19 | 89.03 | 93.02 | 90.20 | 94.34 | 95.53 | 95.15 | 96.60 | |
| Kappa | 85.20 | 84.91 | 90.45 | 86.60 | 92.25 | 93.85 | 93.39 | 95.37 | |
| Method | CNN | U-Net | FCN | CL-CNN | CL-FCN | WT | MCFCN* | MCFCN | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Class | |||||||||
| Water | 96.94 | 99.68 | 99.19 | 98.11 | 99.27 | 98.73 | 99.69 | 99.72 | |
| Urban | 89.66 | 92.88 | 97.95 | 96.41 | 97.26 | 90.76 | 97.13 | 97.60 | |
| Vegetation | 78.88 | 82.96 | 62.92 | 40.40 | 75.37 | 94.54 | 76.21 | 77.94 | |
| OA | 92.17 | 95.23 | 95.94 | 93.06 | 96.56 | 95.79 | 96.75 | 97.12 | |
| Kappa | 86.52 | 91.69 | 92.74 | 87.50 | 93.90 | 93.95 | 94.24 | 94.88 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hua, W.; Wang, Y.; Yang, S.; Jin, X. PolSAR Image Classification Based on Multi-Modal Contrastive Fully Convolutional Network. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 296. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16020296
Hua W, Wang Y, Yang S, Jin X. PolSAR Image Classification Based on Multi-Modal Contrastive Fully Convolutional Network. Remote Sensing. 2024; 16(2):296. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16020296
Chicago/Turabian StyleHua, Wenqiang, Yi Wang, Sijia Yang, and Xiaomin Jin. 2024. "PolSAR Image Classification Based on Multi-Modal Contrastive Fully Convolutional Network" Remote Sensing 16, no. 2: 296. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16020296
APA StyleHua, W., Wang, Y., Yang, S., & Jin, X. (2024). PolSAR Image Classification Based on Multi-Modal Contrastive Fully Convolutional Network. Remote Sensing, 16(2), 296. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16020296






