Robust Cloud Suppression and Anomaly Detection in Time-Lapse Thermography
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
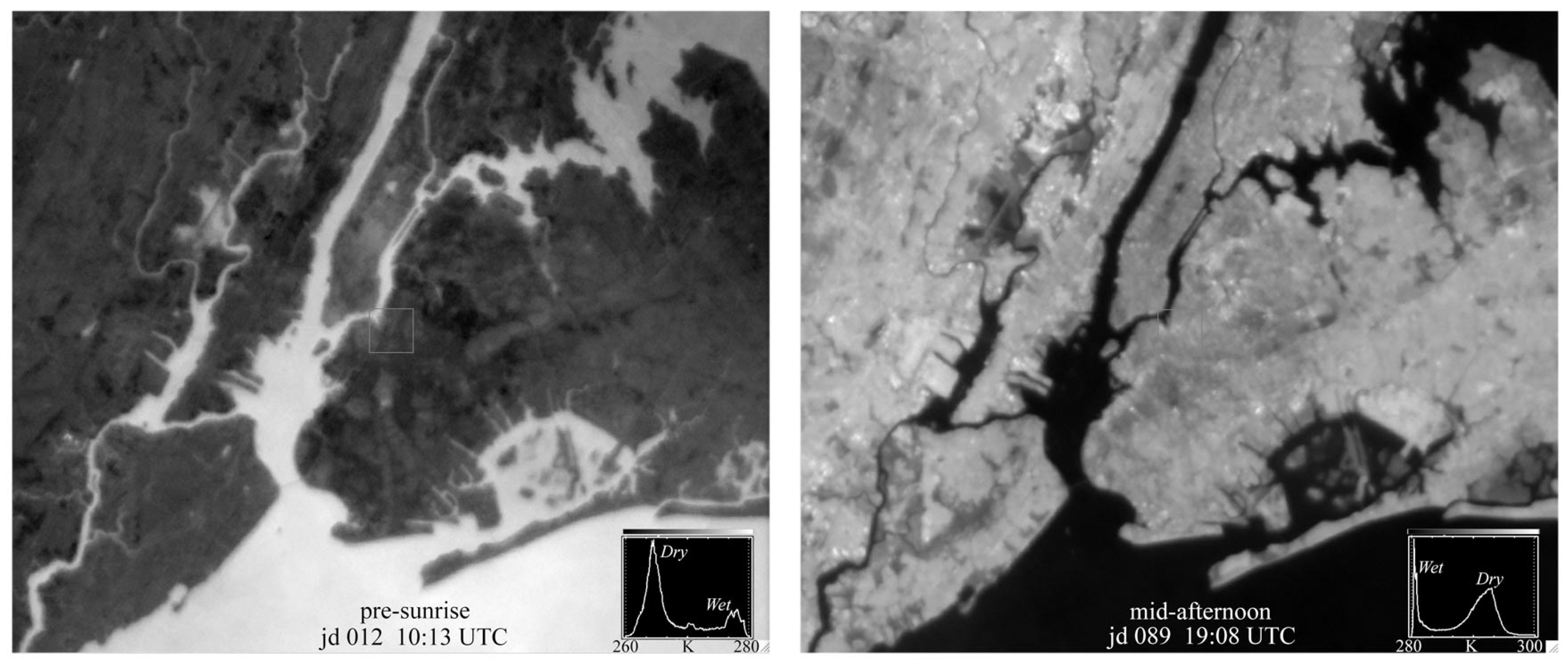
2.1. Data
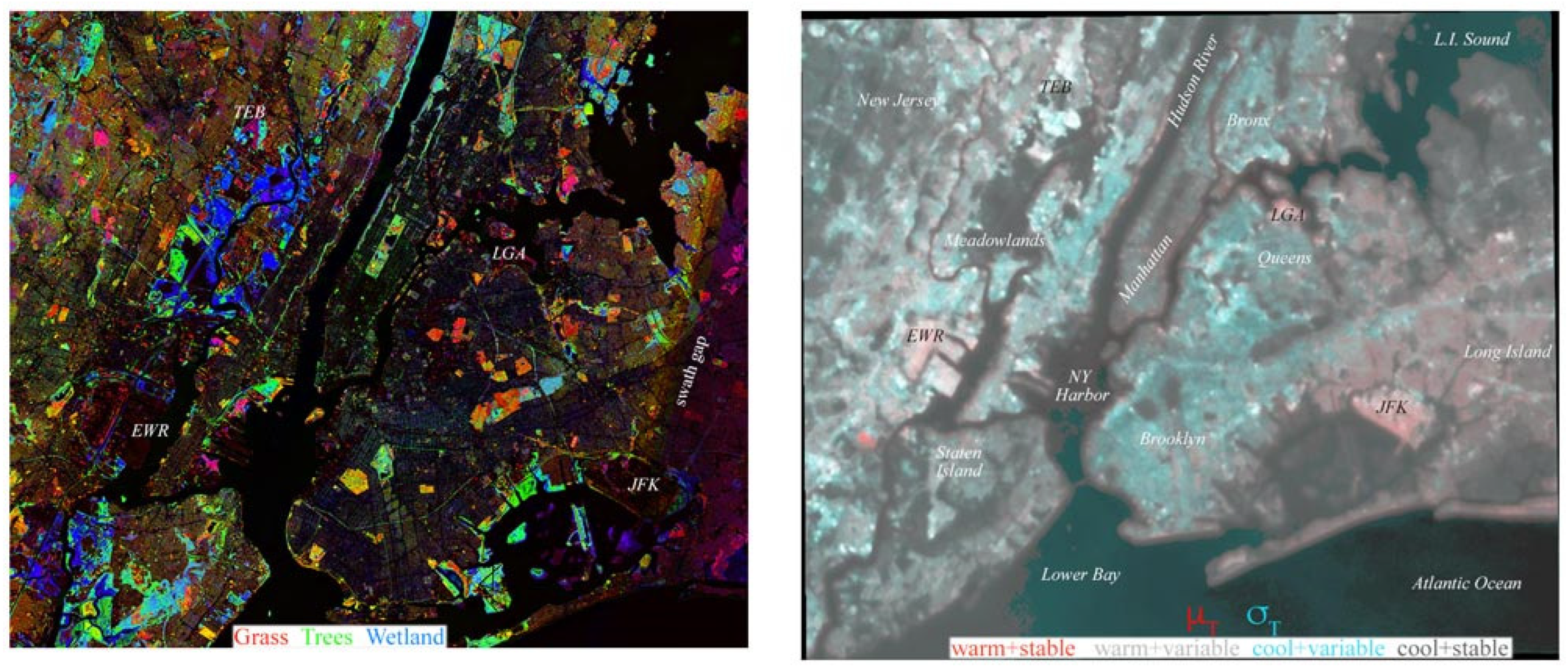
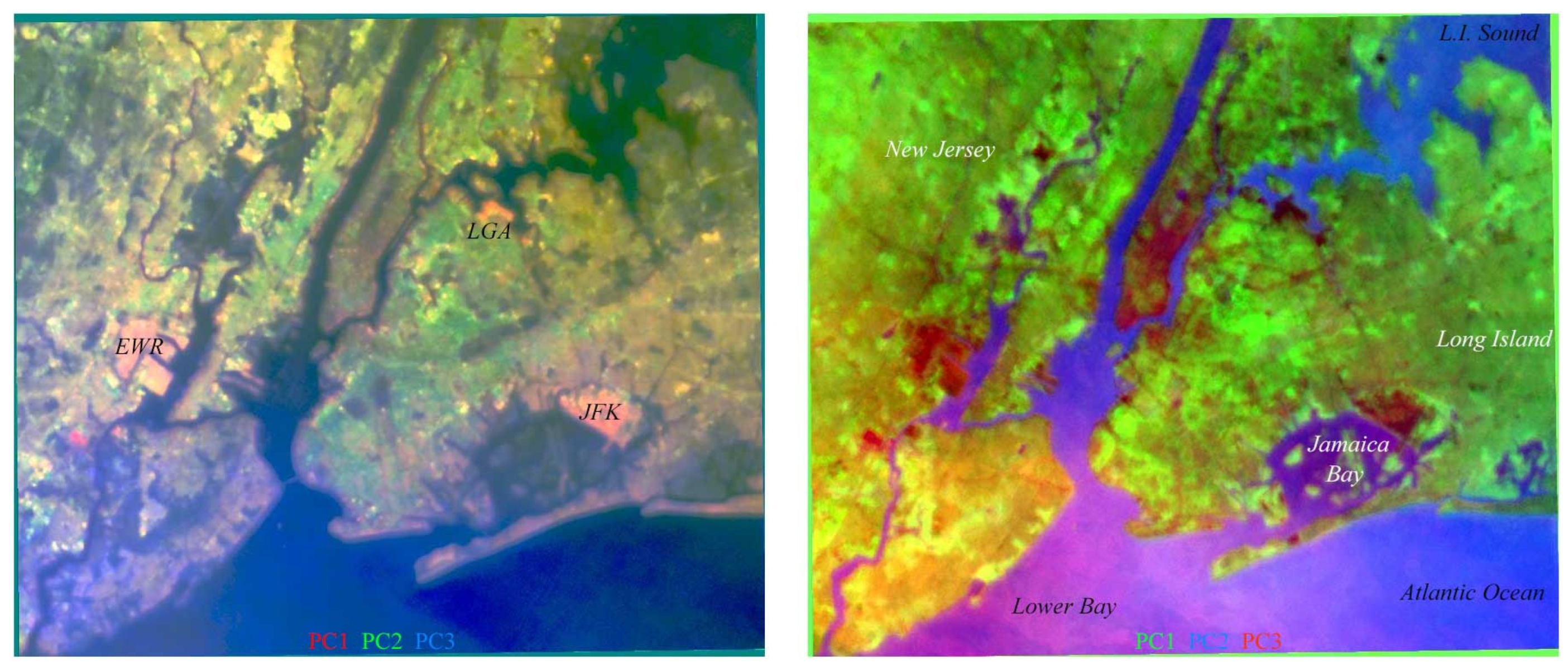
2.2. Study Area
2.3. Methods
3. Results
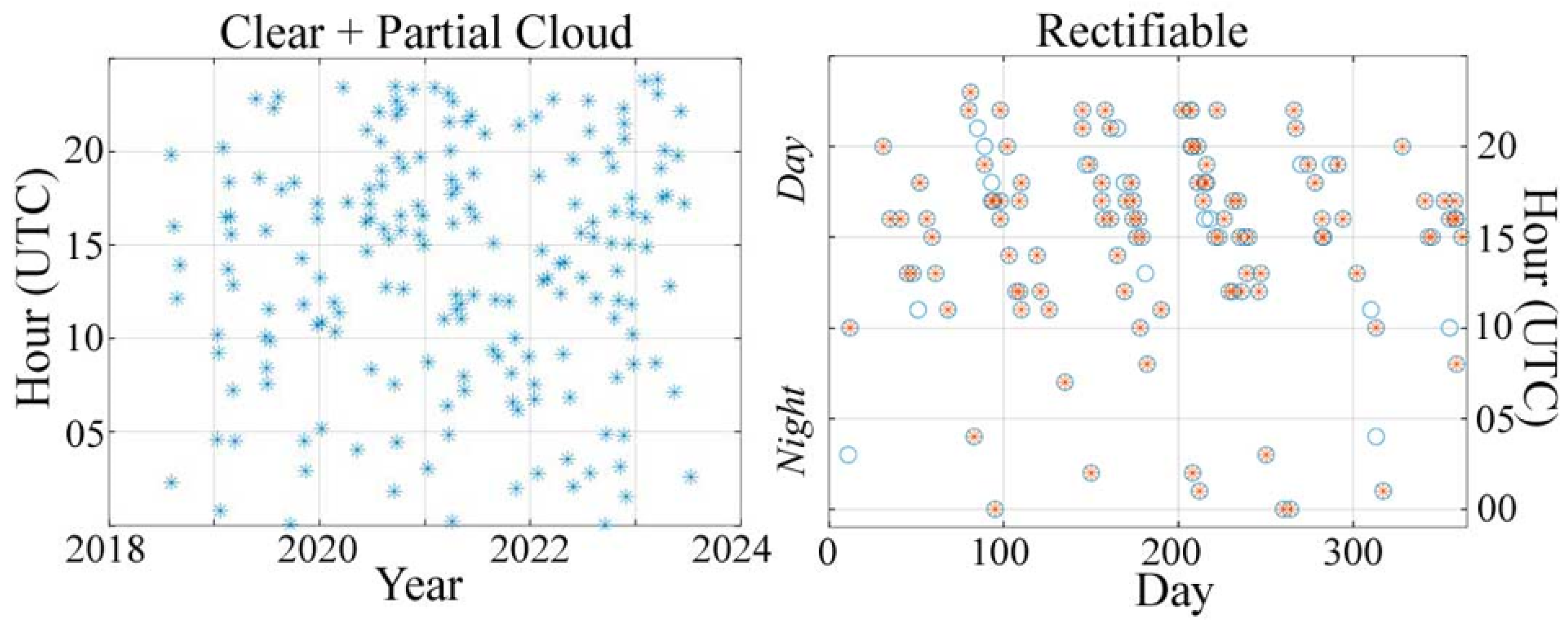
3.1. Spatiotemporal Characterization
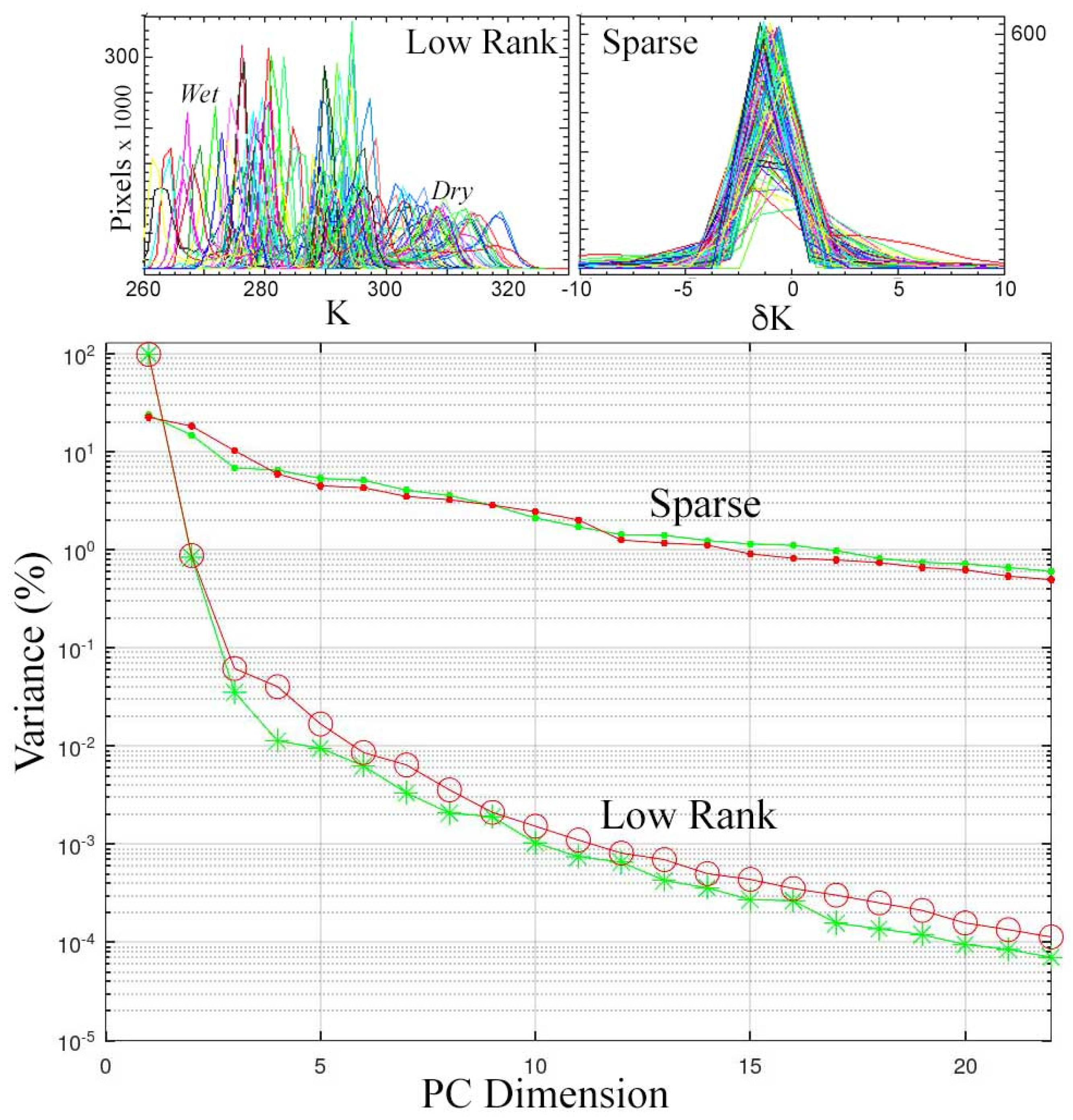
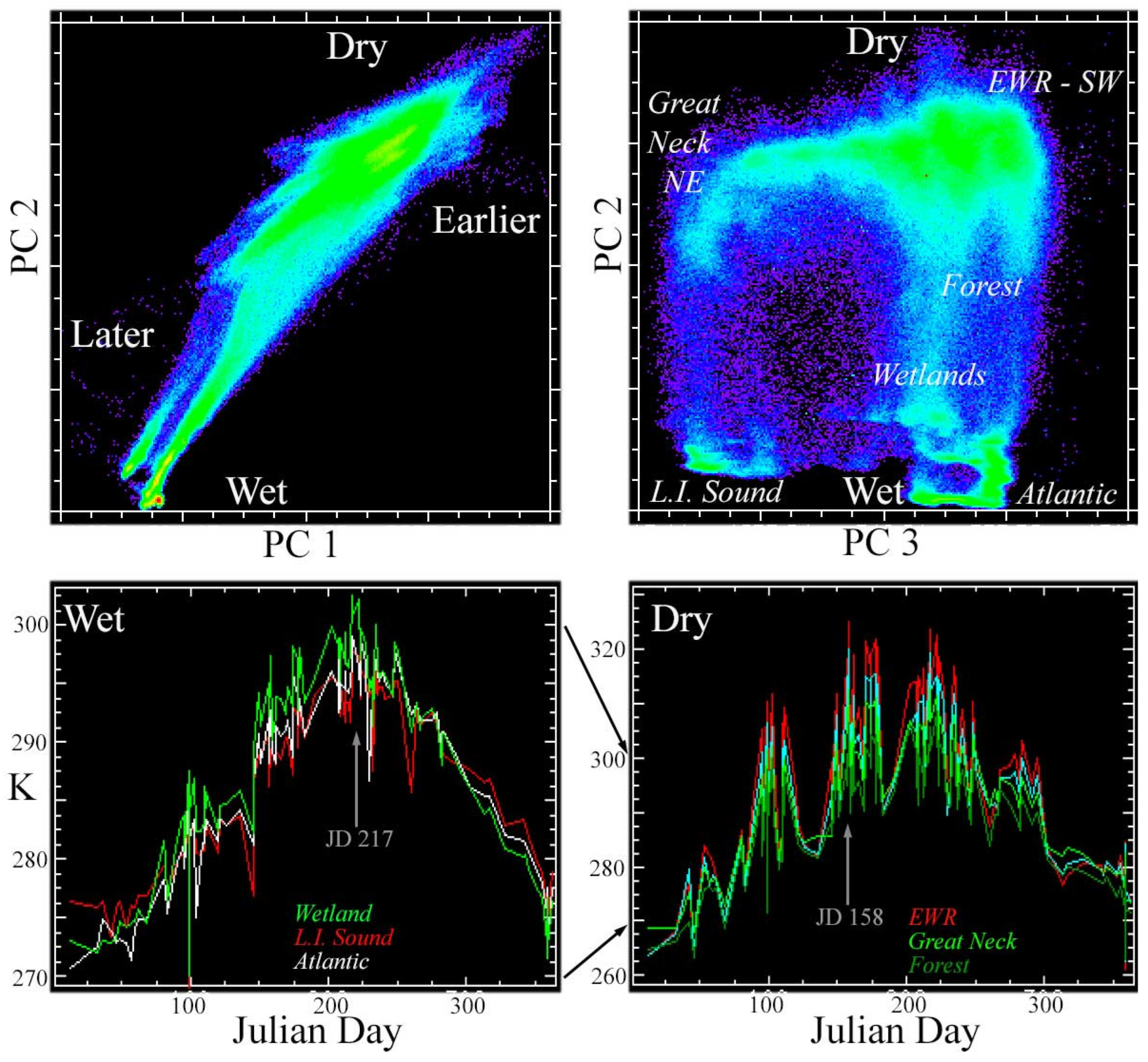
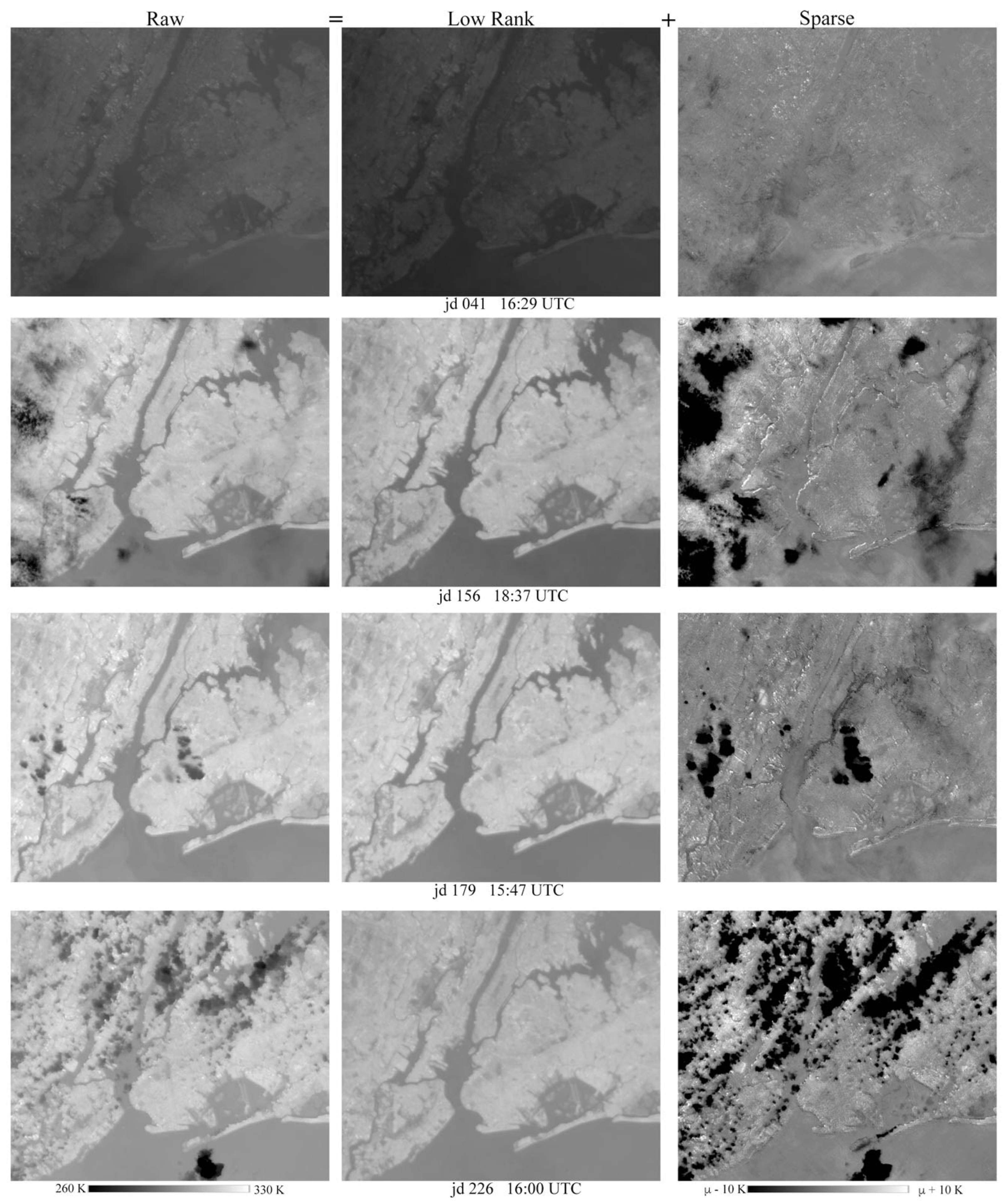
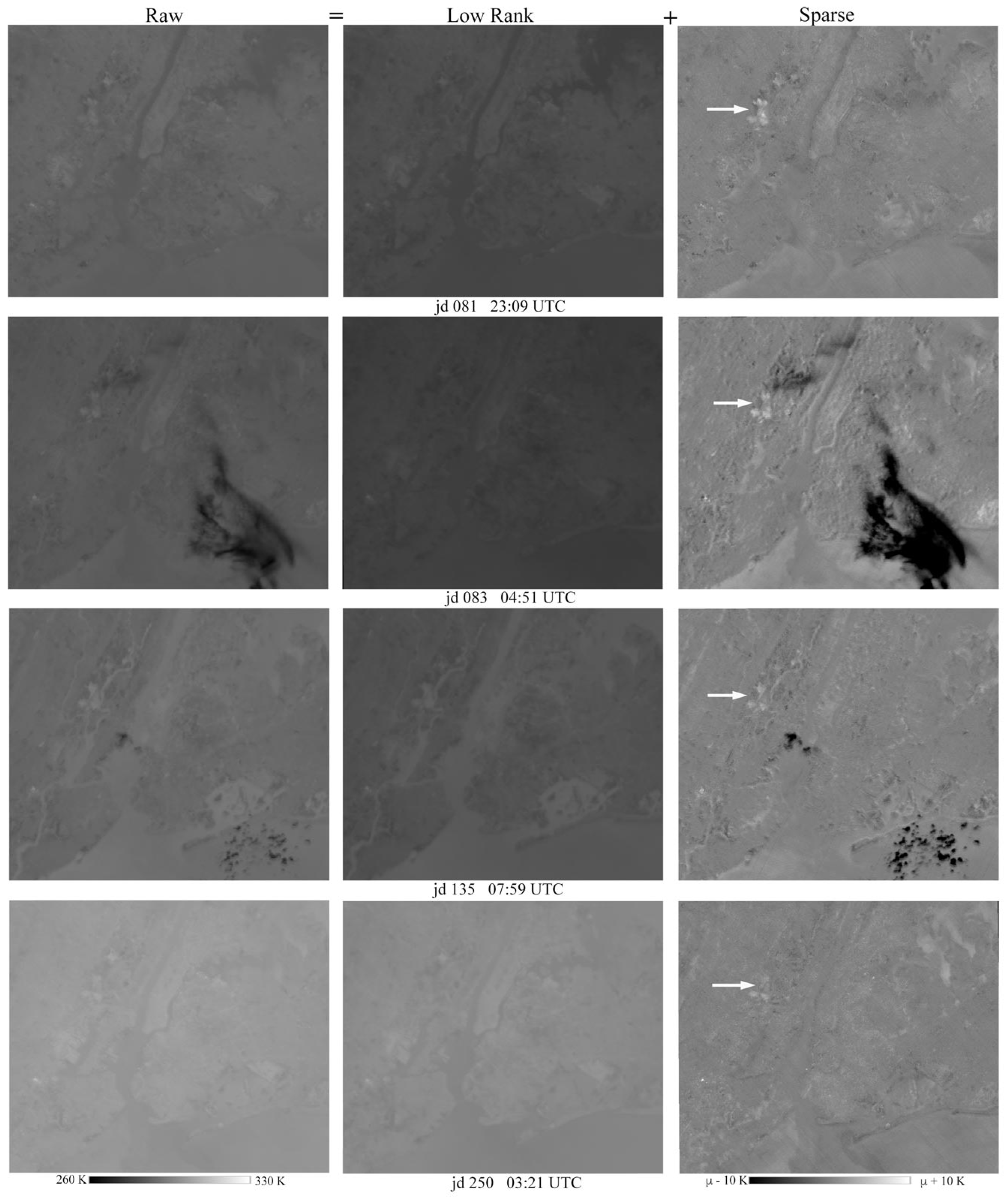
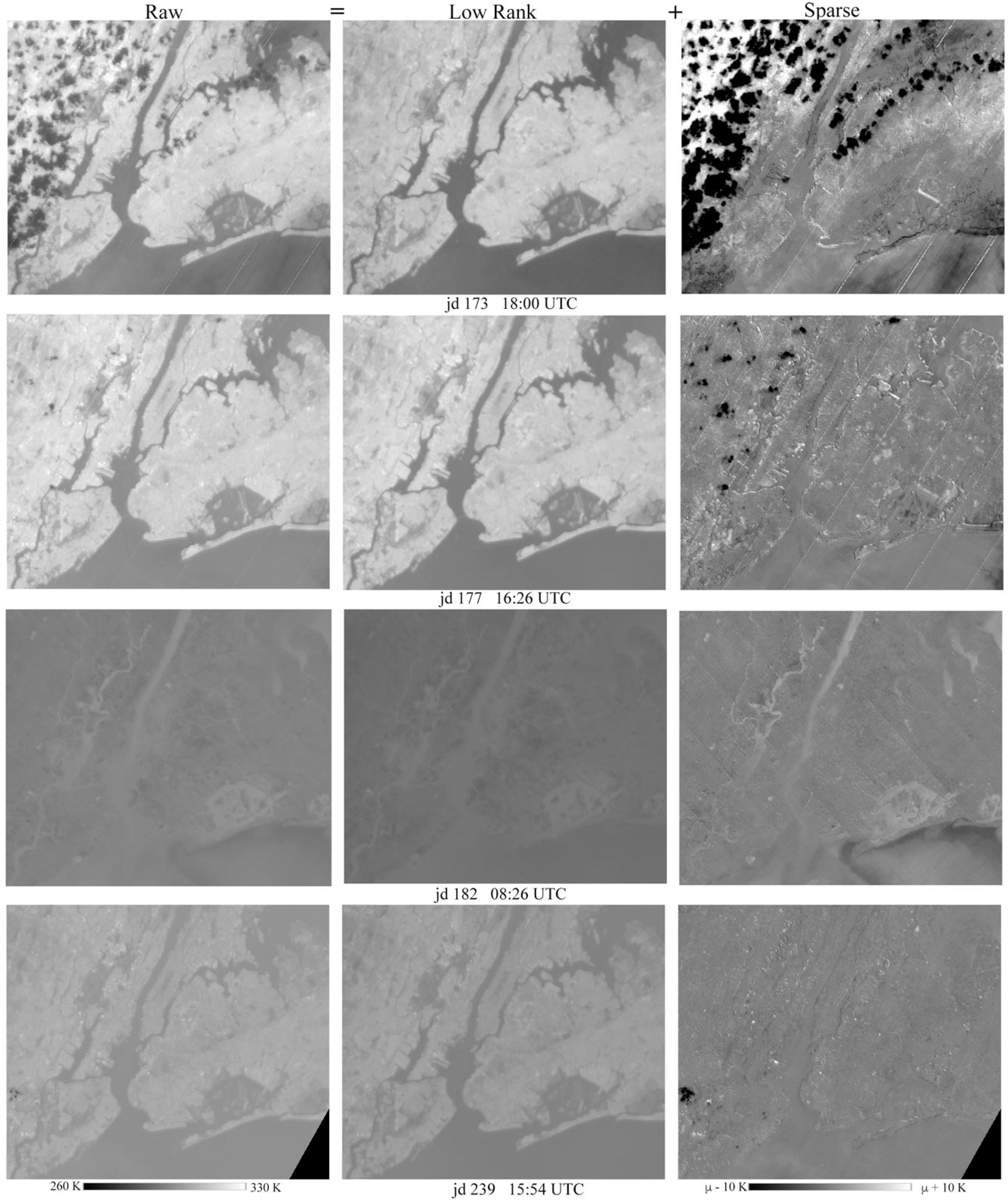
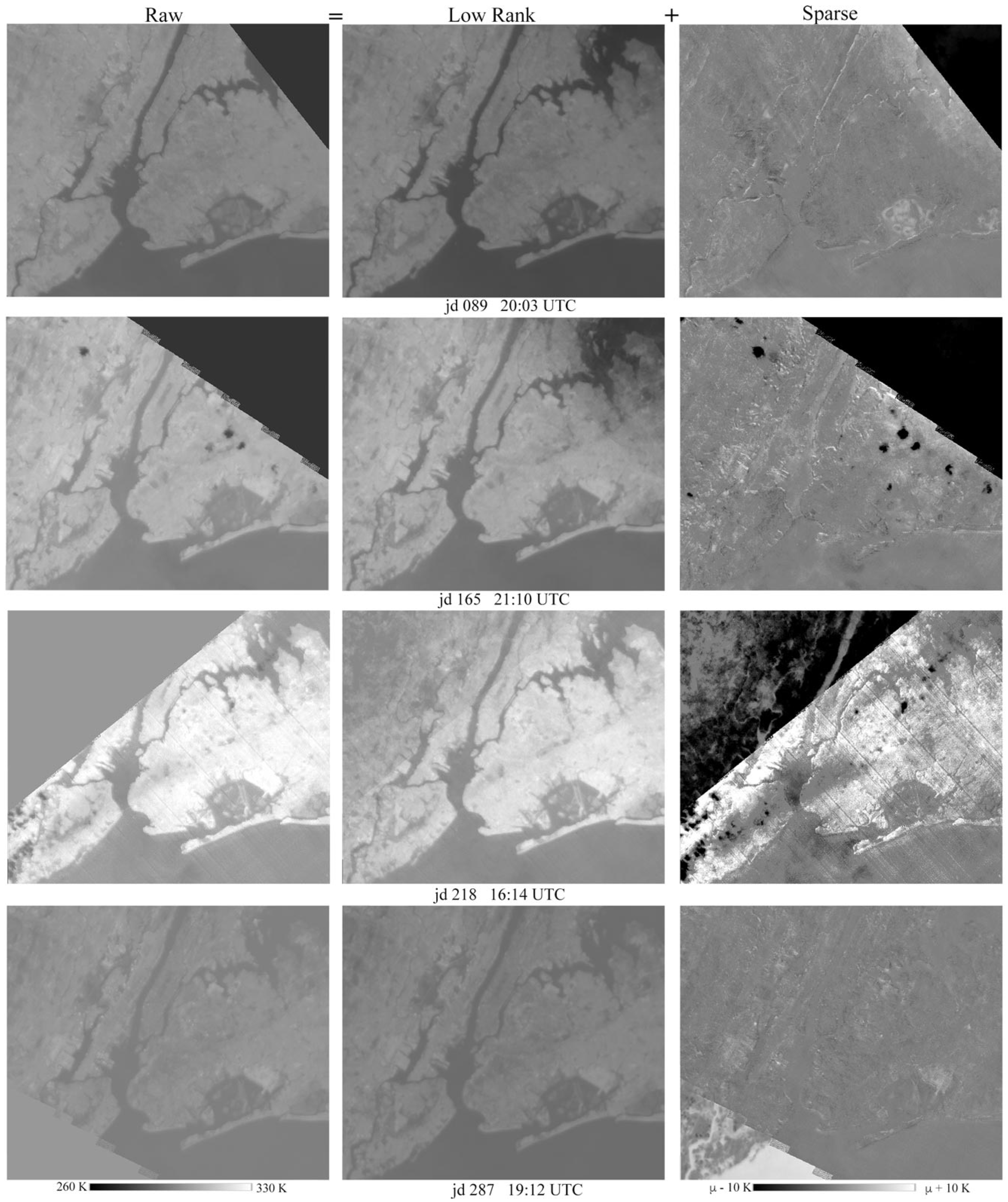
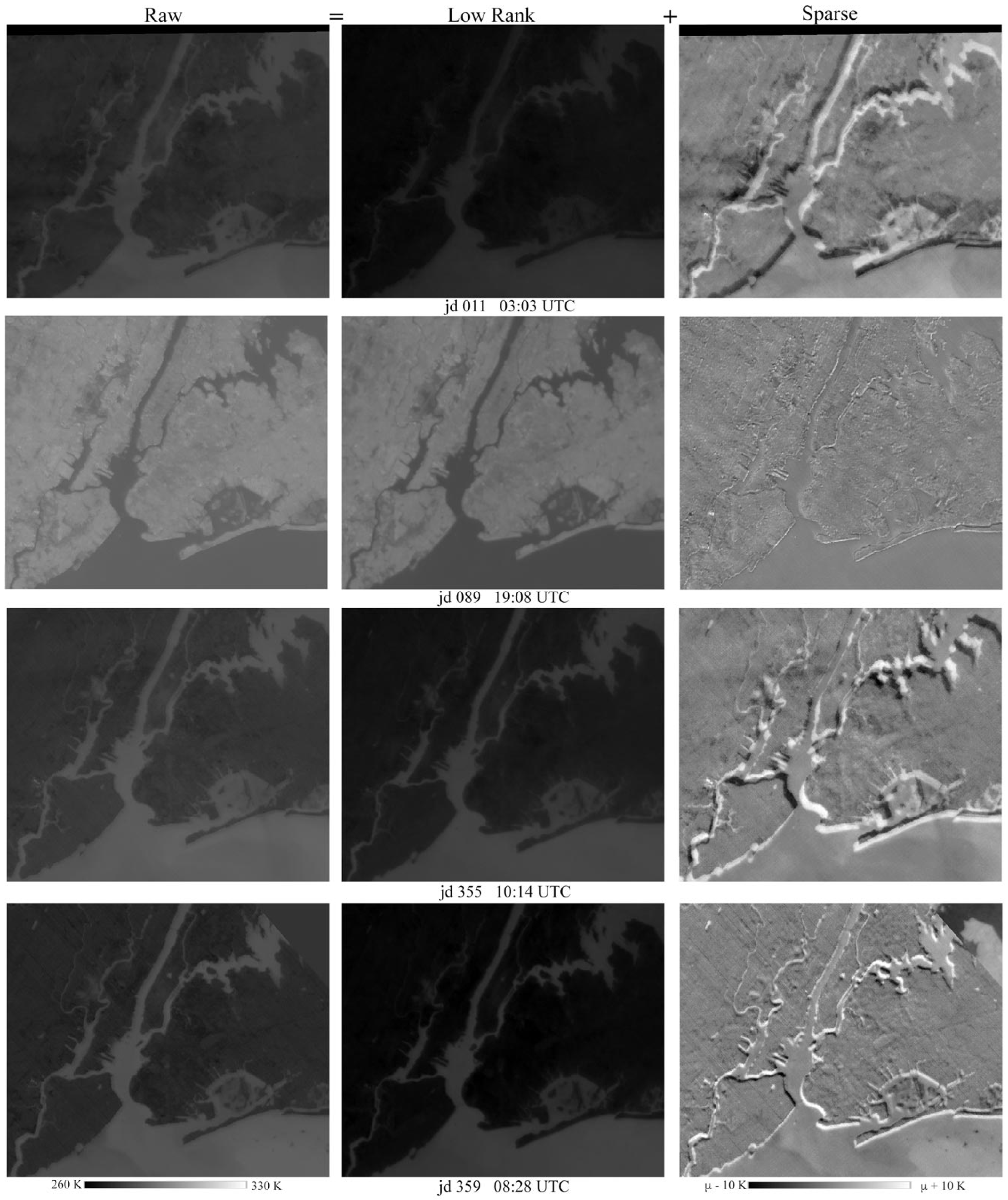
3.2. Examples of Low-Rank and Sparse Component Separation
4. Discussion
4.1. Process Segregation—Why It Works
4.2. Limitations
4.3. Additional Spatiotemporal Applications
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Irish, R.R. Landsat 7 Automatic Cloud Cover Assessment. In Proceedings of the AeroSense 2000, Orlando, FL, USA, 24–28 April 2000; Volume 4049, pp. 348–355. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Z.; Wang, S.; Woodcock, C.E. Improvement and Expansion of the Fmask Algorithm: Cloud, Cloud Shadow, and Snow Detection for Landsats 4–7, 8, and Sentinel 2 Images. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 159, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hovis, W.; Blaine, L.; Forman, M. Infrared Reflectance of High Altitude Clouds. Appl. Opt. 1970, 9, 561–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Twomey, S.; Cocks, T. Spectral Reflectance of Clouds in the Near-Infrared: Comparison of Measurements and Calculations. J. Meteorol. Soc. Japan Ser. II 1982, 60, 583–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, S.J. Diffuse Reflectance of Clouds: A Semiempirical Model. Appl. Opt. 1979, 18, 1881–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kokhanovsky, A. Optical Properties of Terrestrial Clouds. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2004, 64, 189–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, J. Measurements of Cloud Emissivity in the 8–13 μ Waveband. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 1971, 10, 260–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, S.K. Observations of Cloud Infrared Effective Emissivity. J. Atmos. Sci. 1976, 33, 287–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Liu, L.; Zhang, T.; Wu, Y.; Niu, Z.; Wang, Q. Cloud Effective Emissivity Retrievals Using Combined Ground-Based Infrared Cloud Measuring Instrument and Ceilometer Observations. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackerman, S.A.; Strabala, K.I.; Menzel, W.P.; Frey, R.A.; Moeller, C.C.; Gumley, L.E. Discriminating Clear Sky from Clouds with MODIS. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1998, 103, 32141–32157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B.-C.; Kaufman, Y.J. Selection of the 1.375-Μm MODIS Channel for Remote Sensing of Cirrus Clouds and Stratospheric Aerosols from Space. J. Atmos. Sci. 1995, 52, 4231–4237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Woodcock, C.E. Object-Based Cloud and Cloud Shadow Detection in Landsat Imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 118, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Small, C. Spatiotemporal Dimensionality and Time-Space Characterization of Multitemporal Imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 124, 793–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Small, C.; Okujeni, A.; Van der Linden, S.; Waske, B. Remote Sensing of Urban Environments, in Comprehensive Remote Sensing. In Comprehensive Remote Sensing; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2018; pp. 96–127. [Google Scholar]
- Fisher, J.B.; Lee, B.; Purdy, A.J.; Halverson, G.H.; Dohlen, M.B.; Cawse-Nicholson, K.; Wang, A.; Anderson, R.G.; Aragon, B.; Arain, M.A.; et al. ECOSTRESS: NASA’s Next Generation Mission to Measure Evapotranspiration From the International Space Station. Water Resour. Res. 2020, 56, e2019WR026058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hook, S.J.; Cawse-Nicholson, K.; Barsi, J.; Radocinski, R.; Hulley, G.C.; Johnson, W.R.; Rivera, G.; Markham, B. In-Flight Validation of the ECOSTRESS, Landsats 7 and 8 Thermal Infrared Spectral Channels Using the Lake Tahoe CA/NV and Salton Sea CA Automated Validation Sites. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 58, 1294–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logan, T.; Johnson, W. ECOSTRESS Level-1 Focal Plane Array and Radiometric Calibration Algorithm Theoretical Basis Document (ATBD); Jet Propulsion Laboratory, California Institute of Technology: Pasadena, CA, USA, 2015; p. 18.
- Smyth, M.; Leprince, S. ECOSTRESS Level-1B Resampling and Geolocation Algorithm Theoretical Basis Document (ATBD); Jet Propulsion Laboratory, California Institute of Technology: Pasadena, CA, USA, 2018; p. 29.
- Hulley, G.; Hook, S. ECOSTRESS Level-2 Land Surface Temperature and Emissivity Algorithm Theoretical Basis Document (ATBD); Jet Propulsion Laboratory, California Institute of Technology: Pasadena, CA, USA, 2015.
- Gillespie, A.; Rokugawa, S.; Matsunaga, T.; Cothern, J.S.; Hook, S.; Kahle, A.B. A Temperature and Emissivity Separation Algorithm for Advanced Spaceborne Thermal Emission and Reflection Radiometer (ASTER) Images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1998, 36, 1113–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kealy, P.S.; Hook, S.J. Separating Temperature and Emissivity in Thermal Infrared Multispectral Scanner Data: Implications for Recovering Land Surface Temperatures. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1993, 31, 1155–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsunaga, T. A Temperature-Emissivity Separation Method Using an Empirical Relationship between the Mean, the Maximum, and the Minimum of the Thermal Infrared Emissivity Spectrum. J. Remote Sens. Soc. Jpn. 1994, 14, 230–241. [Google Scholar]
- Candès, E.J.; Li, X.; Ma, Y.; Wright, J. Robust Principal Component Analysis? J. ACM (JACM) 2011, 58, 1–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Yang, J. Sparse and Low-rank Matrix Decomposition via Alternating Direction Methods. Pac. J. Optim. 2013, 9, 167. [Google Scholar]
- Lorenz, E. Empirical Orthogonal Functions and Statistical Weather Prediction; Statistical Forecasting Project; Massachusetts Institute of Technology: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1956; p. 49. [Google Scholar]
- Bechtel, B. Robustness of Annual Cycle Parameters to Characterize the Urban Thermal Landscapes. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2012, 9, 876–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bechtel, B. A New Global Climatology of Annual Land Surface Temperature. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 2850–2870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bechtel, B.; Zakšek, K.; Hoshyaripour, G. Downscaling Land Surface Temperature in an Urban Area: A Case Study for Hamburg, Germany. Remote Sens. 2012, 4, 3184–3200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sismanidis, P.; Bechtel, B.; Keramitsoglou, I.; Goettsche, F.; Kiranoudis, C.T. Satellite-Derived Quantification of the Diurnal and Annual Dynamics of Land Surface Temperature. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 265, 112642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sismanidis, P.; Bechtel, B.; Keramitsoglou, I.; Kiranoudis, C.T. Mapping the Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Europe’s Land Surface Temperatures. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2017, 15, 202–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Small, C.; Sousa, D. Spatiotemporal Characterization of Mangrove Phenology and Disturbance Response: The Bangladesh Sundarban. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, D.; Small, C. Joint Characterization of Spatiotemporal Data Manifolds. Front. Remote Sens. 2022, 3, 760650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Small, C.; Sousa, D. Robust Cloud Suppression and Anomaly Detection in Time-Lapse Thermography. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 255. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16020255
Small C, Sousa D. Robust Cloud Suppression and Anomaly Detection in Time-Lapse Thermography. Remote Sensing. 2024; 16(2):255. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16020255
Chicago/Turabian StyleSmall, Christopher, and Daniel Sousa. 2024. "Robust Cloud Suppression and Anomaly Detection in Time-Lapse Thermography" Remote Sensing 16, no. 2: 255. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16020255
APA StyleSmall, C., & Sousa, D. (2024). Robust Cloud Suppression and Anomaly Detection in Time-Lapse Thermography. Remote Sensing, 16(2), 255. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16020255






