Comparison of Time-Lapse Ground-Penetrating Radar and Electrical Resistivity Tomography Surveys for Detecting Pig (Sus spp.) Cadaver Graves in an Australian Environment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site
2.2. Set Up, Simulated Grave Creation, and Survey Repetitions
2.3. GPR Surveys
2.4. ERT Surveys
2.5. Soil Testing
3. Results
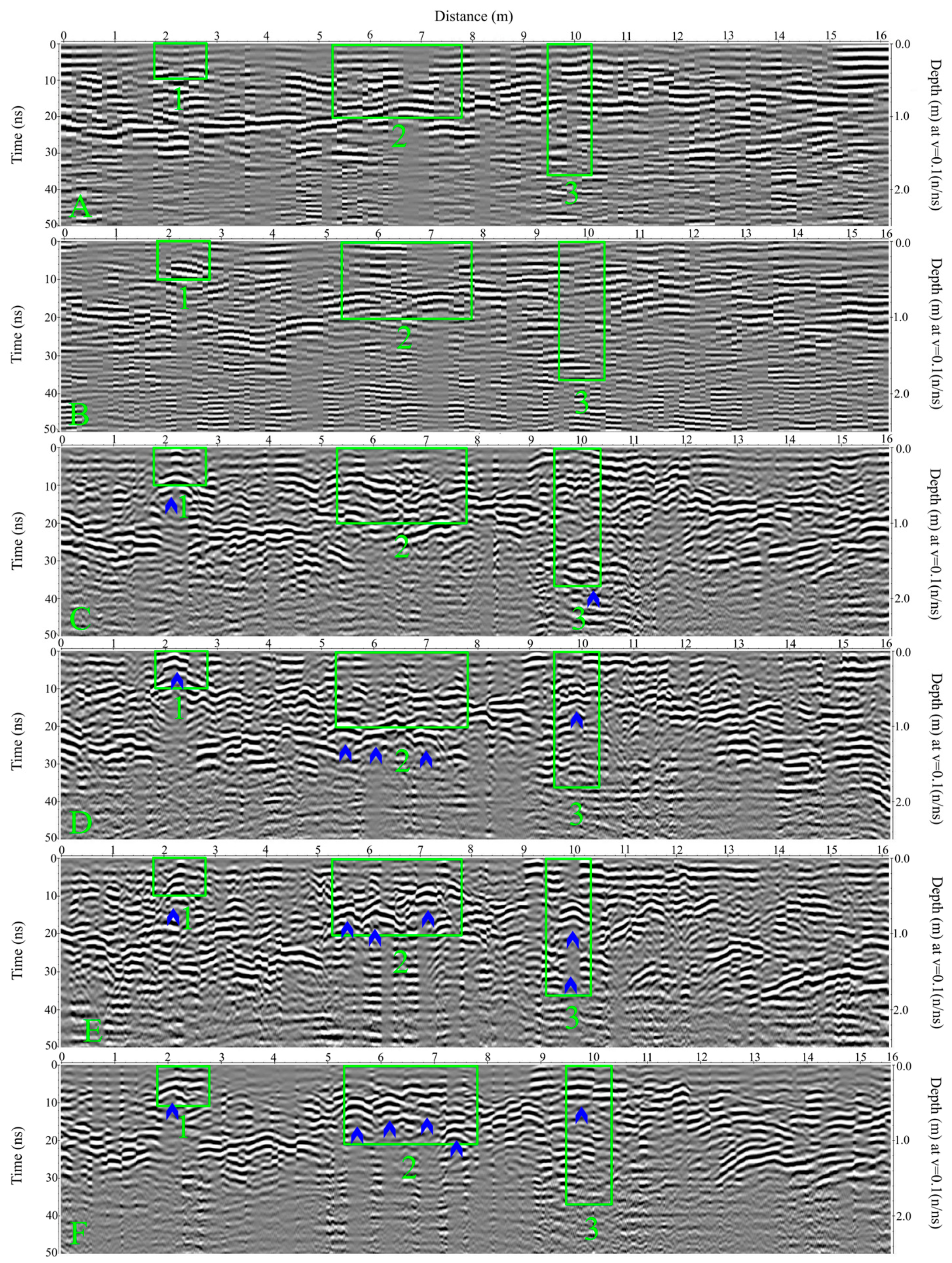
3.1. GPR Surveys
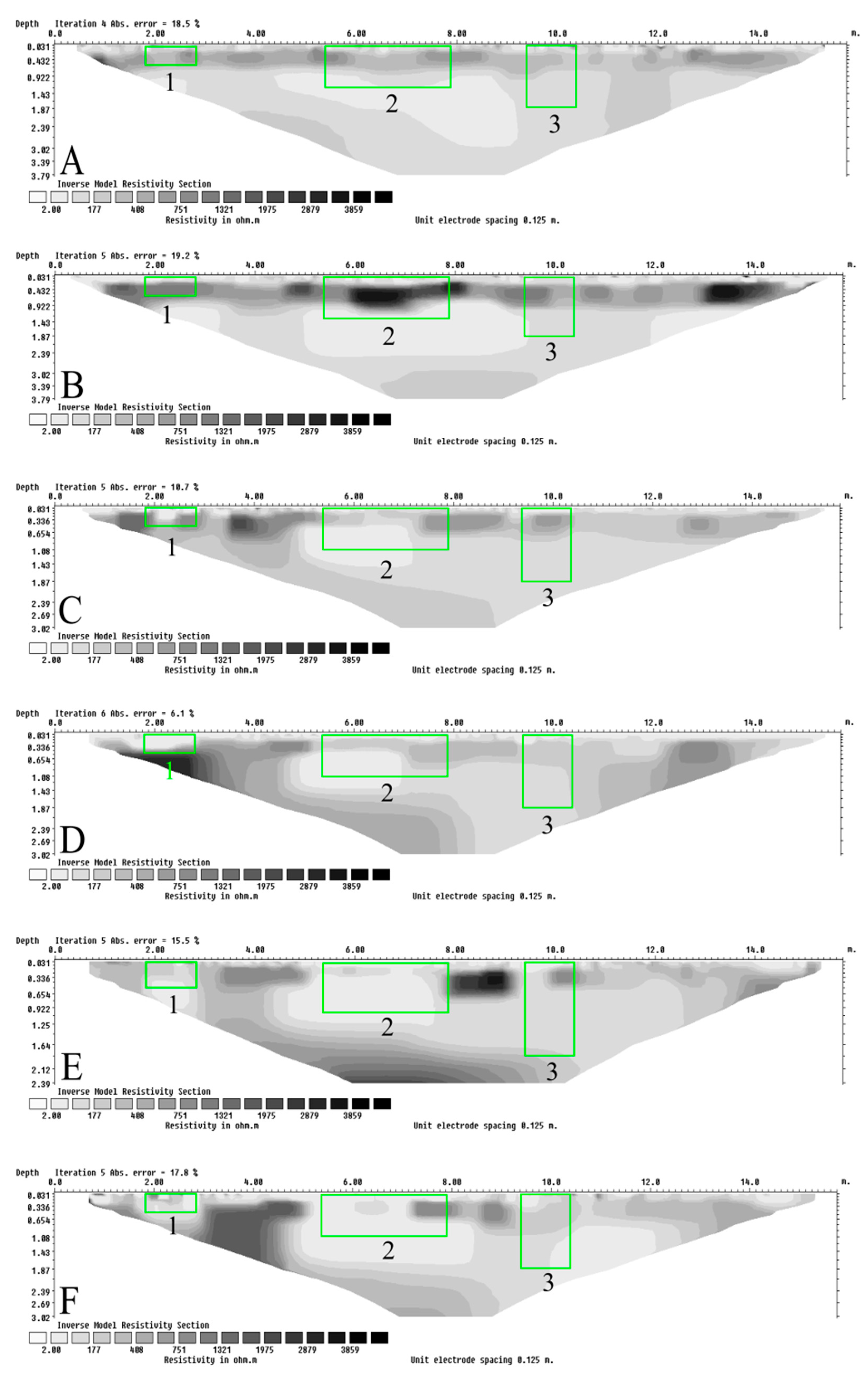
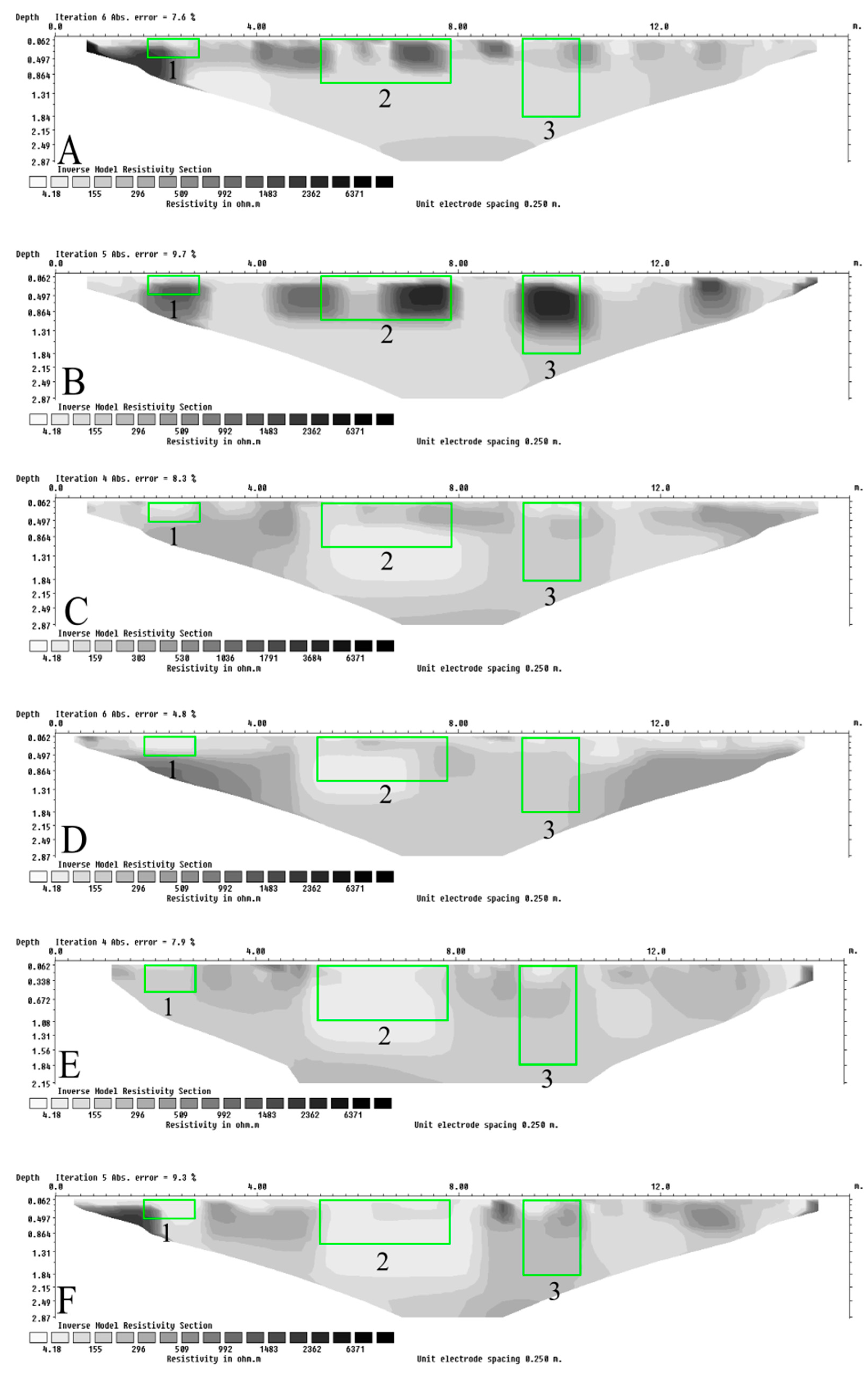
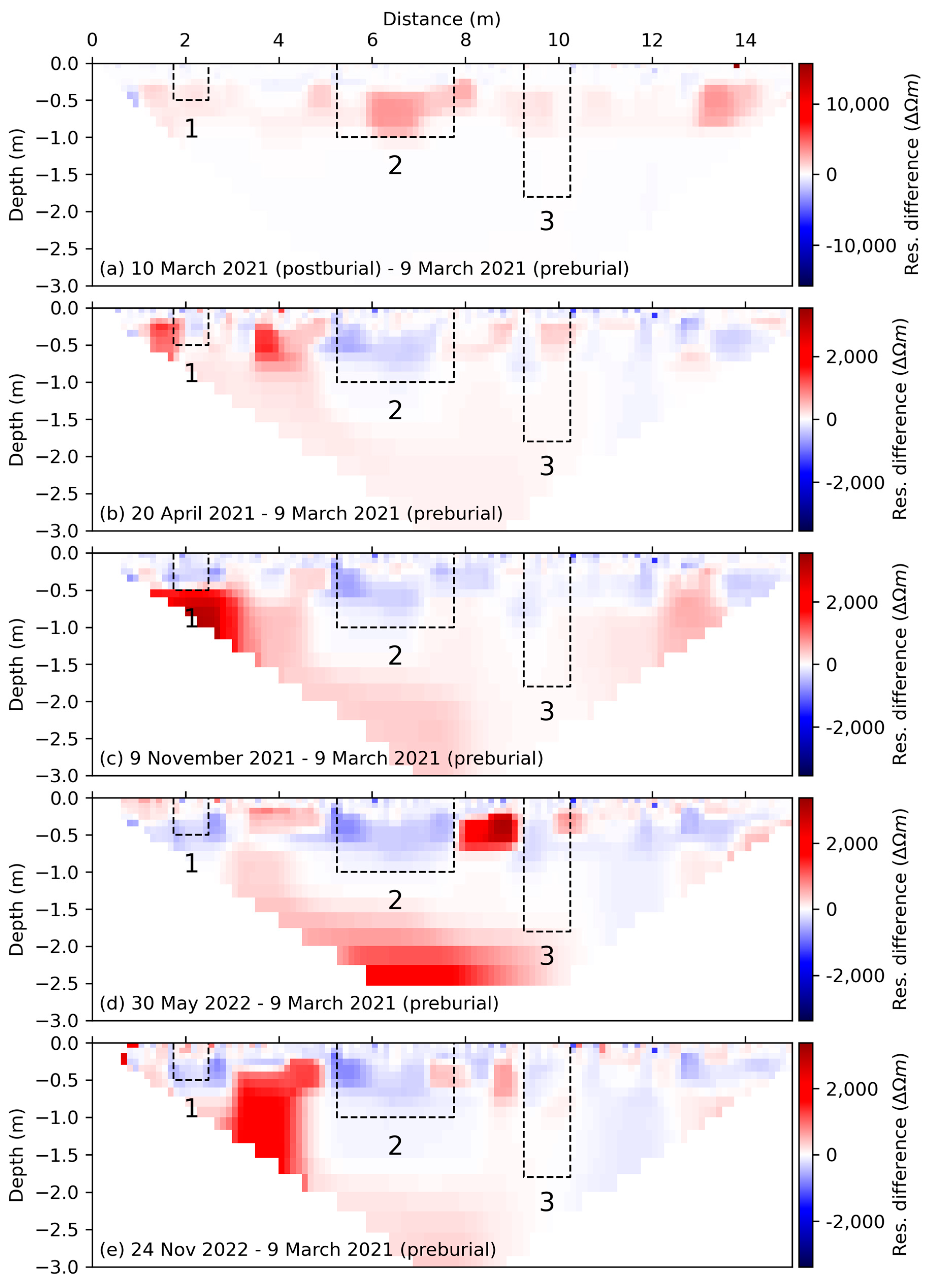
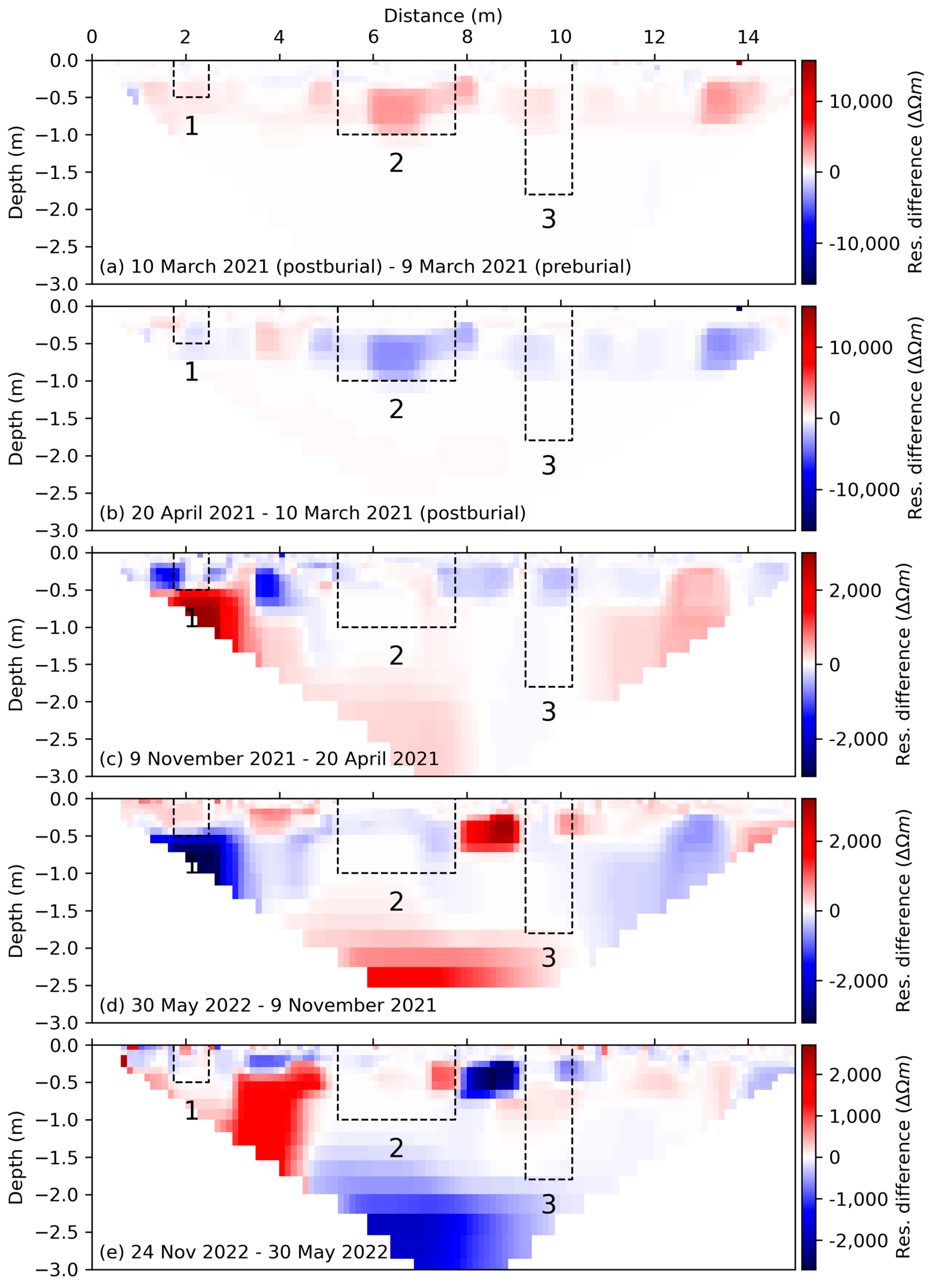
3.2. ERT Surveys
3.3. Soil Sample Testing
4. Discussion
4.1. Are the Graves Observable Using GPR and ERT?
4.2. How Do the Geophysical Responses Change over Time?
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Correction Statement
References
- Keatley, D.; O’Donnell, C.; Chapman, B.; Clarke, D.D. The psycho-criminology of burial sites: Developing the winthropping method for locating clandestine burial sites. J. Police Crim. Psychol. 2021, 37, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, C. Forensically aware offenders and homicide investigations: Challenges, opportunities and impacts. Aust. J. Forensic Sci. 2019, 51, S128–S131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berezowski, V.; Moffat, I.; Shendryk, Y.; MacGregor, D.; Ellis, J.; Mallett, X. A multidisciplinary approach to locating clandestine gravesites in cold cases: Combining geographic profiling, LiDAR, and near surface geophysics. Forensic Sci. Int. Synerg. 2022, 5, 100281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Missing Persons Coordination Centre. Missing Persons; Australian Federal Police (AFP): Canberra, ACT, Australia, 2021.
- Ferguson, C.; Pooley, K. Australian no-body homicides: Exploring common features of solved cases. J. Forensic Leg. Med. 2019, 66, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, C.; Pooley, K. Comparing solved and unsolved no-body homicides in Australia: An exploratory analysis. Homicide Stud. 2019, 23, 381–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinkes, M. Forensic anthropology in cold cases. In Cold Case Homicides: Practical investigative Techniques, 2nd ed.; Walton, R.H., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017; pp. 381–400. [Google Scholar]
- Donnelly, L.; Harrison, M. Geoforensic Search Strategy (GSS): Ground searches related to homicide graves, counter-terrorism and serious and organized crime. In A Guide to Forensic Geology; Geological Society: London, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds, J.M. An Introduction to Applied and Environmental Geophysics; John Wiley & Sons: West Sussex, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Telford, W.M.; Geldart, L.; Sheriff, R.E. Applied Geophysics; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Berezowski, V.; Mallett, X.; Ellis, J.; Moffat, I. Using ground penetrating radar and resistivity methods to locate unmarked graves: A review. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultz, J.J. Sequential monitoring of burials containing small pig cadavers using ground penetrating radar. J. Forensic Sci. 2008, 53, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schultz, J.J.; Collins, M.E.; Falsetti, A.B. Sequential monitoring of burials containing large pig cadavers using ground-penetrating radar. J. Forensic Sci. 2006, 51, 607–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jervis, J.R.; Pringle, J.K.; Tuckwell, G.W. Time-lapse resistivity surveys over simulated clandestine graves. Forensic Sci. Int. 2009, 192, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damiata, B.N.; Steinberg, J.M.; Bolender, D.J.; Zoëga, G. Imaging skeletal remains with ground-penetrating radar: Comparative results over two graves from Viking Age and Medieval churchyards on the Stóra-Seyla farm, northern Iceland. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2013, 40, 268–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, K. Detecting buried human remains using near-surface geophysical instruments. Explor. Geophys. 2004, 35, 88–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pringle, J.K.; Jervis, J.R.; Hansen, J.D.; Jones, G.M.; Cassidy, N.J.; Cassella, J.P. Geophysical Monitoring of Simulated Clandestine Graves Using Electrical and Ground-Penetrating Radar Methods: 0–3 Years After Burial. J. Forensic Sci. 2012, 57, 1467–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pringle, J.K.; Jervis, J.R.; Roberts, D.; Dick, H.C.; Wisniewski, K.D.; Cassidy, N.J.; Cassella, J.P. Long-term Geophysical Monitoring of Simulated Clandestine Graves using Electrical and Ground Penetrating Radar Methods: 4–6 Years After Burial. J. Forensic Sci. 2016, 61, 309–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pringle, J.K.; Stimpson, I.G.; Wisniewski, K.D.; Heaton, V.; Davenward, B.; Mirosch, N.; Spencer, F.; Jervis, J.R. Geophysical monitoring of simulated homicide burials for forensic investigations. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 7544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina, C.M.; Pringle, J.K.; Saumett, M.; Evans, G.T. Geophysical monitoring of simulated graves with resistivity, magnetic susceptibility, conductivity and GPR in Colombia, South America. Forensic Sci. Int. 2016, 261, 106–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalcanti, M.M.; Rocha, M.P.; Blum, M.L.B.; Borges, W.R. The forensic geophysical controlled research site of the University of Brasilia, Brazil: Results from methods GPR and electrical resistivity tomography. Forensic Sci. Int. 2018, 293, 101.e1–101.e21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doro, K.O.; Kolapkar, A.M.; Bank, C.-G.; Wescott, D.J.; Mickleburgh, H.L. Geophysical imaging of buried human remains in simulated mass and single graves: Experiment design and results from pre-burial to six months after burial. Forensic Sci. Int. 2022, 335, 111289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doro, K.O.; Emmanuel, E.D.; Adebayo, M.B.; Bank, C.-G.; Wescott, D.J.; Mickleburgh, H.L. Time-lapse electrical resistivity tomography imaging of buried human remains in simulated mass and individual graves. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 882496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NSW Office of Environment and Heritage. NSW Soil and Land Information System (SALIS) Database. 2012. Available online: https://datasets.seed.nsw.gov.au/dataset/nsw-soil-profiles15bf7 (accessed on 22 November 2022).
- Department of Planning, Industry and Environment. Australian Soil Classification (ASC) Soil Type map of NSW. 2021. Available online: https://datasets.seed.nsw.gov.au/dataset/australian-soil-classification-asc-soil-type-map-of-nsweaa10 (accessed on 22 November 2022).
- Moffat, I. Locating graves with geophysics. In Best Practices of Geoinformatic Technologies for the Mapping of Archaeolandscapes; Archaeopress Archaeology: Oxford, UK, 2015; pp. 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pringle, J.K.; Jervis, J.; Cassella, J.P.; Cassidy, N.J. Time-lapse geophysical investigations over a simulated urban clandestine grave. J. Forensic Sci. 2008, 53, 1405–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berezowski, V.; Mallett, X.; Simyrdanis, K.; Kowlessar, J.; Bailey, M.; Moffat, I. Ground penetrating radar and electrical resistivity tomography surveys with a subsequent intrusive investigation in search for the missing Beaumont children in Adelaide, South Australia. Forensic Sci. Int. 2024, 357, 111996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berezowski, V.; Moffat, I.; Seckiner, D.; Crebert, I.; Ellis, J.; Mallett, X. The suitability of using domestic pigs (Sus spp.) as human proxies in the geophysical detection of clandestine graves. J. Forensic Sci. 2023, 69, 316–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berezowski, V.; Mallett, X.; Crebert, I.; Seckiner, D.; Ellis, J.; Moffat, I. A technical protocol for using ground penetrating radar and electrical resistivity tomography in the search for covert graves. Aust. J. Forensic Sci. 2023, 56, 534–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loke, M.H.; Barker, R.D. Least-squares deconvolution of apparent resistivity pseudosections. Geophysics 1995, 60, 1682–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wentworth, C.K. A Scale of Grade and Class Terms for Clastic Sediments. J. Geol. 1922, 30, 377–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heiri, O.; Lotter, A.F.; Lemcke, G. Loss on ignition as a method for estimating organic and carbonate content in sediments: Reproducibility and comparability of results. J. Paleolimnol. 2001, 25, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berezowski, V.; Mallett, X.; Seckiner, D.; Crebert, I.; Ellis, J.; Rau, G.C.; Moffat, I. Data Associated with “Comparison of Time-Lapse Ground-Penetrating Radar and Electrical Resistivity Tomography for Detecting Clandestine Graves Using Pigs”. Open Science Framework. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultz, J.J. Using ground-penetrating radar to locate clandestine graves of homicide victims: Forming forensic archaeology partnerships with law enforcement. Homicide Stud. 2007, 11, 15–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conyers, L.B. Ground-Penetrating Radar for Archaeology, 3rd ed.; Geophysical Methods for Archaeology; Conyers, L.B., Kvamme, K.L., Eds.; Alta Mira Press: Lanham, MD, USA, 2013; Volume 4. [Google Scholar]
- Jervis, J.R.; Pringle, J.K.; Cassella, J.P.; Tuckwell, G. Using soil and groundwater data to understand resistivity surveys over a simulated clandestine grave. In Criminal and Environmental Soil Forensics; Ritz, K., Dawson, L., Miller, D., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 271–284. [Google Scholar]
- Nero, C.; Aning, A.A.; Danuor, S.K.; Noye, R.M. Delineation of graves using electrical resistivity tomography. J. Appl. Geophys. 2016, 126, 138–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carey, A.M.; Paige, G.B.; Carr, B.J.; Dogan, M. Forward modeling to investigate inversion artifacts resulting from time-lapse electrical resistivity tomography during rainfall simulations. J. Appl. Geophys. 2017, 145, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frohlich, R.K.; Parke, C.D. The electrical resistivity of the vadose zone—Field survey. Groundwater 1989, 27, 524–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archie, G.E. The electrical resistivity log as an aid in determining some reservoir characteristics. Trans. AIME 1942, 146, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina, C.M.; Wisniewski, K.; Heaton, V.; Pringle, J.K.; Avila, E.F.; Herrera, L.A.; Guerrero, J.; Saumett, M.; Echeverry, R.; Duarte, M. Monitoring of simulated clandestine graves of dismembered victims using UAVs, electrical tomography, and GPR over one year to aid investigations of human rights violations in Colombia, South America. J. Forensic Sci. 2022, 67, 1060–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barone, P.M.; Matsentidi, D.; Mollard, A.; Kulengowska, N.; Mistry, M. Mapping Decomposition: A Preliminary Study of Non-Destructive Detection of Simulated body Fluids in the Shallow Subsurface. Forensic Sci. 2022, 2, 620–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina, C.M.; Wisniewski, K.D.; Drake, J.; Baena, A.; Guatame, A.; Pringle, J.K. Testing Application of Geographical Information Systems, Forensic Geomorphology and Electrical Resistivity Tomography to Investigate Clandestine Grave Sites in Colombia, South America. J. Forensic Sci. 2020, 65, 266–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abate, D.; Colls, C.S.; Moyssi, N.; Karsili, D.; Faka, M.; Anilir, A.; Manolis, S. Optimizing search strategies in mass grave location through the combination of digital technologies. Forensic Sci. Int. Synerg. 2019, 1, 95–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dearing, J. Environmental Magnetic Susceptibility: Using the Bartington MS2 System; British Library Cataloguing: London, UK, 1999. [Google Scholar]
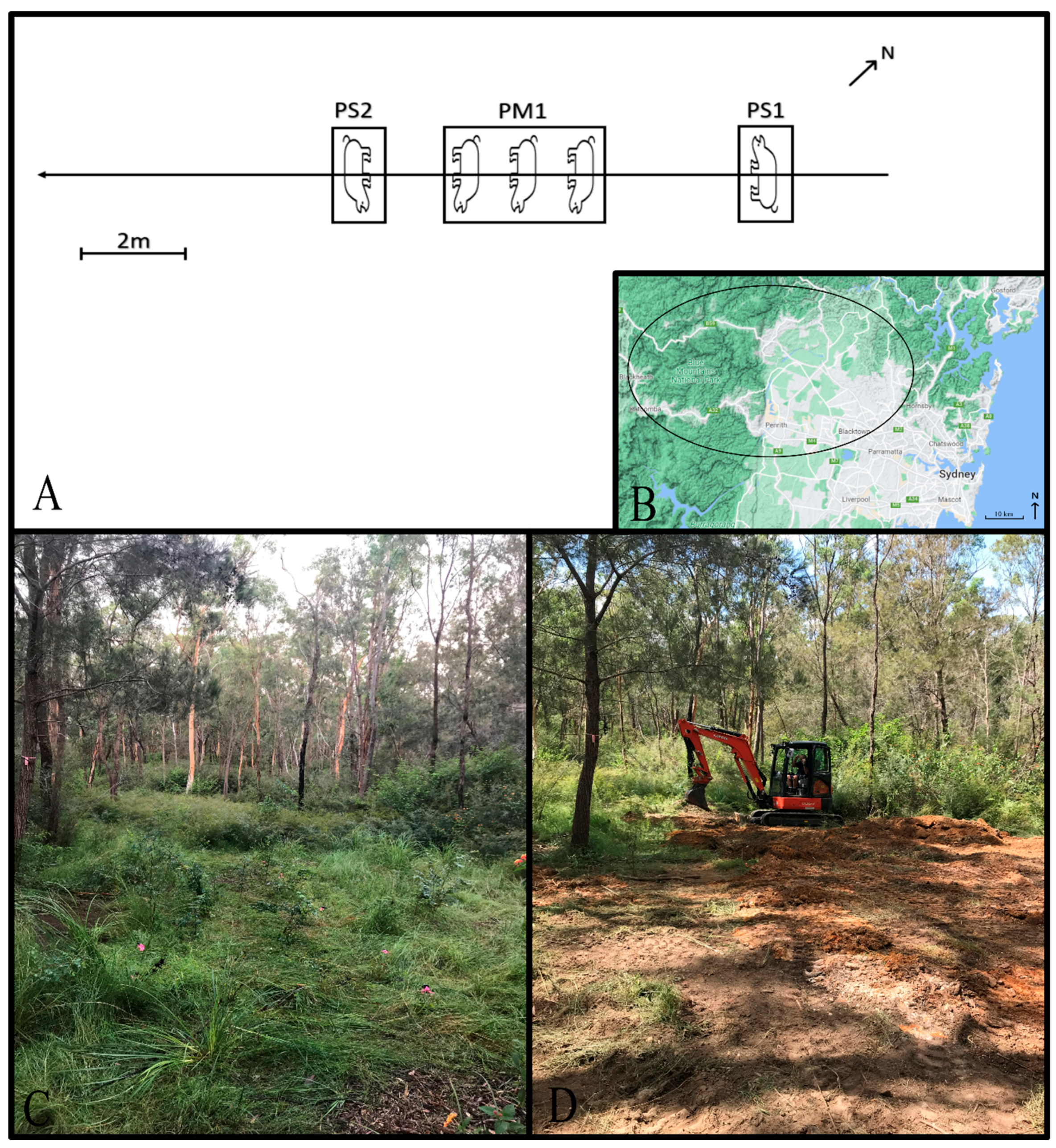





| Grave ID | Grave Dimensions (LxWxD in m) | Type (and # of Pig Cadavers) | Sex | Weight (kg) | Position in Grave |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PS1 | 2 × 1 × 0.5 | Single (1) | Female | 60 | Side laying; head at NW end of grave and facing SW |
| PM1 | 2 × 2.5 × 1 | Mass (3) | Males | 70, 80, 90 | Side laying; head at SE end of grave and facing SW |
| PS2 | 2 × 1 × 1.8 | Single (1) | Female | 50 | Side laying; head at SE end of grave and facing NE |
| Survey Time in Relation to Pig Burial Creation (Letter in Figure 4) [mm-yy] | Summary of Observations | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| PS1 | PM1 | PS2 | |
| Pre-burial (A) [Mar-21] | No grave/control | No grave/control | No grave/control |
| Post-burial (B) [Mar-21] | Similar to (A) | Similar to (A) | Similar to (A) |
| One-month (C) [Apr-21] | Hyperbola with 0.09 ns velocity * | No clear grave-indicating anomaly; similar to surrounding soil | Dislocation to reflectors at base of grave; similar to surrounding soil up to 1 m deep |
| Eight-month (D) [Nov-21] | Dislocation in reflectors | Dislocations to reflectors at base of grave | Dislocation to reflectors; similar to surrounding soil up to 1 m deep |
| Fourteen-month (E) [May-22] | Hyperbola with 0.075 ns velocity * | Dislocations to reflectors | Dislocation to reflectors at surface, ~15 ns, and ~30 ns |
| Twenty-month (F) [Nov-22] | Dislocation to reflectors | Dislocation to reflectors | Dislocation to reflectors; similar to surrounding soil up to 1 m deep |
| Survey Time in Relation to Pig Burial Creation (Letter in Figure 5 and Figure 6) [mm-yy] | Summary of Observations | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PS1 | PM1 | PS2 | ||||
| Dipole-Dipole | Wenner | Dipole-Dipole | Wenner | Dipole-Dipole | Wenner | |
| Pre-burial (A) [Mar-21] | No grave/control | No grave/control | No grave/control | No grave/control | No grave/control | No grave/control |
| Post-burial (B) [Mar-21] | No clearly observable grave anomalies | High-resistivity anomaly | High-resistivity anomaly in the centre of the grave area; low resistivity anomaly below the grave | High resistivity anomaly | No clearly observable grave anomalies | High resistivity anomaly |
| One-month (C) [Apr-21] | No clearly observable grave anomalies | Low resistivity anomaly | Low resistivity anomaly | Low resistivity anomaly | High resistivity anomaly near surface of the grave | No clearly observable grave anomalies |
| Eight-month (D) [Nov-21] | Low resistivity anomaly; similar to surrounding non-grave areas | Low resistivity anomaly | Low resistivity anomaly | Low resistivity anomaly | No clearly observable grave anomalies | No clearly observable grave anomalies |
| fourteen-month (E) [May-22] | Low resistivity anomaly below grave floor | No clearly observable grave anomalies | Low resistivity anomaly | Low resistivity anomaly | No clearly observable grave anomalies | No clearly observable grave anomalies |
| twenty-month (F) [Nov-22] | Non-uniform low resistivity anomaly | Low resistivity anomaly | Low resistivity anomaly | Low resistivity anomaly | No clearly observable grave anomalies | No clearly observable grave anomalies |
| Geophysical Observability | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PS1 | PM1 | PS2 | |||||||
| GPR | ERT (DD) | ERT (W) | GPR | ERT (DD) | ERT (W) | GPR | ERT (DD) | ERT (W) | |
| Pre-burial | |||||||||
| Post-burial | |||||||||
| One-month | |||||||||
| Eight-month | |||||||||
| Fourteenfourteen-month | |||||||||
| Twentytwenty-month | |||||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Berezowski, V.; Mallett, X.; Seckiner, D.; Crebert, I.; Ellis, J.; Rau, G.C.; Moffat, I. Comparison of Time-Lapse Ground-Penetrating Radar and Electrical Resistivity Tomography Surveys for Detecting Pig (Sus spp.) Cadaver Graves in an Australian Environment. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 3498. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16183498
Berezowski V, Mallett X, Seckiner D, Crebert I, Ellis J, Rau GC, Moffat I. Comparison of Time-Lapse Ground-Penetrating Radar and Electrical Resistivity Tomography Surveys for Detecting Pig (Sus spp.) Cadaver Graves in an Australian Environment. Remote Sensing. 2024; 16(18):3498. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16183498
Chicago/Turabian StyleBerezowski, Victoria, Xanthé Mallett, Dilan Seckiner, Isabella Crebert, Justin Ellis, Gabriel C. Rau, and Ian Moffat. 2024. "Comparison of Time-Lapse Ground-Penetrating Radar and Electrical Resistivity Tomography Surveys for Detecting Pig (Sus spp.) Cadaver Graves in an Australian Environment" Remote Sensing 16, no. 18: 3498. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16183498
APA StyleBerezowski, V., Mallett, X., Seckiner, D., Crebert, I., Ellis, J., Rau, G. C., & Moffat, I. (2024). Comparison of Time-Lapse Ground-Penetrating Radar and Electrical Resistivity Tomography Surveys for Detecting Pig (Sus spp.) Cadaver Graves in an Australian Environment. Remote Sensing, 16(18), 3498. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16183498






