A Two-Component Polarimetric Target Decomposition Algorithm with Grassland Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
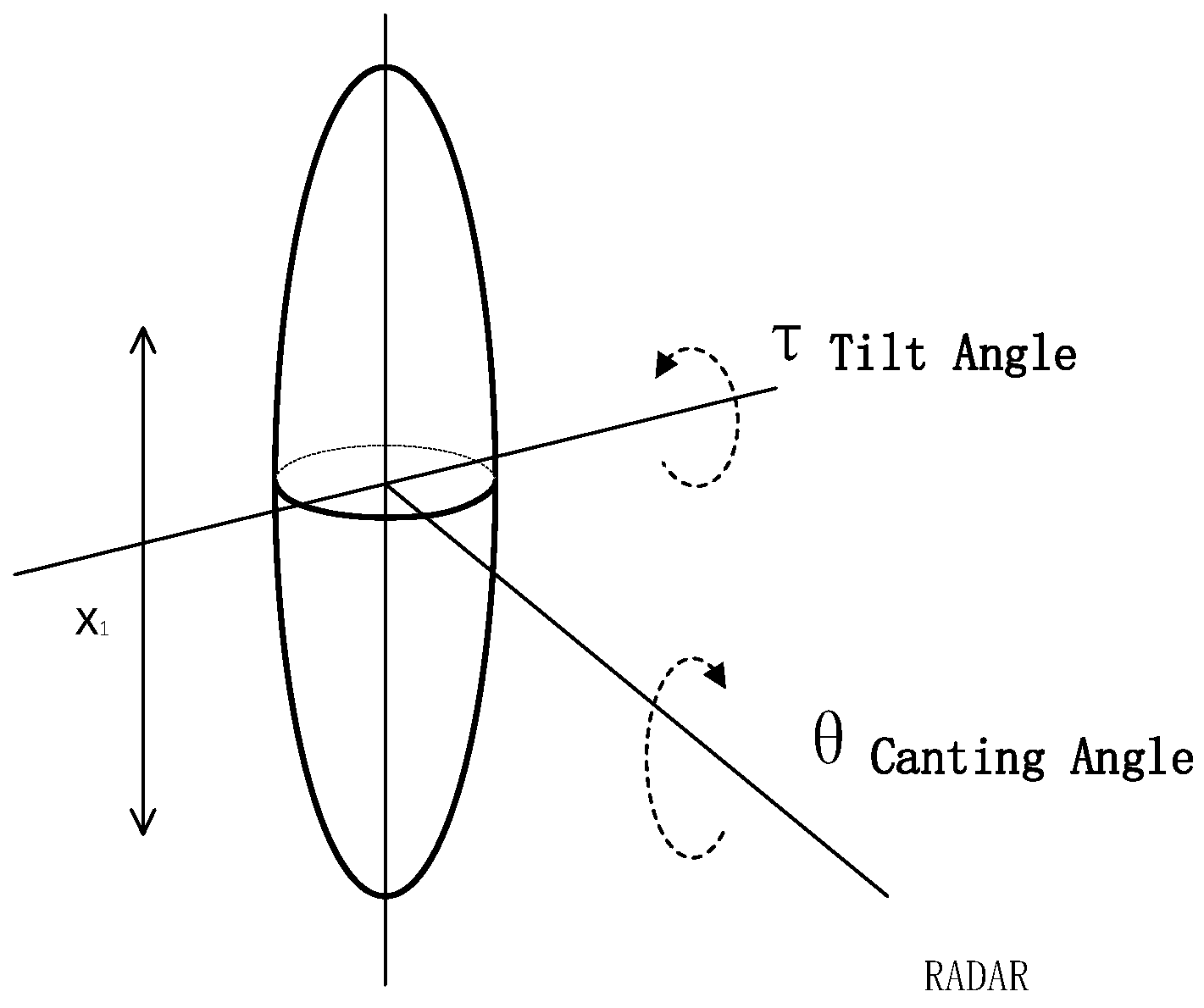
2.1. Orientation Angle Compensation
2.2. Adaptive Volume Scattering Model
2.3. Polarimetric Target Decomposition Algorithm
3. Results and Analysis
3.1. Experiments on X-Band Data from the Grasslands of Xiwuqi in the Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region
3.2. Experiments on C-Band Data from the Hunsandak Grassland in Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, B.; Tian, Z.; Zhang, W.; Chen, G.; Guo, Y.; Wang, M. Retrieval of Green-up Onset Date From MODIS Derived NDVI in Grasslands of Inner Mongolia. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 77885–77893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stiles, J.M.; Sarabandi, K. Electromagnetic scattering from grassland. I. A fully phase-coherent scattering model. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2000, 38, 339–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, I.; Cawkwell, F.; Dwyer, E.; Barrett, B.; Green, S. Satellite remote sensing of grasslands: From observation to management. J. Plant Ecol. 2016, 9, 649–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.-W.; Xuesong, W.; Xiao, S.-P.; Sato, M. Target Scattering Mechanism in Polarimetric Synthetic Aperture Radar—Interpretation and Application; Springer: Singapore, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Jawak, S. A Review on Applications of Imaging Synthetic Aperture Radar with a Special Focus on Cryospheric Studies. Adv. Remote Sens. 2015, 4, 163–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, L.; Zou, B. A new Six-Component Decomposition based on New Volume Scattering Models for PolSAR Image. In Proceedings of the 2021 CIE International Conference on Radar (Radar), Haikou, China, 15–19 December 2021; pp. 631–634. [Google Scholar]
- Huynen, J.R. Phenomenological Theory of Radar Targets. Ph.D. Thesis, Electrical Engineering, Mathematics and Computer Science (EEMCS) (TU Delft), Delft, The Netherlands, 1970. [Google Scholar]
- Cloude, S.R.; Pottier, E. A review of target decomposition theorems in radar polarimetry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1996, 34, 498–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holm, W.A.; Barnes, R.M. On radar polarization mixed target state decomposition techniques. In Proceedings of the 1988 IEEE National Radar Conference, Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 20–21 April 1988; pp. 249–254. [Google Scholar]
- Cloude, S.R.; Pottier, E. An entropy based classification scheme for land applications of polarimetric SAR. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1997, 35, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, W.; Cui, Y.; Yang, J.; Zhang, H. Fast Alternatives to $H/\alpha$ for Polarimetric SAR. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2010, 7, 343–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, A.; Durden, S.L. A three-component scattering model for polarimetric SAR data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1998, 36, 963–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriyama, T.; Uratsuka, S.; Umehara, T.; Maeno, H.; Satake, M.; Nadai, A.; Nakamura, K.J.I.T.C. Polarimetric SAR Image Analysis Using Model Fit for Urban Structures. IEICE Trans. Commun. 2005, 88-B, 1234–1243. [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi, Y.; Moriyama, T.; Ishido, M.; Yamada, H. Four-component scattering model for polarimetric SAR image decomposition. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2005, 43, 1699–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, Q.; Xie, Q.; Peng, X.; Lai, K.; Wang, J.; Lopez-Sanchez, J.M.; Shang, J.; Shi, H.; Fu, H.; Zhu, J. Soil moisture retrieval over crop fields based on two-component polarimetric decomposition: A comparison of generalized volume scattering models. J. Hydrol. 2022, 615, 128696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Yang, J. Target Decomposition Based on Symmetric Scattering Model for Hybrid Polarization SAR Imagery. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2021, 18, 494–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yajima, Y.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Sato, R.; Yamada, H.; Boerner, W.M. POLSAR Image Analysis of Wetlands Using a Modified Four-Component Scattering Power Decomposition. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2008, 46, 1667–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, G.; Yamaguchi, Y. Model-Based Six-Component Scattering Matrix Power Decomposition. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 56, 5687–5704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, G.; Malik, R.; Mohanty, S.; Rathore, V.S.; Yamada, K.; Umemura, M.; Yamaguchi, Y. Seven-Component Scattering Power Decomposition of POLSAR Coherency Matrix. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 8371–8382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, Y.; Sato, A.; Boerner, W.M.; Sato, R.; Yamada, H. Four-Component Scattering Power Decomposition With Rotation of Coherency Matrix. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 49, 2251–2258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, W.; Cui, Y.; Yang, J. Three-Component Model-Based Decomposition for Polarimetric SAR Data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2010, 48, 2732–2739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S.; Ainsworth, T.L. The Effect of Orientation Angle Compensation on Coherency Matrix and Polarimetric Target Decompositions. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 49, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, Y.; Singh, G.; Park, S.E.; Yamada, H. Scattering power decomoosition using fully polarimetric information. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Munich, Germany, 22–27 July 2012; pp. 91–94. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Li, Q.; Wu, G.; Chen, J.; Liang, S. Adaptive Two-Component Model-Based Decomposition for Polarimetric SAR Data Without Assumption of Reflection Symmetry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 55, 197–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, W.; Lin, M. A Reflection Symmetry Approximation of Multilook Polarimetric SAR Data and its Application to Freeman–Durden Decomposition. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 3649–3660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zyl, J.J.V.; Arii, M.; Kim, Y. Model-Based Decomposition of Polarimetric SAR Covariance Matrices Constrained for Nonnegative Eigenvalues. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 49, 3452–3459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cloude, S. Polarisation: Applications in Remote Sensing; Oxford Academic: Oxford, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Yang, J.; Kobayashi, H.; Park, S.E.; Singh, G. On Complete Model-Based Decomposition of Polarimetric SAR Coherency Matrix Data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 1991–2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, B.; Lu, D.; Zhang, L.; Moon, W.M. Eigen-Decomposition-Based Four-Component Decomposition for PolSAR Data. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2016, 9, 1286–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurya, H.; Bhattacharya, A.; Mishra, A.K.; Panigrahi, R.K. Hybrid Three-Component Scattering Power Characterization From Polarimetric SAR Data Isolating Dominant Scattering Mechanisms. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 4415315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumann, M.; Ferro-Famil, L.; Reigber, A. Estimation of Forest Structure, Ground, and Canopy Layer Characteristics From Multibaseline Polarimetric Interferometric SAR Data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2010, 48, 1086–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arii, M.; Zyl, J.J.V.; Kim, Y. A General Characterization for Polarimetric Scattering From Vegetation Canopies. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2010, 48, 3349–3357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-S.; Ainsworth, T.L.; Wang, Y. Generalized Polarimetric Model-Based Decompositions Using Incoherent Scattering Models. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 2474–2491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.W.; Wang, X.S.; Xiao, S.P.; Sato, M. General Polarimetric Model-Based Decomposition for Coherency Matrix. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 1843–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arii, M.; van Zyl, J.J.; Kim, Y. Adaptive Model-Based Decomposition of Polarimetric SAR Covariance Matrices. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 49, 1104–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antropov, O.; Rauste, Y.; Hame, T. Volume Scattering Modeling in PolSAR Decompositions: Study of ALOS PALSAR Data Over Boreal Forest. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 49, 3838–3848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Wang, J.; Shang, J. An Adaptive Two-Component Model-Based Decomposition on Soil Moisture Estimation for C-Band RADARSAT-2 Imagery Over Wheat Fields at Early Growing Stages. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2016, 13, 414–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zeng, Q.; Jiao, J. An adaptive decomposition approach with dipole aggregation model for polarimetric sar data. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Suo, Z.; Jiang, P.; Ti, J.; Ding, Z.; Qin, T. An Optimal Polarization SAR Three-Component Target Decomposition Based on Semi-Definite Programming. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 5292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.W.; Sato, M. Tsunami Damage Investigation of Built-Up Areas Using Multitemporal Spaceborne Full Polarimetric SAR Images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2013, 51, 1985–1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zou, B.; Cai, H.; Zhang, Y. Multiple-Component Scattering Model for Polarimetric SAR Image Decomposition. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2008, 5, 603–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, D.; Ban, Y.; Su, Y. Model-Based Decomposition With Cross Scattering for Polarimetric SAR Urban Areas. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2015, 12, 2496–2500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajnsek, I.; Pottier, E.; Cloude, S.R. Inversion of surface parameters from polarimetric SAR. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2003, 41, 727–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-S.; Pottier, E. Polarimetric Radar Imaging: From Basics to Applications; Routledge: London, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Manuel, L.-S.J. Analysis and Estimation of Biophysical Parameters of Vegetation by Radar Polarimetry. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidad Politecnica de Valencia, Valencia, Spain, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Karam, M.A.; Fung, A.K. Electromagnetic scattering from a layer of finite length, randomly oriented, dielectric, circular cylinders over a rough interface with application to vegetation. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1988, 9, 1109–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Liu, Y.; Huang, P.; Liu, X.; Tan, W.; Fu, W.; Li, C. A Hybrid Polarimetric Target Decomposition Algorithm with Adaptive Volume Scattering Model. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monsivais-Huertero, A.; Sarabandi, K.; Chenerie, I. Multipolarization Microwave Scattering Model for Sahelian Grassland. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2010, 48, 1416–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, A. Fitting a Two-Component Scattering Model to Polarimetric SAR Data From Forests. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2007, 45, 2583–2592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.W.; Ohki, M.; Shimada, M.; Sato, M. Deorientation Effect Investigation for Model-Based Decomposition Over Oriented Built-Up Areas. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2013, 10, 273–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurya, H.; Panigrahi, R. Non-Negative Scattering Power Decomposition for PolSAR Data Interpretation. IET Radar Sonar Navig. 2018, 12, 593–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, W.; Fu, H.; Zhu, J.; Xie, Q.; Zhang, S. Orthogonal Scattering Model-Based Three-Component Decomposition of Polarimetric SAR Data. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]












| Area | Component | FRE2 | Y4R | HTCD | OSM | Proposed |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 34.77 | 35.94 | 41.80 | 29.69 | 45.70 | |
| 39.84 | 51.56 | 23.83 | 62.11 | 36.72 | ||
| 25.39 | 12.50 | 34.37 | 8.20 | 17.58 | ||
| B | 1.59 | 3.91 | 4.69 | 3.91 | 7.81 | |
| 62.47 | 82.03 | 40.63 | 87.50 | 80.47 | ||
| 35.94 | 14.06 | 54.68 | 8.59 | 11.72 | ||
| C | 6.25 | 7.81 | 8.20 | 12.50 | 11.33 | |
| 57.81 | 50.00 | 29.69 | 61.33 | 58.59 | ||
| 35.94 | 42.19 | 62.11 | 26.17 | 30.08 |
| Region | Component | FRE2 | Y4R | HTCD | OSM | Proposed |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 45.33 | 49.63 | 45.32 | 51.67 | 62.90 | |
| 49.63 | 1.04 | 0.12 | 0.54 | 3.15 | ||
| 5.04 | 49.33 | 54.56 | 47.79 | 33.95 | ||
| B | 2.18 | 3.16 | 2.19 | 6.20 | 7.61 | |
| 87.83 | 47.71 | 1.95 | 36.89 | 65.64 | ||
| 9.99 | 49.13 | 95.86 | 56.91 | 26.75 | ||
| C | 3.92 | 4.61 | 3.92 | 7.88 | 2.04 | |
| 93.81 | 9.96 | 0 | 5.11 | 14.99 | ||
| 2.27 | 85.43 | 96.08 | 87.01 | 82.97 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, P.; Chen, Y.; Li, X.; Tan, W.; Chen, Y.; Yang, X.; Dong, Y.; Lv, X.; Li, B. A Two-Component Polarimetric Target Decomposition Algorithm with Grassland Application. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 2832. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16152832
Huang P, Chen Y, Li X, Tan W, Chen Y, Yang X, Dong Y, Lv X, Li B. A Two-Component Polarimetric Target Decomposition Algorithm with Grassland Application. Remote Sensing. 2024; 16(15):2832. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16152832
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Pingping, Yalan Chen, Xiujuan Li, Weixian Tan, Yuejuan Chen, Xiangli Yang, Yifan Dong, Xiaoqi Lv, and Baoyu Li. 2024. "A Two-Component Polarimetric Target Decomposition Algorithm with Grassland Application" Remote Sensing 16, no. 15: 2832. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16152832
APA StyleHuang, P., Chen, Y., Li, X., Tan, W., Chen, Y., Yang, X., Dong, Y., Lv, X., & Li, B. (2024). A Two-Component Polarimetric Target Decomposition Algorithm with Grassland Application. Remote Sensing, 16(15), 2832. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16152832







