Abstract
The study of ancient irrigation is crucial in the archaeological research of arid regions. It covers a wide range of topics, with the Near East being the focus for decades. However, political instability and limited data have posed challenges to these studies. The primary objective is to establish a standardised method applicable to different arid environments using the Google Earth Engine platform, considering local relief of terrain and seasonal differences in vegetation. This study integrates multispectral data from LANDSAT 5, Sentinel-2, SAR imagery from Sentinel 1, and TanDEM-X (12 m and 30 m) DSMs. Using these datasets, calculations of selected vegetation indices such as the SMTVI and NDVSI, spectral decomposition methods such as TCT and PCA, and topography-based methods such as the MSRM contribute to a comprehensive understanding of landscape irrigation. This paper investigates the influence of modern environmental conditions on the visibility of features like levees and palaeo-channels by testing different methods and parameters. This study aims to identify the most effective approach for each case study and explore the possibility of applying a consistent method across all areas. Optimal results are achieved by combining several methods, adjusting seasonal parameters, and conducting a comparative analysis of visible features.
1. Introduction
The climate in the Near East, Iran, and Central Asia is predominantly arid. This area includes some of the driest deserts. Only mountainous regions, coastal areas, piedmonts, or highlands, such as the Fertile Crescent in the Near East, are suitable for dry farming. A significant part of this area receives less than 250 mm of annual rainfall, making it unsuitable for agriculture without supplementary irrigation. This is aggravated by climate change, making irrigation even more crucial for the modern economy [1].
The study of irrigation is a key part of the archaeology of the Near East, Iran, and Central Asia. It comprises a wide range of topics, including community irrigation practices, water harvesting techniques, agricultural intensification, and the role of irrigation in the formation and maintenance of complex societies and ancient empires [2,3,4,5,6,7].
The methods usually employed in this type of research range from historical records, surface survey, archaeological investigations, isotope analysis, archaeobotany, and zooarchaeology. Geographic Information Systems (GIS) have been an important tool in this research as they have allowed us to effectively map canals and study their relationship with their surrounding landscape and the distribution of ancient sites [3,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16].
Water management studies are complex as they need to consider multiple factors such as land cover, topography and the wide variability of landscape elements associated with water management. The irrigated landscapes are palimpsests, which contain both modern and ancient manmade and natural features. In the case of the Middle Eastern arid landscapes under study, the most typical features associated with ancient canals are raised elongated embankments (levees) characteristic of floodplains. They are formed because of the region’s low slope, silt rich rivers, and high evapotranspiration causing the need for regular cleaning. In the piedmont areas, where the slope is more steep, more typical are incised canals, river terraces and ravines caused by water erosion. The traces of ancient irrigation might be difficult to detect if it was not long-term. Other water management-related features occurring in various types of landscapes may include, for example, modern or ancient river and stream beds and associated features (meanders, crevasse splays, and cut-offs), alluvial fans or cones, palaeo-channels, lakes, wetlands, terraced agricultural structures, ancient field patterns, water harvesting structures, ditches, rock cut channels, aqueducts and qanats. Therefore, the study of ancient irrigation requires the use of multiple methods [3,17,18,19,20,21].
The political situation in the Middle East, where most of the early research took place, has been a major obstacle to the development of water management studies in recent decades. However, these studies have recently gained momentum due to advances in computing power, the emergence of new methods and the increasing availability of satellite data, much of which is distributed as cloud-stored datasets. Many approaches have emerged alongside the implementation of Digital Surface Models (DSMs) and archived CORONA images [17,18]. While archival images showed the existence of potential ancient canals or former riverbeds, DSM allowed the study of characteristic geomorphological features formed by long-term irrigation [3]. Particularly interesting results have been achieved using multi-temporal and multi-spectral satellite imagery with Google Earth Engine (GEE) [22] in particular those from the TwoRains project at Cambridge, which suggested that natural and partially modified palaeo-channels could be revealed using mean values of vegetation indexes from the data collected over thirty years of LANDSAT 5 satellite imagery [23,24].
An overview of the papers published during the last few years indicates that GEE finds its use in many applications and disciplines for the analysis of satellite imagery and digital elevation models. The appearance of the platform has contributed to an exponential growth of remote sensing applications [25,26,27]. It was successfully used for mapping urban sprawl [28], land cover change [29] and dynamics of fluvial geomorphology [30,31,32,33,34,35]. There were also very effective GEE applications in archaeology, such as detecting archaeological sites [36,37], traces of looting [38], heritage monitoring [39,40,41], mapping communication paths [42], and monitoring agricultural impact to archaeological sites [43].
The aim of this study is to test the potential of multi-temporal Sentinel 1 and 2, LANDSAT 5, and TanDEM-X digital surface models using GEE to map palaeo-channels and irrigation canals in the Middle East, Iran, and Central Asia, which are part of the UnderTheSands project. Four research areas have been chosen for this study (Figure 1). The first selected area of study is the Central Floodplain of the Euphrates River in Iraq (CFE1). One area was selected in Iran: Gorgan Plain (G1). Two areas have been chosen in Turkmenistan: the Murghab (M1) and the area between Serakhs and ancient Geoksyur oases watered by the Tedjen River (T1) (Table 1). All selected areas have been the subject of intensive field survey projects. The studies conducted in the past also allowed the mapping of irrigation networks, but lower-resolution datasets were used.
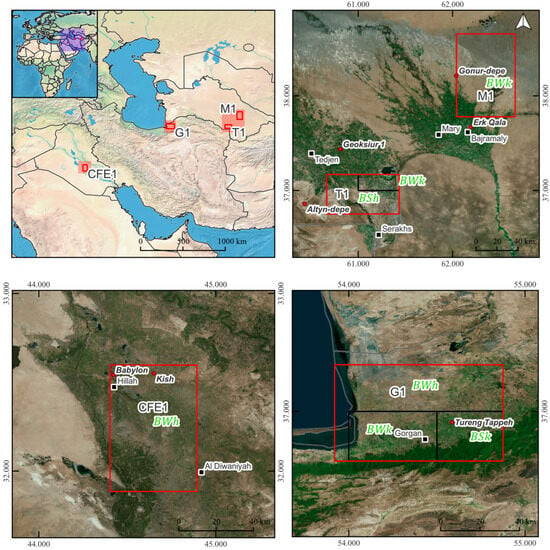
Figure 1.
The location of the research areas (Bing maps, Made with Natural Earth).

Table 1.
The characteristics of research areas.
The selected areas have diverse geomorphological and environmental characteristics, allowing the development of a novel workflow for the comprehensive analysis of large-scale irrigation networks. The intention is to investigate whether it is possible to develop a unified methodology that can be applied to all selected regions based on the local relief and multi-temporal seasonal changes in vegetation. This study will also determine if and how modern differences in the climatic conditions of each area can be used to improve the detection of water management features studied using selected multisource imagery (Table 1; Figure 2, Figure 3 and Figure 4).
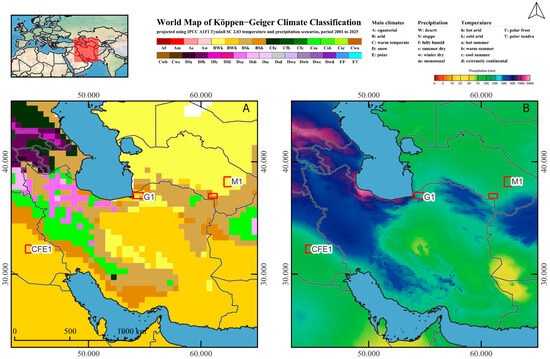
Figure 2.
Climate of the areas according to Köppen-Geiger Climate Classification (A1FI: 2001–2025) (A) and mean precipitation (B) (Made with Natural Earth) [44,45].
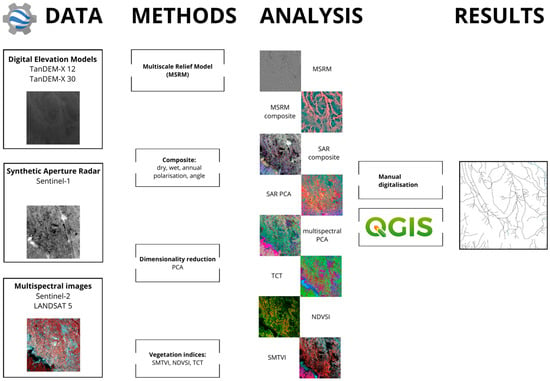
Figure 3.
Methods applied in this study.
1.1. Research Areas
1.1.1. Central Floodplain of Euphrates (CFE1)
The Central Floodplain of the Euphrates is located in Iraq and is watered by the Euphrates and partially Tigris rivers. The region has a hot desert climate (BWh). In winter, temperatures can drop as low as −8.3 °C, while in summer the maximum temperature can reach 50 °C. Annual rainfall ranges from 72.3 to 315.7 mm, with an average of around 148.3 mm. Rainfall is typically absent from mid-May to early October. Average evapotranspiration is between 1900 and 2000 mm. Due to low rainfall and high temperature, agriculture relies heavily on artificial irrigation systems. As a result, the modern landscape has been altered by the construction of numerous canals, dams and reservoirs [47,48].
The primary research area is situated approximately 70 km south of Baghdad, between Hillah and Al Diwaniya, encompassing a land area of 3651 square km (Table 1: CFE1; Figure 2). This region holds great significance for irrigation studies, given its historical association with ancient Babylon and Kish. Consequently, it is not surprising that this area constitutes an important location for the investigation of irrigation practices [49,50]. The irrigation network is preserved in the form of levees and traces of palaeo-channels, which have been mapped using single LANDSAT images [48], CORONA imagery and SRTM [51,52], which have been used as reference data in this study.
1.1.2. Gorgan Plain
The Gorgan Plain, situated in Northern Iran, is a piedmont zone of the Elburz Mountains, located east of the Caspian Sea. The region is irrigated by the Gorgan River and is separated from the Misrian Plain in Turkmenistan by the Atrek River. Additionally, several streams flow from the surrounding mountains, contributing to the area’s water supply [53].
The Gorgan plain has a diversified climate depending on the distance from the mountains or the Caspian Sea. The southern part experience cold desert (BWk) climate, southeastern a cold semi-arid (BSk), while southwestern, northern, and northeastern parts—hot desert climate (BWh) [44]. Average temperatures in the area range from 7.8 °C in winter to 27.8 °C in summer. Rainfall can range from 800 to 1000 mm in the mountainous part of Gorgan Plain, typically between December and April. However, the northern region of the Gorgan plain tends to be drier, with an annual rainfall of around 200 mm. Evapotranspiration of the area exceeds 1500 mm [54].
The primary research area is situated in the western section of the Gorgan Plain, near the delta of the Gorgan River. It covers 5154 km2 (Table 1: G1; Figure 2). The region is divided by the river itself. The southern part experiences higher precipitation and is irrigated through a combination of canals and qanats. In contrast, the northern part of the study area is more arid. The western part of the area is particularly intricate, consisting of a complex network of canals and palaeo-channels.
The earliest evidence for irrigation practices dates back to the middle of the first millennium BCE. Later, the plain witnessed the construction of an important irrigation project during the Sasanian period (224–651 CE), when the Gorgan wall was built. The irrigation network and the layout of streams and palaeo-channels were studied using SRTM and CORONA, which allowed large and medium-sized features to be identified in the selected study area. The resolution of the available data did not allow a more detailed investigation of the westernmost part of the area, which will be re-examined in this study [53,55].
1.1.3. Murghab Fan
The Murghab River Fan is located in Southern Turkmenistan, south-west of the Amu Darya River. It is recognized as a crucial area for irrigation studies in Central Asia [56]. The region has a cold desert climate (BWk) [44]. Summers are very hot with temperatures reaching approximately 40 °C, while winters are relatively mild as temperatures hover around 2 °C. The annual precipitation in the area ranges from 139 to 249 mm, with an average of approximately 157 mm. Precipitation predominantly occurs as rain or snow during winter or early spring and is generally absent from July to September/October [57,58,59]. The mean annual evapotranspiration for the Murghab fan is estimated to be around 2000 mm [46]. Traditionally, agriculture in the Murghab fan relied on irrigation from the Murghab River. However, the landscape underwent significant changes with the construction of the Karakum Canal in the 1960s that diverts water from the Amu Darya River [60,61]. Scholars assume that the economy of Murghab fan in times of the earliest extensive settlement, known as Oxus Civilization (2250–1700 BCE), was mostly based on natural water management [62]. The significant transformation of the fan began after the middle of I millennium BCE, when the first large canals were built. The irrigation network and layout of the former beds of the Murghab have been investigated by several teams. Most of the information on water management comes from coarse or medium-resolution data: SRTM [56,63], ALOS World 3D [64], CORONA imagery [65], which are used as reference data in this study. Some small portions of the Murghab fan have been the subject of detailed analysis [66,67,68], but these were scattered in different zones of the fan. The current study will be analyse the irrigation network in more detail, covering the gap between these areas.
The primary test area is situated in the central western section of the Murghab fan, encompassing an area of 5283 km2. It comprises a diverse archaeological landscape. The southwestern part of the area is near the Karakum Canal and exhibits extensive modifications related to modern irrigation practices. The region then extends towards the north, encompassing desertic terrain that includes notable sites such as Gonur-depe [69]. The northern and eastern parts of the research area are covered by the Karakum Desert and some wetlands created by water spills from the Karakum Canal (Table 1: M1; Figure 2).
1.1.4. Area between Serakhs and Geoksyur Oases
The last selected area is irrigated by the Tedjen River (Har-i rud), which originates in Afghanistan. Upon reaching the plains in Turkmenistan, the river forms a small alluvial cone known as the Serakhs oasis. From there, it flows northward for approximately a hundred km before drying out and creating an alluvial fan. The Tedjen fan has migrated westward, leaving a significant dry area known as the Geoksyur oasis, inhabited during the Chalcolithic period and crucial for understanding irrigation development in the region [70] (4000–2250 BCE). The climate in the area is classified as hot semi-arid (BSh) in the south and cold desert (BWk) in the north. It is similar to that to the Murghab fan but experiences slightly higher annual rainfall, with an average of 179 mm [59]. The irrigation network has been studied using the SRTM terrain model, ALOS World 3D, and CORONA imagery [21,64,71]. The recent discovery of the Berdysyčran-depe site has also revealed the existence of new former riverbeds of the Tedjen River [70], although the state of their recognition is still incomplete.
The selected study area (T1—3179 km2) is situated in the Serakhs oasis’s northern periphery and the Geoksyur oasis’s southern part (Table 1: T1; Figure 2). Unlike the Murghab and Tedjen fans or the Geoksyur oasis, the area has not been modified by the construction of the Karakum Canal. This location offers an opportunity to investigate the origins of the palaeo-channels that supply water to the Geoksyur oasis, and their detailed layout. The central part of the area is predominantly deserted. In the northern and southern regions modern canals are present.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
The workflow presented here relies on the application of multisource and multi-temporal satellite LANDSAT 5 and Sentinel-2 multispectral imagery, Sentinel-1 SAR and TanDEM-X digital elevation models (12 and 30 m).
The LANDSAT 5 archive is a multispectral satellite imagery dataset, with images from March 1984 to May 2012, and provides 16-day revisit times. It provides seven spectral bands, RGB, NIR, and SWIR with a spatial resolution of 30 m, and a thermal band of 120 m. LANDSAT 5’s extended operational period spans 28 years, resulting in a significant amount of data for any location on Earth. Numerous raw and pre-processed image datasets are available for the LANDSAT 5 dataset on Google Earth Engine (GEE).
The Copernicus Sentinel-2 constellation consists of two identical satellites, A and B. The first satellite, Sentinel-2A, was launched into orbit on 23 June 2015 followed by Sentinel-2B on 7 March 2017. This satellite system operates on a 10-day revisit schedule and provides valuable data in 13 spectral bands. Sentinel-2 has been providing data continuously for eight years since its launch. Among the spectral bands, the RGB and NIR bands provide a resolution of 10 m. The Red Edge and SWIR bands provide a 20-metre resolution, while the remaining bands provide 60-metre spatial resolution. Users can access two primary datasets based on Sentinel-2 imagery within the GEE platform. These datasets include orthorectified top-of-atmosphere reflectance, available since 2015, and orthorectified atmospherically corrected surface reflectance, available since 2017. Both are available in harmonised and non-harmonised versions.
The Sentinel-1 constellation comprises two polar-orbiting satellites that operate using C-band (5.405 GHz) synthetic aperture radar imaging (SAR). Sentinel-1A was launched into orbit on 3 April 2014, followed by Sentinel-1B on 25 April 2016. Both satellites were placed in the same orbit, maintaining a 180° orbital phasing difference. Sentinel-1B has been decommissioned due to power issues. To address the decommissioning of Sentinel-1B, plans are underway to replace the satellites with Sentinel-1C and Sentinel-1D. The data from the Sentinel-1 constellation provides a spatial resolution of 10 m, enabling detailed imaging of the Earth’s surface regardless of the weather. The revisit cycle of the satellites is set at 12 days [72]. GEE offers preprocessed Sentinel-1 SAR GRD, with data available since 2014. Sentinel-1 operates in four exclusive acquisition modes, namely Stripmap (SM), Interferometric Wide Swath (IW), Extra-Wide Swath (EW), and Wave (WV), among which SM, IW, and EW are available in GEE. Two different orbit angles (ascending or descending) and four bands are available (HH—Single co-polarization, horizontal transmit/horizontal receive; HV—dual-band cross-polarization, horizontal transmit/vertical receive; VV—single co-polarization, vertical transmit/vertical receive; and VH—dual-band cross-polarization, vertical transmit/horizontal receive). Interferometric Wide Swath (IW), which is the most suitable for the research areas UnderTheSands contains only VV and VH polarisations [73].
TanDEM-X is a digital surface model produced by the German Aerospace Center (DLR) using bistatic X-band interferometric TerraSAR-X imagery. The horizontal resolution of the DSM is 12 m (0.4 arcsec) [74]. The data were made available to the UnderTheSands project through the TanDEM-X Science Digital Elevation Models call (DEM_HYDR3723). As one of the areas covered by the project has limited access to TanDEM-X 12 m, namely the area in Iraq, we decided to use TanDEM-X EDEM (30 m) instead.
TanDEM-X 30 m Edited DEM is an edited version of TanDEM-X (1 arcsec). Similar to TanDEM-X Global DEM, it does not represent the bare earth surface. The data have been corrected by filling in the gaps and flattening the water bodies [75,76,77].
2.2. Methods
The studies presented here are based on the analysis of multisource multitemporal datasets available on the Google Earth Engine (GEE) platform, which allow the enhancement of the visibility of landscape features through the use of pixel-based statistics and spectral decomposition techniques for dry or wet seasons calculated over several years of available data. Previously, to access and use such a large dataset, it had to be downloaded to local storage. However, through GEE, this massive dataset can now be accessed and analysed ion the cloud. The flexibility of the GEE platform allows users to calculate any spectral index needed, enabling customised analysis based on specific research needs. This makes working with the vast earth observation archive much more convenient and efficient.
The study presented in this paper examined potential use of Principal Component Analysis (PCA), Tasselled Cap Transformation (TCT), Seasonal Multi-Temporal Vegetation Indices (SMTVI), Normalised Difference Vegetation Seasonality Index (NDVSI), for wet and dry season to study the location of levees and river channels. The Sentinel 1 SAR images have been analysed using composites and PCA consisting of different polarisations, scanning direction or seasons. A topographic approach has been included using the Multi-Scale Relief Model (MSRM) [24] (Figure 3). The above-mentioned methods have been selected in this study, because they have been already successfully applied for detection of palaeo-channels in the Northwestern India [23,24,34,35]. We expect that they can be used in arid landscapes, however, some parameters had to be adjusted to the climatic conditions during which the earth observation data were gathered (Table 1; Figure 2 and Figure 4).
Principal Component Analysis (PCA) was used for initial examination of the Sentinel-2 and LANDSAT 5 datasets. As a spectral decomposition technique it can reduce a complex dataset to reveal hidden patterns [78]. The algorithm’s code allowed to select a specific bands and seasonal parameters [23]. The first version of Sentinel-2 PCA, called RE-SWIR in the paper, was calculated using Vegetation Red Edge (Band 5–7, 8a) and Short-wavelength infrared (Bands 11–12) bands. The second version, called VNIR-SWIR contained also Blue (Band 2), Green (Band 3), Red (Band 4), and Near Infrared (Band 8). The LANDSAT 5 PCA was based on all bands except the thermal infrared (Band 6).
Three versions of PCA of Sentinel-1 data were used. The first, allowed us to calculate two principal components using VV and VH polarisations. The algorithm allowed users to choose ascending or descending directions and different seasonal parameters—wet, dry, whole year, or the difference between dry and wet seasons. All the selected multitemporal SAR images were reduced to median values to decrease the presence of speckle in the images. The second algorithm followed similar principles, but both ascending and descending directions were used to calculate the four principal components. The third version of the PCA combined VV and VH polarisations using ascending or ascending directions in wet and dry seasons.
Tasselled Cap Transformation (TCT) is also a method to reduce the complexity of the multispectral datasets for visualisation. It is calculated by multiplying each spectral band with a matrix of coefficients and reducing the data into wetness, greenness, and brightness bands that are then used as a composite. It was initially developed for the LANDSAT 1 sensor [79,80,81]. The coefficients for Sentinel-2 data are provided by Nedkov [82]. The TCT transformation has been used in archaeological research in some extent for enhancing or extracting features using various types of satellite images [23,83,84,85,86], but its use for studies of irrigation, although not widely adopted, has proven useful in previous research [23,87].
Seasonal Multi-Temporal Vegetation Indices (SMTVI) [23] is a method originally based on the 8-day Enhanced Vegetation Indices calculated from LANDSAT 5 multispectral images. This method involves filtering the data into sets of 60 days (two months) and then combining them into a composite that matches the wet months. In the original studies, the Indian Winter rainy season and Summer Monsoon months were selected for the composite, namely July–August (Day of the Year: 181–240), March–April (DoY: 61–120), and January–February (DoY: 1–60) [23]. By selecting these pairs, the visibility of the channels was enhanced, and even further enhancement occurred when each of the bands was combined into the composite. The SMTVI has been tested several times to detect palaeo-channels [35,88]. Similar approaches were, for instance, successfully applied for the detection of field boundaries [89].
Enhanced Vegetation Indices are not available as a separate dataset for Sentinel-2 imagery. Garcia-Molsosa, Orengo, and Petrie demonstrated in recent studies that the Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) can also be used as a base for SMTVI [35].
In this approach Enhanced Vegetation Indices will be used, which can be calculated using NIR (NIR = B8), Red (R = B5) and Blue (B = B2) bands with following formula by A. Huete [90,91,92]:
where coefficient values are as follows: G = 2.5, C1 = 6.0, C2 = 7.5, L = 1.0.
Normalised Difference Vegetation Seasonality Index (NDVSI) is a method based on the differences between dry and wet seasons using Normalized Vegetation Index calculated from multispectral data. The formula was provided by Orengo and Petrie [23]. The method does not allow to detect palaeo-channels as such, but is primarily used as an indicator where the most significant changes in the vegetation occur, facilitating the selection of seasonal parameters for other methods [87].
Two algorithms exploring possibilities of using composites of Sentinel 1 images have been created. The first algorithm calculated mean values of three seasons (Spring, Summer and Autumn), and allowed to select polarisation (VV or VH) and look angles (ascending or descending). The second algorithm did not divide images into separate seasons, but entire year was used. The composite consisted of VH ascending, VH descending and mean values of both descending and ascending angles of VV polarisation. Additionally, the standard deviation could be calculated.
The Multi-Scale Relief Model (MSRM) is an algorithm for the processing of digital elevation models aiming to increase the visibility of microreliefs at different planar scales. The algorithm was initially designed for the visualisation of palaeorivers and any other structures that present small relief but can extend over large areas. MSRM uses the differences between several sets of smoothed rasters with low-pass filters, adding them together and calculating the mean. The number of smoothed surfaces (rasters) are calculated based on the selected parameters of maximum and minimum size of the features, scaling factor, and the resolution of the DEM [24]. The algorithm is now widely used for microrelief analysis and as part of deep learning workflows employing high-resolution terrain data and is available as plugins for QGIS and ArcGIS and as open code for python and Google Earth Engine’s implementation of JavaScript [35,93].
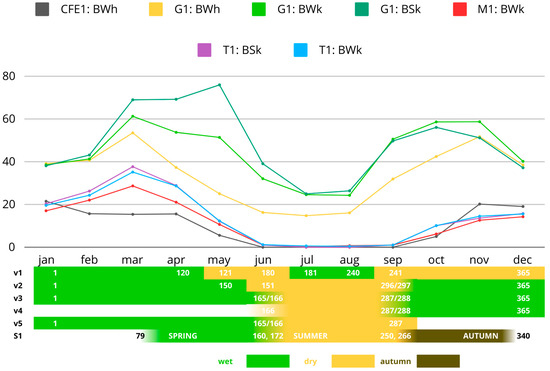
Figure 4.
The versions of seasonal parameters used in the paper compared to OpenLandMap Precipitation Monthly dataset values for each study areas [94].
The landscape of each of the test areas has been examined using MSRM, PCA (LANDSAT 5, Sentinel-1, Sentinel-2), spectral decomposition techniques (TCT), and multitemporal vegetation indices (SMTVI, NDVSI). Different seasonal parameters have been analysed when it was possible (Figure 4).
The digitalisation focused on the features identifiable in the MSRM composite, PCA, SMTVI and Sentinel-1 composites. The MSRM composite was created by combining several rasters calculated using different parameters to detect small (0–250 m), medium (0–500, 250–750 m) and large (500–1000, 1000–5000 m) features. This method was proven useful to enhance the visibility of traces of long-term irrigation, while maintaining the visibility of the gentle relief of modern irrigation. The results were then compared with each other.
3. Results
The studies indicate that seasonal vegetation changes can help detect paleochannels using multitemporal datasets. It was not possible, however, to use a uniform method that could be used in all analysed areas.
In the Central Floodplain of the Euphrates test area (CFE1 (3651 km2)), about 2879.7 km of levees have been mapped, which constitute potential traces of ancient irrigation. Most of them represented lateral canals of medium or small size that were not visible using SRTM (2120 km) [20,48,51,52], 297 km of ravines, which represented the modern course of the Euphrates River and its already-known former beds, have also been mapped.
The test area selected in Iran, Gorgan Plain (G1 (5154 km2)), was particularly rich in traces of former riverbeds and ravines. About 2142 km of levees, 832 km of ravines, and 772 km of rivers and streams have been digitized. Most of the newly digitized levees (1857 km) or ravines (633 km) belong to a dense network of canals and traces of streams in the eastern and northern sectors, which are not visible within CORONA or SRTM data. Additionally, it was possible to correct the shape of some of the previously mapped large palaeo-channels or rivers [53,55].
In Turkmenistan, the area studied in Murghab fan (M1 (5283 km2)) allowed the mapping of 802 km of levees (552 km new ones), 352 km of ravines, and 219 of palaeo-channels. The layout of levees in the Murghab fan was previously studied using SRTM, but its resolution allowed only the detection of the largest ones in the form of polygons, the length of which in the study area can be estimated to be 250 km. The detected ravines and palaeo-channels correspond to features digitized by Cremaschi and Castelli [95], excluding some short lines that were not well visible. Additionally, previously unknown incised palaeo-channels located in the east of the fan were documented.
The second area, the Tedjen Plain (T1 (3176 km2)), contained 1257 km levees (860 km new ones), 625 km ravines (479 km were unknown), and meanders visible in the multitemporal images (255 km). It was also possible to map meander traces inside of the Serakhs oasis, which suggested the existence of branches of the alluvial fan or an alternative route of the river, which was already reported recently, but their layout was schematic [70]. Recent studies indicate that they were preserved differently, partly as ravines, but also as levees or traces visible in the soil.
4. Discussion
The selected methods and seasonal parameters varied in each of the tested areas, most of which can be classified as arid.
The Central Floodplain of the Euphrates (CFE1) levee network is best visible using MSRM composite enhancing small, medium, and large landscape features, and the dry season version of LANDSAT 5 TCT (Figure 4: version 5) (Figure 5). It can be observed that limiting the data so that only the driest available days are available is beneficial, as also suggested by Orengo and Petrie for desertic areas in Northwestern India [23]. The TCT calculated from Sentinel-2 also allowed us to see most of the levees, but the extended, thin levees were difficult to distinguish due to the increasing aridity of the climate. Additionally, fields attached to the main levees impair their visibility, which may be related to the continuation of irrigation during the dry season in recent years.
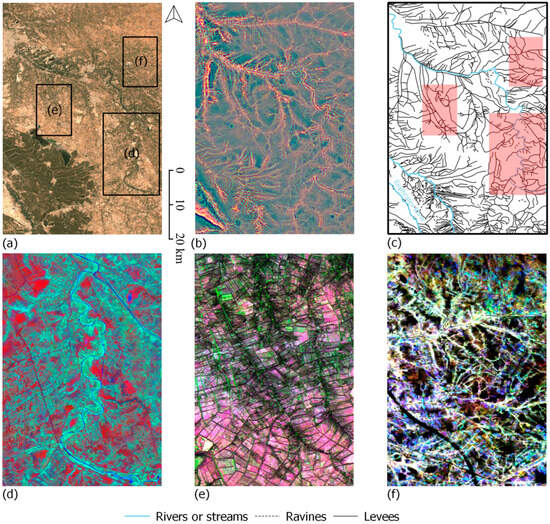
Figure 5.
The Central Euphrates Floodplain (CFE_1): (a): mean annual values of LANDSAT 5 images; (b): composite of three MSRM rasters (0–250, 250–750, 1000–5000); (c): network of levees and Euphrates branches (in blue); (d): LANDSAT 5 TCT dry v5; (e): composite of standard deviation of VH asc, VV, and VH desc bands of Sentinel-1; (f): LANDSAT 5 SMTVI: May–June, July–August, September–October (TanDEM-X 30 m Edited Digital Elevation Model (EDEM).
The Central Floodplain of the Euphrates (CFE1) levee network was also visible using a composite of Sentinel 1 SAR data. The best results have been achieved using the standard deviation of the values and combining these into composite rasters (Figure 5), or seasonal composites based on VH polarisation.
TheSMTVI, consisting of months representing low precipitation conditions (May–June, July–August, September–October), or a combination of late spring and summer months with pre-vegetation season (January–February, May–June, July–August), can be considered useful for mapping levees as well. These conditions allow us to eliminate the months during which fields are covered by crops. Therefore, differences in soil composition or moisture content are more evident, probably because areas closer to canals retain some of the water while those farther away are dry. The use of images from the wet season months causes complete obliteration of any vegetation differences that could indicate the presence of levees (Figure 5), in contrast with the results obtained by Orengo and Petrie [23], where rainy months boosted the visibility of levees as marked by their lower agricultural production compared to surrounding areas.
The hydrologic network of the Gorgan plain (G1) is more visible using MSRM, TCT calculated from LANDSAT 5 data, and composite of Sentinel-1 data (Figure 6). The combination of those methods allowed to map all the key water management features. The analysis indicates, however, that the location of relatively short-term features or features in areas intensively modified in later periods such as some sections of South and North Canals mentioned by Hopper in Gorgan plain (G1) are more difficult to distinguish from the modern ones. Part of the route of those canals are poorly visible in TanDEM-X data (Figure 6) [53].
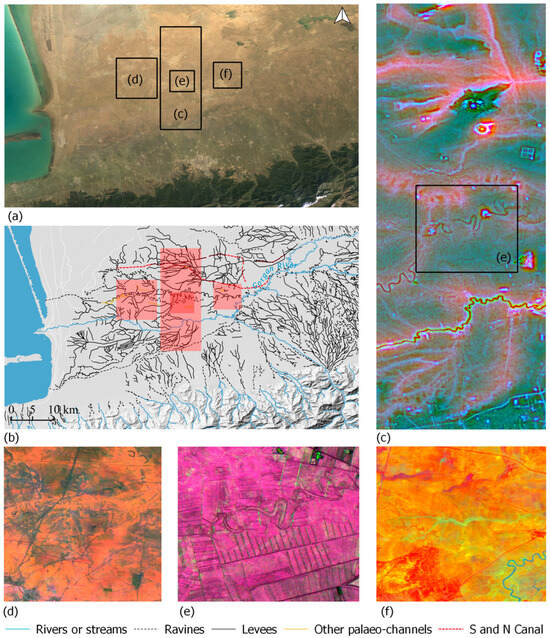
Figure 6.
Gorgan plain (G1): (a): mean annual values of LANDSAT 5 images; (b): network of levees and palaeo-channels; (c): composite of three MSRM rasters (0–250, 250–750, 1000–5000); (d): LANDSAT 5 SMTVI: March-April, May–June, July–August; (e): composite of standard deviation of VH asc, VV, VH desc bands of Sentinel-1; (f): LANDAT 5 TCT wet v1; (© DLR 2022, TanDEM-X Science Digital Elevation Models call (DEM_HYDR3723)).
The custom SMTVI created by March–April, May–June, July–August or September–October combination allowed to delineate large palaeo-channels, levees, and mountain streams. The combination uses the contrast between wet and dry months. Using all wet season months (first half of the year), only main palaeo-channels are visible. When using only dry season months (summer and early autumn), only the main riverbed and modern levees are visible (Figure 6).
The results of the application of TCT in the Gorgan plain were different from those in Iraq (CFE1). The wet version of TCT performed better (Figure 4: version 1). Similarly, LANDSAT 5 TCT outperformed Sentinel-2 significantly due to its higher temporal resolution. The first version of the seasonal parameters presents the best capabilities in this area, which all contained spring months combined with summer (Figure 4: version 1). The second, third, and fifth versions, which combine spring with autumn, have also provided good results (Figure 4: versions 2, 3, 5) (Figure 6).
Since the Gorgan plain (G1) contains fewer levees but the palaeo-channels predominate in the landscape, their visibility was enhanced by VH polarisation. What is more, the VH polarisation enhanced the possibilities of differentiation of modern roads from the palaeo-channels, which is not possible using MSRM. The usage of the VH and VV polarisation as a composite obliterated the visibility of channels located within modern agricultural fields. Nevertheless, using the composite consisting of the standard deviation of the values enhanced the visibility of both modern canals and palaeo-channels in great detail (Figure 6).
The Murghab fan was a particularly interesting case study because Sentinel-2 was more useful than LANDSAT 5 in mapping traces of ancient canals. The most robust method for water management studies is MSRM, and in particular, the composite produced by combining different versions to detect small, medium, and large features (Figure 7). The applied methods were well suited for mapping levees and large palaeo-channels. The small ones were not easily recognized because of the resolution of the Sentinel-2 data. Some of them have also been visible in TanDEM-X data, excluding the smallest ones. Considering that some of the features already recognized in CORONA images have not been detected [95].
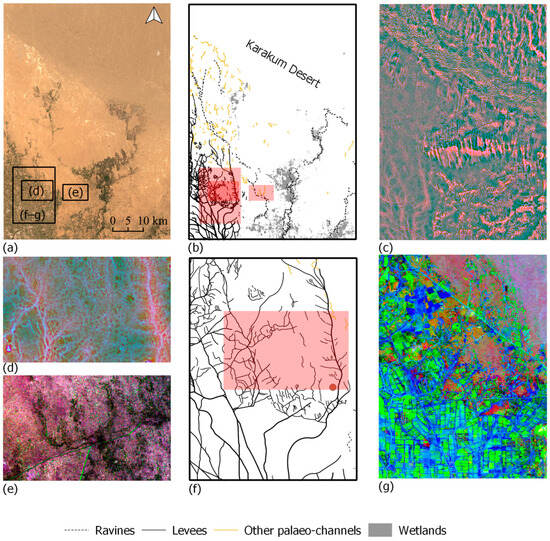
Figure 7.
The eastern part of Murghab fan (M1). (a): mean annual values of Sentinel-2 images; (b,f): network of levees and palaeo-channels; (c,d): composite of three MSRM rasters (0–250, 250–750, 1000–5000); (e): composite of standard deviation of VH asc, VV, and VH desc bands of Sentinel-1; (g): PCA of Sentinel-2 RE-SWIR bands (components 2, 3, and 4) (© DLR 2022, TanDEM-X Science Digital Elevation Models call (DEM_HYDR3723)).
Murghab’s fan TCT image helped to locate main levees, which were visible using the dry season version of the algorithm (Figure 4: version 5). The Sentinel-2 TCT provided better results in the case of the Murghab fans, because the main levees became more visible in recent years, most possibly because of the increased aridity. Their presence can also be observed using the PCA of the RE-SWIR Sentinel-2 bands (Figure 7).
No significant palaeo-channels or levees could be observed with SMTVI using LANDSAT 5. However, Sentinel-2 SMTVI was able to detect main levees in the southern part of the fan, but their visibility was low. The best SMTVI combination represented the dry months (May–June, July–August and September–October) or the combination of dry months with the pre-vegetation season (January–February, May–June, July–August). The area as shown by LANDSAT 5 seemed to have been better irrigated all the years before 2013 thanks to the water from the Karakum Canal, causing vegetation differences to correspond mostly to modern agriculture. At the same time, the northern part of the studied area was deserted, so many of the palaeo-channels could not be detected. The Sentinel-2 data are more recent and have a better spectral and spatial resolution, which makes it possible to detect soil differences associated with the main levees and some partially activated palaeo-channels (Figure 7).
The use of Sentinel-1 PCA, which includes all angles and polarisations, helped to enhance the topography in the deserted parts of the oasis and improve the visibility of the modern canals. The visibility of canals located in the desert, partially activated by modern irrigation or those with a clear relief of the terrain, was improved.
The area located between Serakhs and Geoksyur oases (T1) is best visualised using MSRM and the dry version of the TCT (Figure 8). The Sentinel-2 version of TCT has similar usability as LANDSAT 5, but the LANDSAT 5 version of TCT allows for more analysis of the preserved landscape, particularly the version that uses the summer months as a data source (Figure 4: versions 2–5). The first version of dry TCT uses summer and autumn, so similarly to SMTVI, the mixture of dates is wet and dry. On the other hand, the second, third, and fourth provide a cleaner representation of dry months (Figure 4). It seems it performs better because despite the vegetation, TCT considers brightness and wetness, which beneficial when vegetation is lacking.
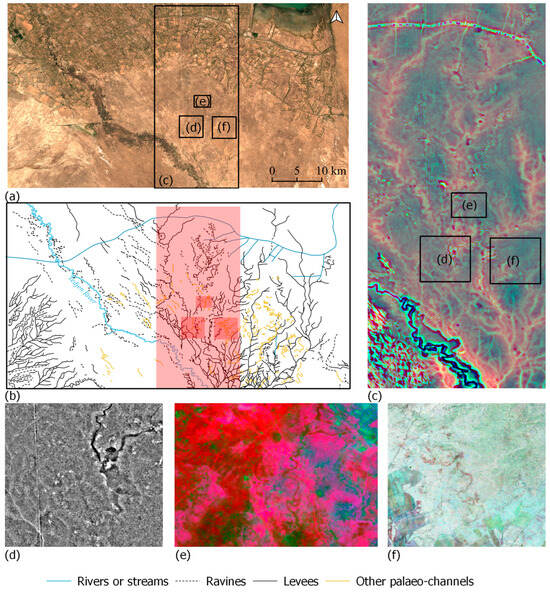
Figure 8.
The area between Serakhs and Geoksyur oases (T1). (a): mean annual values of Sentinel-2 images; (b): network of levees and palaeo-channels; (c): Composite of three MSRM rasters (0–250, 250–750, 1000–5000); (d): MSRM (0–250); (e): Sentinel-2 TCT dry v1; (f): Seasonal composite of VH band in desc polarization of Sentinel-1 (© DLR 2022, TanDEM-X Science Digital Elevation Models call (DEM_HYDR3723).
The LANDSAT 5 data performs better than Sentinel-2; however, some features are more visible using Sentinel-2. It can be assumed that this is related to the increasing aridity of the landscape and the better resolution of the imagery. The best SMTVI combination involves wet and dry (March-April, May-June, July-August), or pre-vegetation, wet and dry (January-June). The dry months significantly reduce the visibility of most of the irrigation canals, but only the main levees and some former riverbeds are visible (Figure 8).
The composite of VH polarisation enhanced differences in ground moisture, which helped confirm the location of some of the meanders located in the southern part of the study area and revealed a few new ones. Some of the detected channels have clear representation in the relief of the terrain, but some of the areas are almost flat, which makes them difficult to locate using TanDEM-X. The results of the analysis indicate that VV polarisation can be used to spot topographic differences in areas where detailed DSM data are missing. The full applicability of those methods can be achieved in areas where the vegetation is sparse (Figure 8).
The visibility of the canals and natural palaeo-channels using multitemporal satellite images in each study area differed because of the ancient and modern land use, types of water management, and modern climate. The Central Floodplain of Euphrates (CFE1) and Murghab fan (M1) areas have undergone intensive landscape modifications due to long-term irrigation and modern land use. The Murghab River’s terminal fan contains natural paleochannels visible to the north of the study areas. The Gorgan plain (G1) receives sufficient precipitation in the southern part but is arid in the north. It contains numerous traces of past riverbeds of the Gorgan River, partially transformed into canals, and areas intensively used for irrigation. The southern part also contains small fans created by streams with gullies (ravines) due to the dynamic nature of their riverbeds and higher slope. The area located between Serakhs and Geoksyur oasis (T1) is likely to contain traces of natural branches of the Tedjen terminal fan and is entirely deserted. The southwestern part of the area also contains small alluvial cones created by streams, similar to the landscapes in the southern part of the Gorgan plain, with many gullies and canals.
Comparing all the areas revealed that MSRM, and in particular its composites, constitutes the most reliable method because it allows the detection of features of different sizes: main watercourses, meanders, cut-offs, and levees. What is more, the use of TanDEM-X allowed the mapping of the water courses in unprecedented detail. However, this method, as most applications of SAR in this study are based on microtopographic analysis, can leave out traces that do not present any relief. Therefore, its use should be complemented by one of those methods using multispectral data, which are more dependent on specific climatic and environmental conditions. Tasseled Cap Transformation seems to be another universal method; however, its applicability varies from area to area. Some areas required TCT calculated from the images corresponding to the wet season (G1), while others required dry TCT (CFE 1, M1, T1), or a mixture of both (T1).
It is possible to use SMTVI combinations to detect palaeo-channels, but its applicability differs from Northwestern India because the original composite consisted of rainy season months [23,34,35], while in the areas studied in this paper, it is the combination of dry and wet months similarly to [96]. This is due to the different climates of the areas (Figure 1, Figure 2, Figure 3 and Figure 4). Northwestern India presented a wet environment where extended agriculture was practiced. The 28 years of LANDSAT 5 data were able to reflect small changes in agricultural productivity linked to grainer soil in the proximal part of levees. None of the study areas under investigation presented identical conditions. The analyses indicate that using three pairs of dry months or a combination of wet and dry months can increase the visibility of the features studied in those areas where there is no significant vegetation (T1) or areas with higher precipitation (G1). The palaeo-channels and large modern canals appeared as darker lines in the G1 and T1 areas. Levees and the direct surroundings of the large palaeo-channels had brighter colours in G1. A few examples of meander-shaped features had a brighter colour than the background (T1). The areas covered by modern fields can be mostly studied using images selected from the dry season (CFE1 and M1) when the fields are not covered by crops. In those cases, all the detected levees were brighter than the background. Modern rivers and palaeo-channels were darker, which is typical for modern rivers and ancient palaeo-channels in Northwestern India [23,34,35].
Analysis of the NDVSI index calculated from multispectral data indicates that vegetation differences, as demonstrated in Northwestern India, do not play an importance role in all analysed areas [23,35]. An example of such areas is the Central Floodplain of the Euphrates (CFE1) and Murghab’s fan (M1), which are related to the characteristics of water-related features and the fact that they are significantly modified by irrigation. In both areas, levees dominate, which can be as the analysis suggests, detected by their ability to preserve moisture during the dry season. Gorgan plain on the other hand, is dominated by meander-shaped palaeo-channels, which differ in the quality of vegetation and can be analysed when the dry and wet seasons are compared. The last area, which is located between Serakhs and Geoksyur oases (T1), seems to indicate that vegetation can be used to some extent for the detection of palaoe-channels. In this situation, moisture and vegetation reveal different layers of the landscape.
Even though PCA can be used universally, the results cannot be directly compared. It is proven helpful to locate palaeo-channels in other areas and to explore the visibility of main landscape features, such as wetlands, deserts, urban areas, and irrigated plots [23,34,35]. In the case of the areas under study, PCA is mostly allowed to map large palaeo-channels or modern active canals. The best results of the PCA methods were obtained in the cases of the Murghab fan (M1) and the Central Floodplain of Euphrates (CFE1). Comparison of PCA and MSRM results revealed large levees that were not visible in RGB satellite imagery. The size of the visible features suggested the presence of significant soil differences caused by long-term irrigation. It was not possible to use the same method to map smaller canals, as many of those detected in PCA only represented the modern irrigation network, while those once visible in MSRM were often absent in PCA. Furthermore, as PCA is a non-parametric method depending on the band values in the specific region under analysis, it is not possible to use the same colour schemes or combinations in different datasets. For example, in the M1 area, a composite of the 2, 3, and 4 principal components of the RE-SWIR bands identified large levees. In the case of CFE1, the 1, 2, and 3 principal components were useful for the RE-SWIR and VNIR-SWIR versions of PCA. The application of PCA based on Sentinel-2 data to the northern edge of the Serakhs Oasis (T1) and the Gorgan Plain (G1) was less useful but allowed to delineate the extent of the river’s current floodplain or the area covered by modern irrigation. The visibility of the inactive river traces was much poorer than the results from the M1 and CFE1 study areas.
The PCA method was also used to process the Sentinel 1 SAR data. Three versions were used. The analysis performed did not allow for improved mapping of levees. The only exception can be the Murghab fan (M1), where PCA calculated all directions and polarisation types, allowing to improve the relief of the desert and trace some of the palaeo-channels. The result of using PCA calculated from Sentinel 1 imagery was rather negative for most areas.
Better results were obtained by combining different polarisations or scanning directions in the form of composites. The VH band enhanced differences in moisture content, which allowed for the detection of canals when a composite of three seasons was used. In this way, some of the most important levees were detected in CFE1 or palaeo-channels in G1. However, the VH band works better in areas where there is no modern infrastructure, as the results from the T1 and M1 areas suggest.
The use of VV polarisation was problematic because it significantly improved the visibility of modern canals and urban areas. The visibility of irrigation features depended on the direction of scanning and the orientation of the irrigation network. For instance, in Gorgan Plain (G1), the river is oriented on an east-west axis, while the orthogonal irrigation network is inclined towards the northwest. Therefore, the descending angle enhanced the visibility of plowing patterns and modern canals, while the ascending one showed modern canals and some major palaeo-channels. In Murghab, the ascending direction amplified the visibility of sand dunes and palaeo-channels located in the desert, as they were oriented on the north-south axis. Major ancient levees, although sharing a similar orientation, were masked by modern orthogonal irrigation. In the case of the Central Euphrates Floodplain (CFE1), the irrigation network was oriented towards the south-east. All SAR scanning directions for VV polarisation impede the visibility of irrigation levees because the modern canal system has a large density. On the other hand, the T1 area had little modern infrastructure, so enhancing the visibility of features of different orientations had a positive impact. The composite of VV and VH can be another good method in areas where there is no modern infrastructure, as the VV band improves the visibility of the relief of the terrain while VH moisture content. It can be used when there is no access to a good-quality DEM. The composite of the standard deviation of the VV and VH bands, which emphasises all seasonal changes, is another good alternative.
In summary, of the methods tested in the study, only custom combinations of SMTVI bands and TCT have the potential to analyse seasonal differences in vegetation and moisture in different areas—modified by modern agriculture or deserted ones. The methods based on Sentinel-1 data can only be used in desert areas where there are no urban areas. The analysis should be supplemented by studying the local relief of the terrain (MSRM).
The analysis suggests that the weakness of using single methods to detect palaeo-channels or canals is the difficulty of recognizing modern from older elements of the landscape. Using multiple methods, we can compare the visibility of the feature based on the amount of moisture, vegetation, type of soil, or topography. The multitemporal dataset also enhances the visibility of more prominent features barely visible in topography because mean and median values homogenize differences between fields covered with crops in different seasons or years.
It should be noted that methods do not directly point to ancient canals as such or provide their dating, but rather, comparison of different sources allows to reveal different layers of the landscape. Field studies, geomorphological research, and absolute dating are needed to prove the existence of ancient irrigation features. Moreover, palaeo-channels and canals are preserved differently in the landscape because of the different factors that can mask or erase them [21].
5. Conclusions
The proposed methods can complement the standard tools used to study irrigation networks in arid areas, such as the analysis of CORONA or the SRTM digital elevation model [18,52,97,98,99]. The present research also indicates that they bring much better results than the analysis of single-look images. The multitemporal vegetation differences method can be applied to areas heavily modified by modern agriculture, particularly if good-quality archival images are missing. It should be taken into account, however, that the data’s resolution will only allow the medium and large palaeo-channels and levees to be mapped. The studies also confirm that analysing local relief of terrain, such as MSRM [24], gives better results than viewing the raw data [100,101] because it allows the visualisation of the entire layout of the irrigation network. In addition, although TanDEM-X is a digital surface model, it provides much better analysis capabilities than SRTM. One reason is that it has a better resolution, higher quality, and no oblique distortions, which need to be removed before any automatic calculations can be applied [102].
The research shows that although the majority of the study areas represent arid climates, it was not possible to distinguish a single method for detecting canals and palaeo-channels. There are many factors that make each landscape different. Most of the landscape types studied are alluvial plains, but there are also piedmont areas where streams and gullies are more common, such as the southern parts of G1 and the south-western parts of T1. The second key factor is modern land use practices, the stability of the water supply, and the presence or absence of annual vegetation trends.
The largest differences have been observed between G1 and T1 landscapes, even though both contain traces of numerous former riverbeds. The Gorgan area (G1) is intensively modified by modern agriculture and has more precipitation. The area between the oases of Serakhs and Geoksyur (T1) is very dry, with little vegetation or relief variability.
The topography and differences in vegetation make it possible to locate the main palaeo-channels in G1 and T1 with MSRM when TanDEM-X is used. Wet season TCT is more appropriate for G1 areas, and dry TCT for T1. Both areas were studied using the composite of standard deviation values calculated from Sentinel-1 images. The visibility of palaeo-channels was less effective using a custom combination of SMTVI [96], but it could still be used.
The southern and western parts of the Murghab (M1) and the Central Floodplain of the Euphrates (CFE1) have many things in common. Both developed a strong irrigated relief of the terrain and were significantly modified by modern irrigation. The eastern part of the M1 study area is covered by dunes like T1, but with several wetlands created by modern canal leaks, which are exceptional in comparison to other tested areas. Both areas are linked by the presence of distinctive levee patterns, which are sparse in the G1 and T1 areas. Both M1 and CFE1 were studied mostly using MSRM and dry-season TCT, while other methods had a minor impact on canal detection.
Almost all studied examples showed that LANDSAT 5 is a better source of data for the detection of water management features than Sentinel-2 because it has a larger temporal coverage [35]. Sentinel-2 mean values nevertheless prove highly valuable for landscapes experiencing increased drought conditions in recent years, which exposed soil differences or capabilities to store more moisture. The best results were achieved by combining several methods and comparing the visible features, as demonstrated in the T1 case study.
The results show that even areas entirely covered by modern agriculture contain differences in microrelief and soil that cause different moisture preservation capabilities, which can expose the location of prominent levees in specific seasons. That can help locate areas of long-term irrigation, which may reflect the location of ancient canals.
The implications of this research can be extended to ancient irrigation studies of areas with similar environmental conditions, such as, for instance, the delta of the Amu Darya River, river fans, and alluvial plains located in Uzbekistan, Afghanistan, Armenia, or Southern Mesopotamia. The presented methods are particularly useful in areas without modern land use and with limited accessibility to high-resolution DSM. Nevertheless, the presence of modern crops should not be an obstacle if the mean or median values are calculated from several years of data because it is still possible to detect large or medium-sized features. The application of the proposed workflow in other areas should include initial studies of the landscape and its modern environmental characteristics (Table 1; Figure 4). This will ensure the selection of more appropriate days of the year representing dry or wet seasons in a specific area, which are used for filtering the image collections in GEE.
The main limitation of the present research, as with all studies based on satellite imagery, is that the dating of the palaeo-channels and canals identified is not known. Some of the features may be important from an archaeological point of view, as they may have functioned during periods of archaeological interest. Others could be modern or, on the contrary, could have been formed in the early Holocene or earlier. Therefore, it is necessary to verify them in the field, excavate, and apply absolute dating. Secondly, the possibility of detecting palaeo-channels and canals is based on the seasonal growth of vegetation, which requires regular and repeated analyses at certain times of the year, regardless of the agricultural cycle of sowing, harvesting, and fallowing. This means that the above-mentioned features (palaeo-channels and canals) must contain the moisture that ensures this vegetation growth. This can come from rain, irrigation, or run-off flooding. In the case of extremely deserted areas, precipitation rarely occurs, so other methods may be more reliable, such as archival imagery or SAR. Lastly, the application of modern multisource imagery might have limitations in detecting older water management features because of an intensive modification of the landscape or differentiation between modern water spills in the desert and the ancient palaeo-channels. Another important limitation is the spatial resolution of the data. Taking the example of the M1 area, it is clear that some of the features, such as small paleochannels, might be already destroyed, or the resolution is not enough to detect them. Therefore, we could not digitize all of them using Sentinel-2 data. In this situation, it is necessary to compare the results to local relief of terrain (MSRM) and particularly archival imagery, such as CORONA or HEXAGON [98,103].
Given the variability in the shape and visibility of the features, no automated method was employed for mapping water-related structures in this study. However, the research results will be used for further studies on the water management of arid areas. We hope to develop deep learning-based automatic detection methods that can be applied to selected types of landscapes and feature types. Not all water management features were mapped, such as qanat shafts, which were located in Gorgan plain (G1). However, future research will incorporate CNN-based object detection methods for the location of features showing repetitive and clearly defined shapes.
Supplementary Materials
The SMTVI, TCT, NDVSI, and PCA algorithms have been published in Orengo and Petrie 2017 [23] and are available under Open Access conditions. The modified versions used in this paper are available at the following links: https://github.com/horengo/Orengo_Petrie_2017_RS (accessed on 20 September 2022). The MSRM algorithm has been published in [24]. The modified version is available here: https://github.com/horengo/Orengo_Petrie_2018_MSRM (accessed on 15 December 2022). The code for the PCA method for Sentinel 1 data and the composites are available here: https://github.com/horengo/Bulawka_Orengo_2024_RS (accessed on 11 April 2023).
Author Contributions
N.B. wrote the paper with the collaboration of H.A.O. N.B. conducted the investigation and created illustrations. H.A.O. designed the algorithms. N.B. customized the algorithms for the studied areas. H.A.O. supervised the project. H.A.O. and N.B. designed the project and obtained funding for its development. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by HORIZON EUROPE Marie Sklodowska-Curie Actions project “UnderTheSands: Ancient irrigation detection and analysis using advanced remote sensing methods” (HORIZON-MSCA-2021-PF-01-101062705). The TanDEM-X 12 m was made available through the German Aerospace Center (Deutsches Zentrum für Luft- und Raumfahrt, DLR) Science Digital Elevation Models call DEM_HYDR3723.
Data Availability Statement
This paper presents a combination of (i) publicly accessible remote sensing imagery and (ii) commercially available digital elevation data that is not publicly accessible. (iii) The results of the analysis were carried out using open-access algorithms. The remote sensing imagery (NASA Landsat 5; European Space Agency Sentinel 2 and Sentinel 1) is freely available via Google Earth Engine and other platforms. The TanDEM-X digital elevation model data has been provided by the German Aerospace Center (Proposal ID: DEM_HYDR3723) and is not open access. All relevant algorithms have been made available as Supplementary Materials.
Acknowledgments
We would like to deeply thank Kristen Hopper, Barbara Cerasetti, Barbara Kaim, and Jaafar Jotheri for the comparative irrigation data and the possibility of working in the study areas, and Arnau Garcia-Molsosa, Alfredo Mayoral, and Francesc Conesa for consultations and feedback. We are extremely grateful to Thomas Busche and the German Aerospace Center (DLR) for providing the TanDEM-X, which was awarded under the Science Digital Elevation Models call DEM_HYDR3723.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Bazza, M. Overview of the History of Water Resources and Irrigation Management in the Near East Region. Water Supply 2007, 7, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rost, S. Introduction. In Irrigation in Early States New Directions; Rost, S., Ed.; Oriental Institute of the University of Chicago: Chicago, IL, USA, 2022; pp. ix–xxvi. ISBN 978-1-61491-071-8. [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson, T.J. Landscape of Irrigation. In Archaeological Landscapes of the Near East; University of Arizona Press: Tucson, AZ, USA, 2003; pp. 71–99. ISBN 0-8165-2173-5. [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson, T.J.; Rayne, L. Hydraulic Landscapes and Imperial Power in the Near East. Water Hist. 2010, 2, 115–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, T.J.; Rayne, L.; Jotheri, J. Hydraulic Landscapes in Mesopotamia: The Role of Human Niche Construction. Water Hist. 2015, 7, 397–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrower, M.J. Is the Hydraulic Hypothesis Dead yet? Irrigation and Social Change in Ancient Yemen. World Archaeol. 2009, 41, 58–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagg, A.M. Irrigation. In A Companion to the Archaeology of the Ancient Near East: Volume I; Potts, D.T., Ed.; Wiley-Blackwell: Chichester, UK, 2012; pp. 261–278. [Google Scholar]
- Cole, S.W.; Gasche, H. Second and First Millennium B.C. Rivers in Northern Babylonia. In Changing Watercourses in Babylonia. Towards a Reconstruction of the Ancient Environment in Lower Mesopotamia; Gasche, H., Tanret, M., Eds.; Mesopotamian History and Environment, Series II, Memoirs, V. 5; University of Ghent: Ghent, Belgium; Oriental Institute Publications: Chicago, IL, USA, 1998; pp. 1–64. [Google Scholar]
- Madella, M.; Lancelotti, C. Archaeobotanical Perspectives on Water Supply and Water Management in the Indus Valley Civilization. In Irrigation in Early States New Directions; Rost, S., Ed.; The University of Chicago: Chicago, IL, USA, 2022; pp. 113–136. ISBN 978-1-61491-071-8. [Google Scholar]
- Oates, D.; Oates, J. Early Irrigation Agriculture in Mesopotamia. In Problems in Economic and Social Archaeology; Sieveking, G., de, G., Longworth, I.H., Wilson, K.E., Eds.; Duckworth: London, UK, 1976; pp. 109–135. [Google Scholar]
- Helbaek, H. Ecological Effects of Irrigation in Ancient Mesopotamia. Iraq 1960, 22, 186–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charles, M.P.; Hoppé, C. The Effects of Irrigation on the Weed Floras of Winter Cereal Crops in Wadi Ibn Hamad (Southern Jordan). Levant 2003, 35, 213–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, E.; Jamjoum, K.; Nuimat, S.; Stafford, R.; Nortcliff, S.; Mithen, S. Identifying Ancient Water Availability through Phytolith Analysis: An Experimental Approach. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2016, 73, 82–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farquhar, G.D.; Richards, R. Isotopic Composition of Plant Carbon Correlates with Water—Use Efficiency of Wheat Genotypes. Aust. J. Plant Physiol. 1984, 11, 539–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albarella, U.; Dobney, K.; Ervynck, A.; Rowley-Convy, P. (Eds.) Pigs and Humans: 10,000 Years of Interaction; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2007; ISBN 978-0-19-920704-6. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, N.F.; Zeder, M.A.; Arter, S.R. From Food and Fuel to Farms and Flocks: The Integration of Plant and Animal Remains in the Study of the Agropastoral Economy at Gordion, Turkey. Curr. Anthropol. 2009, 50, 915–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, T.J.; Jotheri, J. The Origins of Levee and Levee-Based Irrigation in the Nippur Area—Southern Mesopotamia. In Cycles and Stages in Jeeps and Passats: Studies in the Ancient Near East in Honour of McGuire Gibson; Altaweel, M., Hritz, C., Eds.; University of Chicago Oriental Institute: Chicago, IL, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Richason, B.F.; Hritz, C. Remote Sensing and GIS Use in the Archaeological Analysis of the Central Mesopotamian Plain. In Remote Sensing in Archaeology; Wiseman, J., El-Baz, F., Eds.; Interdisciplinary Contributions To Archaeology; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2007; pp. 283–325. ISBN 978-0-387-44453-6. [Google Scholar]
- Eger, A.A. The Swamps of Home : Marsh Formation and Settlement in the Early Medieval Near East. J. East. Stud. 2011, 70, 55–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jotheri, J. Recognition Criteria for Canals and Rivers in the Mesopotamian Floodplain. In Water Societies and Technologies from the Past and Present; Zhuang, Y., Altaweel, M., Eds.; UCL Press: London, UK, 2018; pp. 111–126. ISBN 978-1-911576-71-6. [Google Scholar]
- Buławka, N.; Kaim, B. The Iron Age in Serakhs Oasis (Turkmenistan). The Preliminary Results of the Application of Geographic Information System in the Study of the Settlement Pattern of the Earliest Confirmed Occupation of the Oasis. In Proceedings of the CAA 2015. Keep The Revolution Going Proceedings of the 43rd Annual Conference on Computer Applications and Quantitative Methods in Archaeology; Campana, S., Scopigno, R., Carpentiero, G., Cirillo, M., Eds.; Archaeopress: Oxford, UK, 2016; Volume 2, pp. 791–801. [Google Scholar]
- Gorelick, N.; Hancher, M.; Dixon, M.; Ilyushchenko, S.; Thau, D.; Moore, R. Google Earth Engine: Planetary-Scale Geospatial Analysis for Everyone. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 202, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orengo, H.A.; Petrie, C.A. Large-Scale, Multi-Temporal Remote Sensing of Palaeo-River Networks: A Case Study from Northwest India and Its Implications for the Indus Civilisation. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orengo, H.A.; Petrie, C.A. Multi-Scale Relief Model (MSRM): A New Algorithm for the Visualization of Subtle Topographic Change of Variable Size in Digital Elevation Models. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2018, 43, 1361–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Driscol, J.; Sarigai, S.; Wu, Q.; Chen, H.; Lippitt, C.D. Google Earth Engine and Artificial Intelligence (AI): A Comprehensive Review. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Yu, L.; Li, X.; Peng, D.; Zhang, Y.; Gong, P. Progress and Trends in the Application of Google Earth and Google Earth Engine. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amani, M.; Ghorbanian, A.; Ahmadi, S.A.; Kakooei, M.; Moghimi, A.; Mirmazloumi, S.M.; Moghaddam, S.H.A.; Mahdavi, S.; Ghahremanloo, M.; Parsian, S.; et al. Google Earth Engine Cloud Computing Platform for Remote Sensing Big Data Applications: A Comprehensive Review. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2020, 13, 5326–5350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldblatt, R.; You, W.; Hanson, G.; Khandelwal, A. Detecting the Boundaries of Urban Areas in India: A Dataset for Pixel-Based Image Classification in Google Earth Engine. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidhu, N.; Pebesma, E.; Câmara, G. Using Google Earth Engine to Detect Land Cover Change: Singapore as a Use Case. Eur. J. Remote Sens. 2018, 51, 486–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boothroyd, R.J.; Williams, R.D.; Hoey, T.B.; Barrett, B.; Prasojo, O.A. Applications of Google Earth Engine in Fluvial Geomorphology for Detecting River Channel Change. WIREs Water 2021, 8, e21496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aman, M.A.; Chu, H.-J. Long-Term River Extent Dynamics and Transition Detection Using Remote Sensing: Case Studies of Mekong and Ganga River. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 876, 162774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Tang, Q. Meandering Characteristics of the Yimin River in Hulun Buir Grassland, Inner Mongolia, China. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langhorst, T.; Pavelsky, T. Global Observations of Riverbank Erosion and Accretion from Landsat Imagery. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2023, 128, e2022JF006774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, A.; Orengo, H.; Conesa, F.; Green, A.; Petrie, C. Remote Sensing and Historical Morphodynamics of Alluvial Plains. The 1909 Indus Flood and the City of Dera Ghazi Khan (Province of Punjab, Pakistan). Geosciences 2019, 9, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Molsosa, A.; Orengo, H.A.; Petrie, C.A. Reconstructing Long-Term Settlement Histories on Complex Alluvial Floodplains by Integrating Historical Map Analysis and Remote-Sensing: An Archaeological Analysis of the Landscape of the Indus River Basin. Herit. Sci. 2023, 11, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orengo, H.A.; Conesa, F.C.; Garcia-Molsosa, A.; Lobo, A.; Green, A.S.; Madella, M.; Petrie, C.A. Automated Detection of Archaeological Mounds Using Machine-Learning Classification of Multisensor and Multitemporal Satellite Data. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 18240–18250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liss, B.; Howland, M.D.; Levy, T.E. Testing Google Earth Engine for the Automatic Identification and Vectorization of Archaeological Features: A Case Study from Faynan, Jordan. J. Archaeol. Sci. Rep. 2017, 15, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agapiou, A. Detecting Looting Activity through Earth Observation Multi-Temporal Analysis over the Archaeological Site of Apamea (Syria) during 2011–2012. J. Comput. Appl. Archaeol. 2020, 3, 219–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fattore, C.; Abate, N.; Faridani, F.; Masini, N.; Lasaponara, R. Google Earth Engine as Multi-Sensor Open-Source Tool for Supporting the Preservation of Archaeological Areas: The Case Study of Flood and Fire Mapping in Metaponto, Italy. Sensors 2021, 21, 1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agapiou, A. Remote Sensing Heritage in a Petabyte-Scale: Satellite Data and Heritage Earth Engine© Applications. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2017, 10, 85–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elfadaly, A.; Abutaleb, K.; Naguib, D.M.; Lasaponara, R. Detecting the Environmental Risk on the Archaeological Sites Using Satellite Imagery in Basilicata Region, Italy. Egypt. J. Remote Sens. Space Sci. 2022, 25, 181–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lepori, M.; Zamora, D. Análisis espacial mediante Google Earth Engine para el estudio y comprensión de las vías de circulación entre la Puna y los Valles Altos catamarqueños. Relaciones 2023, 48, e051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conesa, F.C.; Orengo, H.A.; Lobo, A.; Petrie, C.A. An Algorithm to Detect Endangered Cultural Heritage by Agricultural Expansion in Drylands at a Global Scale. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubel, F.; Kottek, M. Observed and Projected Climate Shifts 1901–2100 Depicted by World Maps of the Köppen-Geiger Climate Classification. Meteorol. Z. 2010, 19, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- New, M.; Lister, D.; Hulme, M.; Makin, I. A High-Resolution Data Set of Surface Climate over Global Land Areas. Clim. Res. 2000, 21, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zomer, R.J.; Xu, J.; Trabucco, A. Version 3 of the Global Aridity Index and Potential Evapotranspiration (ET0) Climate Database. Sci. Data 2022, 9, 409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yaseen, Z.M.; Sulaiman, S.O.; Sharif, A. The Nature of Tigris–Euphrates Rivers Flow: Current Status and Future Prospective. In Tigris and Euphrates Rivers: Their Environment from Headwaters to Mouth; Jawad, L.A., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 229–242. ISBN 978-3-030-57569-4. [Google Scholar]
- Adams, R.M. Heartland of Cities. Surveys of Ancient Settlement and Land Use on the Central Floodplain of the Euphrates; University of Chicago Press: Chicago, IL, USA; London, UK, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Adamo, N.; Al-Ansari, N. In Old Babylonia: Irrigation and Agriculture Flourished Under the Code of Hammurabi (2000–1600 BC). J. Earth Sci. Geotech. Eng. 2020, 10, 41–57. [Google Scholar]
- van Soldt, W. Irrigation in Kassite Babylonia. Bull. Sumer. Agric. 1988, 4, 105–120. [Google Scholar]
- Jotheri, J.; Allen, M.B.; Wilkinson, T.J. Holocene Avulsions of the Euphrates River in the Najaf Area of Western Mesopotamia: Impacts on Human Settlement Patterns. Geoarchaeology 2016, 31, 175–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altaweel, M.; Marsh, A.; Jotheri, J.; Hritz, C.; Fleitmann, D.; Rost, S.; Lintner, S.F.; Gibson, M.; Bosomworth, M.; Jacobson, M.; et al. New Insights on the Role of Environmental Dynamics Shaping Southern Mesopotamia: From the Pre-Ubaid To the Early Islamic Period. Iraq 2019, 81, 23–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopper, K. The Gorgan Plain of Northeast Iran: A Diachronic Analysis of Settlement and Land Use Patterns Relating to Urban, Rural and Mobile Populations on a Sasanian Frontier. Doctoral Thesis, Durham University, Durham, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Kehl, M. Quaternary Climate Change in Iran—The State of Knowledge. ERDKUNDE 2009, 63, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, T.J.; Rekavandi, H.O.; Hopper, K.; Priestman, S.; Roustaei, K.; Galiatsatos, N. The Landscapes of the Gorgān Wall. In Persia’s Imperial Power in Late Antiquity: The Great Wall of Gorgān and Frontier Landscapes of Sasanian Iran; Sauer, E., Omrani Rekavandi, H., Wilkinson, T.J., Nokandeh, J., Eds.; British Institute of Persian Studies Archaeological Monographs Series; Oxbow Books: Oxford, UK, 2013; pp. 24–132. [Google Scholar]
- Salvatori, S.; Tosi, M.; Cerasetti, B. The Archaeological Map of the Murghab Delta. Studies and Reports. In The Bronze Age and Early Iron Age in the Margiana Lowlands: Facts and Methodological Proposal for a Redefinition of the Research Strategies; BAR International Series 1806; Archaeopress: Oxford, UK, 2008; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Dolukhanov, P.M. The Ecological Prerequisities for Early Farming in Southern Turkmenia. In The Bronze Age Civilization of Central Asia. Recent Soviet Discoveries; Kohl, P.L., Ed.; Sharpe: New York, NY, USA, 1981; pp. 359–385. [Google Scholar]
- Šul’c, V.L. Reki Srednej Azii. Časti I i II; Gidrometeoizdat: Leningrad, Russia, 1960. [Google Scholar]
- Orlovsky, N.S. Climate of Turkmenistan. In Biogeography and Ecology of Turkmenistan; Fet, V., Atamuradov, K.I., Eds.; Monographiae Biologicae, 77; Springer Science/Business Media: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1994; pp. 23–48. [Google Scholar]
- Efremov, K.F.; Lavronenko, O.S.; Sarkisov, M.M. The V. I. Lenin Karakum Canal in the Turkmen SSR. Hydrotech. Constr. 1970, 4, 346–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zonn, I.S. Karakum Canal: Artificial River in a Desert. In The Turkmen Lake Altyn Asyr and Water Resources in Turkmenistan; Zonn, I.S., Kostianoy, A.G., Eds.; The Handbook of Environmental Chemistry 28; Springer: Heidelberg, Germany; New York, NY, USA; Dordrecht, The Netherlands; London, UK, 2014; pp. 95–106. [Google Scholar]
- Lyonnet, B.; Dubova, N.A. Questioning the Oxus Civilization or Bactria-Margiana Archaeological Culture (BMAC). In The World of the Oxus Civilization; Lyonnet, B., Dubova, N.A., Eds.; Routledge Worlds; Routledge: London, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2020; pp. 7–65. [Google Scholar]
- Dal Pozzo, A.; Immordino, F.; Candigliota, E. Remote Sensing Multitemporal Data for Geomorphological Analysis of the Murghab Alluvial Fan in Turkmenistan. J. Earth Sci. Eng. 2017, 7, 55–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buławka, N. Osadnictwo Kultury Jaz w Oazach Tedżenu i Murgabu w Turkmenistanie. The Settlement of Yaz Culture in the Oases of Tedjen and Murghab in Turkmenistan. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Warsaw, Warszawa, Poland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Cremaschi, M. Palaeohydrography and Middle Holocene Desertification in the Northern Fringe of the Murghab Delta. In The Archaeological Map of the Murghab Delta: Preliminary Reports 1990-1995. Volume 1; Gubaev, A., Koshelenko, G.A., Tosi, M., Eds.; Centro Scavi e Ricerche Archeologiche, Reports and Memoirs, Series Minor; Istituto Italiano per l’Africa e l’Oriente: Roma, Italy, 1998; Volume 3, pp. 14–25. [Google Scholar]
- Arciero, R. Irrigating the Desert: Approaches to Paleochannel Reconstruction in the Murghab (Turkmenistan) during the Bronze Age. In Proceedings of the Problems of Chronology and Cultural Genesis of Ancient Sedentary Societies of Eurаsia (from the Neolithic Period through the Early Iron Age); Institute for the History of Material Culture Russian Academy of Sciences: St Petersburg, Russia, 2019; pp. 64–66. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, T. Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Photography: Exploring the Medieval City of Merv, on the Silk Roads of Central Asia. Archaeol. Int. 2012, 15, 54–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markofsky, S.B. Windows on a Delta Margin: A Case Study from the Murghab Delta, Turkmenistan. In Proceedings of the 8th International Congress on the Archaeology of the Ancient Near East. Archaeology of Fire, Conservation, Preservation and Site Management, Bioarchaeology in the Ancient Near East; Session, I., Bieliński, P., Gawlikowski, M., Koliński, R., Ławecka, D., Sołtysiak, A., Wygnańska, Z., Eds.; Harrassowitz Verlag: Wiesbaden, Germany, 2014; Volume 3, pp. 561–576. [Google Scholar]
- Lyonnet, B.; Dubova, N.A. The World of the Oxus Civilizations; Lyonnet, B., Dubova, N.A., Eds.; Routledge: Oxford, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Buławka, N.; Kaim, B.; Rzeplińska, M. Berdysyčran-Depe: A Bronze Age Site in the Lower Tedjen River Valley, Turkmenistan. Archaeol. Res. Asia 2021, 28, 100326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buławka, N. Settlement Patterns of the Yaz Culture in the Deltas of the Tedzhen River in Turkmenistan. In Proceedings of the A Millennium of History: The Iron Age in southern Central Asia (2nd and 1st Millennia BC), Berlin, Germany, 23–25 June 2014; Dedicated to the Memory of Viktor Ivanovich Sarianidi; Lhuillier, J., Boroffka, N., Eds.; Archäologie in Iran und Turan : Band 17/Mémoires de la Délégation Archéologique Française en Afghanistan: Volume XXXV; Deutsches Archäologisches Institut. Eurasien-Abteilung/Délégation Archéologique Française en Afghanistan: Berlin, Germany, 2018; pp. 143–158. ISBN 978-3-496-01594-9. [Google Scholar]
- Torres, R.; Snoeij, P.; Geudtner, D.; Bibby, D.; Davidson, M.; Attema, E.; Potin, P.; Rommen, B.; Floury, N.; Brown, M.; et al. GMES Sentinel-1 Mission. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 120, 9–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullissa, A.; Vollrath, A.; Odongo-Braun, C.; Slagter, B.; Balling, J.; Gou, Y.; Gorelick, N.; Reiche, J. Sentinel-1 SAR Backscatter Analysis Ready Data Preparation in Google Earth Engine. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wessel, B. TanDEM-X Ground Segment—DEM Products Specification Document. EOC, DLR, Oberpfaffenhofen, Germany, Public Document TD-GS-PS-0021, Issue 3.2. 2018. Available online: https://tandemx-science.dlr.de/pdfs/TD-GS-PS-0021_DEM-Product-Specification_v3.2.pdf (accessed on 10 January 2022).
- González, C.; Bachmann, M.; Bueso-Bello, J.-L.; Rizzoli, P.; Zink, M. A Fully Automatic Algorithm for Editing the TanDEM-X Global DEM. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bueso-Bello, J.-L.; Martone, M.; González, C.; Sica, F.; Valdo, P.; Posovszky, P.; Pulella, A.; Rizzoli, P. The Global Water Body Layer from TanDEM-X Interferometric SAR Data. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 5069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martone, M.; Rizzoli, P.; Wecklich, C.; González, C.; Bueso-Bello, J.-L.; Valdo, P.; Schulze, D.; Zink, M.; Krieger, G.; Moreira, A. The Global Forest/Non-Forest Map from TanDEM-X Interferometric SAR Data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 205, 352–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolliffe, I.T. Principal Component Analysis, 2nd ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Kauth, R.J.; Thomas, G.S. The Tasselled Cap—A Graphic Description of the Spectral-Temporal Development of Agricultural Crops as Seen by Landsat. In Proceedings of the Symposium on Machine Processing of Remotely Sensed Data, Purdue University, West Lafayette, Indiana, 29 June–1 July 1976; Proceedings (A77-15051 04-43). Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers: New York, NY, USA, 1976; pp. 41–51. [Google Scholar]
- Crist, E.P. Application of the Tasseled Cap Concept to Simulated Thematic Mapper Data. Photogramm. Eng. 1984, 50, 343–352. [Google Scholar]
- Crist, E.P.; Kauth, R.J. The Tasseled Cap De-Mystified. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 1986, 52, 81–86. [Google Scholar]
- Nedkov, R. Orthogonal Transformation of Segmented Images from the Satellite Sentinel-2. Comptes Rendus Académie Sci. Vie Sci. 2017, 70, 687–691. [Google Scholar]
- Lasaponara, R.; Masini, N. QuickBird-Based Analysis for the Spatial Characterization of Archaeological Sites: Case Study of the Monte Serico Medieval Village. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2005, 32, L12313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasaponara, R.; Masini, N. Image Enhancement, Feature Extraction and Geospatial Analysis in an Archaeological Perspective. In Satellite Remote Sensing; Lasaponara, R., Masini, N., Eds.; Remote Sensing and Digital Image Processing; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2012; Volume 16, pp. 17–63. ISBN 978-90-481-8800-0. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, R.E.; Sarris, A. Geophysical and Related Techniques Applied to Archaeological Survey in the Mediterranean: A Review. J. Mediterr. Archaeol. 2000, 13, 3–75. [Google Scholar]
- Abate, N.; Elfadaly, A.; Masini, N.; Lasaponara, R. Multitemporal 2016-2018 Sentinel-2 Data Enhancement for Landscape Archaeology: The Case Study of the Foggia Province, Southern Italy. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramkumar, M.; Kumaraswamy, K.; Balasubramani, K.; Nagarajan, R.; Santosh, M.; Abdul Rahman, S.; Prasad, K.A.; Juni, K.J.; Fathima, A.; Siddiqui, N.A.; et al. Neolithic Cultural Sites and Extreme Climate Related Channel Avulsion: Evidence from the Vaigai River Basin, Southern India. J. Archaeol. Sci. Rep. 2021, 40, 103204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, R.N.; Ramachandran, A.; Tripathi, V.; Badola, R. Syed Ainul Hussain Spatio-Temporal Habitat Assessment of the Gangetic Floodplain in the Hastinapur Wildlife Sanctuary. Ecol. Inform. 2022, 72, 101851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, S.; Jeganathan, C.; Sinha, N.K.; Rajan, H.; Roy, T.; Kumar, P. Extracting Seasonal Cropping Patterns Using Multi-Temporal Vegetation Indices from IRS LISS-III Data in Muzaffarpur District of Bihar, India. Egypt. J. Remote Sens. Space Sci. 2014, 17, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huete, A.; Justice, C.; Liu, H. Development of Vegetation and Soil Indices for MODIS-EOS. Remote Sens. Environ. 1994, 49, 224–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huete, A. A Comparison of Vegetation Indices over a Global Set of TM Images for EOS-MODIS. Remote Sens. Environ. 1997, 59, 440–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huete, A.; Didan, K.; Miura, T.; Rodriguez, E.P.; Gao, X.; Ferreira, L.G. Overview of the Radiometric and Biophysical Performance of the MODIS Vegetation Indices. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 83, 195–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berganzo-Besga, I.; Orengo, H.A.; Lumbreras, F.; Carrero-Pazos, M.; Fonte, J.; Vilas-Estévez, B. Hybrid MSRM-Based Deep Learning and Multitemporal Sentinel 2-Based Machine Learning Algorithm Detects near 10k Archaeological Tumuli in North-Western Iberia. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hengl, T.; Parente, L. Monthly Precipitation in Mm at 1 Km Resolution (Multisource Average) Based on SM2RAIN-ASCAT 2007-2021, CHELSA Climate and WorldClim (0.3) [Data Set]. 2022. Zenodo. Available online: https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6458580 (accessed on 10 January 2023).
- Cremaschi, M.; Castelli, R. Map 3. The Geomorphological Map of the Northern Frindge of the Murghab Delta. 1996. Scale 1: 75000 [Mapa]. In The Archaeological Map of the Murghab Delta: Preliminary Reports 1990–1995; Gubaev, A., Koshelenko, G.A., Tosi, M., Eds.; Centro Scavi e Ricerche Archeologiche, Reports and Memoirs, Series Minor, Volume 3; Istituto Italiano per l’Africa e l’Oriente: Rome, Italy, 1998; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Mayoral, A.; Ejarque, A.; Garcia-Molsosa, A.; Georgiadis, M.; Apostolou, G.; Gaertner, V.; Kallintzi, C.; Kefalidou, E.; Orengo, H. A City against the Current: A Reconstruction of Holocene Sea-Level Changes and the Evolution of Coastal Landscapes in Ancient Abdera (Thrace, Gr.). CATENA 2024, 235, 107638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jotheri, J.; Allen, M.B. Recognition of Ancient Channels and Archaeological Sites in the Mesopotamian Floodplain Using Satellite Imagery and Digital Topography. In New agenda in remote sensing and landscape archaeology in the Near East: Studies in Honor of T.J. Wilkinson; Lawrence, D., Altaweel, M., Philip, G., Eds.; The Oriental Institute of the University of Chicago: Chicago, IL, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Hritz, C. A Malarial-Ridden Swamp: Using Google Earth Pro and Corona to Access the Southern Balikh Valley, Syria. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2013, 40, 1975–1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casana, J.; Wright, R. Remote Sensing-Based Evidence of Indus-Era Irrigation Works in Punjab, Pakistan. Water Hist. 2023, 15, 293–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ur, J. Remote Sensing of Ancient Canal and Irrigation Systems. In Irrigation in Early States New Directions; Rost, S., Ed.; The University of Chicago: Chicago, IL, USA, 2022; pp. 65–82. ISBN 978-1-61491-071-8. [Google Scholar]
- Hritz, C.; Wilkinson, T.J. Using Shuttle Radar Topography to Map Ancient Water Channels. Antiquity 2006, 80, 415–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perego, A. AlsperGIS: SRTM DEM Destriping with SAGA GIS: Consequences on Drainage Network Extraction. Available online: http://www.alspergis.altervista.org/software/destriping.html (accessed on 1 September 2012).
- Hammer, E.; FitzPatrick, M.; Ur, J. Succeeding CORONA: Declassified HEXAGON Intelligence Imagery for Archaeological and Historical Research. Antiquity 2022, 96, 679–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).