A Comparative Analysis of the Effect of Orbital Geometry and Signal Frequency on the Ionospheric Scintillations over a Low Latitude Indian Station: First Results from the 25th Solar Cycle
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- i.
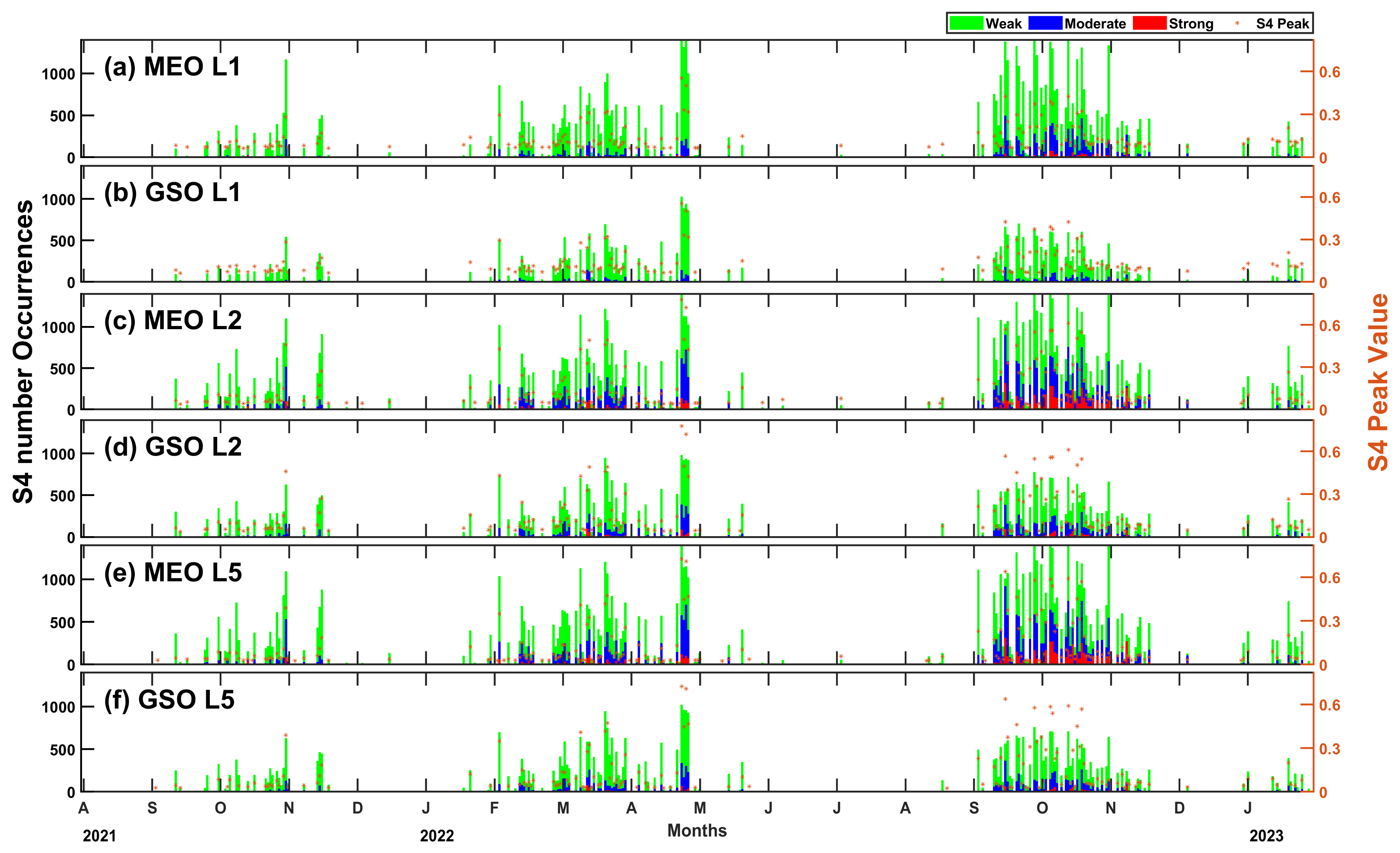
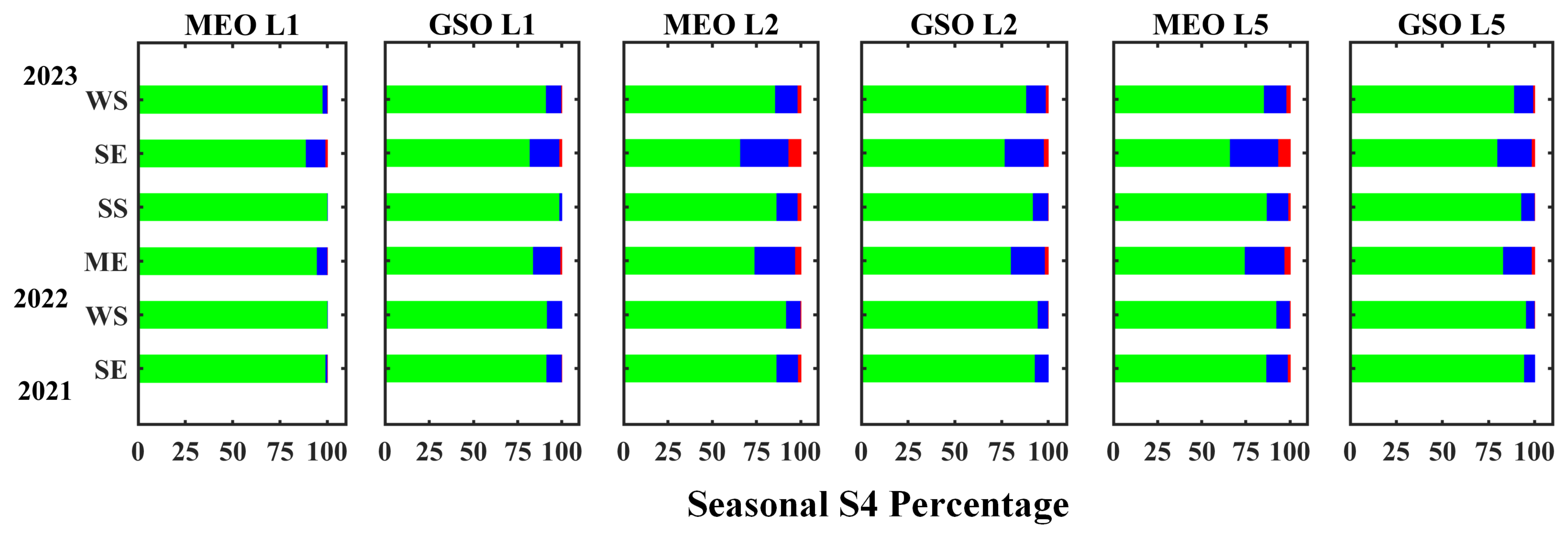
- The observed pattern of scintillations from the geostationary and geosynchronous satellites (called GSO) is found to be different from the other medium Earth-orbiting GNSS satellites (called MEO) in terms of a lesser temporal extent on a given night. Furthermore, moderate and strong scintillations (i.e., overall S4 > 0.5) are observed on a greater number of nights with higher occurrence from the MEO group of GNSS satellites. Similarly, the statistically derived peak S4 for a night is found to be weighted by the number of occurrences of scintillations of different intensities (i.e., weak, moderate, or strong). This implies confidence in the peak S4 to represent the scintillation scenario of a night.
- ii.
- The number of occurrences of scintillations is found to be always higher for MEO than GSO for any category of scintillations. The occurrence of strong and moderate scintillation is found to be higher on L2 and L5 for both the MEO and GSO groups, where the occurrence of weak scintillations is found to be highest on all of the signals. The statistical average of peak S4 values on a given night is found to provide higher confidence on the occurrence of the severity of scintillations.
- iii.
- The percentage occurrence of scintillation-affected satellites is found to be higher on L1 compared to other signals, wherein a contrasting higher percentage of affected satellites over GSO than MEO is observed. This could possibly be due to the higher number of MEO satellites transmitting L1 as a standard navigation signal. The faster movement of MEO links compared to GSO links can also enhance the possibility of a higher occurrence of scintillations from the multiple drifting plasma bubbles. However, it shall also be noted that the higher number of closely spaced GSO satellites could also produce similar results owing to lesser space diversity which needs further investigation. Thus, the number of satellites transmitting a particular signal and the angular spacing and elevation angle also play a crucial role in the percentage occurrence pattern.
- iv.
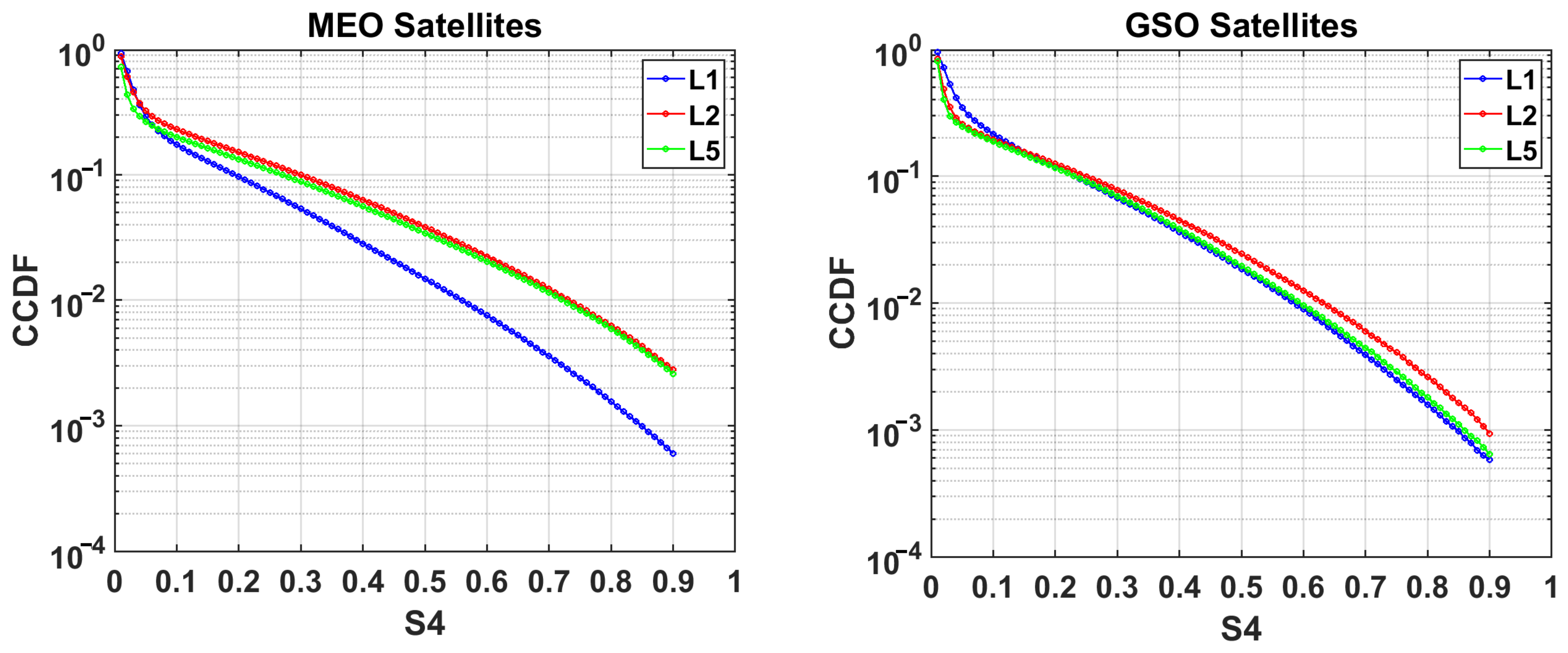
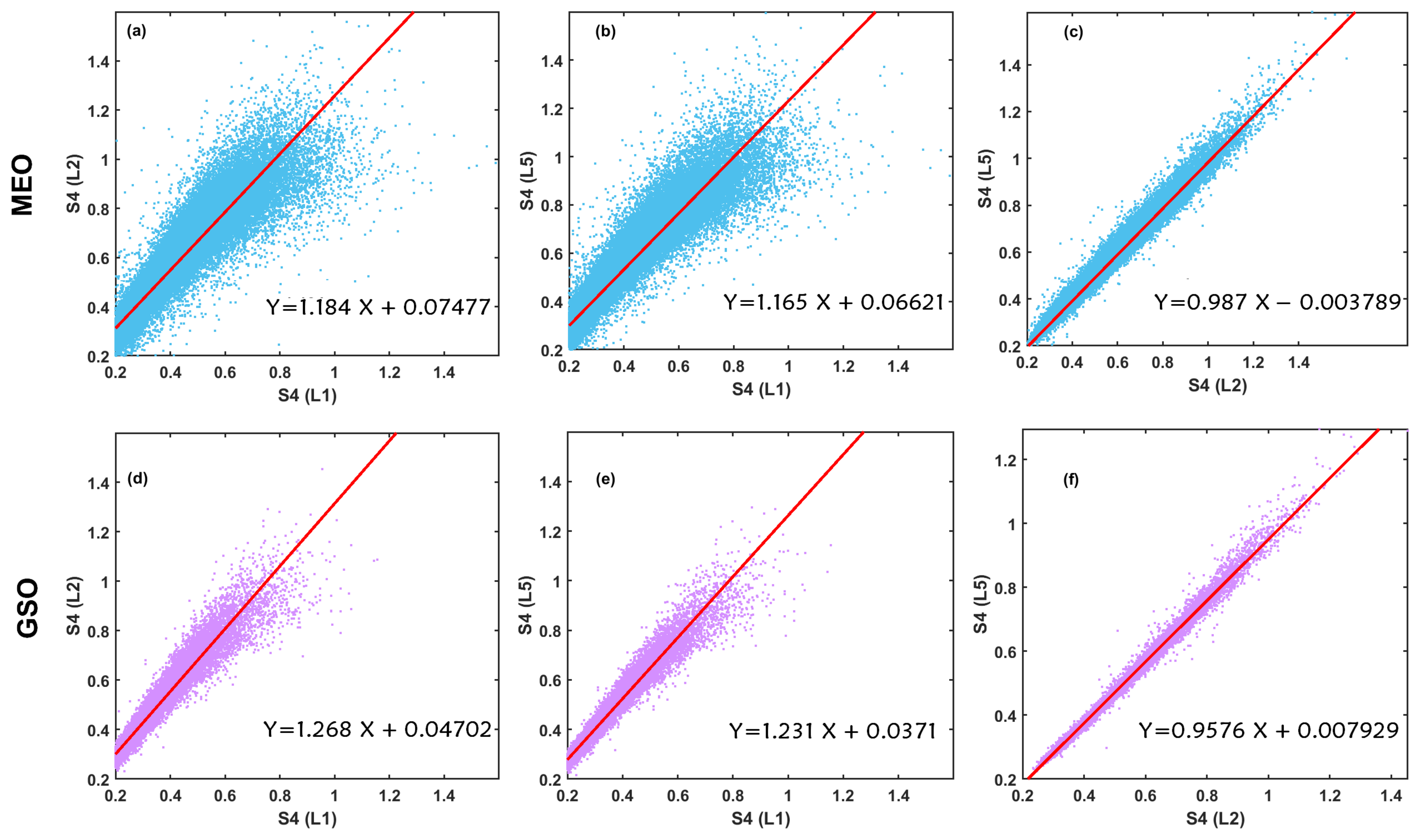
- The complementary probability (CCDF) of S4 occurrence shows a lesser occurrence of more severe scintillations with different variations among signals of MEO and GSO satellites. While a clear demarcation between the L2/L5 signals and L1 is found over the MEO, in case of GSO, the CCDF over L5 is found to match mostly with the L1 signal. This could possibly originate from the space diversity gain effect known to impact the closely spaced geostationary satellite links. However, the scintillation relationship between L1 and the other two signals is found to be weighted towards lower frequencies (with higher slopes and lesser scatter on GSO signals).
- v.
- The analysis of the percentage of satellites affected on L1 shows a close match between MEO and GSO for the total number of minutes in each 10% bin up to 60%. But the number of minutes for which the percentage of affected satellites remains larger than 60% is found to be higher for GSO. This result indicates homogeneous spatial patterns in the scintillation distribution over a low latitude site, which could originate from closely spaced GSO links and highlight the role of the number of available satellites with the geometry of the links, being the deciding factor.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yeh, K.C.; Liu, C.-H. Radio Wave Scintillations in the Ionosphere. Proc. IEEE 1982, 70, 324–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasu, V.K.D.; Dashora, N.; Prasad, D.S.V.V.D.; Niranjan, K. Loss of Lock on GNSS Signals and Its Association with Ionospheric Irregularities Observed over Indian Low Latitudes. GPS Solut. 2022, 26, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousuf, M.; Dashora, N.; Sridhar, M.; Dutta, G. Long-Term Impact of Ionospheric Scintillations on Kinematic Precise Point Positioning: Seasonal and Solar Activity Dependence over Indian Low Latitudes. GPS Solut. 2022, 27, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damaceno, J.G.; Bolmgren, K.; Bruno, J.; De Franceschi, G.; Mitchell, C.; Cafaro, M. GPS Loss of Lock Statistics over Brazil during the 24th Solar Cycle. Adv. Space Res. 2020, 66, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pezzopane, M.; Pignalberi, A.; Coco, I.; Consolini, G.; De Michelis, P.; Giannattasio, F.; Marcucci, M.F.; Tozzi, R. Occurrence of GPS Loss of Lock Based on a Swarm Half-Solar Cycle Dataset and Its Relation to the Background Ionosphere. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Michelis, P.; Consolini, G.; Pignalberi, A.; Lovati, G.; Pezzopane, M.; Tozzi, R.; Giannattasio, F.; Coco, I.; Marcucci, M.F. Ionospheric Turbulence: A Challenge for GPS Loss of Lock Understanding. Space Weather 2022, 20, e2022SW003129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann-Wellenhof, B.; Lichtenegger, H.; Wasle, E. (Eds.) Satellite Signals. In GNSS—Global Navigation Satellite Systems: GPS, GLONASS, Galileo, and More; Springer Vienna: Vienna, Austria, 2008; pp. 55–104. ISBN 978-3-211-73017-1. [Google Scholar]
- Aarons, J. The Role of the Ring Current in the Generation or Inhibition of Equatorial F Layer Irregularities during Magnetic Storms. Radio Sci. 1991, 26, 1131–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, S.; Kudeki, E.; Basu, S.; Valladares, C.E.; Weber, E.J.; Zengingonul, H.P.; Bhattacharyya, S.; Sheehan, R.; Meriwether, J.W.; Biondi, M.A.; et al. Scintillations, Plasma Drifts, and Neutral Winds in the Equatorial Ionosphere after Sunset. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 1996, 101, 26795–26809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanmugam, S.; Jones, J.; MacAulay, A.; Van Dierendonck, A.J. Evolution to Modernized GNSS Ionoshperic Scintillation and TEC Monitoring. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE/ION Position, Location and Navigation Symposium, Myrtle Beach, SC, USA, 23–26 April 2012; pp. 265–273. [Google Scholar]
- Hlubek, N.; Berdermann, J.; Wilken, V.; Gewies, S.; Jakowski, N.; Wassaie, M.; Damtie, B. Scintillations of the GPS, GLONASS, and Galileo Signals at Equatorial Latitude. J. Space Weather Space Clim. 2014, 4, A22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salles, L.A.; Vani, B.C.; Moraes, A.; Costa, E.; de Paula, E.R. Investigating Ionospheric Scintillation Effects on Multifrequency GPS Signals. Surv. Geophys. 2021, 42, 999–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salles, L.A.; Moraes, A.; Vani, B.; Sousasantos, J.; Affonso, B.J.; Monico, J.F.G. A Deep Fading Assessment of the Modernized L2C and L5 Signals for Low-Latitude Regions. GPS Solut. 2021, 25, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Oliveira Moraes, A.; da Silveira Rodrigues, F.; Perrella, W.J.; de Paula, E.R. Analysis of the Characteristics of Low-Latitude GPS Amplitude Scintillation Measured During Solar Maximum Conditions and Implications for Receiver Performance. Surv. Geophys. 2012, 33, 1107–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, K.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, C.; Zhu, Y. Study of Ionospheric Scintillation Characteristics in Australia with GNSS during 2011–2015. Adv. Space Res. 2017, 59, 2909–2922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, Y.; Xu, D.; Morton, Y.; Rino, C. Equatorial Scintillation Amplitude Fading Characteristics Across the GPS Frequency Bands. Navigation 2016, 63, 267–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delay, S.H.; Carrano, C.S.; Groves, K.M.; Doherty, P.H. A Statistical Analysis of GPS L1, L2, and L5 Tracking Performance during Ionospheric Scintillation. In Proceedings of the 2015 ION Pacific PNT Conference, Honolulu, HI, USA, 20–23 April 2015; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Carrano, C.; Groves, K.; McNeil, W.J.; Doherty, P.H. Scintillation Characteristics Across the GPS Frequency Band. In Proceedings of the 25th International Technical Meeting of the Satellite Division of the Institute of Navigation 2012, ION GNSS 2012, Nashville, TN, USA, 17–21 September 2012; Volume 3, pp. 1972–1989. [Google Scholar]
- De Oliveira Moraes, A.; Costa, E.; Abdu, M.A.; Rodrigues, F.S.; de Paula, E.R.; Oliveira, K.; Perrella, W.J. The Variability of Low-Latitude Ionospheric Amplitude and Phase Scintillation Detected by a Triple-Frequency GPS Receiver. Radio Sci. 2017, 52, 439–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moraes, d.O.A.; Vani, B.C.; Costa, E.; Sousasantos, J.; Abdu, M.A.; Rodrigues, F.; Gladek, Y.C.; de Oliveira, C.B.A.; Monico, J.F.G. Ionospheric Scintillation Fading Coefficients for the GPS L1, L2, and L5 Frequencies. Radio Sci. 2018, 53, 1165–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akala, A.O.; Awoyele, A.; Doherty, P.H. Statistics of GNSS Amplitude Scintillation Occurrences over Dakar, Senegal, at Varying Elevation Angles during the Maximum Phase of Solar Cycle 24. Space Weather 2016, 14, 233–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghafoori, F.; Skone, S. Impact of Equatorial Ionospheric Irregularities on GNSS Receivers Using Real and Synthetic Scintillation Signals. Radio Sci. 2015, 50, 294–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otsuka, Y.; Shiokawa, K.; Ogawa, T. Equatorial Ionospheric Scintillations and Zonal Irregularity Drifts Observed with Closely-Spaced GPS Receivers in Indonesia. J. Meteorol. Soc. Japan. Ser. II 2006, 84, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valladares, C.E.; Villalobos, J.; Sheehan, R.; Hagan, M.P. Latitudinal Extension of Low-Latitude Scintillations Measured with a Network of GPS Receivers. Ann. Geophys. 2004, 22, 3155–3175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dashora, N.; Pandey, R. Observations in Equatorial Anomaly Region of Total Electron Content Enhancements and Depletions. Ann. Geophys. 2005, 23, 2449–2456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelley, M.C. The Earth’s Ionosphere: Plasma Physics and Electrodynamics; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2009; ISBN 0-08-091657-0. [Google Scholar]
- Rino, C. The Theory of Scintillation with Applications in Remote Sensing; Wiley-IEEE Press: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011; ISBN 978-0-470-64477-5. [Google Scholar]
- Rino, C.; Breitsch, B.; Morton, Y.; Jiao, Y.; Xu, D.; Carrano, C. A Compact Multi-Frequency GNSS Scintillation Model. Navigation 2018, 65, 563–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelley, M.C.; Makela, J.J.; Paxton, L.J.; Kamalabadi, F.; Comberiate, J.M.; Kil, H. The First Coordinated Ground- and Space-Based Optical Observations of Equatorial Plasma Bubbles. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2003, 30, 1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledvina, B.M.; Makela, J.J. First Observations of SBAS/WAAS Scintillations: Using Collocated Scintillation Measurements and All-Sky Images to Study Equatorial Plasma Bubbles. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2005, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrano, C.S.; Rino, C.L. A Theory of Scintillation for Two-Component Power Law Irregularity Spectra: Overview and Numerical Results. Radio Sci. 2016, 51, 789–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, A.; Kakad, B.; Gurram, P.; Sripathi, S.; Sunda, S. Development of Intermediate-Scale Structure at Different Altitudes within an Equatorial Plasma Bubble: Implications for L-Band Scintillations. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2017, 122, 1015–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DasGupta, A.; Ray, S.; Paul, A.; Banerjee, P.; Bose, A. Errors in Position-Fixing by GPS in an Environment of Strong Equatorial Scintillations in the Indian Zone. Radio Sci. 2004, 39, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goswami, S.; Paul, K.S.; Paul, A. Assessment of GPS Multifrequency Signal Characteristics during Periods of Ionospheric Scintillations from an Anomaly Crest Location. Radio Sci. 2017, 52, 1214–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rama Rao, P.; Gopi Krishna, S.; Niranjan, K.; Prasad, D. Study of Spatial and Temporal Characteristics of L-Band Scintillations over the Indian Low-Latitude Region and Their Possible Effects on GPS Navigation; Copernicus GmbH: Göttingen, Germany, 2006; Volume 24, pp. 1567–1580. [Google Scholar]
- Srinivasu, V.K.D.; Dashora, N.; Prasad, D.S.V.V.D.; Niranjan, K.; Krishna, S.G. On the Occurrence and Strength of Multi-Frequency Multi-GNSS Ionospheric Scintillations in Indian Sector during Declining Phase of Solar Cycle 24. Adv. Space Res. 2018, 61, 1761–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sripathi, S.; Sreekumar, S.; Banola, S. Characteristics of Equatorial and Low-Latitude Plasma Irregularities as Investigated Using a Meridional Chain of Radio Experiments Over India. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2018, 123, 4364–4380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, A.; Sur, D.; Haralambous, H. Multi-Wavelength Coordinated Observations of Ionospheric Irregularity Structures from an Anomaly Crest Location during Unusual Solar Minimum of the 24th Cycle. Adv. Space Res. 2020, 65, 1402–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.B.; Rathore, V.S.; Singh, A.K.; Singh, A.K. Ionospheric Irregularities at Low Latitude Using VHF Scintillations during Extreme Low Solar Activity Period (2008–2010). Acta Geod. Geophys. 2017, 52, 35–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engavale, B. Spatial Correlation Function of Intensity Variations in the Ground Scintillation Pattern Produced by Equatorial Spread-F Irregularities. Indian J. Radio Space Phys. 2005, 34, 22–32. [Google Scholar]
- Biswas, T.; Paul, A. Signal-In-Space Performance Under Multiconstellation Environment From an Indian Low Latitude Station. Radio Sci. 2021, 56, e2020RS007119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, E.; Roddy, P.A.; Ballenthin, J.O. Space Diversity Mitigation Effects on Ionospheric Amplitude Scintillation with Basis on the Analysis of C/NOFS Planar Langmuir Probe Data. Radio Sci. 2020, 55, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, W.-H.; Lin, C.-Y.; Liu, J.-Y.; Chen, S.-P.; Hsiao, T.-Y.; Huang, C.-Y. Superposition Property of the Ionospheric Scintillation S4 Index. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2020, 17, 597–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dierendonck, A.J. Ionospheric Scintillation Monitoring Using Commercial Single Frequency C/A Code Receivers. In Proceedings of the ION GPS 93, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 22–24 September 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Secan, J.A.; Bussey, R.M.; Fremouw, E.J.; Basu, S. An Improved Model of Equatorial Scintillation. Radio Sci. 1995, 30, 607–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphreys, T.E.; Psiaki, M.L.; Kintner, P.M. Modeling the Effects of Ionospheric Scintillation on GPS Carrier Phase Tracking. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2010, 46, 1624–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphreys, T.E.; Psiaki, M.L.; Ledvina, B.M.; Cerruti, A.P.; Kintner, P.M. Data-Driven Testbed for Evaluating GPS Carrier Tracking Loops in Ionospheric Scintillation. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2010, 46, 1609–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilà-Valls, J.; Linty, N.; Closas, P.; Dovis, F.; Curran, J.T. Curran Survey on Signal Processing for GNSS under Ionospheric Scintillation: Detection, Monitoring, and Mitigation. Navigation 2020, 67, 511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sethi, H.S.; Dashora, N. Automated Power Spectrum Analysis of Low-Latitude Ionospheric Scintillations Recorded Using Software GNSS Receiver. GPS Solut. 2020, 24, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousasantos, J.; Affonso, B.J.; Moraes, A.; Rodrigues, F.S.; Abdu, M.A.; Salles, L.A.; Vani, B.C. Amplitude Scintillation Severity and Fading Profiles Under Alignment Between GPS Propagation Paths and Equatorial Plasma Bubbles. Space Weather 2022, 20, e2022SW003243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muella, M.T.A.H.; de Paula, E.R.; Kantor, I.J.; Rezende, L.F.C.; Smorigo, P.F. Occurrence and Zonal Drifts of Small-Scale Ionospheric Irregularities over an Equatorial Station during Solar Maximum—Magnetic Quiet and Disturbed Conditions. Adv. Space Res. 2009, 43, 1957–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abadi, P.; Saito, S.; Srigutomo, W. Low-Latitude Scintillation Occurrences around the Equatorial Anomaly Crest over Indonesia. Ann. Geophys. 2014, 32, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kintner, P.M.; Ledvina, B.M.; de Paula, E.R.; Kantor, I.J. Size, Shape, Orientation, Speed, and Duration of GPS Equatorial Anomaly Scintillations. Radio Sci. 2004, 39, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdu, M.A.; Bittencourt, J.A.; Batista, I.S. Magnetic Declination Control of the Equatorial F Region Dynamo Electric Field Development and Spread F. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 1981, 86, 11443–11446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsunoda, R.T. Control of the Seasonal and Longitudinal Occurrence of Equatorial Scintillations by the Longitudinal Gradient in Integrated E Region Pedersen Conductivity. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 1985, 90, 447–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodman, R.F.; La Hoz, C. Radar Observations of F Region Equatorial Irregularities. J. Geophys. Res. (1896–1977) 1976, 81, 5447–5466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farley, D.T.; Bonelli, E.; Fejer, B.G.; Larsen, M.F. The Prereversal Enhancement of the Zonal Electric Field in the Equatorial Ionosphere. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 1986, 91, 13723–13728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hysell, D.L.; Burcham, J.D. JULIA Radar Studies of Equatorial Spread F. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 1998, 103, 29155–29167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, L.M. Equatorial F-region Irregularities during Low and High Solar Activity Conditions. Indian J. Radio Space Phys. 2012, 41, 208. [Google Scholar]
- Das, S.K.; Patra, A.K.; Kherani, E.A.; Chaitanya, P.P.; Niranjan, K. Relationship Between Presunset Wave Structures and Interbubble Spacing: The Seeding Perspective of Equatorial Plasma Bubble. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2020, 125, e2020JA028122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moraes, A.; Sousasantos, J.; Costa, E.; Pereira, B.A.; Rodrigues, F.; Galera Monico, J.F. Characterization of Scintillation Events With Basis on L1 Transmissions From Geostationary SBAS Satellites. Space Weather 2024, 22, e2023SW003656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboelmagd, N.; Karamat, T.B.; Jacques, G. Fundamentals of Inertial Navigation, Satellite-Based Positioning and Their Integration; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
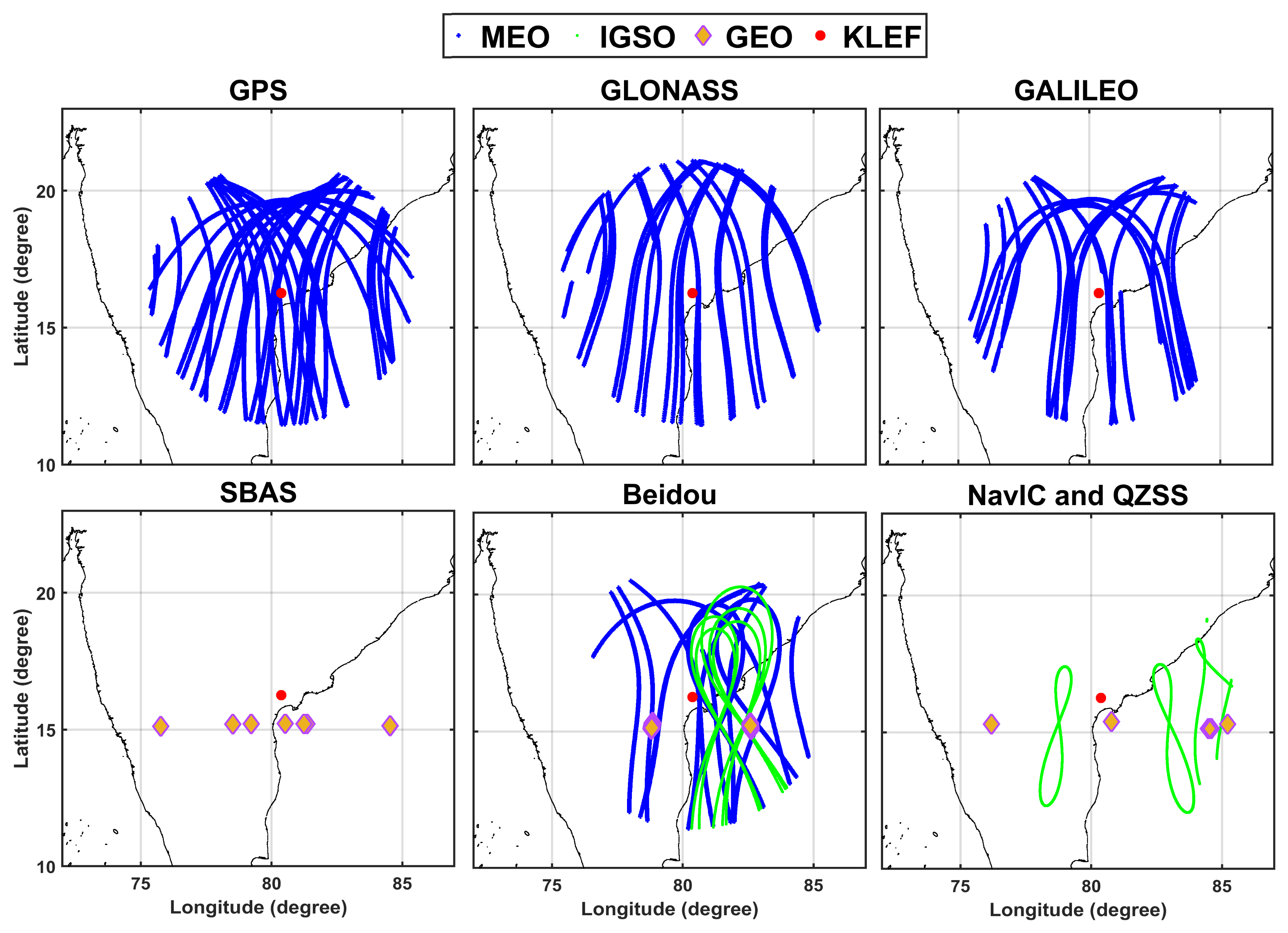



| Constellation /Group | L1 (Frequency in MHz) (Number of PRNs) | L2 (Frequency in MHz) (Number of PRNs) | L5 (Frequency in MHz) (Number of PRNs) | Mean Altitude (Km) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GPS (MEO) | L1CA: 1575.42 (32) | L2C: 1227.60 (24) | L5 (I + Q): 1176.45 (17) | ~20,200 |
| GLONASS (MEO) | L1CA: 1602 (24) | L2C: 1246 (21) | ~19,100 | |
| GALILEO (MEO) | L1BC: 1575.42 (21) | E5b: 1207.14 (21) | E5a: 1176.45 (21) | ~23,222 |
| SBAS (GEO) | L1CA: 1575.42 (8) | L5: 1176.45 (6) | ~36,000 | |
| QZSS (1 GEO + 3 IGSO) | L1CA: 1575.42 (6) | L2C: 1227.60 (5) | L5: 1176.45 (5) | ~36,000 |
| BeiDou (MEO + 3 GEO + 2 IGSO) | B1: 1561.098 (26) | B3: 1268.52 (26) B2: 1207.14 (13) | ~21,500 (MEO) ~36,000 (GEO) | |
| NavIC (3 GEO + 4 IGSO) | - | - | L5: 1176.45 (5) | ~36,000 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vankadara, R.; Dashora, N.; Panda, S.K.; Dabbakuti, J.R.K.K. A Comparative Analysis of the Effect of Orbital Geometry and Signal Frequency on the Ionospheric Scintillations over a Low Latitude Indian Station: First Results from the 25th Solar Cycle. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 1698. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16101698
Vankadara R, Dashora N, Panda SK, Dabbakuti JRKK. A Comparative Analysis of the Effect of Orbital Geometry and Signal Frequency on the Ionospheric Scintillations over a Low Latitude Indian Station: First Results from the 25th Solar Cycle. Remote Sensing. 2024; 16(10):1698. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16101698
Chicago/Turabian StyleVankadara, Ramkumar, Nirvikar Dashora, Sampad Kumar Panda, and Jyothi Ravi Kiran Kumar Dabbakuti. 2024. "A Comparative Analysis of the Effect of Orbital Geometry and Signal Frequency on the Ionospheric Scintillations over a Low Latitude Indian Station: First Results from the 25th Solar Cycle" Remote Sensing 16, no. 10: 1698. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16101698
APA StyleVankadara, R., Dashora, N., Panda, S. K., & Dabbakuti, J. R. K. K. (2024). A Comparative Analysis of the Effect of Orbital Geometry and Signal Frequency on the Ionospheric Scintillations over a Low Latitude Indian Station: First Results from the 25th Solar Cycle. Remote Sensing, 16(10), 1698. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16101698







