Spatial Patterns of Turbidity in Cartagena Bay, Colombia, Using Sentinel-2 Imagery
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Field Measurements
2.2.1. Turbidity and Secchi Depth measurements
2.2.2. Remote Sensing Reflectance
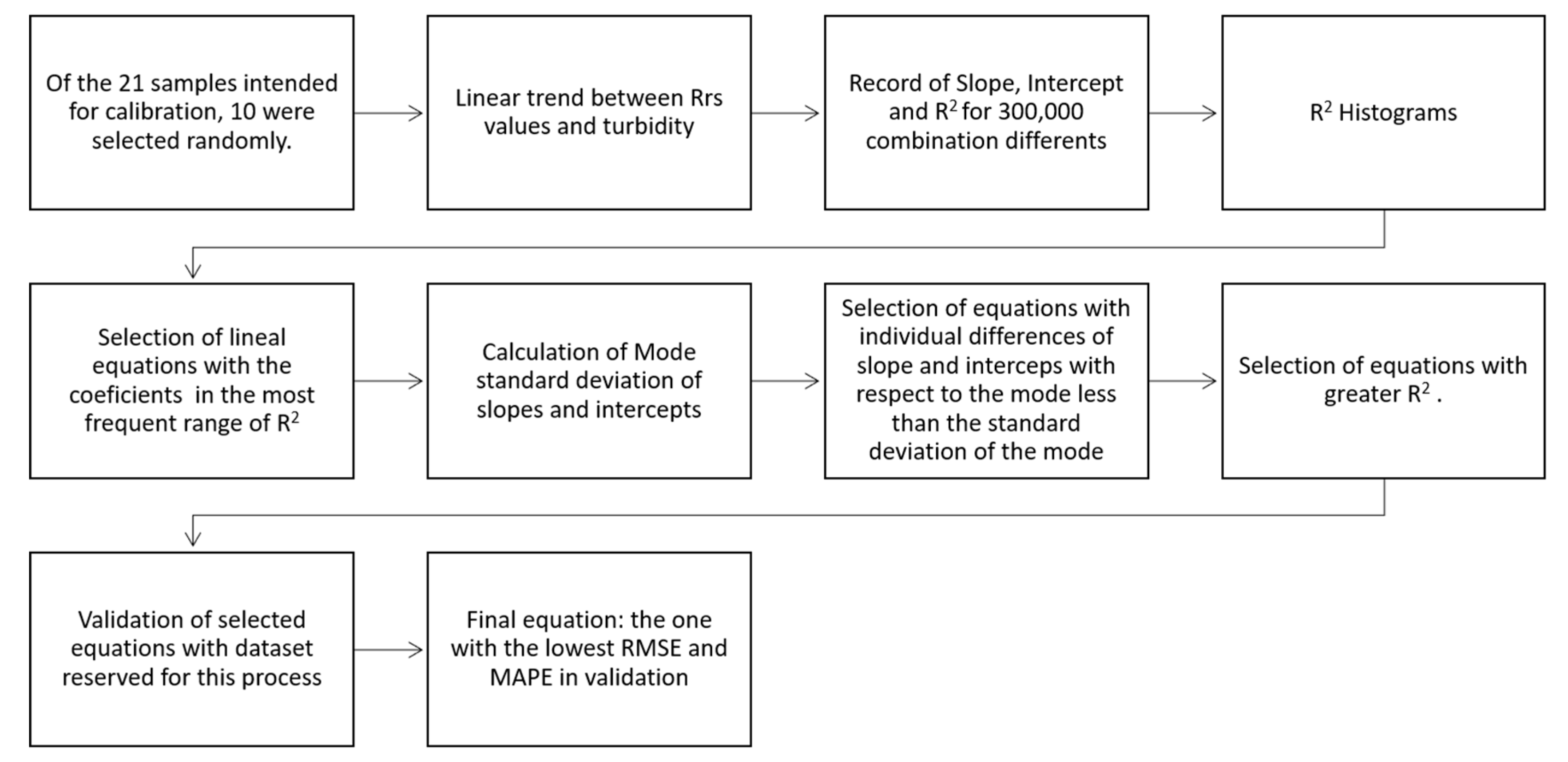
2.3. Turbidity Algorithm
2.4. Cartagena Bay Turbidity Spatial Analysis
3. Results
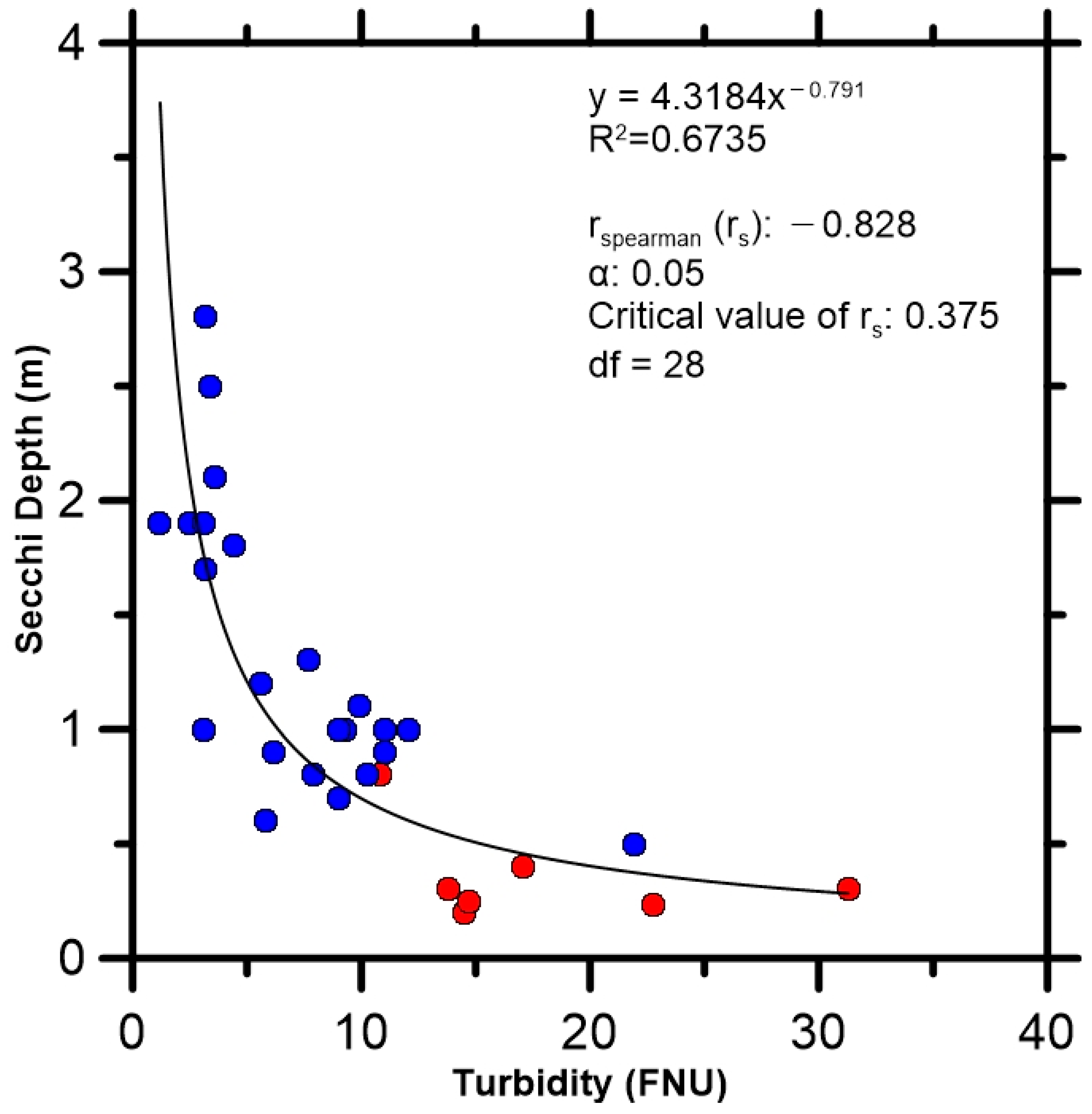
3.1. In Situ Turbidity and Secchi Depth
3.2. In Situ Remote Sensing Reflectance
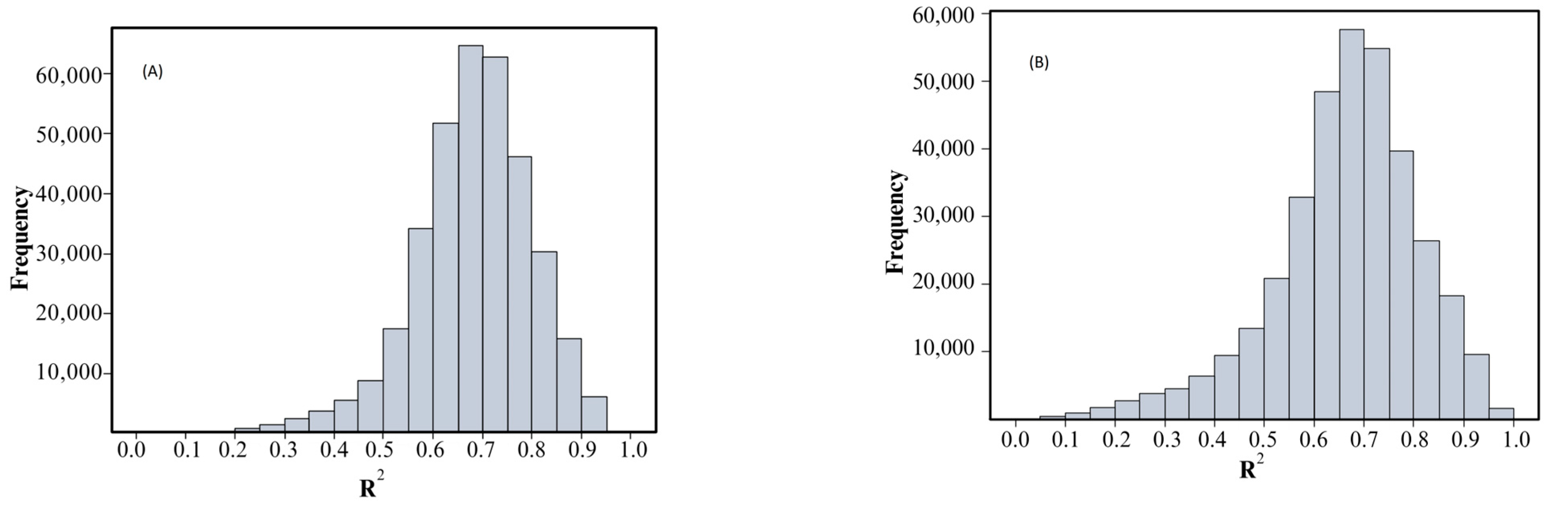
3.3. Turbidity Algorithm
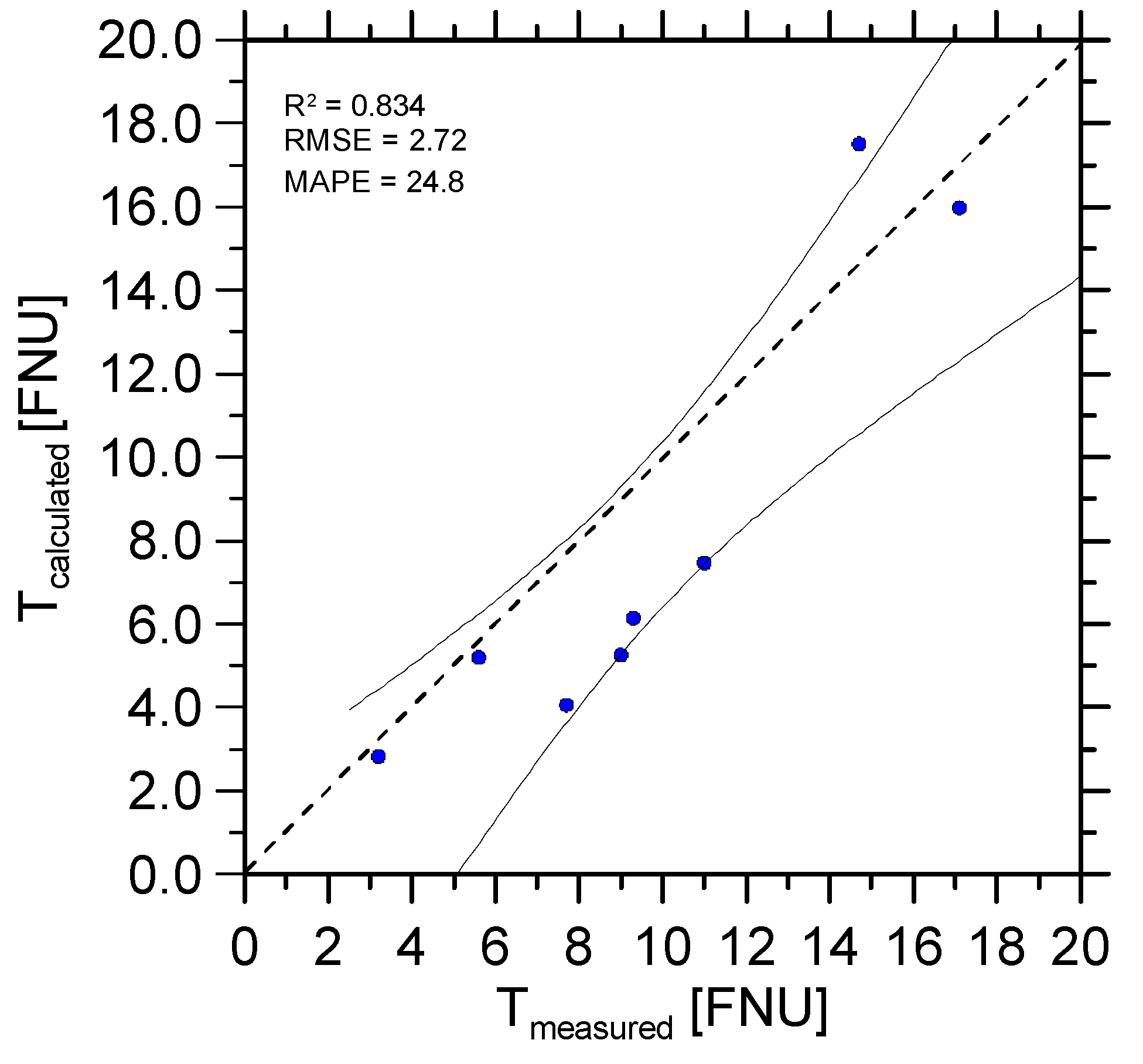
3.3.1. Calibration and Validation
3.3.2. Comparison with other Algorithms
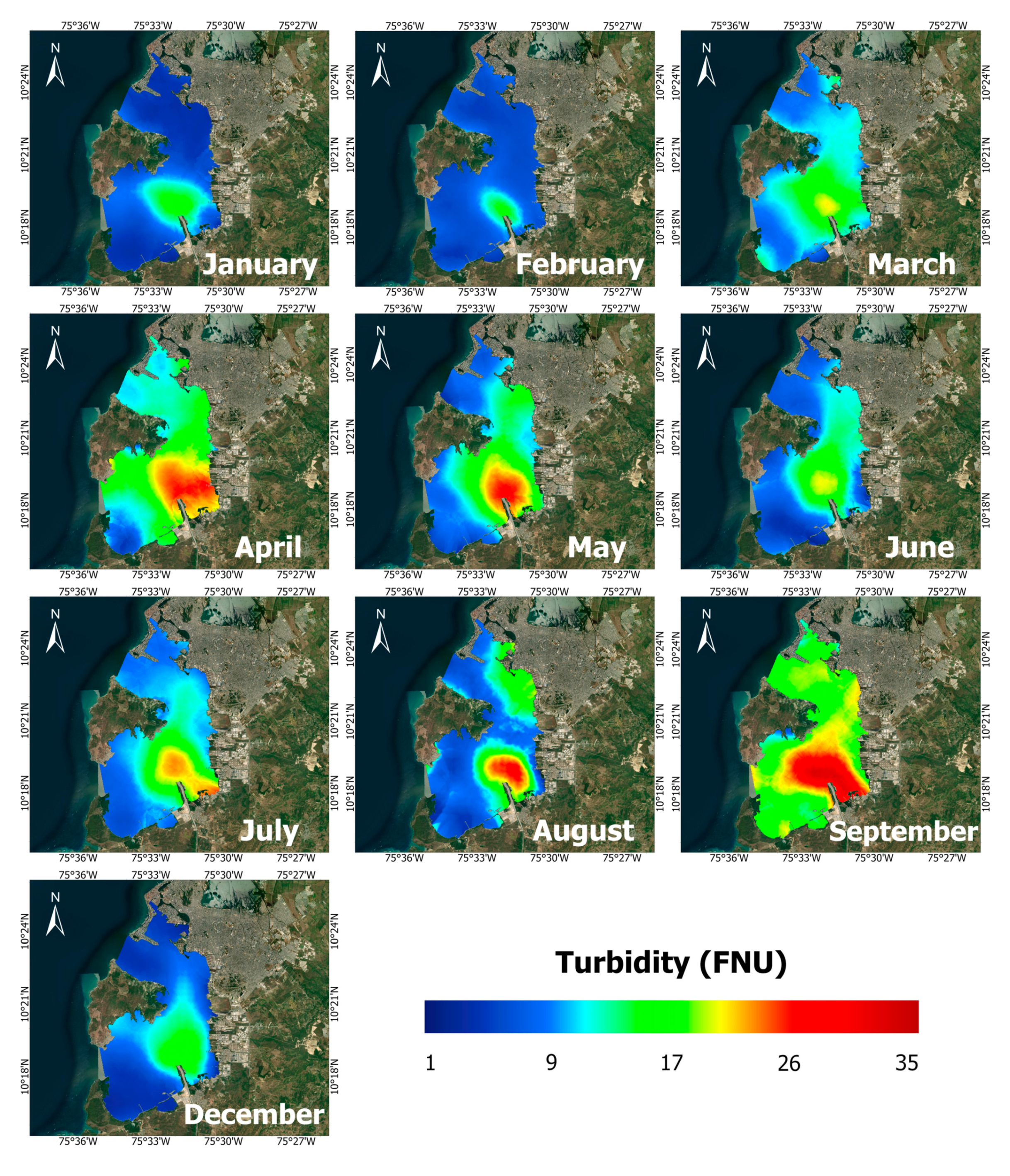
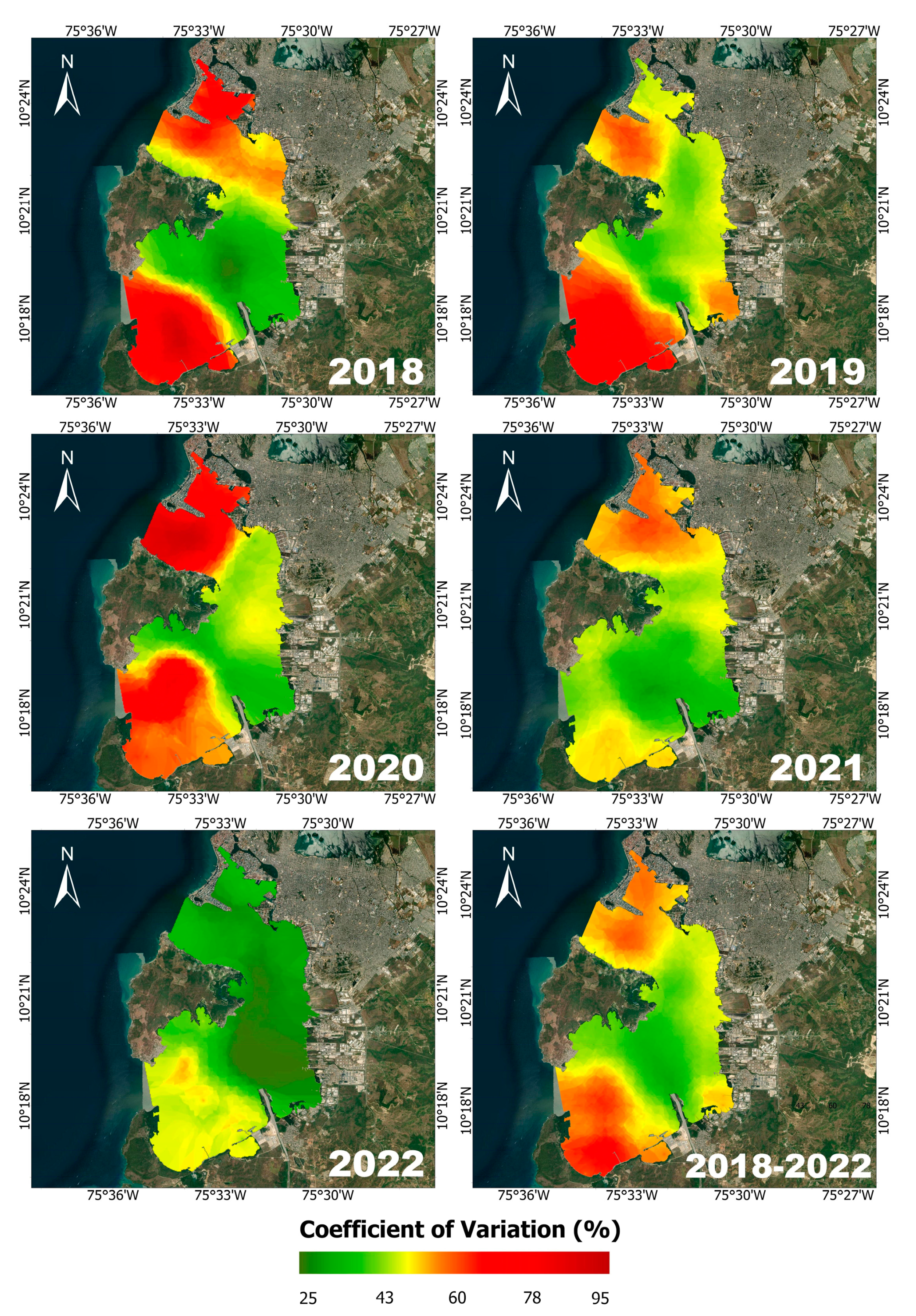
3.4. Turbidity Spatial Patterns
4. Discussion
4.1. Turbid Algorithm
4.2. Turbidity Patterns
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Superintendencia de Transporte. Tráfico Portuario en Colombia, 2022. Boletín Estadistíco 2022. 2023. Available online: https://www.supertransporte.gov.co/documentos/2023/Febrero/Puertos_28/BOLETIN-TRAFICO-PORTUARIO-2022.pdf (accessed on 15 October 2023).
- Cartagena Como Vamos. Informe de Calidad de Vida Cartagena 2022; Cartagena Como Vamos: Cartagena, Colombia, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- ANLA. Reporte de Análisis Regional de la Bahía de Cartagena y Canal del Dique; ANLA: Bogotá, Colombia, 2021. Available online: https://www.anla.gov.co/documentos/biblioteca/27-01-2022-anla-reporte-de-analisis-regional-cartagena4.pdf (accessed on 6 November 2023).
- Tosic, M.; Restrepo, J.D.; Lonin, S.; Izquierdo, A.; Martins, F. Water and sediment quality in Cartagena Bay, Colombia: Seasonal variability and potential impacts of pollution. Estuarine Coast. Shelf Sci. 2019, 216, 187–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lonin, S.; Parra, C.; Andrade, C.; Thomas, Y.F. Patrones de la pluma turbia del canal del Dique en la bahía de Cartagena. Bol. Cient. CIOH 2004, 22, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lonin, S.; Menanteau, L. Aspectos morfodinámicos de la bahía de Cartagena de Indias. Bol. Cient. CIOH 2004, 22, 90–104. [Google Scholar]
- Restrepo, J.C.; Escobar, J.; Otero, L.; Franco, D.; Pierini, J.; Correa, I. Factors Influencing the Distribution and Characteristics of Surface Sediment in the Bay of Cartagena, Colombia. J. Coast. Res. 2017, 331, 135–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tosic, M.; Martins, F.; Lonin, S.; Izquierdo, A.; Restrepo, J.D. Hydrodynamic modelling of a polluted tropical bay: Assessment of anthropogenic impacts on freshwater runoff and estuarine water renewal. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 236, 695–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- INVEMAR. Diagnóstico de Calidad Ambiental Marina REDCAM. 2023. Available online: https://www.invemar.org.co/web/guest/noticias/-/asset_publisher/LDoaFqdaVjYL/content/redcam-inicia-el-diagnostico-de-calidad-de-aguas-en-el-departamento-de-cordoba (accessed on 6 October 2023).
- Dogliotti, A.; Ruddick, K.; Guerrero, R. Seasonal and inter-annual turbidity variability in the Río de la Plata from 15 years of MODIS: El Niño dilution effect. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2016, 182, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Z.; Chen, J.; Pan, D.; Tao, B.; Zhu, Q. A regional remote sensing algorithm for total suspended matter in the East China Sea. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 124, 819–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Lee, Z.; Shen, F.; Wang, M.; Wei, J.; Jiang, L.; Shang, Z. An empirical algorithm to seamlessly retrieve the concentration of suspended particulate matter from water color across ocean to turbid river mouths. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 235, 111491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binding, C.; Greenberg, T.; Bukata, R. An analysis of MODIS-derived algal and mineral turbidity in Lake Erie. J. Great Lakes Res. 2012, 38, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherukuru, N.; Martin, P.; Sanwlani, N.; Mujahid, A.; Müller, M. A Semi-Analytical Optical Remote Sensing Model to Estimate Suspended Sediment and Dissolved Organic Carbon in Tropical Coastal Waters Influenced by Peatland-Draining River Discharges off Sarawak, Borneo. Remote Sens. 2020, 13, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, C.E.; Castelao, R.M. Mississippi River Plume Variability in the Gulf of Mexico from SMAP and MODIS-Aqua Observations. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2018, 123, 6620–6638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavora, J.; Fernandes, E.H.L.; Thomas, A.C.; Weatherbee, R.; Schettini, C.A.F. The influence of river discharge and wind on Patos Lagoon, Brazil, Suspended Particulate Matter. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2019, 40, 4506–4525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, B.; Gholamalifard, M.; Kutser, T.; Vignudelli, S.; Kostianoy, A. Spatio-Temporal Variability in Bio-Optical Properties of the Southern Caspian Sea: A Historic Analysis of Ocean Color Data. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gohin, F.; Loyer, S.; Lunven, M.; Labry, C.; Froidefond, J.-M.; Delmas, D.; Huret, M.; Herbland, A. Satellite-derived parameters for biological modelling in coastal waters: Illustration over the eastern continental shelf of the Bay of Biscay. Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 95, 29–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, S.; Wang, M. VIIRS-Derivedwater turbidity in the Great Lakes. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.H.; Son, S.; Kim, H.-C.; Kim, B.; Park, Y.-G.; Nam, J.; Ryu, J. Application of satellite remote sensing in monitoring dissolved oxygen variabilities: A case study for coastal waters in Korea. Environ. Int. 2019, 134, 105301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd-Al Zahra, L.J.; Ali, H.M. Estimation of pollution rates and spatial distribution of the total suspended solids of the euphrates river to selected sites from the shatt al-kufa by using remote sensing data. NeuroQuantology 2020, 18, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabiri, K.; Moradi, M. Landsat-8 imagery to estimate clarity in near-shore coastal waters: Feasibility study—Chabahar Bay, Iran. Cont. Shelf Res. 2016, 125, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, K.; Zha, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, M. A Landsat 8 OLI-Based, Semianalytical Model for Estimating the Total Suspended Matter Concentration in the Slightly Turbid Xin ’ anjiang Reservoir (China). IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2016, 9, 398–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, V.S.; Kaleita, A.; Barbosa, C.C.; Fassoni-Andrade, A.C.; Lobo, F.D.L.; Novo, E.M.L.M. Remote sensing of large reservoir in the drought years: Implications on surface water change and turbidity variability of Sobradinho reservoir (Northeast Brazil). Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2019, 13, 275–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashikur, M.; Rupom, R.; Sazzad, M. A remote sensing approach to ascertain spatial and temporal variations of seawater quality parameters in the coastal area of Bay of Bengal, Bangladesh. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2021, 23, 100593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erkkilä, A.; Kalliola, R. Patterns and dynamics of coastal waters in multi-temporal satellite images: Support to water quality monitoring in the Archipelago Sea, Finland. Estuarine, Coast. Shelf Sci. 2004, 60, 165–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, N.C.; Kudela, R.M. Spatial Variability of Suspended Sediments in San Francisco Bay, California. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanda, A.; Šerić, L.; Bugarić, M.; Braović, M. Mapping Chlorophyll-a Concentrations in the Kaštela Bay and Brač Channel Using Ridge Regression and Sentinel-2 Satellite Images. Electronics 2021, 10, 3004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poddar, S.; Chacko, N.; Swain, D. Estimation of Chlorophyll-a in Northern Coastal Bay of Bengal Using Landsat-8 OLI and Sentinel-2 MSI Sensors. Front. Mar. Sci. 2019, 6, 598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Zhong, Y.; Liu, S.; Lao, Q.; Chen, C.; Fu, D.; Chen, F. Remote Sensing Estimates of Particulate Organic Carbon Sources in the Zhanjiang Bay Using Sentinel-2 Data and Carbon Isotopes. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 3768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapalanga, T.S.; Hoko, Z.; Gumindoga, W.; Chikwiramakomo, L. Remote-sensing-based algorithms for water quality monitoring in Olushandja Dam, north-central Namibia. Water Supply 2020, 21, 1878–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Song, K.; Wen, Z.; Liu, G.; Shang, Y.; Fang, C.; Lyu, L.; Wang, Q. Quantifying Turbidity Variation for Lakes in Daqing of Northeast China Using Landsat Images from 1984 to 2018. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2021, 14, 8884–8897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, R.M.; Forsythe, R.D.; Vaughan, G.E.; Olmsted, L.L. Assessing Water Quality in Catawba River Reservoirs Using Landsat Thematic Mapper Satellite Data. Lake Reserv. Manag. 1998, 14, 405–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nechad, B.; Ruddick, K.; Park, Y. Calibration and validation of a generic multisensor algorithm for mapping of total suspended matter in turbid waters. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 854–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nechad, B.; Ruddick, K.G.; Neukermans, G. Calibration and validation of a generic multisensor algorithm for mapping of turbidity in coastal waters. In Proceedings of the SPIE—The International Society for Optical Engineering, Berlin, Germany, 9 September 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Dogliotti, A.; Ruddick, K.; Nechad, B.; Doxaran, D.; Knaeps, E. A single algorithm to retrieve turbidity from remotely-sensed data in all coastal and estuarine waters. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 156, 157–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Restrepo, J.D.; Zapata, P.; Díaz, J.M.; Garzón-Ferreira, J.; García, C.B.; Restrepo, J.C. Aportes Fluviales al mar Caribe y Evaluación Preliminar del Impacto sobre los Ecosistemas Costeros; Universidad Eafit: Medellin, Colombia, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Molares, R.; Mestres, M. Efectos de la descarga estacional del Canal del Dique en el mecanismo de intercambio de aguas de una bahía semicerrada y micromareal: Bahía de Cartagena, Colombia. Bol. Cient. CIOH 2012, 30, 53–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IDEAM. Consulta y Descarga de Datos Hidrometeorológicos. 2023. Available online: http://dhime.ideam.gov.co/atencionciudadano/ (accessed on 6 November 2023).
- Instituto de Hidraulica y Saneamiento Ambiental, Universidad de Cartagena. Valoración de los Niveles de Riesgos Ambientales en el Distrito de Cartagena; Payares-Romero, R., Mouthon-Bello, V., Eds.; Universidad de Cartagena: Cartagena, Colombia, 2014; 314p. [Google Scholar]
- Molares, B.R. Clasificación e identificación de las componentes de marea del Caribe colombiano. Bol. Cient. CIOH 2004, 22, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mobley, C.D. Estimation of the remote-sensing reflectance from above-surface measurements. Appl. Opt. 1999, 38, 7442–7455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- IOCCG. IOCCG Ocean Optics and Biogeochemistry Protocols for Satellite Ocean Colour Sensor Validation; IOCCG Protocol Series; International Ocean Colour Coordinating Group (IOCCG): Dartmouth, NS, Canada, 2019; Volume 3, 67p. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augusto-Silva, P.B.; Ogashawara, I.; Barbosa, C.C.F.; De Carvalho, L.A.S.; Jorge, D.S.F.; Fornari, C.I.; Stech, J.L. Analysis of MERIS Reflectance Algorithms for Estimating Chlorophyll-a Concentration in a Brazilian Reservoir. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 11689–11707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maciel, D.; Novo, E.; de Carvalho, L.S.; Barbosa, C.; Júnior, R.F.; Lobo, F.D.L. Retrieving Total and Inorganic Suspended Sediments in Amazon Floodplain Lakes: A Multisensor Approach. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanhellemont, Q.; Ruddick, K. Acolite for Sentinel-2: Aquatic applications of MSI imagery. In Proceedings of the 2016 ESA Living Planet Symposium, Prague, Czech Republic, 9–13 May 2016; ESA Special Publication SP-740. pp. 9–13. [Google Scholar]
- Bernardo, N.; Watanabe, F.; Rodrigues, T.; Alcântara, E. Atmospheric correction issues for retrieving total suspended matter concentrations in inland waters using OLI/Landsat-8 image. Adv. Space Res. 2017, 59, 2335–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caballero, I.; Steinmetz, F.; Navarro, G. Evaluation of the first year of operational Sentinel-2A data for retrieval of suspended solids in medium- to high-turbiditywaters. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çako, V. Water Transparency as One as of Trophic State Indices in Narta Lagoon. IOSR J. Eng. 2014, 4, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baughman, C.A.; Jones, B.M.; Bartz, K.K.; Young, D.B.; Zimmerman, C.E. Reconstructing Turbidity in a Glacially Influenced Lake Using the Landsat TM and ETM+ Surface Reflectance Climate Data Record Archive, Lake Clark, Alaska. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 13692–13710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Liu, H.; Beck, R.A.; Reif, M.K.; Emery, E.B.; Young, J.L. Regional Analysis of Lake and Reservoir Water Quality with Multispectral Satellite Remote Sensing Images. Technical Report, U.S. Army Corps of Engineers, Engineer Research and Development Center, ERDC/EL TR-19-19. Available online: https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/Regional-analysis-of-lake-and-reservoir-water-with-Xu-Liu/0fdfe983b8024fb915694ebd8bd534960f4ba242 (accessed on 3 November 2023).
- Gholizadeh, M.H.; Melesse, A.M.; Reddi, L. A Comprehensive Review on Water Quality Parameters Estimation Using Remote Sensing Techniques. Sensors 2016, 16, 1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bukata, R.P.; Jerome, J.H.; Kondratyev, K.Y.; Pozdnyakov, D.V. Optical Properties and Remote Sensing of Inland and Coastal Waters; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Uudeberg, K.; Ansko, I.; Põru, G.; Ansper, A.; Reinart, A. Using opticalwater types to monitor changes in optically complex inland and coastalwaters. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, G.C.; Barnard, A.H.; McLean, S.; Egli, P.J.; Moore, C.; Zaneveld, J.R.V.; Dickey, T.D.; Hanson, A. In situ optical variability and relationships in the Santa Barbara Channel: Implications for remote sensing. Appl. Opt. 2006, 45, 3593–3604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lubac, B.; Loisel, H. Variability and classification of remote sensing reflectance spectra in the eastern English Channel and southern North Sea. Remote Sens. Environ. 2007, 110, 45–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Q.; Li, J.; Zhang, F.; Sun, X.; Li, J.; Li, W.; Zhang, B. Classification of Several Optically Complex Waters in China Using in Situ Remote Sensing Reflectance. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 14731–14756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maza, M.; Voulgaris, G.; Subrahmanyam, B. Subtidal inner shelf currents off Cartagena de Indias, Caribbean coast of Colombia. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33, L21606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavora, J.; Boss, E.; Doxaran, D.; Hill, P. An Algorithm to Estimate Suspended Particulate Matter Concentrations and Associated Uncertainties from Remote Sensing Reflectance in Coastal Environments. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.; Loisel, H.; Vantrepotte, V.; Mériaux, X.; Bryère, P.; Ouillon, S.; Dessailly, D.; Xing, Q.; Zhu, J. Development of a Semi-Analytical Algorithm for the Retrieval of Suspended Particulate Matter from Remote Sensing over Clear to Very Turbid Waters. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katlane, R.; Nechad, B.; Ruddick, K.; Zargouni, F. Optical remote sensing of turbidity and total suspended matter in the Gulf of Gabes. Arab. J. Geosci. 2011, 6, 1527–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maimouni, S.; Moufkari, A.A.; Daghor, L.; Fekri, A.; Oubraim, S.; Lhissou, R. Spatiotemporal monitoring of low water turbidity in Moroccan coastal lagoon using Sentinel-2 data. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2022, 26, 100772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odermatt, D.; Gitelson, A.; Brando, V.E.; Schaepman, M. Review of constituent retrieval in optically deep and complex waters from satellite imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 118, 116–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Restrepo, J.D.; Escobar, R.; Tosic, M. Fluvial fluxes from the Magdalena River into Cartagena Bay, Caribbean Colombia: Trends, future scenarios, and connections with upstream human impacts. Geomorphology 2018, 302, 92–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

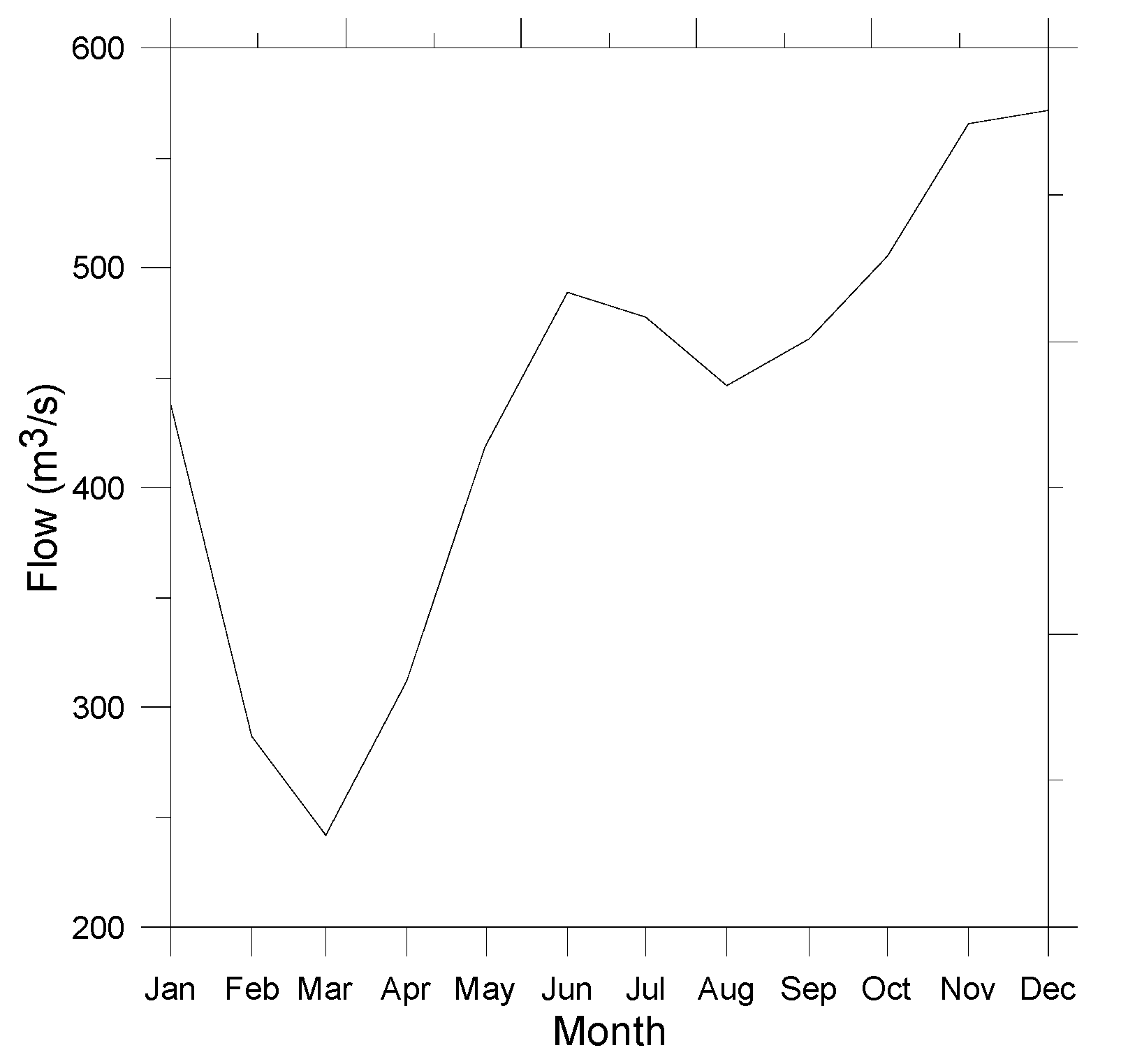
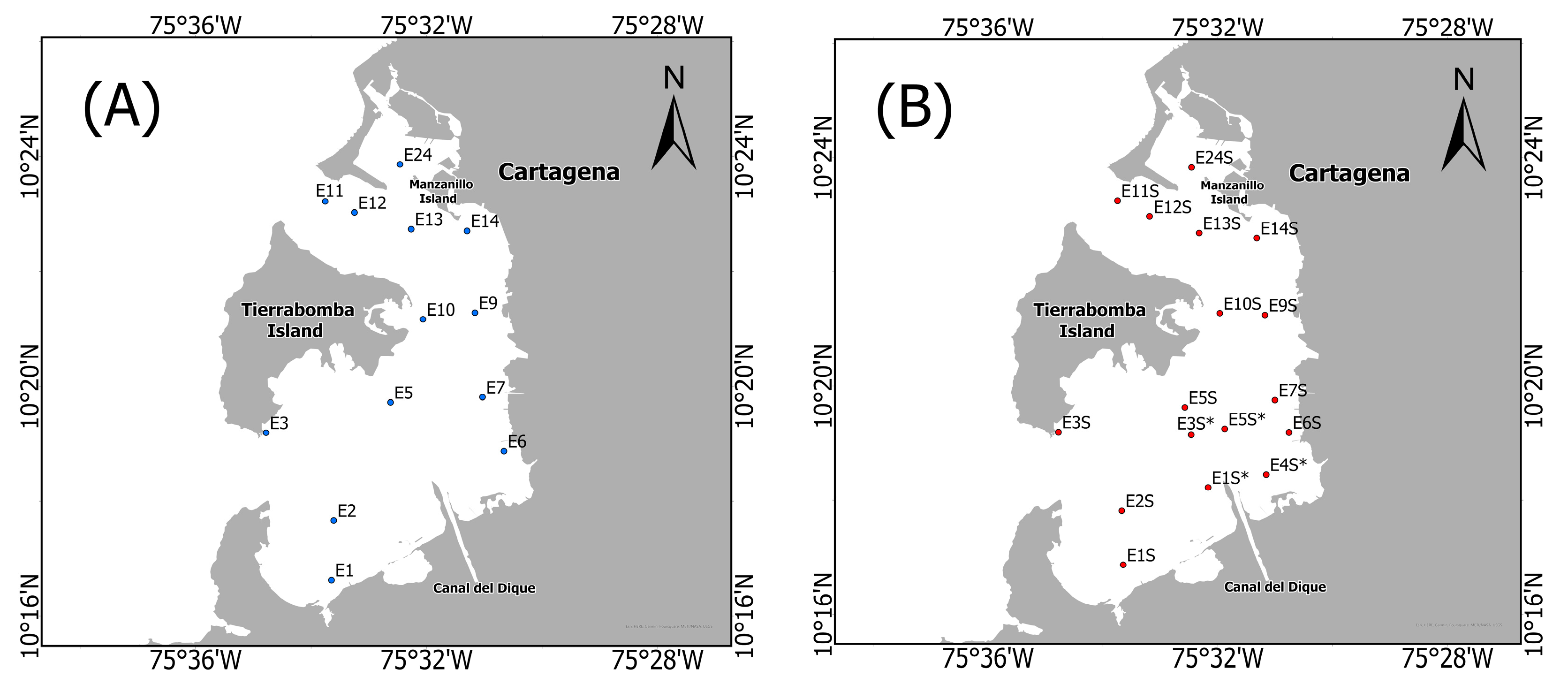
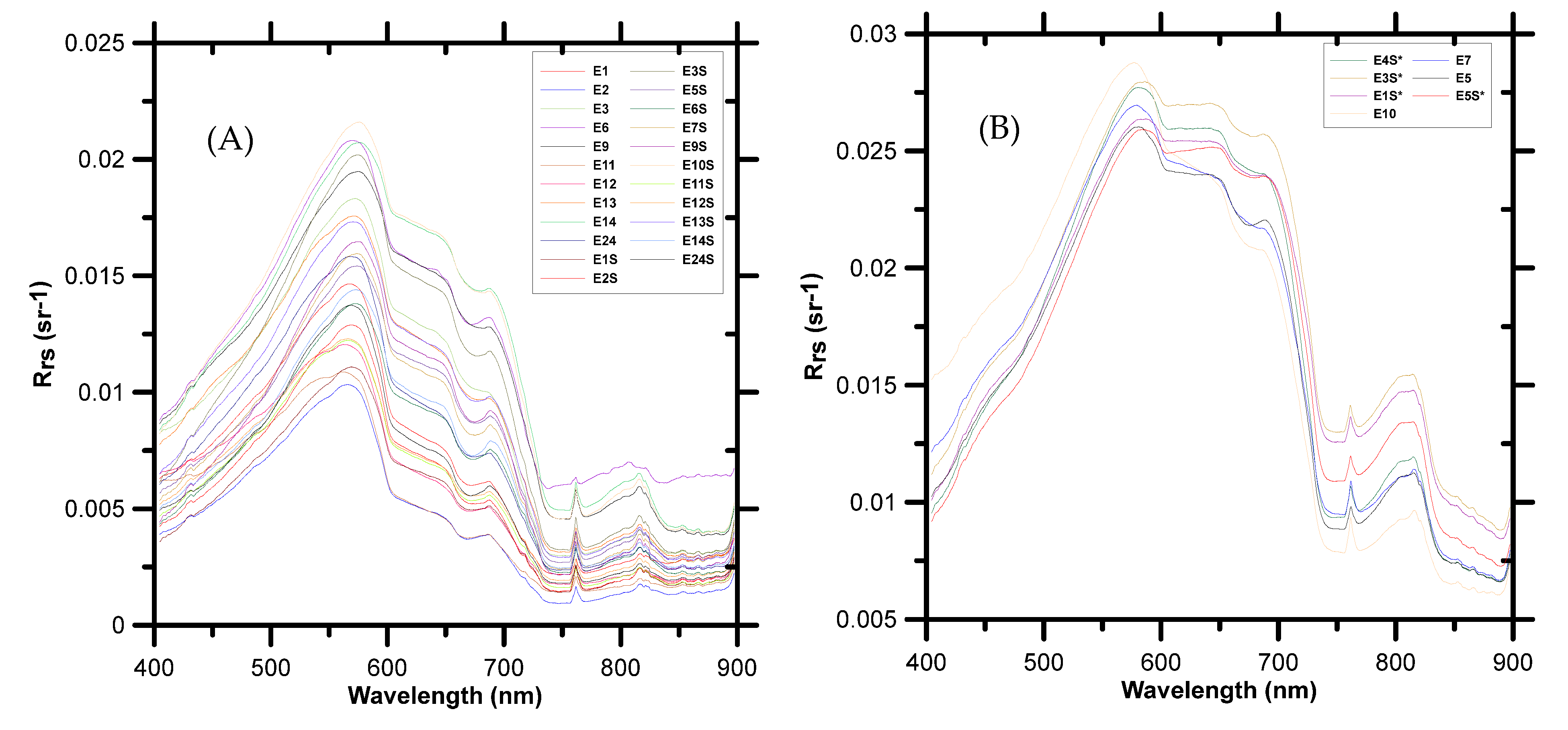
| Campaign | Calibration Stations | Validation Stations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inside the Plume | Outside the Plume | Inside the Plume | Outside the Plume | |
| January, 2022 | E7, E10 | E1, E2, E3, E6, E9, E14, E24 | E5 | E11, E13, E24 |
| February, 2022 | E1S*, E3S*, E5S* | E13S, E1S, E2S, E5S, E3S, E9S, E10S, E11S, E12S | E4S* | E6S, E7S, E14S |
| Total Stations | 5 | 16 | 2 | 6 |
| Model | Algorithm |
|---|---|
| Dogliotti et al. [36] | nm, |
| Nechad et al. [35] | |
| Kapalanga et al. [31] | |
| Wang et al. [32] | |
| Cox et al. [33] |
| Date | Flow Measured at Santa Helena Station (m3/s) | Wind Speed Range (9 a.m.–12:30 p.m.), Rafael Nuñez Station (m/s) | Wind Speed Range (9 a.m.–12:30 p.m.) Measured during Fieldwork (m/s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 26 January 2022 | 537.06 | NA | 1.8–5.0 |
| 28 January 2022 | 511.82 | NA | 0.5–4.0 |
| 2 February 2022 | 459.30 | NA | 1.3–5.0 |
| 3 February 2022 | 457.75 | 1.5-3.9 | 0.4–5.0 |
| Wavelength (nm) | Intercept | Slope | R2 | RMSE | MAPE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 665 | 0.03 | 707.98 | 0.7 | 3.1 | 25.9 |
| 865 | 0.77 | 2341.96 | 0.7 | 4.6 | 34.7 |
| Algorithm | R2 | RMSE | MAPE |
| This study: Cartagena Bay | 0.83 | 2.72 | 24.8 |
| Dogliotti et al. [36] | 0.75 | 31.4 | 107.9 |
| Nechad et al. [35] | 0.77 | 10.6 | 45.1 |
| Kapalanga et al. [31] | 0.72 | 15.6 | 188.3 |
| Wang et al. [32] | 0.80 | 43.2 | 565.2 |
| Cox et al. [33] | 0.79 | 83.3 | 93 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Eljaiek-Urzola, M.; Sander de Carvalho, L.A.; Betancur-Turizo, S.P.; Quiñones-Bolaños, E.; Castrillón-Ortiz, C. Spatial Patterns of Turbidity in Cartagena Bay, Colombia, Using Sentinel-2 Imagery. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 179. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16010179
Eljaiek-Urzola M, Sander de Carvalho LA, Betancur-Turizo SP, Quiñones-Bolaños E, Castrillón-Ortiz C. Spatial Patterns of Turbidity in Cartagena Bay, Colombia, Using Sentinel-2 Imagery. Remote Sensing. 2024; 16(1):179. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16010179
Chicago/Turabian StyleEljaiek-Urzola, Monica, Lino Augusto Sander de Carvalho, Stella Patricia Betancur-Turizo, Edgar Quiñones-Bolaños, and Carlos Castrillón-Ortiz. 2024. "Spatial Patterns of Turbidity in Cartagena Bay, Colombia, Using Sentinel-2 Imagery" Remote Sensing 16, no. 1: 179. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16010179
APA StyleEljaiek-Urzola, M., Sander de Carvalho, L. A., Betancur-Turizo, S. P., Quiñones-Bolaños, E., & Castrillón-Ortiz, C. (2024). Spatial Patterns of Turbidity in Cartagena Bay, Colombia, Using Sentinel-2 Imagery. Remote Sensing, 16(1), 179. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16010179







