Activities to Promote the Moon as an Absolute Calibration Reference
Abstract
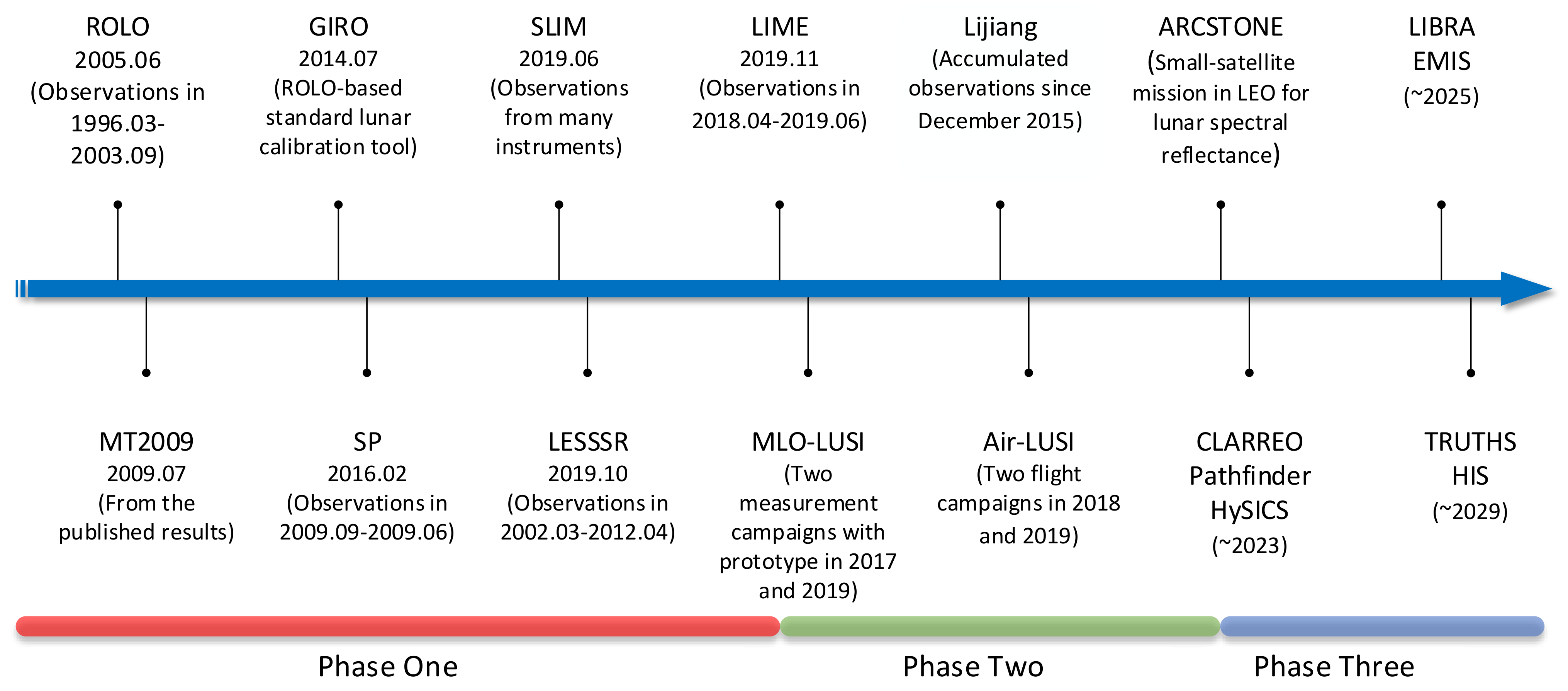
1. Introduction
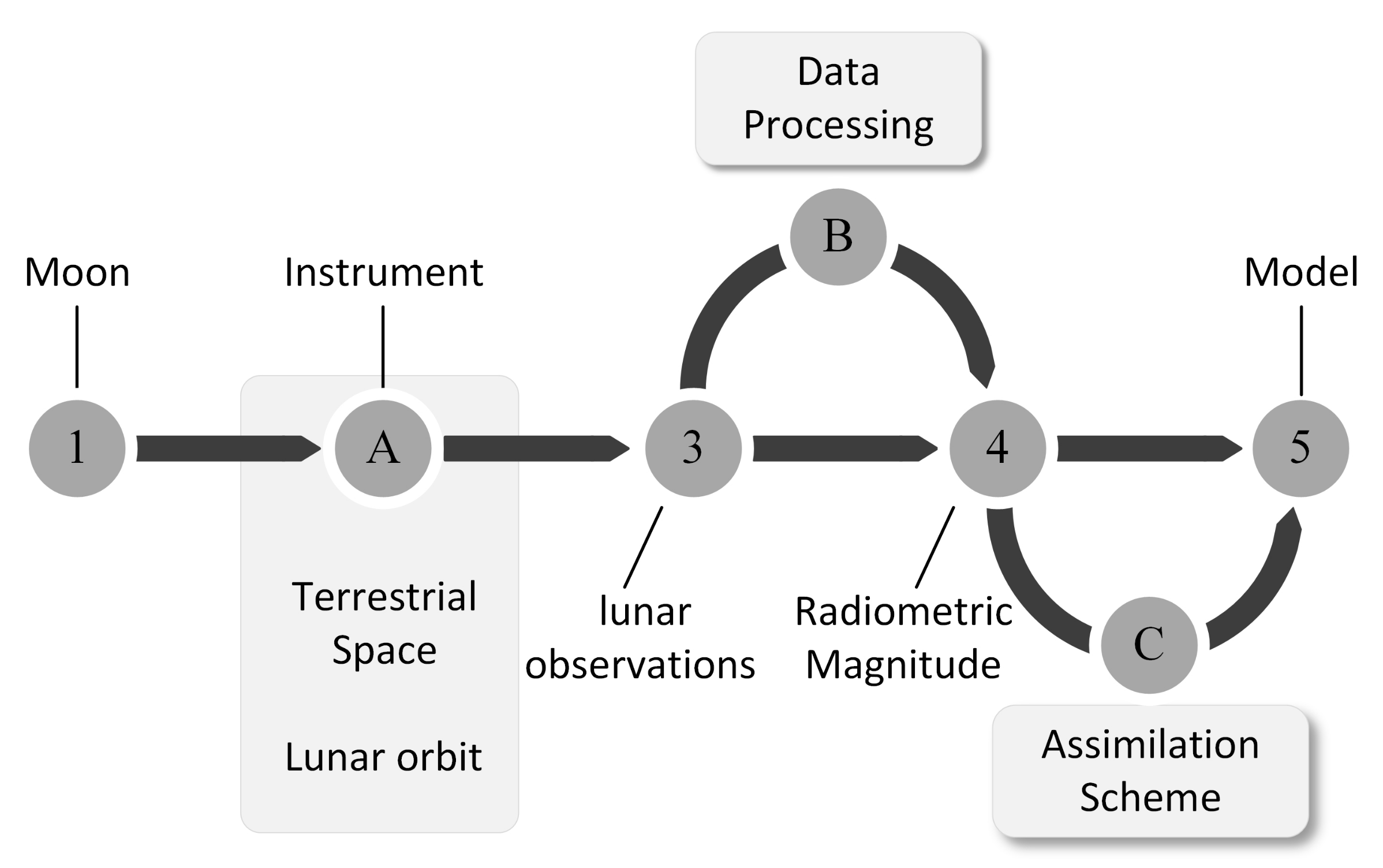
2. Lunar Models in Radiometric Calibration
2.1. General Form
2.2. Early Lunar Observations
2.3. First Lunar Irradiance Model
2.4. Lunar Irradiance Based on Early Observations
2.5. Hyperspectral Reflectance Model from Lunar Orbital Data
2.6. Irradiance Modeling with Integrated Multi-Source Data
2.7. Improved Irradiance Model Using CE318 Data
2.8. Lunar Irradiance Model with Space-Based Data
2.9. Overview of Model Performance and Applications
2.9.1. Model Performance Profile
2.9.2. Application and Refinement Activities
3. High-Accuracy Lunar Spectral Irradiance Project
3.1. Lunar Spectral Irradiance at the Mauna Loa Observatory
3.2. Airborne Lunar Spectral Irradiance
3.3. ARCSTONE
3.4. Lijing Project
4. SI-Traceable Satellites Lunar Observation Program
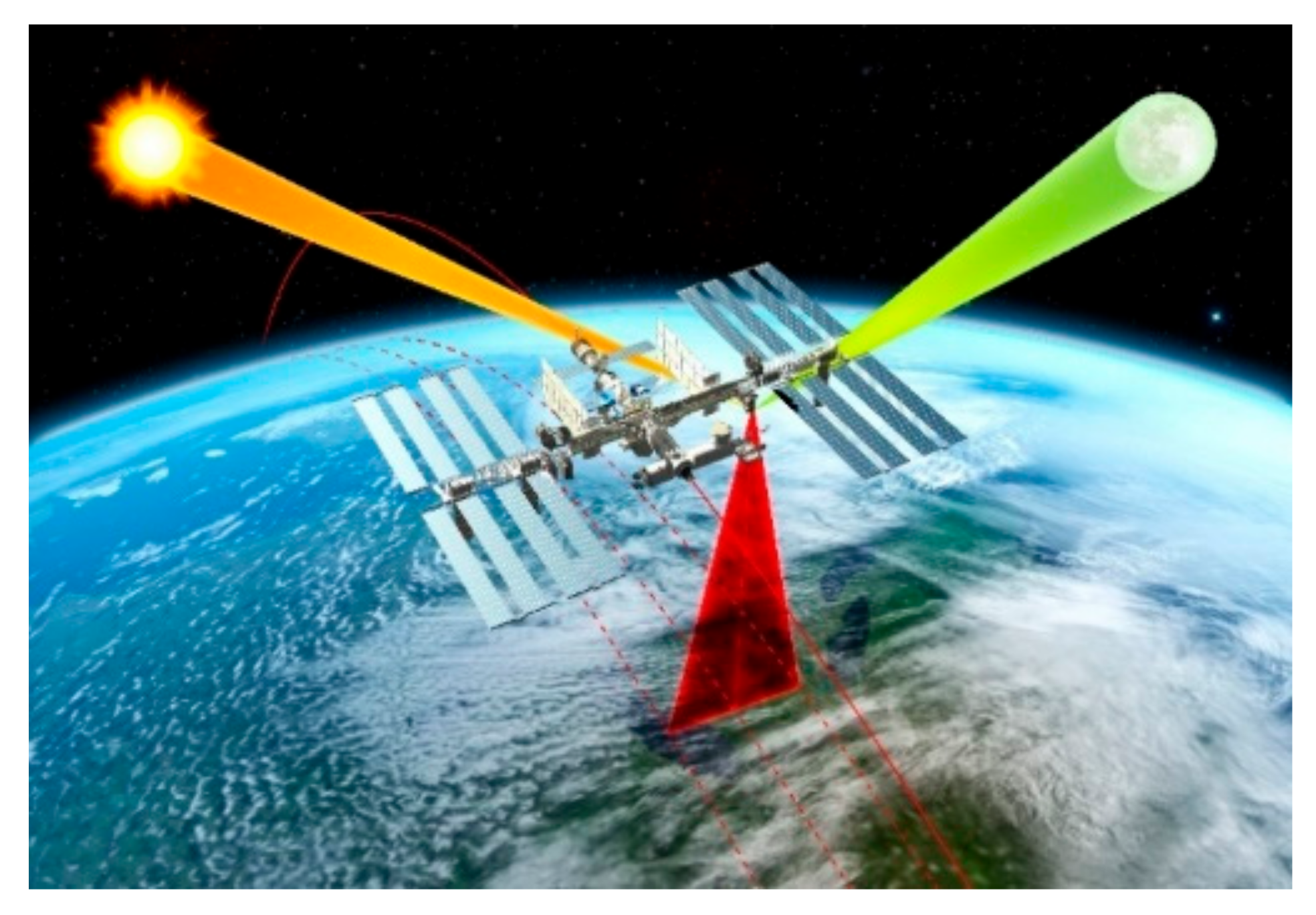
4.1. CLARREO Pathfinder
4.2. TRUTHS
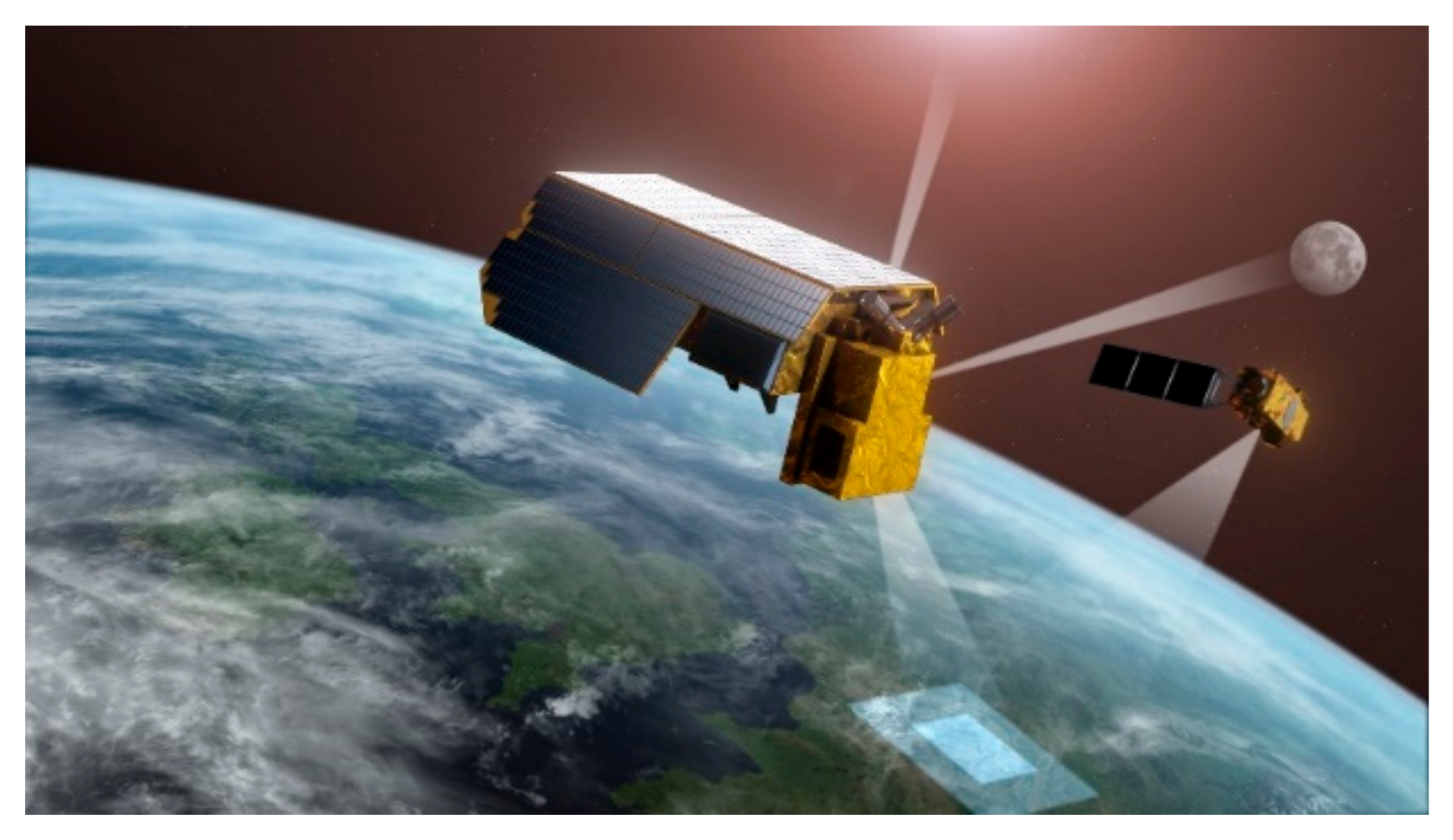
4.3. LIBRA
5. Discussion
5.1. Data Fusion
5.2. Model Formulation
5.3. Radiance of Specific Parts
5.4. Usage Policy
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tatem, A.J.; Goetz, S.J.; Hay, S.I. Fifty years of Earth-observation satellites—Views from space have led to countless advances on the ground in both scientific knowledge and daily life. Am. Sci. 2008, 96, 390–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GCOS. The Global Observing System for Climate: Implementation Needs. Available online: https://library.wmo.int/doc_num.php?explnum_id=3417 (accessed on 12 November 2021).
- Meygret, A.; Blanchet, G.; Latry, C.; Kelbert, A.; Gross-Colzy, L. On-orbit star-based calibration and modulation transfer function measurements for PLEIADES high-resolution optical sensors. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 5525–5534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, X.; Aldoretta, E.; Angal, A.; Chang, T.; Geng, X.; Link, D.; Salomonson, V.; Twedt, K.; Wu, A. Terra MODIS: 20 years of on-orbit calibration and performance. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2020, 14, 037501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterckx, S.; Brown, I.; Kääb, A.; Krol, M.; Morrow, R.; Veefkind, P.; Boersma, K.F.; De Mazière, M.; Fox, N.; Thorne, P. Towards a European Cal/Val service for Earth observation. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2020, 41, 4496–4511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberg, M.; Ohring, G.; Butler, J.; Cao, C.; Datla, R.; Doelling, D.; Gaertner, V.; Hewison, T.; Iacovazzi, B.; Kim, D.; et al. The global space-based inter-calibration system. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2011, 92, 467–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belward, A. International co-operation in satellite sensor calibration: The role of the CEOS working group on calibration and validation. Adv. Space Res. 1999, 23, 1443–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Hu, X.; Guo, M.; Xu, N. Multisite calibration tracking for FY-3A MERSI solar bands. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2012, 50, 4929–4942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helder, D.; Thome, K.J.; Mishra, N.; Chander, G.; Xiong, X.; Angal, A.; Choi, T. Absolute radiometric calibration of Landsat using a pseudo invariant calibration site. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2013, 51, 1360–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chander, G.; Xiong, X.; Choi, T.; Angal, A. Monitoring on-orbit calibration stability of the Terra MODIS and Landsat 7 ETM+ sensors using pseudo-invariant test sites. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 925–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.; Shao, X.; Qiu, S.; Ma, L.; Gao, C.; Li, C. Stability monitoring of the VIIRS Day/Night Band over Dome C with a lunar irradiance model and BRDF correction. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, X.; Wu, A.; Wenny, B.N. Using Dome C for moderate resolution imaging spectroradiometer calibration stability and consistency. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2009, 3, 033520. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Hu, X.; Zheng, Z.; Chen, L. Radiometric calibration tracking detection for FY-3A/MERSI by joint use of snow targets in south and north poles. Acta Opt. Sin. 2018, 38, 0212003. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidinger, A.K.; Cao, C.Y.; Sullivan, J.T. Using Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectrometer (MODIS) to calibrate Advanced Very High Resolution Radiometer reflectance channels. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2002, 107, AAC-11-1–AAC-11-10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hewison, T.J.; Wu, X.; Yu, F.; Tahara, Y.; Hu, X.; Kim, D.; Koenig, M. GSICS inter-calibration of infrared channels of geostationary imagers using Metop/IASI. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2013, 51, 1160–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Chu, M.; Wang, M. Degradation nonuniformity in the solar diffuser bidirectional reflectance distribution function. Appl. Opt. 2016, 55, 6001–6016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farhad, M.M.; Kaewmanee, M.; Leigh, L.; Helder, D. Radiometric cross calibration and validation using 4 angle BRDF model between Landsat 8 and Sentinel 2A. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, A.; Geng, X.; Wald, A.; Angal, A.; Xiong, X. Assessment of Terra MODIS on-orbit polarization sensitivity using pseudoinvariant desert sites. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 55, 4168–4176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chander, G.; Helder, D.L.; Aaron, D.; Mishra, N.; Shrestha, A.K. Assessment of spectral, misregistration, and spatial uncertainties inherent in the cross-calibration study. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2013, 51, 1282–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Qi, C.; Hu, X.; Gu, M.; Yang, T.; Xu, H.; Lee, L.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, P. FY-3D HIRAS radiometric calibration and accuracy assessment. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 58, 3965–3976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatt, R.; Doelling, D.R.; Wu, A.; Xiong, X.; Scarino, B.R.; Haney, C.O.; Gopalan, A. Initial stability assessment of S-NPP VIIRS reflective solar band calibration using invariant desert and deep convective cloud targets. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 2809–2826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouyama, T.; Kato, S.; Kikuchi, M.; Sakuma, F.; Miura, A.; Tachikawa, T.; Tsuchida, S.; Obata, K.; Nakamura, R. Lunar calibration for ASTER VNIR and TIR with observations of the Moon in 2003 and 2017. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santer, R.; Martiny, N.; Cabot, F. Two different approaches to achieve vicarious calibration without a priori on the aerosol model: Application to SPOT5 over the test site of La Crau, France. In Proceedings of the Sensors, Systems, & Next-Generation Satellites VII, Barcelona, Spain, 8–12 September 2003; pp. 456–467. [Google Scholar]
- Obata, K.; Tsuchida, S.; Iwao, K. Inter-band radiometric comparison and calibration of ASTER visible and near-infrared bands. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 15140–15160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kieffer, H.H. Photometric stability of the lunar surface. Icarus 1997, 130, 323–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kieffer, H.; Wildey, R. Absolute calibration of Landsat instruments using the Moon. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 1985, 51, 1391–1393. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, T.; Angal, A.; Xiong, X. Orbital path and spacecraft attitude correction for the MODIS lunar spatial characterization. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 58, 1063–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, T.; Xiong, X. Planning lunar observations for satellite missions in low-Earth orbit. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2019, 13, 024513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Xiong, X.; Fulbright, J.; Lei, N. VIIRS Day/Night Band radiometric calibration stability monitoring using the Moon. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2017, 122, 5616–5624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.Q.; Xiong, X.; Barnes, W.L.; Guenther, B. MODIS reflective solar bands on-orbit lunar calibration. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2007, 45, 2383–2393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.; Zhang, P.; Xu, N.; Hu, X.; Chen, L.; Zhang, L.; Yang, Z. FY-3D MERSI on-orbit radiometric calibration from the lunar view. Sensors 2020, 20, 4690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.; Zhang, P.; Zheng, X.; Hu, X.; Xu, N.; Zhang, L.; Qiao, Y. Data collection and irradiance conversion of lunar observation for MERSI. Opt. Precis. Eng. 2019, 27, 1819–1827. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Change, C. Achieving Satellite Instrument Calibration for Climate Change (ASIC3). Available online: http://wcrp.ipsl.jussieu.fr/Documents/ACC/WOAP/WOAP_SatelliteObs4CC2007.pdf (accessed on 3 October 2021).
- Kouyama, T.; Nakamura, R.; Kato, S.; Miyashita, N. One-year lunar calibration result of Hodoyoshi-1, Moon as an ideal target for small satellite radiometric calibration. In Proceedings of the Small Satellite Conference, Logan, UT, USA, 4–9 August 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Roux, J.; Christopher, S.; Maskey, M. Exploring the use of PlanetScope data for particulate matter air quality research. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, C.L.; Lukashin, C.; Taylor, P.C.; Swanson, R.; Kirk, W.S.; Cooney, M.; Swartz, W.H.; Goldberg, A.; Stone, T.; Jackson, T.; et al. Trutinor: A conceptual study for a next-generation Earth radiant energy instrument. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, S.C.; Hewison, T.; Stone, T.; Lachérade, S.; Fougnie, B.; Xiong, X. A summary of the joint GSICS—CEOS/IVOS lunar calibration workshop: Moving towards intercalibration using the Moon as a transfer target. In Proceedings of the Sensors Systems, & Next-Generation Satellites XIX, Toulouse, France, 21–24 September 2015; p. 96390Z. [Google Scholar]
- Kieffer, H.H.; Stone, T.C. The spectral irradiance of the Moon. Astron. J. 2005, 129, 2887–2901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, S.D.; Turner, R.E. A dynamic lunar spectral irradiance data set for NPOESS/VIIRS Day/Night Band nighttime environmental applications. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2009, 47, 2316–2329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokota, Y.; Matsunaga, T.; Ohtake, M.; Haruyama, J.; Nakamura, R.; Yamamoto, S.; Ogawa, Y.; Morota, T.; Honda, C.; Saiki, K.; et al. Lunar photometric properties at wavelengths 0.5–1.6 μm acquired by SELENE Spectral Profiler and their dependency on local albedo and latitudinal zones. Icarus 2011, 215, 639–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouyama, T.; Yokota, Y.; Ishihara, Y.; Nakamura, R.; Yamamoto, S.; Matsunaga, T. Development of an application scheme for the SELENE/SP lunar reflectance model for radiometric calibration of hyperspectral and multispectral sensors. Planet. Space Sci. 2016, 124, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lane, A.P.; Irvine, W.M. Monochromatic phase curves and albedos for the lunar disk. Astron. J. 1973, 78, 267–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, A.T.; Irvine, W.M. Multicolor photoelectric photometry of the brighter planets. I. Program and Procedure. Astron. J. 1967, 72, 945–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, I. Effective extinction values in wide-band photometry. Astron. J. 1952, 57, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buratti, B.J.; Hiller, J.K.; Wang, M. The lunar opposition surge: Observations by Clementine. Icarus 1996, 124, 490–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hapke, B.W.; Nelson, R.M.; Smythe, W.D. The opposition effect of the Moon—The contribution of coherent backscatter. Science 1993, 260, 509–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peacock, K. Multicolor photoelectric photometry of the Lunar surface. Icarus 1968, 9, 16–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wildey, R.L.; Pohn, H.A. Detailed photoelectric photometry of the Moon. Astron. J. 1964, 69, 619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, G.L. Three-color photoelectric photometry of the Moon. Icarus 1966, 5, 555–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, J.M.; Becker, K.J.; Kieffer, H.H.; Dodd, D.N. Real-time control of the robotic lunar observatory telescope. Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 1999, 111, 737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, T.C.; Kieffer, H.H. Absolute irradiance of the Moon for on-orbit calibration. In Proceedings of the Conference on Earth Observing Systems VII, Seattle, WA, USA, 7–11 July 2002; pp. 211–221. [Google Scholar]
- Strecker, D.W.; Erickson, E.F.; Witteborn, F.C. Airborne stellar spectrophotometry from 1.2 to 5.5 microns: Absolute calibration and spectra of stars earlier than M3. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 1979, 41, 501–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, D.S.; Pasinetti, L.E.; Philip, A.D. Calibration of Fundamental Stellar Quantities: Proceedings of the 111th Symposium of the International Astronomical Union, Como, Italy, 24–29 May 1984; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Castelli, F.; Kurucz, R.L. Model atmospheres for Vega. Astron. Astrophys. 1994, 281, 817–832. [Google Scholar]
- Stone, T.C.; Kieffer, H.H.; Anderson, J.M. Status of use of lunar irradiance for on-orbit calibration. In Proceedings of the Conference on Earth Observing Systems VI, San Diego, CA, USA, 29 July–3 August 2001; pp. 165–175. [Google Scholar]
- Lucey, P.G.; Hawke, B.R.; Pieters, C.M.; Head, J.W.; McCord, T.B. A compositional study of the Aristarchus region of the Moon using near-infrared reflectance spectroscopy. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 1986, 91, 344–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pieters, C.M.; Mustard, J.F. Exploration of crustal/mantle material for the Earth and Moon using reflectance spectroscopy. Remote Sens. Environ. 1988, 24, 151–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarah, T.; Emma, W.; Andrew, B.; Stefan, A.; Carlos, T.; Africa, B.; Alberto, B. D1: Strategy for the Derivation of an Improved Lunar Spectral Irradiance Model Based on Lunar Photometer Measurements. Available online: https://calvalportal.ceos.org/lime (accessed on 12 September 2021).
- Pieters, C.M. The Moon as a spectral calibration standard enabled by lunar samples: The Clementine example. In Proceedings of the Workshop on New Views of the Moon II: Understanding the Moon through the Integration of Diverse Datasets, Flagstaff, AZ, USA, 22–24 September 1999; pp. 47–48. [Google Scholar]
- Viticchie, B.; Stone, T.; Wagner, S.; Takahashi, M.; Hewison, T. Preparation of the GIRO Executable. Available online: http://gsics.atmos.umd.edu/pub/Development/20140916/2_GIRO_preparation_second_webmeeting.pptx (accessed on 10 September 2021).
- Wagner, S.; Hewison, T.; Stone, T.; Lachérade, S.; Fougnie, B.; Xiong, J. Outcome of the GSICS/CEOS-IVOS Lunar Calibration Workshop. Available online: https://digitalcommons.usu.edu/calcon/CALCON2015/All2015Content/47/ (accessed on 16 May 2021).
- EUMETSAT. High Level Description of the GIRO Application and Definition of the Input/Output Formats. Available online: http://gsics.atmos.umd.edu/pub/Development/LunarWorkArea/GSICS_ROLO_HighLevDescript_IODefinition.pdf (accessed on 1 March 2020).
- Shaw, J.A. Modeling infrared lunar radiance. Opt. Eng. 1999, 38, 1763–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younkin, R.L. Optical reflectance of local areas of the Moon. Astron. J. 1970, 75, 831–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, S.J.; Lau, E.; Steutel, D.; Stopar, J.D.; Wilcox, B.B.; Lucey, P.G. A new measurement of the absolute spectral reflectance of the Moon. In Proceedings of the 34th Lunar and Planetary Science Conference, League City, TX, USA, 17–21 March 2003; p. 1269. [Google Scholar]
- Nozette, S.; Rustan, P.; Pleasance, L.P.; Horan, D.M.; Regeon, P.; Shoemaker, E.M.; Spudis, P.D.; Acton, C.H.; Baker, D.N.; Blamont, J.E.; et al. The Clementine mission to the Moon: Scientific overview. Science 1994, 266, 1835–1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, M.; Takizawa, Y.; Sasaki, S. The SELENE (Kaguya) mission: Present status and preliminary science. In Proceedings of the 37th COSPAR Scientific Assembly, Montréal, QC, Canada, 13–20 July 2008; p. 1463. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, H.; Wu, J.; Dai, S.; Zhao, B.; Shu, R.; Chang, J.; Wang, H.; Zhang, X.; Ren, Q.; Chen, X.; et al. Introduction to the payloads and the initial observation results of Chang’E-1. Chin. J. Space Sci. 2008, 28, 374–384. [Google Scholar]
- Goswami, J.N. An overview of the Chandrayaan-1 mission. In Proceedings of the 41st Annual Lunar and Planetary Science Conference, Houston, TX, USA, 1–5 March 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Sobue, S.-I.; Sasaki, S.; Kato, M.; Maejima, H.; Minamino, H.; Konishi, H.; Otake, H.; Nakazawa, S.; Tateno, N.; Hoshino, H. The result of SELENE(KAGUYA) development and operation. Recent Patents Space Technol. 2009, 1, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohtake, M.; Haruyama, J.; Matsunaga, T.; Yokota, Y.; Morota, T.; Honda, C.; Team, L. Performance and scientific objectives of the SELENE (KAGUYA) Multiband Imager. Earth Planet. Space 2008, 60, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcewen, A.S. A precise lunar photometric function. In Proceedings of the Lunar and Planetary Science Conference, Houston, TX, USA, 18–22 March 1996; pp. 841–842. [Google Scholar]
- Mcewen, A.; Eliason, E.; Lucey, P.; Malaret, E.; Sucharski, T. Summary of radiometric calibration and photometric normalization steps for the clementine UVVIS images. In Proceedings of the 29th Annual Lunar and Planetary Science Conference, Houston, TX, USA, 16–20 March 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Yokota, Y.; Honda, R.; Iijima, Y.; Mizutani, H. New method of photometric correction for lunar UVVIS images. In Proceedings of the 34th Annual Lunar and Planetary Science Conference, League City, TX, USA, 17–21 March 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Kieffer, H.H. Multiple-instrument-based spectral irradiance of the Moon. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2022, 16, 038502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kieffer, H.; Stone, T. A Model of the Spectral Irradiance of the Moon for Calibration of Earth-Orbiting Spacecraft Instruments. Available online: https://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/document?repid=rep1&type=pdf&doi=7299ea94db402100489bc6b4dfbea63b31866b15 (accessed on 10 March 2020).
- Kieffer, H. Seeking a Consensus Evolutionary Lunar Calibration Model, Many Observations, One Moon. Available online: https://digitalcommons.usu.edu/calcon/CALCON2019/invitedspeaker/1/ (accessed on 6 April 2020).
- Kieffer, H. A Lunar Calibration Model Based on Many Instruments and One Moon. Available online: https://digitalcommons.usu.edu/calcon/CALCON2020/all2020content/27/ (accessed on 6 August 2021).
- Kieffer, H. Advances in the SLIM Lunar Spectral Irradiance Model; Many Observations, One Moon. Available online: https://digitalcommons.usu.edu/calcon/CALCON2021/all2021content/23/ (accessed on 6 December 2021).
- Coddington, O.M.; Richard, E.C.; Harber, D.; Pilewskie, P.; Woods, T.N.; Chance, K.; Liu, X.; Sun, K. The TSIS-1 Hybrid solar reference spectrum. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2021, 48, e2020GL091709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barreto, A.; Cuevas, E.; Damiri, B.; Guirado, C.; Berkoff, T.; Berjon, A.J.; Hernandez, Y.; Almansa, F.; Gil, M. A new method for nocturnal aerosol measurements with a lunar photometer prototype. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2013, 6, 585–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barreto, A.; Cuevas, E.; Granados-Munoz, M.-J.; Alados-Arboledas, L.; Romero, P.M.; Groebner, J.; Kouremeti, N.; Almansa, A.F.; Stone, T.; Toledano, C.; et al. The new sun-sky-lunar Cimel CE318-T multiband photometer—A comprehensive performance evaluation. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2016, 9, 631–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umow, V.N. Chromatische depolarisation durch lichtzerstreuung. Phys. Z. 1905, 6, 674–676. [Google Scholar]
- Shkuratov, Y.G.; Opanasenko, N. Is there Umov effect for the Moon in polarization minimum? In Proceedings of the 25th Lunar and Planetary Science Conference, Houston, TX, USA, 14–18 March 1994; p. 1271. [Google Scholar]
- Zubko, E.; Videen, G.; Shkuratov, Y.; Muinonen, K.; Yamamoto, T. The Umov effect for single irregularly shaped particles with sizes comparable with wavelength. Icarus 2011, 212, 403–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottwald, M.; Bovensmann, H. SCIAMACHY—Exploring the Changing Earth’s Atmosphere; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Bovensmann, H.; Burrows, J.P.; Buchwitz, M.; Frerick, J.; Noel, S.; Rozanov, V.V.; Chance, K.V.; Goede, A.P.H. SCIAMACHY: Mission objectives and measurement modes. J. Atmos. Sci. 1999, 56, 127–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frerick, J.; Cozzoni, B.; Slijkhuis, E.; Debeek, R.; Skupin, J. SCIAMACHY In-Flight Calibration. Available online: https://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/document?repid=rep1&type=pdf&doi=ecb0d75ae276b3e9615d2e40af659744a37cab00 (accessed on 6 December 2021).
- Liebing, P.; Krijger, M.; Snel, R.; Bramstedt, K.; Noel, S.; Bovensmann, H.; Burrows, J.P. In-flight calibration of SCIAMACHY’s polarization sensitivity. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2018, 11, 265–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilbig, T.; Weber, M.; Bramstede, K.; Noel, S.; Burrows, J.P.; Krijger, J.M.; Snel, R.; Meftah, M.; Dame, L.; Bekki, S.; et al. The new SCIAMACHY reference solar spectral irradiance and its validation. Sol. Phys. 2018, 293, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krijger, J.; Snel, R.; Van Harten, G.; Rietjens, J.; Aben, I. Mirror contamination in space I: Mirror modelling. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2014, 7, 3387–3398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krijger, M. Development of an Alternative Hyperspectral Moon Phase Reddening Model. Available online: https://www-cdn.eumetsat.int/files/2021-02/ESS-AMM-RP-001-Rev5_LunarModel_FINAL_EUMETSATwebsite.pdf (accessed on 6 December 2021).
- Urabe, T.; Xiong, X.; Hashiguchi, T.; Ando, S.; Okamura, Y.; Tanaka, K. Radiometric model and inter-comparison results of the SGLI-VNR on-board calibration. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, T.C. Radiometric calibration stability and inter-calibration of solar-band instruments in orbit using the Moon. In Proceedings of the Conference on Earth Observing Systems XIII, San Diego, CA, USA, 11–13 August 2008; pp. 268–276. [Google Scholar]
- Eplee, R.E.; Barnes, R.A.; Patt, F.S.; Meister, G.; McClain, C.R. SeaWiFS lunar calibration methodology after six years on orbit. In Proceedings of the Conference on Earth Observing Systems IX, Denver, CO, USA, 2–6 August 2004; pp. 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, T.; Shao, X.; Cao, C. On-orbit radiometric calibration of Suomi NPP VIIRS reflective solar bands using the Moon and solar diffuser. Appl. Opt. 2018, 57, 9533–9542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imai, M.; Kurihara, J.; Kouyama, T.; Kuwahara, T.; Fujita, S.; Sakamoto, Y.; Sato, Y.; Saitoh, S.I.; Hirata, T.; Yamamoto, H.; et al. Radiometric calibration for a multispectral sensor onboard RISESAT microsatellite based on lunar observations. Sensors 2021, 21, 2429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angal, A.; Xiong, X.; Wilson, T. Unscheduled lunar observations for radiometric characterization of VIIRS reflective solar bands. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 60, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuchida, S.; Yamamoto, H.; Kouyama, T.; Obata, K.; Sakuma, F.; Tachikawa, T.; Kamei, A.; Arai, K.; Czapla-Myers, J.S.; Biggar, S.F.; et al. Radiometric degradation curves for the ASTER VNIR processing using vicarious and lunar calibrations. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouyama, T.; Yokota, Y.; Ishihara, Y.; Nakamura, R.; Yamamoto, S.; Matsunaga, T.; Yamada, M.; Kameda, S.; Sawada, H.; Suzuki, H. Lunar calibration for planetary explorers using SELENE/SP lunar reflectance model. In Proceedings of the 47th Annual Lunar and Planetary Science Conference, Woodlands, TX, USA, 21–25 March 2016; p. 1723. [Google Scholar]
- Kouyama, T.; Nakamura, R.; Kato, S.; Kimura, M. Moon observations for small satellite radiometric calibration. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Geoscience & Remote Sensing Symposium, Fort Worth, TX, USA, 23–28 July 2017; pp. 3529–3532. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, T.; Shao, X.; Cao, C.; Weng, F. Radiometric stability monitoring of the Suomi NPP Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite (VIIRS) reflective solar bands using the Moon. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, X.; Cao, C.; Uprety, S.; Padula, F.; Choi, T. Comparing Hyperion lunar observation with model calculations in support of GOES-R Advanced Baseline Imager (ABI) calibration. In Proceedings of the Conference on Earth Observing Systems XIX, San Diego, CA, USA, 18–20 August 2014; pp. 634–642. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, S.; Adriaensen, S.; Toledano, C.; Barreto, Á.; Woolliams, E.; Bouvet, M. LIME: The Lunar Irradiance Model of the European Space Agency. In Proceedings of the EGU General Assembly 2021, Online, 19–30 April 2021; p. EGU21-10066. [Google Scholar]
- Neneman, M.; Wagner, S.; Bourg, L.; Blanot, L.; Bouvet, M.; Adriaensen, S.; Nieke, J. Use of Moon observations for characterization of Sentinel-3B Ocean and Land Color Instrument. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kieffer, H.H.; Wildey, R.L. Establishing the moon as a spectral radiance standard. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 1996, 13, 360–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, T.C.; Kieffer, H.H. Assessment of uncertainty in ROLO lunar irradiance for on-orbit calibration. In Proceedings of the Conference on Earth Observing Systems IX, Denver, CO, USA, 2–6 August 2004; pp. 300–310. [Google Scholar]
- Stone, T.C.; Kieffer, H.; Lukashin, C.; Turpie, K. The Moon as a climate-quality radiometric calibration reference. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, D. Stellar absolute fluxes and energy distributions from 0.32 to 4.0 μm. In Proceedings of the Symposium-International Astronomical Union, Tokyo, Japan, 11–15 November 1985; pp. 225–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, D.M.; Hummel, C.A.; Pauls, T.A.; Armstrong, J.T.; Benson, J.A.; Gilbreath, G.C.; Hindsley, R.B.; Hutter, D.J.; Johnston, K.J.; Mozurkewich, D.; et al. Vega is a rapidly rotating star. Nature 2006, 440, 896–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, S.W.; Eplee, R.E., Jr.; Xiong, X. SI-Traceable Top-of-the-Atmosphere lunar irradiance: Potential tie-points to the output of the ROLO model. In Proceedings of the Conference on Earth Observing Systems XXII, San Diego, CA, USA, 6–10 August 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, P.; Hu, X.; Chen, L.; Min, M. A novel hyperspectral lunar irradiance model based on ROLO and mean equigonal albedo. Optik 2017, 142, 657–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacherade, S.; Aznay, O.; Fougnie, B.; Lebegue, L. POLO: A unique dataset to derive the phase angle dependence of the Moon irradiance. In Proceedings of the Conference on Sensors, Systems, and Next-Generation Satellites XVIII, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 22–25 September 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Lacherade, S.; Viticchié, B.; Stone, T.; Lebégue, L.; Wagner, S.; Hewison, T. On the phase-angle dependence of the moon calibration results. GSICS Quat Lunar Calibration 2013, 7, 6–7. [Google Scholar]
- Viticchiè, B.; Wagner, S.C.; Hewison, T.J.; Stone, T.C.; Nain, J.; Gutierrez, R.; Müller, J.; Hanson, C. Lunar calibration of MSG/SEVIRI solar channels. In Proceedings of the EUMETSAT Meteorological Satellite Conference, Vienna, Austria, 16–20 September 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Barreto, A.; Roman, R.; Cuevas, E.; Berjon, A.J.; Fernando Almansa, A.; Toledano, C.; Gonzalez, R.; Hernandez, Y.; Blarel, L.; Goloub, P.; et al. Assessment of nocturnal aerosol optical depth from lunar photometry at the Izana high mountain observatory. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2017, 10, 3007–3019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, M. Lunar data preparation for Himawari-8/-9 AHI. In Proceedings of the 2nd GSICS/CEOS Lunar Calibration Workshop, Xi’an, China, 13–17 November 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Velikodsky, Y.I.; Opanasenko, N.V.; Akimov, L.A.; Korokhin, V.V.; Shkuratov, Y.G.; Kaydash, V.G.; Videen, G.; Ehgamberdiev, S.A.; Berdalieva, N.E. New Earth-based absolute photometry of the Moon. Icarus 2011, 214, 30–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saiki, K.; Saito, K.; Okuno, H.; Suzuki, A.; Yamanoi, Y.; Hirata, N.; Nakamura, R. Estimation of the lunar reflectance by ground-based observation using a tunable liquid-crystal filter telescope. Earth Planets Space 2008, 60, 417–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shkuratov, Y.; Kaydash, V.; Korokhin, V.; Velikodsky, Y.; Opanasenko, N.; Videen, G. Optical measurements of the Moon as a tool to study its surface. Planet. Space Sci. 2011, 59, 1326–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tompkins, S.; Pieters, C.M. Mineralogy of the lunar crust: Results from Clementine. Meteorit. Planet. Sci. 1999, 34, 25–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, S.; Matsunaga, T.; Ogawa, Y.; Nakamura, R.; Yokota, Y.; Ohtake, M.; Haruyama, J.; Morota, T.; Honda, C.; Hiroi, T.; et al. Preflight and in-flight calibration of the spectral profiler on board SELENE (Kaguya). IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 49, 4660–4676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besse, S.; Yokota, Y.; Boardman, J.; Green, R.; Haruyama, J.; Isaacson, P.; Mall, U.; Matsunaga, T.; Ohtake, M.; Pieters, C. One Moon, many measurements 2: Photometric corrections. Icarus 2013, 226, 127–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohtake, M.; Pieters, C.; Isaacson, P.; Besse, S.; Yokota, Y.; Matsunaga, T.; Boardman, J.; Yamomoto, S.; Haruyama, J.; Staid, M. One Moon, many measurements 3: Spectral reflectance. Icarus 2013, 226, 364–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walther, A.; Heidinger, A.K.; Miller, S. The expected performance of cloud optical and microphysical properties derived from Suomi NPP VIIRS Day/Night Band lunar reflectance. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 13230–13240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Ma, S.; Yan, W.; Jiang, J.; Huang, Y. A new multichannel threshold algorithm based on radiative transfer characteristics for detecting fog/low stratus using night-time NPP/VIIRS data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2017, 38, 5919–5933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kieffer, H.H.; Anderson, J.M. Use of the Moon for spacecraft calibration over 350–2500 nm. In Proceedings of the Conference on Sensors, Systems, and Next-Generation Satellites II, Barcelona, Spain, 21–24 September 1998; pp. 325–336. [Google Scholar]
- Sindy, S.; Stefan, A. PROBA-V Vicarious Calibration: Investigation into the Impact of In-Orbit Temperature Variation. Available online: http://gsics.atmos.umd.edu/pub/Development/20210812/PROBAV_calibration_GSICS_aug2021.pdf (accessed on 12 December 2021).
- Kieffer, H. Status of the SLIMED lunar model. GSICS Quat 2022, 15, 7–9. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, C.; Bai, Y.; Wang, W.; Choi, T. Radiometric inter-consistency of VIIRS DNB on Suomi NPP and NOAA-20 from observations of reflected lunar lights over deep convective clouds. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, S.; Changyong, C.; Sirish, U. Comparing Hyperion-Observed with Model-Predicted Lunar Irradiances in Support of GOES-R ABI Calibration. Available online: https://digitalcommons.usu.edu/calcon/CALCON2012/All2012Content/55/ (accessed on 12 December 2019).
- Kieffer, H.H.; Jarecke, P.; Pearlman, J. Initial lunar calibration observations by the EO-1 Hyperion imaging spectrometer. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Optical Science and Technology, San Diego, CA, USA, 29 July–3 August 2002; pp. 247–258. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, X.; Sun, J.; Fulbright, J.; Wang, Z.; Butler, J.J. Lunar calibration and performance for S-NPP VIIRS reflective solar bands. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 54, 1052–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meygret, A.; Blanchet, G.; Colzy, S.; Gross-Colzy, L. Improving ROLO lunar albedo model using PLEIADES-HR satellites extra-terrestrial observations. In Proceedings of the Conference on Earth Observing Systems XXII, San Diego, CA, USA, 6–10 August 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Mishra, N.; Haque, M.O.; Leigh, L.; Aaron, D.; Helder, D.; Markham, B. Radiometric cross calibration of Landsat 8 Operational Land Imager (OLI) and Landsat 7 Enhanced Thematic Mapper Plus (ETM plus). Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 12619–12638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, X.; Angal, A.; Twedt, K.A.; Chen, H.; Link, D.; Geng, X.; Aldoretta, E.; Mu, Q. MODIS reflective solar bands on-orbit calibration and performance. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 6355–6371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zhang, P.; Wu, R.; Hu, X.; Zhang, L. Monitoring radiometric response change of visible band for FY-2 geostationary meteorological satellite by lunar target. J. Remote Sens. 2018, 22, 211–219. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wu, R.; Zhang, P.; Yang, Z.; Hu, X.; Ding, L.; Chen, L. Monitor radiance calibration of the remote sensing instrument with reflected lunar irradiance. J. Remote Sens. 2016, 20, 278–289. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Sun, J.; Xiong, X. Improved lunar irradiance model using multiyear MODIS lunar observations. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 59, 5154–5170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roman, R.; Gonzalez, R.; Toledano, C.; Barreto, A.; Perez-Ramirez, D.; Benavent-Oltra, J.A.; Olmo, F.J.; Cachorro, V.E.; Alados-Arboledas, L.; de Frutos, A.M. Correction of a lunar-irradiance model for aerosol optical depth retrieval and comparison with a star photometer. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2020, 13, 6293–6310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, P.; Hu, X.; Chen, L.; Min, M.; Xu, N.; Wu, R. Radiometric cross-calibration for multiple sensors with the Moon as an intermediate reference. J. Meteorol. Res. 2019, 33, 925–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, C.; Vermote, E.; Xiong, X. Using AVHRR lunar observations for NDVI long-term climate change detection. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2009, 114, D20105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, X.; Choi, T.; Cao, C.; Blonski, S.; Wang, W.; Bai, Y. Trending of Suomi-NPP VIIRS radiometric performance with lunar band ratio. In Proceedings of the Conference on Earth Observing Missions and Sensors—Development, Implementation, and Characterization III, Beijing, China, 13–15 October 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Bali, M.; Ferraro, R.R.; Zou, C.Z.; Hewison, T.; Flynn, L.E.; Doelling, D.R. GSICS references for monitoring geostationary and polar instruments. In AGU Fall Meeting Abstracts; American Geophysical Union: Washington, DC, USA, 2018; p. A24B-07. [Google Scholar]
- Cramer, C.E.; Lykke, K.R.; Woodward, J.T.; Smith, A.W. Precise measurement of lunar spectral irradiance at visible wavelengths. J. Res. Natl. Inst. Stand. Technol. 2013, 118, 396–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, S.; Mattioli, V.; Stone, T.; Hu, X.; Wu, X. Outcome of the Third Joint GSICS/IVOS Lunar Calibration Workshop. Available online: https://repository.library.noaa.gov/view/noaa/29005/noaa_29005_DS1.pdf (accessed on 6 October 2020).
- Stone, T.C. Addressing Needs to Achieve High-Accuracy Lunar Calibration. Available online: https://digitalcommons.usu.edu/calcon/CALCON2022/All2022Content/5/ (accessed on 6 January 2023).
- Cataford, A.; Gadsden, S.A.; Turpie, K. Air-LUSI: Autonomous telescope design for lunar spectral irradiance measurements. In Proceedings of the Conference on Advanced Optics for Imaging Applications—UV through LWIR IV, Baltimore, MD, USA, 14–15 April 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Newton, A.; Maxwell, S.E.; Gadsden, S.A.; Turpie, K. Air-LUSI: Performance analysis of a high-altitude robotic telescope used for tracking the Moon. In Proceedings of the 2020 Canadian Society for Mechanical Engineering International Congress, Charlottetown, PE, Canada, 21–24 June 2020; pp. 21–24. [Google Scholar]
- Turpie, K.; Brown, S.; Woodward, J.; Gadsden, A.; Stone, T.; Grantham, S.; Maxwell, S.; Larason, T.; Newton, A.; Rice, J. Airborne Lunar Spectral Irradiance (Air-LUSI) Mission Capability Demonstration. Available online: https://digitalcommons.usu.edu/calcon/CALCON2020/all2020content/25/ (accessed on 6 February 2021).
- Woodward, J.T.; Turpie, K.; Stone, T.; Gadsden, S.; Newton, A.; Maxwell, S.; Grantham, S.; Larason, T.; Brown, S. Measurements of absolute, SI-traceable lunar irradiance with the airborne lunar spectral irradiance (air-LUSI) instrument. Metrologia 2022, 59, 034001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, T.C.; Turpie, K.; Brown, S.; Maxwell, S.; Woodward, J. Evaluation of Air-LUSI Measurements to Advance Lunar Modeling and the ROLO Lunar Calibration Reference. Available online: https://digitalcommons.usu.edu/calcon/CALCON2020/all2020content/25/ (accessed on 18 December 2021).
- Kopp, G.; Smith, P.; Belting, C.; Castleman, Z.; Drake, G.; Espejo, J.; Heuerman, K.; Lanzi, J.; Stuchlik, D. Radiometric flight results from the HyperSpectral Imager for Climate Science (HySICS). Geosci. Instrum. Meth. 2017, 6, 169–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukashin, C.; Jackson, T.; Cooney, M.; Ryan, N.; Beverly, J.; Young, C.; Rutherford, G.; Davis, W.; Nguyen, T.; Swanson, R.; et al. ARCSTONE: Calibration of Lunar Spectral Reflectance. Available online: https://digitalcommons.usu.edu/calcon/CALCON2018/all2018content/24/ (accessed on 10 February 2020).
- Lukashin, C.; Stone, T.; Kopp, G.; Jackson, T.; Swanson, R.; Abraham, N.; Minda, E.; Buleri, C.; Carvo, J.; Cooney, M.; et al. ARCSTONE: Calibration of Lunar Spectral Reflectance from Space. Available online: https://digitalcommons.usu.edu/calcon/CALCON2019/all2019content/9/ (accessed on 3 January 2020).
- Lukashin, C.; Kopp, G.; Jackson, T.; Swanson, R.; Buleri, C.; Young, C.; Gorman, M.; Zeigler, M.; Stone, T. ARCSTONE: Calibration of Lunar Spectral Reflectance from Space ESTO InVEST (Update). Available online: https://digitalcommons.usu.edu/calcon/CALCON2022/All2022Content/4/ (accessed on 6 January 2023).
- Swanson, R.; Kehoe, M.; Stebbins, M.; Courrier, H.; Lukashin, C.; Jackson, T.; Cooney, M.; Davis, W.; Kopp, G.; Smith, P.; et al. The ARCSTONE project to calibrate lunar reflectance. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE Aerospace Conference, Big Sky, MT, USA, 7–14 March 2020; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Wang, S.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Hu, X.; Zhang, P. Ground-based observation system development for the Moon hyper-spectral imaging. Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 2017, 129, 055002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berk, A.; Conforti, P.; Kennett, R.; Perkins, T.; Hawes, F.; Van Den Bosch, J. MODTRAN® 6: A major upgrade of the MODTRAN® radiative transfer code. In Proceedings of the 2014 6th Workshop on Hyperspectral Image and Signal Processing: Evolution in Remote Sensing (WHISPERS), Lausanne, Switzerland, 24–27 June 2014; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Hu, X.; Chen, L.; Huang, Y.; Li, Z.; Wang, S.; Zhang, P.; Wu, R.; Zhang, L.; Wang, W. Comparison of the lunar models using the hyper-spectral imager observations in Lijiang, China. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hewison, T.J.; Doelling, D.R.; Lukashin, C.; Tobin, D.; John, V.O.; Joro, S.; Bojkov, B. Extending the Global Space-based Inter-Calibration System (GSICS) to tie satellite radiances to an absolute scale. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Lu, N.; Li, C.; Ding, L.; Zheng, X.; Zhang, X.; Hu, X.; Ye, X.; Ma, L.; Xu, N.; et al. Development of the Chinese space-based radiometric benchmark mission LIBRA. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wielicki, B.A.; Young, D.F.; Mlynczak, M.G.; Thome, K.J.; Leroy, S.; Corliss, J.; Anderson, J.G.; Ao, C.O.; Bantges, R.; Best, F.; et al. Achieving climate change absolute accuracy in orbit. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2013, 94, 1519–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leckey, J. Climate Absolute Radiance and Refractivity Observatory (CLARREO). In Proceedings of the 36th International Symposium on Remote Sensing of the Environment (ISRSE), Berlin, Germany, 11–15 May 2015; pp. 213–217. [Google Scholar]
- Fox, N.; Green, P.; Brindley, H.; Russell, J.; Smith, D.; Lobb, D.; Cutter, M.; Barnes, A. TRUTHS (Traceable Radiometry Underpinning Terrestrial and Helio Studies): A mission to achieve climate quality data. In Proceedings of the ESA Living Planet Symposium 2013, Edinburgh, UK, 9–13 September 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Shea, Y.L.; Baize, R.; Fleming, G.; Johnson, D.; Lukashin, C.; Mlynczak, M.; Thome, K.; Wielicki, B. Climate Absolute Radiance and Refractivity Observatory (CLARREO) Pathfinder Mission: Status Overview. Available online: https://digitalcommons.usu.edu/calcon/CALCON2016/all2016content/3/ (accessed on 11 April 2020).
- Shea, Y.; Fleming, G.; Kopp, G.; Lukashin, C.; Pilewskie, P.; Smith, P.; Thome, K.; Wielicki, B.; Liu, X.; Wu, W.; et al. CLARREO Pathfinder: Mission overview and current status. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Online, 26 September–2 October 2020; pp. 3286–3289. [Google Scholar]
- Stone, T.C.; Lukashin, C.; Kopp, G. Calibration Acquisitions of the Moon by CLARREO Pathfinder. Available online: https://digitalcommons.usu.edu/calcon/CALCON2016/all2016content/3/ (accessed on 15 November 2019).
- NASA. NASA CLARREO Pathfinder Web Page. Available online: https://clarreo-pathfinder.larc.nasa.gov/gallery/clarreo-pathfinder-iss-inter-calibration-with-sun-and-moon/# (accessed on 1 January 2021).
- NASA. Mission Overview. Available online: https://clarreo-pathfinder.larc.nasa.gov/mission-overview/#project-timeline (accessed on 10 January 2020).
- Fox, N.; Green, P. Traceable Radiometry Underpinning Terrestrial- and Helio-Studies (TRUTHS): An element of a space-based climate and calibration observatory. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, N.; Shea, Y.; Fehr, T.; Gary, F.; Lukashin, C.; Pilewskie, P.; Remedios, J.; Smith, P. Toward a climate and calibration observatory in space: NASA CLARREO Pathfinder and ESA TRUTHS. In Proceedings of the 23rd EGU General Assembly Conference, Online, 19–30 April 2021; p. EGU21-14656. [Google Scholar]
- Fox, N.; Green, P.; Gorron, J. Traceable Radiometry Underpinning Terrestrial- and Helio-Studies (TRUTHS): Enabling a Space-Based Climate and Calibration Observatory—An ESA Earth Watch Mission. Available online: http://newrad2021.aalto.fi/docs/EAO/EAO_OR_012.pdf (accessed on 7 December 2021).
- ESA. TRUTHS: A Standards Laboratory in Space. Available online: https://www.esa.int/ESA_Multimedia/Images/2021/10/TRUTHS_a_standards_laboratory_in_space (accessed on 1 January 2021).
- Lu, N.; Ding, L.; Zheng, X.; Ye, X.; Li, C.; Lyu, D.; Zhang, P.; Hu, X.; Zhou, C.; You, Z.; et al. Introduction of the radiometric benchmark satellite being developed in China for remote sensing. J. Remote Sens. 2020, 24, 672–680. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Hu, X.; Wang, H.; Ye, X.; Fang, W. Standard transfer chain for radiometric calibration of optical sensing instruments with traceability in solar reflective bands. Opt. Precis. Eng. 2015, 23, 1807–1812. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korokhin, V.; Velikodsky, Y.I.; Shkuratov, Y.G.; Mall, U. The phase dependence of brightness and color of the lunar surface: A study based on integral photometric data. Sol. Syst. Res. 2007, 41, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaydash, V.; Pieters, C.; Shkuratov, Y.; Korokhin, V. Lunar opposition effect as inferred from Chandrayaan-1 M3 data. J. Geophys. Res. Planets 2013, 118, 1221–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berezhnoi, A.; Velikodsky, Y.I.; Pakhomov, Y.V.; Wöhler, C. The surface of the Moon as a calibration source for Na and K observations of the lunar exosphere. Planet. Space Sci. 2023, 228, 105648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hapke, B. Theory of Reflectance and Emittance Spectroscopy; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
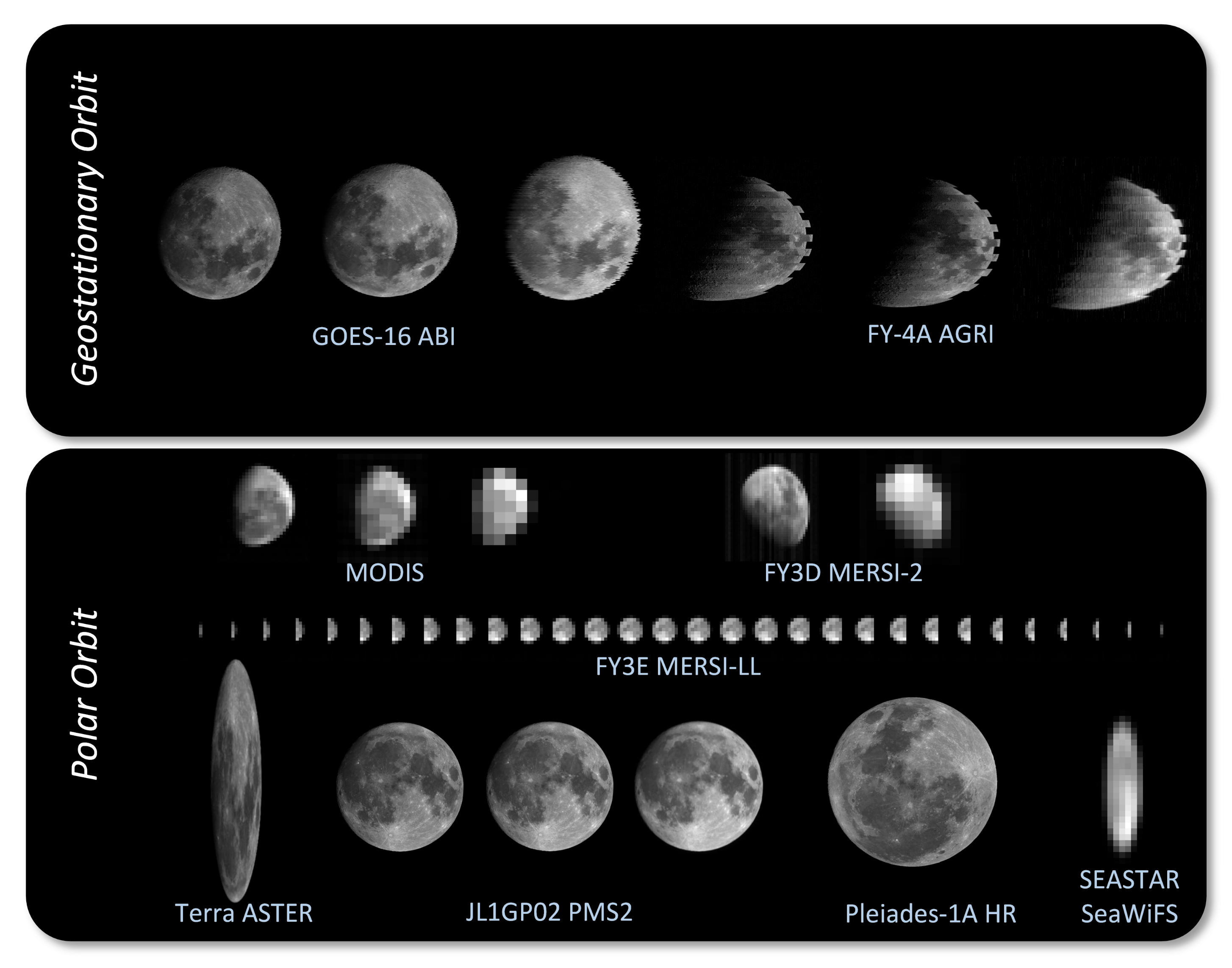




| Model | ROLO | SP | LIME | LESSSR |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Instrument | ROLO telescope | SELENE SP | CE318-TP9 | Envisat SCIAMACHY |
| Duration | VNIR: March 1996–September 2003 SWIR: January 1998–September 2003 | 14 September 2007–10 June 2009 | April 2018–October 2020 | 1 March 2002–8 April 2012 |
| Orbit/Site | USGS Flagstaff Field Center | Lunar polar orbit (No sun-synchronous orbit) | Teide Peak Observatory, Izaña Observatory | Polar orbit |
| Altitude | 2148 m | ~100 km | 3555, 2401 m | ~799 km |
| FOV | 35′ | 0.23° | 1.3° | 1.833 × 0.0458° |
| No. of bands | VNIR: 23; SWIR: 9 | 296 | 9 | — |
| Wavelength | VNIR: 350–945 nm SWIR: 945–2500 nm | VIS: 520–960 nm NIR1: 900–1700 nm NIR2: 1007–2600 nm | 340–1640 nm | 240–2380 nm |
| Spectral resolution | — | 6–8 nm | — | 0.24–1.48 nm |
| Total observations | >1.1 × 105 (>106 star images) | ~7000 orbits | ~300 | ~1133 |
| Symbol | Description | Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Distance | Mean Sun–Earth distance | 149,598,022.6 km | |
| Mean Moon–Earth distance | 384,400 km | ||
| Earth radius (equatorial) | 6378.14 km | ||
| Moon radius | 1737.4 km | ||
| Astronomical unit | 149,597,870.7 km | ||
| Observer–Moon distance | — | ||
| Sun–Moon distance in AU | — | ||
| Moon–Earth distance | — | ||
| Angle | Solid angle of the Moon | 6.41775 × 10−5 | |
| Solid angle of the individual pixel | — | ||
| Incidence angle | — | ||
| Emission angle | — | ||
| Phase angle | — | ||
| , | Selenographic longitude and latitude of the observer | — | |
| , | Selenographic longitude and latitude of the Sun | — |
| Model | Publication | Wavelength Coverage (nm) | Phase Angle Coverage (deg) | Uncertainty (Overall Uncertainty) | Related Studies |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ROLO (GIRO) | [38] | 300–2500 | ±[2, 92] | 5–10% (AP) 2 <1% or 2% (RP) 3 | [22,93,94,95,96,97,98,99] |
| SP | [40,41] | 500–1600 | ±[5, 85] | <1% or 2% (RP) | [22,34,97,99,100,101] |
| MT2009 | [39] | 200–2800 (200–1200) 1 | ±[5, 120] | 7–17% | [96,102,103] |
| LIME | [58,104] | 340–1640 | ±[2, 90] | 2% (AP) 1% (RP) | [105] |
| LESSSR | [92] | 250–2600 | [−80, 20] | ~5% (<1.5%, 500–1600 nm) | — |
| SLIM | [75] | 350–2400 | ±[3, 92] | — | — |
| Air-LUSI (Air-Based) | MLO-LUSI (Ground-Based) | ARCSTONE (Space-Based) | Lijing (Ground-Based) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Altitude | 21.6 km | 3397 m | 500–600 km | 3175 m |
| Duration | >2 years | >3 years | >3 years | >3 years |
| Spectral range | 350–1100 nm | 300–1100 nm | 350–2300 nm | 400–1000 nm |
| Spectral resolution | 4 nm | 3.7 nm | 4 nm | 2–10 nm |
| Accuracy goals | <0.5% (k = 1) | <0.5% (k = 1) | <0.5% (k = 1) | <3% (k = 2 early observations) |
| Funding | NASA/NIST | NIST | NASA | CMA |
| CLARREO Pathfinder (HySICS) | LIBRA Earth-Moon Imaging Spectrometer (EMIS) | TRUTHS Hyperspectral Imaging Spectrometer (HIS) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Operation | ~2023 | ~2025 | ~2029 |
| Lifetime | 1 year | 5–8 years | 5–8 years |
| Platform | International Space Station (ISS) | LIBRA satellite | Small satellite |
| Orbit | 52° | 90° | 90° |
| Altitude | 400 km | 600 km | 609 km |
| Swath width | 70 km | 50 km | 100 km |
| Spatial resolution | 500 m | 100 m | 50–60 m |
| Spectral range | 350–2300 nm | 380–2350 nm | 320–2400 nm |
| Spectral resolution | 3 nm | 10 nm | 4–8 nm |
| Accuracy goals | 0.3% (k = 1) | 1% (k = 2) | 0.3% (k = 2) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jing, Z.; Hu, X.; Wang, Y.; Wu, R.; Chen, L.; Zhang, L.; Huang, Y.; Wang, S.; Li, S.; Zhang, P. Activities to Promote the Moon as an Absolute Calibration Reference. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2431. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15092431
Jing Z, Hu X, Wang Y, Wu R, Chen L, Zhang L, Huang Y, Wang S, Li S, Zhang P. Activities to Promote the Moon as an Absolute Calibration Reference. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(9):2431. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15092431
Chicago/Turabian StyleJing, Zhenhua, Xiuqing Hu, Yang Wang, Ronghua Wu, Lin Chen, Lu Zhang, Yu Huang, Shuang Wang, Shuang Li, and Peng Zhang. 2023. "Activities to Promote the Moon as an Absolute Calibration Reference" Remote Sensing 15, no. 9: 2431. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15092431
APA StyleJing, Z., Hu, X., Wang, Y., Wu, R., Chen, L., Zhang, L., Huang, Y., Wang, S., Li, S., & Zhang, P. (2023). Activities to Promote the Moon as an Absolute Calibration Reference. Remote Sensing, 15(9), 2431. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15092431












