Abstract
Disasters caused by landslides pose a considerable threat to people’s lives and property, resulting in substantial losses each year. Landslide displacement rate prediction (LDRP) provides a useful fundamental tool for mitigating landslide disasters. However, more accurately predicting LDRP remains a challenge in the study of landslides. Lately, ensemble deep learning algorithms have shown promise in delivering a more precise and effective spatial modeling solution. The core aims of this research are to explore and evaluate the prediction capability of three progressive evolutionary deep learning (DL) techniques, i.e., a recurrent neural network (RNN), long short-term memory (LSTM), and a gated recurrent unit (GRU) ensemble AdaBoost algorithm for modeling rainfall-induced and reservoir-induced landslides in the Baihetan reservoir area in China. The outcomes show that the ensemble DL model could predict the Wangjiashan landslide in the Baihetan reservoir area with improved accuracy. The highest accuracy was achieved in the testing set when the window length equaled 30. However, assembling two predictors outperformed the accuracy of assembling three predictors, with the mean absolute error and root mean square error reaching 1.019 and 1.300, respectively. These findings suggest that the combination of strong learners and DL can yield satisfactory prediction results.
1. Introduction
The second-largest hydropower plant in the world is the Baihetan Dam. However, large hydropower projects, due to the need for storing water in reservoirs and periodic changes in reservoir water levels during operation, can alter the original geological environment of the reservoir area, causing geological hazards to occur more frequently on the reservoir banks [1,2,3]. Waterways and the established infrastructure could be seriously threatened by landslides in the reservoir area. Therefore, it is critical to use multi-source monitoring data to analyze and predict geological hazards to mitigate the resulting severe damage [4,5]. The reservoir area of Baihetan began storing water on 6 April 2021 and, as of 30 September 2021, had risen to its highest water-level line of 816.51 m. The steep topography and changes in the highest water level line have created signs of landslides and the resurrection of ancient landslides in the reservoir area. One of the larger deformed slopes is the Wangjiashan landslide, located in the Baihetan reservoir area [6,7,8]. Various methods, such as the global positioning system (GNSS) and unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) photogrammetry, are being used to monitor the Wangjiashan landslide. Predicting and forecasting landslides early can reduce property damage and human casualties. Currently, the international community is conducting numerous studies on landslide geohazards [9]. For example, Ghorbanzadeh et al. introduced multi-source landslide benchmark data and compared the performance of several machine learning methods for landslide detection [10,11]. In addition, the high-precision rate prediction of landslides also provides important analytical reference information for landslide prediction and early warning systems [12,13,14,15,16,17]. Landslide sliding is mainly manifested in changes in internal physical and mechanical mechanisms, external slope morphology, or changes in a certain number of values [18]. However, in the process of landslide destabilization, the external deformation of a certain parameter is an important representation of internal changes in the landslide [19,20,21,22].
During landslide movement, continuous changes in displacement in the key deformation area are the primary external characteristics [23,24]. Therefore, it is crucial to carry out automatic frequency conversion real-time monitoring and prediction for landslide displacement. Most strategies for predicting the displacement of landslides are physically based and data-driven models [25]. Starting with Saito’s postulated three stages for landslide creep [26], established models such as the Saito model [26,27] and the Voight model [28] exist. However, these models have obvious limitations and strongly rely on the experts’ experience, while the simplified models may not conform to the facts. Therefore, physical models are difficult to use to accurately predict the landslide displacement rate. Statistical models have been widely used in landslide displacement rate prediction, and, although they are not as effective as physical models in revealing the evolutionary mechanism of landslide displacement, they have provided accurate predictions in several landslide cases [18,22,29]. However, statistical models, such as the Verhulst model [30] and the gray system model [31], are mostly linear models, and they treat displacement prediction as a static regression problem. However, landslide displacements are usually nonlinear and dynamic [21], wherein the displacements are usually influenced by time-dependent factors (e.g., an increase in reservoir and rainfall) [32]. To consider the time-varying characteristics of landslide triggers, dynamic prediction methods are needed. As artificial intelligence (AI) advances [33,34,35,36], particularly deep learning, a type of deep learning called a recurrent neural network (RNN) has been utilized for landslide prediction [16,17,37]. The RNN structure is designed for time series data and has shown better computing power than traditional machine learning methods. The RNN’s architecture faces a significant issue regarding the explosion or disappearance of gradients [38]; newly developed models, including long-term and short-term memory neural networks (LSTM) and gated recurrent neural networks (GRU) have been improved from the basic RNN structure. The long-term and short-term memory neural network (LSTM) is a special RNN that has been designed to deal with the problem of gradient disappearance and explosion in long sequence training [21,39,40,41]. A gated recurrent neural network (GRU) is an improvement of LSTM that simplifies the gate structure and enables the efficient handling of large amounts of data. The RNN and its upgraded models, such as LSTM and GRU, have been widely used for predicting landslide displacement rates [20,21,42,43].
Differencing can help stabilize the mean of a time series by removing changes in the level of a time series, thereby eliminating (or reducing) trend and seasonality [44]. The landslide displacement rate is made different by the landslide displacement time series. Each landslide displacement rate model mentioned above presents a different prediction accuracy under different slope conditions, and each has certain disadvantages. However, with the innovation of models and the improvement of prediction accuracy, the advantages of integrated model algorithms are becoming more and more prominent. AdaBoost provides the framework for building sub-classifiers using various methods, including RNN, LSTM, GRU, and so on, and can avoid the overfitting phenomenon present in individual machine learning models. Additionally, since the AdaBoost algorithm does not require prior knowledge of weak classifiers, learning accuracy may be greatly increased [45,46]. At the same time, the algorithm can aggregate weak classifiers to construct a strong classifier with high classification ability and adaptively adjust the assumed error rate, based on the feedback from the weak classifiers, to improve execution efficiency.
To address the aforementioned problem, this study proposes an AdaBoost integrated three progressive evolutionary deep-learning model algorithms to predict the rate of the Wangjiashan landslide of the Baihetan hydropower station, using the GNSS displacement rate. For landslide displacement rate prediction, the study compares the prediction results of the individual artificial intelligence models, RNN, LSTM, and GRU, with the integrated AdaBoost model, using time series of measured displacement rate to verify the accuracy of various algorithms and the feasibility of the integrated AdaBoost model. The proposed model provides a novel approach to predicting landslide displacement rates.
2. Case Study
2.1. Topography and Geological Setting
The Baihetan Hydropower Station is situated in the upper reaches of the Jinsha River, from Panzhihua to Yibin. It represents the second stage of the four-stage cascade of hydropower stations in the region, consisting of Wudongde, Baihetan, Xiluodu, and Xiangjiaba. Recently, a hazardous landslide was exposed in the Wangjiashan area, which is approximately 92.4 km from the dam site. The north side of Wangjiashan reveals the Wangjiashan landslide, on the right bank of the Xiaojiang Branch Reservoir, about 1.3 km away from the Elephant Trunk Ridge settlement on the left bank of Xiaojiang (diagonally opposite), as illustrated in Figure 1. The landslide plane has an approximately triangular shape, measuring 800 m in length and ranging from 90 to 500 m in width. The height difference between the front and triggering zones of the landslide is about 400 m, a trench has developed on each side of the slope, and the landslide volume is 6.11 million m3. The terrain within the landslide area is steep, with slope angles ranging from 35–45° and occasionally reaching up to 50°. At the central elevation of 870–900 m, the terrain becomes gentler, with flat-topped hills and landslide depressions, and a slope angle of 15–20°. Here, arable land and signal towers are distributed. The elevation increases to 900 m above sea level, and the source area of the landslide is around 1125 m high. The terrain is steep, with a slope angle of 30–35°, and is mostly a barren mountain. The altitude of the source area of the Wangjiashan landslide is more than 1125 m and it has a steep bedrock slope with a slope angle of 40–50°. The stability of the Wangjiashan landslide is weak and is expected to change to some extent after the reservoir of Baihetan Hydropower Station is filled. If the landslide becomes unstable under certain working conditions, it may cause swells, which would adversely affect the safety of surrounding residents and potentially endanger shipping traffic. Therefore, it is crucial to anticipate and forewarn the displacement of the Wangjiashan landslide to prevent potential disasters.
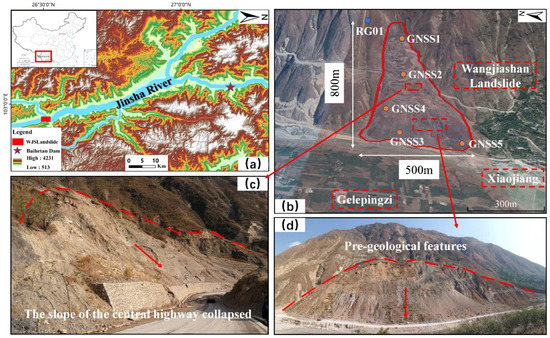
Figure 1.
The case study’s site and the GPS monitoring stations. (a) The pattern of the Jinsha River system and study area DEM; (b) the Wangjiashan landslide boundary, rain gauge (RG01), and GNSS displacement monitoring point layout; (c) the slope of the central highway that collapsed; (d) geomorphological features of the landslide front.
The landslide body has a total thickness ranging from 14.0 m to 87.6 m. While the leading edge and triggering zone of the landslide are thinner, the center of the slide is thicker, indicating that this is a large-scale soil landslide. The landslide material consists primarily of pebbles, blocks, and fragments mixed with soil, and the composition of the crushed and block stone is primarily limestone and dolomite, with sandstone in small amounts. The lower bedrock is composed of dolomite, quartz sandstone, and argillaceous siltstone. The soil in the slippery zone is composed of gravel-bearing clay, as illustrated in Figure 2.
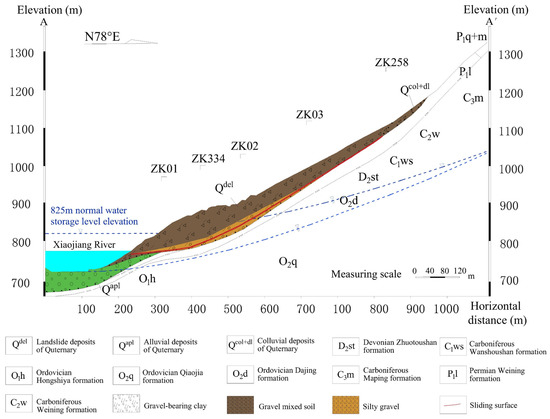
Figure 2.
The case study’s geological profile.
From a geomorphological perspective, the triggering zone of the landslide exhibits clear characteristics, including the topographic characteristics of “double-groove homologous” and “circle chair-shaped” features, along with the exposure of Permian and Carboniferous limestone, dolomite, and sandstone. Two gullies border the left and right flanks on both sides, and the bedrock at the bottom of the trench is exposed, primarily consisting of Ordovician, Devonian, and Carboniferous dolomite, limestone, quartz sandstone, and shale. As the front edge of the landslide approaches the tiny river margin, the terrain becomes steep, with the slope ranging from 35° to 45°.
2.2. Data from Time Series Monitoring and Study of the Deformation
In the area of the landslide study, the following five monitoring-point data were mainly obtained: GNSS1, GNSS2, GNSS3, GNSS4, and GNSS5. The GNSS displacement meters (ZWGNSS-1) provide landslide surface displacement measurement. Some of the basic specifications are as follows: the acceleration measurement accuracy is not less than 0.01 g, and the positioning output frequency is 0.1 to 50 Hz. The GNSS system can receive data from the global positioning system, Beidou navigation satellite system, GLONASS, and Galileo satellite navigation system, and its plane accuracy is about 2 mm, while its elevation accuracy is about 3 mm. The data was collected at a time step of one day to monitor the displacement and displacement rate. The monitoring data were mainly selected for a period of eight months from 1 July 2021 to 29 March 2022. Similarly, the reservoir water level and rainfall data for these three months were selected; the reservoir water level data was provided by the China Three Gorges Corporation and the rainfall data was measured by a rain gauge (RG01) installed on the periphery of the right boundary of the Wangjiashan landslide. The sampling interval was recorded every hour and the average of the monitoring data over the 24-h period was used as the reservoir water level value for that day. The total displacement and total horizontal displacement of the five monitoring points showed an upward trend over time, with the value for the GNSS2 monitoring point reaching the maximum. The GNSS5 displacement no longer increased around 28 November 2021, and the displacement data for all five monitoring points showed an upward trend when the reservoir water level reached more than 792 m, as shown in Figure 3.

Figure 3.
The cumulative displacement, reservoir water level, and daily rainfall in the Wangjiashan landslide.
The current situation of the landslide in Wangjiashan is generally stable, although there are areas of instability, and it is currently in a slippery deformation state. Monitoring of the displacement rate at five points, as shown in Figure 4, reveals that from around 21 August, the landslide displacement rate increased as the reservoir water level climbed. By 12 September, when the reservoir water level reached 782 m, both GNSS2 and GNSS3 recorded rates exceeding 200 mm/d. The displacement rate continued to fluctuate and increase, reaching a peak around 6 October, when the reservoir water level was approximately 812 m. At this time, the largest displacement rate was recorded by GNSS2, which was about 994 mm/d, and reached 600 mm/d around 4 October to 8 October. After reaching its peak, as the reservoir water level dropped to around 797 m, the displacement rate decreased. It is evident that from September to October, the landslide underwent significant displacement changes due to the varying water levels of the reservoir. Ultimately, this resulted in a sliding failure along the base cover interface, causing a large overburden landslide with traction.

Figure 4.
Reservoir water level and the Wangjiashan landslide’s measured cumulative displacement rate.
3. Methodology
The processes of creating and validating the proposed models are presented in Figure 5. The landslide displacement rate is triggered by two external causes—rainfall and reservoir water level; these were analyzed to develop the AdaBoost RNN, LSTM, and GRU coupling model, along with six comparison models. The training data set used to train the prediction model covered the period from 3 July 2021 to 31 October 2021, while the testing data set comprised the landslide displacement data from 1 February 2022 to 27 March 2022. Root mean square error (RMSE) and mean absolute error (MAE) metrics were used as common measures of prediction accuracy. Then, ablation experiments were set to study the importance of landslides’ influencing factors. By changing the length of the window, its influence on prediction could be clarified. Finally, comparative ensemble DL models were utilized and the best performance for LDRP was selected.
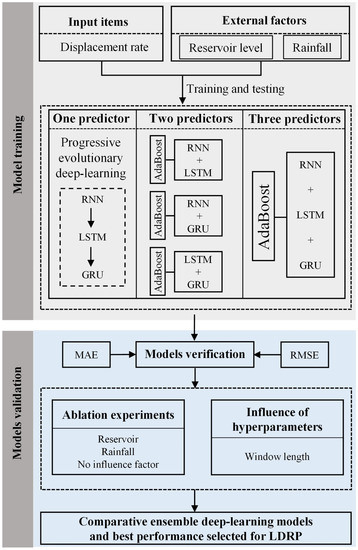
Figure 5.
The flowchart of the proposed models for LDRP.
3.1. Deep Learning (DL) Models
AdaBoost combines three progressive evolutionary deep learning (RNN, LSTM, GRU) algorithms to predict LDRP using GNSS displacement data. The RNN is a deep learning network used to predict sequence data. LSTM is a modified form of the RNN, which is composed of an input gate, output gate, and forget gate. The GRU has also been improved, based on LSTM. The GRU unit does not need to use a memory unit to control the flow of information in the same way as the LSTM unit. It can take advantage of all hidden states without any control (Figure 6). The details of each model are explained below, with the final AdaBoost ensemble DL prediction for LDRP.

Figure 6.
(a) RNN neural network structure; (b) LSTM neural network structure; (c) GRU neural network structure.
3.1.1. RNN
The recurrent neural network (RNN) is a sophisticated neural network model that takes into account the sequential relationship between input data, introducing the concept of “time series” [47]. It differs from the traditional artificial neural network as follows. The information of the points in the RNN model in the hidden layer can be transmitted to the next time point in an orderly manner, allowing the information contained in the data to be continuously propagated. The RNN’s fundamental design model is shown in Figure 7a, where h represents the hidden unit, o denotes the output, L depicts the loss function, x is the input, y is the training set label, t is the state at time t, and V, U, and W represent the weights, with the connection weights of the same type being taken to be the same.

Figure 7.
Sketch of the RNN structure: (a) basic structure; (b) complete structure.
As depicted in Figure 7, the algorithmic idea behind the RNN model is to continuously update the model state while retaining the current state of the input and output data, allowing for the full extension of the input and output sequences. The complete model structure is shown in Figure 7b, where at the timestep t, the input sequence data is denoted by x, the output layer is denoted by y, and the input from the previous node and the current node determines the value size. In this model, the relationship can be obtained using the following calculations:
where f and g are activation functions; Wh and Uh are weight matrices; b is the offset vector.
3.1.2. LSTM
Although the recurrent neural network (RNN) is superior in terms of processing time series data among the many machine learning algorithms, its performance is still limited by the problems of gradient vanishing and gradient explosion in Figure 6a. The emergence of long short-term memory (LSTM) is to solve these two intractable obstacles [48]. Compared to a traditional RNN, LSTM can perform better with longer sequences. Figure 6b shows the structure of LSTM, which uses gate functions to regulate the information flow, including the forget gate, input gate, and output gate. These gates operate to dictate which pieces of information should be discarded, added, and output. Here are the functions of the three gates:
The vector values of a neural network node’s forgetting gate, input gate, and output gate at time t are denoted by the letters ft, It, and Ot. The forgetting gate selectively forgets some components in the previous unit state and does not allow too much memory to affect the neural network’s processing of the present input. The associated bias terms for each gate are denoted by the letters bf, bi, and bo. xt is the intake at time t; ht-1 is the outcome at time t-1; ct-1 is the memory unit’s vector value at time t-1; tanh is indeed the hyperbolic tangent function, which maps real numbers to the range [−1, 1]. The sigmoid activation function maps real numbers to the range [0, 1]. A value of 1 indicates that all the information from the previous time step has been retained, while a value of 0 indicates that all the information has been lost.
3.1.3. GRU
The gate recurrent unit (GRU) is similar to the LSTM in that it is designed to handle long-term memory and gradient issues during backpropagation. In many cases, the GRU and LSTM perform similarly, but the GRU is easier to compute [49]. The GRU consists of an update gate and a reset gate, as shown in Figure 6c.
The reset gate regulates how the new input data are merged with the prior memory, while the update gate fulfills a role similar to that of the forget and input gates in the LSTM. The calculation formula is as follows:
where Zt is the update gate and rt stands for the reset gate in the formula. The current candidate vector is t. The buried layer’s output vector at time t is called Ct. The input vector at time t is xt; the update gate vector at time t is Zt; the hidden layer’s output vector at time t is ht; the updated candidate vector is (), which is the vector at time t; , , , , , and denote the weight matrix between each connection vector; is the sigmoid function.
3.1.4. AdaBoost
Boosting is a crucially important integrated learning technology that enhances weak learners with low prediction accuracy to form strong learners with high prediction accuracy [50]. This greatly improves the prediction accuracy of learners and also provides a new idea and method by which to solve the problem of directly constructing strong learners. Based on this idea, our predecessors proposed a highly successful application algorithm called the AdaBoost algorithm, which is short for “adaptive boosting”. The structure of the AdaBoost model is depicted in Figure 8.

Figure 8.
The AdaBoost structure.
The calculation process of this model is explained below: firstly, the sample of the previous basic classifier is divided into two parts. The weight of the sample that is wrongly classified is increased, while the weight of the sample that is correctly classified is decreased. Then, the weight of the correct classification is used to train the next basic classifier. Additionally, a new weak classifier is introduced in each round of iterative calculation, and the final criterion for the strong classifier is that either the error rate reaches a predetermined small index value, or the number of iterations extends a predetermined maximum index value.
The AdaBoost algorithm can be roughly separated into the following steps:
(1) Set the training samples and classify them as(,…(,), where the range is {−1, +1}, then initialize the sample weight and set ; the maximum number of cycles is T and conduct training proceeds.
(2) Start the iteration from t = 1 and use the sample weight distribution Dt to train the weak classifier.
(3) Obtain the weak classification assumption of : X → {−1, +1}, then calculate the error rate of the weak classifier according to the following formula:
(4) Calculate the value according to the following formula:
(5) Calculate the weight distribution after the t + 1 iteration, as below:
where is the normalized parameter.
(6) Obtain ,, …, T. After T iterations, weak classifiers are obtained.
(7) Finally, calculate the strong classifier required by the target according to the formula, through weighted voting:
3.2. Model Validation
To measure the predictive performance of the methods mentioned in this research, two widely used indicators are adopted for measurement, namely, the mean absolute error (MAE) and root mean square error (RMSE). The metrics above are computed as follows:
where and represent the measured landslide displacement rate and prediction displacement rate.
The root mean square error (RMSE) and mean absolute error (MAE) metrics were used as common measures of prediction accuracy, with smaller RMSE and MAPE values indicating higher accuracy [51,52,53].
4. Results and Discussions
4.1. Model Training and Testing
4.1.1. Hyperparameter Settings
For the RNN, LSTM, and GRU, the hidden dimension is an important hyperparameter. The hidden dimension is the size of the feature maps for each hidden layer. Increasing the hidden dimension of a layer helps to increase the complexity of the model and allows it to potentially capture more complex decision boundaries. It also allows for more expressibility for the hidden states. The window length is a crucially important hyperparameter for models used to make predictions. When predicting the landslide displacement rate at time T, the rainfall, reservoir level, and LDRP at times T−L to T−1 are used as features to be inputted into models for the window length, L. The size of the feature diagrams for each hidden layer of the model is referred to as the hidden dimension. In terms of this study, the hidden dimension was set to a value of 25. We used window rolling with a length of 30 to make the prediction. As shown in Table 1, the AdaBoost model takes the results of the first three models as input and then predicts the final result, resulting in a combined algorithm model. The learning rate and the number of estimators are the two hyperparameters of AdaBoost, which were set to 1 and 50, respectively. The learning rate is the weight applied to each regressor at each boosting iteration, while the number of estimators is the maximal number of estimators that terminate the boosting.

Table 1.
Hypermeters and explanations of the models.
4.1.2. Prediction of Displacement Rate and Accuracy Verification
In this research, three kinds of progressive evolutionary deep learning algorithms, comprising RNN, LSTM, and GRU, were chosen as weak predictors. By assembling weak predictors in different combinations, we investigated which integration model had the highest prediction accuracy. Reservoir water level and rainfall were chosen as landslide-inducing factors and the training set was from 1 February 2022 to 1 July 2022, while the testing set was from 2 February 2022 to 28 March 2022.
Figure 9 describes the predicted landslide displacement rate of each model in the testing set. As seen in Figure 9, the accuracy of the RNN is lower and less accurate than that of the LSTM and GRU models, while the accuracy of the LSTM and GRU models is approximately the same. This suggests that improved RNNs with gate structures can remember long-term time series and can thus achieve higher accuracy. GRU simplifies the architecture of LSTM, which can reduce the complexity of the model without reducing the prediction accuracy. The performance accuracy of a single model is lower than that of the ensemble model, indicating that the integrated model reduces epistemic uncertainty. However, the accuracy when integrating three models is lower than that when integrating two models. The possible explanation is that at some time points, the prediction of RNN, LSTM, and GRU is inaccurate, which increases the out-of-distribution uncertainty regarding the samples, leading to a reduction in the prediction accuracy of the three integrated models. AdaBoost is sensitive to abnormal samples; therefore, abnormal samples may be given higher weights in the iteration, which can reduce the prediction accuracy of the final strong learner, affecting the accuracy of the overall prediction.
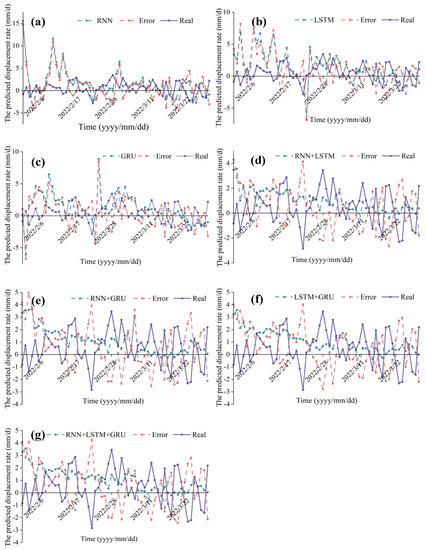
Figure 9.
The predicted landslide displacement rate of each model: (a) RNN; (b) LSTM; (c) GRU; (d) RNN+LSTM; (e) RNN+GRU; (f) LSTM+GRU; (g) RNN+LSTM+GRU.
In Figure 10, the absolute error of each predicted model was drawn. As is shown in Figure 11, the coupling algorithm of RNN and LSTM performs the best in terms of prediction, with MAE and RMSE scores of 1.019 and 1.37, respectively. Moreover, it is evident from Figure 11 that the coupled models outperform the single model, and the coupling of the two models was better than that of the three models.

Figure 10.
The predicted absolute error of each model.
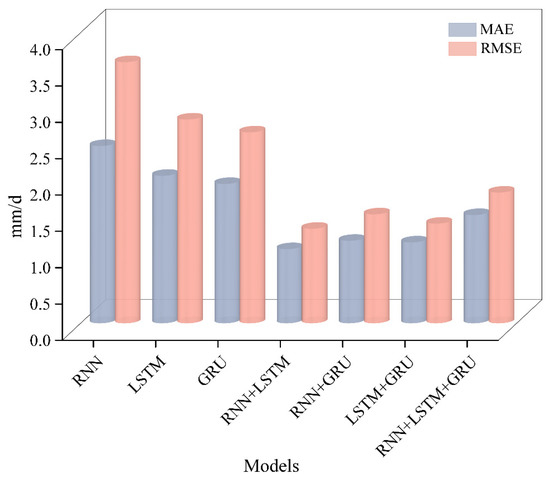
Figure 11.
The MAE and RMSE of the models.
The values of MAE and RMSE for the RNN model were 2.439 and 3.594, respectively. For the LSTM model, the MAE and RMSE were 2.029 and 2.804, respectively. The MAE of the RNN and LSTM coupled model was 1.019 and RMSE was 1.3. The popular RNN and GRU models had an MAE and RMSE of 1.134 and 1.498, respectively. The LSTM and GRU coupled model’s MAE and RMSE were 1.112 and 1.37, respectively. The ensemble model comprising the three models had an MAE and RMSE of 1.489 and 1.798, respectively. Figure 11 shows that before 1 March 2022, the absolute amount of the displacement rate predicted by RNN, LSTM, and GRU was relatively large, and the prediction results improved throughout the whole month of March. However, after using the AdaBoost ensemble model, the prediction error values increased during the entire prediction period.
4.2. Uncertainty Analysis
4.2.1. The Influence of Distinct Hyperparameter Settings
This study takes window length as an example to investigate the impact of distinct hyperparameter settings on model accuracy. The window length is a crucially important hyperparameter for models used to make predictions. When predicting the landslide displacement rate at time T, the rainfall, reservoir water level, and LDRP at time T−L to T−1 are used as the features to be inputted into models for the window length L.
The length of the input time series is represented by the window. If the window length is too short, the model may be underfitting due to the insufficient number of input samples and insufficient features. On the other hand, if the window length is too long, the multicollinearity may increase, making it difficult for the model to predict accurately.
By changing the window length and analyzing the results, we found that the precision of the testing data set reaches its highest precision when the window length is 30. At this point, the MAE is 1.065 and RMSE is 1.371, demonstrating that the results in Table 2 and the sample taken within a month had the strongest association.

Table 2.
The metrics of models according to changing window length.
Table 2 demonstrates that there is not a straightforward linear correlation between landslide prediction accuracy and window length. As the number of window lengths increases, the accuracy of the prediction decreases. The highest prediction accuracy is achieved with window lengths of between 16 and 22, while the lowest accuracy is observed with window lengths of between 24 and 28. The lag between the influence of landslide factors and the resulting displacement creates uncertainty in the prediction process, highlighting the complexity of these factors.
4.2.2. Ablation Experiments Disentangling the Impact of External Factors
Choosing the appropriate influencing factors is essential for accurate periodic displacement prediction. One of the main inducing factors leading to landslides is rainfall. On the one hand, rainfall causes the underground water level to rise in the landslide body, softening the rock and soil, and lowering the shear strength on the surface of the rupture via penetrating rock fissures and soil porosity. As a result, the opposing forces are lessened. Alternatively, seeping water makes the landslide body heavier, which increases the driving forces. As a result, the landslide becomes unstable and moves slowly. In addition, rainfall raises the level of the subsurface water in the landslide body, causing the rock and soil to become softer and the shear strength of the surface of the rupture to decrease as water seeps into the soil pores and rock cracks. The seepage of water, on the other hand, makes the landslide body heavier, which increases the driving forces, causes instability, and increases displacement. Note that the variations in a wide range of external triggering conditions caused the periodic displacement of the Wanjiashan landslide to change. This might be explained by the fact that the landslide remained constant as long as the rainfall did not go over a certain amount. The primary landslide-inducing elements that affect the displacement of step-like reservoir landslides are mainly reservoir level fluctuations and rainfall. The periodic displacement of landslides is lag-affected by rainfall and reservoir water level and it also exhibits autocorrelation. Therefore, we chose periodic displacement, precipitation, and reservoir water level over the previous three months as landslide-inducing elements after consulting earlier studies.
To examine the impact of landslide external factors on the operation of the system, ablation experiments were carried out under three distinct conditions—only the reservoir water level, only rainfall, and neither. As seen in Table 3, the findings indicated that prediction accuracy was comparable in both reservoir and rainfall conditions. It is difficult to determine which factor is more important. However, the LDRP accuracy was lower when there were no landslide-influencing factors considered. Therefore, it can be concluded that both reservoir water level and rainfall are equally important in improving prediction accuracy, and both factors should be considered when predicting landslide displacement rates.

Table 3.
The predicted metrics of three ablation experiments.
4.2.3. Limitations
Rainfall and reservoir water level are considered the influencing parameters in models that forecast the landslide displacement rate. However, it is evident that the selected influencing factors are not comprehensive enough, resulting in an insufficiently accurate displacement rate prediction. Future research should take into account additional affecting elements, such as groundwater level and deep displacement. By incorporating these more precise influencing factors, the prediction accuracy of displacement rates can be further improved.
Moreover, it is important to increase the impact of physical mechanisms on the prediction of landslide displacement rates. For instance, expanding the spatial observation points and incorporating additional monitoring points can enhance prediction accuracy. Multiple monitoring points can help realize the temporal and spatial correlation of landslide displacement prediction and build a multi-dimensional landslide displacement prediction system.
5. Conclusions
The Wangjiashan landslide, in the vicinity of the Baihetan reservoir, is the focus of this paper. The landslide displacement rate, reservoir water level, and rainfall data collected by GNSS are used as the inputs for predictors. Three progressive evolutionary deep-learning models and an AdaBoost model were employed to forecast the landslide displacement rate and the ensemble model achieved high accuracy. The MAE and RMSE of assembling the RNN and LSTM are 1.019 and 1.300, respectively, while the MAE and RMSE of assembling the RNN, LSTM, and GRU are 1.489 and 1.789, respectively. Notably, assembling two predictors yielded higher accuracy than assembling three predictors, indicating that additional weak predictors do not improve accuracy. AdaBoost’s flexible use of several regression models to create weak predictors is advantageous, but the weighting of aberrant values during iteration may affect prediction accuracy. Experimentation with different window lengths revealed that a window length of 30 achieved the highest precision on the testing data set. Ablation experiments on landslide-inducing factors indicated that the prediction accuracy was similar when using only reservoir or only rainfall data. However, the accuracy decreased when landslide-influencing factors were excluded from the prediction.
It is crucial to establish a more reliable and comprehensive model for predicting displacement volatility to monitor long-term safety and detect landslides early. Enhancing the model’s capacity to incorporate landslide-inducing factors and displacement data can increase the prediction accuracy.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, W.N. and J.D.; data curation, L.Z. (Lele Zhang); formal analysis, J.D., L.Z. (Liuyuan Zhao) and K.X.; funding acquisition, J.D. and L.Z. (Liuyuan Zhao); investigation, W.N. and L.Z. (Liuyuan Zhao); methodology, J.D., L.Z. (Lele Zhang) and K.X.; resources W.N. and L.Z. (Liuyuan Zhao); supervision, J.D.; validation, K.X.; visualization, J.D. and K.X.; writing—original draft, J.D., L.Z. (Lele Zhang) and K.X.; writing—review and editing, J.D., W.N., L.Z. (Liuyuan Zhao), L.Z. (Lele Zhang) and K.X. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research is sponsored by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 42090054 and No. 52239006), the Key Science and Technology Plan Project of Power China Huadong Engineering Corporation Limited (Grant No. KY2021-ZD-03), and the Natural Science Foundation of Hubei Province of China (Innovation Group Program: No. 2022CFA002).
Data Availability Statement
If possible, the related data can be collected on demand.
Acknowledgments
We thank Xiang Zilin, Luo Wanqi, Zhang Ruiqiand Wang Rui for processing the data and editing the draft.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Tang, H.; Wasowski, J.; Juang, C.H. Geohazards in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area, China—Lessons Learned from Decades of Research. Eng. Geol. 2019, 261, 105267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Li, C.; Hu, X.; Wang, L.; Criss, R.; Su, A.; Wu, Y.; Xiong, C. Deformation Response of the Huangtupo Landslide to Rainfall and the Changing Levels of the Three Gorges Reservoir. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2015, 74, 933–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Tang, H.; Li, C.; Sun, R. Stability of Huangtupo Riverside Slumping Mass II# under Water Level Fluctuation of Three Gorges Reservoir. J. Earth Sci. 2012, 23, 326–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, W.; Juang, C.H.; Wasowski, J. Geohazards and Human Settlements: Lessons Learned from Multiple Relocation Events in Badong, China—Engineering Geologist’s Perspective. Eng. Geol. 2021, 285, 106051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Fu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Tang, H.; Yan, J.; Gong, W.; Yao, W.; Criss, R.E. Susceptibility of Reservoir-Induced Landslides and Strategies for Increasing the Slope Stability in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area: Zigui Basin as an Example. Eng. Geol. 2019, 261, 105279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, K.; Chen, C.; Shi, X.; Wu, M.; Feng, W.; Xu, Q.; Liang, R.; Zhuo, G.; Li, Z. International Journal of Applied Earth Observations and Geoinformation Dynamic Landslides Susceptibility Evaluation in Baihetan Dam Area during Extensive Impoundment by Integrating Geological Model and InSAR Observations. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2023, 116, 103157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Yi, X.; Dun, J.; Yang, J.; Cai, W.; Zhang, G. Understanding the Slow Motion of the Wangjiashan Landslide in the Baihetan Reservoir Area (China) from Space-Borne Radar Observations. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2022, 2022, 1766038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, X.; Feng, W.; Wu, M.; Ye, Z.; Fang, Y.; Wang, P.; Li, R.; Dun, J. The Initial Impoundment of the Baihetan Reservoir Region (China) Exacerbated the Deformation of the Wangjiashan Landslide: Characteristics and Mechanism. Landslides 2022, 19, 1897–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Z.; Dou, J.; Yunus, A.P.; Zhang, L.; Wang, X.; Luo, W. Vegetation-Landslide Nexus and Topographic Changes Post the 2004 Mw 6.6 Chuetsu Earthquake. Catena 2023, 223, 106946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorbanzadeh, O.; Xu, Y.; Ghamisi, P.; Kopp, M.; Kreil, D. Landslide4Sense: Reference Benchmark Data and Deep Learning Models for Landslide Detection. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorbanzadeh, O.; Xu, Y.; Zhao, H.; Wang, J.; Zhong, Y.; Zhao, D.; Zang, Q.; Wang, S.; Zhang, F.; Shi, Y.; et al. The Outcome of the 2022 Landslide4Sense Competition: Advanced Landslide Detection From Multisource Satellite Imagery. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2022, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Xu, C.; Huang, B.; Ren, X.; Liu, C.; Hu, B.; Chen, Z. Landslide Displacement Prediction Based on Multi-Source Data Fusion and Sensitivity States. Eng. Geol. 2020, 271, 105608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzzetti, F.; Gariano, S.L.; Peruccacci, S.; Brunetti, M.T.; Marchesini, I.; Rossi, M.; Melillo, M. Geographical Landslide Early Warning Systems. Earth Sci. Rev. 2020, 200, 102973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petley, D.N.; Mantovani, F.; Bulmer, M.H.; Zannoni, A. The Use of Surface Monitoring Data for the Interpretation of Landslide Movement Patterns. Geomorphology 2005, 66, 133–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, J.; Yunus, A.P.; Merghadi, A.; Shirzadi, A.; Nguyen, H.; Hussain, Y.; Avtar, R.; Chen, Y.; Pham, B.T.; Yamagishi, H. Different Sampling Strategies for Predicting Landslide Susceptibilities Are Deemed Less Consequential with Deep Learning. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 720, 137320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, W.; Dou, J.; Fu, Y.; Wang, X.; He, Y.; Ma, H.; Wang, R.; Xing, K. A Novel Hybrid LMD–ETS–TCN Approach for Predicting Landslide Displacement Based on GPS Time Series Analysis. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Tang, H.; Huang, J.; Wen, T.; Ma, J.; Zhang, J. A Comparative Study of Different Machine Learning Methods for Reservoir Landslide Displacement Prediction. Eng. Geol. 2022, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Yin, K.; Lacasse, S. Displacement Prediction in Colluvial Landslides, Three Gorges Reservoir, China. Landslides 2013, 10, 203–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baum, R.L.; Godt, J.W. Early Warning of Rainfall-Induced Shallow Landslides and Debris Flows in the USA. Landslides 2010, 7, 259–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Luo, H.; Xu, Q.; Lu, Z.; Liao, L.; Li, H.; Hao, L. A Graph Convolutional Incorporating GRU Network for Landslide Displacement Forecasting Based on Spatiotemporal Analysis of GNSS Observations. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Yin, K.; Lacasse, S.; Liu, Z. Time Series Analysis and Long Short-Term Memory Neural Network to Predict Landslide Displacement. Landslides 2019, 16, 677–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhao, Y.; Bai, L.; Guo, W.; Meng, Q. Landslide Displacement Prediction Method Based on GA-Elman Model. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Tang, H.; Ma, X.; Wu, Y.; Hu, X.; Wang, L.; Criss, R.; Yuan, Y.; Xu, Y. Identification of Movement Characteristics and Causal Factors of the Shuping Landslide Based on Monitored Displacements. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2019, 78, 2093–2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, W.; Li, C.; Zuo, Q.; Zhan, H.; Criss, R.E. Spatiotemporal Deformation Characteristics and Triggering Factors of Baijiabao Landslide in Three Gorges Reservoir Region, China. Geomorphology 2019, 343, 34–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Xu, Q.; He, Y.; Fan, X.; Li, S. Modeling and Predicting Reservoir Landslide Displacement with Deep Belief Network and EWMA Control Charts: A Case Study in Three Gorges Reservoir. Landslides 2020, 17, 693–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, M. Forecasting the Time of Occurrence of a Slope Failure. In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Soil Mechanics and Foundation Engineering, Montreal, QC, Canada, 8–15 September 1965; pp. 537–541. [Google Scholar]
- Saito, M. Forecasting Time of Slope Failure by Tertiary Creep. In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Soil Mechanics and Foundation Engineering, Mexico City, Mexico, 25–29 August 1969; Volume 2, pp. 677–683. [Google Scholar]
- Voight, B. A Relation to Describe Rate-Dependent Material Failure. Science 1989, 243, 200–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lévy, C.; Gendrey, S.; Bernardie, S.; Chanut, M.-A.; Vallet, A.; Dubois, L.; Duranthon, J.-P. Prediction of Displacement Rates at an Active Landslide Using Joint Inversion of Multiple Time Series. In Advancing Culture of Living with Landslides: Volume 3 Advances in Landslide Technology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 85–92. [Google Scholar]
- Li, T.B.; Chen, M.D.; Wang, L.S. Landslide Real-Time Tracking Prediction; Chengdu University of Science and Technology Press: Chengdu, China, 1999; pp. 27–31. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, P.; Rosenbaum, M.S. Artificial Neural Networks and Grey Systems for the Prediction of Slope Stability. Nat. Hazards 2003, 30, 383–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, W.; Zeng, Z.; Lian, C.; Tang, H. Training Enhanced Reservoir Computing Predictor for Landslide Displacement. Eng. Geol. 2015, 188, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merghadi, A.; Yunus, A.P.; Dou, J.; Whiteley, J.; ThaiPham, B.; Bui, D.T.; Avtar, R.; Abderrahmane, B. Machine Learning Methods for Landslide Susceptibility Studies: A Comparative Overview of Algorithm Performance. Earth Sci. Rev. 2020, 207, 103225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, J.; Yunus, A.P.; Tien Bui, D.; Merghadi, A.; Sahana, M.; Zhu, Z.; Chen, C.W.; Khosravi, K.; Yang, Y.; Pham, B.T. Assessment of Advanced Random Forest and Decision Tree Algorithms for Modeling Rainfall-Induced Landslide Susceptibility in the Izu-Oshima Volcanic Island, Japan. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 662, 332–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, L.; Chen, T.; Dou, J.; Plaza, A. A Hybrid Ensemble-Based Deep-Learning Framework for Landslide Susceptibility Mapping. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2022, 108, 102713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, J.; Xiang, Z.; Qiang, X.; Zheng, P.; Wang, X.; Su, A.; Liu, J.; Luo, W. Application and Development Trend of Machine Learning in Landslide Intelligent Disaster Prevention and Mitigation. Earth Sci. 2022. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, X.; Ma, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Chen, H.; Tang, H. A Novel Decomposition-Ensemble Learning Model Based on Ensemble Empirical Mode Decomposition and Recurrent Neural Network for Landslide Displacement Prediction. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 4684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zeng, Z.; Tang, H. Landslide Deformation Prediction Based on Recurrent Neural Network. Neural Process. Lett. 2015, 41, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, P.; Zhou, A.; Chai, B. The Application of Long Short-Term Memory(LSTM) Method on Displacement Prediction of Multifactor-Induced Landslides. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 54305–54311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Y.; Yue, J.; Chen, C. Interval Estimation of Landslide Displacement Prediction Based on Time Series Decomposition and Long Short-Term Memory Network. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 3187–3196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Sun, X.; Ji, Y. Landslide Displacement Prediction Model Using Time Series Analysis Method and Modified LSTM Model. Electronics 2022, 11, 1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Li, H.; Tang, L.; Gu, X.; Wang, L.; Wang, L. Displacement Prediction of Jiuxianping Landslide Using Gated Recurrent Unit (GRU) Networks. Acta Geotech. 2022, 17, 1367–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Tang, J.; He, Z.; Tan, J.; Li, C. A Novel Displacement Prediction Method Using Gated Recurrent Unit Model with Time Series Analysis in the Erdaohe Landslide; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2021; Volume 105, ISBN 0123456789. [Google Scholar]
- Hyndman, R.J.; Athanasopoulos, G. Forecasting: Principles and Practice; OTexts: Melbourne, Australia, 2018; ISBN 0987507117. [Google Scholar]
- Ying, C.; Qi-Guang, M.; Jia-Chen, L.; Lin, G. Advance and Prospects of AdaBoost Algorithm. Acta Autom. Sin. 2013, 39, 745–758. [Google Scholar]
- Schapire, R.E. The Boosting Approach to Machine Learning: An Overview. In Nonlinear Estimation and Classification; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2003; pp. 149–171. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Tang, J.; Dai, L.R. RNN-BLSTM Based Multi-Pitch Estimation. In Proceedings of the Annual Conference of the International Speech Communication Association, INTERSPEECH 2016, San Francisco, CA, USA, 8–12 September 2016; pp. 1785–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gers, F.A.; Schmidhuber, J.; Cummins, F. Learning to Forget: Continual Prediction with LSTM. Neural Comput. 2000, 12, 2451–2471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, J.; Gulcehre, C.; Cho, K.; Bengio, Y. Empirical Evaluation of Gated Recurrent Neural Networks on Sequence Modeling. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.3555. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, X.; Li, Z.; Jin, Y.; Zhang, W. Fair-AdaBoost: Extending AdaBoost Method to Achieve Fair Classification. Expert Syst. Appl. 2022, 202, 117240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyndman, R.J.; Koehler, A.B. Another Look at Measures of Forecast Accuracy. Int. J. Forecast. 2006, 22, 679–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, J.; Yunus, A.P.; Bui, D.T.; Merghadi, A.; Sahana, M.; Zhu, Z.; Chen, C.W.; Han, Z.; Pham, B.T. Improved Landslide Assessment Using Support Vector Machine with Bagging, Boosting, and Stacking Ensemble Machine Learning Framework in a Mountainous Watershed, Japan. Landslides 2020, 17, 641–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; He, Z.; Han, Z.; Li, Y.; Dou, J.; Huang, J. Mapping the Susceptibility to Landslides Based on the Deep Belief Network: A Case Study in Sichuan Province, China. Nat. Hazards 2020, 103, 3239–3261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).