A Modified U-Net Model for Predicting the Sea Surface Salinity over the Western Pacific Ocean
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Source
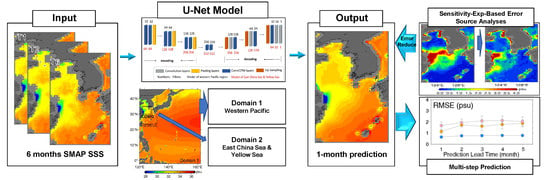
2.2. The U-Net Model
2.3. Model and Domain Settings
2.4. Pre- and Post-Processing
2.5. Model Validation
3. Results
3.1. The Western Pacific
3.2. The East China Sea and the Yellow Sea
4. Discussion
4.1. Optimization of Model Performance Using Training Data
4.2. Influences of the Filter Numbers
4.3. Model Performance in Multi-Step Prediction
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mu, Z.Y.; Zhang, W.M.; Wang, P.Q.; Wang, H.Z.; Yang, X.F. Assimilation of SMOS sea surface salinity in the regional ocean model for South China Sea. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.B.; Wang, Z.Z.; Liu, Y.G. A new algorithm for microwave radiometer remote sensing of sea surface salinity without influence of wind. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2008, 29, 6789–6800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.; Boutin, J.; Reverdin, G.; Lee, T.; Arnault, S.; Martin, N. SMOS sea surface salinity signals of tropical instability waves. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2014, 119, 7811–7826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Zhang, Y. Satellite and Argo observed surface salinity variations in the tropical Indian ocean and their association with the Indian Ocean dipole mode. J. Clim. 2015, 28, 695–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horinouchi, T. Modulation of Seasonal Precipitation over the tropical western/central Pacific by convectively coupled mixed Rossby-gravity waves. J. Atmos. Sci. 2013, 70, 600–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subrahmanyam, B.; Trott, B.C.; Murty, V.S.N. Detection of intraseasonal oscillations in SMAP salinity in the Bay of Bengal. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2018, 45, 7057–7065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinogradova, N.T.; Ponte, R.M. In search of fingerprints of the recent intensification of the ocean water cycle. J. Clim. 2017, 30, 5513–5528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fournier, S.; Vialard, J.; Lengaigne, M.; Lee, T.; Gierach, M.M. Modulation of the Ganges-Brahmaputra River plume by the Indian Ocean Dipole and eddies inferred from satellite observations. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2017, 122, 9591–9604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Eidell, C.; Comiso, J.C.; Berkelhammer, M.; Stock, L. Interrelationships of sea surface salinity, Chlorophyll-α con-centration, and sea surface temperature near the Antarctic Ice Edge. J. Clim. 2021, 34, 6069–6086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.B.; Alabbadi, C.H.; Tan, T.; Wang, S.; Li, K.C. Predicting sea surface salinity using an improved genetic algorithm combining operation tree method. J. Indian Soc. Remote Sens. 2017, 45, 699–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, T.; Wang, Z.H.; Xie, P.F.; Han, N.S.; Jiang, J.Y.; Xu, D.Y. A novel dual path gated recurrent unit model for sea surface salinity prediction. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2020, 37, 317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urquhart, E.A.; Zaitchik, B.F.; Hoffman, M.J.; Guikema, S.D.; Geiger, E.F. Remotely sensed estimates of surface salinity in the Chesapeake Bay: A statistical approach. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 123, 522–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, H.; Dong, J.Y.; Zhong, G.Q.; Sun, X. Prediction of sea surface temperature using long short-term memory. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2017, 14, 1745–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.Z.; Tian, Z.Q.; Yu, J.C.; Zhang, Y.S.; Liu, S.; Du, S.Y.; Lan, X.G. A review of object detection based on deep learning. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2020, 79, 23729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elman, J.L. Finding structure in time. Cogn. Sci. 1990, 14, 179–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bengio, Y.; Simard, P.; Frasconi, P. Learning long-term dependencies with gradient descent is difficult. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 1994, 5, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaefer, A.M.; Udluft, S.; Zimmermann, H.G. Learning long-term dependencies with recurrent neural networks. Neurocomputing 2008, 71, 2481–2488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascanu, R.; Mikolov, T.; Bengio, Y. On the difficulty of training recurrent neural networks. In Proceedings of the 30th International Conference on Machine Learning—Volume 28, Atlanta, GA, USA, 16–21 June 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochreiter, S.; Schmidhuber, J.L. Long Short-Term Memory. Neural Comput. 1997, 9, 1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, T.; Ha, G.; Gou, Y. TD-LSTM: Temporal dependence-based LSTM networks for marine temperature prediction. Sensors 2018, 18, 3797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, C.; Chen, N.C.; Hu, L.; Wang, K.; Xu, Z.W.; Cai, Y.P.; Xu, L.; Chen, Z.; Gong, J. A spatiotemporal deep learning model for sea surface temperature field prediction using time-series satellite data. Environ. Model. Softw. 2019, 120, 104502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Guan, L. Seven-day sea surface temperature prediction using a 3DConv-LSTM model. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 905848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.J.; Chen, Z.R.; Wan, H.; Yeung, D.Y.; Wong, W.K. Convolutional LSTM network: A machine learning approach for precipitation nowcasting. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Montreal, QC, Canada, 7–12 December 2015; p. 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waibel, A.; Hanazawa, T.; Hinton, G.; Shikano, K.; Lang, K.J. Phoneme recognition using time-delay neural networks. IEEE Trans. Acoust. 1989, 37, 328–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, Y.; Pan, W.; Yan, C.Q.; Wu, D.J.; Tang, J.H. A deep learning approach to predict the spatial and temporal distribution of flight delay in network. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 2019, 37, 6029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.Y.; Li, S.Q.; Wang, A.N.; Yang, J.E.; Chen, G. Altimeter observation-based eddy nowcasting using an improved Conv-LSTM network. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrou, Z.I.; Tian, Y.L. Prediction of sea ice motion with convolutional long short-term memory networks. IEEE Trans Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 6865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, R.; Nishio, M.; Do, R.K.G.; Togashi, K. Convolutional neural networks: An overview and application in radiology. Insights Imaging 2018, 9, 611–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, R.; Lv, Z.; Dang, S.P.; Su, T.Y.; Li, X.F. Application of machine learning in ocean data. Multimed. Syst. 2021, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.Y.; Li, Q.; Yu, J.; Wang, L.; Xie, J.; Shi, S.X. Spatial-temporal predictions of sst time series in china’s offshore waters using a regional convolution long short-term memory (RC-LSTM) network. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2020, 41, 3368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Pan, X.L.; Jiang, T.; Sui, B.K.; Liu, C.X.; Sun, W.F. Monthly and quarterly sea surface temperature prediction based on gated recurrent unit neural network. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.; Zhang, T.Y.; Lin, M.J.; Lu, W.F.; Yan, X.H. Predicting subsurface thermohaline structure from remote sensing data based on long short-term memory neural networks. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 260, 112465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.X.; Wang, W.C. Short-Term Precipitation Prediction for Contiguous United States Using Deep Learning. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2022, 49, e2022GL097904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Gorriz, E.; Garcia-Sanchez, J. Prediction of sea surface temperatures in the western Mediterranean Sea by neural networks using satellite observations. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34, L11603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Font, J.; Ballabrera-Poy, J.; Camps, A.; Corbella, I.; Duffo, N.; Duran, I. A new space technology for ocean observation: The SMOS mission. Sci. Mar. 2012, 76, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reul, N.; Grodsky, S.A.; Arias, M.; Boutin, J.; Catany, R.; Chapron, B.; D’Amico, F.; Dinnat, E.; Donlon, C.; Fore, A.; et al. Sea surface salinity estimates from spaceborne L-band radiometers: An overview of the first decade of observation (2010–2019). Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 242, 111769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T.T. U-Net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention (MICCAI), Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; Lecture Notes in Computer Science. Volume 9351, p. 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lguensat, R.; Sun, R.M.; Fablet, P.; Tandeo, E.; Mason, M.; Chen, G. EddyNet: A Deep Neural Network For Pixel-Wise Classification of Oceanic Eddies. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Geoscience and Remote Sensing IGARSS, Valencia, Spain, 22–27 July 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, L.B.; Huo, L.Z.; Hu, C.M.T. Refined UNet: UNet-based refinement network for cloud and shadow precise segmentation. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Rui, X.; Zhang, G.; Yu, T.; Xu, X.; Poslad, S. Feature Merged Network for Oil Spill Detection Using SAR Images. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, S.Q.; Wang, P.; Chung, A.C.S. 3D Randomized Connection Network with Graph-Based Inference. In Proceedings of the 3rd MICCAI International Workshop on Deep Learning in Medical Image Analysis (DLMIA), 7th International Workshop on Multimodal Learning for Clinical Decision Support (ML-CDS), Quebec, QC, Canada, 14 December 2017; Cardoso, M.J., Arbel, T., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Computer Science. Volume 10553, pp. 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, R.; Irving, B.J.; Markelc, B.; Kaeppler, J.; Muschel, R.; Grau1, V.; Schnabell, J.A. Extracting 3D Vascular Structures from Microscopy Images using Convolutional Recurrent Networks. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1705.09597. [Google Scholar]
- Rajabi-Kiasari, S.; Hasanlou, M. An efficient model for the prediction of SMAP sea surface salinity using machine learning approaches in the Persian Gulf. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2022, 41, 3221–3242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trebing, K.; Staǹczyk, T.; Mehrkanoon, S. SmaAt-UNet: Precipitation nowcasting using a small attention-UNet architecture. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2021, 145, 178–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, T.; Wang, X.; Chen, T.J.; Ding, C.W. Fault Recognition Method Based on Attention Mechanism and the 3D-UNet. Comput. Intel. Neurosci. 2022, 2022, 9856669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, H. Changing Kuroshio and Its Affected Shelf Sea: A Physical View. In Changing Asia-Pacific Marginal Seas. Atmosphere, Earth, Ocean & Space; Chen, C.T., Guo, X., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-T.A.; Wang, S.-L. A salinity front in the southern East China Sea separating the Chinese coastal and Taiwan Strait waters from Kuroshio waters. Cont. Shelf. Res. 2006, 26, 1636–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kido, S.; Nonaka, M.; Tanimoto, Y. Impacts of salinity variation on the mixed-layer processes and sea surface temperature in the Kuroshio-Oyashio confluence region. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2021, 126, e2020JC016914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delcroix, T.; Murtugudde, R. Sea surface salinity changes in the East China Sea during 1997–2001: Influence of the Yangtze River. J. Geophys. Res. 2002, 107, 8008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, T.; Jang, C.J.; Jungclaus, J.H.; Haak, H.; Park, W.; Oh, I.S. Effects of the Changjiang river discharge on sea surface warming in the Yellow and East China Seas in summer. Cont. Shelf. Res. 2011, 31, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remote Sensing Systems (RSS). SMAP Sea Surface Salinity Products; Version 4.0; PO.DAAC: Pasadena, CA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fournier, S.; Le, T.; Tang, W.Q.; Steele, M.; Olmedo, E. Evaluation and intercomparison of SMOS, Aquarius, and SMAP sea surface salinity products in the Arctic Ocean. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 3043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, S.L.; Wang, H.Z.; Zhang, R.; Yan, H.Q.; Chen, J. Comparison of satellite-derived sea surface salinity products from SMOS, Aquarius, and SMAP. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2019, 124, 1932–1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meissner, T.; Wentz, F.J.; Manaster, R.; Lindsley, A. Remote Sensing Systems SMAP Ocean Surface Salinities [Level 2C, Level 3 Running 8-Day, Level 3 Monthly; Version 4.0 validated release; Remote Sensing Systems: Santa Rosa, CA, USA, 2019; Available online: www.remss.com/missions/smap (accessed on 10 April 2022). [CrossRef]
- Park, S.J.; Lim, C.G.; Ahn, C.B. Network slimming for compressed: Ensuing cardiac cine MRI. Electron. Lett. 2021, 57, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.B.; Pan, Y.Z.; Luan, J.H.; Yang, X.; Xi, Y.W. Open-Pit mining area segmentation of remote sensing images based on DUSegNet. J. Indian Soc. Remote Sens. 2021, 49, 1257–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.Q.; Tao, H.F.; Li, W.; Yuan, H.T.; Li, T.J. Dynamic gesture recognition based on feature fusion network and variant ConvLSTM. IET Image Process. 2020, 14, 2480–2486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.J.; Chao, S.Y.; Liu, K.K. Effects of reduced Yangtze River discharge on the circulation of surrounding seas. Terr. Atmos. Ocean. Sci. 2004, 15, 111–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Wang, X.C.; Liang, W.H.; Zhang, W.J. Validation and application of soil moisture active passive sea surface salinity observation over the Changjiang River Estuary. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2020, 39, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Geng, X.; Yan, X.H. Prediction of 3-D ocean temperature by multilayer convolutional LSTM. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2020, 17, 1303–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, H.D.R.; Xu, Q.; Ishizaka, J.; Carpenter, E.J.; Yager, P.L.; Goes, J.I. The Influence of Riverine Nutrients in Niche Partitioning of Phytoplankton Communities—A Contrast Between the Amazon River Plume and the Changjiang (Yangtze) River Diluted Water of the East China Sea. Front. Mar. Sci. 2018, 5, 2296–7745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Q.; Wu, Y.Q.; Taylor, S.; Zhao, B. Influence of the Three Gorges Project on saltwater intrusion in the Yangtze River Estuary. Environ. Geol. 2009, 56, 1679–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillou, N.; Chaplain, G.; Petton, S. Predicting sea surface salinity in a tidal estuary with machine learning. Oceanologia 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dossa, A.N.; Alory, G.; daSilva, A.C.; Dahunsi, A.M.; Bertrand, A. Global Analysis of Coastal Gradients of Sea Surface Salinity. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichikawa, H.; Beardsley, R.C. The Current System in the Yellow and East China Seas. J. Oceanogr. 2002, 58, 77–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslan, S.; Zennaro, F.; Furlan, E.; Critto, A. Extensive study of recurrent neural network architectures with a multivariate approach for water quality assessment in complex coastal lagoon environments: A case study on the Venice Lagoon. Environ. Model. Softw. 2022, 154, 105403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, J.; Feng, M. A deep learning model for forecasting global monthly mean sea surface temperature anomalies. Front. Clim. 2022, 4, 932932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, S.Y.; Li, W.G.; Liu, T.Y.; Zhou, S.G.; Guan, J.H.; Qin, R.F.; Wang, Z.F. D2CL: A Dense Dilated Convolutional LSTM Model for Sea Surface Temperature Prediction. IEEE J.-STARS 2021, 14, 12514–12523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, X.; Zhao, N.; Han, Z. A Modified U-Net Model for Predicting the Sea Surface Salinity over the Western Pacific Ocean. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1684. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15061684
Zhang X, Zhao N, Han Z. A Modified U-Net Model for Predicting the Sea Surface Salinity over the Western Pacific Ocean. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(6):1684. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15061684
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Xuewei, Ning Zhao, and Zhen Han. 2023. "A Modified U-Net Model for Predicting the Sea Surface Salinity over the Western Pacific Ocean" Remote Sensing 15, no. 6: 1684. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15061684
APA StyleZhang, X., Zhao, N., & Han, Z. (2023). A Modified U-Net Model for Predicting the Sea Surface Salinity over the Western Pacific Ocean. Remote Sensing, 15(6), 1684. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15061684