Abstract
Increased and enhanced utilisation of remote sensing and robotics in the Arctic can further enhance cultural safety and well-being and reduce the risks posed to archaeologists, heritage workers and others in the field. In this preliminary scoping survey, the authors review the current use of these technologies and consider a range of related issues, from cultural safety to nefarious use by criminals. Initial discussions with experts have informed areas of concern; and the potential for further integration. In the future, the University of Tromsø’s new Tromsø Arctic Simulation Integration Centre (TASIC) will be utilised to evaluate a range of scenarios to inform risk analysis and contribute towards safety enhancement in the Arctic Heritage at Risk Project (Arctic-HARP). The following is an overview of the significant state-of-the-art technologies and related matters.
1. Introduction
Climate change in the Arctic is impacting cultural heritage on a devastating scale, ranging from coastal erosion that is damaging or destroying coastal archaeological sites to accelerating biological and chemical processes causing decay, disturbance and obliteration of objects and structures [1,2,3,4]. Climate change has allowed the pillaging of woolly mammoth tusks from thawing ground, many from archaeological sites, and increased general tourist ‘souveniring’ of material culture. The cultural safety of local communities is at risk through the theft, damage or destruction of cultural objects and places of spiritual, cultural and historical significance. The physical risks associated with responding include the usual challenges of Arctic field operations, potential exposure to hazardous materials from the past industrial and military activity and, in some instances, encountering criminal activity. This is a challenge for governments and industries, including tourism. In addition, it concerns NGOs such as the International Council on Monuments and Sites’ International Polar Heritage Committee, academia and local communities [5]. Remote sensing and robotics are increasingly integrated into the data collection necessary for computational and human assessment to inform heritage-at-risk policy, analysis, planning, preparation, and considering how to respond safely. The spatial and temporal data collected in these ways, and the technical tools required to analyse them, are increasingly becoming freely available in the public domain, often through open-source platforms. Of particular note are the European Union’s Copernicus programme and the Sentinel satellite series that supports it [6], the associated SNAP (Sentinel Application Platform) analysis toolbox [7], and the cloud computing resources made available through the Google Earth Engine [8]. In particular, the conception of the Copernicus programme as an integrated Earth Observation data collection system operating in or near real-time is highly aligned with the applications defined in this paper and, as we note below, the range of spatiotemporal observation characteristics that it can achieve is in general well matched to them. Ultra-high spatial resolutions, down to the centimetre scale, can be achieved using remote sensing systems carried by Uninhabited Autonomous Vehicles (UAVs—‘drones’) and are well-matched to the scale of sites, structures and artefacts. Changes to the environmental setting, such as coastal erosion, permafrost thawing, and boreal advances, can be routinely and effectively monitored using spaceborne remote sensing to understand cumulative changes better and monitor extreme events. Remote sensing, robotics and analytical resources can enhance heritage fieldwork, inform broader situational awareness, and contribute to further research.
Integrating local communities’ expert knowledge with remote sensing and robotics resources is a culturally appropriate effect multiplier to improve safety and resilience in the Arctic heritage domain. This will allow the limited number of archaeologists, other heritage professionals, and support members to be deployed more efficiently, effectively and safely. Analysis in the field can be enhanced by utilising more extensive computational resources, with additional human analysis ground-truthing. In extreme events, ranging from major storms and fires to criminality or civil conflict, remote sensing has a vital overwatch role of heritage sites and heritage personnel. The security of related data is an area of concern. Robust retention procedures and access control protocols are required to avoid the loss of data or inappropriate access in the context of cultural privacy or by criminals. The aim of this technical note is to provide an overview of the ways in which modern data collection technologies, represented by remote sensing and robotics, can address some of the specific challenges relating to the safety of cultural heritage in the Arctic. We do not present any new research results, although we hope to stimulate the development of a new field of research by synthesising ideas from existing technologies.
2. Risk and Safety
Cultural respect and safety should inform all processes and decisions regarding the utilisation of remote sensing and robotics in Arctic cultural matters. Prior consultation with the source and, in some instances, associated communities should be the first step with a clear and transparent overview of how remote sensing and robotics could be utilised in the operational phase and how the data gathered would be stored, shared and utilised in the media, academic publications and other fora such development of government policy. There is also the potential that remote sensing and robotics can enhance and validate traditional narratives and understandings of the past [9,10]. This can lead to enhanced pride in the past and confidence in the future [11]. However, it may well be that communities choose not to allow these new technologies to be used to examine their ancestors’ settlements, pathways and lifeways or—directly or indirectly—their current lives. Remote sensing is a surveillance technology, and there may be restrictions on certain times of the year and locations to respect the privacy of the community and ceremonial activities. The engagement between local communities and researchers should result in a legacy of new information and when desired, enhanced skills in the local community to utilise remote sensing and robotic resources in their endeavours. The Nunalleq Project in Quinhagak, Alaska, is an example of a local community initiating an archaeological project, and through participatory research methods, based on their traditional knowledge and ethical engagement from the academic community, founded on the belief that …’. Indigenous participation should also reflect Indigenous autonomy’ [12]. This includes the transfer of technology and expertise to the local community to enable the coproduction of knowledge can occur or if the community decides, the production of knowledge that is exclusively for the community to know and utilise. The increasing use of artificial intelligence (AI) has led to associated endeavours to produce explainable AI (XAI) that allows an ‘Understanding of “what goes on in the black box”…’ [12,13]. Integral to the coproduction of knowledge is a clear understanding of the AI being utilised. Local communities and the resources of the state, technical, organisational and human, can also work in partnership to protect sites such as those of Franklin’s lost Northwest Passage expedition with HMS Erebus and HMS Terror [14] (See Figure 1).

Figure 1.
The wrecks of HMS Erebus and HMS Terror sites are protected through the combined endeavours of the local Inuit guardians and the resources of the Canadian state [14].
The physical and biological environment of the Arctic can pose risks both to the physical integrity and stability of cultural sites and artefacts and also to the health and safety of people who may be interacting with them, e.g., as guardians of heritage sites or as researchers. Existing threats may be posed by the ruggedness of terrain or by changes in the terrain through landslides, coastal or thermokarst erosion, earthquakes or volcanic eruption; glacier surges or sudden glacial lake outburst flood events; an explosion of subterranean methane; and extreme weather. Climate change can alter the physical characteristics of the environment in adverse ways, for example, by thawing permafrost and destabilising the ground or even opening sinkholes, enhancing the rate of coastal erosion and increasing the frequency of extreme weather events [15]. Dangerous alterations to terrain can be caused by anthropogenic interventions such as illegal tunnels made in riverbanks to steal woolly mammoth tusks [16]. The archaeology and heritage professions have developed risk evaluation methodologies and methods that can be utilised in the Arctic [17] for cultural heritage. However, with rapid climate change, these need to be reviewed regularly.
3. Remote Sensing
Remote Sensing methods represent a mature yet dynamically evolving set of techniques and data sources that offer a relatively good fit to the task of enhancing risk analysis and safety assessment for arctic heritage. A fundamental consideration of the utility of any remote sensing system in this or any other area of application is its spatiotemporal characteristics. These are illustrated schematically in Figure 2, which considers four model observing systems: ‘UAV’, representing a user-operated Uninhabited Airborne Vehicle system (which could mean simply an off-the-shelf consumer-grade ‘drone’ with an integrated camera, or something more sophisticated); ‘Worldview’, representing commercially available ultra-high-resolution satellite imagery (the example in the figure assumes WorldView-3 imagery from the DigitalGlobe corporation); ‘Sentinel-2’, representing freely-available medium-resolution satellite imagery such as that from the Sentinel-2 Multispectral Imager system; and ‘MODIS’, representing freely-available, coarse-resolution but high temporal resolution satellite imagery such as that from the MODIS (Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer) sensor. Each of these systems has a limiting spatial resolution, i.e., the smallest scale of detail capable of being resolved. It also has maximum useful spatial coverage. For the satellite systems, this exceeds 10 km, but for the UAV, we set this somewhat arbitrarily to 100 m to represent an area that could be surveyed in a reasonable length of time. The minimum revisit time for satellite-based systems is set mainly by the laws of orbital dynamics and is, broadly speaking, inversely proportional to the spatial resolution [18]. Thus a system like MODIS, with a spatial resolution of 250 metres, can revisit a given location daily, while the Sentinel-2 system with a 10 m resolution has a 5-day revisit capability. We also suppose that observing systems have a maximum useful duration of observations. For satellite-based systems, these are assumed to be effectively infinite going into the future, though, for retrospective data, they extend back only as far as the satellite record, which is a matter of a few decades. For UAV-based systems, we consider the upper limit for the revisit to be set by the typical three-year duration of a funded research project.
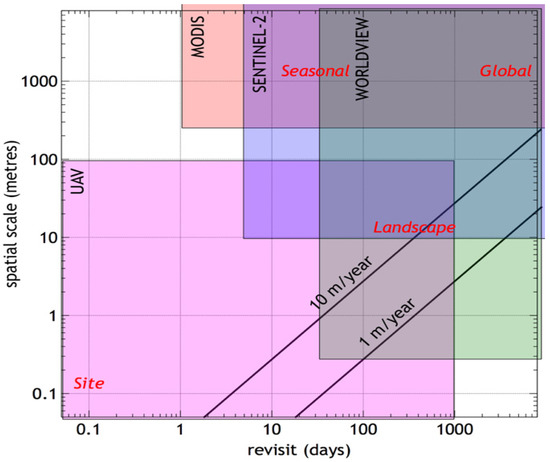
Figure 2.
Schematic illustration of the useful ranges of spatial and temporal coverage of various representative remote sensing systems: UAV (Uninhabited Autonomous Vehicle), MODIS (Moderate-Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer), Sentinel-2 and WorldView. The oblique lines show the combination of spatial and temporal resolution needed to capture a spatial process, such as coastal erosion or vegetation advance at a particular rate, as discussed in the text. The phenomena labelled in red represent different observation objectives, also discussed in the text.
Figure 2 also shows the requirements of four representative data applications. ‘Site’ is intended to represent the requirements for monitoring the security of a site; we suppose a spatial resolution of 0.1 m and a revisit time of 0.1 days (=2.4 h, although perhaps even more frequent reacquisition could be desirable). As the figure shows, satellite-based systems would be incapable of providing this level of surveillance, although UAV systems could do so. ‘Landscape’, ‘seasonal’ and ‘global’ are intended to suggest the observing parameters necessary to represent the site’s characteristics at the landscape scale, assumed to vary not more rapidly than annually, and at the regional scale where broad global characteristics may need to be established every few years, or seasonal variations may need to be established with weekly observations. As the figure suggests, these seasonal, global, and landscape characteristics are well within the scope of freely available satellite data.
From the perspective of risk to Arctic heritage, the most important aspects of the physical environment are likely to be centred on landscape stability and erosion. Coastal erosion is a widespread phenomenon around the Arctic [19], with rates of retreat as high as 10–20 metres per year in some parts of Alaska and Canada, although rates around 1 metre per year are generally more usual [19]. Remote sensing methods provide an effective tool to monitor this phenomenon since discrimination between land and water in optical and especially near-infrared imagery is generally straightforward. The reliably measurable rate of coastline retreat depends on both the spatial resolution and the locational accuracy of imagery and the time interval before its reacquisition. For example, the freely-available Multispectral Imager (MSI) imagery from the European Space Agency’s Sentinel-2 mission has a spatial resolution of 10 m and a positioning accuracy of 20 m or better, so that images would have to be acquired at least three years apart in order to resolve a rate of retreat of 10 m/year (and, by extension, a rate of 1 m/year would require a decades-long time-series).
This is illustrated by the oblique lines in Figure 2. For example, the line labelled ‘10 m/year’ passes through the point with a spatial scale (on the vertical axis) of 10 m and a revisit time (on the horizontal axis) of 365 days, showing that a revisit time of at least one year would be needed to capture change at a rate of 10 m/year at a spatial scale of 10 m. Thus, the area to the right of the oblique line shows combinations of spatial scale and revisit time capable of capturing such a change. The figure shows that this area overlaps with the observed characteristics of the Sentinel-2 MSI instrument.
Higher-resolution satellite imagery, such as that available from WorldView or Planet observing systems, has also demonstrated their value. Figure 3, reproduced from [12], illustrates the effectiveness of high-resolution satellite imagery and the scope for automation of the change-detection workflow. In this particular instance, a single erosion event caused the destruction of an isthmus and the conversion of a peninsula into an island. Identification and analysis of this event were collaborative between Yupik hunters and remote sensing specialists [12]. The effectiveness of satellite radar imagery for detecting coastal erosion has also been demonstrated [20]. Aerial images, from UAVs or otherwise, are capable of resolving much smaller rates of change and have proved their value in monitoring and predicting coastal erosion rates [21,22]. Figure 2 illustrates the good match between the observing characteristics offered by UAV systems and the phenomenon of coastal erosion and shows that satellite-based systems are also potentially useful.
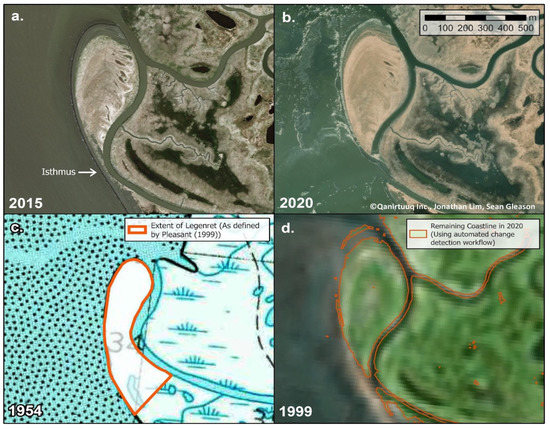

Figure 3.
Erosion of the Legenret peninsula at the mouth of the Uyak (Oyak) creek, near Quinhagak, southwest Alaska. (a,b): Planet satellite imagery at 3 m resolution, (c): the extent of the peninsula as defined by USGS in 1954; (d) the result of automated coastline change detection. Reproduced from [12] with permission of the authors.
Remote sensing methods can also be applied effectively to monitor the stability of terrain, although this is a more complex task than identifying coastal erosion processes. The latter is essentially a two-dimensional problem which involves drawing lines on a map while mapping the configuration of the land surface is a three-dimensional problem. A number of techniques are available for constructing a Digital Elevation Model (DEM: a digital representation of the terrain surface height) from remotely sensed data, including automated stereophotogrammetric methods from digital imagery, radar interferometry, and LiDAR (laser ranging) methods. These are all, in principle, possible from both spaceborne and airborne platforms, and a number of DEM products created from spaceborne data have been placed in the public domain, although in general, they are of too low spatial or temporal resolution to be useful for characterising cultural heritage sites (unless the disturbance is a very large one like a methane blowout [23]. Measurements from airborne platforms, however, are well-matched to the scale of sites. Here, the two most useful approaches are airborne LiDAR and Structure from Motion (SfM) [24]. Both can resolve height differences down to centimetres at a horizontal resolution of decimetres. SfM, in particular, is a technique that can be applied using digital images collected from a relatively simple and inexpensive UAV system [25], although the data processing is somewhat demanding. Terrain stability can also be modelled using GIS methods, with suitable input layers including geological and DEM data and mapping of existing features indicative of instability. This approach has been successfully demonstrated by Nicu et al. [26].
The commonest form of remotely sensed data, at least when obtained from spaceborne platforms, is imagery covering the visible and near-infrared (VNIR) parts of the electromagnetic spectrum. This type of imagery is especially well suited to making qualitative and quantitative observations of vegetation, and it has been widely exploited for this purpose for decades. The presence and vigour of green-leafed vegetation can be estimated using the normalised difference vegetation index (NDVI), a mathematical derivative of the imagery that is strongly correlated to the leaf-area index (LAI) [27]. Differences between plant types can be inferred from the multispectral characteristics of images and used to make maps which can, in turn, be used to assess phenomena such as vegetation encroachment [28] or retreat and, indirectly, human foot traffic [29].
Archaeological sites are not inherently sterile or benign biologically; they may contain dangerous bacteria or viruses, such as the 1918 influenza N1H1 virus [30,31]. Remote sensing can reveal large-scale impacts of pollution, which may have an adverse effect on cultural artefacts [32] and indicate areas that would be suitable host habitats for pathogens. The arctic and subarctic regions are subject to some local and regional disturbance from chemical pollution [33], as well as transboundary pollution advected from lower latitudes. The presence of chemical pollutants can sometimes be inferred indirectly through their effects on vegetation (which can become stressed, or even be killed, or which can undergo an abnormal succession) or on a water surface (which can change its optical reflectance properties as a result of suspended sediments or a surface layer of hydrocarbon contaminants) [34]. In addition to the Arctic being the location of the largest nuclear explosion in history, a legacy of radiological sources poses a risk. These, however, remain inaccessible to remote sensing technology.
4. Robotics
The deployment of robotic resources with onboard sensors, both mobile and static site monitoring, can enhance safety. Robots: airborne, terrestrial or underwater, provide agile platforms on which to examine physically dangerous or demanding spaces with the option, if suitably equipped, of physically manipulating objects that are encountered. One instance in which robots could be utilised is when an illegal tunnel, dug by thieves seeking woolly mammoth tusks, is discovered as the tunnel may be dangerously unstable. Former industrial sites, including mines and military sites, are best examined, before entry by humans, by robots for structural integrity and radiological, chemical and biological hazards. In the event of hazards being encountered or access being physically impossible for a human, a robotic heritage survey, e.g., utilising photogrammetry-SfM and other technologies, can be conducted (ROVINA 2021) (See Figure 4) and, if suitably equipped, archaeological examination and excavation can be accomplished. The Centre for Ice and Climate’s ‘CIC’ rover (See Figure 5) is an example of the transformation in robotics occurring through reduced costs utilising 3-D printing, institutional workshops and enhanced onboard processing [35].
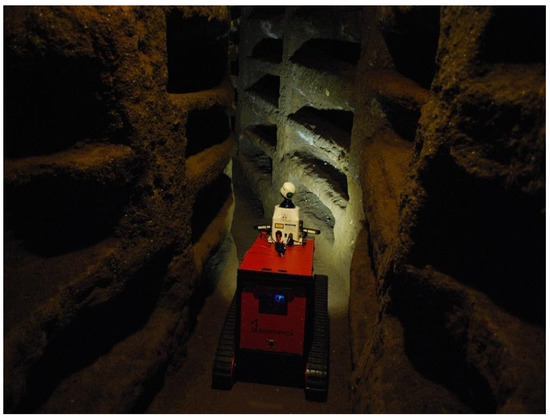

Figure 4.
The ROVINA project demonstrated the ability to produce a rover capable of sophisticated exploration and mapping (ROVINA Project).

Figure 5.
The ‘CIC’ rover is the type of platform that could be used with ice-penetrating radar for archaeological surveys to search for former bases that have been covered and associated equipment, such as aircraft within the ice (CIC Project).
Early assessment of utilising radar to detect the presence and movements of polar bears around a site had demonstrated potential (although based on a small sample) with a two-thirds detection rate, including when human observation was not possible due to lack of visibility [36]. The future deployment of enhanced technical surveillance—in combination with human vigilance—has the potential to enhance safety and reduce stress.
The seabed is the repository of millennia of material culture. The potential exists for ship or benthic-based platforms, in combination with Autonomous Underwater Vehicles (AUV) and Remotely Operated Vehicles (ROVs) that could examine large areas of seabed before sending divers or more specialised equipment to the chosen sites [37]. Conversely, the accessibility of robotic equipment in the public domain will enable criminals, or the naïve amateur, to access locations and artefacts previously protected by their remoteness.
5. Discussion
It has been the aim of this technical note to stimulate the development of a field of study which brings modern information and data collection technologies to bear on issues related to heritage at risk in the Arctic. Heritage in the Arctic, and those associated with it, are confronted by dynamic risks that have the potential to cause harm, ranging from community and cultural loss to physical injury or worse. Proactively utilising and enhancing remote sensing and robotics in heritage endeavours has the potential to improve safety for Arctic communities, archaeologists and other heritage practitioners. In addition, ongoing co-productive research regarding the preservation and protection of data related to heritage is required to ensure that the use of remote sensing technologies and techniques, including AI, occurs in ways that respect and protect cultural privacy. There is also concern regarding how criminals could utilise remote sensing technologies and techniques in their attempts to plunder sites in the maritime and terrestrial realms. The authors are engaged, with others, in the creation of the Tromsø Arctic Simulation Centre (TASIC), currently in development at UiT Norway’s Arctic University. It is hoped that this will provide the resources for the ARCTIC HARP (Heritage at Risk Project) to conduct sophisticated simulated exercises with associated machine learning to examine individual and compound risks to cultural heritage. UiT’s robotic resources will also be utilised to understand better and enhance how these resources can be deployed in situ and related to remote sensing. Central to the project will be integration with heritage organisations and colleagues across the Arctic. TASIC should generate some novel insights in this newly developing field; the authors would welcome additional information and suggestions that may enhance research on this topic.
6. Conclusions
This preliminary survey indicates that whilst some related technologies and techniques have already been deployed, there is scope for further integration of technologies and techniques, dissemination of lessons learnt, and empowerment of local communities. There is also the ongoing technical issue of utilising equipment designed for more moderate climates in the demanding Arctic environment.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, both authors; methodology, both authors; formal analysis, both authors; investigation, both authors; resources, both authors; writing both authors; review and editing, both authors; visualization, G.R. (Figure 2). All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the reviewers whose input has significantly improved the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
Gareth Rees reported no conflict of interest. Bryan Lintott noted that he is a member of ICOMOS, whose publications are cited.
References
- ICOMOS Climate Change and Heritage Working Group. The Future of Our Pasts: Engaging Cultural Heritage in Climate Action. Outline of Climate Change and Cultural Heritage; ICOMOS: Paris, France, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Hollesen, J.; Matthiesen, H.; Elberling, B. The Impact of Climate Change on an Archaeological Site in the Arctic. Archaeometry 2017, 59, 1175–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollesen, J.; Callanan, M.; Dawson, T.; Fenger-Nielsen, R.; Friesen, T.M.; Jensen, A.M.; Markham, A.; Martens, V.V.; Pitulko, V.V.; Rockman, M. Climate Change and the Deteriorating Archaeological and Environmental Archives of the Arctic. Antiquity 2018, 92, 573–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollesen, J.; Matthiesen, H.; Fenger-Nielsen, R.; Abermann, J.; Westergaard-Nielsen, A.; Elberling, B. Predicting the Loss of Organic Archaeological Deposits at a Regional Scale in Greenland. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 9097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barr, S.; Pearson, M. Heritage at Risk in the Polar Regions. In Heritage at Risk: World Report 2016–2019 on Monuments and Sites in Danger; Machat, C., Ziesemer, J., Eds.; ICOMOS Deutschland: Berlin, Germany, 2020; ISBN 978-3-945880-67-8. [Google Scholar]
- Thepaut, J.; Pinty, B.; Dee, D.; Engelen, R. The Copernicus Programme and Its Climate Change Service. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2018—2018 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Valencia, Spain, 22–27 July 2018; pp. 1591–1593. [Google Scholar]
- Metrikaityte, G.; Suziedelyte Visockiene, J.; Papsys, K. Digital Mapping of Land Cover Changes Using the Fusion of SAR and MSI Satellite Data. Land 2022, 11, 1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amani, M.; Ghorbanian, A.; Ahmadi, S.A.; Kakooei, M.; Moghimi, A.; Mirmazloumi, S.M.; Moghaddam, S.H.A.; Mahdavi, S.; Ghahremanloo, M.; Parsian, S.; et al. Google Earth Engine Cloud Computing Platform for Remote Sensing Big Data Applications: A Comprehensive Review. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2020, 13, 5326–5350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillerdal, C.; Knecht, R.; Jones, W. Nunalleq: Archaeology, Climate Change, and Community Engagement in a Yup’ik Village. Arct. Anthropol. 2019, 56, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, A.M. Culture and Change: Learning from the Past through Community Archaeology on the North Slope. Polar Geogr. 2012, 35, 211–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friesen, M. Arctic Cultural Heritage at Risk Arctic (CHAR) Climate Change Impacts on the Inuvialuit 327 Archaeological Record; Inuvialuit Cultural Resource Centre, University of Toronto: Inuvik, NT, Cananda, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, J.; Gleason, S.; Jones, W.; Church, W. Nuna Nalluyuituq (The Land Remembers): Remembering Landscapes and Refining Methodologies through Community-Based Remote Sensing in the Yukon-Kuskokwim Delta, Southwest Alaska. Archaeol. Prospect. 2021, 28, 339–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiok, K.; Farahani, F.V.; Karwowski, W.; Ahram, T. Explainable Artificial Intelligence for Education and Training. J. Def. Model. Simul. 2022, 19, 133–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parks Canada Agency, G. of C. Inuit Guardians Program. Available online: https://parks.canada.ca/lhn-nhs/nu/epaveswrecks/culture/inuit/gardiens-guardians (accessed on 9 November 2021).
- Solsten, B.; Aitken, A. An Application of GIS Techniques to Assess the Risk of Disturbance of Archaeological Sites by Mass Movement and Marine Flooding in Auyuittuq National Park Reserve, Nunavut. Géographie Phys. Quat. 2006, 60, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basilyan, A.; Anisimov, M.; Nikolskiy, P.; Pitulko, V. Wooly Mammoth Mass Accumulation next to the Paleolithic Yana RHS Site, Arctic Siberia: Its Geology, Age, and Relation to Past Human Activity. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2011, 38, 2461–2474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canadian Conservation Institute. The ABC Method: A Risk Management Approach to the Preservation of Cultural Heritage—Canada.Ca. Available online: https://www.canada.ca/en/conservation-institute/services/risk-management-heritage-collections/abc-method-risk-management-approach.html (accessed on 4 January 2023).
- Rees, G.; Brown, I.; Mikkola, K.; Virtanen, T.; Werkman, B. How Can the Dynamics of the Tundra-Taiga Boundary Be Remotely Monitored? Ambio 2002, Special Report 12, 56–62. [Google Scholar]
- Frederick, J.M.; Thomas, M.A.; Bull, D.L.; Jones, C.A.; Roberts, J.D. The Arctic Coastal Erosion Problem; US Department of Energy Office of Scientific and Technical Information: Oak Ridge, TN, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Philipp, M.; Dietz, A.; Ullmann, T.; Kuenzer, C. Automated Extraction of Annual Erosion Rates for Arctic Permafrost Coasts Using Sentinel-1, Deep Learning, and Change Vector Analysis. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunliffe, A.M.; Tanski, G.; Radosavljevic, B.; Palmer, W.F.; Sachs, T.; Lantuit, H.; Kerby, J.T.; Myers-Smith, I.H. Rapid Retreat of Permafrost Coastline Observed with Aerial Drone Photogrammetry. Cryosphere 2019, 13, 1513–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicu, I.C.; Rubensdotter, L.; Stalsberg, K.; Nau, E. Coastal Erosion of Arctic Cultural Heritage in Danger: A Case Study from Svalbard, Norway. Water 2021, 13, 784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogoyavlensky, V.; Bogoyavlensky, I.; Nikonov, R.; Kargina, T.; Chuvilin, E.; Bukhanov, B.; Umnikov, A. New Catastrophic Gas Blowout and Giant Crater on the Yamal Peninsula in 2020: Results of the Expedition and Data Processing. Geosciences 2021, 11, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowe, D.G. Distinctive Image Features from Scale-Invariant Keypoints. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2004, 60, 91–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauhala, A.; Tuomela, A.; Davids, C.; Rossi, P.M. UAV Remote Sensing Surveillance of a Mine Tailings Impoundment in Sub-Arctic Conditions. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicu, I.C.; Lombardo, L.; Rubensdotter, L. Preliminary Assessment of Thaw Slump Hazard to Arctic Cultural Heritage in Nordenskiöld Land, Svalbard. Landslides 2021, 18, 2935–2947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rees, W.G.; Golubeva, E.I.; Tutubalina, O.V.; Zimin, M.V.; Derkacheva, A.A. Relation between Leaf Area Index and NDVI for Subarctic Deciduous Vegetation. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2020, 41, 8573–8589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barlindhaug, S.; Holm-Olsen, I.M.; Tømmervik, H. Monitoring Archaeological Sites in a Changing Landscape–Using Multitemporal Satellite Remote Sensing as an ‘Early Warning’ Method for Detecting Regrowth Processes. Archaeol. Prospect. 2007, 14, 231–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thuestad, A.E.; Tømmervik, H.; Solbø, S.A. Assessing the Impact of Human Activity on Cultural Heritage in Svalbard: A Remote Sensing Study of London. Polar J. 2015, 5, 428–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poirier, D.; Feder, K. Dangerous Places: Health, Safety, and Archaeology; Bergin & Garvey: Westport, CT, USA, 2001; ISBN 0-89789-632-7. [Google Scholar]
- Taubenberger, J.K.; Hultin, J.V.; Morens, D.M. Discovery and Characterization of the 1918 Pandemic Influenza Virus in Historical Context. Antivir. Ther. 2007, 12, 581–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roots, O.; Roose, A.; Eerme, K. Remote Sensing of Climate Change, Long-Term Monitoring of Air Pollution and Stone Material Corrosion in Estonia. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2011, 32, 9691–9705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rees, W.G.; Rigina, O. Methodologies for Remote Sensing of the Environmental Impacts of Industrial Activity in the Arctic and Sub-Arctic. In Social and Environmental Impacts in the North; Kluwer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2003; pp. 67–88. [Google Scholar]
- Bondur, V.G.; Vorobev, V.E. Satellite Monitoring of Impact Arctic Regions. Izv. Atmos. Ocean. Phys. 2015, 51, 949–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, A.; Steen-Larsen, H.; Christianson, K.; Hvidberg, C. A Low-Cost Autonomous Rover for Polar Science. Geosci. Instrum. Methods Data Syst. 2019, 8, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cocksedge, A. The Use of Compact Surveillance Radar to Study Polar Bears (Ursus Maritimus) 315 near Churchill, Manitoba, Canada. Master’s Thesis, University of Toronto, Toronto, ON, Canada, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Aguzzi, J.; Albiez, J.; Flögel, S.; Godø, O.R.; Grimsbø, E.; Marini, S.; Pfannkuche, O.; Rodriguez, E.; Thomsen, L.; Torkelsen, T.; et al. A Flexible Autonomous Robotic Observatory Infrastructure for Bentho-Pelagic Monitoring. Sensors 2020, 20, 1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).