Satellite-Based Localization of IoT Devices Using Joint Doppler and Angle-of-Arrival Estimation
Abstract
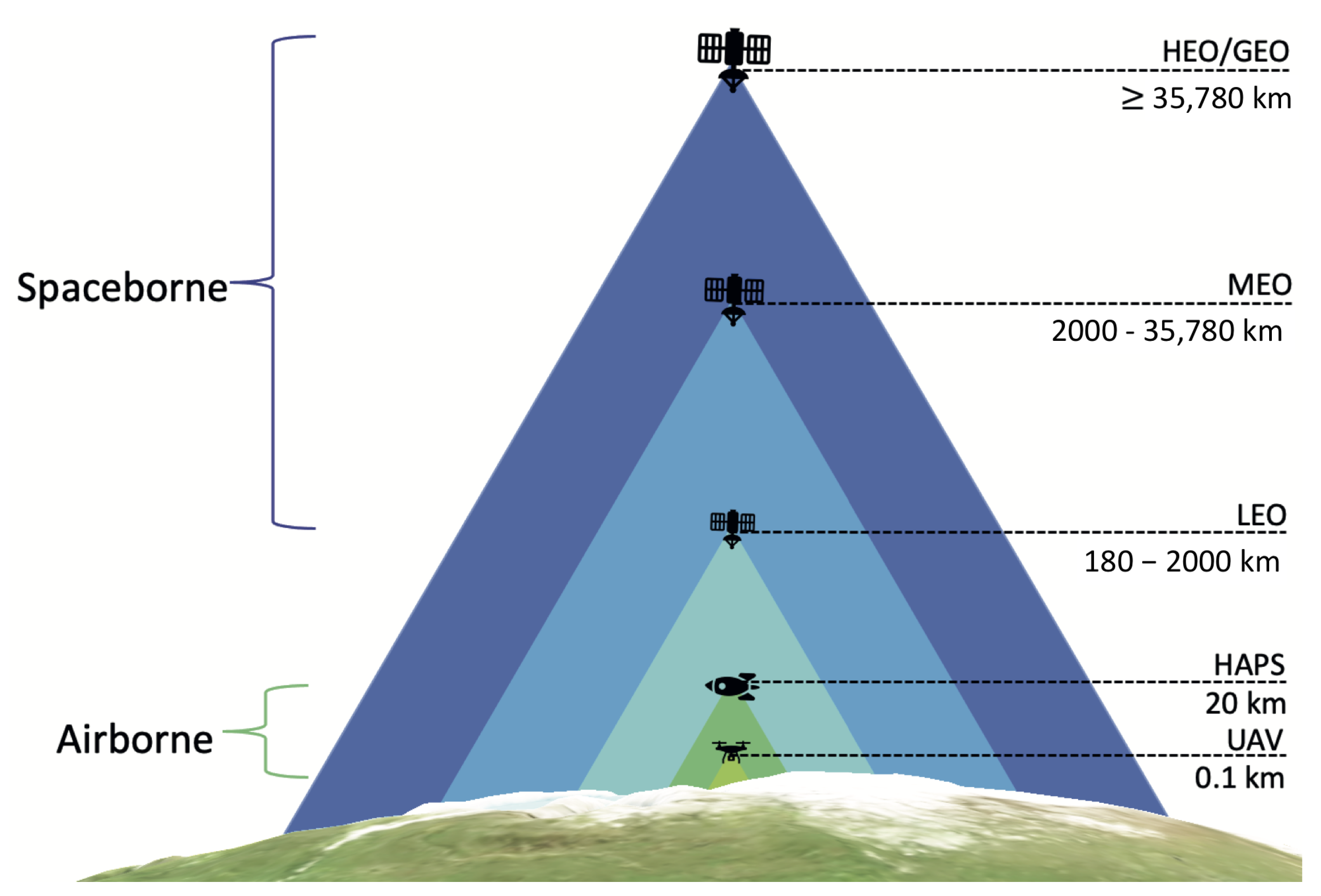
:1. Introduction
- A satellite-based localization method using joint Doppler and AoA measurements received from the ground IoT device is proposed.
- The likelihood function of Doppler and AoA measurements based is derived on the Gaussian error and estimated Kent error distributions, respectively.
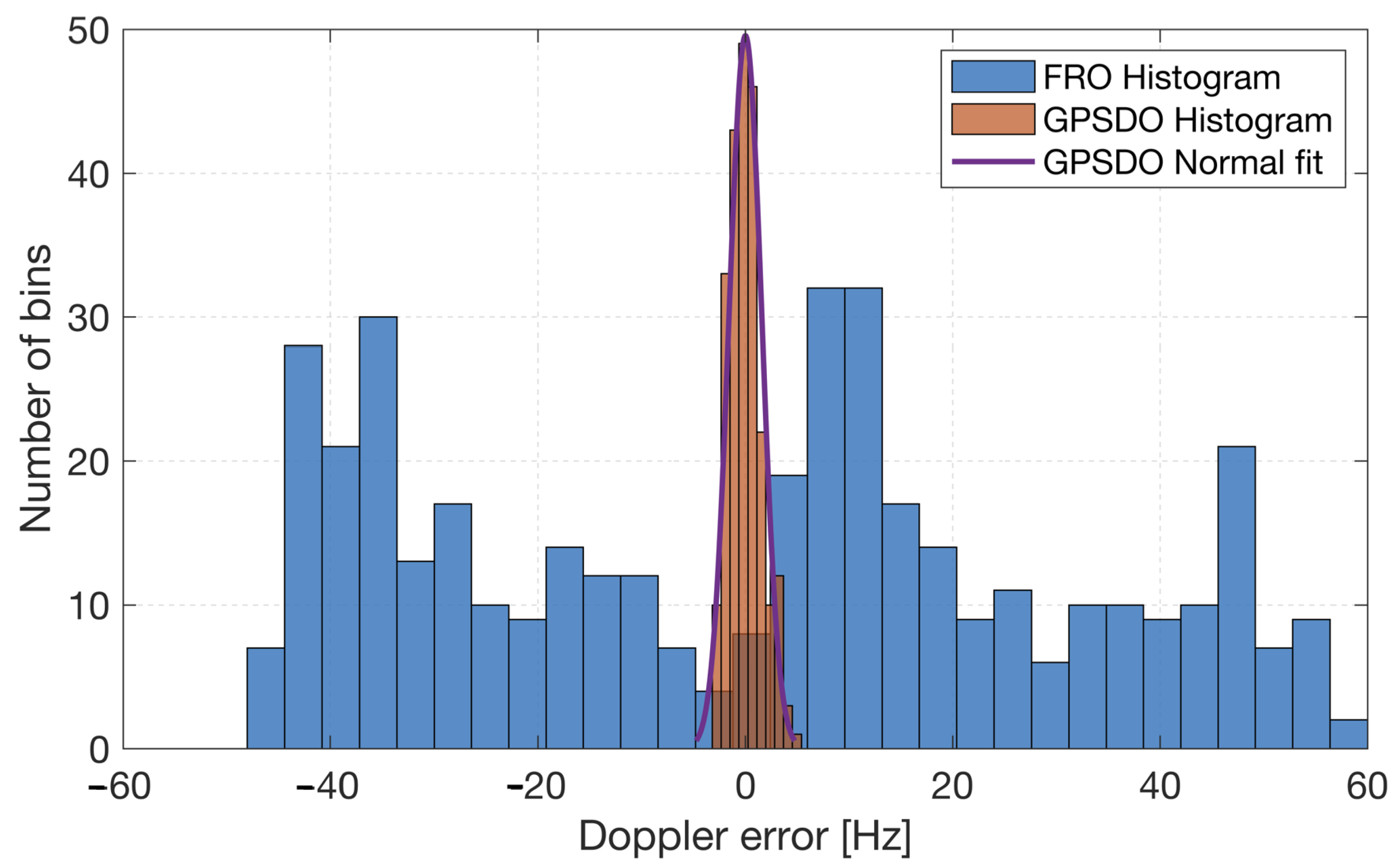
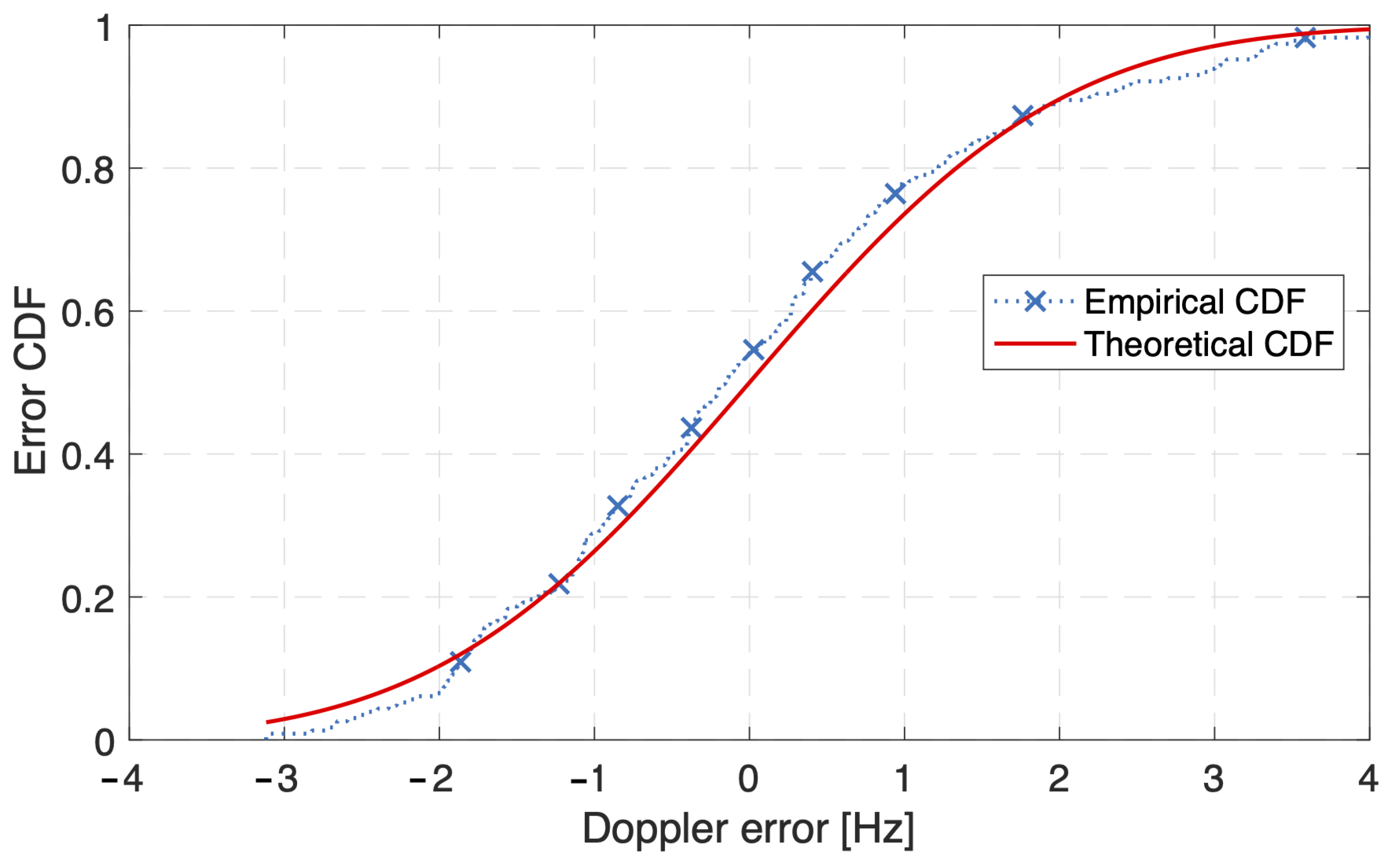
- The Doppler measurement error was investigated using real measurements from LEO satellites.
- The localization performance behavior against varying Doppler and AoA error deviations is illustrated.
2. Related Works
3. System Model
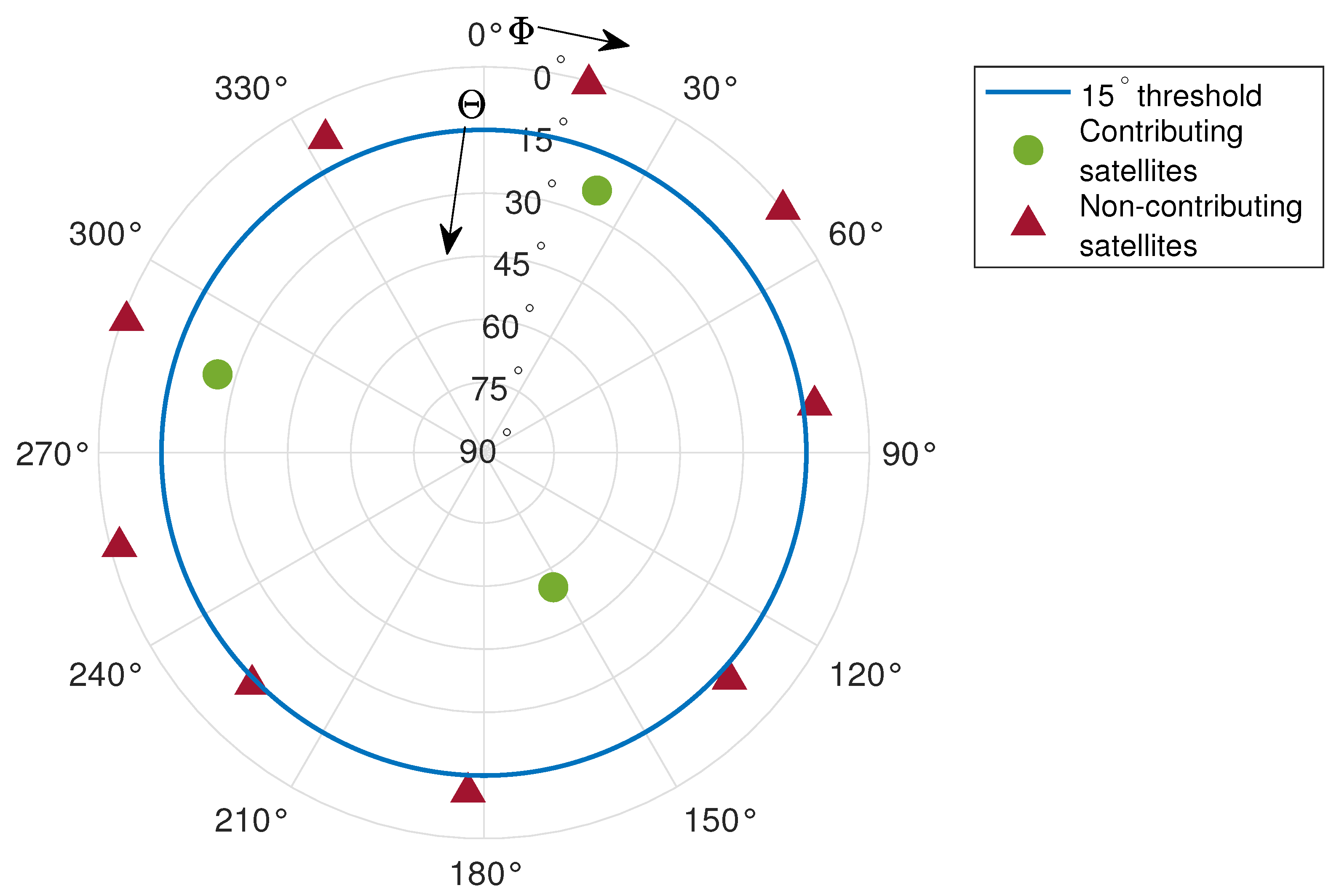
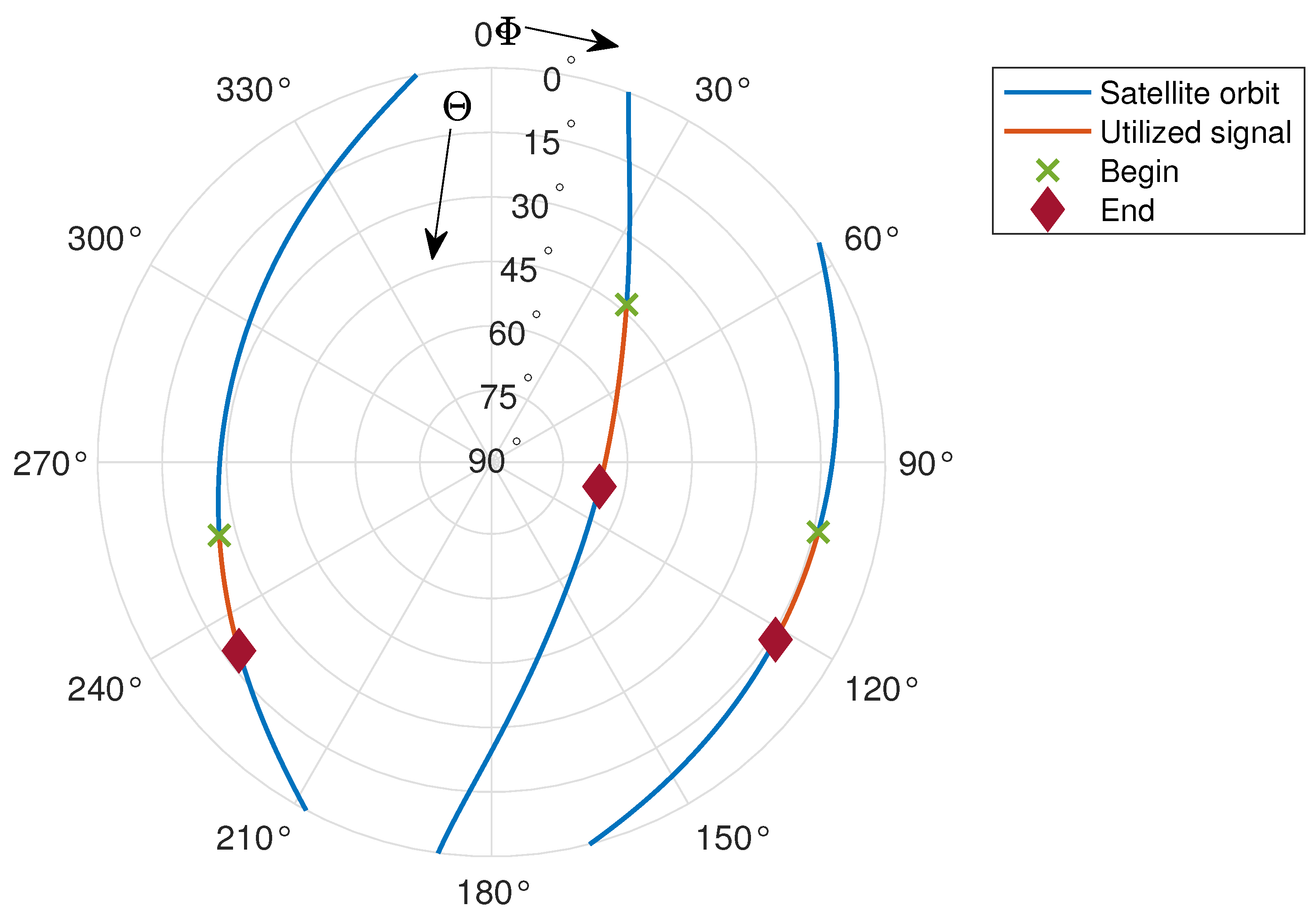
3.1. Constellation Geometric Model
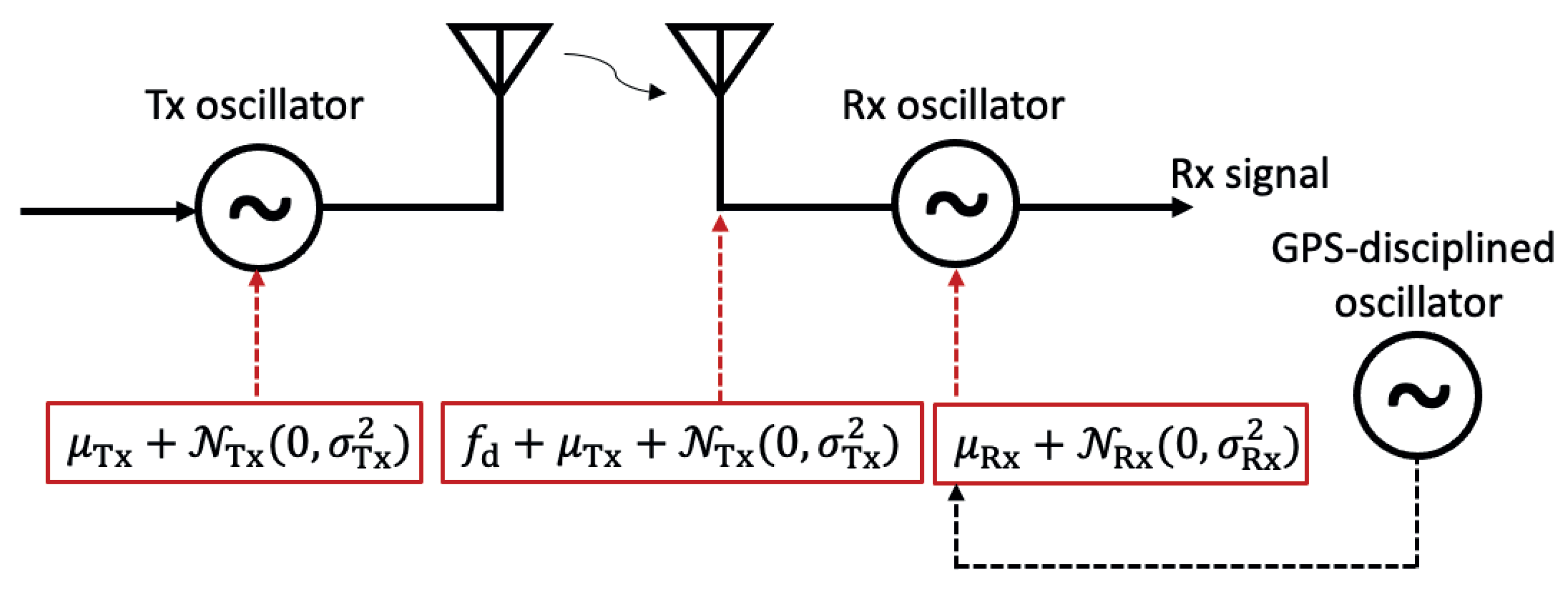
3.2. Doppler Model
3.3. Angle-of-Arrival Model
4. Likelihood Derivation
4.1. Doppler and Angle-of-Arrival Likelihood Derivation
4.2. Joint Likelihood of Doppler and Angle of Arrival
4.3. Minimizing Negative Log Likelihood
5. Localization Framework
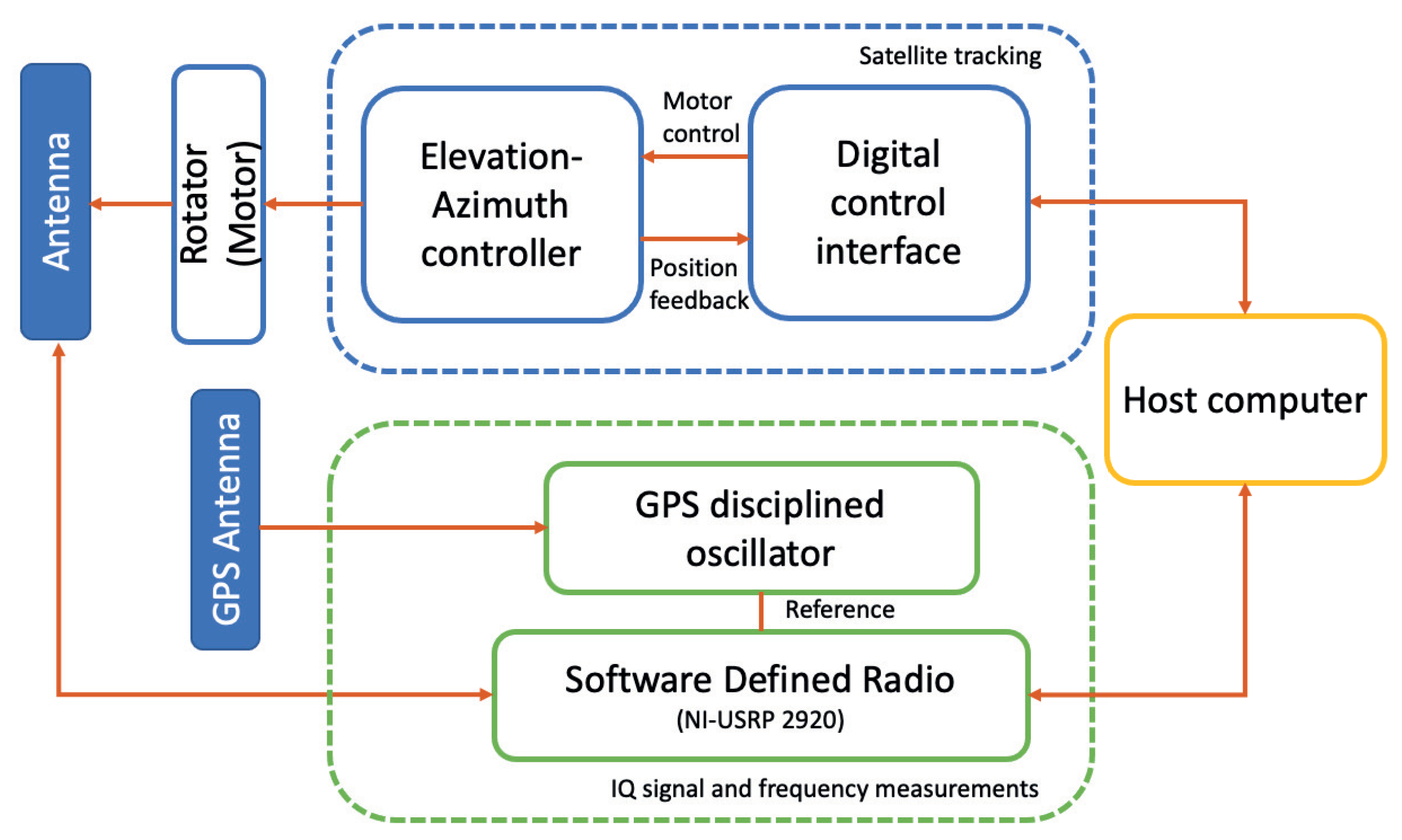
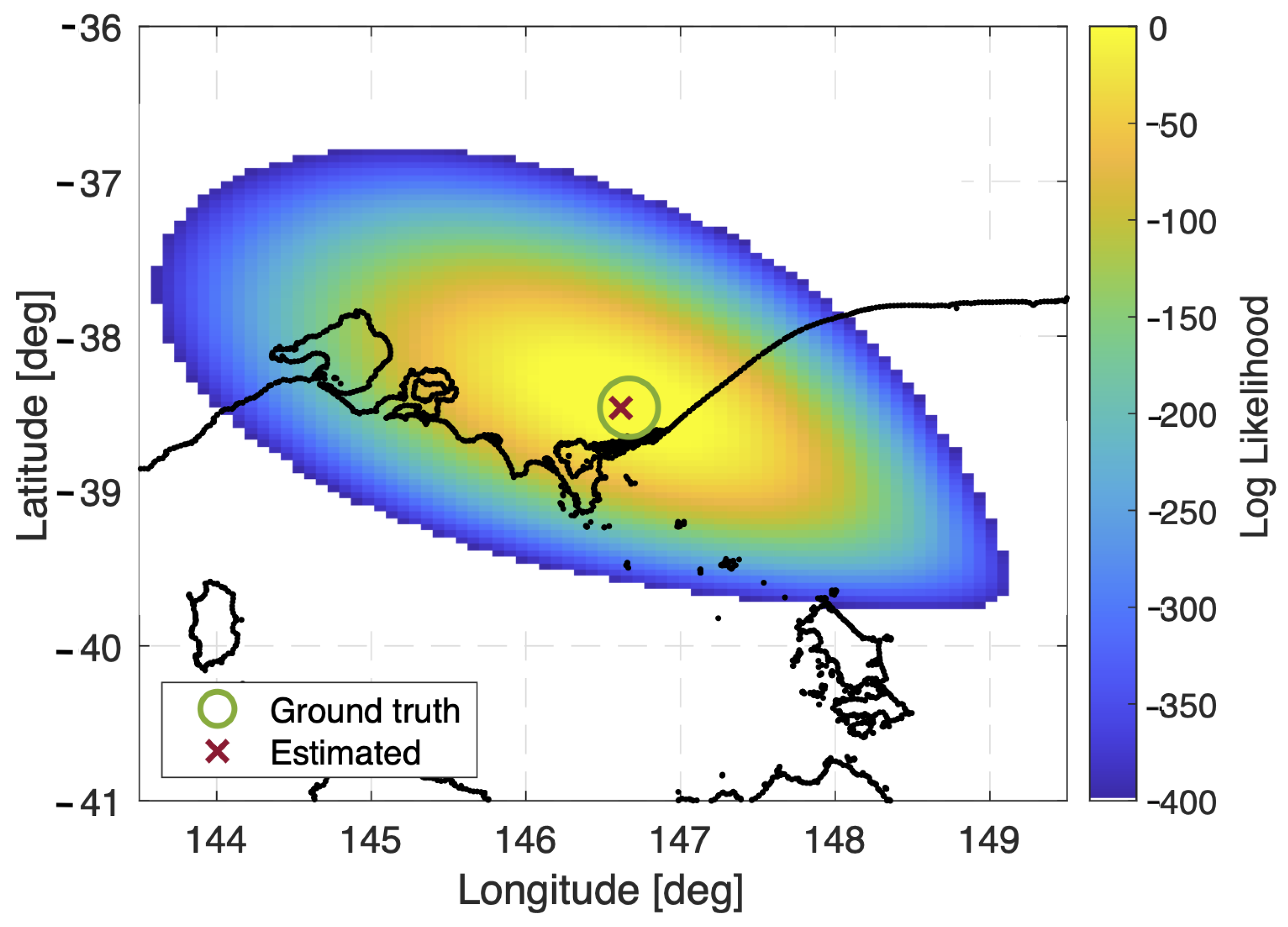
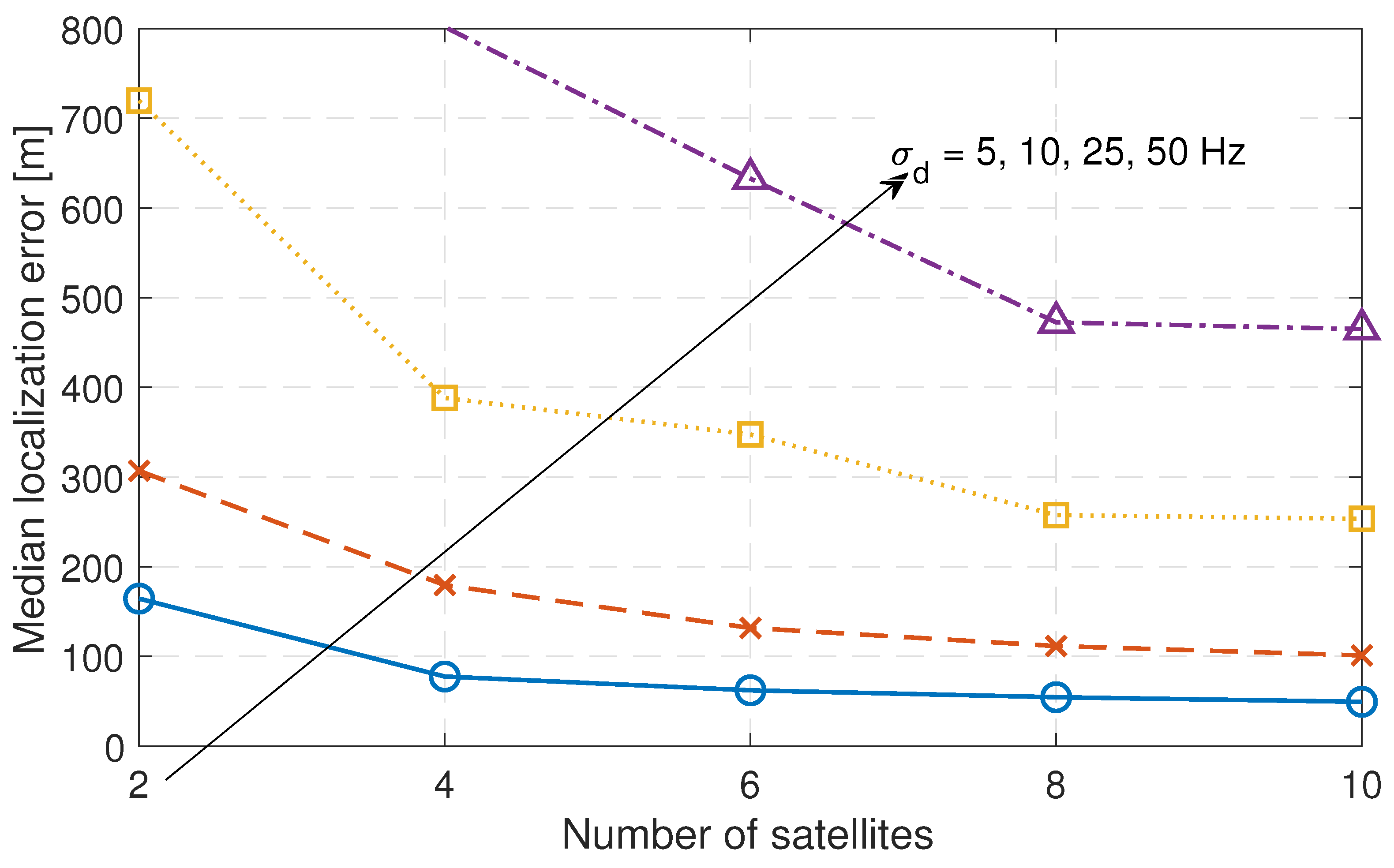
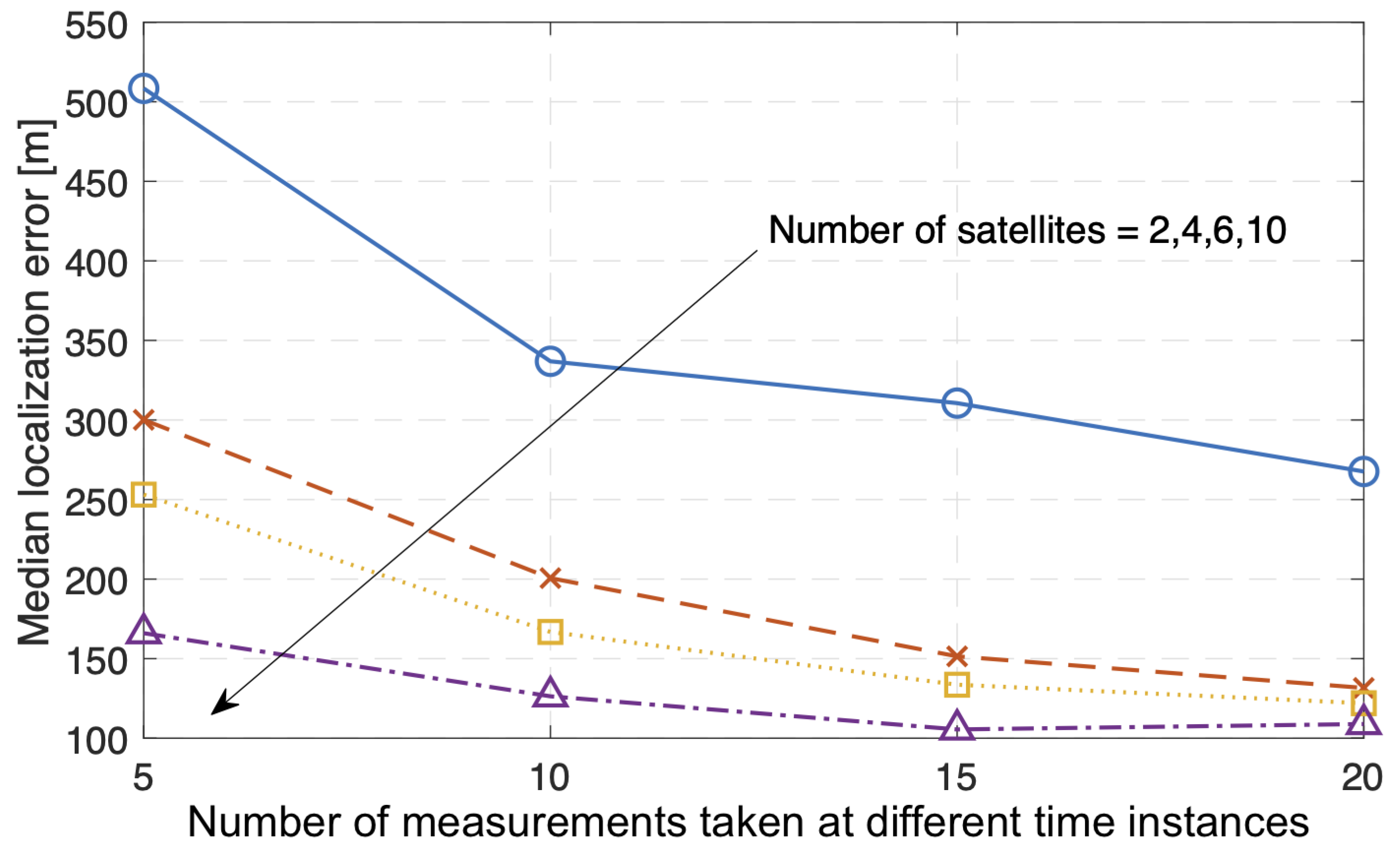
6. Experiment and Results
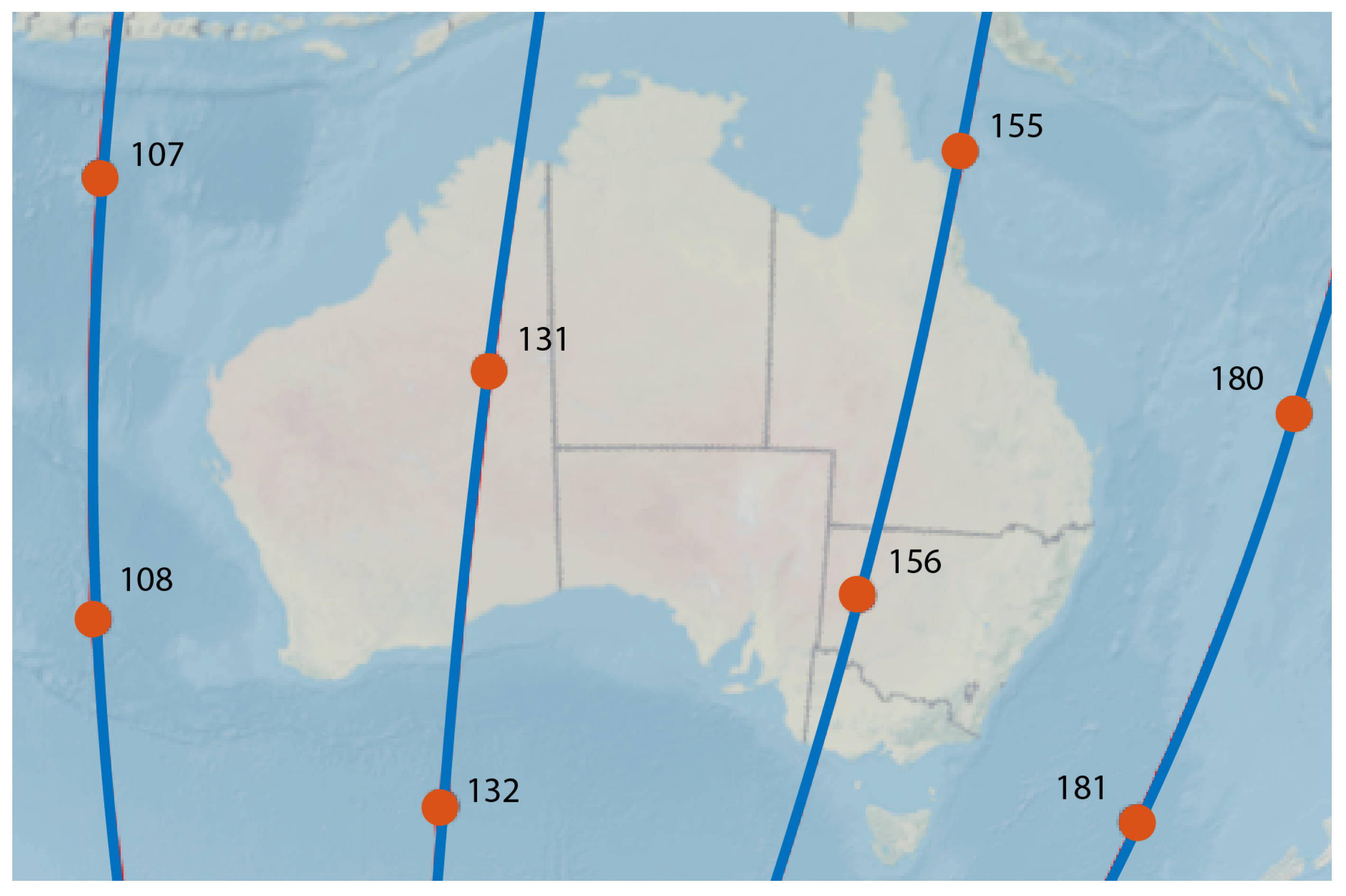
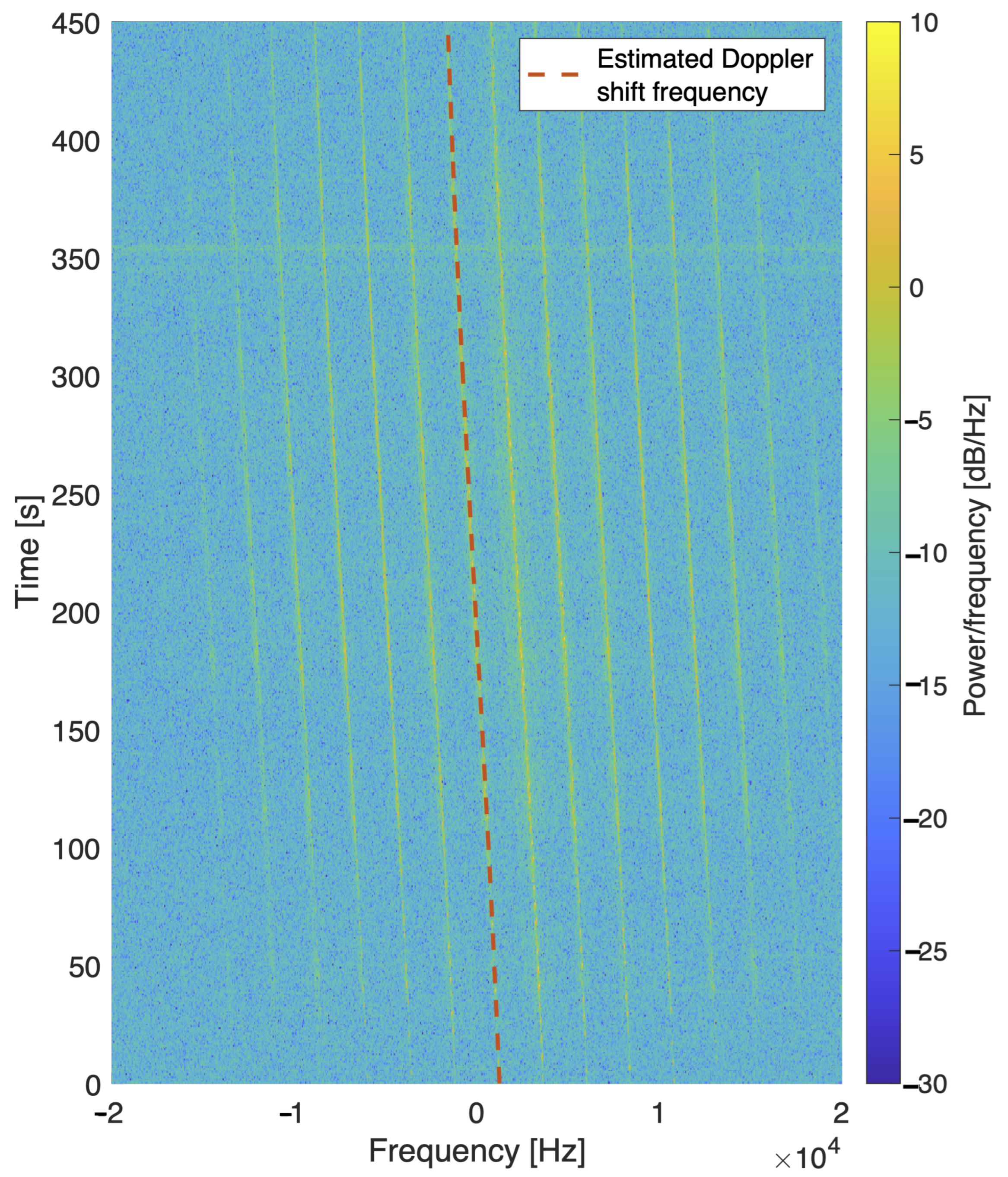
6.1. Doppler Error Measurements
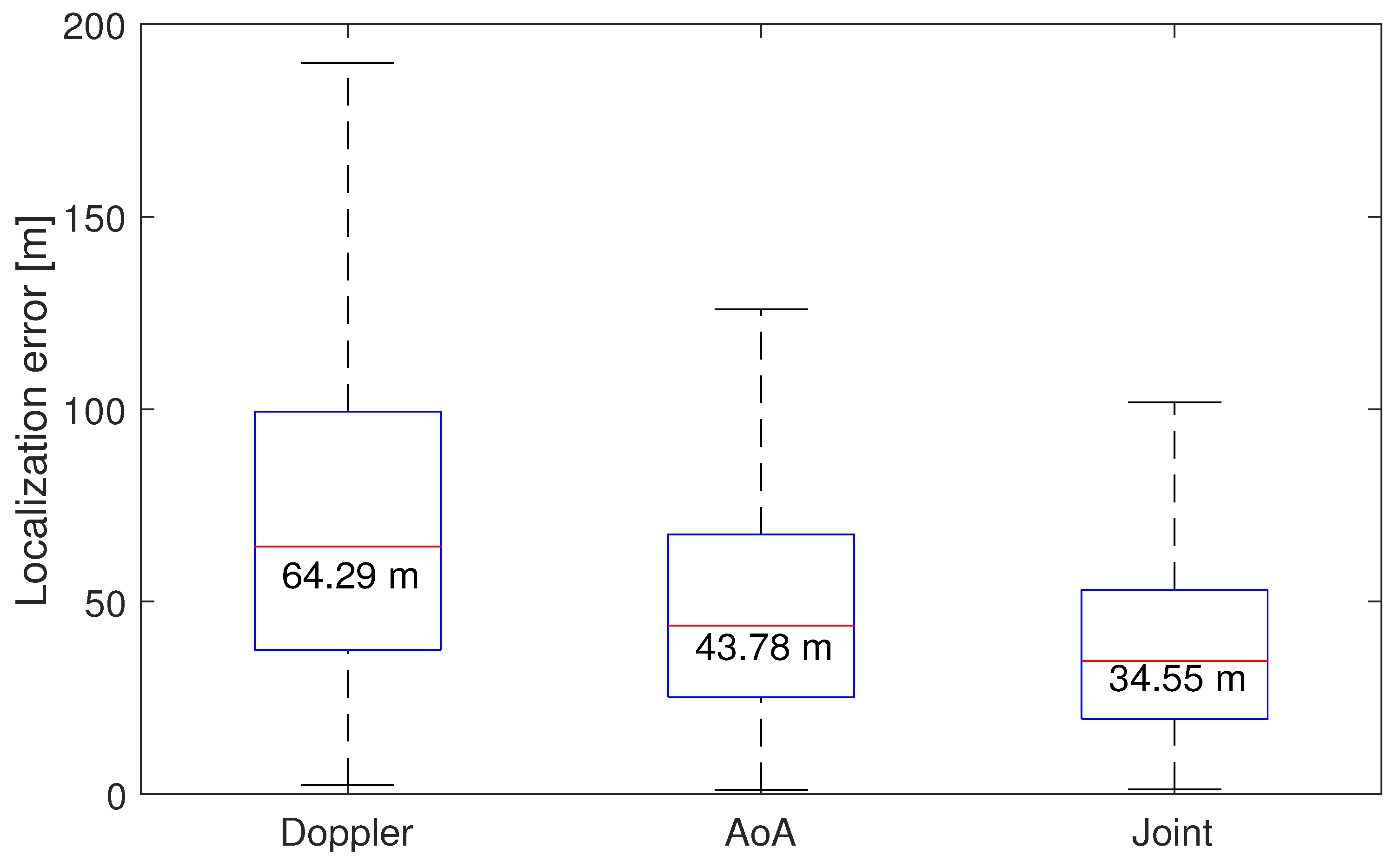
6.2. Localization Simulation and Performance
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Symbol | Definition | Value (Unit) |
| N | Number of satellites | 288 |
| P | Number of orbital planes | 12 |
| F | Phasing parameter | - |
| j | Orbital plane index | - |
| l | Order within orbital plane | - |
| Right ascension of ascending node | 0–2 | |
| Initial true anomaly | 0–2 | |
| S | Number of satellites on an orbital plane | 24 |
| True radial velocity | variable (m/s) | |
| Slant distance between a satellite and | variable (m) | |
| a ground IoT device | ||
| t | Time variable | - |
| Simulation time step | 5 (s) | |
| Classical & relativistic Doppler shift | - (Hz) | |
| frequency | ||
| c | Speed of light | 299,792,458 (m/s) |
| f | Center operating frequency | 2 (GHz) |
| True Doppler shift frequency | - (Hz) | |
| Standard deviation of Doppler error | - (Hz) | |
| Azimuth angle of arrival | - () | |
| Off-nadir angle of arrival | - () | |
| Latitude of the source (ground IoT device) | - () | |
| Longitude of the source (ground IoT device) | - () | |
| Position vector | - | |
| Coordinate transformation matrix | refer to (6) | |
| Satellite coordinate in ECEF frame | - | |
| Ground IoT device coordinate in ECEF frame | - | |
| Concentration parameter in Kent | - | |
| distribution | ||
| Ovalness parameter in Kent distribution | - | |
| Identity matrix of size 3 | - | |
| Standard deviation of azimuth AoA error | - () | |
| Standard deviation of off-nadir AoA error | - () | |
| State vector (latitude and | - () | |
| longitude of ground IoT device) | ||
| Doppler and AoA measurement vector | - | |
| k | Discrete-measurement index | - |
| Doppler likelihood function | - | |
| AoA likelihood function | - | |
| True azimuth angle of arrival | - () | |
| True off-nadir angle of arrival | - () | |
| Joint likelihood of Doppler and AoA | - |
References
- Silva, P.F.E.; Kaseva, V.; Lohan, E.S. Wireless Positioning in IoT: A Look at Current and Future Trends. Sensors 2018, 18, 2470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Homssi, B.; Al-Hourani, A.; Wang, K.; Conder, P.; Kandeepan, S.; Choi, J.; Allen, B.; Moores, B. Next Generation Mega Satellite Networks for Access Equality: Opportunities, Challenges, and Performance. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2022, 60, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzoor, B.; Al-Hourani, A.; Al Homssi, B. Improving IoT-Over-Satellite Connectivity Using Frame Repetition Technique. IEEE Wirel. Commun. Lett. 2022, 11, 736–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatti, G. Machine Learning Based Localization in Large-Scale Wireless Sensor Networks. Sensors 2018, 18, 4179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellis, P.; Rheeden, D.V.; Dowla, F. Use of Doppler and Doppler Rate for RF Geolocation Using a Single LEO Satellite. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 12907–12920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, R.; Malardé, J.; Royer, F.; Gaspar, P. Improving ARGOS Doppler Location Using Multiple-Model Kalman Filtering. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 4744–4755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argentiero, P.; Marint, J. Ambiguity Resolution for Satellite Doppler Positioning Systems. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 1979, AES-15, 439–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scales, W.C.; Swanson, R. Air and Sea Rescue via Satellite Systems: Even Experimental Systems have Helped Survivors of Air and Sea Accidents. Two Different Approaches are Discussed. IEEE Spectr. 1984, 21, 48–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartzell, S.; Burchett, L.; Martin, R.; Taylor, C.; Terzuoli, A. Geolocation of Fast-Moving Objects From Satellite-Based Angle-of-Arrival Measurements. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2015, 8, 3396–3403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norouzi, Y.; Kashani, E.S.; Ajorloo, A. Angle of Arrival-based Target Localisation with Low Earth Orbit Satellite Observer. IET Radar Sonar Navig. 2016, 10, 1186–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Zhang, M.; Guo, F. Bias Compensation for AoA-Geolocation of Known Altitude Target Using Single Satellite. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 54295–54304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoica, P.; Nehorai, A. MUSIC, Maximum Likelihood, and Cramer-Rao Bound: Further Results and Comparisons. IEEE Trans. Acoust. Speech Signal Process. 1990, 38, 2140–2150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, R.; Kailath, T. ESPRIT-Estimation of Signal Parameters via Rotational Invariance Techniques. IEEE Trans. Acoust. Speech Signal Process. 1989, 37, 984–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, B.; Zhang, W.; Wu, Q. Weighted Subspace Fitting for Two-Dimension DoA Estimation in Massive MIMO Systems. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 14020–14027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trinh-Hoang, M.; Viberg, M.; Pesavento, M. Partial Relaxation Approach: An Eigenvalue-Based DoA Estimator Framework. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2018, 66, 6190–6203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Kay, S. Maximum Likelihood Angle-Doppler Estimator using Importance Sampling. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2010, 46, 610–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsakalides, P.; Raspanti, R.; Nikias, C.L. Angle/Doppler Estimation in Heavy-tailed Clutter Backgrounds. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 1999, 35, 419–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Wang, X.; Moran, B.; Al-Hourani, A.; Rowe, W.S.T. Radio Source Localization Using Received Signal Strength in a Multipath Environment. In Proceedings of the 2019 22th International Conference on Information Fusion (FUSION), Ottawa, ON, Canada, 2–5 July 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Hung Nguyen, N.; Dogancay, K. Improved Weighted Instrumental Variable Estimator for Doppler-Bearing Source Localization in Heavy Noise. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Calgary, AB, Canada, 15–20 April 2018. [Google Scholar]
- NASA. Catalog of Earth Satellite Orbits. 2009. Available online: https://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/features/OrbitsCatalog (accessed on 1 September 2023).
- Ghosh, A.; Maeder, A.; Baker, M.; Chandramouli, D. 5G Evolution: A View on 5G Cellular Technology Beyond 3GPP Release 15. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 127639–127651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamad Hashim, I.S.; Al-Hourani, A.; Ristic, B. Satellite Localization of IoT Devices using Signal Strength and Doppler Measurements. IEEE Wirel. Commun. Lett. 2022, 11, 1910–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ARGOS. ARGOS User’s Manual. 2016. Available online: https://www.argos-system.org/wp-content/uploads/2016/08/r363_9_argos_users_manual-v1.6.6.pdf (accessed on 1 September 2023).
- Mo, L.; Song, X.; Zhou, Y.; Sun Zhong, K.; Bar-Shalom, Y. Unbiased Converted Measurements for Tracking. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 1998, 34, 1023–1027. [Google Scholar]
- Rui, L.; Ho, K.C. Bias Analysis of Maximum Likelihood Target Location Estimator. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2014, 50, 2679–2693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogancay, K. Bias Compensation for the Bearings-only Pseudolinear Target Track Estimator. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2006, 54, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athley, F. Asymptotically Decoupled Angle-Frequency Estimation with Sensor Arrays. In In Proceedings of the Conference Record of the Thirty-Third Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems, and Computers, Pacific Grove, CA, USA, 24–27 October 1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.D.; Fang, W.H.; Wang, Y.Y.; Chen, J.T. FSF MUSIC for Joint DoA and Frequency Estimation and Its Performance Analysis. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2006, 54, 4529–4542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, J.G. Satellite Constellations. J. Br. Interplanet. Soc. 1984, 37, 559. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Hourani, A. Session Duration Between Handovers in Dense LEO Satellite Networks. IEEE Wirel. Commun. Lett. 2021, 10, 2810–2814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, M.; Xu, T.; Gao, F.; Nie, W.; Yang, H. Optimal Walker Constellation Design of LEO-Based Global Navigation and Augmentation System. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ristic, B.; Farina, A. Target Tracking via Multi-Static Doppler Shifts. IET Radar Sonar Navig. 2013, 7, 508–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subedi, S.; Zhang, Y.D.; Amin, M.G.; Himed, B. Group Sparsity Based Multi-Target Tracking in Passive Multi-Static Radar Systems Using Doppler-Only Measurements. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2016, 64, 3619–3634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, J.; Khalife, J.; Kassas, Z.M. Simultaneous Tracking of Orbcomm LEO Satellites and Inertial Navigation System Aiding Using Doppler Measurements. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 89th Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC2019-Spring), Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 28 April–1 May 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Psiaki, M.L. Navigation using Carrier Doppler Shift from a LEO Constellation: TRANSIT on Steroids. J. Inst. Navig. 2021, 68, 621–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subirana, J.S.; Zornoza, J.M.J.; Hernandez-Pajares, M. Transformations between ECEF and ENU Coordinates. 2011. Available online: https://gssc.esa.int/navipedia/index.php/Transformations_between_ECEF_and_ENU_coordinates (accessed on 1 September 2023).
- Garcia-Fernandez, A.; Maskell, S.; Horridge, P.; Ralph, J. Gaussian Tracking With Kent-Distributed Direction-of-Arrival Measurements. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2021, 70, 7249–7254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Wan, Q. Position Determination for Moving Transmitter Using Single Station. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 61103–61116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hourani, A.; Guvenc, I. On Modeling Satellite-to-Ground Path-Loss in Urban Environments. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2021, 25, 696–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirkpatrick, S.; Gelatt, C.D.; Vecchi, M.P. Optimization by Simulated Annealing. Sci. Am. Assoc. Adv. Sci. 1983, 220, 671–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clerc, M. Particle Swarm Optimization; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: London, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, M. An Introduction to Genetic Algorithms; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Koziel, S. Surrogate-Based Modeling and Optimization: Applications in Engineering, 1st ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Nocedal, J. Numerical Optimization; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Ziskind, I.; Wax, M. Maximum Likelihood Localization of Diversely Polarized Sources by Simulated Annealing. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 1990, 38, 1111–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
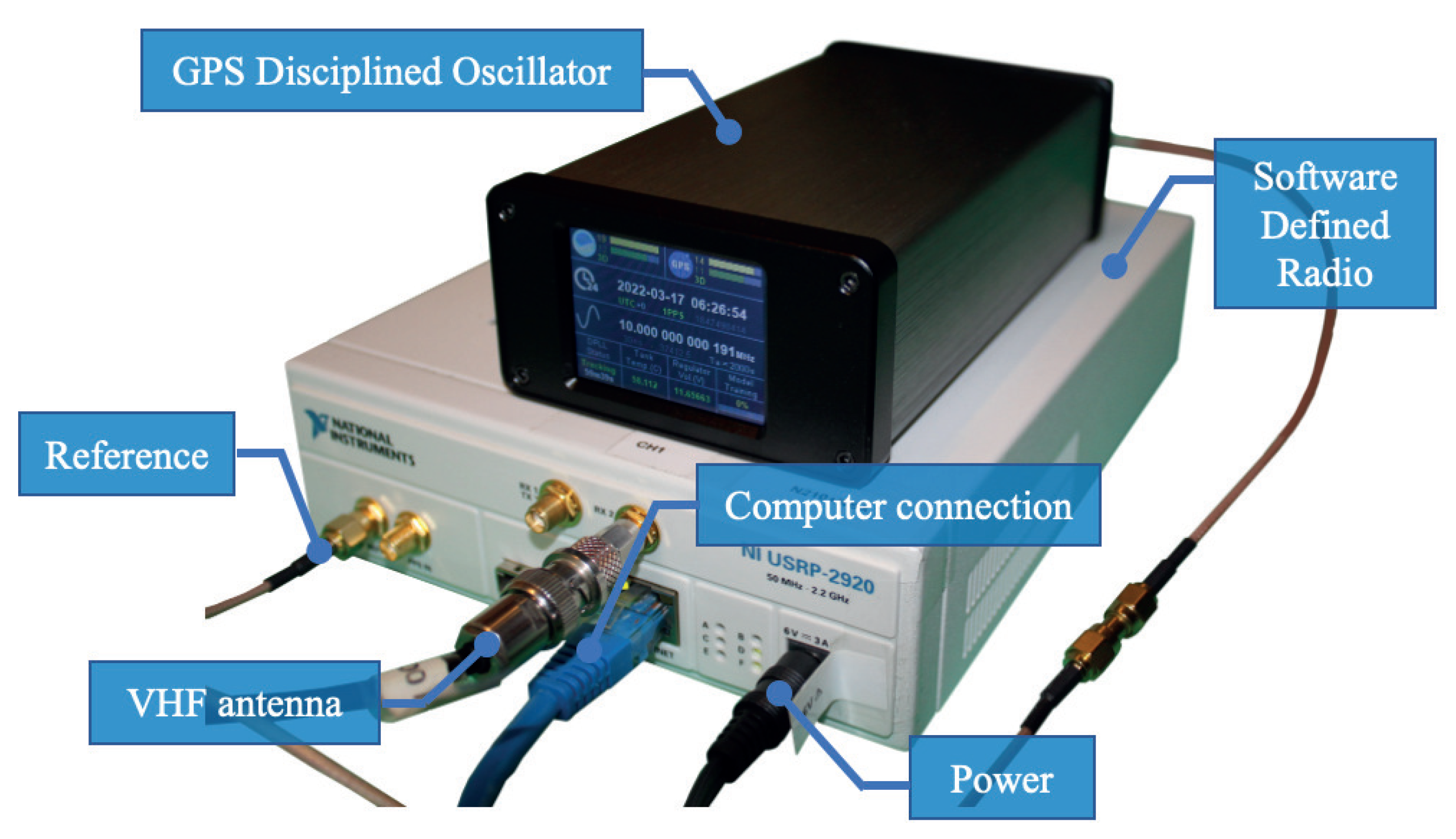








Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mohamad Hashim, I.S.; Al-Hourani, A. Satellite-Based Localization of IoT Devices Using Joint Doppler and Angle-of-Arrival Estimation. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 5603. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15235603
Mohamad Hashim IS, Al-Hourani A. Satellite-Based Localization of IoT Devices Using Joint Doppler and Angle-of-Arrival Estimation. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(23):5603. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15235603
Chicago/Turabian StyleMohamad Hashim, Iza S., and Akram Al-Hourani. 2023. "Satellite-Based Localization of IoT Devices Using Joint Doppler and Angle-of-Arrival Estimation" Remote Sensing 15, no. 23: 5603. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15235603
APA StyleMohamad Hashim, I. S., & Al-Hourani, A. (2023). Satellite-Based Localization of IoT Devices Using Joint Doppler and Angle-of-Arrival Estimation. Remote Sensing, 15(23), 5603. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15235603





