Mapping Forest Abrupt Disturbance Events in Southeastern China—Comparisons and Tradeoffs of Landsat Time Series Analysis Algorithms
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Materials
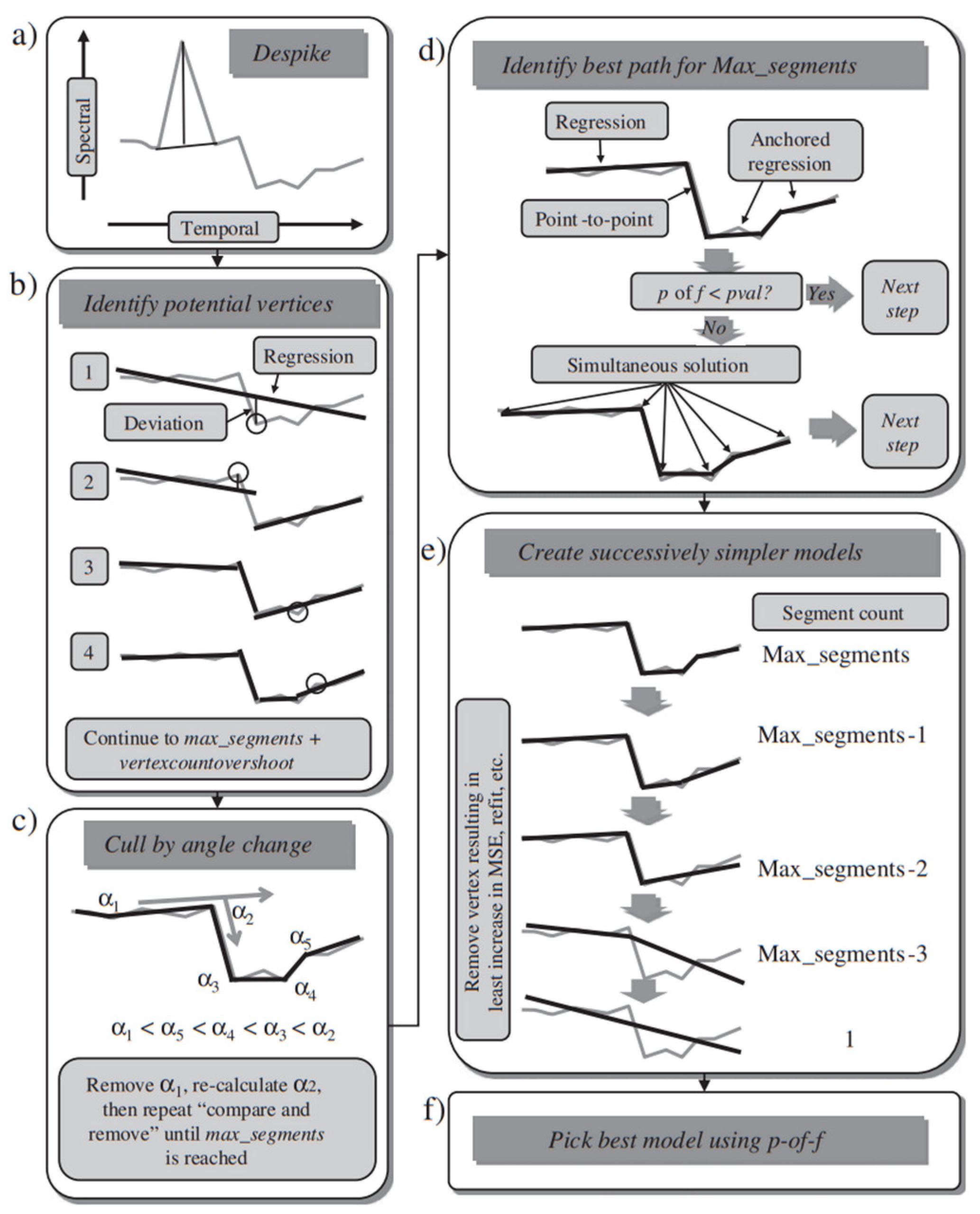
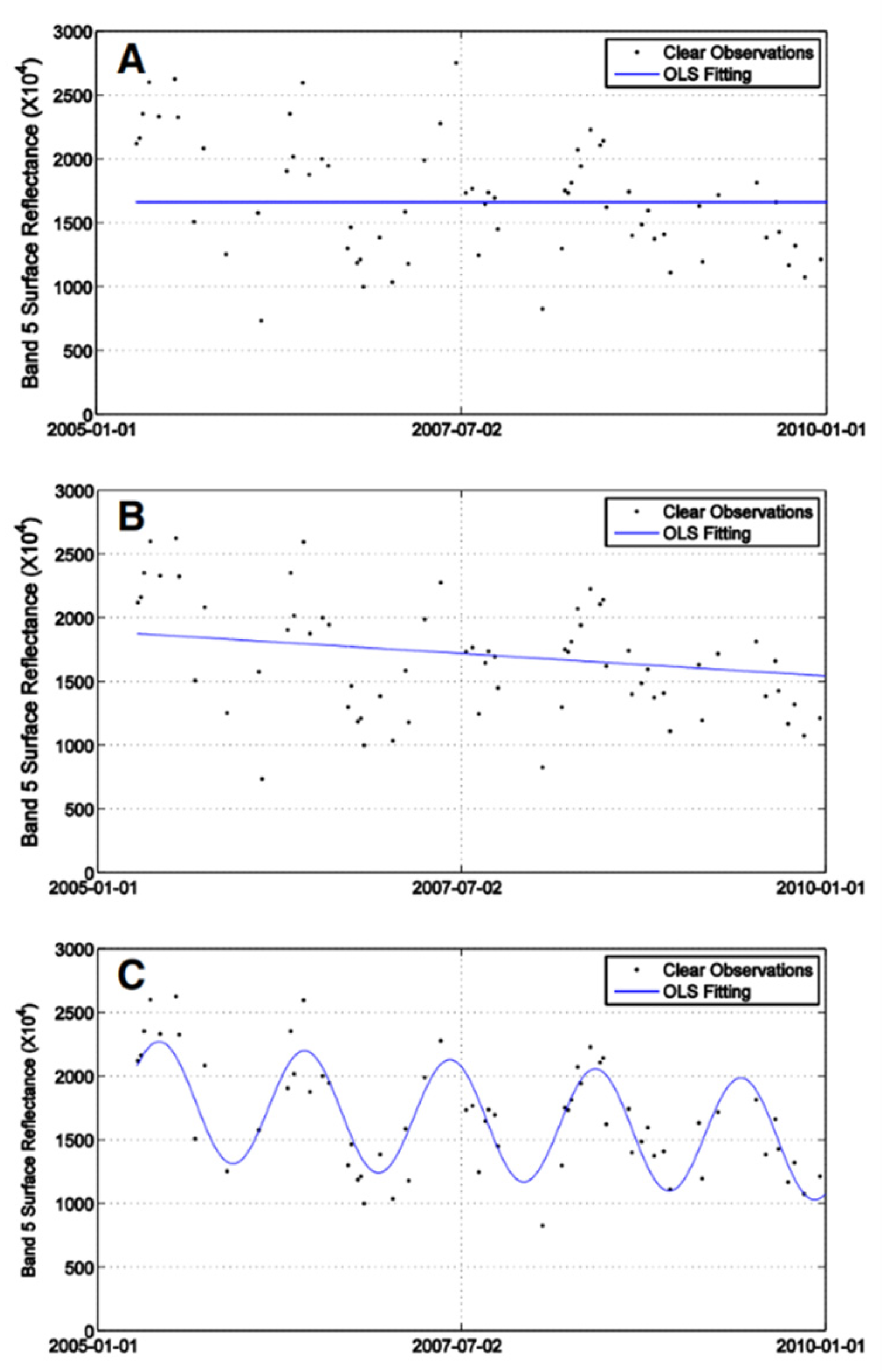
3. Method
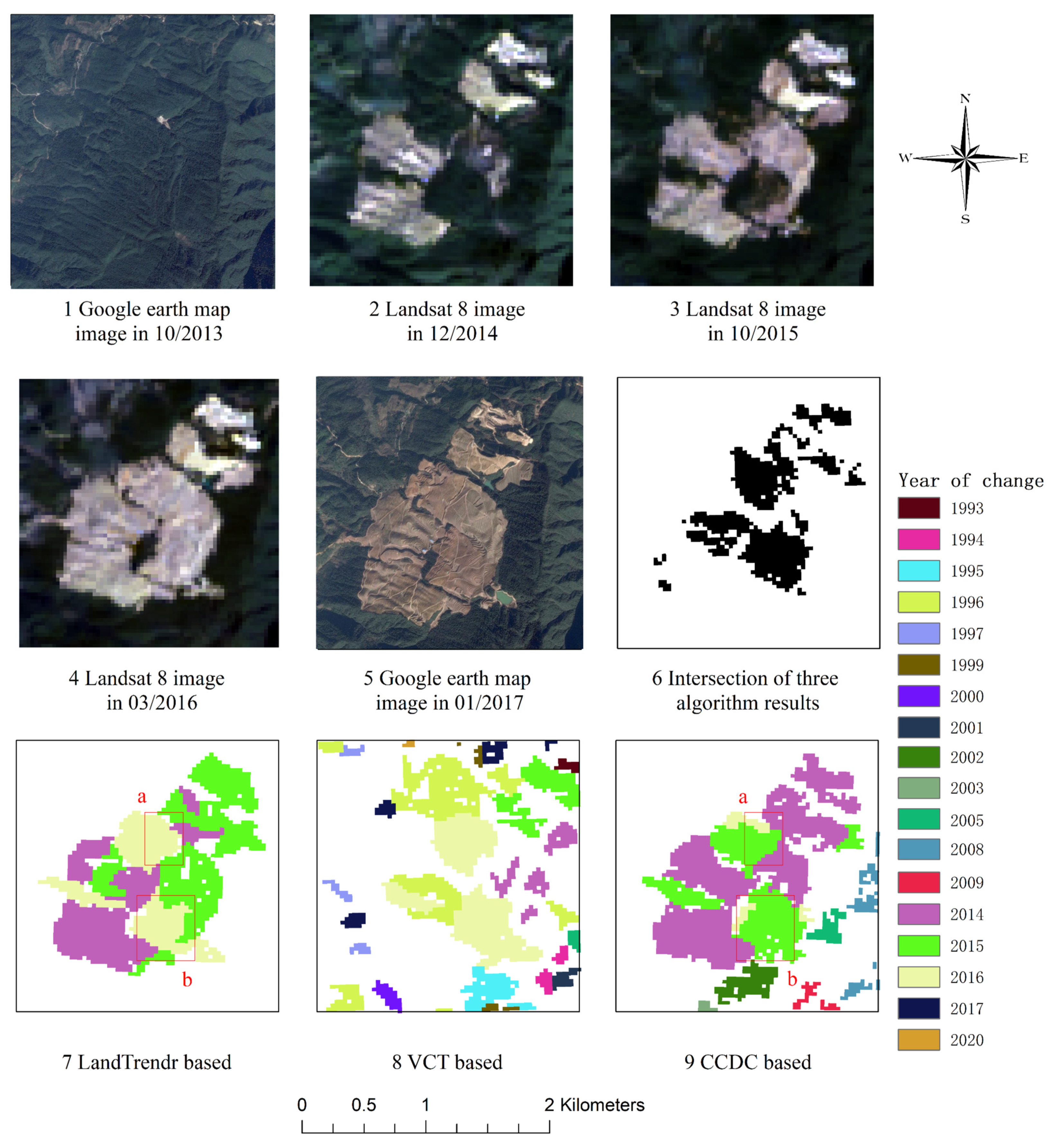
4. Results
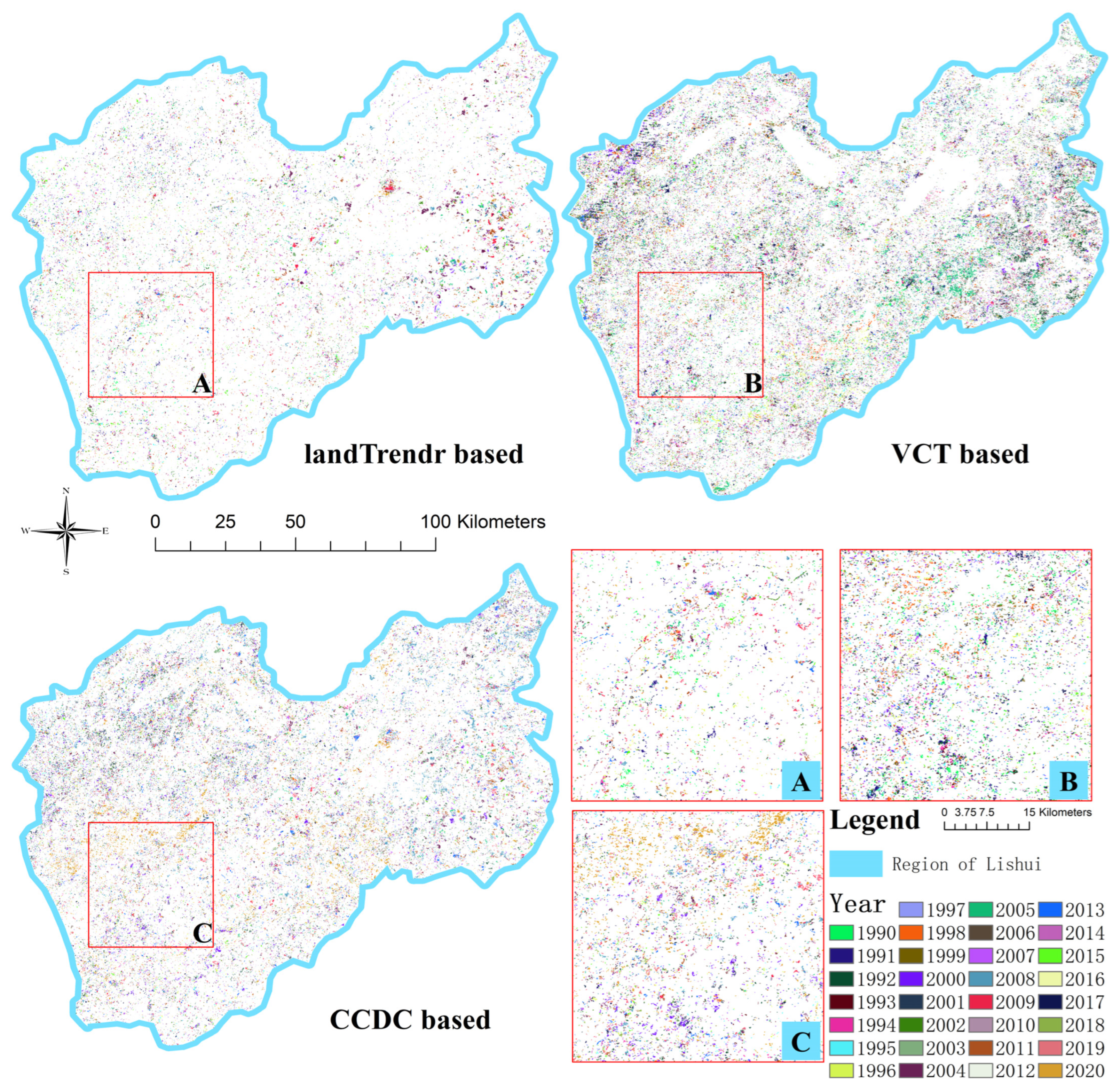
4.1. Spatial Accuracy of the Detected Disturbance Events
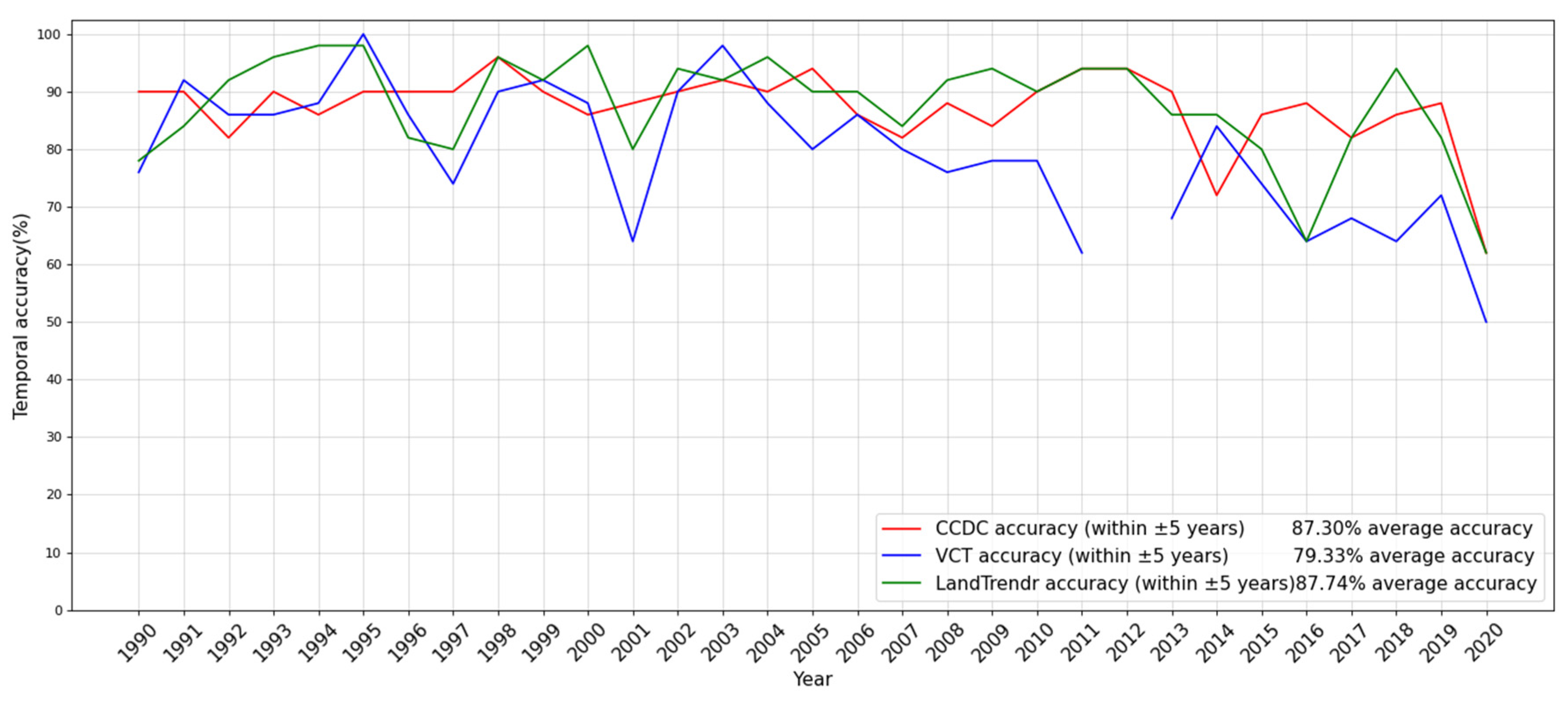
4.2. Temporal Accuracy of the Detected Disturbance Events
4.3. Field Patch Matching
5. Discussion
5.1. Comparative Evaluation of the Algorithms
5.2. Characteristics and Adaptability of the Three Algorithms
5.3. Forest Disturbance Monitoring Algorithm Suited to Southeastern China
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xu, W.; Jin, X.; Liu, J.; Yang, X.; Ren, J.; Zhou, Y. Analysis of spatio-temporal changes in forest biomass in China. J. For. Res. 2021, 33, 261–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y. The 11th session of the United Nations Forum on Forests. Green China 2015, 13, 8–23. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, J.; Liu, Z. A review on disturbance ecology of forest. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2004, 10, 1703–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogelmann, J.E.; Xian, G.; Homer, C.; Tolk, B. Monitoring gradual ecosystem change using Landsat time series analyses: Case studies in selected forest and rangeland ecosystems. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 122, 92–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, W.B.; Fiorella, M.; Gray, J.; Helmer, E.; Anderson, K. An Efficient and Accurate Method for Mapping Forest Clearcuts in the Pacific Northwest Using Landsat Imagery. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 1998, 64, 293–300. [Google Scholar]
- Serneels, S.; Said, M.Y.; Lambin, E.F. Land cover changes around a major east African wildlife reserve: The Mara Ecosystem (Kenya). Int. J. Remote Sens. 2001, 22, 3397–3420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coppin, P.; Jonckheere, I.; Nackaerts, K.; Muys, B.; Lambin, E. Review ArticleDigital change detection methods in ecosystem monitoring: A review. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2004, 25, 1565–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, W.; Healey, S.; Yang, Z.; Stehman, S.; Brewer, C.; Brooks, E.; Gorelick, N.; Huang, C.; Hughes, M.; Kennedy, R.; et al. How Similar Are Forest Disturbance Maps Derived from Different Landsat Time Series Algorithms? Forests 2017, 8, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, W.; Li, M.; Huang, C. Review of remote sensing algorithms for monitoring forest disturbance from time series and multi-source data fusion. J. Remote Sens. 2018, 22, 1005–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Goward, S.N.; Masek, J.G.; Thomas, N.; Zhu, Z.; Vogelmann, J.E. An automated approach for reconstructing recent forest disturbance history using dense Landsat time series stacks. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 183–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verbesselt, J.; Hyndman, R.; Newnham, G.; Culvenor, D. Detecting trend and seasonal changes in satellite image time series. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 106–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, R.E.; Yang, Z.; Cohen, W.B. Detecting trends in forest disturbance and recovery using yearly Landsat time series: 1. LandTrendr—Temporal segmentation algorithms. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 2897–2910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, W.B.; Yang, Z.; Kennedy, R. Detecting trends in forest disturbance and recovery using yearly Landsat time series: 2. TimeSync—Tools for calibration and validation. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 2911–2924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Woodcock, C.E.; Holden, C.; Yang, Z. Generating synthetic Landsat images based on all available Landsat data: Predicting Landsat surface reflectance at any given time. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 162, 67–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, B.; Yang, X.; Qiu, J. Research Progress and Application of Remote Sensing Big Data Analysis Based on Google Earth Engine. Geospat. Inf. 2021, 19, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, W.B.; Yang, Z.; Healey, P.S.; Kennedy, E.R.; Gorelick, N. A LandTrendr multispectral ensemble for forest disturbance detection. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 205, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obata, S.; Bettinger, P.; Cieszewski, J.C.; Lowe, C.R., III. Mapping Forest Disturbances between 1987–2016 Using All Available Time Series Landsat TM/ETM+ Imagery: Developing a Reliable Methodology for Georgia, United States. Forests 2020, 11, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arévalo, P.; Bullock, E.L.; Woodcock, C.E.; Olofsson, P. A Suite of Tools for Continuous Land Change Monitoring in Google Earth Engine. Front. Clim. 2020, 2, 576740–576758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, X.; Jin, Y. Dynamic Monitoring of Construction Land Expansion in Shanxi Province based on Landsat Time Series. J. Shanxi Norm. Univ. Nat. Sci. Ed. 2019, 33, 118–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, W. Monitoring and Driving Factors of Forest Disturbance and Restoration of “Three Mountains” Nature Reserve in Ningxia. Master’s Thesis, Ningxia University, Yinchuan, China, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Xie, H.; Zhang, C.; Du, M.; Wang, Y. Applicability Analysis of LandTrendr and CCDC Algorithms for Vegetation Damage Identification in Shendong Coal Base. Met. Mine 2023, 1, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.; Chen, B.; Gu, X. Rapid Monitoring of Tropical Forest Disturbance in Hainan Island Based on GEE Platform and LandTrendr Algorithm. J. Geo-Inf. Sci. 2023, 25, 2093–2106. [Google Scholar]
- Pasquarella, V.J.; Arévalo, P.; Bratley, K.H.; Bullock, E.L.; Gorelick, N.; Yang, Z.; Kennedy, R.E. Demystifying LandTrendr and CCDC temporal segmentation. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2022, 110, 102806–102818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C. An analysis of the economic effects of forestry in the Lishui area. J. Zhejiang For. Sci. Technol. 1981, 3, 133–138. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, F.; Cheng, Q. Natural resources in the Lishui area and proposals for the protection and development of forests. Environ. Pollut. Control 1983, 2, 41–44. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Wei, X.; Li, D.; Lu, D. Examining Forest Disturbance and Recovery in the Subtropical Forest Region of Zhejiang Province Using Landsat Time-Series Data. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diao, J.; Feng, T.; Li, M.; Zhu, Z.; Liu, J.; Biging, G.; Zheng, G.; Shen, W.; Wang, H.; Wang, J.; et al. Use of vegetation change tracker, spatial analysis, and random forest regression to assess the evolution of plantation stand age in Southeast China. Ann. For. Sci. 2020, 77, 27–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Wulder, M.A.; Roy, D.P.; Woodcock, C.E.; Hansen, M.C.; Radeloff, V.C.; Healey, S.P.; Schaaf, C.; Hostert, P.; Strobl, P.; et al. Benefits of the free and open Landsat data policy. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 224, 382–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryant, R.; Moran, M.; McElroy, S.; Holifield, C.; Thome, K.; Miura, T.; Biggar, S. Data continuity of earth observing 1 (eo-1) advanced land imager (ali) and landsat tm and etm+. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2003, 41, 1204–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, D.P.; Kovalskyy, V.; Zhang, H.K.; Vermote, E.F.; Yan, L.; Kumar, S.S.; Egorov, A. Characterization of Landsat-7 to Landsat-8 reflective wavelength and normalized difference vegetation index continuity. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 185, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markham, B.L.; Helder, D.L. Forty-year calibrated record of earth-reflected radiance from Landsat: A review. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 122, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masek, J.G.; Vermote, E.F.; Saleous, N.E.; Wolfe, R.; Hall, F.G.; Huemmrich, K.F.; Gao, F.; Kutler, J.; Lim, T.K. A Landsat Surface Reflectance Dataset for North America, 1990–2000. Ieee Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2006, 3, 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermote, E.; Justice, C.; Claverie, M.; Franch, B. Preliminary analysis of the performance of the Landsat 8/OLI land surface reflectance product. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 185, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhe, Z.; Curtis, E.W. Continuous change detection and classification of land cover using all available Landsat data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 144, 152–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhe, Z. Change detection using landsat time series: A review of frequencies, preprocessing, algorithms, and applications. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2017, 130, 370–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Huang, X.; Zhao, S.; Chen, Y. Analysis of Forest Disturbance and Recovery Dynamic Characteristics Based on LandTrendr Time Segmental Algorithm. J. Subtrop. Resour. Environ. 2020, 15, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Shen, W.; Li, M.; Lv, Y. Integrating Landsat Time Series Observations and Corona Images to Characterize Forest Change Patterns in a Mining Region of Nanjing, Eastern China from 1967 to 2019. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Huang, C.; Zhu, Z.; Wen, W.; Xu, D.; Liu, A. Use of remote sensing coupled with a vegetation change tracker model to assess rates of forest change and fragmentation in Mississippi, USA. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2009, 30, 6559–6574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Fu, Y.; Woodcock, C.E.; Olofsson, P.; Vogelmann, J.E.; Holden, C.; Wang, M.; Dai, S.; Yu, Y. Including land cover change in analysis of greenness trends using all available Landsat 5, 7, and 8 images: A case study from Guangzhou, China (2000–2014). Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 185, 243–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Yang, Z.; Aljaddani, A.H.; Cohen, W.B.; Qiu, S.; Zhou, C. Continuous monitoring of land disturbance based on Landsat time series. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 238, 111116–111133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, M. A new method for monitoring start of season (SOS) of forest based on multisource remote sensing. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2021, 104, 102556–102568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, S.; Rogan, J.; Zhu, Z.; Eastman, J.R. A near-real-time approach for monitoring forest disturbance using Landsat time series: Stochastic continuous change detection. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 252, 112167–112183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasquarella, V.J.; Holden, C.E.; Woodcock, C.E. Improved mapping of forest type using spectral-temporal Landsat features. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 210, 193–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Healey, S.P.; Cohen, W.B.; Yang, Z.; Brewer, C.K.; Brooks, E.B.; Gorelick, N.; Hernandez, A.J.; Huang, C.; Hughes, M.J.; Kennedy, R.E.; et al. Mapping forest change using stacked generalization: An ensemble approach. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 204, 717–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, W.B.; Healey, S.P.; Yang, Z.; Zhu, Z.; Gorelick, N. Diversity of Algorithm and Spectral Band Inputs Improves Landsat Monitoring of Forest Disturbance. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, J. Spatiotemporal Patterns of Forest Disturbance and Recovery Using Integrated LandTrendr Algorithm and Machine Learning Method. Master’s Thesis, Zhejiang A&F University, Hangzhou, China, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Wei, Y.; Liu, C.; Li, X.; Fang, H. A Scheme for the Long-Term Monitoring of Impervious−Relevant Land Disturbances Using High Frequency Landsat Archives and the Google Earth Engine. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Li, Q.; Xie, H.; Li, J.; Qiao, L.; Zhang, C.; Yang, G.; Wang, F. Monitoring of Vegetation Disturbance and Restoration at the Dumping Sites of the Baorixile Open-Pit Mine Based on the LandTrendr Algorithm. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 9066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Wu, S.; Wang, H. Managing planted forests for multiple uses under a changing environment in China. N. Z. J. For. Sci. 2014, 44, S3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| LandTrendr | Reference Data | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Forest Change | Non-Change | Total | User’s Accuracy | |
| Forest change | 466 | 34 | 500 | 0.932 |
| Non-change | 114 | 386 | 500 | 0.772 |
| Total | 580 | 420 | 1000 | |
| Producer’s accuracy | 0.803 | 0.919 | ||
| OA: | 0.852 | Kappa: | 0.704 | |
| VCT | Reference Data | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Forest Change | Non-Change | Total | User’s Accuracy | |
| Forest change | 448 | 52 | 500 | 0.896 |
| Non-change | 108 | 392 | 500 | 0.784 |
| Total | 556 | 444 | 1000 | |
| Producer’s accuracy | 0.806 | 0.883 | ||
| OA: | 0.840 | Kappa: | 0.680 | |
| CCDC | Reference Data | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Forest Change | Non-Change | Total | User’s Accuracy | |
| Forest change | 449 | 51 | 500 | 0.898 |
| Non-change | 87 | 413 | 500 | 0.826 |
| Total | 536 | 454 | 1000 | |
| Producer’s accuracy | 0.838 | 0.890 | ||
| OA: | 0.862 | Kappa: | 0.724 | |
| Terms | LandTrendr | VCT | CCDC |
|---|---|---|---|
| Source | Online documentation with [16] | Code cases with [17] | Online Tools and [18] |
| Online/offline | Offline | Offline | Online |
| Principle | Monitoring “vertices” based on time series, threshold determination changes | Monitoring forest change by calculating IFZ contrast thresholds | Constructing independent segments based on time series and calculating different model coefficients for each segment to record changes |
| Land cover type | all land cover changes | forest changes | all land cover changes |
| Composition of results | Changes are filtered by the platform, and the resultant data are directly exported for a total of 6 bands | Changes by year are exported by the platform, with subsequent filtering to synthesize outcome data | A total of 75 bands were exported by the platform for each individual segment parameter and related information slice file |
| Time of running | Within 1 h | Several hours | Several days |
| Selection of results | Output the patches after filtering | Output all patches yearly | Output all patches monitored |
| Images used | Using vegetation growth period images | Using vegetation growth period images | Using year-round images |
| Types of change | Abrupt and trend changes | Abrupt changes | Abrupt, trend, and gradual ecosystem changes |
| Scale of time | Interannual monitoring | Interannual monitoring | Sub-annual monitoring |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ding, N.; Li, M. Mapping Forest Abrupt Disturbance Events in Southeastern China—Comparisons and Tradeoffs of Landsat Time Series Analysis Algorithms. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 5408. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15225408
Ding N, Li M. Mapping Forest Abrupt Disturbance Events in Southeastern China—Comparisons and Tradeoffs of Landsat Time Series Analysis Algorithms. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(22):5408. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15225408
Chicago/Turabian StyleDing, Ning, and Mingshi Li. 2023. "Mapping Forest Abrupt Disturbance Events in Southeastern China—Comparisons and Tradeoffs of Landsat Time Series Analysis Algorithms" Remote Sensing 15, no. 22: 5408. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15225408
APA StyleDing, N., & Li, M. (2023). Mapping Forest Abrupt Disturbance Events in Southeastern China—Comparisons and Tradeoffs of Landsat Time Series Analysis Algorithms. Remote Sensing, 15(22), 5408. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15225408







