Vertical Profiles of Particle Number Size Distribution and Variation Characteristics at the Eastern Slope of the Tibetan Plateau
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Data and Methods
2.1. Observation Site
2.2. Instrumentation and Data
2.2.1. Vertical Profile Measurement
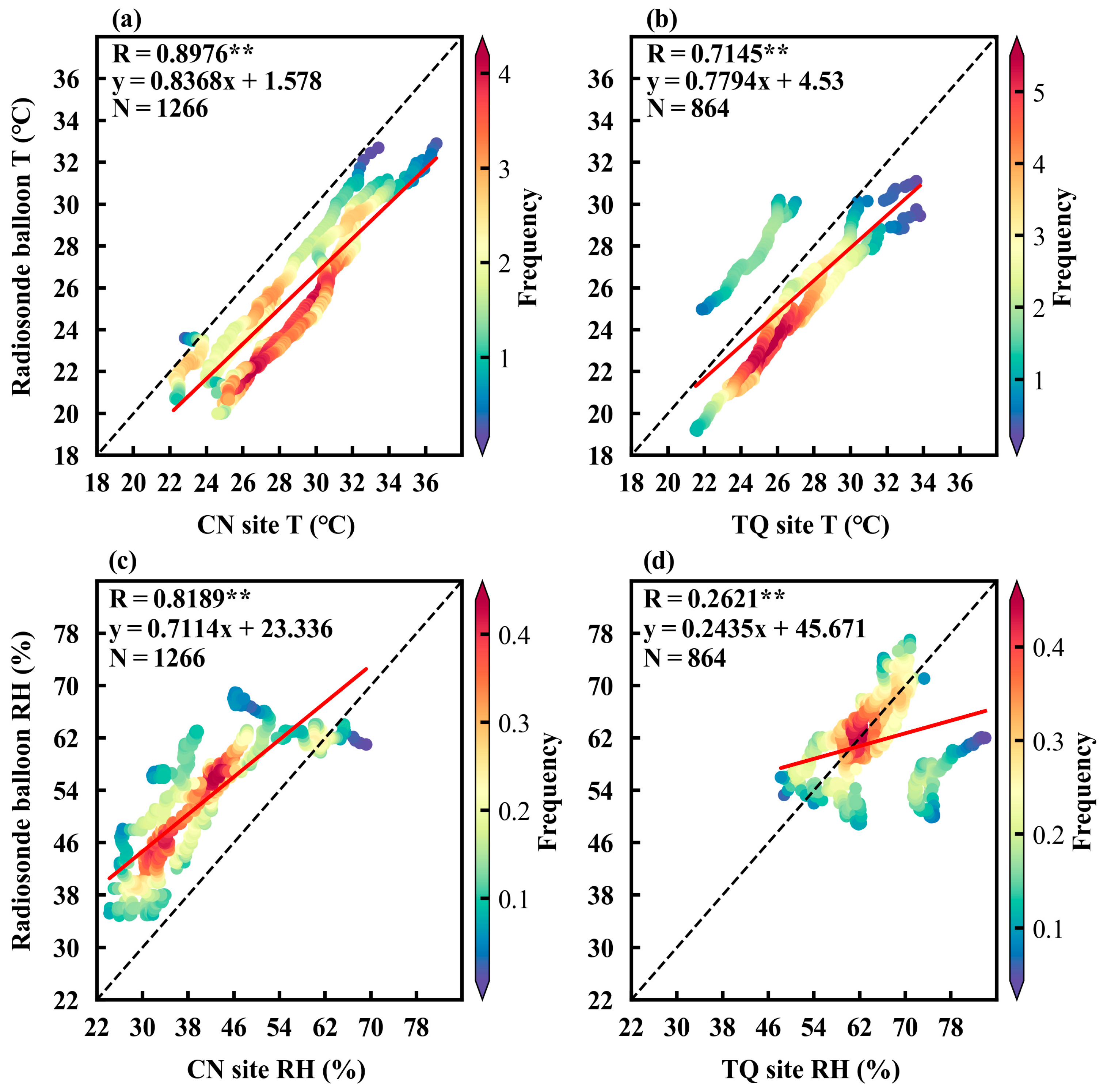
2.2.2. Radiosonde and Surface Observations
2.2.3. ERA-5 Data
2.3. Determination of PBLH
2.4. Air Mass Sources
3. Results and Discussion
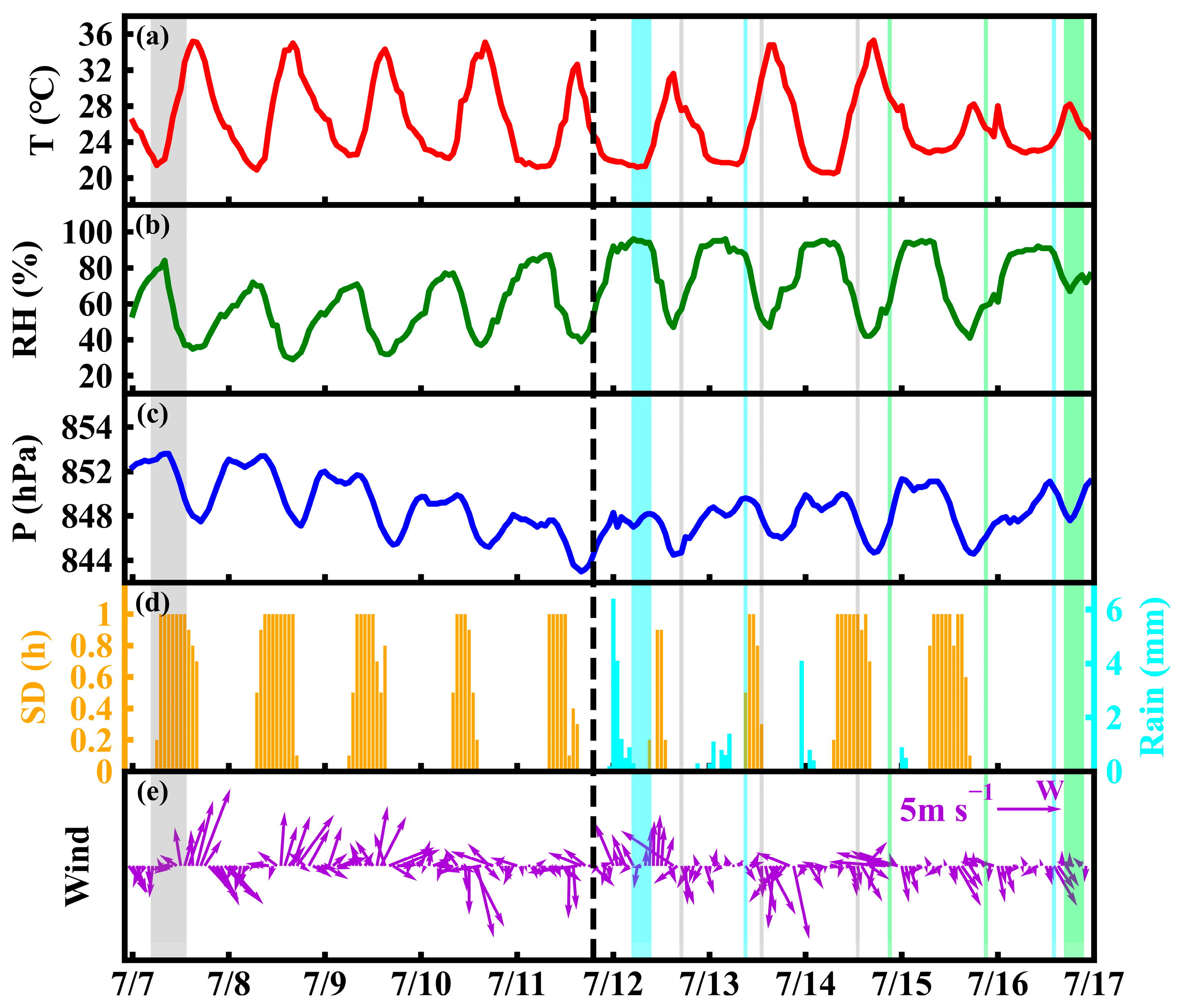
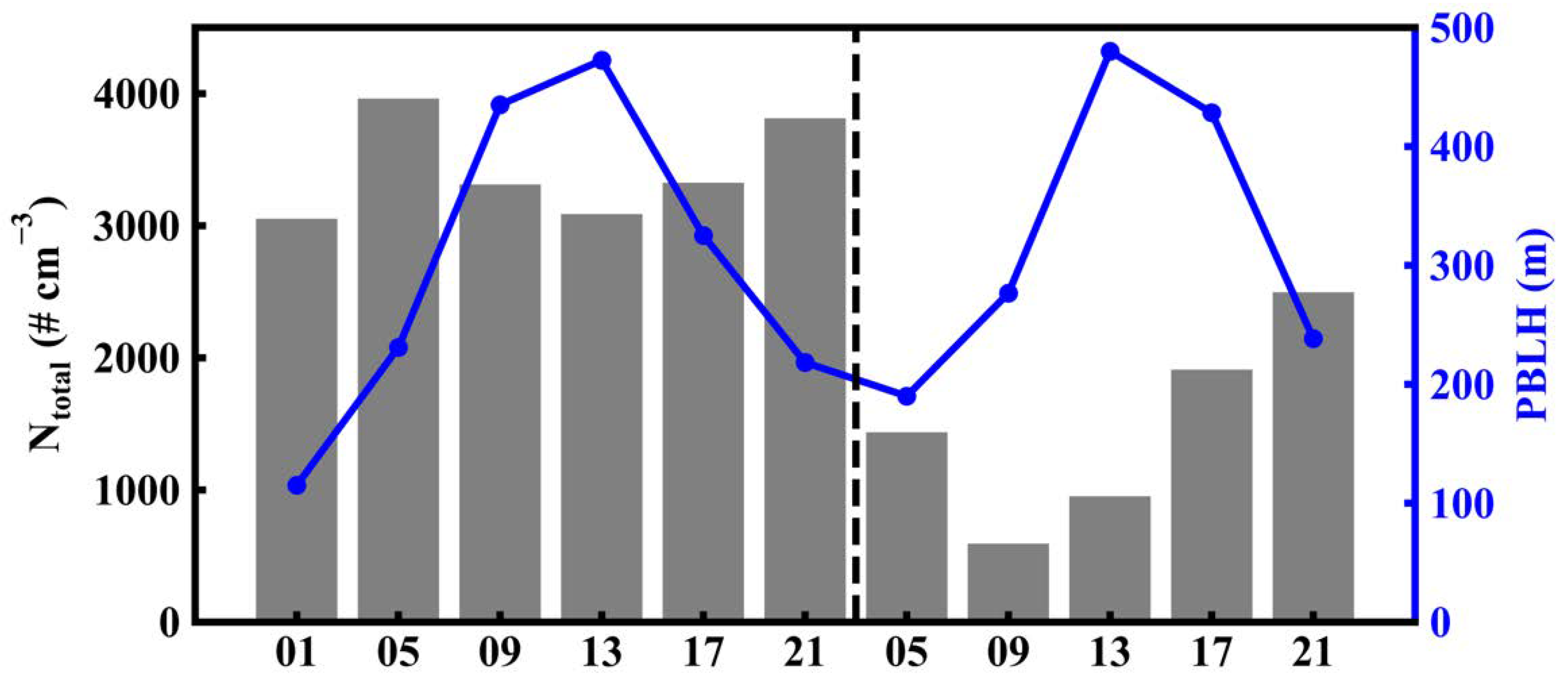
3.1. Temporal Variation of Surface Meteorological Variables
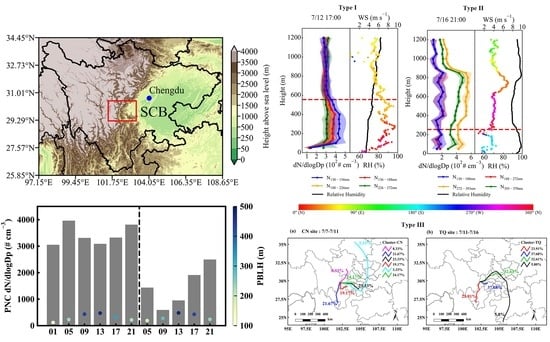
3.2. The Relationship between Particle Number Concentration and PBLH Based on UAV Measurements
3.3. Case Studies of Particle Number Concentration Changes under Various Conditions
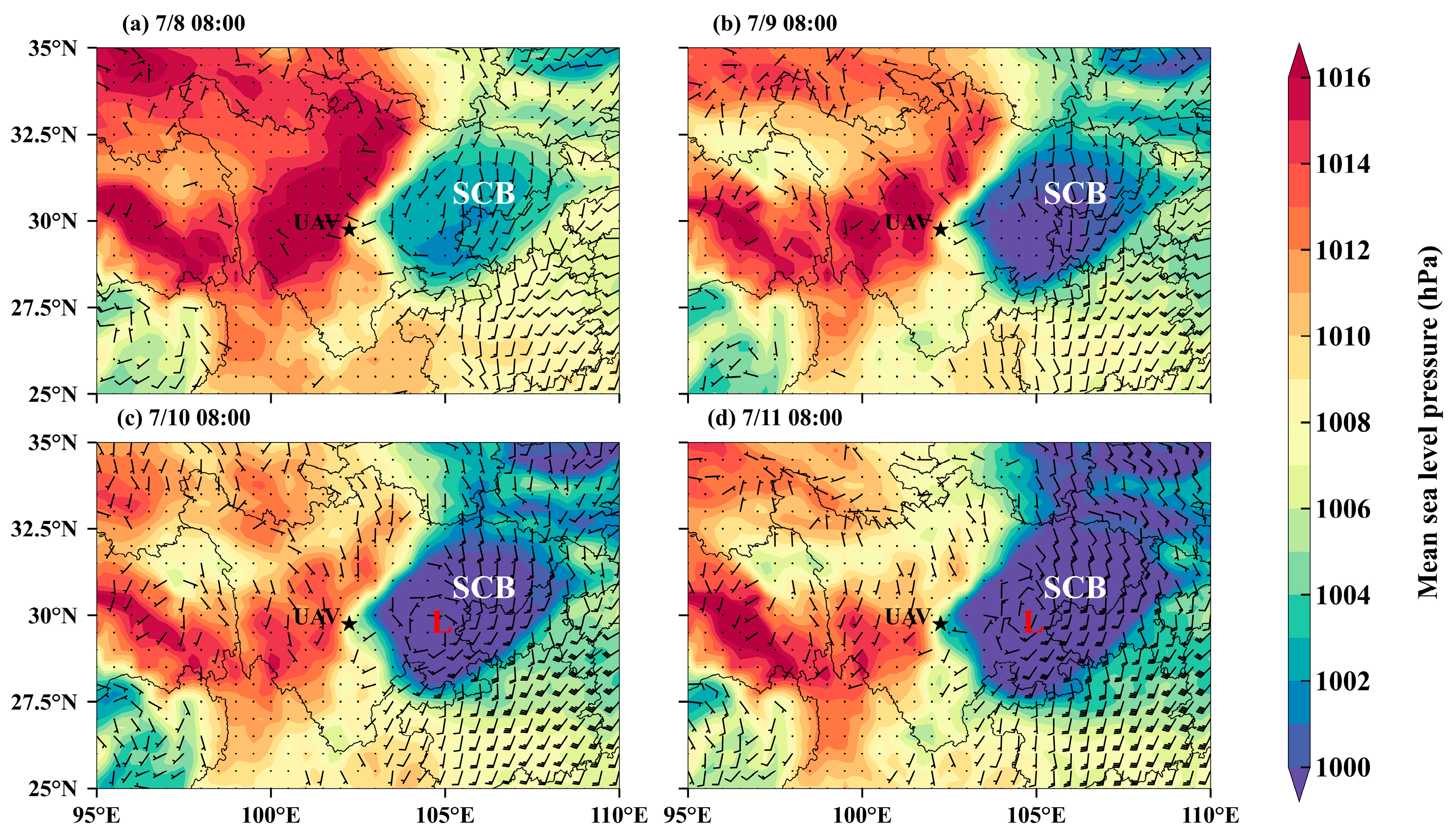
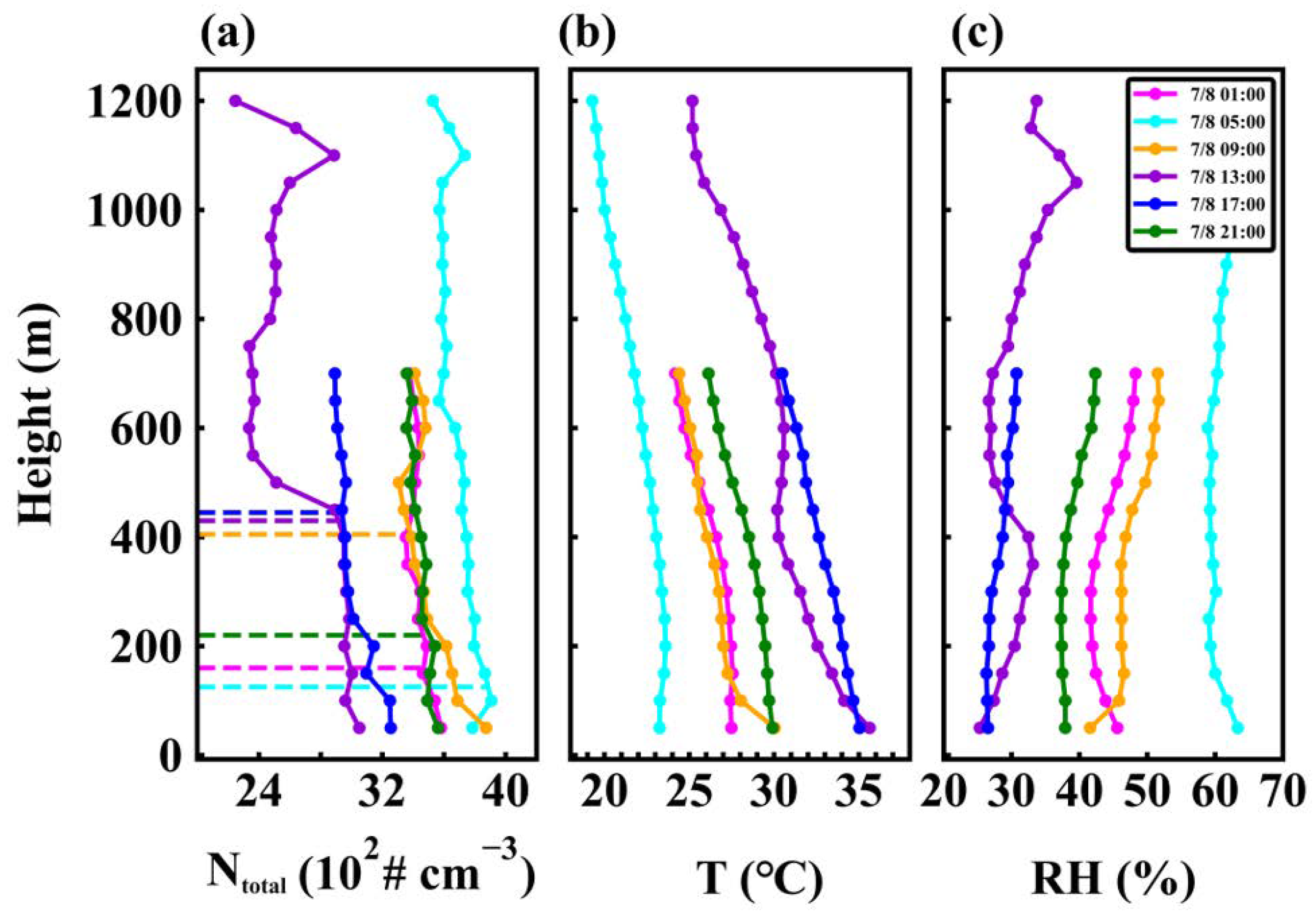
3.3.1. Explosive Growth of Fine Particles
3.3.2. The Process of the Hygroscopic Growth of Particles in the Background of Precipitation Clearance Effect
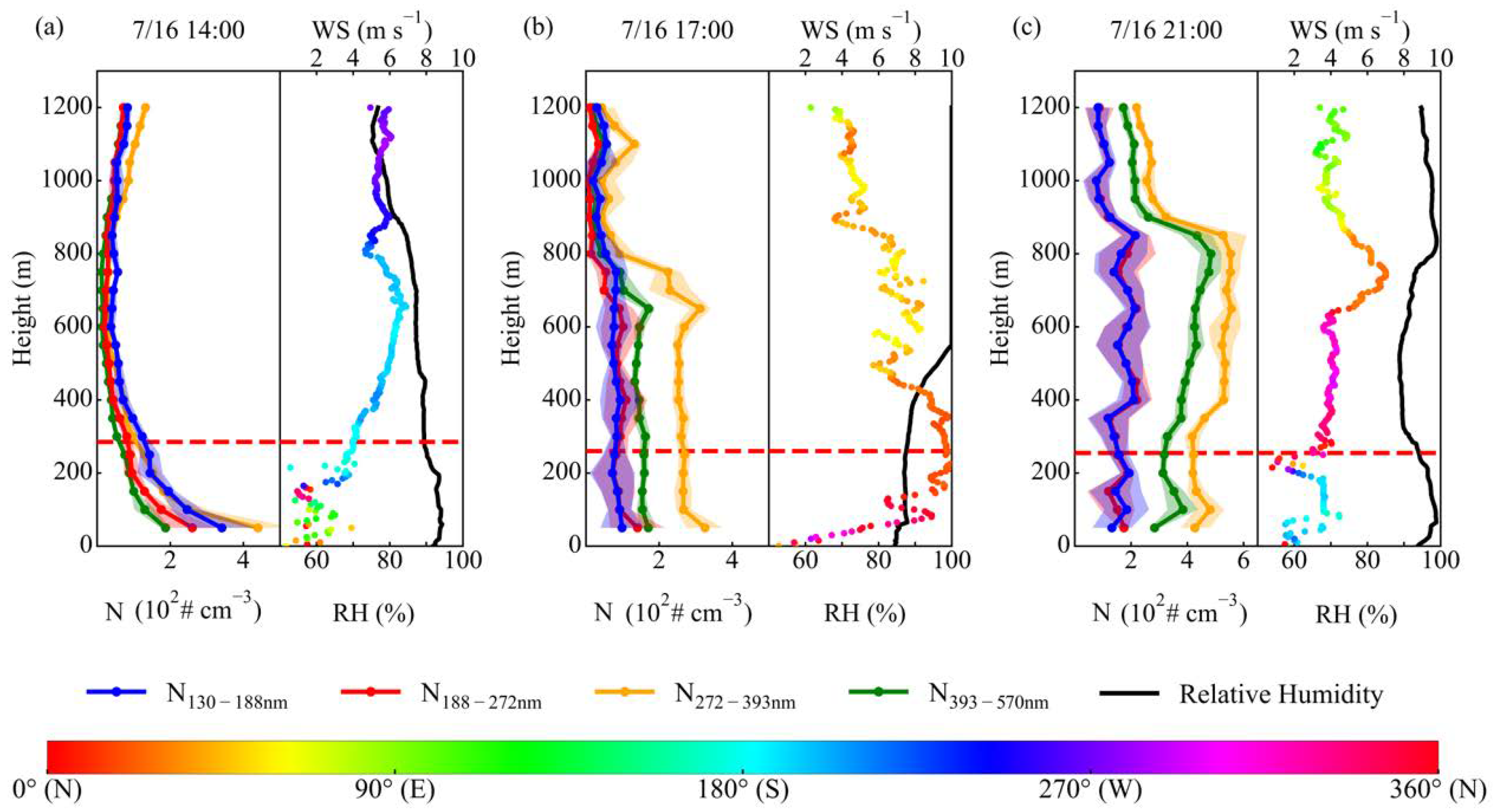
3.3.3. Influence of Air Masses on PNSD Profiles
4. Conclusions and Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, H.F.; Li, Z.Q.; Lv, Y.; Xu, H.; Li, K.; Li, D.; Hou, W.; Zheng, F.; Wei, Y.; Ge, B. Observational study of aerosol-induced impact on planetary boundary layer based on lidar and sunphotometer in Beijing. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 252, 897–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masson-Delmotte, V.; Zhai, P.; Pirani, A.; Connors, S.L.; Péan, C.; Berger, S.; Caud, N.; Chen, Y.; Goldfarb, L.; Gomis, M.I.; et al. IPCC 2021: Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2021; Available online: https://www.ipcc.ch/report/ar6/wg1 (accessed on 1 February 2023).
- Li, Z.; Guo, J.; Ding, A.; Liao, H.; Liu, J.; Sun, Y.; Wang, T.; Xue, H.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, B. Aerosol and boundary-layer interactions and impact on air quality. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2017, 4, 810–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wang, Y.; Guo, J.; Zhao, C.; Cribb, M.C.; Dong, X.; Fan, J.; Gong, D.; Huang, J.; Jiang, M.; et al. East Asian Study of Tropospheric Aerosols and Their Impact on Regional Clouds, Precipitation, and Climate (EAST-AIRCPC). J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2019, 124, 13026–13054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Li, Z.; Chen, X.; Li, C.; Sun, Y.; Wang, J.; Lyapustin, A.; Brasseur, G.; Jiang, M.; Sun, L.; et al. Separating daily 1 km PM2.5 inorganic chemical composition in China since 2000 via deep learning integrating ground, satellite, and model data. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, T.; Zhou, Y.; Habtemicheal, B.A.; Shen, L.; Hu, J.; Ma, X.; Sun, X. Long-term variations in aerosol optical properties, types, and radiative forcing in the Sichuan Basin, Southwest China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 807, 151490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontkanen, J.; Deng, C.; Fu, Y.; Dada, L.; Zhou, Y.; Cai, J.; Daellenbach, K.R.; Hakala, S.; Kokkonen, T.V.; Lin, Z.; et al. Size-resolved particle number emissions in Beijing determined from measured particle size distributions. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 11329–11348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Bismarck-Osten, C.; Birmili, W.; Ketzel, M.; Massling, A.; Petäjä, T.; Weber, S. Characterization of parameters influencing the spatio-temporal variability of urban particle number size distributions in four European cities. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 77, 415–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, R.M.; Shi, J.P.; Xi, S.H.; Khan, A.; Mark, D.; Kinnersley, R.; Yin, J.X. Measurement of number, mass and size distribution of particles in the atmosphere. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A-Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2000, 358, 2567–2580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulmala, M.; Vehkamaki, H.; Petaja, T.; Dal Maso, M.; Lauri, A.; Kerminene, V.-M.; Birmili, W.; McMurry, P.H. Formation and growth rates of ultrafine atmospheric particles: A review of observations. J. Aerosol Sci. 2004, 35, 143–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, T.; Hämeri, K.; Aalto, P.P.; Paatero, P.; Kulmala, M. Modal structure and spatial-temporal variations of urban and suburban aerosols in Helsinki-Finland. Atmos. Environ. 2005, 39, 1655–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, T.V.; Delgado-Saborit, J.M.; Harrison, R.M. Review: Particle number size distributions from seven major sources and implications for source apportionment studies. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 122, 114–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Boor, B.E. Urban aerosol size distributions: A global perspective. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2021, 21, 8883–8914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Li, Z.; Jiang, M.; Liang, C.; Zhang, D.; Wu, T.; Wang, Y.; Cribb, M. Contributions of traffic emissions and new particle formation to the ultrafine particle size distribution in the megacity of Beijing. Atmos. Environ. 2021, 262, 118652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, P.; Rosenlof, K.H.; Liu, S.; Telg, H.; Bai, X.; Portmann, R.W.; Rollins, A.W.; Pan, L.L.; Toon, O.B.; Bian, J.; et al. Efficient transport of tropospheric aerosol into the stratosphere via the Asian summer monsoon anticyclone. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 6972–6977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, B.; Shrivastava, M.; Donahue, N.M.; Gordon, H.; Schervish, M.; Shilling, J.E.; Zaveri, R.A.; Wang, J.; Andreae, M.O.; Zhao, C.; et al. High concentration of ultrafine particles in the Amazon free troposphere produced by organic new particle formation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 25344–25351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Platis, A.; Altstädter, B.; Wehner, B.; Wildmann, N.; Lampert, A.; Hermann, M.; Birmili, W.; Bange, J. An Observational Case Study on the Influence of Atmospheric Boundary-Layer Dynamics on New Particle Formation. Bound.-Lay. Meteorol. 2016, 158, 67–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhao, B. Emissions of air pollutants from Chinese cooking: A literature review. Build. Simul. 2018, 11, 977–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, M.A.; Ditas, F.; Kremper, L.A.; Machado, L.A.T.; Andreae, M.O.; Araújo, A.; Barbosa, H.M.J.; de Brito, J.F.; Carbone, S.; Holanda, B.A.; et al. Occurrence and growth of sub-50 nm aerosol particles in the Amazonian boundary layer. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2022, 22, 3469–3492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.M.; Meskhidze, N.; Rasheeda Satheesh, A.; Petters, M.D. Turbulent flux measurements of the near-surface and residual-layer small particle events. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2022, 127, e2021JD036289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Zhang, D.; Wang, J.; Gao, H.; Yao, X. Variations in Ncn and Nccn over marginal seas in China related to marine traffic emissions, new particle formation and aerosol aging. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 9665–9677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, M.; Liang, B.; Sun, Q.; Liu, L.; Yuan, B.; Shao, M.; Huang, S.; Peng, Y.; Wang, Z.; Tan, H.; et al. The important roles of surface tension and growth rate in the contribution of new particle formation (NPF) to cloud condensation nuclei (CCN) number concentration: Evidence from field measurements in southern China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2021, 21, 8575–8592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Zhu, Y.; Wu, Z.; Zong, T.; Chen, J.; Tan, T.; Wang, H.; Fang, X.; Lu, K.; Zhao, C.; et al. Impact of aerosol-radiation interaction on new particle formation. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2021, 21, 9995–10004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreae, M.O.; Andreae, T.W.; Ditas, F.; Pöhlker, C. Frequent new particle formation at remote sites in the subboreal forest of North America. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2022, 22, 2487–2505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rönkkö, T.; Kuuluvainen, H.; Karjalainen, P.; Keskinen, J.; Hillamo, R.; Niemi, J.V.; Pirjola, L.; Timonen, H.J.; Saarikoski, S.; Saukko, E.; et al. Traffic is a major source of atmospheric nanocluster aerosol. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 7549–7554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wehner, B.; Uhrner, U.; von Löwis, S.; Zallinger, M.; Wiedensohler, A. Aerosol number size distributions within the exhaust plume of a diesel and a gasoline passenger car under on-road conditions and determination of emission factors. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 1235–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Westerdahl, D.; Wu, Y.; Pan, X.; Zhang, K.M. On-road emission factor distributions of individual diesel vehicles in and around Beijing, China. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 503–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Wu, Y.; Xu, J.; Ohara, T.; Hasegawa, S.; Li, J.; Yang, L.; Hao, J. Black carbon at a roadside site in Beijing: Temporal variations and relationships with carbon monoxide and particle number size distribution. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 77, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.S.; Lin, W.H.; Jenq, F.T. Size Distributions of Submicrometer Aerosols from Cooking. Environ. Int. 1993, 19, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeung, L.L.; To, W.M. Size Distributions of the Aerosols Emitted from Commercial Cooking Processes. Indoor Built Environ. 2008, 17, 220–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.L.; Chao, C.Y.H.; Sze-To, G.N.; Wan, M.P.; Chan, T.C. Ultrafine Particle Emissions from Cigarette Smouldering, Incense Burning, Vacuum Cleaner Motor Operation and Cooking. Indoor Built Environ. 2012, 21, 782–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Du, W.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Chen, C.; Xu, W.; Han, T.; Wang, Y.; Fu, P.; Wang, Z.; et al. Insights into aerosol chemistry during the 2015 China Victory Day parade: Results from simultaneous measurements at ground level and 260 m in Beijing. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 3215–3232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Xu, W.; Zhang, Q.; Jiang, Q.; Canonaco, F.; Prévôt, A.S.H.; Fu, P.; Li, J.; Jayne, J.; Worsnop, D.R.; et al. Source apportionment of organic aerosol from 2-year highly time-resolved measurements by an aerosol chemical speciation monitor in Beijing, China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 8469–8489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Chu, B.; Yao, L.; Yan, C.; Heikkinen, L.M.; Zheng, F.; Li, C.; Fan, X.; Zhang, S.; Yang, D.; et al. Size-segregated particle number and mass concentrations from different emission sources in urban Beijing. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 12721–12740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, L.; Garmash, O.; Ehn, M.; Miettinen, P.; Massoli, P.; Mikkonen, S.; Jokinen, T.; Roldin, P.; Aalto, P.; Yli-Juuti, T.; et al. Combined effects of boundary layer dynamics and atmospheric chemistry on aerosol composition during new particle formation periods. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 17705–17716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leino, K.; Lampilahti, J.; Poutanen, P.; Väänänen, R.; Manninen, A.; Buenrostro Mazon, S.; Dada, L.; Franck, A.; Wimmer, D.; Aalto, P.P.; et al. Vertical profiles of sub-3 nm particles over the boreal forest. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 4127–4138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Huang, J.T.; Ren, C.H.; Wang, J.P.; Wang, H.Y.; Wang, J.D.; Yu, H.; Chen, J.; Gao, J.; Ding, A.J. Chemical Boundary Layer and Its Impact on Air Pollution in Northern China. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2020, 7, 826–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, S.Y.; Hai, S.F.; Gao, Y.; Wang, Y.H.; Sheng, L.F.; Lupascu, A.; Ding, A.J.; Nie, W.; Qi, X.M.; Huang, X.; et al. The striking effect of vertical mixing in the planetary boundary layer on new particle formation in the Yangtze River Delta. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 829, 154607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Liu, X.D.; Dai, J.; Wang, Z.; Dong, Z.P.; Dong, Y.; Chen, C.; Li, X.M.; Zhao, N.; Fan, C. Aerosol size distribution and new particle formation events in the suburb of Xi’an, northwest China. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 153, 194–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şahin, Ü.A.; Harrison, R.M.; Alam, M.S.; Beddows, D.C.S.; Bousiotis, D.; Shi, Z.; Crilley, L.R.; Bloss, W.; Brean, J.; Khanna, I.; et al. Measurement report: Interpretation of wide-range particulate matter size distributions in Delhi. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2022, 22, 5415–5433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Lau, W.M.; Ramanathan, V.; Wu, G.; Ding, Y.; Manoj, M.G.; Liu, J.; Qian, Y.; Li, J.; Zhou, T.; et al. Aerosol and monsoon climate interactions over Asia. Rev. Geophys. 2016, 54, 866–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, W.; Zhang, J.; Zhong, C.; Ji, D.; Huang, W. Satellite-derived spatiotemporal PM2.5 concentrations and variations from 2006 to 2017 in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 712, 134577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Ni, C.; Jiang, M.; Chen, Q. Effects of aerosols on the atmospheric boundary layer temperature inversion over the Sichuan Basin, China. Atmos. Environ. 2021, 262, 118647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, D.; Zhao, S.; Qu, J.; Yu, Y.; Kang, S.; Ren, X.; Zhang, J.; Zou, Y.; Dong, L.; Li, J.; et al. The vertical profiles of carbonaceous aerosols and key influencing factors during wintertime over western Sichuan Basin, China. Atmo. Environ. 2020, 223, 1352–2310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Qi, S.; Yu, Y.; Kang, S.; Dong, L.; Chen, J.; Yin, D. Measurement report: Contrasting elevation-dependent light absorption by black and brown carbon: Lessons from in situ measurements from the highly polluted Sichuan Basin to the pristine Tibetan Plateau. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2022, 22, 14693–14708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.Q.; Hao, T.Y.; Zhang, Y.F.; Liu, J.L.; Li, P.Y.; Cai, Z.Y.; Zhang, M.; Wang, Q.L.; Zhang, H. Vertical observation and analysis on rapid formation and evolutionary mechanisms of a prolonged haze episode over central-eastern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 616–617, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Querol, X.; Alastuey, A.; Gangoiti, G.; Perez, N.; Lee, H.K.; Eun, H.R.; Park, Y.; Mantilla, E.; Escudero, M.; Titos, G.; et al. Phenomenology of summer ozone episodes over the Madrid Metropolitan Area, central Spain. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 6511–6533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Liu, J.; Gao, Z.; Li, Y.; Huang, M.; Fan, S.; Zhang, X.; Yang, Y.; Miao, S.; Zou, H.; et al. Vertical observations of the atmospheric boundary layer structure over Beijing urban area during air pollution episodes. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 6949–6967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiliński, M.T.; Markowicz, K.M.; Kubicki, M. UAS as a Support for Atmospheric Aerosols Research: Case Study. Pure Appl. Geophys. 2018, 175, 3325–3342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Osborne, M.; Anderson, K.; Shutler, J.D.; Wilson, A.; Langridge, J.; Yim, S.H.L.; Coe, H.; Babu, S.; Satheesh, S.K.; et al. Characterizing the performance of a POPS miniaturized optical particle counter when operated on a quadcopter drone. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2021, 14, 6101–6118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Cheng, Y.; Bai, X.; Dai, H.; Wei, X.; Sun, L.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Feng, Y.; Li, Y.J.; et al. Vertical profile of aerosol number size distribution during a haze pollution episode in Hefei, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 814, 152693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Z.-R.; Wang, D.; Wang, Z.; Gao, Y.; Lu, S. A study of vertical distribution patterns of PM2.5 concentrations based on ambient monitoring with unmanned aerial vehicles: A case in Hangzhou, China. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 123, 357–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Huang, J.; Wang, Y.; Tao, X.; Hu, C.; Deng, L.; Xu, J.; Xiao, H.W.; Luo, L.; Xiao, H.Y.; et al. Vertical distribution of PM2.5 and interactions with the atmospheric boundary layer during the development stage of a heavy haze pollution event. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 704, 135329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Zhou, T.; Fang, S.; Han, B.; He, Q. Investigation of the Vertical Distribution Characteristics and Microphysical Properties of Summer Mineral Dust Masses over the Taklimakan Desert Using an Unmanned Aerial Vehicle. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 3556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, C.; Liu, C.; Wu, H.; Lin, J.; Wang, F.; Wang, S.; Gao, M. Ground-based vertical profile observations of atmospheric composition on the Tibetan Plateau (2017–2019). Earth Syst. Sci. Data. 2021, 13, 4897–4912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wu, X.; Liu, S.; Bai, Z.; Xia, X.; Chen, B.; Zong, X.; Bian, J. In situ measurements and backward-trajectory analysis of high-concentration, fine-mode aerosols in the UTLS over the Tibetan Plateau. Environ. Res. Lett. 2019, 14, 124068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.Y.; Liu, S.; Bai, Z.; Bian, J.; Li, D.; Fan, K.; McKeen, S.A.; Watts, L.A.; Ciciora, S.J.; Gao, R.-S. Religious burning as a potential major source of atmospheric fine aerosols in summertime Lhasa on the Tibetan Plateau. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 181, 186–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, R.S.; Telg, H.; McLaughlin, R.J.; Ciciora, S.J.; Watts, L.A.; Richardson, M.S.; Schwarz, J.P.; Perring, A.E.; Thornberry, T.D.; Rollins, A.W.; et al. A light-weight, high-sensitivity particle spectrometer for PM2.5 aerosol measurements. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 88–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Miao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, H.; Li, Z.; Zhang, W.; He, J.; Lou, M.; Yan, Y.; Bian, L.; et al. The climatology of planetary boundary layer height in China derived from radiosonde and reanalysis data. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 13309–13319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Huang, X.; Ding, A. Dome effect of black carbon and its key influencing factors: A one-dimensional modelling study. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 2821–2834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hersbach, H.; Bell, B.; Berrisford, P.; Hirahara, S.; Horányi, A.; Muñoz-Sabater, J.; Nicolas, J.; Peubey, C.; Radu, R.; Schepers, D.; et al. The ERA5 global reanalysis. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2020, 146, 1999–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen-Gammon, J.W.; Hu, X.M.; Zhang, F.; Pleim, J.E. Evaluation of planetary boundary layer scheme sensitivities for the purpose of parameter estimation. Mon. Weather Rev. 2010, 138, 3400–3417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Hu, X.-M.; Ma, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, L.; Zhao, Z. Impact of planetary boundary layer structure on the formation and evolution of air-pollution episodes in Shenyang, Northeast China. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 214, 116850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Hu, X.; Gao, S.; Wang, Y. Sensitivity of WRF simulations with the YSU PBL scheme to the lowest model level height for a sea fog event over the Yellow Sea. Atmos. Res. 2019, 215, 253–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Ovadnevaite, J.; Fossum, K.N.; Lin, C.; Huang, R.-J.; O’Dowd, C.; Ceburnis, D. Aerosol hygroscopicity and its link to chemical composition in the coastal atmosphere of Mace Head: Marine and continental air masses. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 3777–3791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Wang, Y.; Li, Z.; Wang, Z.; Dickerson, R.R.; Ren, X.; He, H.; Wang, F.; Gao, Y.; Chen, X.; et al. Vertical profiles of cloud condensation nuclei number concentration and its empirical estimate from aerosol optical properties over the North China Plain. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2022, 22, 14879–14891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, A.F.; Draxler, R.R.; Rolph, G.D.; Stunder, B.J.B.; Cohen, M.D.; Ngan, F. NOAA’s HYSPLIT Atmospheric Transport and Dispersion Modeling System. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2015, 96, 2059–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Chen, Y.; Luo, Y.; Liu, B.; Ren, G.; Zhou, T.; Martinez-Villalobos, C.; Chang, M. Revealing the Circulation Pattern Most Conducive to Precipitation Extremes in Henan Province of North China. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2022, 49, e2022GL098034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, L.; Sun, Y.; Ouyang, B.; Qiu, Y.; Xie, C.; Tang, G.; Zhou, W.; He, Y.; Wang, Q.; Cheng, X.; et al. Vertical Distributions of Primary and Secondary Aerosols in Urban Boundary Layer: Insights into Sources, Chemistry, and Interaction with Meteorology. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 4542–4552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, G.; Qi, X.; Chen, L.; Xue, L.; Lai, S.; Huang, X.; Wang, J.; Chi, X.; Nie, W.; Kerminen, V.-M.; et al. The variation in the particle number size distribution during the rainfall: Wet scavenging and air mass changing. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2023, 23, 7521–7534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, W.; Dada, L.; Zhao, J.; Chen, X.; Daellenbach, K.R.; Xie, C.; Wang, W.; He, Y.; Cai, J.; Yao, L.; et al. A 3D study on the amplification of regional haze and particle growth by local emissions. NPJ Clim. Atmos. Sci. 2021, 4, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, S.; Qian, Y.; Zhao, C.; Leung, R.; Yang, X.Q. A case study of urbanization impact on summer precipitation in the Greater Beijing Metropolitan Area: Urban heat island versus aerosol effects. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2015, 120, 10903–10914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heikenfeld, M.; White, B.; Labbouz, L.; Stier, P. Aerosol effects on deep convection: The propagation of aerosol perturbations through convective cloud microphysics. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 2601–2627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Q.; Jiang, B.; Shen, X.; Lin, W.; Chen, J. Microphysics effects of anthropogenic aerosols on urban heavy precipitation over the Pearl River Delta, China. Atmos. Res. 2021, 253, 105478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Li, Z.; Li, H.; Luo, K.; Wang, Y.; Yan, P.; Hu, F.; Zhang, F.; Sun, Y.; Shang, D.; et al. The impact of the atmospheric turbulence-development tendency on new particle formation: A common finding on three continents. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2020, 8, 140–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.H.; Rossow, W.B. Determination of cloud structure from upper-air observations. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 1995, 34, 2243–2258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Kang, P.; Zhang, X.L.; Schaefer, K.; Yuan, L.; Xiang, W.G.; Lei, Y. Size distribution of atmospheric particles in Chengdu and its influence on visibility. Acta Sci. Circumst. 2020, 40, 4432–4441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, C. Vertical Profiles of Particle Number Size Distribution and Variation Characteristics at the Eastern Slope of the Tibetan Platea. Mendeley Data 2023, V1. Available online: https://data.mendeley.com/datasets/dvjvjhbjtf/1 (accessed on 31 July 2023).



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shu, C.; Zhu, L.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Jiang, X.; Hu, H.; Pu, D.; Liu, M.; Wu, H. Vertical Profiles of Particle Number Size Distribution and Variation Characteristics at the Eastern Slope of the Tibetan Plateau. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 5363. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15225363
Shu C, Zhu L, Yang Y, Zhao X, Jiang X, Hu H, Pu D, Liu M, Wu H. Vertical Profiles of Particle Number Size Distribution and Variation Characteristics at the Eastern Slope of the Tibetan Plateau. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(22):5363. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15225363
Chicago/Turabian StyleShu, Chenyang, Langfeng Zhu, Yinshan Yang, Xingbing Zhao, Xingwen Jiang, Hancheng Hu, Dongyang Pu, Mengqi Liu, and Hao Wu. 2023. "Vertical Profiles of Particle Number Size Distribution and Variation Characteristics at the Eastern Slope of the Tibetan Plateau" Remote Sensing 15, no. 22: 5363. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15225363
APA StyleShu, C., Zhu, L., Yang, Y., Zhao, X., Jiang, X., Hu, H., Pu, D., Liu, M., & Wu, H. (2023). Vertical Profiles of Particle Number Size Distribution and Variation Characteristics at the Eastern Slope of the Tibetan Plateau. Remote Sensing, 15(22), 5363. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15225363