Abstract
Direction-of-arrival (DOA) estimation is still a pivotal research direction in array signal processing. Traditional algorithms based on the signal subspace and compressed sensing theory usually suffer from off-grid and computational complexity. Deep-learning-based methods usually face difficulty in obtaining labeled datasets. With the development of array technology, sparse sensor arrays can effectively reduce the number of sensors, which in turn reduces the complexity of the hardware. Therefore, effective DOA estimation algorithms for sparse sensor arrays need to be further investigated. An unsupervised deep learning method is proposed here to address the above issues. A training model was built based on the residual network structure. The DOA estimation was implemented using Vandermonde decomposition. Finally, the experimental findings confirmed the efficacy of the proposed algorithms presented in this article.
1. Introduction
The implementation of DOA estimation requires arrays with certain geometric configurations, such as uniform linear arrays (ULAs), sparse linear arrays (SLAs), L-shaped arrays, etc. In this paper, the DOA estimation algorithm for sparse linear arrays was investigated. With the wide adoption of direction-of-arrival (DOA) estimation in sonar, radar, unmanned, and wireless communication in the past decades, many algorithms have been proposed [1,2,3].
The multiple signal classification (MUSIC) algorithm [4] and the estimation of signal parameters via rotational invariance techniques (ESPRIT) algorithm are two classical subspace-like algorithms. The MUSIC estimator exploits the orthogonality of the signal subspace with the noise subspace, which SLA signals also possess, and then, performs a 1D spatial search [5]. Similar to the capon-like algorithm, the spatial search undoubtedly leads to off-grid problems. In the literature [6], ESPRIT was used to estimate the DOA, This reduces the computational burden due to the absence of the spatial search. Further, the literature [7,8] proposed the U-ESPRIT algorithm, which transforms the signal covariance matrix to the real-valued domain by a unitary transformation. The U-ESPRIT algorithm not only further reduces the computational burden, but is also more beneficial in the case of discriminating correlated sources [7]. However, SLA signals do not have the rotation invariance property, and the ESPRIT algorithm cannot be applied to the DOA estimation of SLAs.
In fact, the SLA signal is equivalent to sparse sampling of the ULA along the array element dimension. The authors proposed an algorithm for structured matrix completion (called FFH-MC) [9]. The algorithm reconstructs the covariance matrix of the virtual array into a four-fold Hankel matrix without missing the entire row, which allows the matrix complementation algorithm to be utilized. The robust principal component analysis (RPCA) can realize completion and denoising of a low-rank matrix, and it is a robust and effective method [10,11,12]. These algorithms can only achieve high-performance DOA estimation in the case of random sampling of the signal covariance matrix and cannot achieve effective DOA estimation in the case of the absence of the entire row of the covariance matrix.
The theory of compressive sensing (CS) enables distortion-free reconstruction of sparse signals, which provides a novel perspective for DOA estimation [13]. Generally speaking, CS algorithms can be classified into three categories as follows: (1) on-grid; (2) gridless; (3) off-grid. The algorithm based on singular-value decomposition (SVD) with -norm minimization, called L1 SVD, was proposed in the literature [14]. L1 SVD reduces the computational complexity to some extent through SVD. However, the algorithm is a typical on-grid algorithm and requires solving a norm optimization problem to determine the angle, which leads to its computational explosion. The off-grid sparse Bayesian learning (OGSBL) algorithm achieves off-grid estimation of the DOA through Bayesian inference and expectation maximization [15,16]. This method has better performance in terms of accuracy, while it is computationally difficult due to the multiple iterations of the algorithm and the matrix inversion. The above CS algorithms can realize the DOA estimation for SLAs by constructing the corresponding dictionary. The typical gridless algorithm is the atomic norm minimization (ANM) algorithm, which can realize DOA estimation without constructing a dictionary [17,18]. In this algorithm, the Toeplitz matrix about the source can be obtained by solving a semi-positive definite programming (SDP) problem, then the DOAs can be estimated using Vandermonde decomposition or rootMUSIC.
With the development of deep learning (DL), the DOA estimation algorithm based on DL has excellent performance [19,20,21,22,23]. A deep network with fully connected (FC) layers for only two sources has also been proposed to realize DOA estimation [22]. This method trains the network for only two sources, which obviously lacks generalization performance for different numbers of targets. The results in that paper showed a lack of performance of this algorithm at high signal-to-noise ratios (SNRs). A convolutional-neural-network (CNN)-based approach was used to achieve DOA estimation for extreme signal-to-noise ratio cases [23]. This algorithm has outstanding performance in the case of low SNRs, but is limited by the accuracy of the label setting, which is insufficient in the case of high SNRs. For sparse array signals, the paper employed a stacked denoising autoencoder (DAE), which predicts a statistically “richer” version of the sampled matrix [24]. The above deep learning methods are all supervised learning approaches to achieve DOA estimation. They do not consider the availability of data containing labels in real applications.
After analyzing the advantages and disadvantages of the above methods, we propose a gridless algorithm based on residual neural networks (ResNets) and unsupervised learning (UL), which can achieve DOA estimation with low SNRs and few snapshots. UL is the better way to deal with the difficulty of obtaining labeled datasets. How to construct the cost function in UL is the key to whether a high-performance algorithm can be obtained. Atomic norm minimization (ANM) is a method that is robust in the face of both complete and incomplete data [17,25]. Therefore, we used the atomic norm as the cost function of the unsupervised training of the network. The emergence of ResNet has had an impact due to its excellent performance [26]. ResNet is a good solution to the problem of gradient disappearance and gradient explosion in deep networks, and the problem of network degradation is solved to some extent by using the residual structure. Fang et al. [27] and Li and Tian [28] also implemented DOA estimation using ResNet. They essentially did not change the previous training approach, which is limited by the acquisition of labeled datasets. In this paper, we combined residual networks with unsupervised learning to solve the dependence problem of labeled data in traditional deep learning DOA estimation methods. In addition, we considered various factors such as low SNRs, few snapshots, and the presence of both when using SLAs for DOA estimation. Finally, the numerical simulations verified the validity of our algorithm.
The following three points are the main contributions of this paper:
- (1)
- Combined with unsupervised learning, a DOA estimation method for sparse sensor arrays is first proposed. Our proposed method combines the advantages of DL and can reduce the problem of computational complexity to some extent by using the data-driven approach.
- (2)
- We introduce ResNet and combine it with unsupervised learning. The proposed method is a good solution when facing the dilemma that labeled datasets in DOA estimation are hard to obtain. Due to the characteristics of the residual network itself, the network structure proposed in this paper can circumvent gradient disappearance and gradient explosion and can solve the overfitting of the deep network.
- (3)
- We took some complex environments into consideration, such as low SNRs and few snapshots. Methods are given on how to train the network using data containing such errors.
The remainder of the paper is organized as follows: In Section 2, we first give the signal model of the SLA and then derive the cost function for network training. Section 3 describes the network structure and network training method. Section 4 shows the simulation and analysis. In Section 5, we give the conclusion based on the theory and simulations.
The notations used in this paper are as follows. Boldface letters are reserved for vectors and matrices. and denote the transpose and the conjugate transposition of the matrix , respectively. , and denote the , and Frobenius norms, respectively. denotes the trace of the matrix . denotes the set of matrices with the entry being complex numbers. denotes the identity matrix. denotes the result of the estimation of .
2. Model and Cost Function
In this section, we first give the model of the SLA and give the relationship between it and the model of the ULA by mathematical formulas. Then, we give the cost function for network training in conjunction with the ANM theory for the incomplete data.
2.1. Model
Here, we considered the model of the far-field narrowband signals incident on the sparse sensor array. As shown in Figure 1, when there are K signals incident on an array with N sensors in the space domain at the moment l, we can obtain
where , denotes the index of the sensors, is the subset of , and , . M is the number of sensors in a non-sparse linear array with the same array aperture, and . is the direction vector of the incident signals. and represent the transmit signals and the additive Gaussian white noises at the moment l, respectively. L is the number of snapshots. In Equation (1), , where
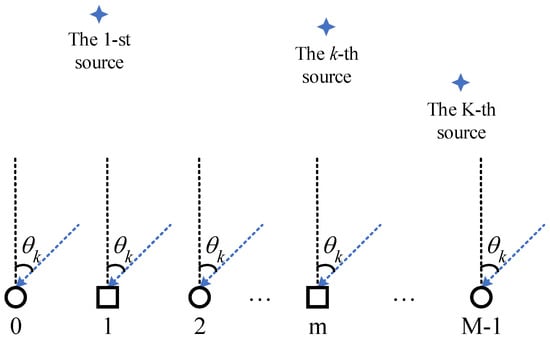
Figure 1.
The sparse sensor array scenario (the circles denote the real sensors; the squares represents the missing sensors).
Finally, the matrix form can be obtained:
As mentioned above, the SLA is actually a subarray of the ULA under the same aperture. Therefore, the sparse signal model can be obtained from the transformation of the ULA. Then, we can obtain the following procedure:
where is the selectionmatrix. The -th position of the n-th column of is one, and the rest are zero. It is easy to obtain from Equation (4) that and . Then, the theoretical covariance matrix of the incident signals can be obtained as follows:
where is the covariance matrix of the ULA, is the noise power, is the identity matrix, is the covariance matrix of , and are the eigenvectors corresponding to the signal eigenvalues and noise eigenvalues, respectively, and and are the diagonal matrices composed of the signal eigenvalues and noise eigenvalues, respectively. If we can obtain from the incident signal , then it is not difficult to calculate the DOAs of the sources by Vandermonde decomposition.
2.2. The Cost Function of Network Training
In this subsection, we give the cost function when training the network. In practice, the signal is sampled. Thus, we can obtain the unbiased estimation of the covariance matrix by
According to the descriptions in [17,18], it is possible to use directly as an input to the ANM estimator. The ANM estimator has the ability to achieve the complement of , as well as the estimation of . However, the large signal dimension leads to high computational burden. Here, we constructed a one-dimensional input vector using the eigenvectors and the corresponding eigenvalue weighting to achieve the data dimensionality reduction. Next, we describe whether the vector constructed by this method is reasonable as an input to the ANM.
The literature [29] proposed an algorithm based on the signal subspace, and combined with the model in this paper, the eigenvectors of the signal covariance matrix are
where is the k-th eigenvalue, . Then, the new input vector is
which is an N-dimensional complex vector. Combined with Equation (7), Equation (8) can be further denoted by
Thus, the physical meaning of is the weighted sum of the steering of the sparse sensor array in different directions. According to [18], we define the set of atoms with respect to the SLA steering vector as
Then, the atomic norm of is defined as
The above equation well constrains the sparsity by using a linear combination of a minimum number of atoms in to compose the . But, minimizing (11) is -hard, so we make it solvable by relaxation [13,17,25], by which
where is the convex hull of .
The cost function of the ANM problem is [30]
where is to be specified. Then, Equation (13) can be written as a positive semidefinite programming (SDP) problem [18]:
where and denotes a Hermitian Toeplitz matrix with
If is determined, then the angle of the source can be obtained using Vandermonde decomposition. Equation (14) has constraints that cannot be directly used as a cost function for the network training. Furthermore, Equation (14) can be written as an unconstrained cost function [31]:
where
and
So far, the cost function can be divided into three parts, and . The square of the -norm part is the first part:
The second part is the trace of the matrix:
The last part is the semi-positive definite constraint on the matrix , which is an essential part. is a conjugate symmetric matrix; therefore, whether the minimum eigenvalue of is greater than or equal to zero is an effective condition for whether is semi-positive definite. The “ELU” function is used to construct :
where b is the minimum eigenvalue of .
3. Deep Networks for DOA Estimation
After the above discussion, we obtain the cost function for the network training. In this section, we introduce how to obtain the angle of the sources from the perspectives of the network structure and the processing of the network outputs.
3.1. Network Structure
As shown in Figure 2, we give the network structure used in this paper. The network structure can be divided into three parts: the feature extraction part, the feature mapping part, and the output part. The feature extraction part is mainly composed of a 34-layer residual network, where all layers are one-dimensional. The 34-layer residual network consists of BasicBlocks cascades [26], where represents three 64-output channels of BasicBlocks, four 128-output channels of BasicBlocks, six 256-output channels of BasicBlocks and three 512-output channels of BasicBlocks, respectively. The second part consists mainly of two linear layers with 4000 and 1000 neurons, respectively. The two linear layers are followed by two dropout layers with the drop rate equal to 0.5. Finally, corresponding to the cost function, the output is divided into three parts , , and , respectively. Then, in Equation (14), , , and . , , and denote the output of the network with respect to , , and , respectively.
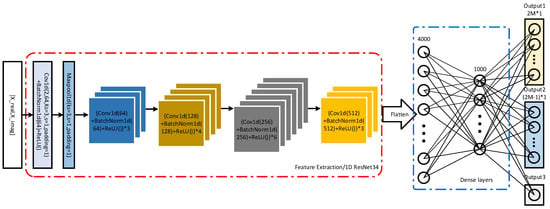
Figure 2.
The network structure.
3.2. DOA Estimation
When we obtain the containing the information of the sources, subsequently, can be easily obtained. After the decomposition of , the DOAs of the sources can be easily derived. Yang [32] and Candes et al. [33] demonstrated that the DOAs of the sources can be obtained using Vandermonde decomposition, which will not be repeated in this paper.
4. Simulations
In this section, we construct several simulations to illustrate the performance of the proposed algorithm. The comparison between different algorithms is also considered.
4.1. Network Training
The specific structure of the network was previously described in Section 3.1, and here, we focus on the training set setup. First, to facilitate the statistical analysis, we set the index of the sparse array to . The number of sources was , and the interval between two sources cannot be less than . The snapshots of the incident signals . The spatial scope was . The SNRs of the incident signals were generated randomly between dB and 5 dB, and the SNR is defined as in Equation (22). The angles of the two sources were two random real numbers in the spatial scope, and their difference was greater than 3. Finally, we generated a total of 60,000 random groups as the training set. The optimizer for network training was the Adam optimizer, and its learning rate was set to 0.0001 [34]. We trained 80 epochs using the dataset, which had a batch size of 128. Finally, the regularization parameter .
In Figure 3, the variation of the values of the three-part cost function during training is shown. The red line represents the total loss, which basically converged by the time 80 epochs had been trained. The blue line represents the norm loss, which tended to zero as the epoch increased. The yellow line represents the third part of the loss, and the eigenvalue of the matrix converged to 1 as the training proceeded. Overall, from the results shown in Figure 3, the three parts’ losses can converge, and the corresponding total loss can converge as well.
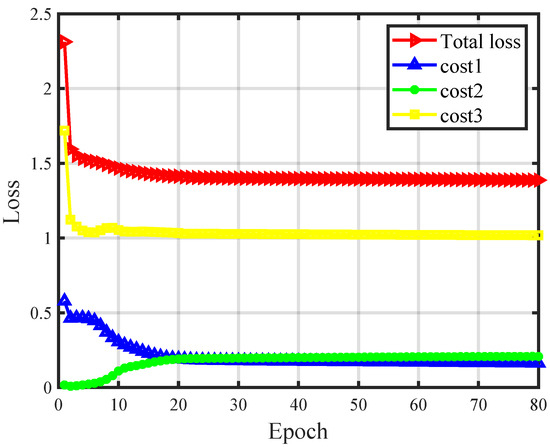
Figure 3.
Training loss variation curve with increasing epoch.
4.2. Performance Analysis
In this paper, we mainly compared several commonly used traditional algorithms. The algorithm names and the corresponding references were as follows:
- (1)
- MUSIC [4];
- (2)
- rootMUSIC [35];
- (3)
- OGSBL [15,16];
- (4)
- L1 SVD [14];
- (5)
- ANM [17,18].
It should be noted here that the input and proposed algorithms of the ANM algorithm are similar, as shown in Equation (9).
To analyze the results more intuitively, we introduce two critical parameters: the SNR and the root-mean-squared error (RMSE). Our definition of the SNR is as follows:
The RMSE can be defined as
where P denotes the number of Monte Carlo trials. is the DOA estimation result, where p denotes the p-th Monte Carlo trial, and the total number of Monte Carlo experiments is denoted by P. Then, we made Table 1 to collect the settings of other parameters.

Table 1.
Parameters’ settings.
Figure 4 shows the results of the first simulation, which compared the variation of the RMSE of different algorithms when facing different SNRs. This simulation was performed for the case of two sources, and . As can be seen in Figure 4, rootMUSIC cannot perform angle estimation in the face of sparse arrays, and the RMSE in the convergence of the MUSIC and L1 SVD algorithms was larger than that of OGSBL and the algorithm in this paper. The RMSE of the OGSBL algorithm converged with the increase of the SNR, which was higher than the traditional gridding algorithm, but not as good as the proposed algorithm. From Figure 4, we can observe that the two algorithms with the best performance were ANM and the proposed algorithm, and the RMSEs of these two algorithms were comparable. When the SNR was greater than −5 dB, the RMSE of the angle was already less than 0.5. The superiority of the proposed algorithm in this paper is mainly reflected in the faster computation while maintaining a certain accuracy, which will be reflected in the subsequent results.
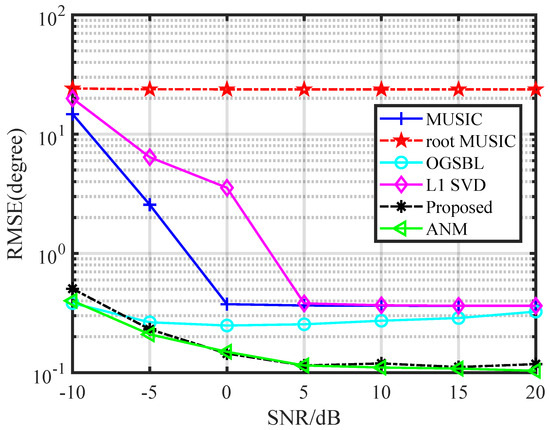
Figure 4.
Comparison of the RMSEs of different algorithms with different SNRs.
As in Figure 5, we counted the RMSE of different algorithms for different snapshots in the case of SNR = 20 dB. Obviously, the proposed algorithm did not perform as well as the model-based algorithm in the case of low snapshots. But, as the number of snapshots became closer to our training set snapshots, its performance outperformed the traditional algorithm. When the snapshots = 1000, the accuracy of the proposed algorithm was comparable to that of the ANM algorithm.
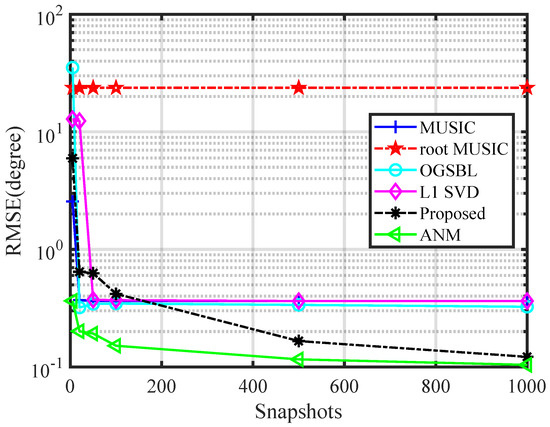
Figure 5.
Comparison of the RMSE of different algorithms with different snapshots.
In the third simulation, we analyzed the effect of different snapshots on the proposed algorithm for different SNRs. As shown in Figure 6, the accuracy of the algorithm increased when the number of snapshots increased. We can see from Figure 6 that the accuracy of the algorithm estimation was similar when the number of snapshots was greater than 500. This simulation showed that the accuracy of the proposed algorithm was better than most of the algorithms when the signal-to-noise ratio was constant and the number of snapshots was greater than 500. Along the horizontal axis, when the number of snapshots was fixed and the SNR increased, the accuracy of the proposed algorithm increased.
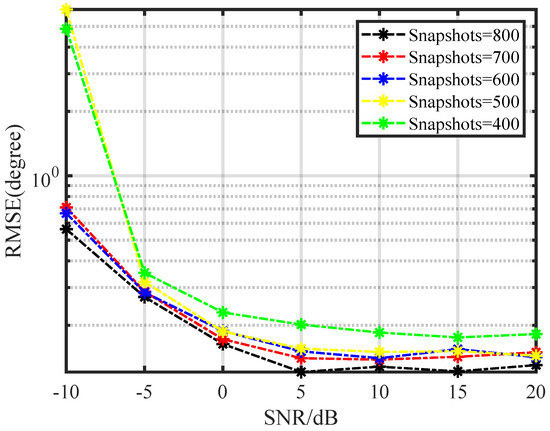
Figure 6.
Comparison of the RMSE of the proposed algorithms with different SNRs and snapshots.
Then, we compared the spectrum of different algorithms to further demonstrate the advantages and disadvantages of the algorithms. In this simulation, we set the scattering amplitudes of the sources to be the same. We first observed the estimation accuracy of the algorithm. From the three results, the proposed algorithm can achieve the estimation of the source angle accurately. Secondly, we observed the estimation of the source amplitudes by different algorithms. As shown in Figure 7, Figure 8 and Figure 9, the proposed algorithm had some bias in the estimation of the intensity of the source in the case of multiple sources. This issue is a common challenge in various algorithms.
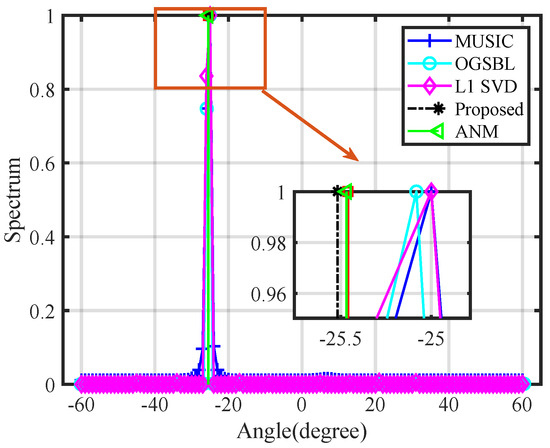
Figure 7.
The spectrum of one source.
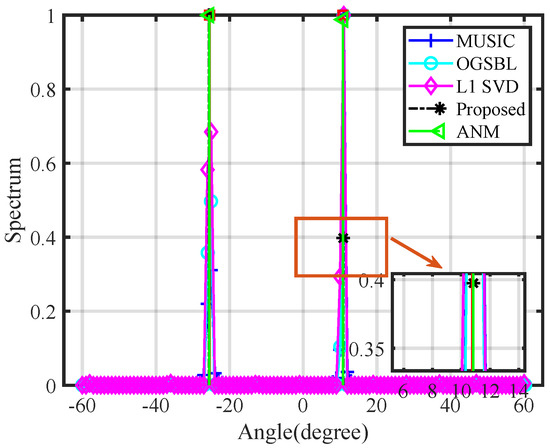
Figure 8.
The spectrum of two sources.
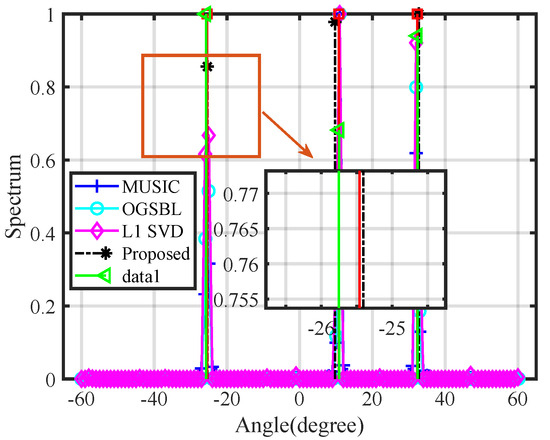
Figure 9.
The spectrum of three sources.
4.3. Computational Complexity Analysis
In this subsection, we analyze the computational time of different algorithms and count their RMSEs. It should be noted here that all experiments were performed on a CPU when we analyzed the computation time. As shown in Table 2, the computing times and RMSEs of different algorithms are shown for the case of 20 dB with 1000 snapshots. We combined the estimation accuracy of the algorithm and the computation time; only the accuracy of the ANM algorithm was similar to the proposed algorithm. However, the computation time of the ANM algorithm was 43.5-times that of the proposed algorithm under the same conditions. Therefore, combining the estimation accuracy, as well as the computation time, the algorithm proposed in this paper was optimal among the compared algorithms.

Table 2.
Operation time of different algorithms.
4.4. Adaptability of Different Network Architectures
In fact, DOA estimation can be realized using either ResNet or a CNN. ResNet can reduce the degradation of very deep network structures, which was the conclusion of [26]. A 34-layer residual network was used in this paper, and it is difficult to use a CNN with the same layers to compare with it here. Here, we utilized a CNN with fewer layers for DOA estimation, and the network structure is shown in Figure 10. And , denote the dimensions of the different output vectors, * denotes multiplication sign. As shown in Figure 11, we give the statistical results about the accuracy of DOA estimation of the CNN and ResNet. We trained the CNN with 80 epochs using the same training dataset. Network testing using the same test dataset yielded the following statistics. From the figure, under the same training epochs, the DOA estimation accuracies of the CNN and ResNet were basically the same. It was demonstrated that the UL framework proposed in this paper can be used in a variety of network structures.
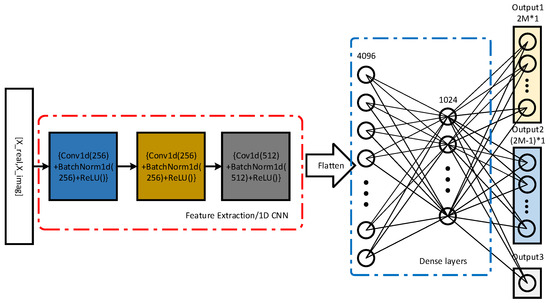
Figure 10.
The network structure of the CNN.
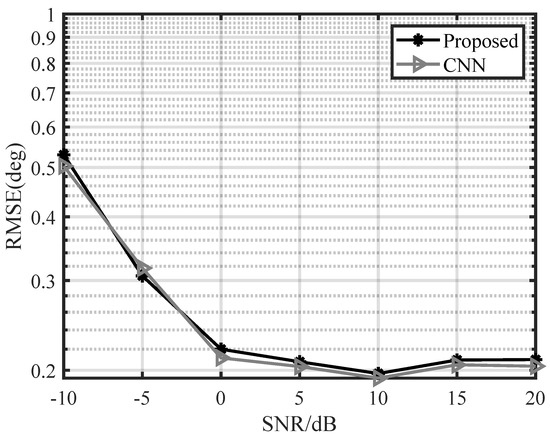
Figure 11.
Comparison of the RMSE of different network structures with different SNRs.
5. Conclusions
In this paper, we proposed an efficient DOA estimation algorithm for the case of sparse sensor arrays. We summarized the shortcomings of model-driven, as well as data-driven class algorithms. An unsupervised learning scheme based on atomic norm theory was proposed to address the problems of the high computational complexity of traditional algorithms and the difficulty of obtaining labeled datasets. Then, we compared various algorithms in terms of both estimation accuracy and computation complexity. From the simulation results, the proposed algorithm has certain advantages over other algorithms in terms of accuracy and computational complexity. Finally, it was also demonstrated that the unsupervised learning framework proposed in this paper can be applied in a variety of network structures.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.G. and H.M.; methodology, S.G.; writing, review and editing, H.M., H.L., J.Y., and Y.Y. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The network was implemented in Pytorch; the operating system was Windows running on an Intel(R) Xeon(R) CPU E5-2697 v4 @2.30GHz CPU and with an NVIDA GeForce RTX 3080 GPU. It should be noted here that all experiments were performed on the CPU when we analyzed the computation time.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Huang, Q.; Fang, W. A Deep Learning Method for DOA Estimation with Covariance Matrices in Reverberant Environments. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 4278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Wu, S.; Wu, M.; Yuan, N. Unsupervised learning strategy for direction-of-arrival estimation network. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2021, 28, 1450–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Zhang, Y.D.; Chen, T. DOA estimation using compressed sparse array. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2018, 66, 4133–4146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, R. Multiple emitter location and signal parameter estimation. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 1986, 34, 276–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallet, P.; Mestre, X.; Loubaton, P. Performance analysis of an improved MUSIC DoA estimator. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2015, 63, 6407–6422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Gershman, A.B. A generalized ESPRIT approach to direction-of-arrival estimation. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2005, 12, 254–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haardt, M.; Nossek, J.A. Unitary ESPRIT: How to obtain increased estimation accuracy with a reduced computational burden. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 1995, 43, 1232–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, G.; Chen, B.; Yang, M. Unitary ESPRIT algorithm for bistatic MIMO radar. Electron. Lett. 2012, 48, 179–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhang, T.; Li, J.; Chen, X. Joint Sensor Failure Detection and Corrupted Covariance Matrix Recovery in Bistatic MIMO Radar With Impaired Arrays. IEEE Sens. J. 2019, 19, 5834–5842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.; Liu, J.; Xie, M.; Zhu, J. Direction-of-Arrival Tracking via Low-Rank Plus Sparse Matrix Decomposition. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2015, 14, 1302–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A. A Bayesian Sparse-Plus-Low-Rank Matrix Decomposition Method for Direction-of-Arrival Tracking. IEEE Sens. J. 2017, 17, 4894–4902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Gu, Y.; So, H.C. DOA Estimation in Impulsive Noise via Low-Rank Matrix Approximation and Weakly Convex Optimization. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2019, 55, 3603–3616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donoho, D.L. Compressed sensing. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2006, 52, 1289–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malioutov, D.; Cetin, M.; Willsky, A.S. A sparse signal reconstruction perspective for source localization with sensor arrays. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2005, 53, 3010–3022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Xie, L.; Zhang, C. Off-grid direction of arrival estimation using sparse Bayesian inference. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2012, 61, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Cao, Z.; Chen, Z.; Wang, X. Off-Grid DOA Estimation Using Sparse Bayesian Learning in MIMO Radar With Unknown Mutual Coupling. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2019, 67, 208–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, G.; Bhaskar, B.N.; Shah, P.; Recht, B. Compressed sensing off the grid. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2013, 59, 7465–7490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Xie, L. On gridless sparse methods for line spectral estimation from complete and incomplete data. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2015, 63, 3139–3153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Yang, J.; Huang, H.; Song, Y.; Gui, G. Deep learning for super-resolution channel estimation and DOA estimation based massive MIMO system. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2018, 67, 8549–8560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, S.; Li, K.; Rum, S.N.B.M. Deep learning approach in DOA estimation: A systematic literature review. Mob. Inf. Syst. 2021, 2021, 6392875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, L.; Sun, Y.; Sun, L.; Ning, Z.; Rodrigues, J.J. Deep learning based autonomous vehicle super resolution DOA estimation for safety driving. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2020, 22, 4301–4315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kase, Y.; Nishimura, T.; Ohgane, T.; Ogawa, Y.; Kitayama, D.; Kishiyama, Y. DOA estimation of two targets with deep learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE 2018 15th Workshop on Positioning, Navigation and Communications (WPNC), Bremen, Germany, 25–26 October 2018; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papageorgiou, G.K.; Sellathurai, M.; Eldar, Y.C. Deep networks for direction-of-arrival estimation in low SNR. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2021, 69, 3714–3729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papageorgiou, G.K.; Sellathurai, M. Fast direction-of-arrival estimation of multiple targets using deep learning and sparse arrays. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Barcelona, Spain, 4–8 May 2020; pp. 4632–4636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Xie, L. On gridless sparse methods for multi-snapshot DOA estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Shanghai, China, 20–25 March 2016; pp. 3236–3240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016. pp. 770–778. [CrossRef]
- Fang, W.; Yu, D.; Wang, X.; Xi, Y.; Cao, Z.; Song, C.; Xu, Z. A deep learning based mutual coupling correction and DOA estimation algorithm. In Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Wireless Communications and Signal Processing (WCSP), Changsha, China, 20–22 October 2021. pp. 1–5. [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Tian, Y. DOA estimation of underwater acoustic signals based on deep learning. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Seminar on Artificial Intelligence, Networking and Information Technology (AINIT), Nanjing, China, 20–22 October 2021; pp. 221–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadzow, J.A.; Kim, Y.S.; Shiue, D.C. General direction-of-arrival estimation: A signal subspace approach. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 1989, 25, 31–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Zhu, W.P.; Yan, J. A Toeplitz covariance matrix reconstruction approach for direction-of-arrival estimation. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2017, 66, 8223–8237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Shen, M.; Guo, L.; Hu, X. A gridless DOA estimation algorithm based on unsupervised deep learning. Digit. Signal Process. 2023, 133, 103823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Xie, L. Exact joint sparse frequency recovery via optimization methods. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2016, 64, 5145–5157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candès, E.J.; Fernandez-Granda, C. Towards a mathematical theory of super-resolution. Commun. Pure Appl. Math. 2014, 67, 906–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kingma, D.P.; Ba, J. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.6980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, B.D.; Hari, K.S. Performance analysis of root-MUSIC. IEEE Trans. Acoust. Speech Signal Process. 1989, 37, 1939–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).