Outlier Denoising Using a Novel Statistics-Based Mask Strategy for Compressive Sensing
Abstract
1. Introduction
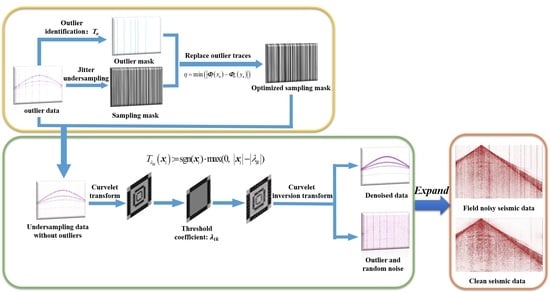
2. Methods
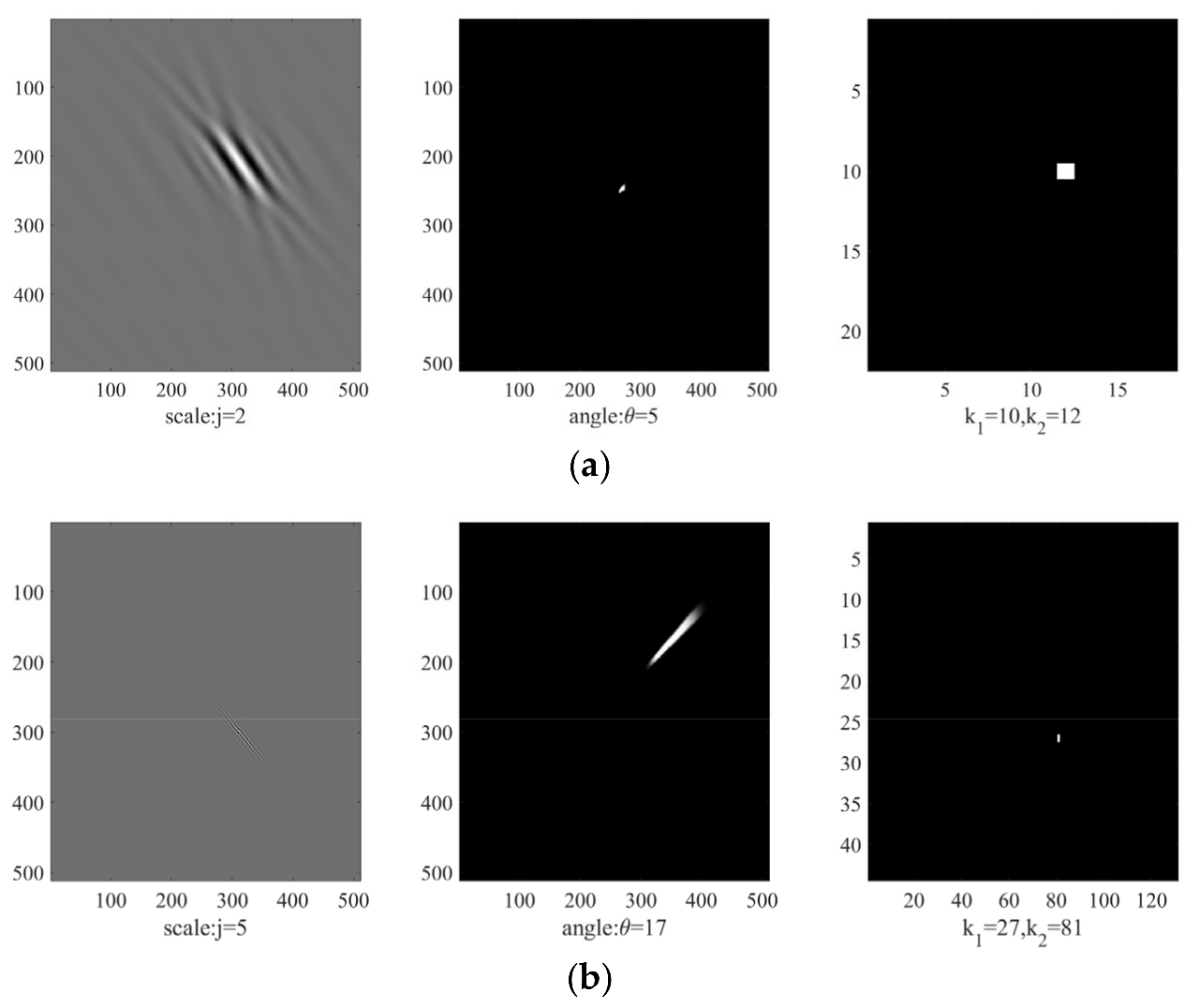
2.1. Review of CS Denoising Theory
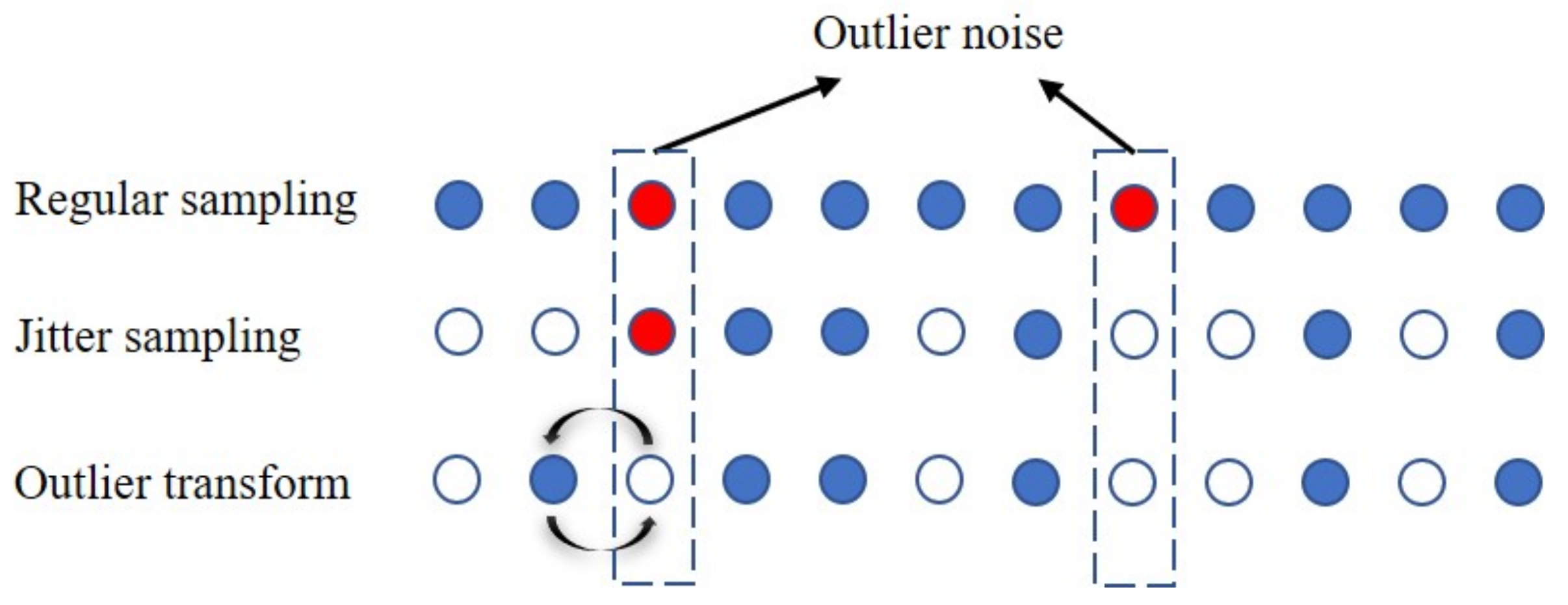
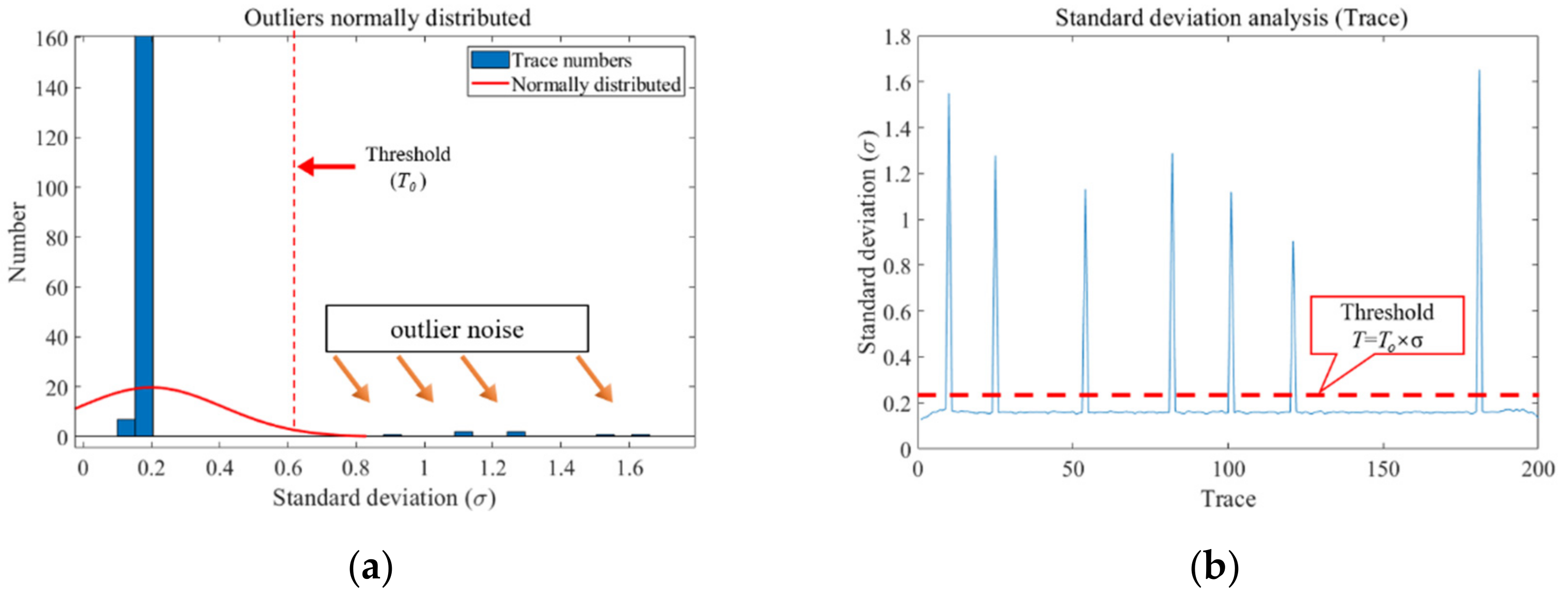
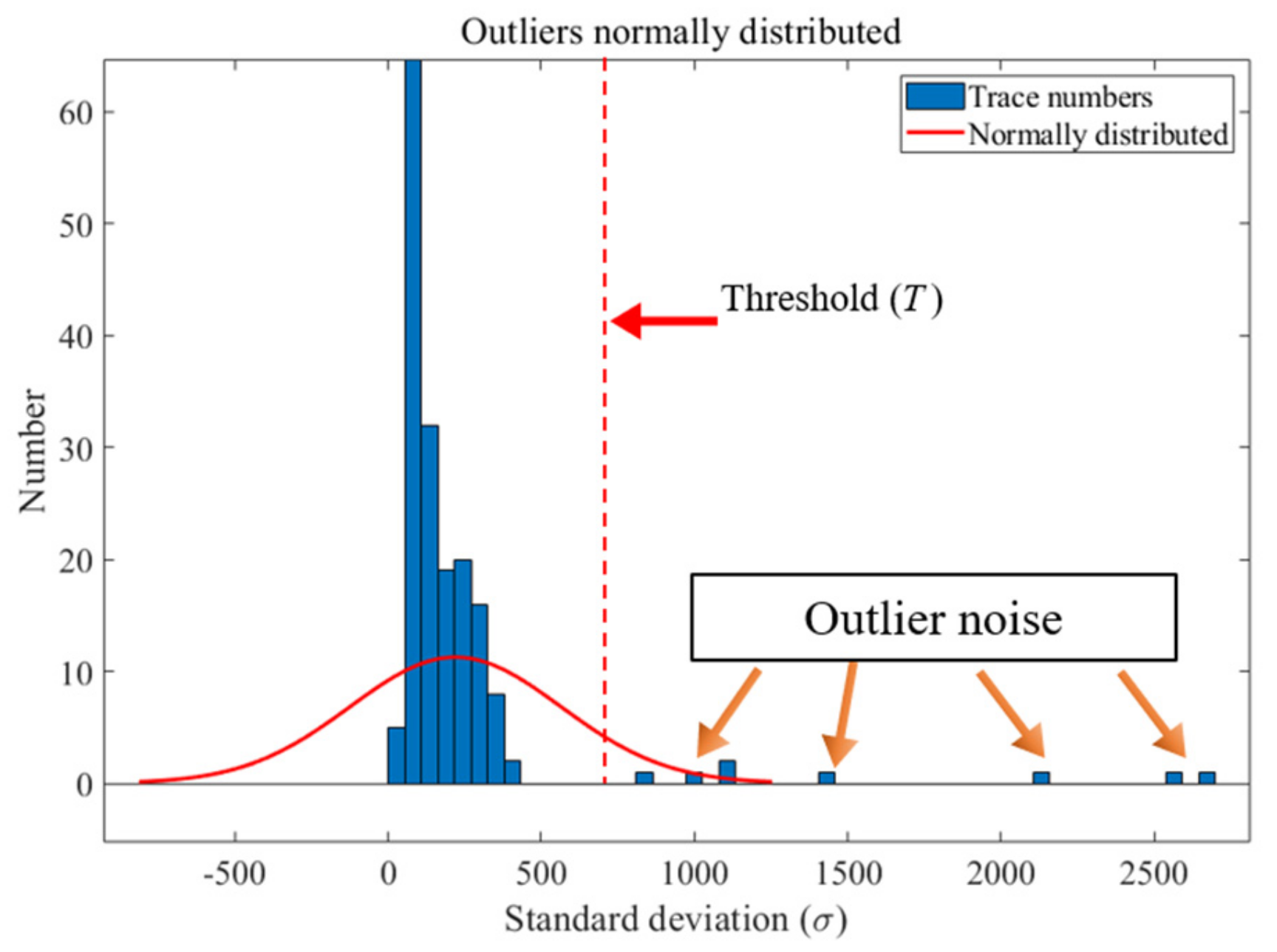
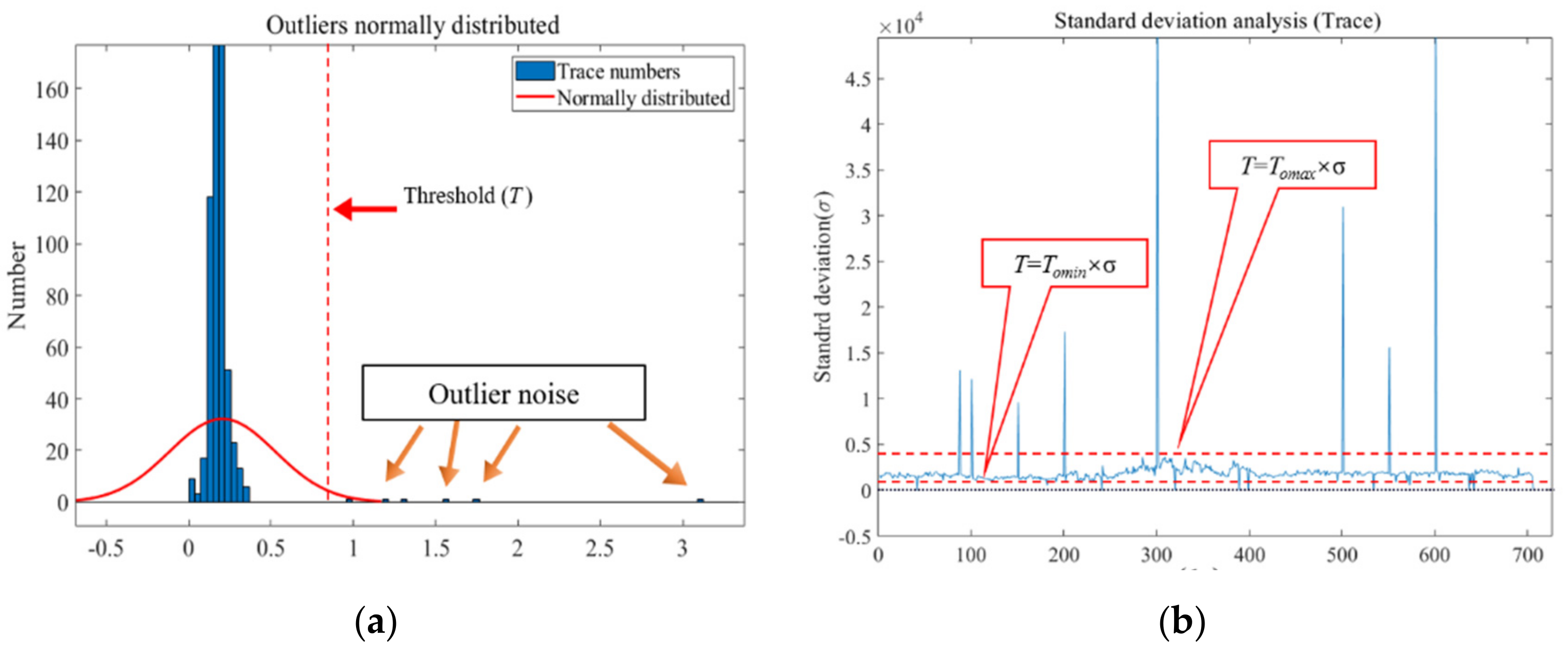
2.2. A Novel Statistics-Based Mask Function for Outlier Noise
2.3. CS Denoising Algorithm with the Proposed Mask
| Algorithm 1 CS denoise based on the CRSI method |
Input: measurement matrix Φtm, measurement data d, Output: signal estimation
|
3. Results
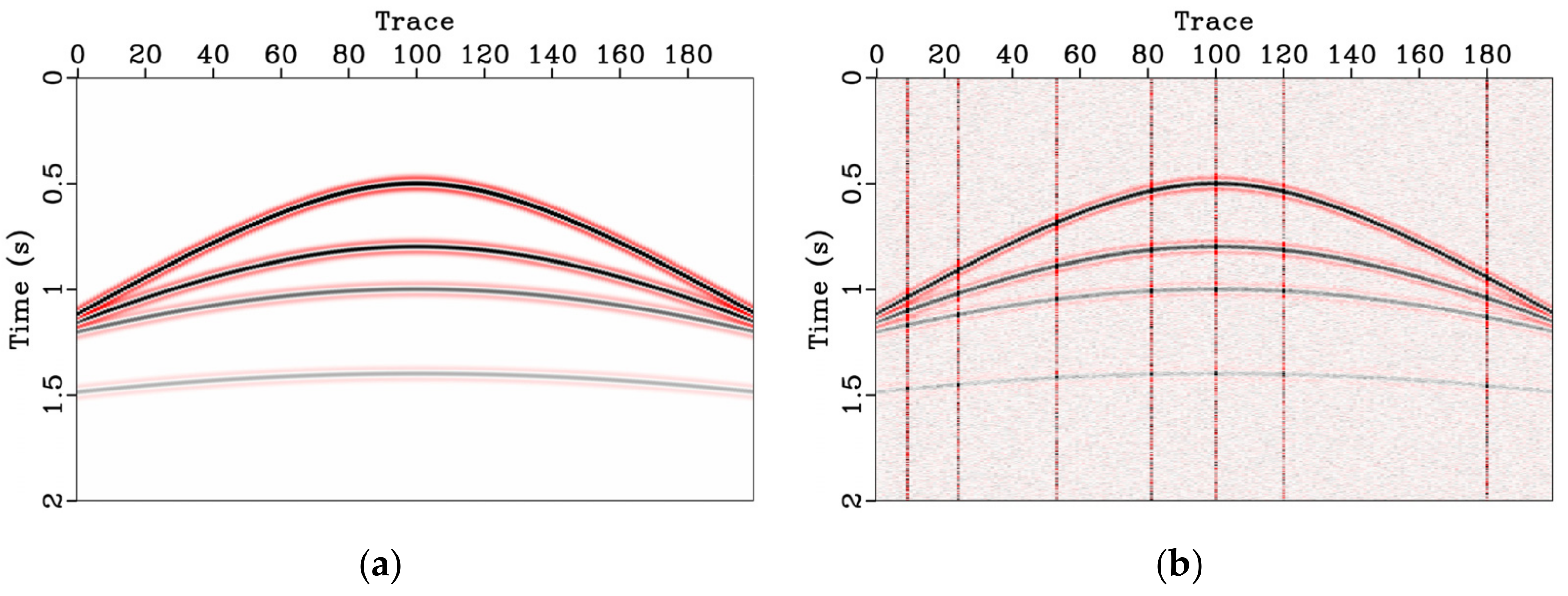
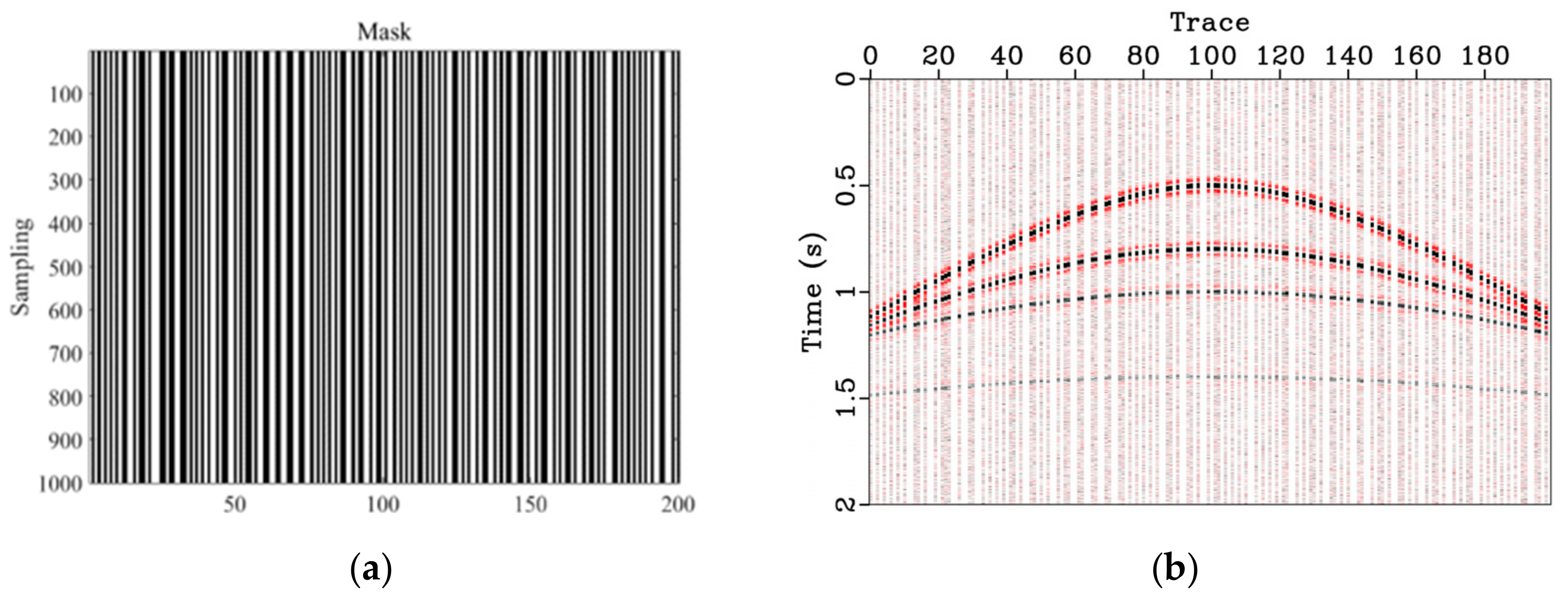
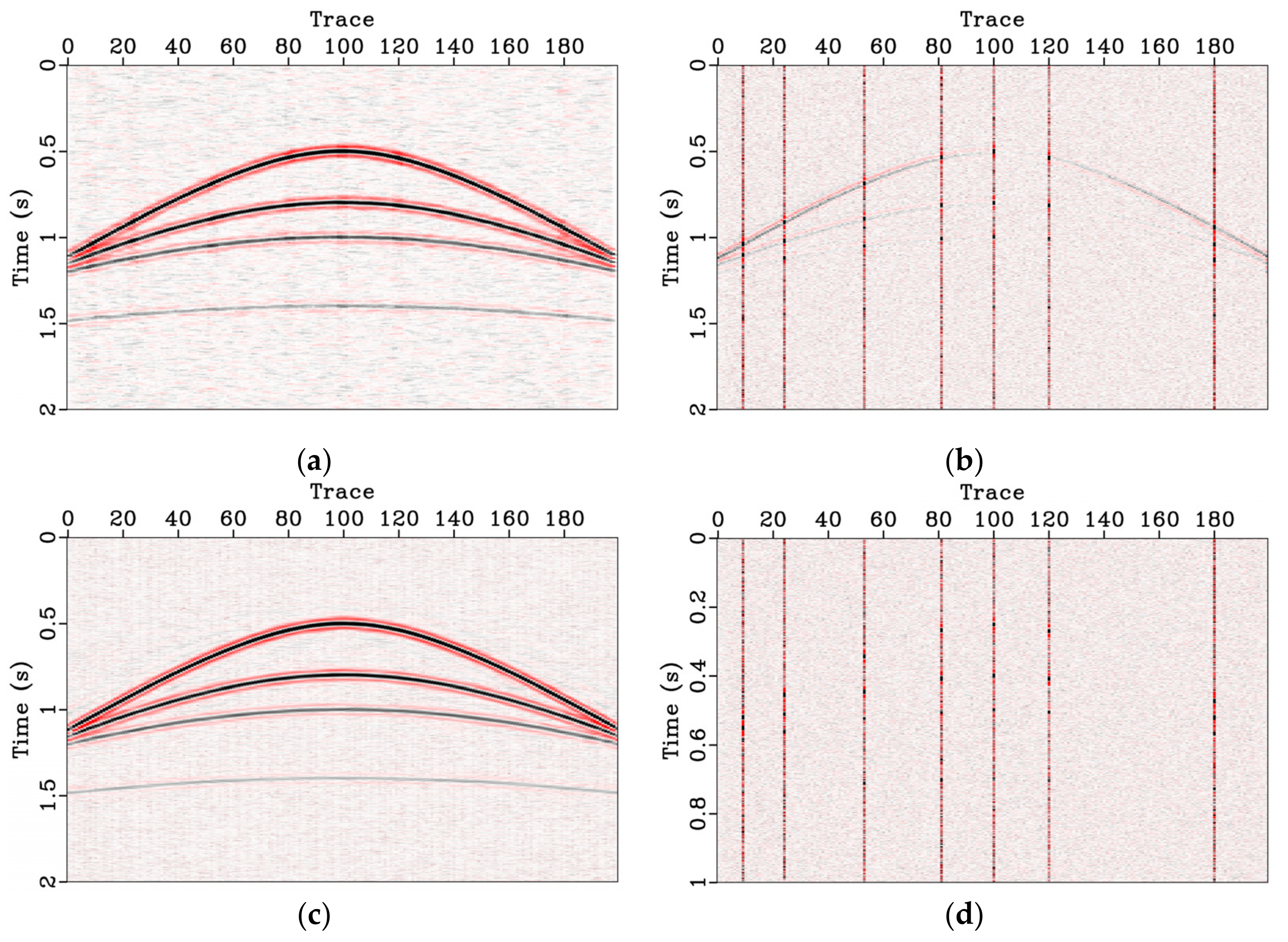
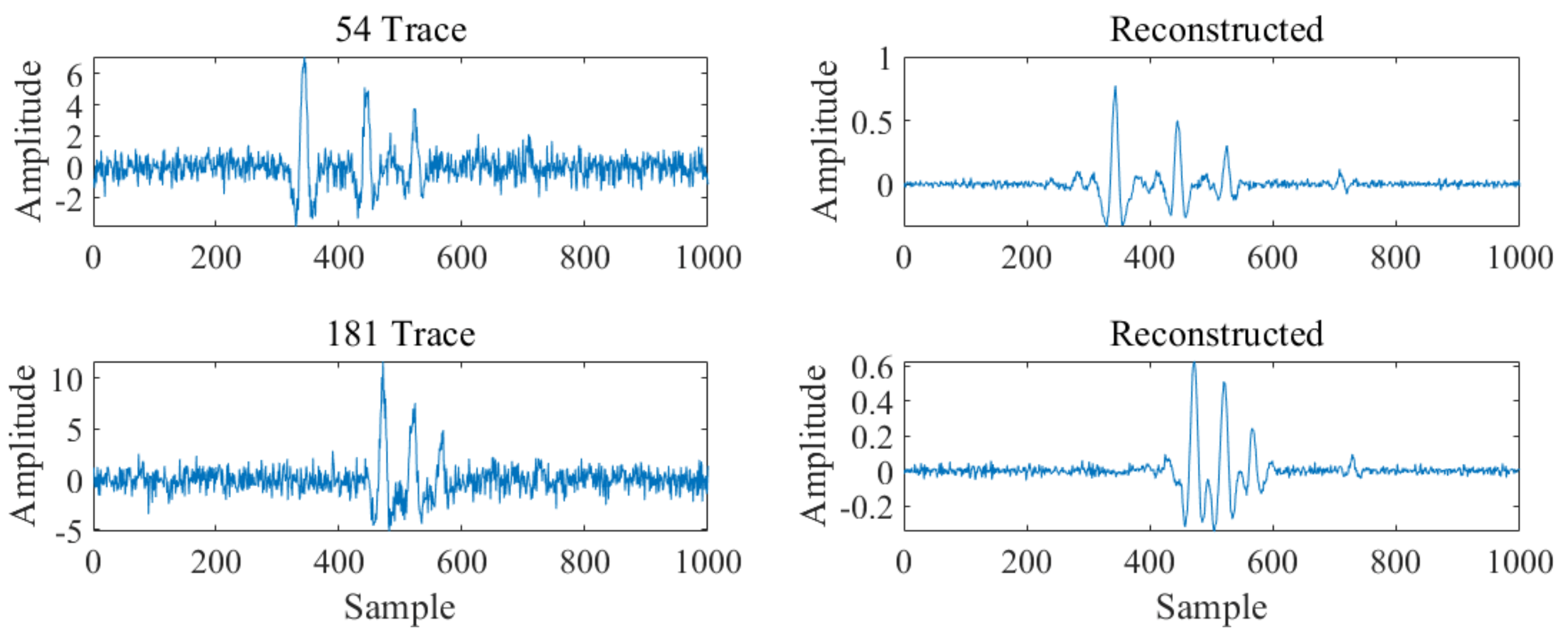
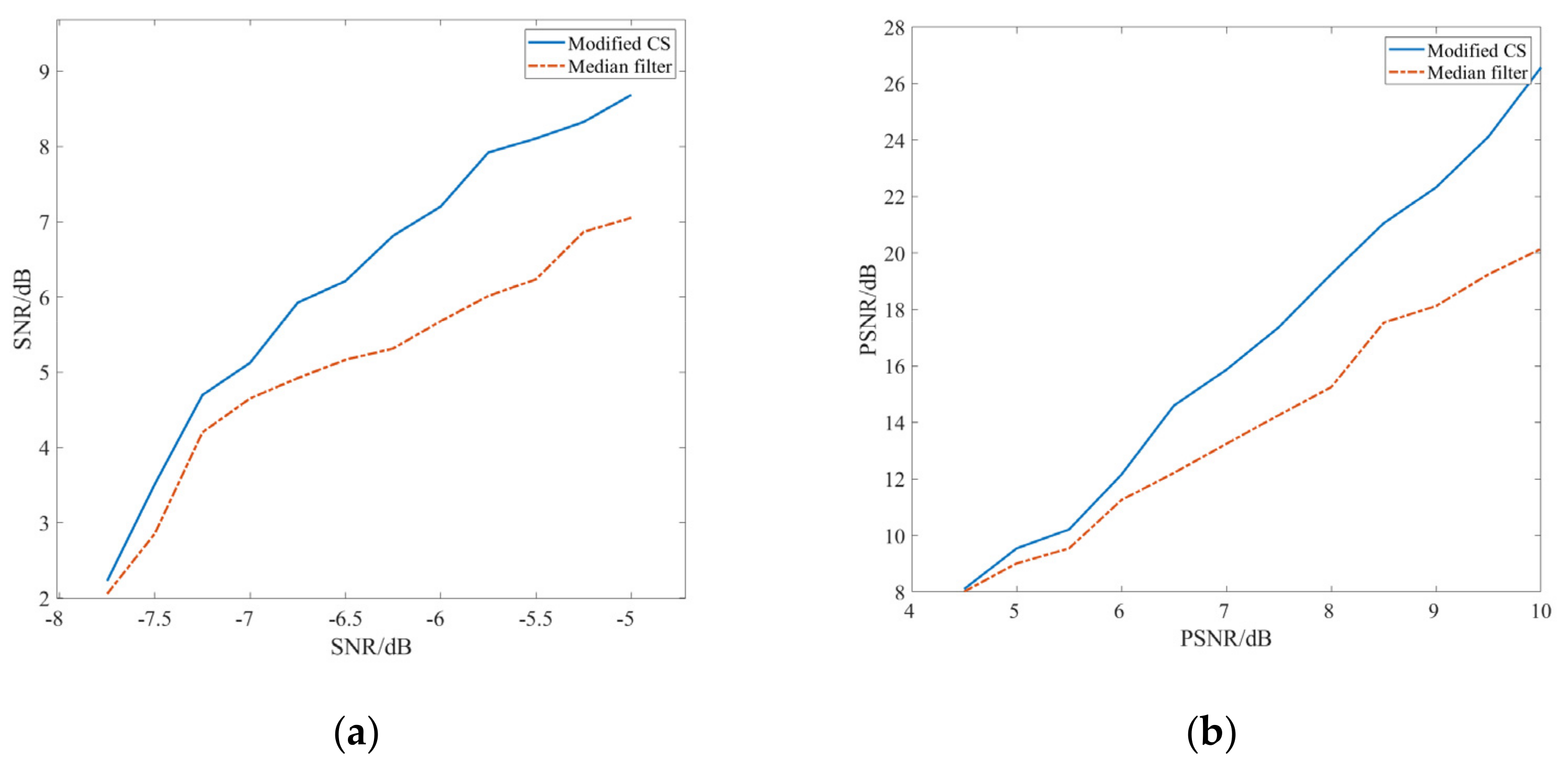
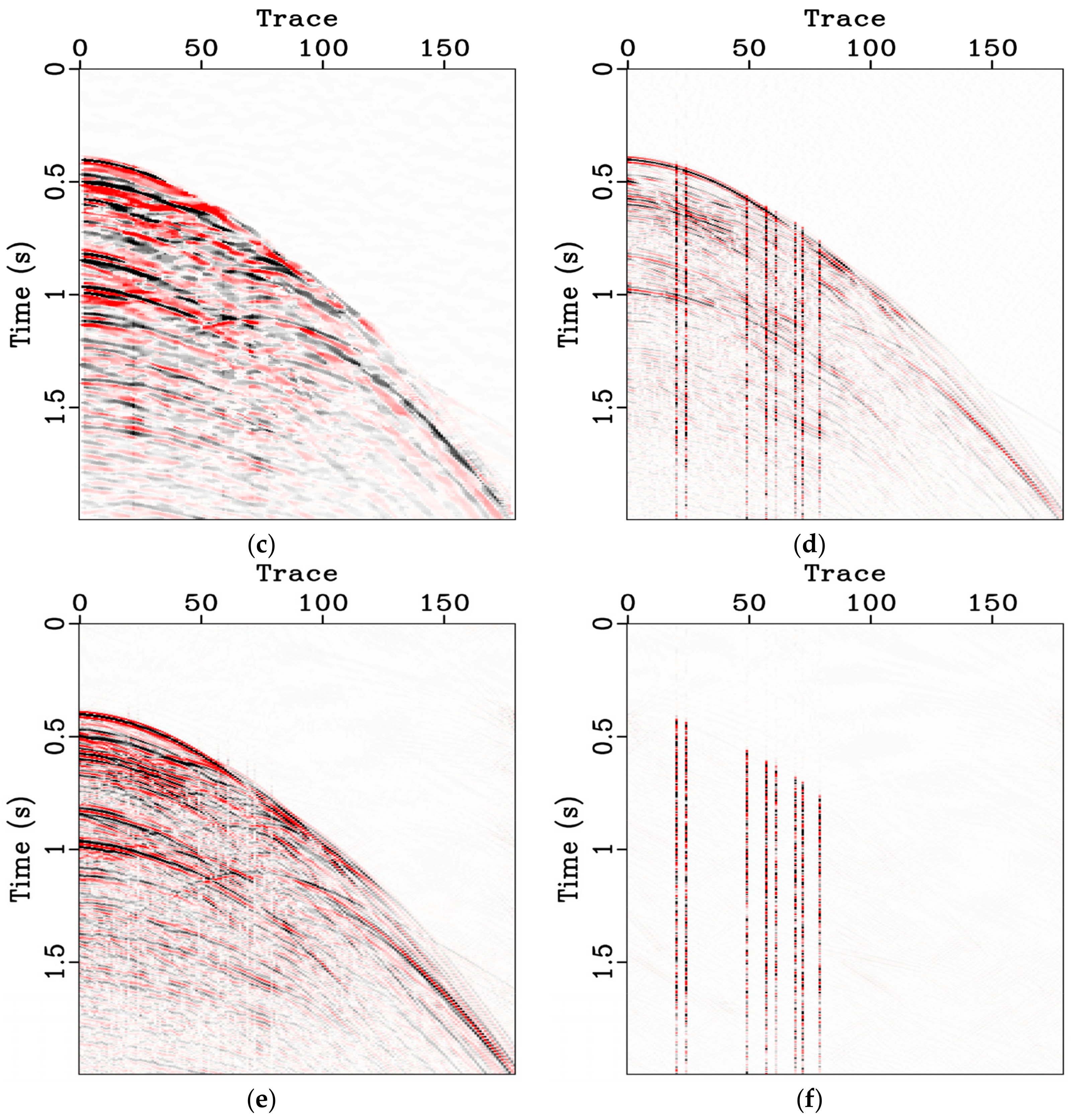
3.1. Synthetic Data
3.2. Marine Data
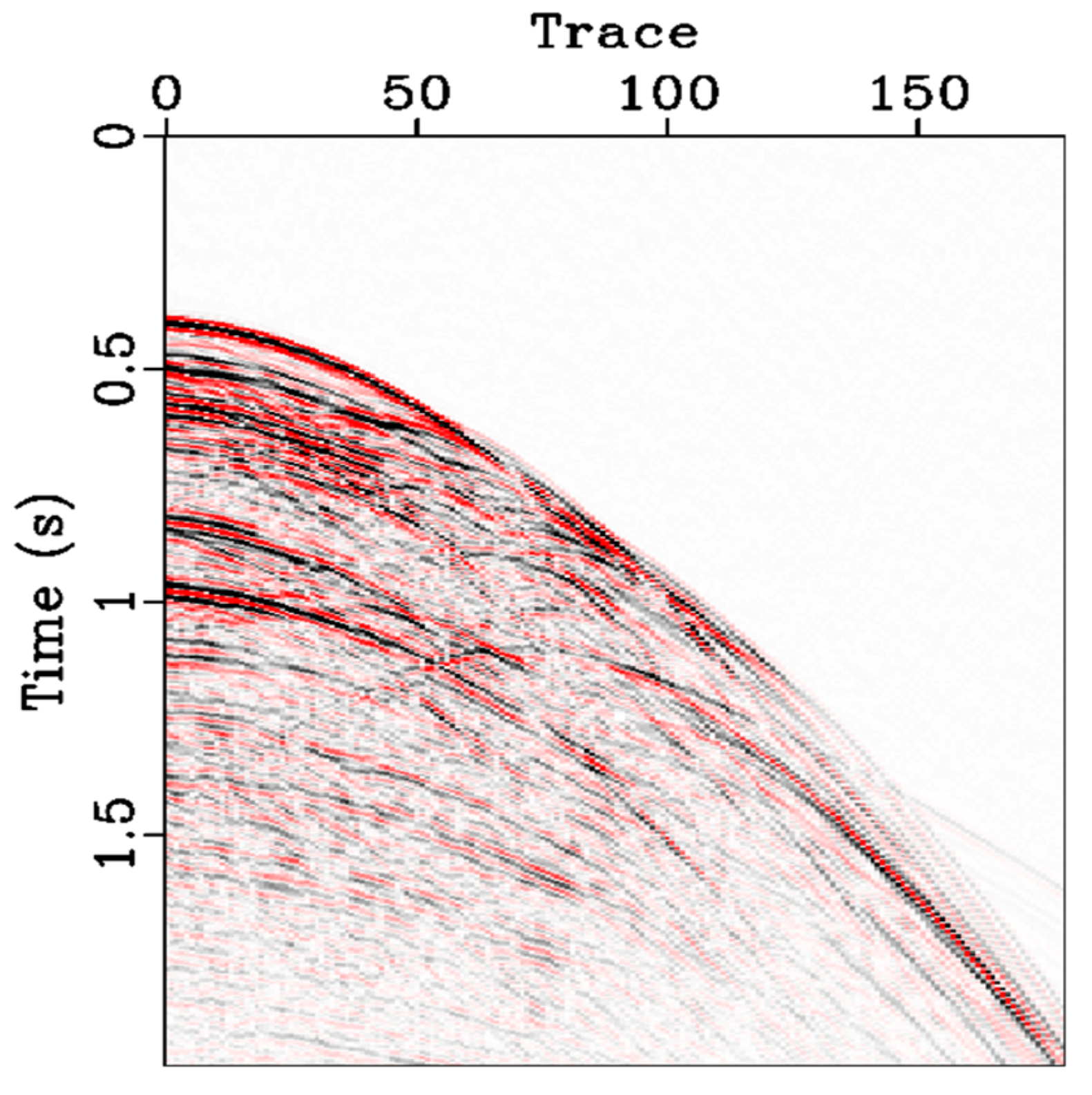
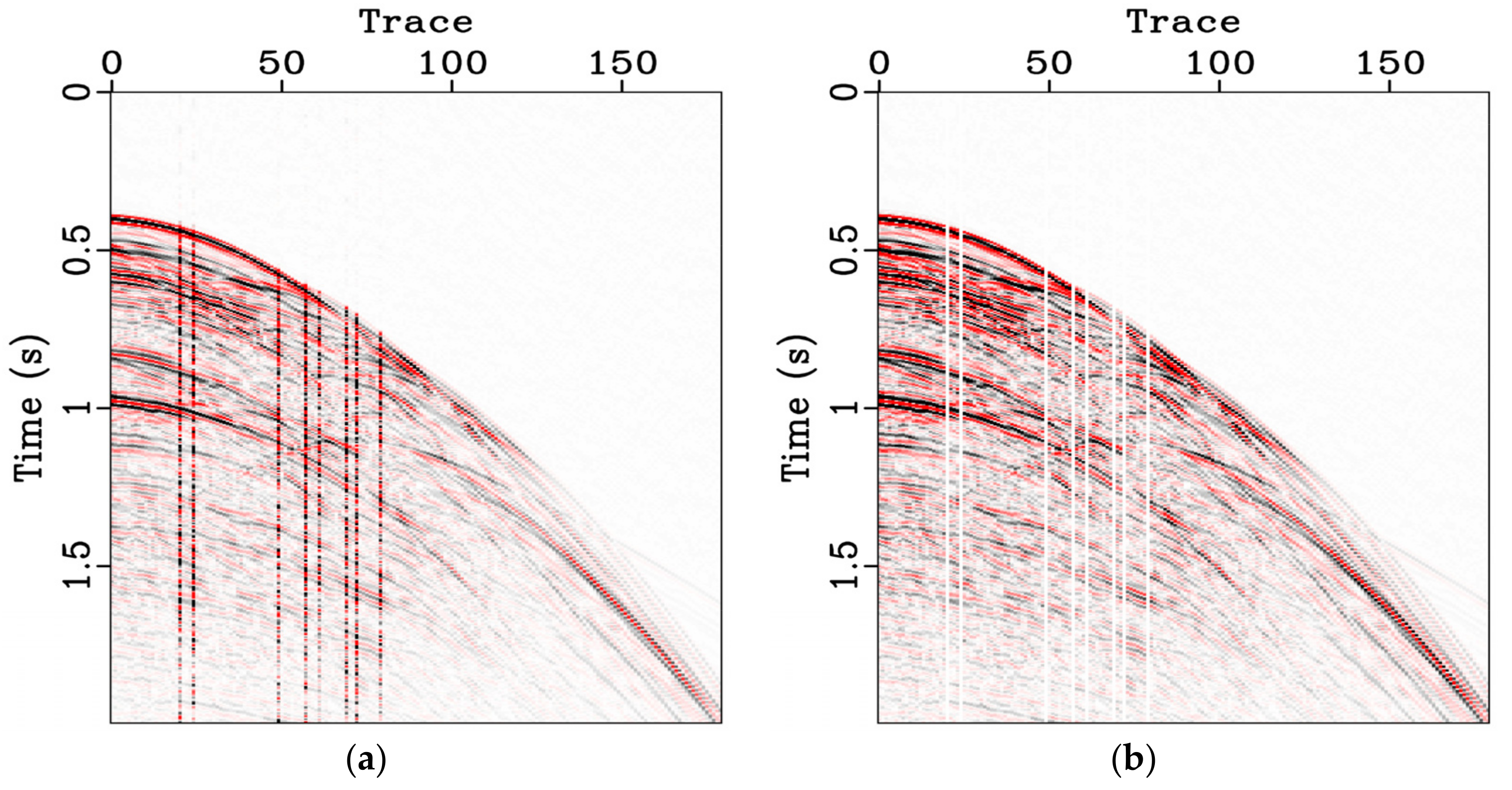
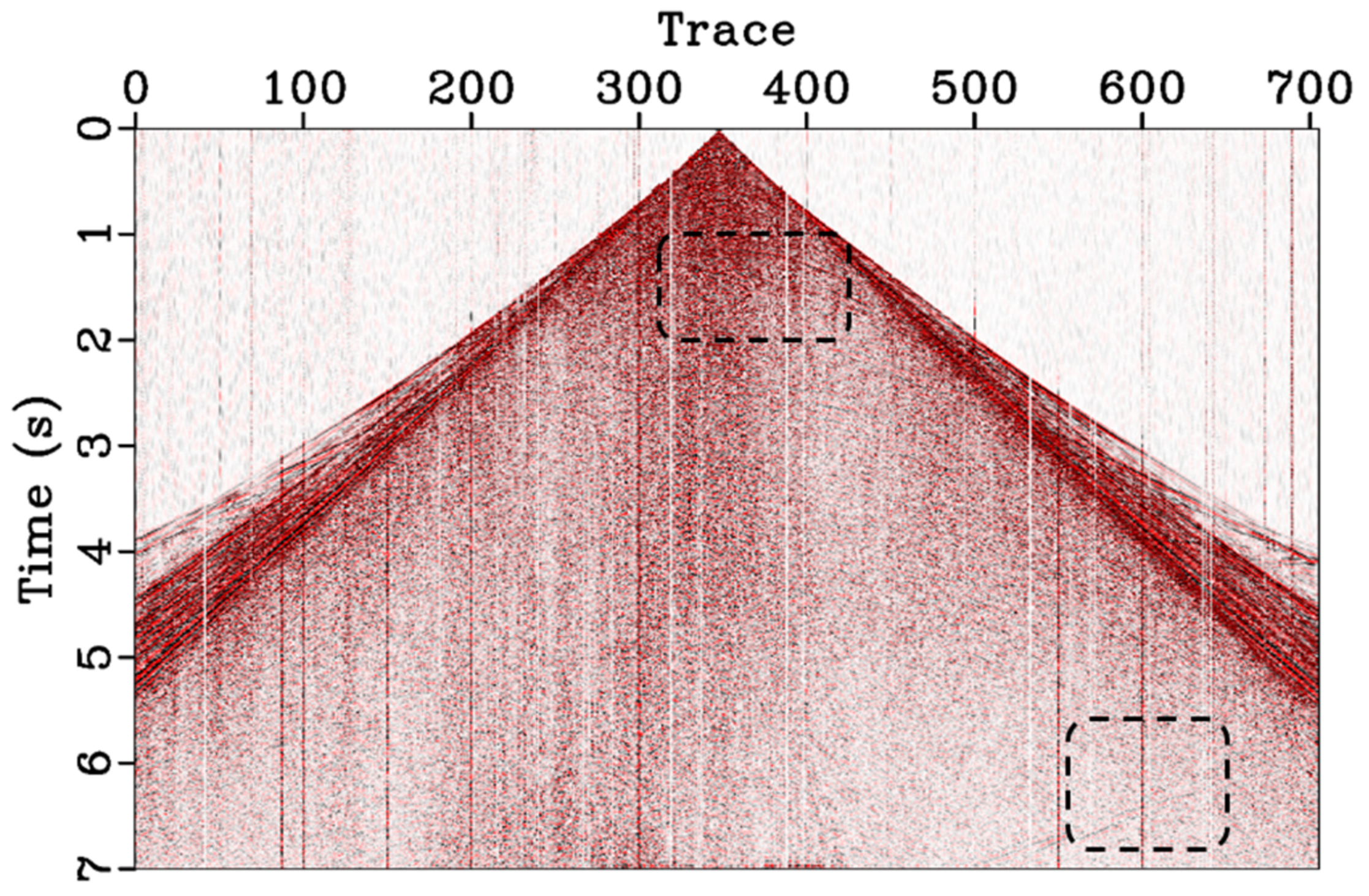
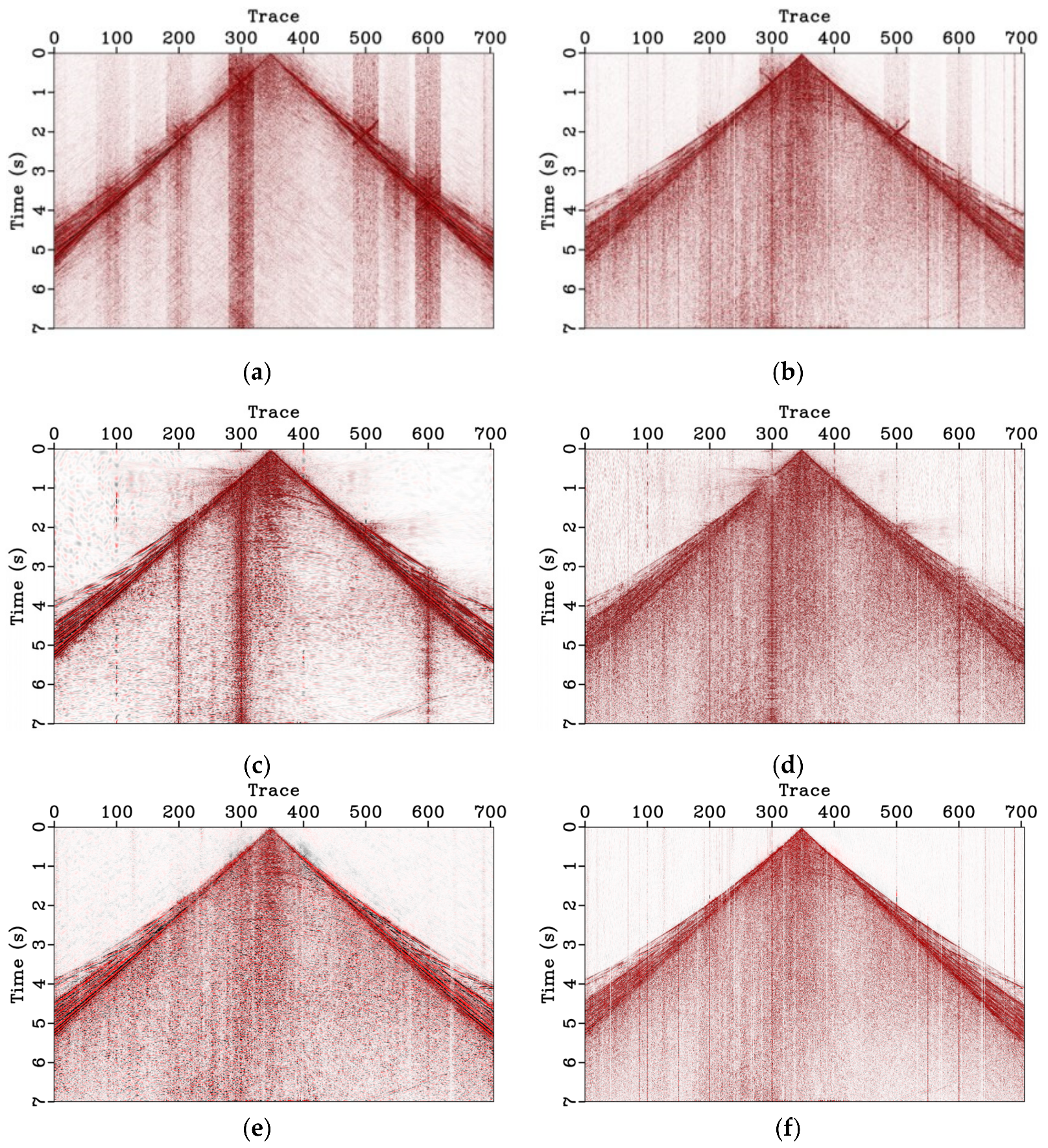
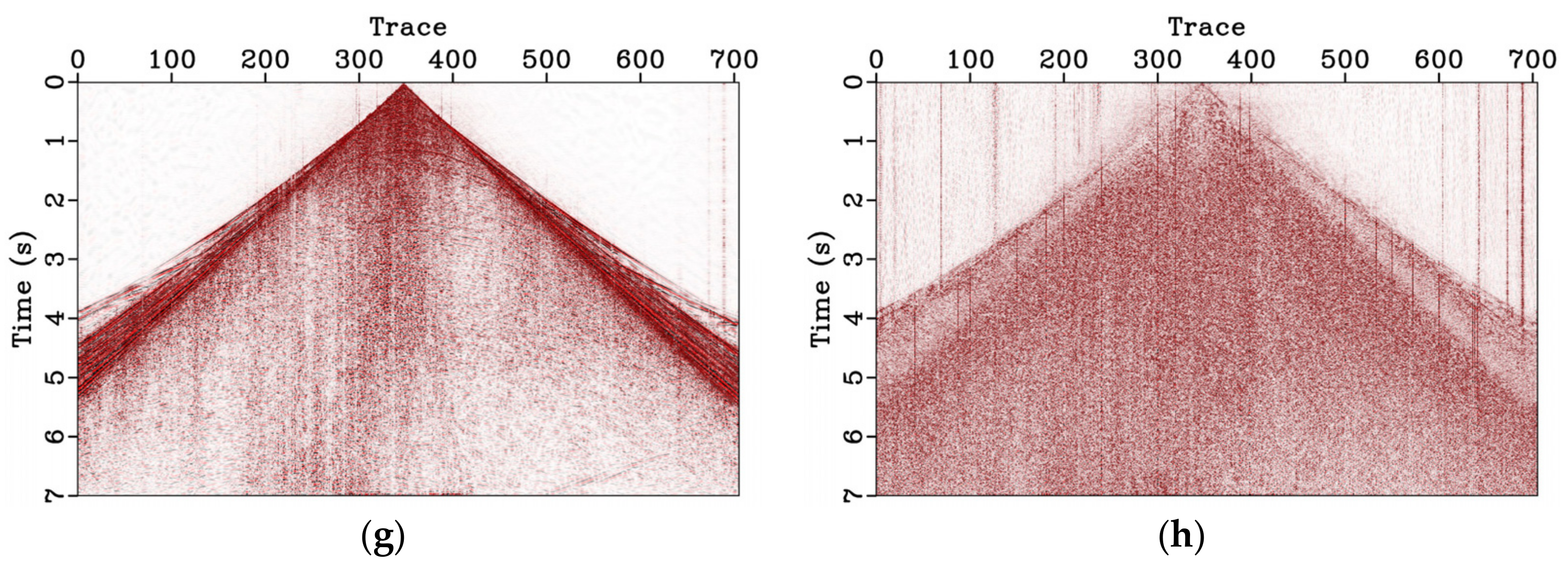
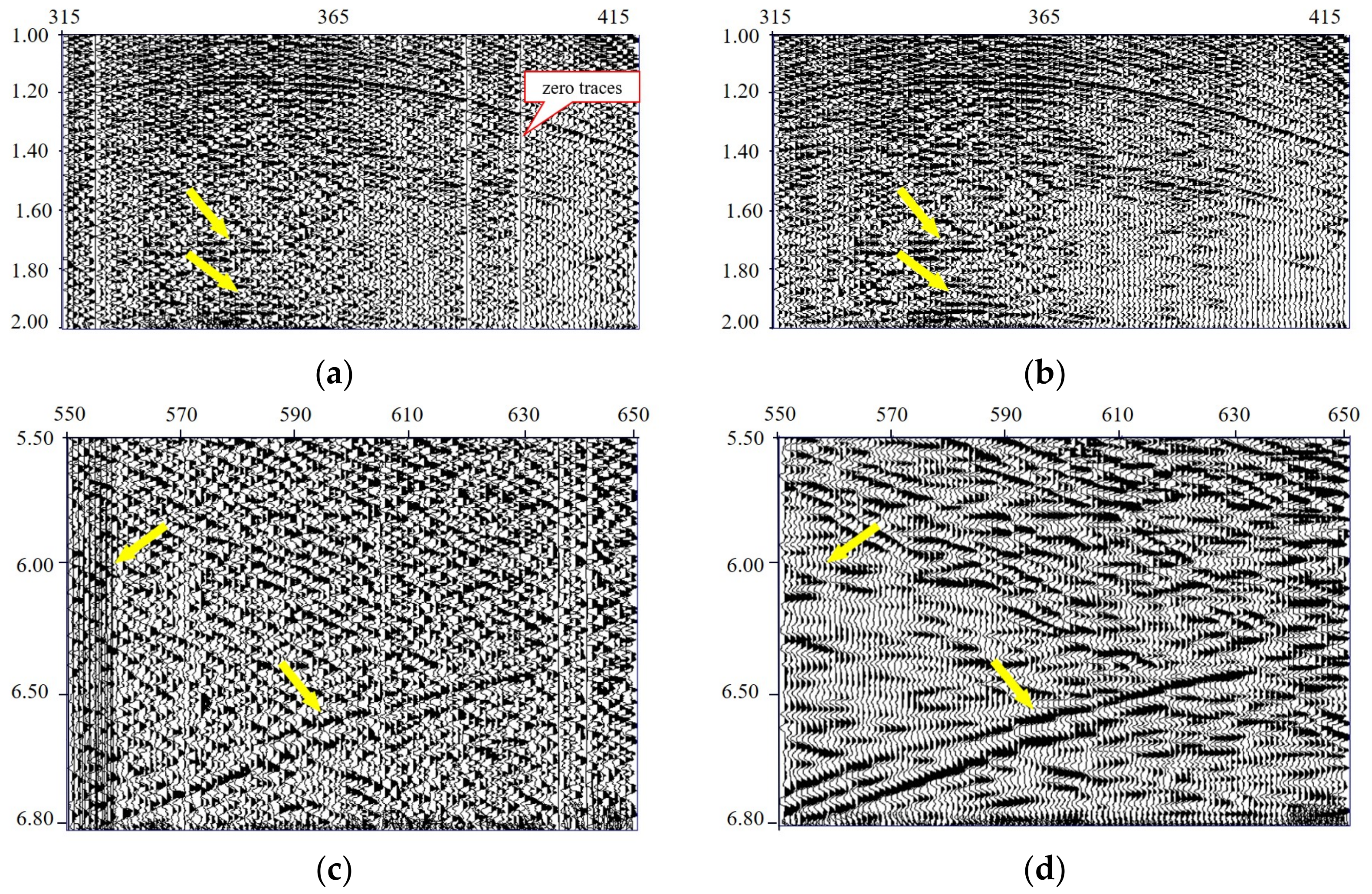
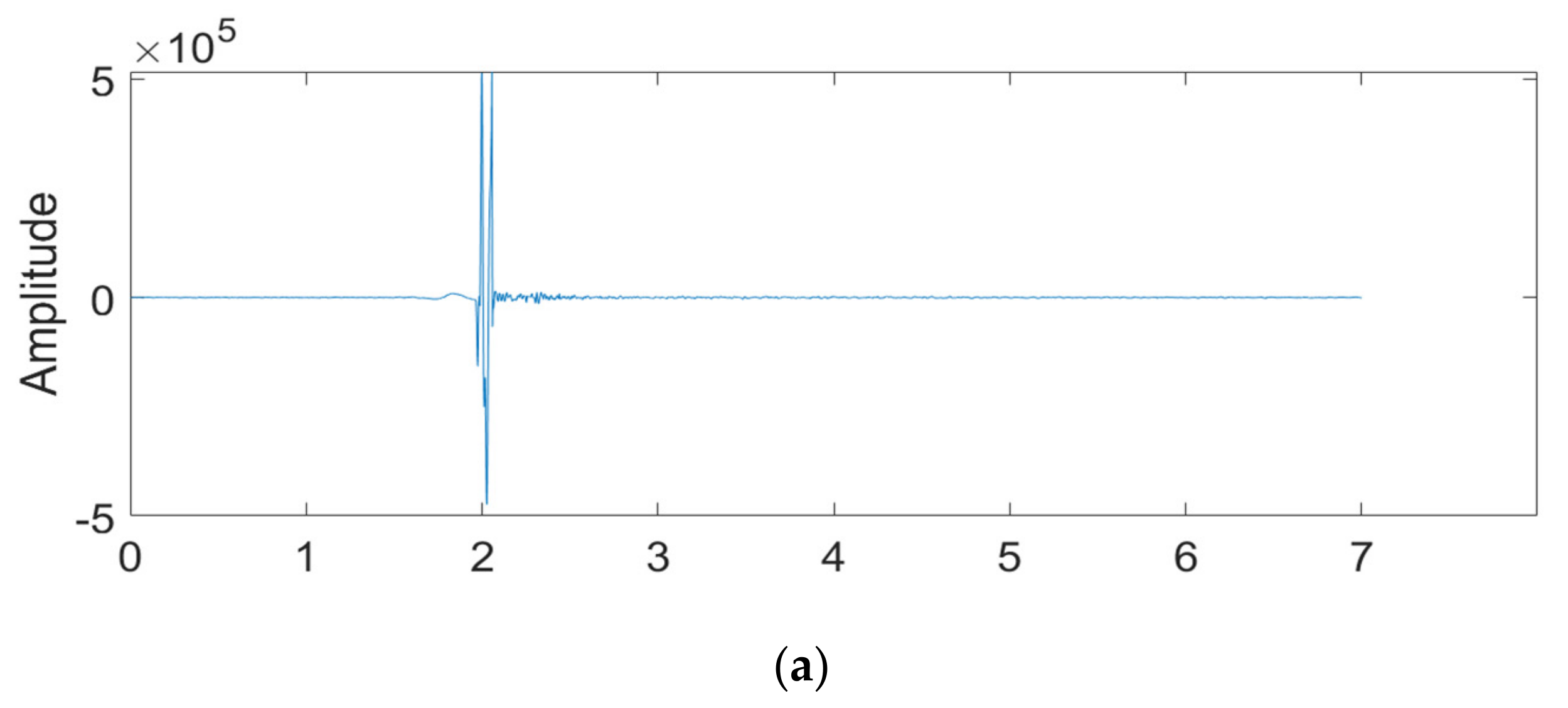
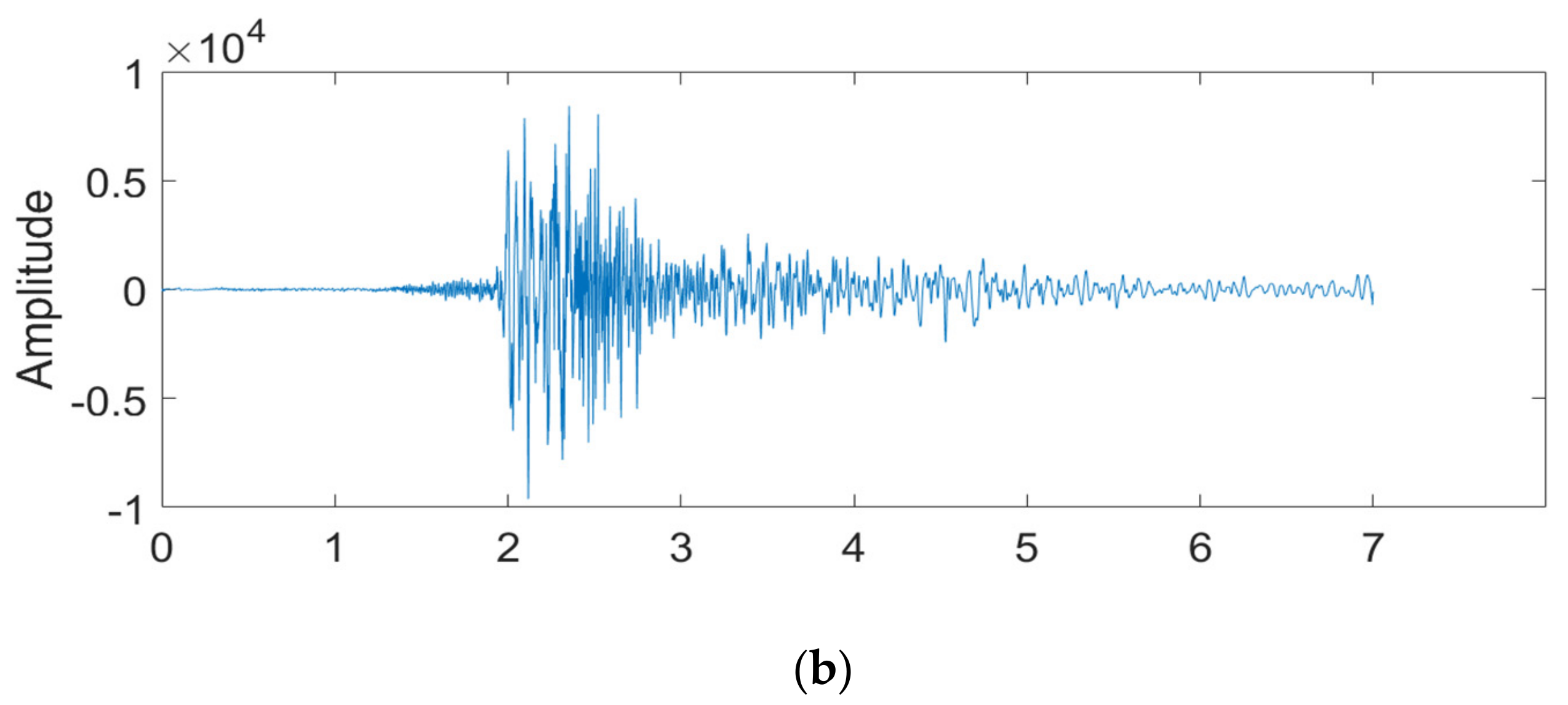
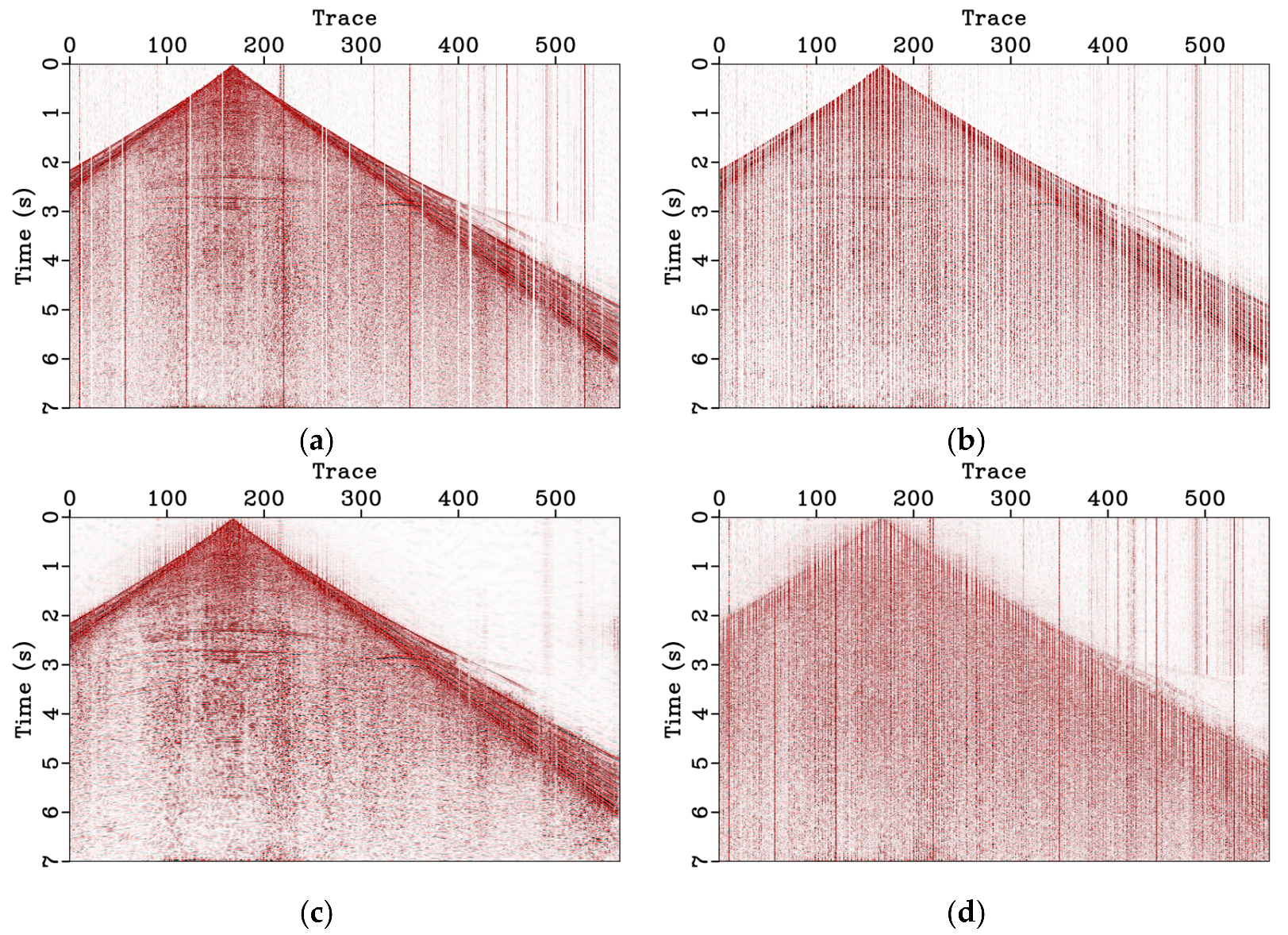
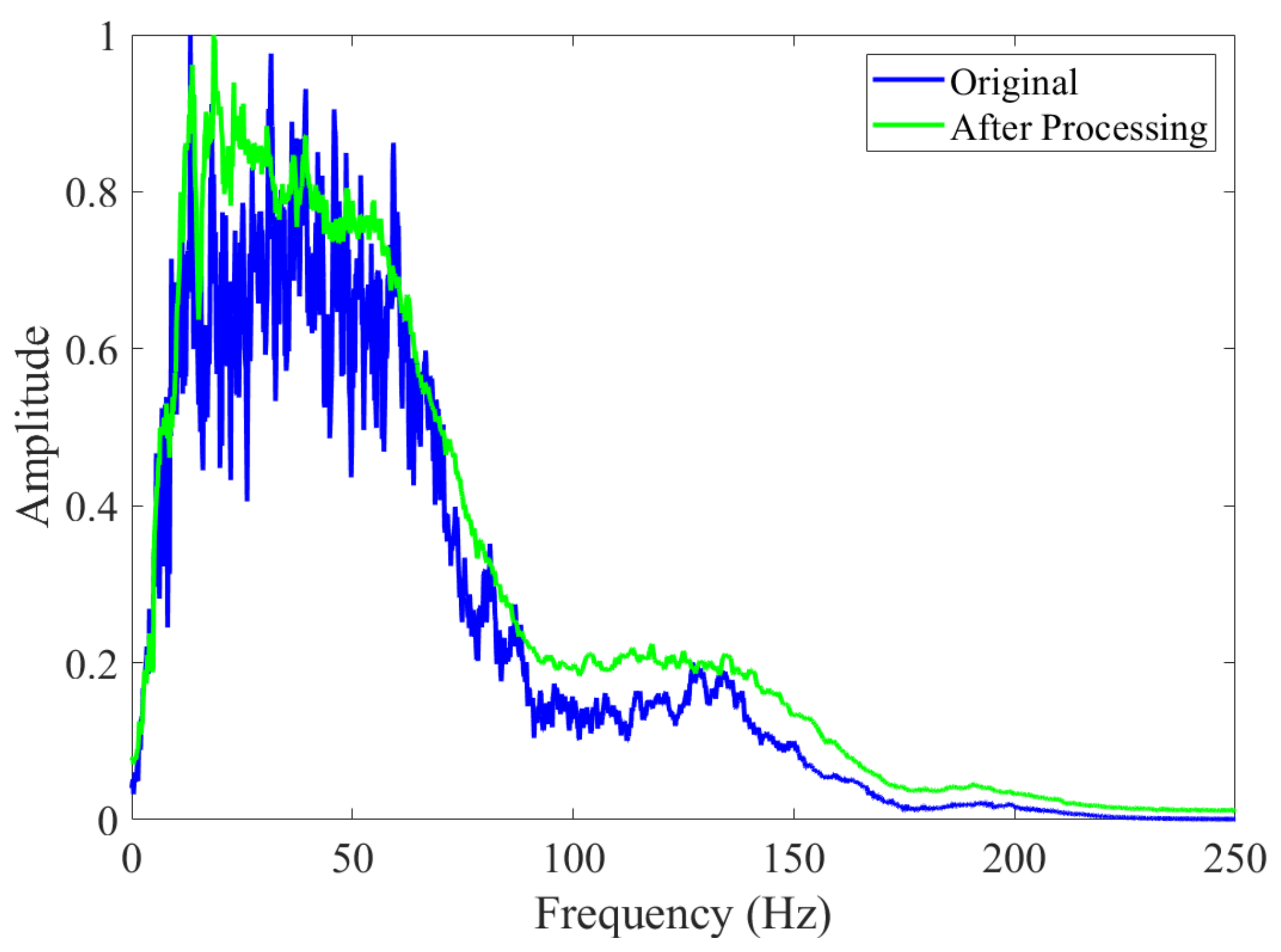
3.3. Land Field Data
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yu, Z.; Abma, R.; Etgen, J.; Sullivan, C. Attenuation of noise and simultaneous source interference using wavelet denoising. Geophysics 2017, 82, V179–V190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.X.; Li, Y.; Yang, B.J. Denoising of seismic data in desert environment based on a variational mode decomposition and a convolutional neural network. Geophys. J. Int. 2020, 221, 1211–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, C.; Wang, D. A 1D time-varying median filter for seismic random, spike-like noise elimination. Geophysics 2009, 74, V17–V24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonar, D.; Sacchi, M. Denoising seismic data using the nonlocal means algorithm. Geophysics 2012, 77, A5–A8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abma, R.; Claerbout, J. Lateral prediction for noise attenuation by tx and fx techniques. Geophysics 1995, 60, 1887–1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacchi, M.D. FX singular spectrum analysis. Cspg Cseg Cwls Conv. 2009, 392–395. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, N.; Liu, C. Adaptive prediction filtering in txy domain for random noise attenuation using regularized nonstationary autoregression. Geophysics 2015, 80, V13–V21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Liu, Y.; Liu, C. Seismic data interpolation using streaming prediction filter in the frequency domain. Geophys. J. Int. 2022, 229, 370–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candes, E.; Demanet, L.; Donoho, D.; Ying, L. Fast discrete curvelet transforms. Multiscale Model. Simul. 2006, 5, 861–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Plonka, G. The curvelet transform. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2010, 27, 118–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, D.; Jin, Z.; Chen, X.; Zu, S. Simultaneous denoising and reconstruction of 5-D seismic data via damped rank-reduction method. Geophys. J. Int. 2016, 206, 1695–1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, B. Separation and Reconstruction of Nonuniform Simultaneous Source Data via a Robust and Sparse Radon Transform. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2022, 19, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oropeza, V.; Sacchi, M. Simultaneous seismic data denoising and reconstruction via multichannel singular spectrum analysis. Geophysics 2011, 76, V25–V32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, R.; Guo, Y.; Carozzi, F.; Sacchi, M.D. Simultaneous deblending and source reconstruction for compressive 3D simultaneous-source acquisition data via interpolated multichannel singular spectrum analysis. Geophysics 2022, 87, V559–V570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, N.E.; Shen, Z.; Long, S.R.; Wu, M.C.; Shih, H.H.; Zheng, Q.; Yen, N.C.; Tung, C.C.; Liu, H.H. The empirical mode decomposition and the Hilbert spectrum for nonlinear and non-stationary time series analysis. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 1998, 454, 903–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Huang, N.E. Ensemble empirical mode decomposition: A noise-assisted data analysis method. Adv. Adapt. Data Anal. 2009, 1, 1–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, J.R.; Shieh, J.S.; Huang, N.E. Complementary ensemble empirical mode decomposition: A novel noise enhanced data analysis method. Adv. Adapt. Data Anal. 2010, 2, 135–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Ma, J. Random noise attenuation by fx empirical-mode decomposition predictive filtering. Geophysics 2014, 79, V81–V91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; van der Baan, M. Microseismic and seismic denoising via ensemble empirical mode decomposition and adaptive thresholding. Geophysics 2015, 80, KS69–KS80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Li, Z.; Li, Z.; Li, Q.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J. A noise attenuation method for weak seismic signals based on compressed sensing and CEEMD. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 71951–71964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Ma, J.; Wang, W. Deep learning for denoising. Geophysics 2019, 84, V333–V350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, A.; Feller, C. Seismic data denoising and deblending using deep learning. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1907.01497. [Google Scholar]
- Saad, O.M.; Chen, Y. Deep denoising autoencoder for seismic random noise attenuation. Geophysics 2020, 85, V367–V376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zu, S.; Cao, J.; Fomel, S.; Yang, L.; Saad, O.M. Robust local slope estimation by deep learning. Geophys. Prospect. 2022, 70, 847–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, C.; Wu, B.; Liu, N.; Zhu, X.; Ren, H. Deep learning prior model for unsupervised seismic data random noise attenuation. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2021, 19, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkins, D.M. Identification of Outliers; Chapman and Hall: London, UK, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Osborne, J.W.; Overbay, A. The power of outliers (and why researchers should always check for them). Prac. Assess. Res. Eval. 2004, 9, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Gemmeke, J.F.; Van Hamme, H.; Cranen, B.; Boves, L. Compressive sensing for missing data imputation in noise robust speech recognition. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Signal Process. 2010, 4, 272–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholami, A.; Sacchi, M.D. Robust Sparse Deconvolution in the Presence of Outliers. In Proceedings of the 73rd EAGE Conference and Exhibition incorporating SPE EUROPEC 2011, Vienna, Austria, 23–27 May 2011; European Association of Geoscientists & Engineers: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011; p. cp-238-00250. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Q.; Du, Q.; Gong, X.; Chen, Y. Signal-preserving erratic noise attenuation via iterative robust sparsity-promoting filter. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 56, 3547–3560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, W.; Tsingas, C.; Almubarak, M.S. Local outlier factor as part of a workflow for detecting and attenuating blending noise in simultaneously acquired data. Geophys. Prospect. 2020, 68, 1523–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Oboué, Y.A.S.I.; Chen, Y. Retrieving useful signals from highly corrupted erratic noise using robust residual dictionary learning. Geophysics 2023, 88, WA55–WA64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donoho, D.L. Compressed sensing. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2006, 52, 1289–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candes, E.J.; Tao, T. Decoding by linear programming. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2005, 51, 4203–4215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baraniuk, R.; Davenport, M.; DeVore, R.; Wakin, M. A simple proof of the restricted isometry property for random matrices. Constr. Approx. 2008, 28, 253–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrmann, F.J.; Hennenfent, G. Non-parametric seismic data recovery with curvelet frames. Geophys. J. Int. 2008, 173, 233–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hennenfent, G.; Herrmann, F.J. Simply denoise: Wavefield reconstruction via jittered undersampling. Geophysics 2008, 73, V19–V28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, S.; Wang, S.; Chen, Y.; Chen, X.; Huang, W.; Chen, H. Compressive sensing for seismic data reconstruction via fast projection onto convex sets based on seislet transform. J. Appl. Geophys. 2016, 130, 194–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, M.Y. Seismic data denoising based on the fractional Fourier transformation. J. Appl. Geophys. 2014, 109, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Sacchi, M.D. An lp-space matching pursuit algorithm and its application to robust seismic data denoising via time-domain Radon transforms. Geophysics 2021, 86, V171–V183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berkner, K.; Wells, R.O. Wavelet transforms and denoising algorithms. In Proceedings of the Conference Record of Thirty-Second Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems and Computers, Pacific Grove, CA, USA, 1–4 November 1998; Cat. No. 98CH36284. IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 1998; Volume 2, pp. 1639–1643. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Liu, C.; Langston, C.A. Processing seismic ambient noise data with the continuous wavelet transform to obtain reliable empirical Green’s functions. Geophys. J. Int. 2020, 222, 1224–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y. Fast dictionary learning for noise attenuation of multidimensional seismic data. Geophys. J. Int. 2017, 209, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starck, J.L.; Candès, E.J.; Donoho, D.L. The curvelet transform for image denoising. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2002, 11, 670–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, W.; Yang, J.; Huang, J.; Li, Z.; Sun, M. Outlier Denoising Using a Novel Statistics-Based Mask Strategy for Compressive Sensing. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 447. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15020447
Wang W, Yang J, Huang J, Li Z, Sun M. Outlier Denoising Using a Novel Statistics-Based Mask Strategy for Compressive Sensing. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(2):447. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15020447
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Weiqi, Jidong Yang, Jianping Huang, Zhenchun Li, and Miaomiao Sun. 2023. "Outlier Denoising Using a Novel Statistics-Based Mask Strategy for Compressive Sensing" Remote Sensing 15, no. 2: 447. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15020447
APA StyleWang, W., Yang, J., Huang, J., Li, Z., & Sun, M. (2023). Outlier Denoising Using a Novel Statistics-Based Mask Strategy for Compressive Sensing. Remote Sensing, 15(2), 447. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15020447