Adaptive Feature Map-Guided Well-Log Interpolation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Theory and Methods
2.1. General Model-Driven Prestack Seismic Inversion
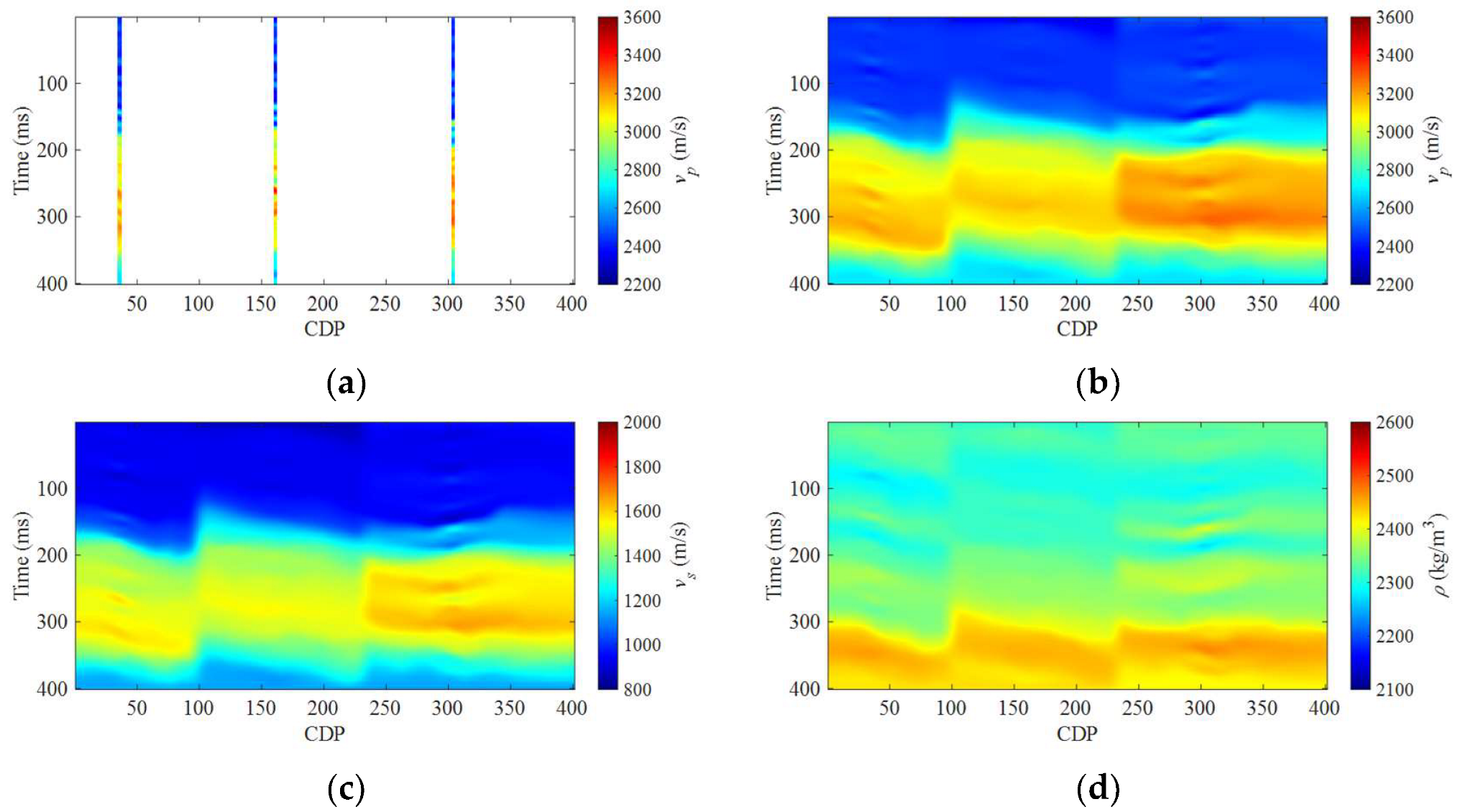
2.2. Well-Log Interpolation by Non-Local Means Algorithm
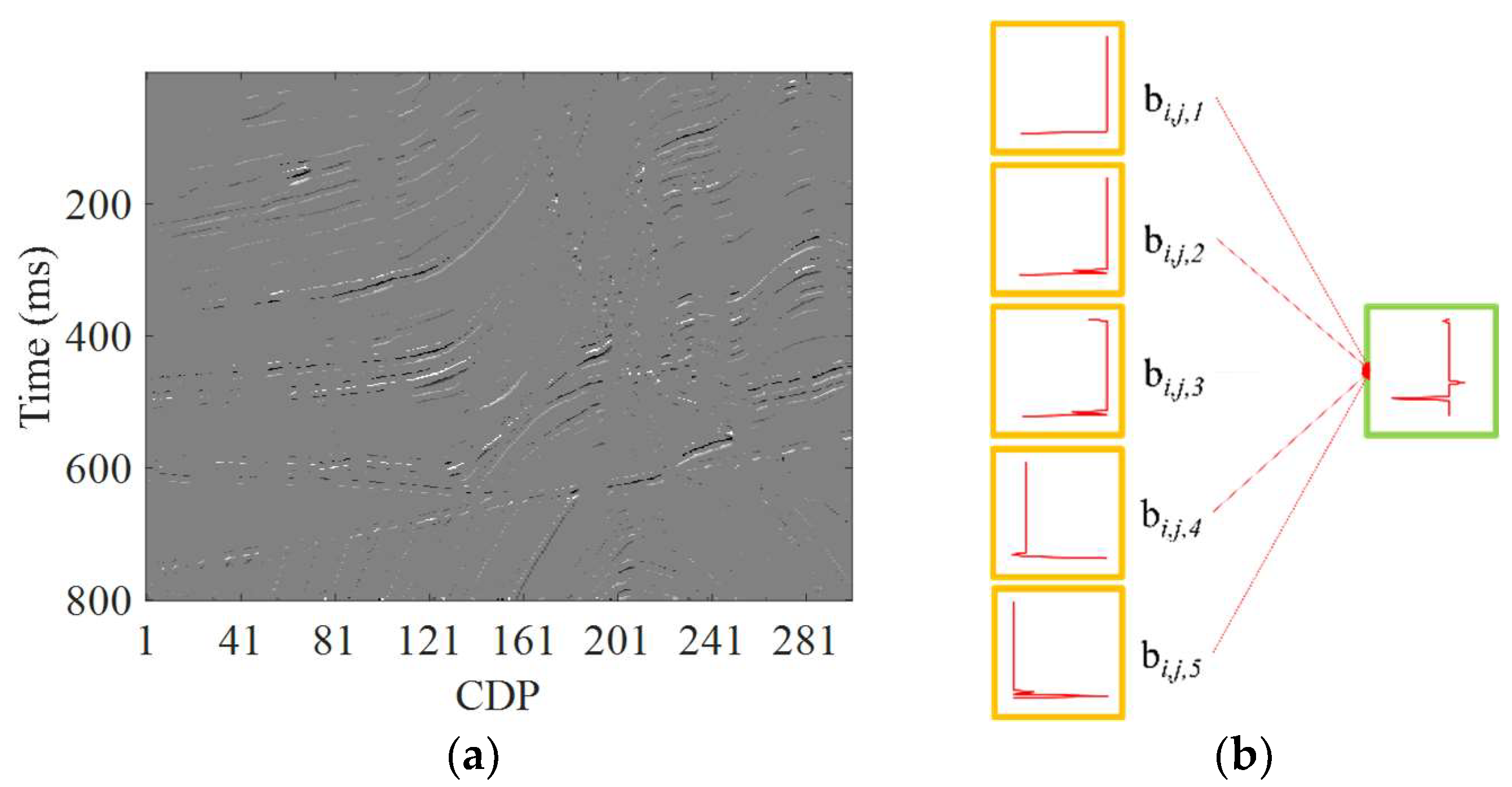
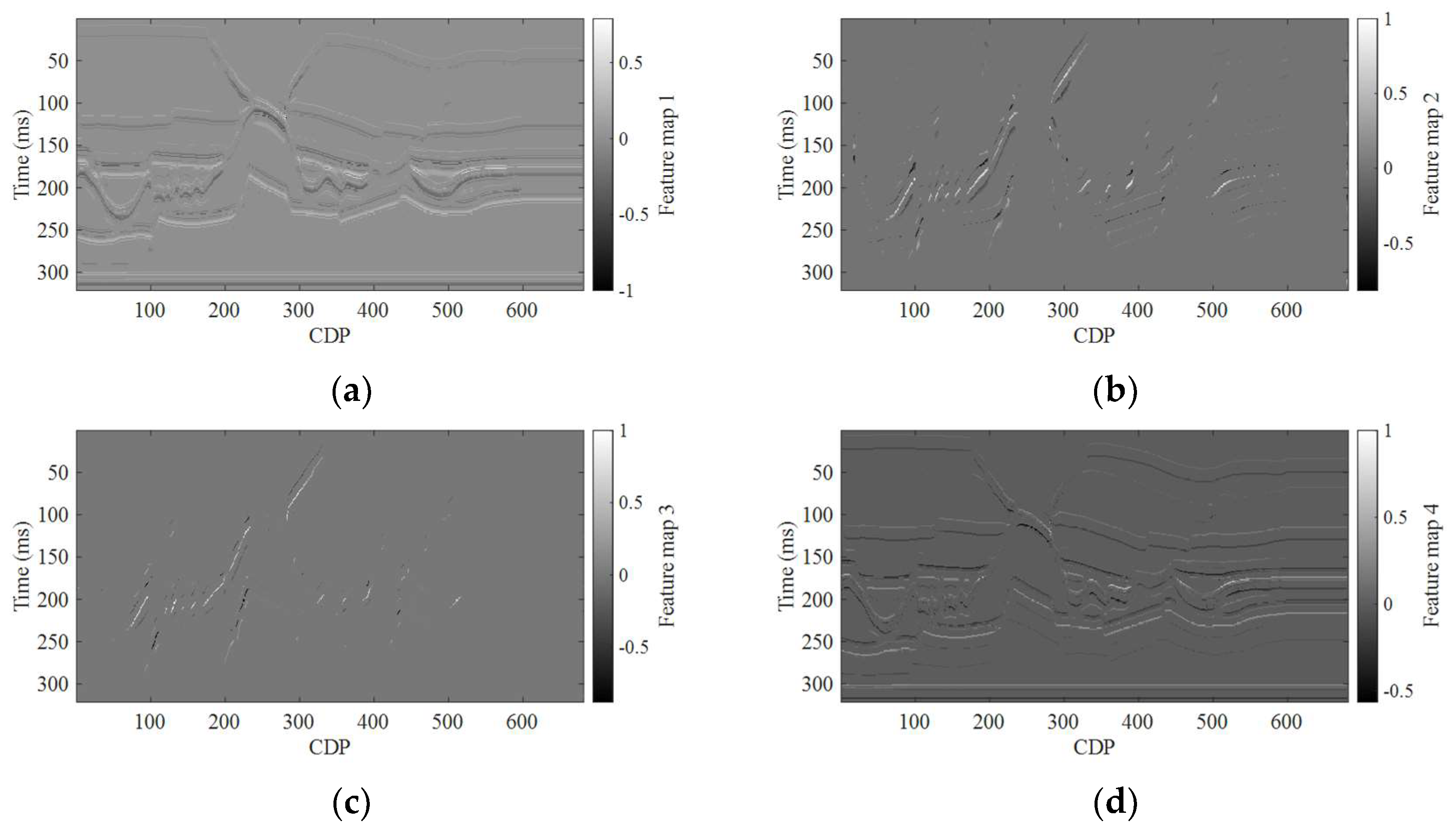
2.3. Feature Map Extraction from Observed Seismic Data
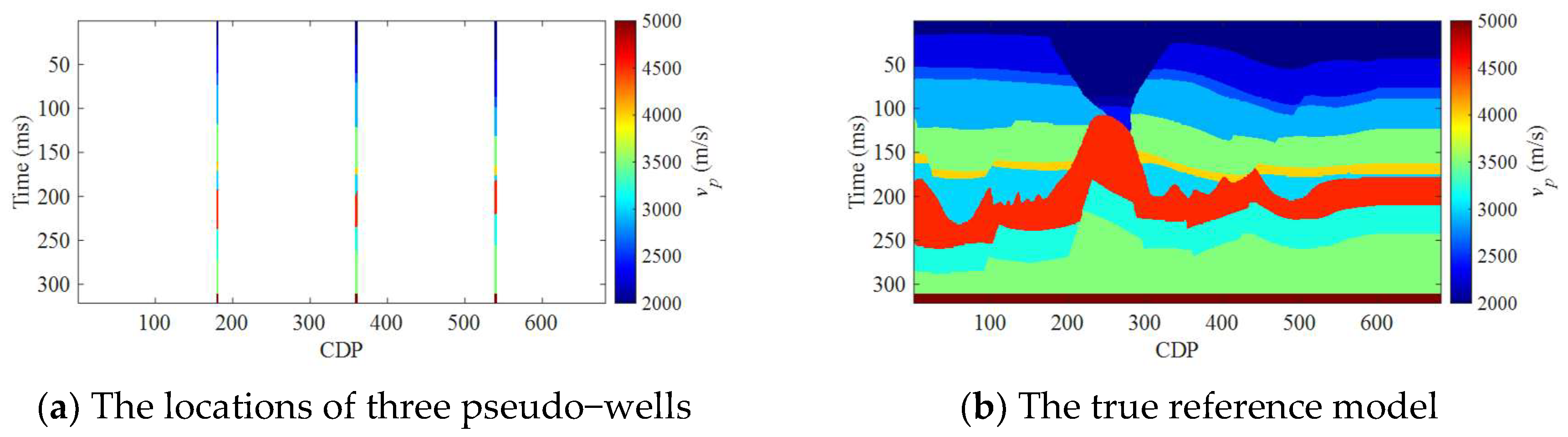
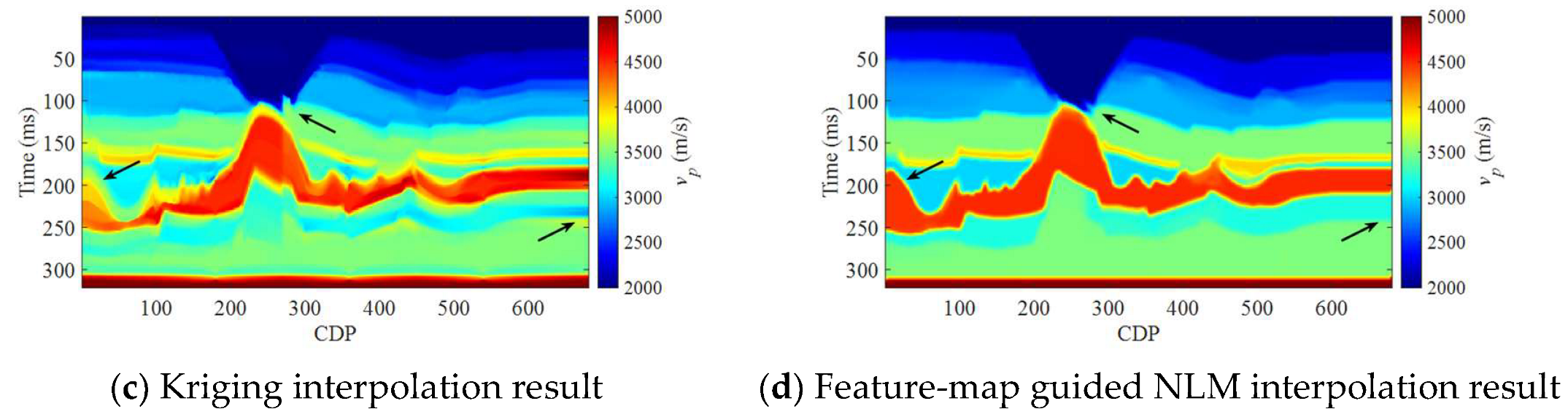
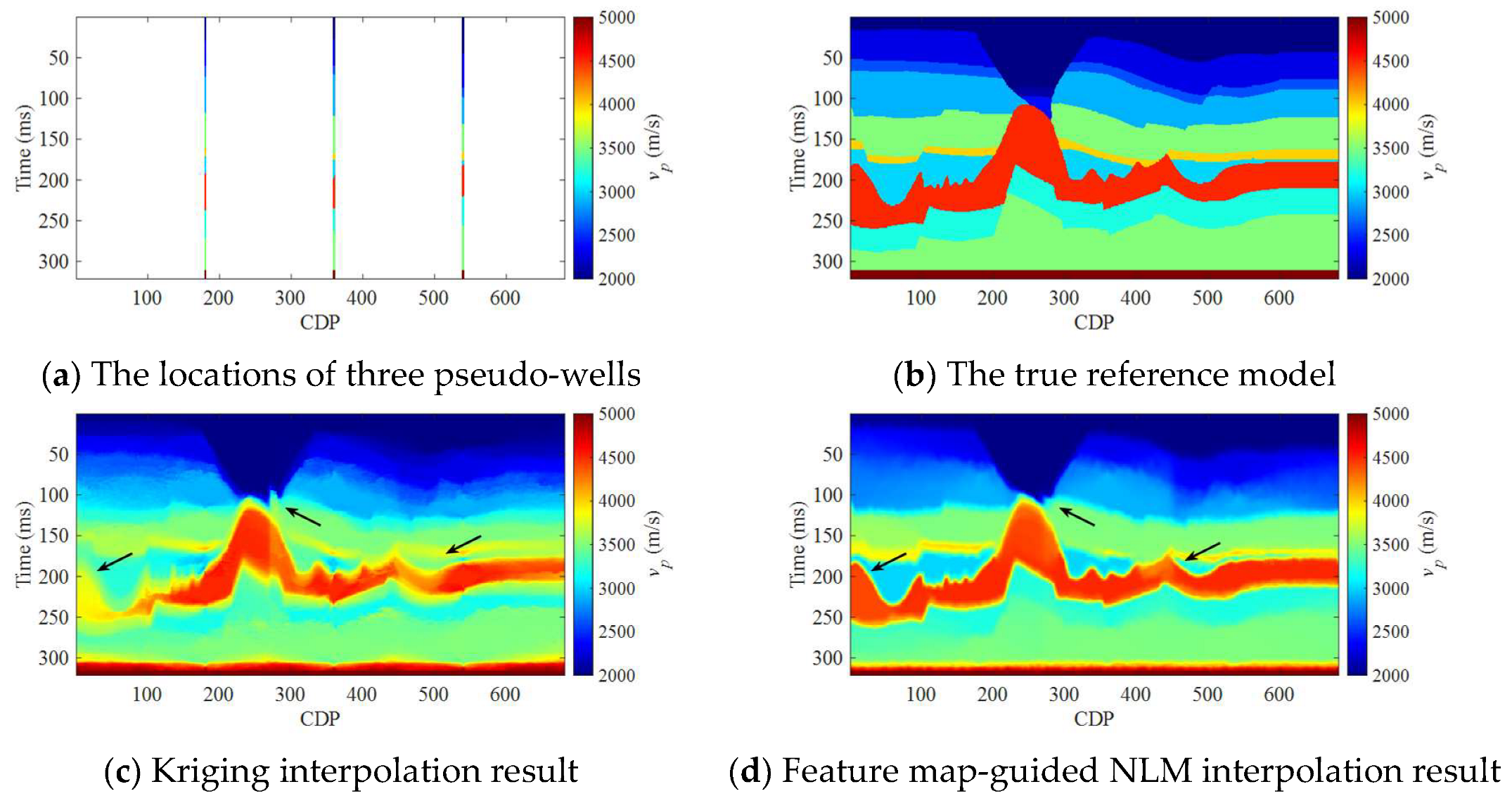
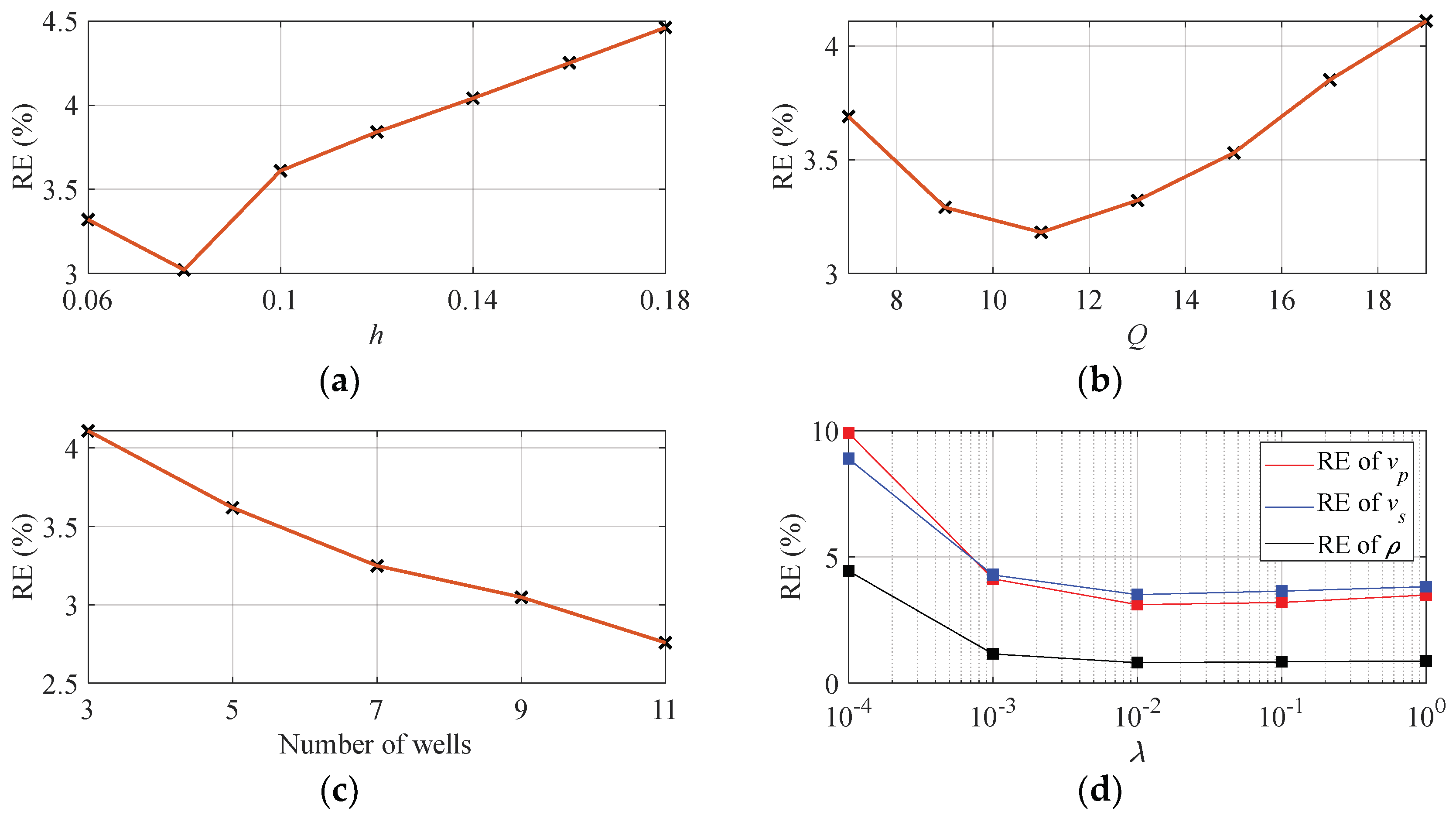
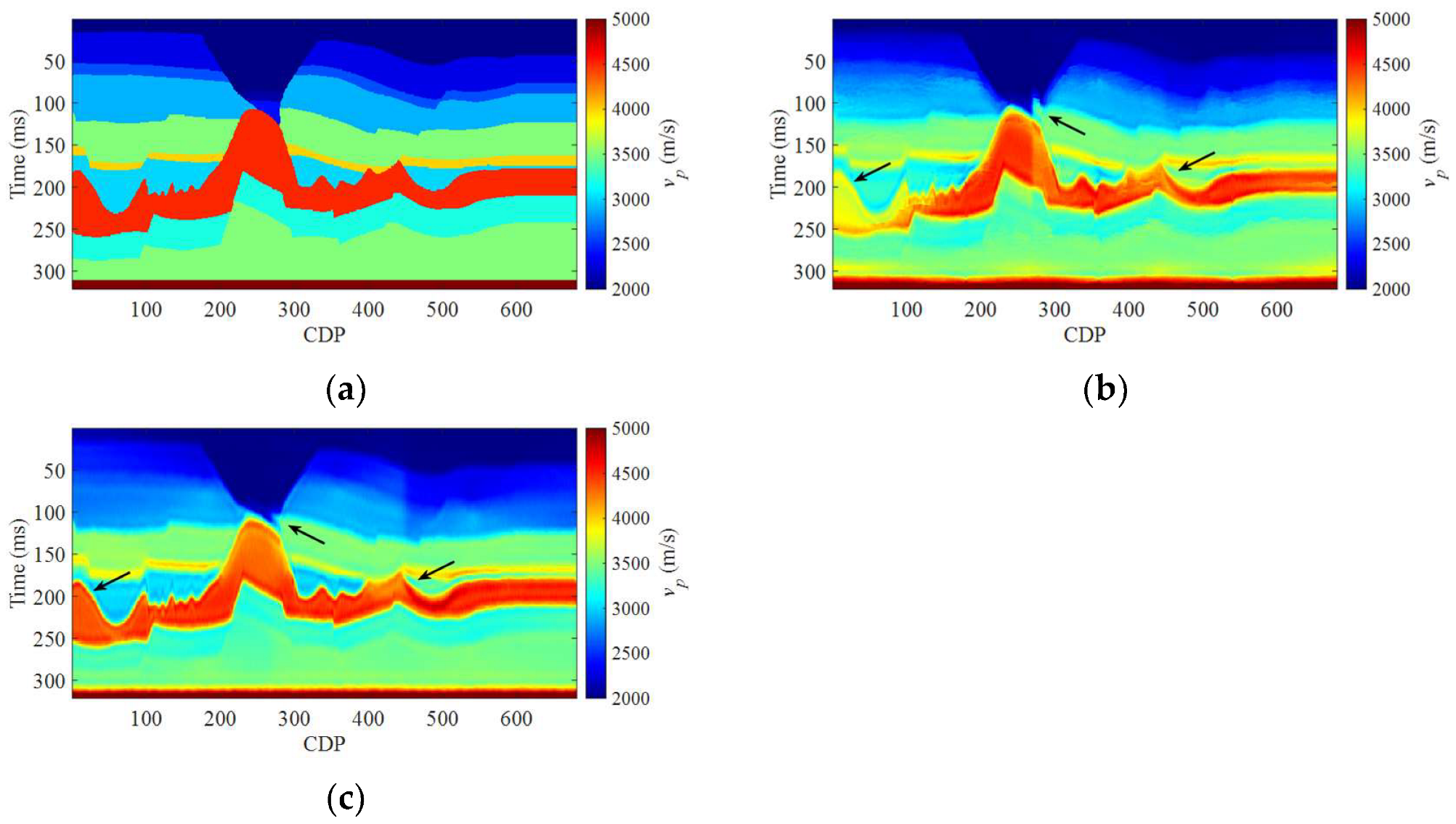
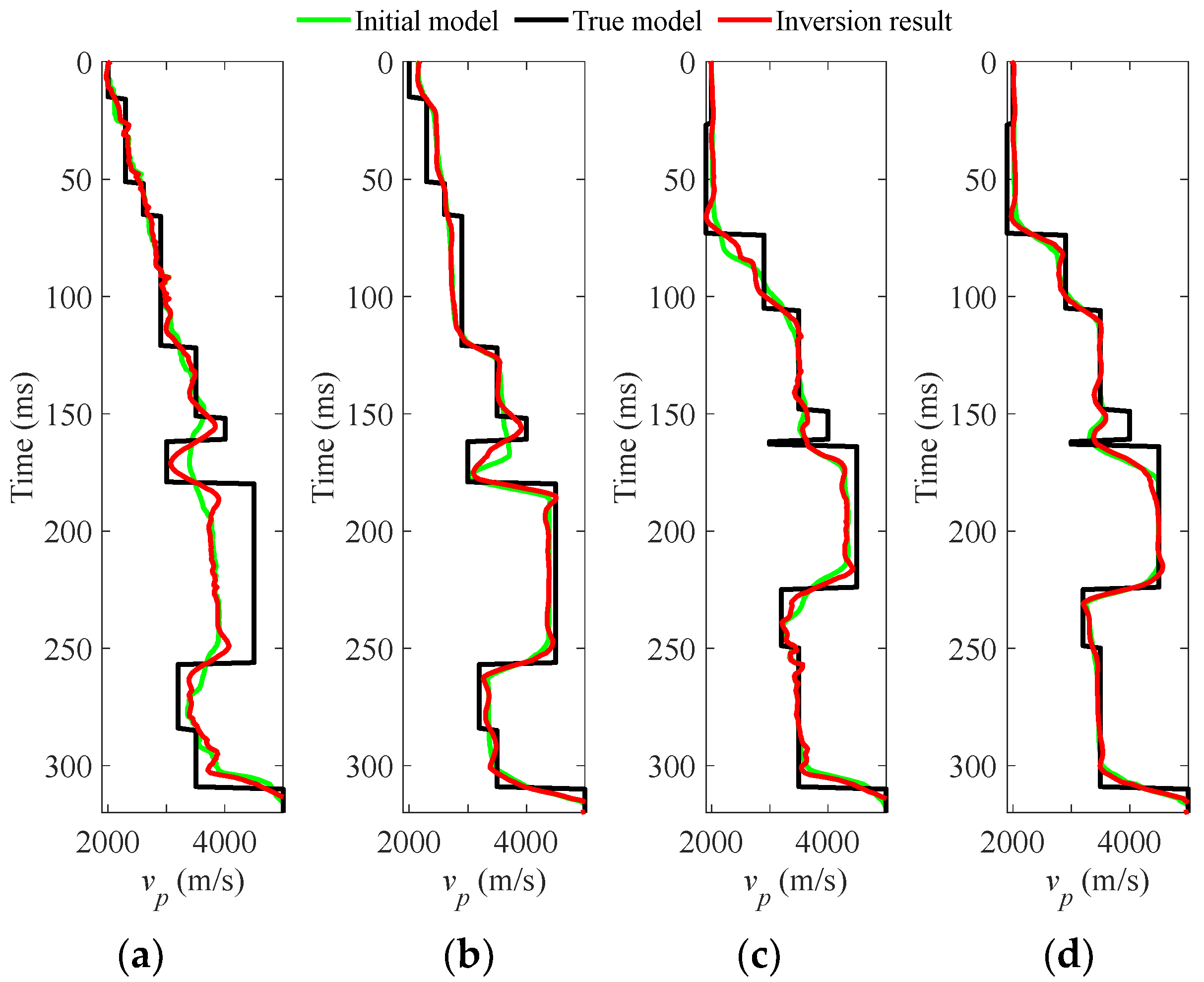
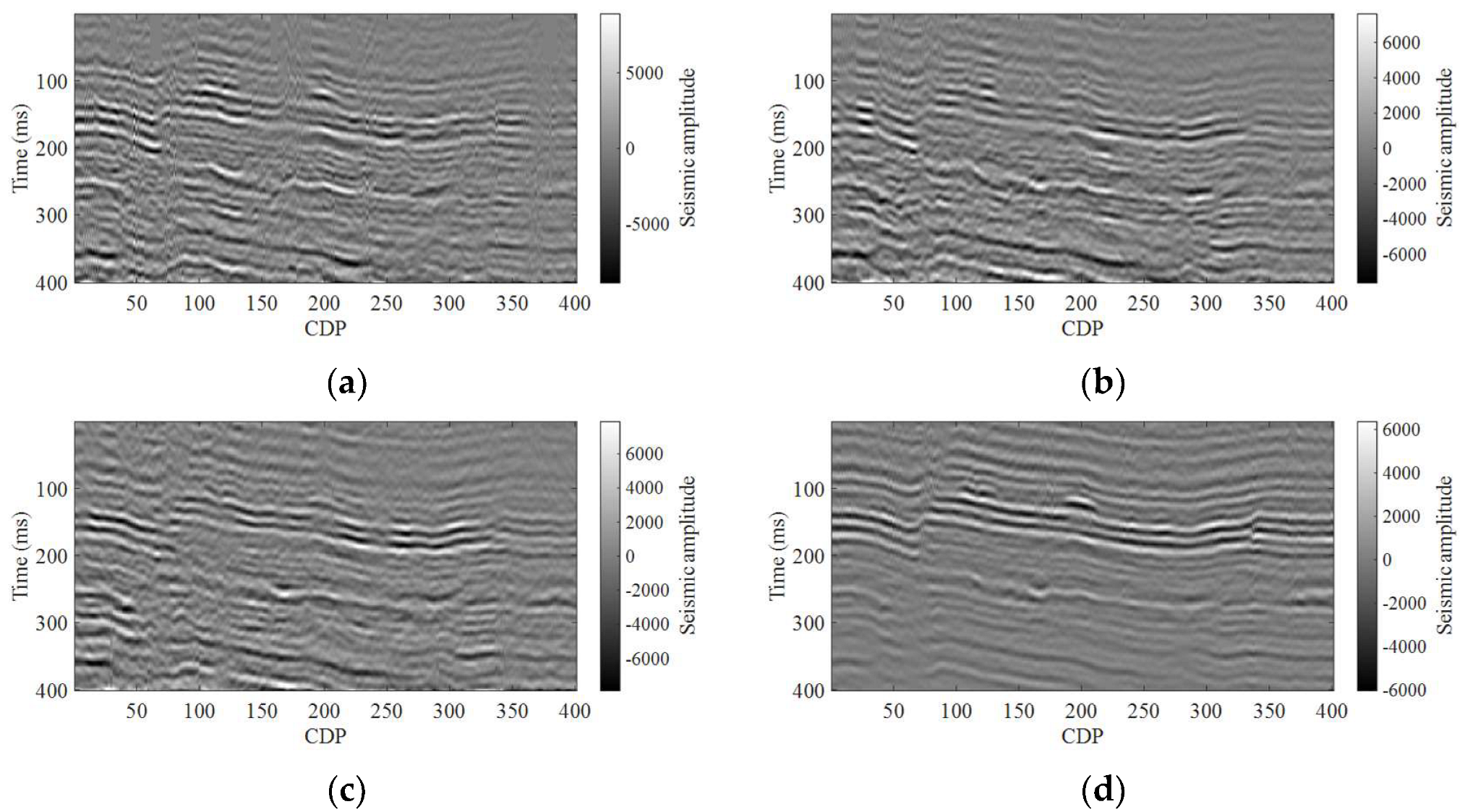
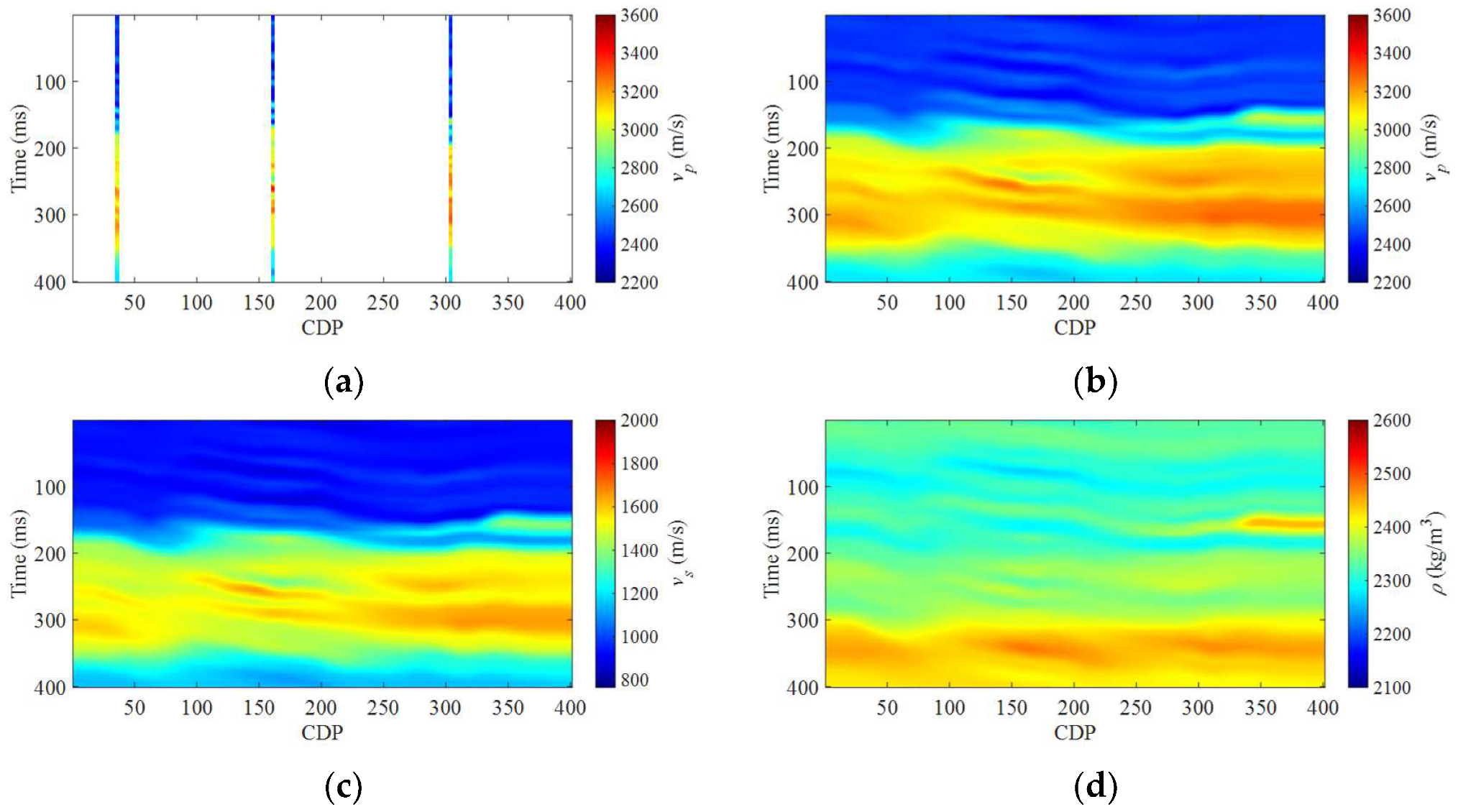
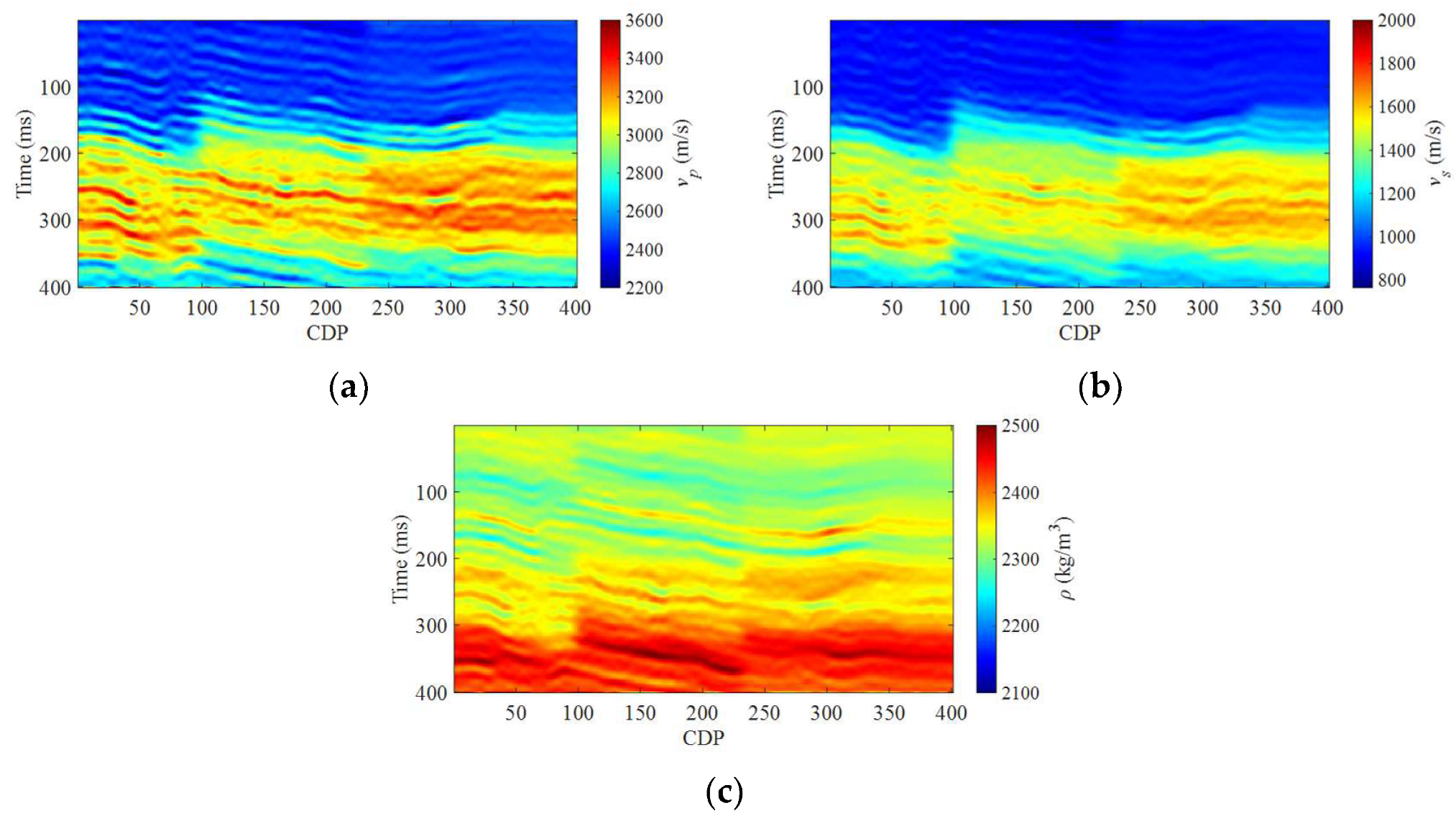
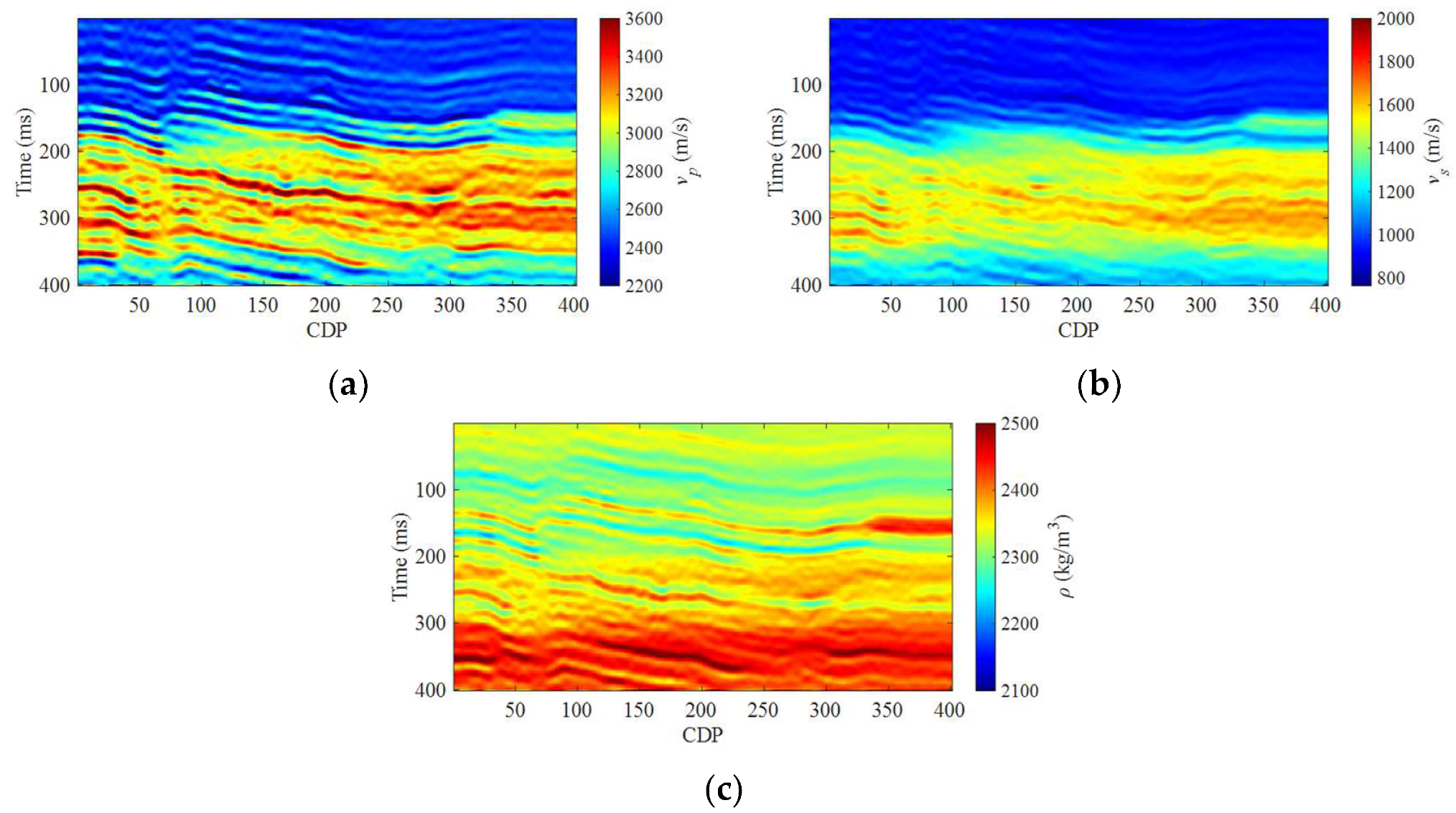
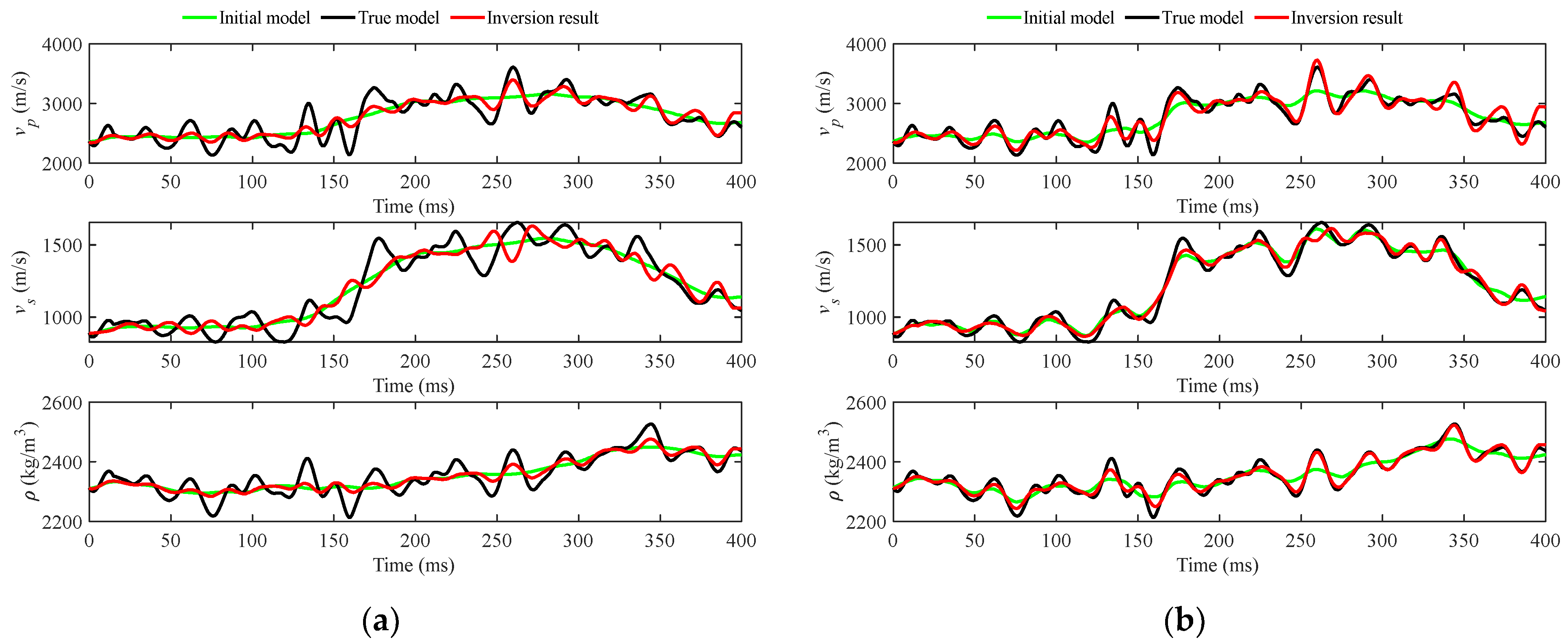
3. Numerical Examples
- (a)
- Input the observed poststack seismic record, and extract feature maps with dictionary learning.
- (b)
- Conduct the proposed FM-NLM interpolation method to construct the vp, vs, and ρ initial models.
- (c)
- Input the observed prestack seismic data and initial models, and apply model-based prestack inversion for elastic parameters vp, vs, and ρ.
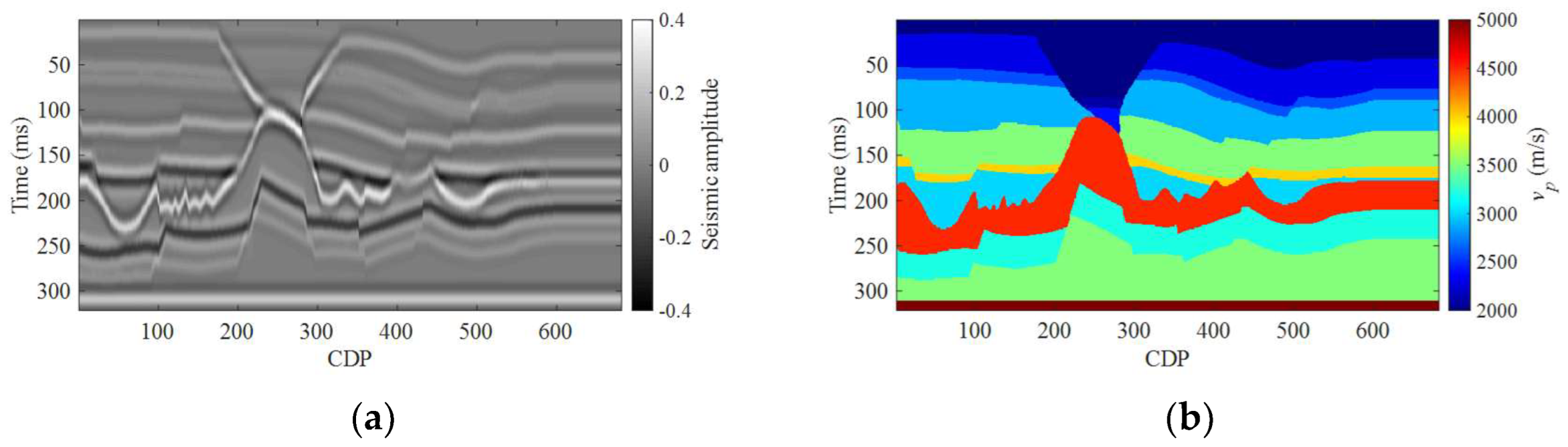
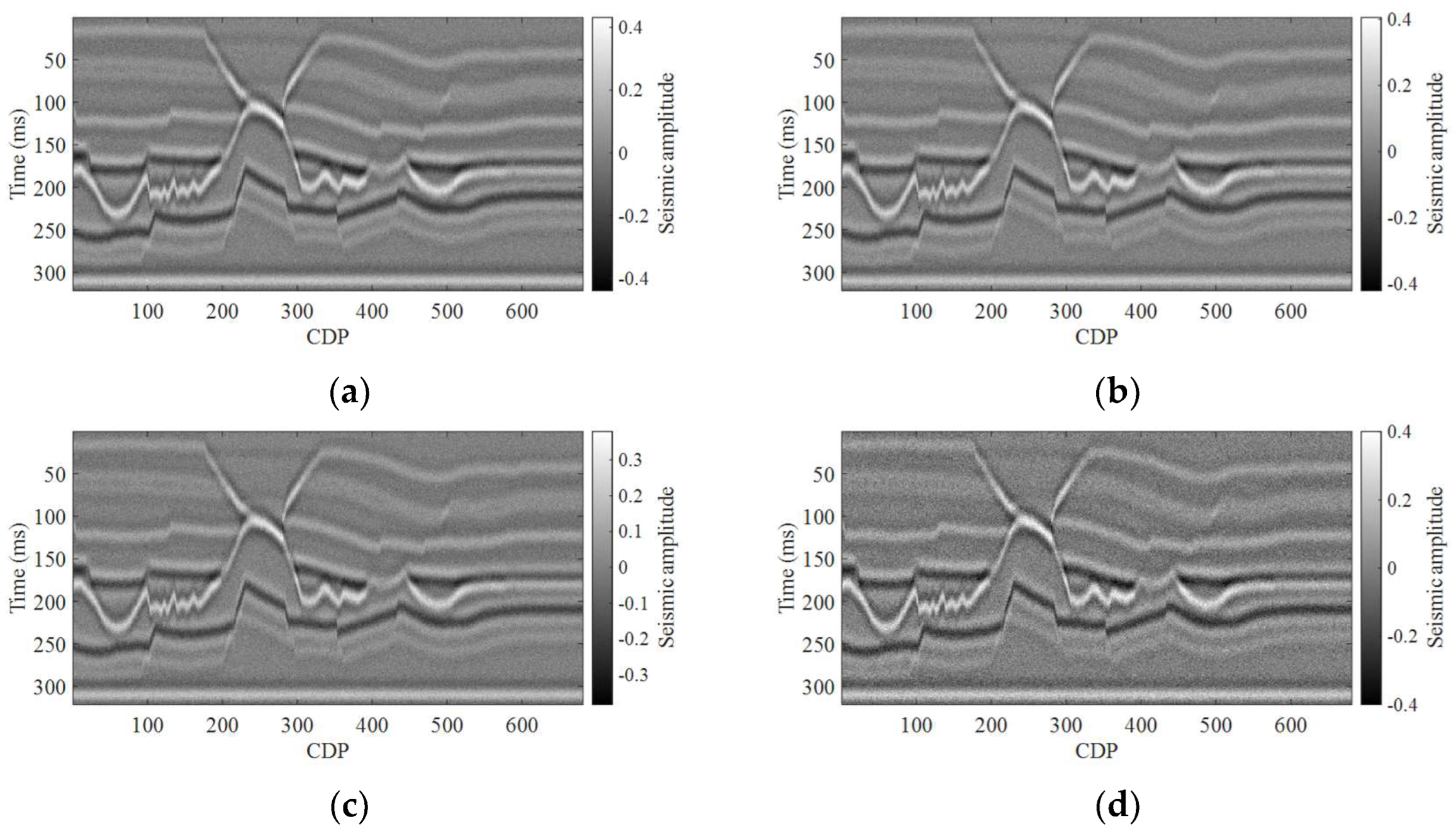
3.1. Synthetic Salt Dome Model Data Example
3.2. Field Data Example
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, L.; Zhou, H.; Wang, Y.; Yu, B.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, W.; Chen, Y. Three-parameter prestack seismic inversion based on L1-2 minimization. Geophysics 2019, 84, R753–R766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Chen, X.; Qu, S.; Bai, M.; Chen, Y. Directional Total Variation Regularized High-Resolution Prestack AVA Inversion. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 60, 4502511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Chen, X.; Luo, C.; Chen, Y. Dynamic Characterization of Reservoirs Constrained by Time-Lapse Prestack Seismic Inversion. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 59, 5549–5562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, C.; Ba, J.; Carcione, J. A Hierarchical Prestack Seismic Inversion Scheme for VTI Media Based on the Exact Reflection Coefficient. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 4507416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamid, H.; Pidlisecky, A.; Lines, L. Prestack structurally constrained impedance inversion. Geophysics 2018, 83, R89–R103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, O.; Omre, H.; Mohammadzadeh, M. Bayesian closed-skew Gaussian inversion of seismic AVO data for elastic material properties. Geophysics 2010, 75, R1–R11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Lu, C.; Zhang, G.; Wang, P.; Liu, J. Seismic Characterization of Naturally Fractured Reservoirs with Monoclinic Symmetry Induced by Horizontal and Tilted Fractures from Amplitude Variation with Offset and Azimuth. Surv. Geophys. 2022, 43, 815–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buland, A.; Omre, H. Bayesian linearized AVO inversion. Geophysics 2003, 68, 185–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buland, A.; Omre, H. Bayesian wavelet estimation from seismic and well data. Geophysics 2003, 68, 2000–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, N.; Weibull, W.; Grana, D. Constrained non-linear AVO inversion based on the adjoint-state optimization. Comput. Geosci. 2022, 16, 105214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, Z.; Wang, Y.; Li, K.; Yin, X. Broadband seismic inversion for low-frequency component of the model parameter. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 56, 5177–5184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S.; Jiao, X.; Luo, Y.; Sang, W.; Wang, S. Double-scale supervised inversion with a data-driven forward model for low-frequency impedance recovery. Geophysics 2022, 87, R165–R181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, G.; Silva, N.; Warner, M.; Wu, D.; Yang, C. Tackling cycle skipping in full-waveform inversion with intermediate data. Geophysics 2019, 84, R411–R427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.; Zhou, H.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, L.; Sun, P.; Zhang, J. Data-driven low-frequency signal recovery using deep-learning predictions in full-waveform inversion. Geophysics 2020, 85, A37–A43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, S.; Wang, S.; Chen, Y.; Qu, S.; Zu, S. Velocity analysis of simultaneous-source data using high-resolution semblance-Coping with the strong noise. Geophys. J. Int. 2016, 204, 768–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taner, M.T.; Koehler, F. Velocity spectra-digital computer derivation applications of velocity functions. Geophysics 1969, 34, 859–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fomel, S. Velocity analysis using ab semblance. Geophys. Prospect. 2009, 57, 311–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zelt, C.A.; Barton, P.J. Three-dimensional seismic refraction tomography: A comparison of two methods applied to data from the Faeroe Basin. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 1998, 103, 7187–7210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korenaga, J.; Holbrook, W.S.; Kent, G.M.; Kelemen, P.B.; Detrick, R.S.; Larsen, H.C.; Hopper, J.R.; Dahl-Jensen, T. Crustal structure of the southeast Greenland margin from joint refraction and reflection seismic tomography. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2000, 105, 21591–21614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noble, M.; Thierry, P.; Taillandier, C.; Calandra, H. High-performance 3D first-arrival traveltime tomography. Lead. Edge 2010, 29, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S.; Wang, S.; Luo, Y.; Wei, W.; Wang, G. Impedance inversion by using the low-frequency full-waveform inversion result as an a priori model. Geophysics 2019, 84, R149–R164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallick, S.; Adhikari, S. Amplitude-variation-with-offset and prestack-waveform inversion: A direct comparison using a real data example from Rock Springs Uplift, Wyoming, USA. Geophysics 2015, 80, B45–B59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, G.; Silva, N.V.; Wu, D. Sensitivity analysis of acoustic impedance inversion with full-waveform inversion. J. Geophys. Eng. 2018, 15, 461–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Chen, X.; Luo, C.; Chen, Y. Geological structure-guided initial model building for prestack AVO/AVA inversion. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 59, 1784–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hampson, D.P.; Schuelke, J.S.; Quirein, J.A. Use of multiattribute transforms to predict log properties from seismic data. Geophysics 2001, 66, 220–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nivlet, P. Low-Frequency Constrain in a Priori Model Building for Stratigraphic Inversion; SEG Technical Program Expanded Abstracts; Society of Exploration Geophysicists: Houston, TX, USA, 2004; pp. 1802–1805. [Google Scholar]
- Hansen, T.K.; Mosegaard, K.; Pedersentatalovic, R.; Uldall, A.; Jacobsen, N.L. Attribute-guided well-log interpolation applied to low-frequency impedance estimation. Geophysics 2008, 73, R83–R95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, A.K.; Chopra, S. Building more robust low-frequency models for seismic impedance inversion. First Break 2016, 34, 47–52. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Chen, X.; Wang, Y.; Zu, S. The interpolation of sparse geophysical data. Surv. Geophys. 2019, 40, 73–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naeini, E.Z.; Hale, D. Image- and horizon-guided interpolation. Geophysics 2014, 80, V47–V56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X. Building 3D subsurface models conforming to seismic structural and stratigraphic features. Geophysics 2017, 82, IM21–IM30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Chen, H.; Xiang, K.; Chen, X. Geological structure guided well log interpolation for high-fidelity full waveform inversion. Geophys. J. Int. 2016, 207, 1313–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.; Zhou, H.; Liu, W.; Wang, L.; Chen, H. Interpolation method based on pattern-feature correlation. Geophysics 2021, 86, R253–R264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Ma, J. Adaptive dictionary learning for blind seismic data denoising. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2020, 17, 1273–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuruguntia, L.; Dodda, V.C.; Elumalai, K. Study of parameters in dictionary learning method for seismic denoising. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 5906213. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.; Ma, J. Structure graph dictionary learning and application on the seismic denoising. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 1883–1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y. Fast dictionary learning for noise attenuation of multidimensional seismic data. Geophys. J. Int. 2020, 222, 1717–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zu, S.; Zhou, H.; Wu, R.; Jiang, M.; Chen, Y. Dictionary learning based on dip patch selection training for random noise attenuation. Geophysics 2019, 84, V169–V183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zu, S.; Zhou, H.; Wu, R.; Mao, W.; Chen, Y. Hybrid-sparsity constrained dictionary learning for iterative deblending of extremely noise simultaneous-source data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 2249–2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Ma, J.; Zhang, X.; Sacchi, M. Interpolation and denoising of high-dimensional seismic data by learning a tight frame. Geophysics 2015, 80, V119–V132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhi, L.; Chen, S.; Li, X. Amplitude variation with angle inversion using the exact Zoeppritz equations-theory and methodology. Geophysics 2016, 81, N1–N15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aki, K.; Richards, P.G. Quantitative Seismology: Theory and Methods; W. H. Freeman: San Francisco, CA, USA, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Yilmaz, O. Seismic Data Analysis: Processing, Inversion, and Interpretation of Seismic Data; SEG: Tulsa, OK, USA, 2001; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Stolt, R.H.; Weglein, A.B. Migration and inversion of seismic data. Geophysics 1985, 50, 2458–2472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, B.; Hampson, D. Comparison of Post-Stack Seismic Inversion Methods; SEG Technical Program Expanded Abstracts; Society of Exploration Geophysicists: Houston, TX, USA, 1991; pp. 876–878. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.B.; Singh, A.; Ahuja, N. Single image super-resolution from transformed self-exemplars. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 5197–5206. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, J.; Ma, X.; Chen, C.; Lu, T.; Wang, Z.; Ma, J. Single image super-resolution via locally regularized anchored neighborhood regression and nonlocal means. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2017, 19, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- She, B.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Cai, H.; Liu, W.; Hu, G. Seismic impedance inversion using dictionary learning-based sparse representation and nonlocal similarity. Interpretation 2019, 7, SE51–SE67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.; Zhang, L.; Shi, G.; Li, X. Nonlocally centralized sparse representation for image restoration. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2013, 22, 1620–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubinstein, R.; Zibulevsky, M.; Elad, M. Efficient implementation of the K-SVD algorithm using batch orthogonal matching pursuit. Technion 2008, 40, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Rubinstein, R.; Zibulevsky, M.; Elad, M. Double sparsity: Learning sparse dictionaries for sparse signal approximation. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2010, 58, 1553–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aharon, M.; Elad, M.; Bruckstein, A. K-SVD: An algorithm for designing overcomplete dictionaries for sparse representation. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2006, 54, 4311–4322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elad, M.; Aharon, M. Image denoising via sparse and redundant representations over learned dictionaries. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2006, 15, 3736–3745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhou, H.; Yu, B.; Chen, H.; An, Y.; Huang, W. The Analysis of the Influence of Vs/Vp on the Elastic Impedance Inversion. In Proceedings of the 81st EAGE Conference and Exhibition, London, UK, 3–6 June 2019; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]


| KI | FM-NLM | |
|---|---|---|
| Time (s) | 1048 | 205 |
| RE | 3.93% | 1.75% |
| vp | vs | ρ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| KI-based inversion | 3.93% | 4.72% | 1.01% |
| FM-NLM based inversion | 3.41% | 3.79% | 0.86% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, L.; Zhou, H.; Chen, H. Adaptive Feature Map-Guided Well-Log Interpolation. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 459. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15020459
Wang L, Zhou H, Chen H. Adaptive Feature Map-Guided Well-Log Interpolation. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(2):459. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15020459
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Lingqian, Hui Zhou, and Hanming Chen. 2023. "Adaptive Feature Map-Guided Well-Log Interpolation" Remote Sensing 15, no. 2: 459. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15020459
APA StyleWang, L., Zhou, H., & Chen, H. (2023). Adaptive Feature Map-Guided Well-Log Interpolation. Remote Sensing, 15(2), 459. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15020459




