Low Blind Zone Atmospheric Lidar Based on Fiber Bundle Receiving
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methodology
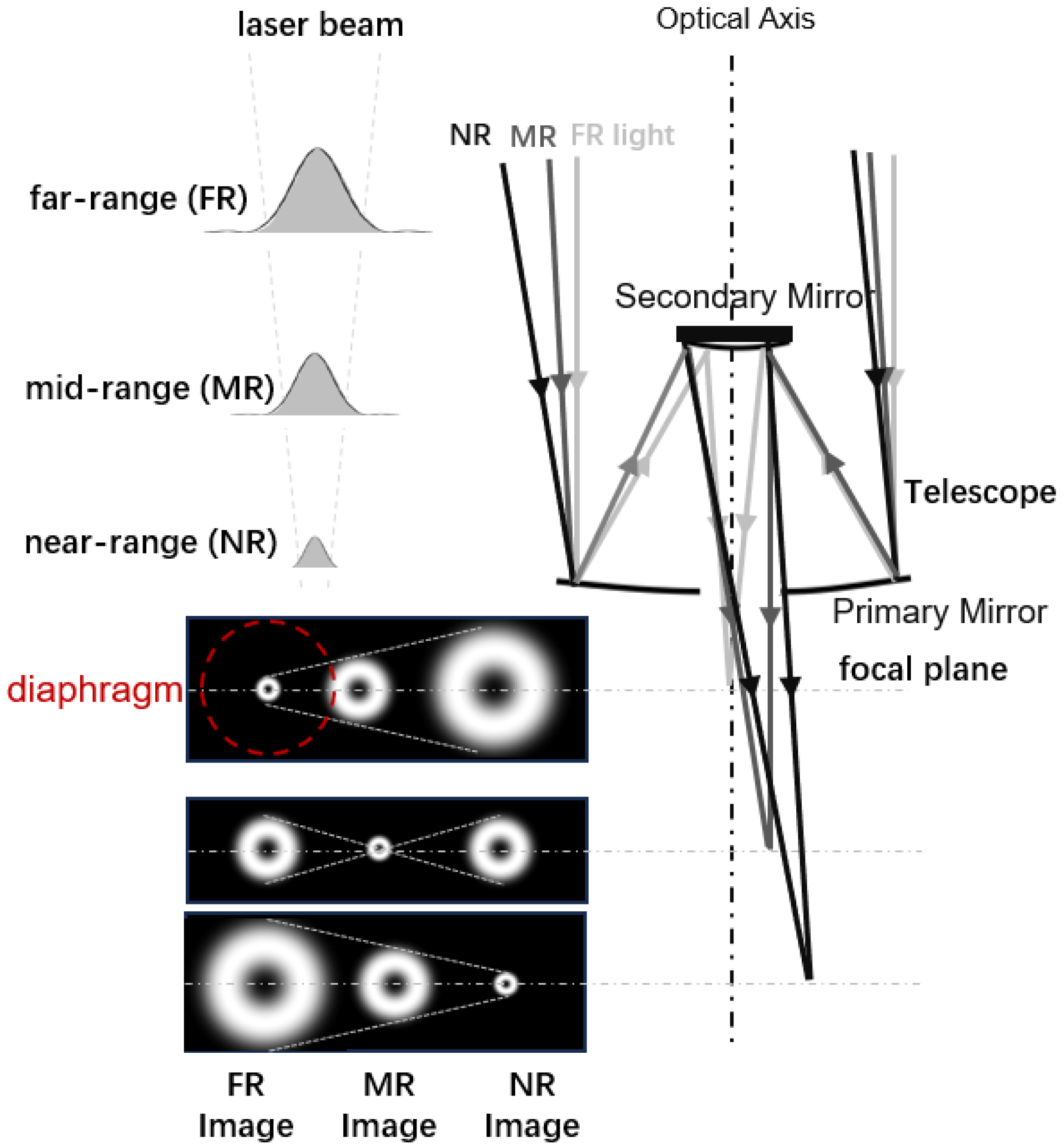
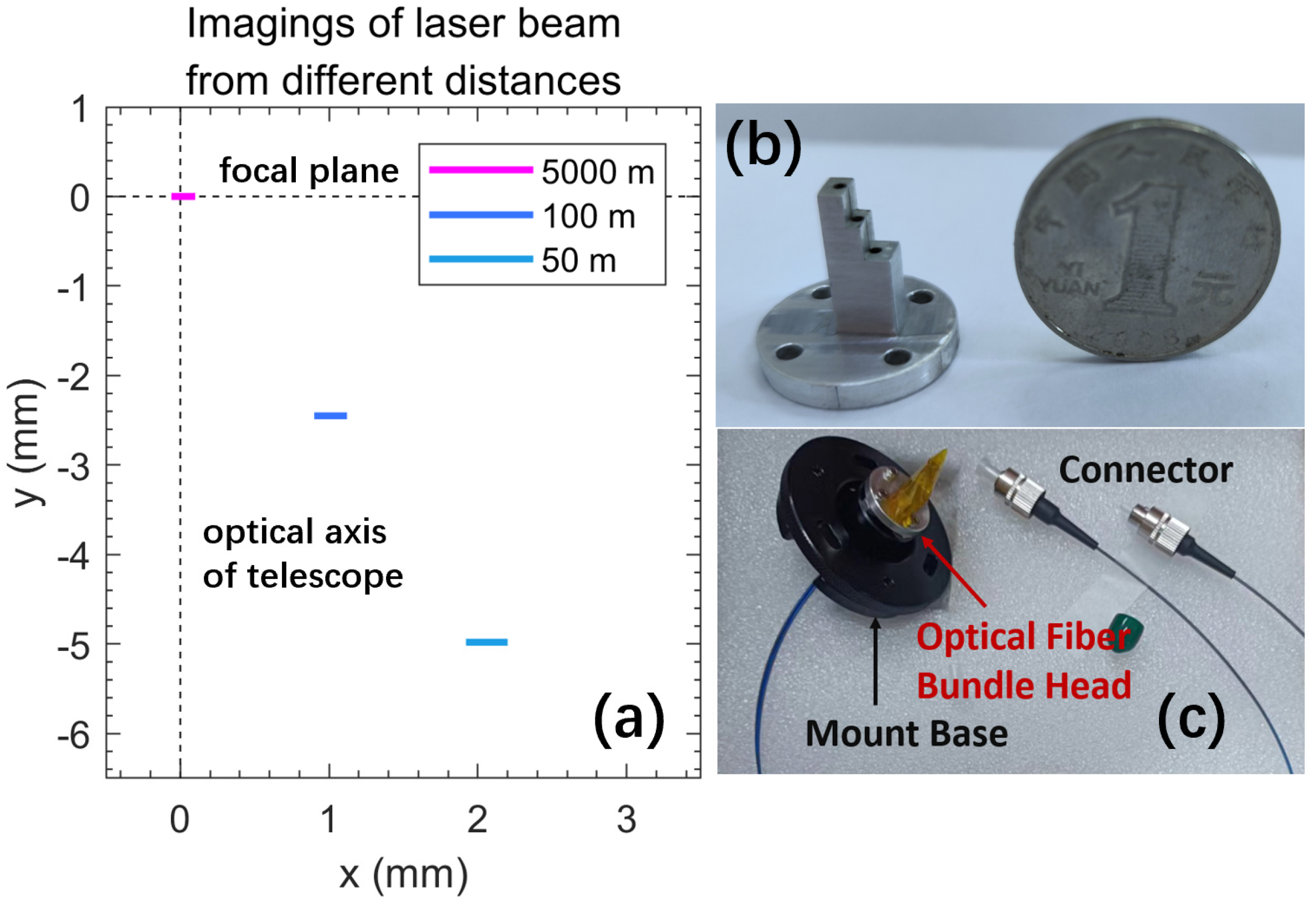
2.1. Imaging of Laser Beam by Receiving Telescope in a Biaxial Lidar System
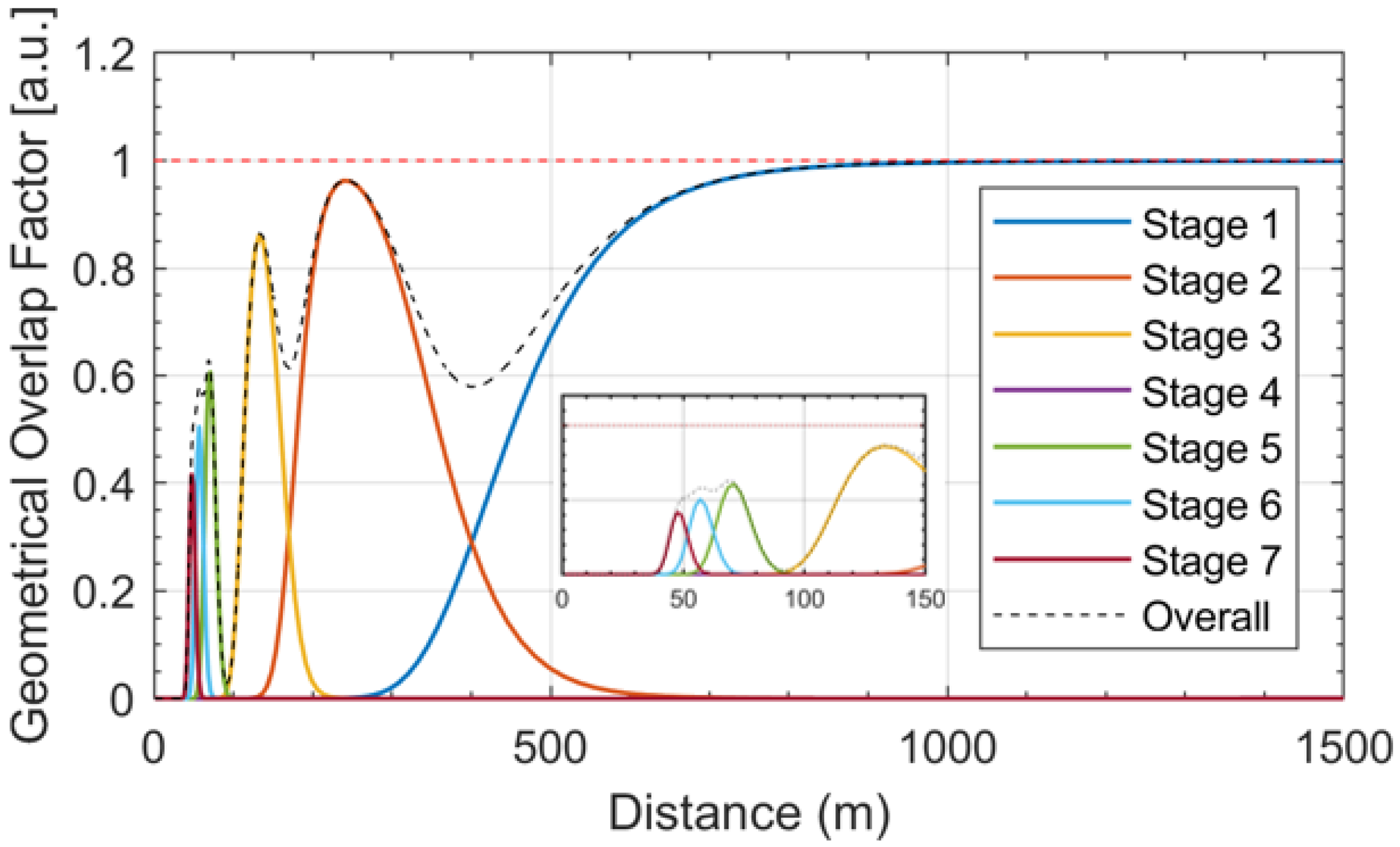
2.2. Optical Fiber Bundle Design
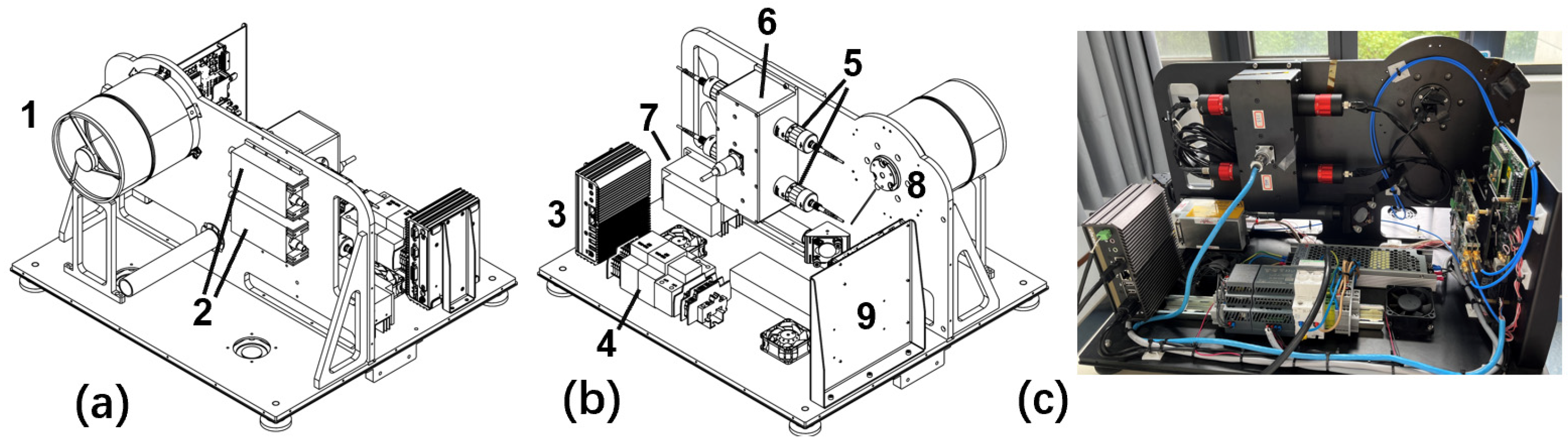
2.3. Low Blind Zone Lidar at 1030 nm
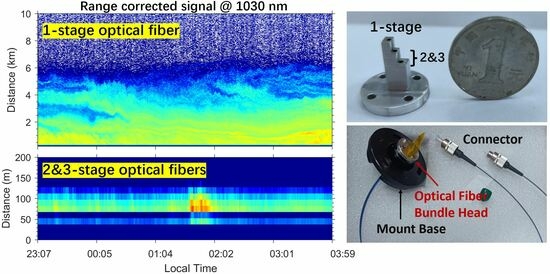
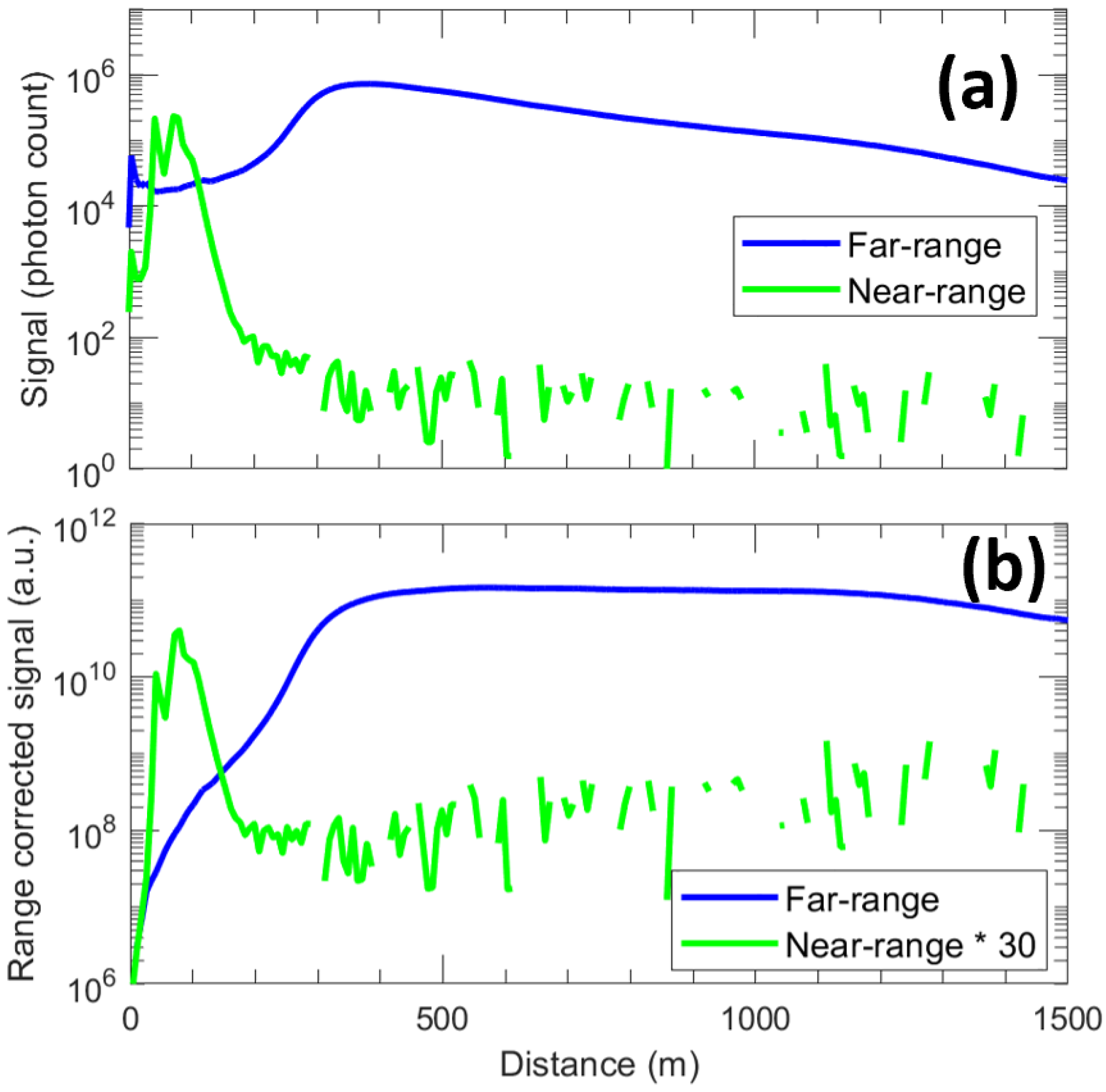
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, Z.; Guo, J.; Ding, A.; Liao, H.; Liu, J.; Sun, Y.; Wang, T.; Xue, H.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, B. Aerosol and boundary-layer interactions and impact on air quality. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2017, 4, 810–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wang, Y.; Guo, J.; Zhao, C.; Cribb, M.C.; Dong, X.; Fan, J.; Gong, D.; Huang, J.; Jiang, M.; et al. East Asian Study of Tropospheric Aerosols and their Impact on Regional Clouds, Precipitation, and Climate (EAST-AIRCPC). J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2019, 124, 13026–13054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wulfmeyer, V.; Hardesty, R.M.; Turner, D.D.; Behrendt, A.; Cadeddu, M.P.; Di Girolamo, P.; Schlüssel, P.; Van Baelen, J.; Zus, F. A review of the remote sensing of lower tropospheric thermodynamic profiles and its indispensable role for the understanding and the simulation of water and energy cycles. Rev. Geophys. 2015, 53, 819–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Yi, F.; Liu, F.; Yin, Z.; Zhou, J. Ice Nucleation of Cirrus Clouds Related to the Transported Dust Layer Observed by Ground-Based Lidars over Wuhan, China. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2022, 39, 2071–2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Yin, Z.; Liu, F.; Yi, F. Technical note: Identification of two ice-nucleating regimes for dust-related cirrus clouds based on the relationship between number concentrations of ice-nucleating particles and ice crystals. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2022, 22, 13067–13085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.; Yi, F.; He, Y.; Liu, F.; Yu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, W. Asian dust impacts on heterogeneous ice formation at Wuhan based on polarization lidar measurements. Atmos. Environ. 2021, 246, 118166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, I.M. Finding boundary layer top: Application of a wavelet covariance transform to lidar backscatter profiles. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2003, 20, 1092–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, S. Monitoring Depth of Shallow Atmospheric Boundary Layer to Complement LiDAR Measurements Affected by Partial Overlap. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 8468–8493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, S.; Lopez, M.; Schmidt, M.; Ramonet, M.; Gibert, F.; Xueref-Remy, I.; Ciais, P. Investigation of the atmospheric boundary layer depth variability and its impact on the 222Rn concentration at a rural site in France. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2015, 120, 623–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, D.; Behrendt, A.; Wulfmeyer, V. Compact Operational Tropospheric Water Vapor and Temperature Raman Lidar with Turbulence Resolution. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2019, 46, 14844–14853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Yin, Z.; Bu, Z.; Wang, A.; Mao, S.; Yi, Y.; Müller, D.; Chen, Y.; Wang, X. Quality assessment of aerosol lidars at 1064 nm in the framework of the MEMO campaign. Atmos. Meas. Tech. Discuss. 2023, 2023, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wandinger, U. Introduction to Lidar. In Lidar: Range-Resolved Optical Remote Sensing of the Atmosphere; Weitkamp, C., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2005; pp. 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Wiegner, M.; Madonna, F.; Binietoglou, I.; Forkel, R.; Gasteiger, J.; Geiß, A.; Pappalardo, G.; Schäfer, K.; Thomas, W. What is the benefit of ceilometers for aerosol remote sensing? An answer from EARLINET. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2014, 7, 1979–1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiegner, M.; Geiß, A. Aerosol profiling with the Jenoptik ceilometer CHM15kx. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2012, 5, 1953–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sassen, K. Polarization in Lidar. In Lidar: Range-Resolved Optical Remote Sensing of the Atmosphere; Weitkamp, C., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2005; pp. 19–42. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Q.; Mao, S.; Yin, Z.; Yi, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, A.; Wang, X. Compact and efficient 1064 nm up-conversion atmospheric lidar. Optics Express 2023, 31, 23931–23943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wandinger, U.; Ansmann, A. Experimental determination of the lidar overlap profile with Raman lidar. Appl. Opt. 2002, 41, 511–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, W.; Mao, F.; Li, J. OFLID: Simple method of overlap factor calculation with laser intensity distribution for biaxial lidar. Opt. Commun. 2011, 284, 2966–2971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harms, J.; Lahmann, W.; Weitkamp, C. Geometrical compression of lidar return signals. Appl. Opt. 1978, 17, 1131–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stelmaszczyk, K.; Dell’Aglio, M.; Chudzyński, S.; Stacewicz, T.; Wöste, L. Analytical function for lidar geometrical compression form-factor calculations. Appl. Opt. 2005, 44, 1323–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, F.; Gong, W.; Li, J. Geometrical form factor calculation using Monte Carlo integration for lidar. Opt. Laser Technol. 2012, 44, 907–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelmann, R.; Kanitz, T.; Baars, H.; Heese, B.; Althausen, D.; Skupin, A.; Wandinger, U.; Komppula, M.; Stachlewska, I.S.; Amiridis, V.; et al. The automated multiwavelength Raman polarization and water-vapor lidar PollyXT: The neXT generation. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2016, 9, 1767–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balin, Y.S.; Bairashin, G.S.; Kokhanenko, G.P.; Penner, I.E.; Samoilova, S.V. LOSA-M2 aerosol Raman lidar. Quantum Electron. 2011, 41, 945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liu, W.; Liu, C.; Zhang, T.; Liu, J.; Chen, Z.; Xiang, Y.; Meng, X. The Determination of Aerosol Distribution by a No-Blind-Zone Scanning Lidar. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comeron, A.; Sicard, M.; Kumar, D.; Rocadenbosch, F. Use of a field lens for improving the overlap function of a lidar system employing an optical fiber in the receiver assembly. Appl. Opt. 2011, 50, 5538–5544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, J.R.; Hlavka, D.L.; Welton, E.J.; Flynn, C.J.; Turner, D.D.; Spinhirne, J.D.; Scott, V.S., III; Hwang, I. Full-time, eye-safe cloud and aerosol lidar observation at atmospheric radiation measurement program sites: Instruments and data processing. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2002, 19, 431–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaixia, Z.; Yinchao, Z.; Zongming, T.; Xiaoqin, L.; Shisheng, S.; Kun, T.; Yonghui, L.; Jun, Z.; Huanling, H. Lidar geometric form factor and its effect on aerosol detection. Chin. J. Quantum Electron. 2005, 2, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Newsom, R.K.; Turner, D.D.; Mielke, B.; Clayton, M.; Ferrare, R.; Sivaraman, C. Simultaneous analog and photon counting detection for Raman lidar. Appl. Opt. 2009, 48, 3903–3914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Yin, Z.; Zhao, B.; Mao, S.; Zhang, Q.; Yi, Y.; Wang, X. Performance of Wide Dynamic Photomultiplier Applied in a Low Blind Zone Lidar. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 4404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agishev, R.R.; Comeron, A. Spatial filtering efficiency of monostatic biaxial lidar: Analysis and applications. Appl. Opt. 2002, 41, 7516–7521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freudenthaler, V. Optimized background suppression in near field lidar telescopes. In Proceedings of the 6th ISTP International Symposium on Tropospheric Profiling: Needs and Technologies, Leipzig, Germany, 14–20 September 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Kokkalis, P. Using paraxial approximation to describe the optical setup of a typical EARLINET lidar system. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2017, 10, 3103–3115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, L.; Brydegaard, M. Atmospheric aerosol monitoring by an elastic Scheimpflug lidar system. Opt. Express 2015, 23, A1613–A1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xian, J.; Sun, D.; Amoruso, S.; Xu, W.; Wang, X. Parameter optimization of a visibility LiDAR for sea-fog early warnings. Opt. Express 2020, 28, 23829–23845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cahalan, R.F.; McGill, M.; Kolasinski, J.; Várnai, T.; Yetzer, K. THOR—Cloud Thickness from Offbeam Lidar Returns. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2005, 22, 605–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vande Hey, J.; Coupland, J.; Foo, M.H.; Richards, J.; Sandford, A. Determination of overlap in lidar systems. Appl. Opt. 2011, 50, 5791–5797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Wang, C.; Xue, X.; Wang, Y.; Shang, X.; Jia, M.; Chen, T. Study on the Parameters of Ice Clouds Based on 1.5 µm Micropulse Polarization Lidar. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Seven-Stage Optical Fiber Head | ||
|---|---|---|
| Stage Number | Distance to the Optical Axis (mm) | Distance to the Base (mm) |
| 1 | 0 | 22.00 |
| 2 | 0.34 | 21.17 |
| 3 | 0.68 | 20.34 |
| 4 | 1.02 | 19.51 |
| 5 | 1.36 | 18.68 |
| 6 | 1.70 | 17.85 |
| 7 | 2.04 | 17.02 |
| Three-stage optical fiber head | ||
| Stage Number | Distance to the optical axis (mm) | Distance to the base (mm) |
| 1 | 0 | 22.00 |
| 2 | 1.01 | 19.55 |
| 3 | 2.06 | 17.02 |
| Item | Parameters |
|---|---|
| Laser | 5 kHz and 160 μJ |
| Telescope | focal length: 500 mm divergence: 0.2 mrad diameter of the primary mirror: 136 mm focus size: ≤30 μm |
| Optical fiber | core size: 200 μm |
| d | 200 mm |
| NIF | 1030 ± 3 nm |
| Fiber collimator | focal length of 40 mm and FC/PC connector |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yin, Z.; Chen, Q.; Yi, Y.; Bu, Z.; Wang, L.; Wang, X. Low Blind Zone Atmospheric Lidar Based on Fiber Bundle Receiving. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 4643. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15194643
Yin Z, Chen Q, Yi Y, Bu Z, Wang L, Wang X. Low Blind Zone Atmospheric Lidar Based on Fiber Bundle Receiving. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(19):4643. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15194643
Chicago/Turabian StyleYin, Zhenping, Qianyuan Chen, Yang Yi, Zhichao Bu, Longlong Wang, and Xuan Wang. 2023. "Low Blind Zone Atmospheric Lidar Based on Fiber Bundle Receiving" Remote Sensing 15, no. 19: 4643. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15194643
APA StyleYin, Z., Chen, Q., Yi, Y., Bu, Z., Wang, L., & Wang, X. (2023). Low Blind Zone Atmospheric Lidar Based on Fiber Bundle Receiving. Remote Sensing, 15(19), 4643. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15194643