Abstract
To overcome the interference of noise on the exploration effectiveness of the controlled-source electromagnetic method (CSEM), we improved the deep learning algorithm by combining the denoising convolutional neural network (DnCNN) with the residual network (ResNet), and propose a method based on the residual denoising convolutional neural network (ResDnCNN) and shift-invariant sparse coding (SISC) for denoising CSEM data. Firstly, a sample library was constructed by adding simulated noises of different types and amplitudes to high-quality CSEM data collected. Then, the sample library was used for model training in the ResDnCNN, resulting in a network model specifically designed for denoising CSEM data. Subsequently, the trained model was employed to denoise the measured data, generating preliminary denoised data. Finally, the preliminary denoised data was processed using SISC to obtain the final denoised high-quality data. Comparative experiments with the ResNet, DnCNN, U-Net, and long short-term memory (LSTM) networks demonstrated the significant advantages of our proposed method. It effectively removed strong noise such as Gaussian, impulse, and square wave, resulting in an improvement of the signal-to-noise ratio by nearly 20 dB. Testing on CSEM data from Sichuan Province, China, showed that the apparent resistivity curves plotted using our method were smoother and more credible.
1. Introduction
Controlled-source electromagnetic method (CSEM), which involves artificially exciting alternating electromagnetic fields, offers advantages such as stable sources and strong resistance to interference compared to natural-source electromagnetic methods [1,2,3,4]. It has been widely applied in various fields, including engineering and environmental surveys, resource and energy exploration, and geological hazard detection [5,6,7]. Similarly, CSEM also plays an important role in exploration of hydrology and engineering geology [8,9,10]. It is also suitable for both ocean and land construction [11,12]. However, due to increasing human activities, CSEM observation data is inevitably affected by electromagnetic noise, which can significantly degrade the detection performance [13,14]. Therefore, suppressing noise and obtaining high-quality data under conditions of strong interference have become the primary challenges in current CSEM research.
When conducting research on CSEM data, denoising is particularly important given the current limited observation conditions [15,16,17]. CSEM data denoising can be performed based on the data characteristics, using both frequency domain and the time domain approaches. Yang et al. [18] optimized the excitation signal to achieve CSEM data denoising in the time domain. Liu et al. [19] applied frequency-domain spread-spectrum-induced polarization methods to remove weak noise from electromagnetic data, although the effectiveness of this method diminishes as the noise amplifies. Liu et al. [20] proposed a time-domain empirical mode decomposition method for periodic CSEM data, but its limitation lies in an increase in residual noise when noise becomes more complex. Singular value decomposition [13] has been employed in the time domain for CSEM data analysis and denoising, yet its performance needs further improvement when dealing with diverse types of noise. Dictionary learning [21,22] can be a feasible approach for denoising electromagnetic data, although the dictionaries used may lack flexibility and adaptability. Li et al. [23] introduced the shift-invariant sparse coding (SISC) to address the issue of fixed dictionaries. By continuously learning data features, the dictionary can be updated. Thus, SISC automatically calculates the sparsity based on different signals, leading to effective noise suppression. Traditional denoising methods can achieve excellent results under certain conditions, but overall, their adaptability and efficiency need to be improved.
With the development of technology in recent years, the application of deep learning networks has become increasingly widespread [24,25,26,27]. As such, many methods for denoising using deep learning have also emerged in the field of controlled–source electromagnetic exploration. Wu et al. [28] proposed the use of wavelet neural network to predict high frequency noise in CSEM data. The denoising autoencoder [29,30] can also learn noise characteristics and was also applied to CSEM data denoising. It has better performance compared to wavelet neural network. Wu et al. [30] proposed a new denoising method by combining the autoencoder and long short-term neural network (LSTM), and the results showed that its effectiveness is superior to any single network. Li et al. [31] fused LSTM with four convolutional neural networks to achieve better denoising performance. Bang et al. [32] proposed a recurrent neural network (RNN) to handle noise in CSEM data. Sun et al. [33] combined the minimum noise fraction (MNF) algorithm with deep neural network (DNN) to extract complex features of the signal and achieved better denoising results. Compared with traditional denoising methods, deep learning-based methods are more intelligent and less susceptible to subjective bias. This demonstrates that deep learning has significant advantages in the denoising of CSEM data.
Zhang et al. [34] introduced the denoising convolutional neural network (DnCNN), and He et al. [35] proposed the residual network (ResNet) in the field of image processing, both of which have achieved great success. DnCNN has good performance for data with different noise levels, while ResNet can avoid network degradation caused by an increase in network layers. They have achieved extremely successful cases in the fields of seismic data denoising [36] and geomagnetic data denoising [37]. These advancements provide insights for CSEM data denoising, leveraging the strengths of these two networks. In this study, an improved deep learning algorithm is proposed based on the two networks, combined with the advantages of the shift-invariant sparse coding (SISC) denoising method. This formed the residual denoising convolutional neural network (ResDnCNN) and shift-invariant sparse coding denoising method, aimed at achieving more accurate and comprehensive denoising results.
The following is the arrangement of this article. In Section 2, we will provide an introduction of DnCNN, ResNet, and the proposed ResDnCNN network, and the overall denoising procedure. Section 3 will describe the construction of the sample library and the training process. In Section 4, we will demonstrate the superiority and reliability of the proposed method through synthetic data and comparative methods. In Section 5, we will further illustrate the effectiveness of the proposed method using field data from Sichuan Province, China, along with comparative methods. Finally, in Section 6, we will summarize and discuss the proposed method.
2. Method Principle
2.1. Overall Experimental Process
The overall experimental process for CSEM data denoising is shown in Figure 1. Firstly, based on the characteristic sampling rate of 1200 Hz for the CSEM data, the data to be processed is divided into segments with 1200 sampling points per cycle and then reassembled. The segmented data is then fed into the pre-trained ResDnCNN network model for initial denoising. Subsequently, the preliminary processed data is input into SISC, where the signal features are learned through SISC to build a learning type redundant dictionary. This learned dictionary is used to further separate the noise from the data, so as to obtain high-quality data after noise removal. This paper focuses on the ResDnCNN network. SISC denoising was reported in Li et al. [11], which can be referred to for more information; this paper does not provide a detailed introduction of SISC.
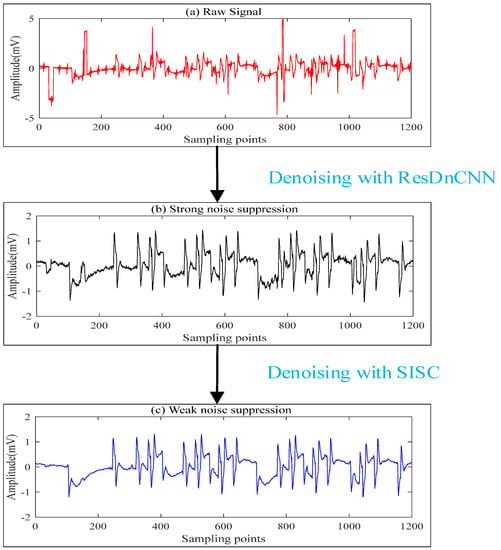
Figure 1.
Overall experimental process for CSEM data denoising.
2.2. Denoising Convolutional Neural Network (DnCNN)
DnCNN [34] is an improved version built upon the convolutional neural network architecture. It deepens the network architecture, incorporates residual learning, and batch normalization (BN) to enhance the denoising performance and improve the robustness of the network. DnCNN is widely used in the field of image denoising. Li et al. [38] addressed the problem of image inpainting by transforming it into an image denoising problem and utilized DnCNN to restore the missing parts of the image edges. Wei et al. [39] proposed a fast block based evolutionary denoising convolutional neural network (FBE-DnCNN) to enhance the competitiveness of image denoising. Karthikeyan et al. [40] improved DnCNN with discrete wavelet transform (DWT) to achieve image quality enhancement and improve image contrast. DnCNN has also made good progress in seismic data denoising. Yuan et al. [41] demonstrated that DnCNN can be well applied to the attenuation of linear noise in seismic data and the extraction of high-quality signal. Dong et al. [42] proposed the integration of spatial attention mechanisms with a multiscale convolutional neural network (CNN), resulting in a multiscale spatial attention denoising network (MSSA-Net). This approach facilitates the suppression of strong seismic background noise and the recovery of weak reflected signals.
The structure diagram of the DnCNN network is shown in Figure 2, the overall DnCNN network consists of 18 layers. The size of the convolutional kernels involved in the convolutional layers contained in the network are set to 3 × 1, the step size is set to 1, and the number of convolutional channels is set to 64. The activation function adopted by the network is rectified linear units (ReLU) function. The first layer of the network transforms the data by convolution and activation functions. Each of the subsequent 2 to 17 layers consist of a convolutional layer, a BN layer, and an activation function. The last layer is only a convolutional layer, which is used to change the number of data channels and make the output data scale to the required scale. Batch normalization of data can narrow the range of changes in data distribution and reduce the convergence difficulties caused by excessive data distribution during training. It also decreases the complexity of network training and minimizes network overfitting.
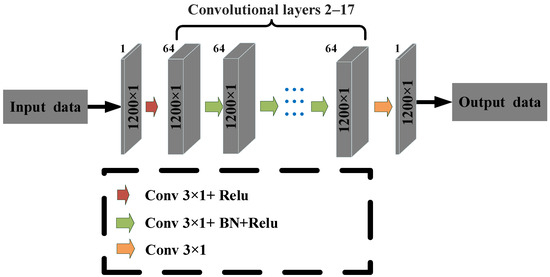
Figure 2.
The structure diagram of DnCNN network.
2.3. Residual Network (ResNet)
The proposed of ResNet [35] network effectively alleviates the dilemma of gradient explosion caused by excessive layers in deep learning neural networks. Unlike other networks, ResNet can converge better in the face of hundreds of layers and avoids the problem of gradient disappearance. The ResNet network with skip connections preserves the input data features and maintains training accuracy despite the deepening of the network. The main feature of ResNet is the use of two different residual modules, as shown in Figure 3. On the left (a) is the identity residual module, where the input data is directly connected to the output by jumping. On the right (b) is the convolutional residual module, where the data are subjected to convolution and batch normalization during the jump connection, with the convolutional kernel size is set to 1 × 1. The use of the two different residual modules depends on the input data size. When the input data size is consistent with the output data, the identical residual module is used. When the input data size is inconsistent with the output data, the convolutional residual module is needed to adjust the data size. Similar to the DnCNN network, applications of ResNet networks can be seen in the field of image denoising. Feng et al. [43] concluded that ResNet network can be useful for the acquisition of high-quality optical remote sensing images. In addition, Duan et al. [44] proposed a dual residual denoising autoencoder method with a channel attention mechanism (DRdA-CA) to improve the quality of communication signal.
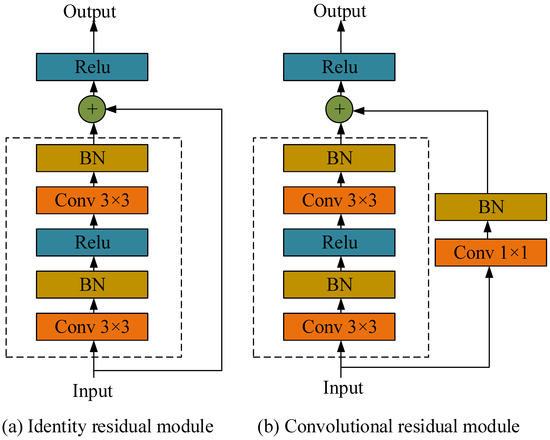
Figure 3.
Two different residual modules.
The ResNet network architecture is shown in Figure 4. It mainly consists of three parts: the input layer, hidden layer, and output layer. The input layer performs preliminary processing of the data through convolution, batch normalization, and activation functions to make the data meet the input requirements of the hidden layer. The size of the convolution kernel involved in the convolution operation is set to 3 × 1, the step size is set to 1, and the number of channels is set to 64. The hidden layer mainly consists of identity residual modules and convolutional residual modules, which will automatically judge the input data. When the size of the input and output data does not match, the convolutional residual module is selected to change the number of output channels. The output layer uses an average pooling layer to discard redundant data and reduce the computational complexity of the network. Then, the data are mapped through a fully connected layer to ultimately restore output data with the same size as the input data.
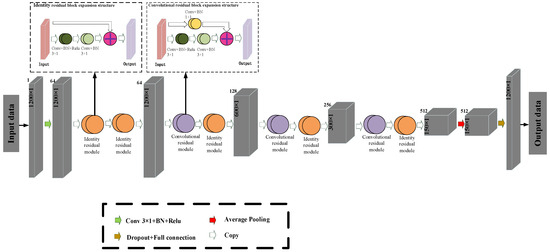
Figure 4.
The structure diagram of ResNet network.
2.4. Residual Denoising Convolutional Neural Network (ResDnCNN)
The DnCNN network provides more flexibility in handling different types of noise, as it can effectively extract and identify specific noise patterns. It is also designed to be compatible with GPU environments, which enhances the computational performance of the network. On the other hand, ResNet is primarily composed of various residual modules that are interconnected. This architectural design ensures the integrity of data features during the training process. Even with deep networks, ResNet promotes model convergence and prevents the occurrence of gradient explosion. In this study, we aimed to leverage the advantages of both networks and achieve complementary effects. We expected to achieve better noise removal results for CSEM data containing multiple types of noise. We refer to this improved neural network as the residual denoising convolutional neural network (ResDnCNN). The network architecture of ResDnCNN is illustrated in Figure 5. It can be seen that the input data is first processed by the DnCNN network. The output of the DnCNN network is then concatenated with the original input data and fed into the ResNet network for further processing. Finally, the residual concept is employed through skip connections, where the original input data are added to the output of the ResNet network, thus complementing the features lost during the network training process.
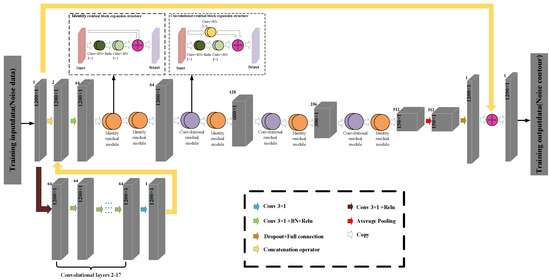
Figure 5.
The structure diagram of ResDnCNN network.
2.5. The Wide-Field Electromagnetic Method
The field data used in this paper were collected with the E − Ex wide-field electromagnetic method (WFEM) [12]. It is a CSEM of frequency domain. E − Ex WFEM uses an electric dipole source and observes the electric field component of the horizontal square line. The signal sent by the transmitter is a pseudo-random multi-frequency wave signal. For example, when a pseudo-random 7-frequency wave is sent, it can be equivalent to a signal composed of 7 square waves. Each transmission contains seven signals with different frequencies but similar energy intensities. The 7-2 signal is composed of seven harmonic signals of 1 Hz, 2 Hz, 4 Hz, 8 Hz, 16 Hz, 32 Hz, and 64 Hz; while the 7-3 signal is composed of seven harmonic signals with the frequencies of 0.75 Hz, 1.5 Hz, 3 Hz, 6 Hz, 12 Hz, 24 Hz, and 48 Hz. The receiver is designed without any filter; that is, it adopts full waveform acquisition. Afterwards, the power–frequency interference is filtered out through digital signal processing in a computer. The relevant instruments and software were developed by Central South University. The maximum power of the transmitter is 200 KW and the maximum transmitting current is 200 A. It can send any pseudo-random square wave signal ranging from 0.01 to 8192 Hz. The receiver adopts a 32-bit analog-to-digital converter (ADC), and its background noise is less than 1 μ Vrms (0.1~10 Hz).
The apparent resistivity parameter of the WFEM method is closely related to the electric field. In actual exploration, the measurement of the horizontal component (Ex) of the electric field is related to the potential difference () between the electrodes M and N, and the equations are as follows:
where I represents the emission current; dL is the length of the electric dipole; i stands for the imaginary symbol; k means the wave number; r is the distance between the observation site and the center of the electric dipole; σ is the conductivity; φ represents the angle between the direction of the electric dipole source and the vector diameter from the midpoint of the source to the receiving site; is composed of frequency, resistivity, and offset, reflecting the propagation characteristic of the electromagnetic wave under the ground; LMN is the distance between the electrodes M and N; and is a geometrical coefficient that is only related to the polar distance.
Therefore, it can be concluded that there is a correlation between the apparent resistivity and the potential difference, and the equation is:
Equation (5) is the WFEM apparent resistivity. As can be seen from the equation, as long as the potential difference, the transmission current, and the related pole distance coefficient are measured, the apparent resistivity information of the underground can be obtained.
3. Production of Sample Library and Model Training
3.1. Production of Sample Library
The quality of the training results of a model is greatly influenced by the sample library and, therefore, a sample library with diverse and rich noise content is crucial for effective training. To enrich the sample library with various types of noise, we selected high-quality CSEM data from Sichuan Province, China, and added multiple types of simulated noise to it. The specific process is as follows. The high-quality CSEM data was duplicated 90 times and labeled as samples 1 to 120. Gaussian white noise ranging from 1 to 30 dB was added to data numbered from 1 to 30, respectively. Then, after adding Gaussian white noise ranging from 1 to 30 dB to the data numbered from 31 to 60, different amplitudes of pulse noise were randomly added; Similarly, after adding Gaussian white noise ranging from 1 to 30 dB to the data numbered from 61 to 90, and then square wave noise of different amplitudes were added separately and randomly. Finally, 90 pairs of samples containing different types and amplitudes of noise were obtained. By selecting different high-quality data and following the above process to create the training set, the number of samples was expanded. The final training set in the sample library consisted of 230,400 samples, while the validation set contained 46,080 samples. The ratio of training set to validation set was 5:1.
Some examples of the noise types in the sample library are shown in Figure 6. Figure 6a–c demonstrates the addition of different intensities of Gaussian white noise to the high-quality CSEM data. Figure 6d–f shows the addition of random pulse noise to the high-quality CSEM data with different intensities of Gaussian white noise. Figure 6g–i depicts the addition of different square wave noise to the high-quality CSEM data with different intensities of Gaussian white noise.
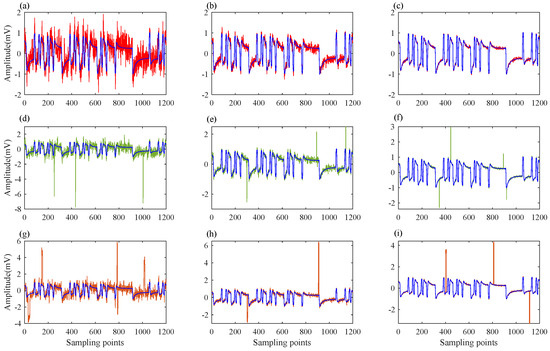
Figure 6.
Types of noise in some sample libraries: (a) add 5 dB of Gaussian white noise to the high-quality CSEM data; (b) add 15 dB of Gaussian white noise to the high-quality CSEM data; (c) add 25 dB of Gaussian white noise to the high-quality CSEM data; (d) add random pulse noise based on (a); (e) add random pulse noise on the basis of (b); (f) add random pulse noise on the basis of (c); (g) add random square wave noise based on (a); (h) add random square wave noise based on (b); (i) add random square wave noise based on (c).
3.2. Model Training
The well-prepared sample library was input into U-Net, LSTM, ResDnCNN, DnCNN, and ResNet networks for training, respectively. During the subsequent network training process, the sample library was encapsulated and shuffled to prevent the network from learning a specific order. The five networks were trained with the same set of parameters, which are as follows: Epoch was set to 300, batch size was set to 130, initial learning rate was set to 0.00001%, and the learning rate was decayed by 0.9 every 10 training epochs using gradient descent. The common Adam optimizer was used, and the loss function was set to mean square error (MSE). Figure 7 displays the training and validation loss curves for the five networks. From Figure 7, it can be observed that the training and validation loss curves of ResDnCNN are closer to each other compared to the other networks, and the curve is smoother. This indicates that ResDnCNN may have better robustness.
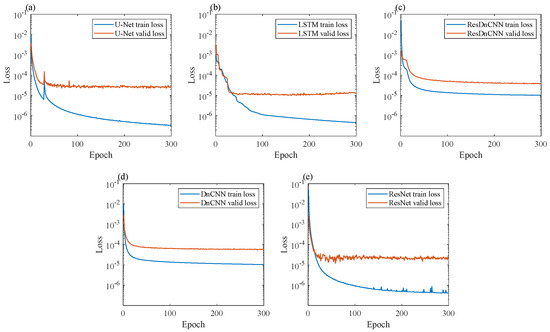
Figure 7.
Training and validation loss curves for (a) U-Net, (b) LSTM, (c) ResDnCNN, (d) DnCNN, (e) ResNet. The blue line represents the training loss curve and the orange line represents the validation loss curve.
3.3. Denoising Resulte of the Validation Set
Figure 8 shows the training results of the ResDnCNN for the validation set. The black curves in Figure 8 represent the expected high-quality signal, while the blue curves represent the actual denoised result of the network. In Figure 8, the red curves in (a–c) represent Gaussian white noise at different SNR. The green curves in (d–f) of Figure 8 represent mixed noise consisting of different levels of Gaussian white noise and pulse noise. The orange curves in (g–i) of Figure 8 represent mixed noise consisting of different levels of Gaussian white noise and square wave noise. Obviously, the training curve of the ResDnCNN model on the validation set is closely fitted to the expected high-quality signal, demonstrating a strong suppression effect on various types of simulated noise.
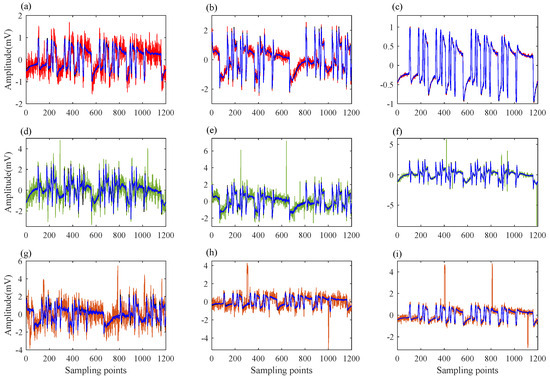
Figure 8.
The denoising effect of ResDnCNN for partial validation set: (a) The denoising effect of Gaussian white noise with low SNR; (b) The denoising effect of Gaussian white noise with medium SNR; (c) The denoising effect of Gaussian white noise with high SNR; (d) The denoising effect of Gaussian white noise and pulse noise with low SNR; (e) The denoising effect of Gaussian white noise and pulse noise with medium SNR; (f) The denoising effect of Gaussian white noise and pulse noise with high SNR; (g) The denoising effect of Gaussian white noise and square wave noise with low SNR; (h) The denoising effect of Gaussian white noise and square wave noise with medium SNR; (i) The denoising effect of Gaussian white noise and square wave noise with high SNR.
4. Synthetic Data
To demonstrate the generalization ability and effectiveness of our method, we processed the synthetic data to showcase the effectiveness of the model. The synthetic data used in this article were made by adding different simulated pulse noise and square wave noise to the measured high-quality data collected in Huidong County, Sichuan Province. There was no obvious noise in both the time domain and the frequency domain, and the Pearson correlation between the observed data and the synchronous transmission signal was about 0.95. The apparent resistivity curves obtained with them were also very smooth and continuous. Therefore, it can be determined that they were almost unaffected by noise pollution. Figure 9 shows the denoising effect of this method on the synthetic pulse data in the time domain. After being processed by ResDnCNN, most of the strong noise was eliminated, with only a small amount of the noise remaining. The preliminary processing data were inputted into SISC for further processing, and finally high-quality data were obtained. Similarly, Figure 10 and Figure 11 also demonstrate the denoising effect of this method on synthetic square wave data and synthetic pulse square wave data in the time domain. The effects shown in the figures indicate the effectiveness of this method in noise suppression.
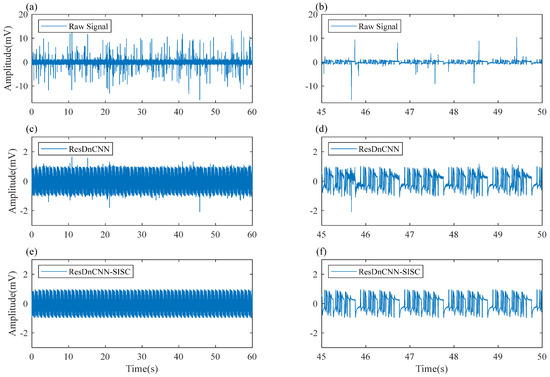
Figure 9.
The denoising effect of synthetic pulse noise in the time domain. (a,c,e) the original synthetic pulse noise data denoised by ResDNCNN, and then denoised by SISC; (b,d,f) the local segments corresponding to the data on the left.
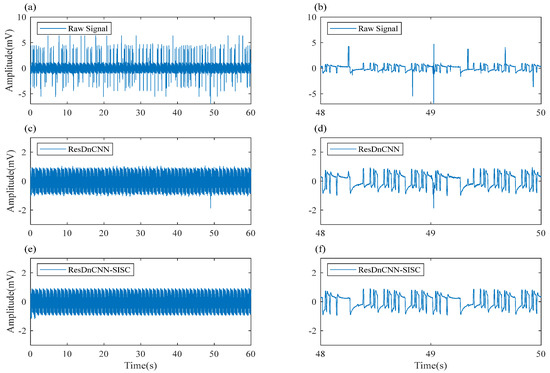
Figure 10.
The denoising effect of synthetic square wave noise in the time domain. (a,c,e) the original synthetic square wave noise data denoised by ResDNCNN, and then denoised by SISC; (b,d,f) the local segments corresponding to the data on the left.
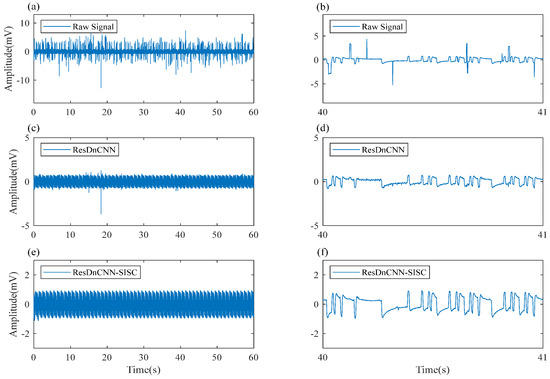
Figure 11.
The denoising effect of synthetic pulse square wave noise in the time domain. (a,c,e) the original synthetic pulse square wave noise data denoised by ResDNCNN, and then denoised by SISC; (b,d,f) the local segments corresponding to the data on the left.
We denoised the same segment of noisy synthetic data in the time domain using U-Net, LSTM, DnCNN, ResNet, ResDnCNN, and ResDnCNN-SISC respectively, and the results are shown in Figure 12. Although the U-Net and DnCNN demonstrated effective results in Figure 12, the denoised signals exhibited significant fluctuations and lacked smoothness. The signals processed by the LSTM network and ResNet network showed obvious overall amplitude compression, exhibiting significant differences in amplitude compared to the original signals. The suppression of square wave noise by the ResDnCNN network was not complete, resulting in residual noise. However, the denoising results were relatively smooth in regions without square wave noise. The data processed by ResDnCNN-SISC, on the other hand, was the smoothest. The noise of the whole signal was effectively removed without altering the signal amplitude. Figure 13 and Figure 14 show the denoising effects of different methods on synthetic pulse noise and synthetic pulse square wave noise, respectively.
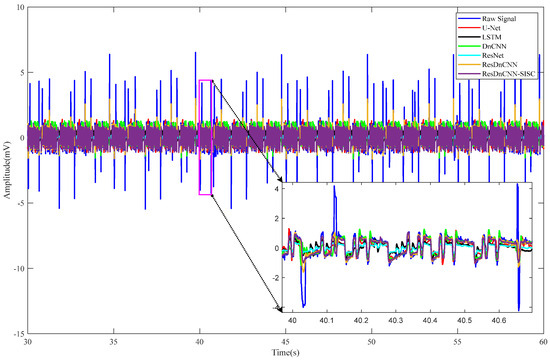
Figure 12.
The denoising results of synthetic square wave data using different methods are as follows: The solid dark blue line represents the signal with square wave noise. The solid red line, black line, green line, light blue line, orange line, and deep purple line represent the denoised signals using U-Net, LSTM, DnCNN, ResNet, ResDnCNN, and ResDnCNN-SISC, respectively.
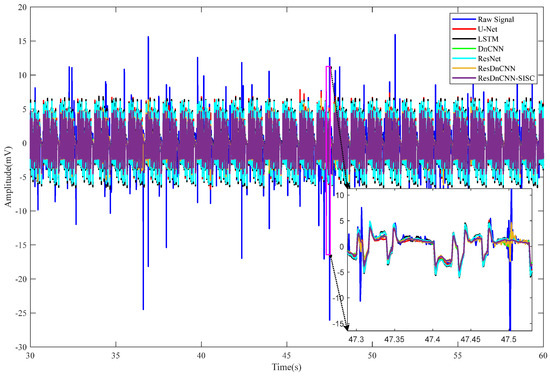
Figure 13.
The denoising results of synthetic pulse data using different methods are as follows: The solid dark blue line represents the signal with pulse noise. The solid dark blue line represents the signal with square wave noise. The solid red line, black line, green line, light blue line, orange line, and deep purple line represent the denoised signals using U-Net, LSTM, DnCNN, ResNet, ResDnCNN, and ResDnCNN-SISC, respectively.
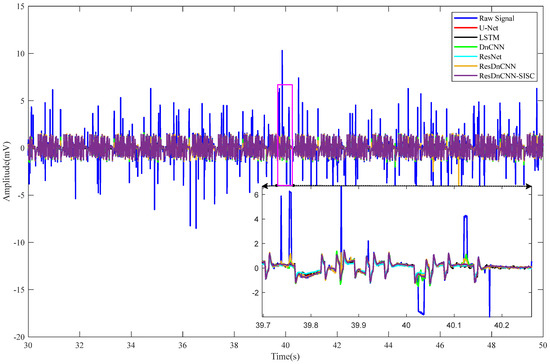
Figure 14.
The denoising results of synthetic pulse square wave data using different methods are as follows: The solid dark blue line represents the signal with pulse square wave noise. The solid dark blue line represents the signal with square wave noise. The solid red line, black line, green line, light blue line, orange line, and deep purple line represent the denoised signals using U-Net, LSTM, DnCNN, ResNet, ResDnCNN, and ResDnCNN-SISC, respectively.
To gain a more intuitive understanding of the denoising effect, we used a tabular form to quantify the data. As shown in Table 1, we calculated the SNR, reconstruction error, and normalized cross-correlation (NCC) for the denoised signals using the six methods. It is clear that the ResDnCNN-SISC method improves the SNR from −2.9118 dB to 14.2147 dB, reduces the reconstruction error from 1.39% to 0.19%, and increases the correlation coefficient from 0.5828 to 0.9848. Among these six methods, the ResDnCNN-SISC method had the best performance. Figure 15 shows the improvement in SNR achieved by different methods for denoising the synthetic data, presenting the quantified SNR data in the form of a line graph to demonstrate the superiority of our approach visually.

Table 1.
Quantification of denoising results using different methods.
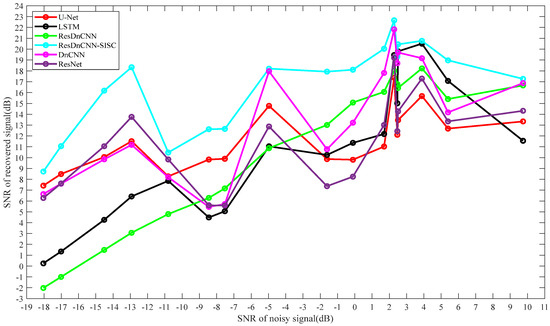
Figure 15.
SNR improvement of synthetic data denoising by different methods.
In geological exploration, it is common to encounter uneven electrical conductivity distribution of subterranean rocks. In such cases, the apparent resistivity can be employed to reflect the variations in electrical conductivity of rocks and ores. When the data are weakly contaminated by noise, the apparent resistivity curve will exhibit a relatively smooth response with frequency variation. However, when the data are contaminated by strong noise, the apparent resistivity curve will jump and exhibit sharp fluctuations. We calculated the WFEM apparent resistivity of the signal after denoising by different methods. Figure 16 shows the apparent resistivity curves obtained by different methods when dealing with different synthetic noise.
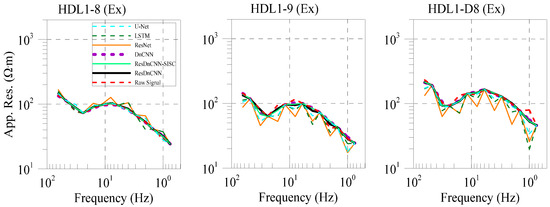
Figure 16.
The apparent resistivity curves of different stations.
As shown in Figure 16, compared with the other five methods, this method can effectively suppress the distorted data when the original data are contaminated by strong noise causing severe distortion. This results in smoother and more regular apparent resistivity curves, aligning with the trend of slow frequency variation observed in wide area of apparent resistivity.
5. Measured Data
To test the application effect of this method in practical scenarios, we next performed denoising on the measured CSEM data. The CSEM data used in this study were obtained from the karst survey of a reservoir in Huidong, Sichuan Province, China, conducted by Central South University with the wide-field electromagnetic method in September 2017. The signal transmitter and receiver used in the survey were developed by Central South University. The signal sent by the signal transmitter was a pseudo-random 7-frequency wave. The length of the transmitter dipole was about 1 km, the distance between the transmitter and receiver was about 7 km, and the maximum transmit current was close to 70 A. The receiver was responsible for collecting the electric field signal parallel to the dipole. Figure 17 shows the denoising effect of the measured data in the time domain. In the figure, the original measured data exhibits significant pulse noise at some moments, indicating that the data was severely contaminated. After the initial ResDnCNN processing, the data noise was suppressed, but there was still some residual noise. Finally, the periodic high-quality data with a stable amplitude and smooth curve were obtained through SISC processing.
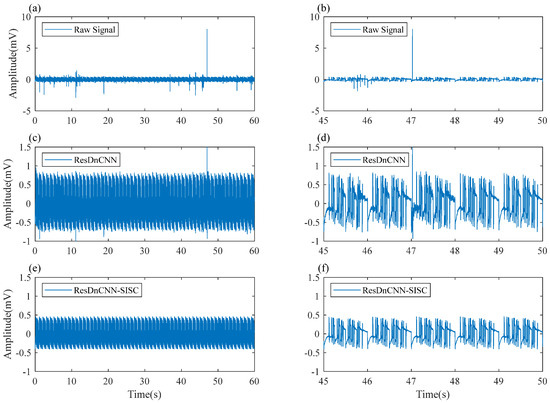
Figure 17.
The denoising effect of the measured data in the time domain. (a,c,e) the measured data denoised by ResDNCNN, and then denoised by SISC; (b,d,f) the local segments corresponding to the data on the left.
As shown in Figure 18, we selected a segment of the measured data and applied different methods for denoising. In Figure 18, it is evident that LSTM and ResNet exhibit significant differences in the amplitude of the data before and after processing. The amplitude width of the data processed by LSTM and ResNet is noticeably smaller compared to the original signal. Although the amplitude of data processed by U-Net and DnCNN has little change, there was still residual Gaussian white noise present in the original data. ResDnCNN effectively suppressed most of the noise, with only minimal weak noise remaining. The ResDnCNN-SISC method successfully removes the noise and yields high-quality data that matches the expected shape. Obviously, our method has significantly improved the quality of the measured data.
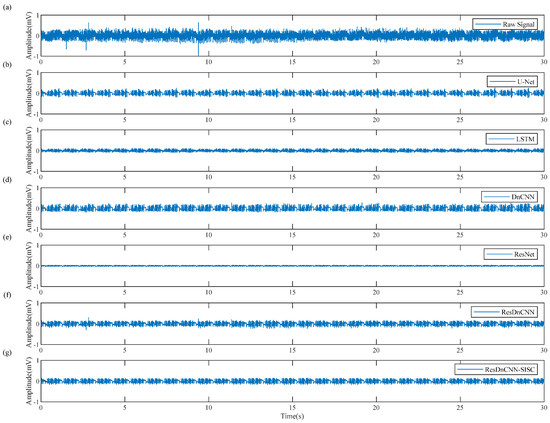
Figure 18.
Results of different methods for processing measured data: (a) original measured data; denoising results of (b) U-Net, (c) LSTM, (d) DnCNN, (e) ResNet, (f) ResDnCNN, (g) ResDnCNN-SISC.
The apparent resistivity curves of the measured data are shown in Figure 19, where different methods were used to denoise different datasets. From Figure 19, it can be observed that the data processed by U-Net, LSTM, and ResNet networks actually became more volatile, resulting in a reverse effect on the data. While DnCNN achieved a certain degree of noise reduction, data jumps still exist, as seen in the figure. The processing effect of ResDnCNN is basically the same as that of ResDnCNN-SISC. For data with jumps at low frequencies, it is able to achieve a smooth apparent resistivity curve by ResDnCNN-SISC processing.
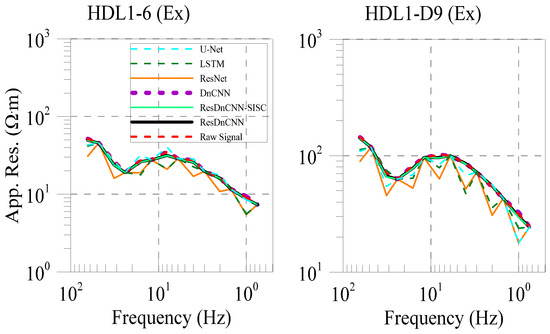
Figure 19.
The apparent resistivity curves of the measured data obtained by different processing methods.
6. Conclusions
To address the challenge of noise interference in the practical application of CSEM and enhance the detection effectiveness of CSEM, this study conducted research on denoising methods for CSEM data. Diverging from conventional signal denoising methods, this study proposed an innovative deep learning denoising approach by synergistically leveraging the advantages of the residual network (ResNet) and denoising convolutional neural network (DnCNN). Moreover, this approach is integrated with shift-invariant sparse coding (SISC) to establish the ResDnCNN-SISC method, which systematically applies to the processing of CSEM data, facilitating a comprehensive investigation of high-precision denoising techniques for CSEM data. By subjecting CSEM data, containing various types of noise, to denoising tests, the effectiveness of our method in effectively suppressing different types of noise was demonstrated, leading to a significant improvement in the data signal-to-noise ratio. Furthermore, the ResDnCNN-SISC method exhibited the advantage of avoiding bias caused by manual threshold setting, resulting in more objective denoising outcomes. Through the application of the ResDnCNN-SISC denoising method to real-world CSEM data and a comparative analysis with other denoising methods such as U-Net, DnCNN, and LSTM, the prominent superiority of the ResDnCNN-SISC method is evident, as it yielded smoother resistivity curve. This enhancement is conducive to improving the effectiveness of the controlled-source electromagnetic method in geophysical exploration under strong interference conditions.
In this study, the WFEM data were taken as an example to illustrate the effectiveness and superiority of the proposed method. Nevertheless, the proposed method is not only applicable to WFEM data, but also to any other CSEM data, as well as periodic or similar periodic signals in other fields. It is worth noting that the ResDnCNN network model employed in this study requires a relatively long training time. To enhance training efficiency, further optimization of the neural network structure will be pursued to reduce the training duration.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, X.W. and X.B.; methodology, X.W. and G.L.; software, X.W., X.B. and H.Y.; visualization, X.W.; validation, X.B. and T.T.; investigation, X.W.; supervision, X.W., G.L., L.S. and H.Y.; writing—original draft, X.W.; writing—review and editing, X.W., X.B., G.L. and T.T.; formal analysis, X.W., X.B. and L.S.; resources, G.L.; data curation, G.L. and H.Y.; funding acquisition, X.B., G.L. and L.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41904076 and 42364006), the Jiangxi Provincial Natural Science Foundation (20232BCJ23051, 20232BAB203070, and 20212BAB203004), the Jiangxi Province Key R&D Project (20223BBG74005), the Open Fund from Nanchang Key Laboratory of Hydrogeology and High Quality Groundwater Resources Exploitation and Utilization (20231B22), the Open Fund from Jiangxi Engineering Technology Research Center of Nuclear Geoscience Data Science and System (JETRCNGDSS202201), and the Open Fund from Key Laboratory of Metallogenic Prediction of Nonferrous Metals and Geological Environment Monitoring (Central South University), Ministry of Education (2021YSJS02).
Data Availability Statement
Data associated with this research are available and can be obtained by contacting the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
We appreciate the editors and reviewers for their valuable comments that greatly improved the paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Cai, H.Z.; Long, Z.D.; Lin, W.; Li, J.H.; Lin, P.R.; Hu, X.Y. 3D multinary inversion of controlled-source electromagnetic data based on the finite-element method with unstructured mesh. Geophysics 2021, 86, E77–E92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.J.; Yogeshwar, P.; Hu, X.Y.; Peng, R.H.; Tezkan, B.; Morbe, W.; Li, J.H. Effects of electrical anisotropy on long-offset transient electromagnetic data. Geophys. J. Int. 2020, 222, 1074–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansen, S.E.; Panzner, M.; Mittet, R.; Amundsen, H.E.F.; Lim, A.; Vik, E.; Landro, M.; Arntsen, B. Deep electrical imaging of the ultraslow-spreading Mohns Ridge. Nature 2019, 567, 379–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danielsen, J.E.; Auken, E.; Jørgensen, F.; Søndergaard, V.; Sørensena, K.L. The application of the transient electromagnetic method in hydrogeophysical surveys. J. Appl. Geophys. 2003, 53, 181–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myer, D.; Constable, S.; Key, K. Broad-band waveforms and robust processing for marine CSEM surveys. Geophys. J. Int. 2011, 184, 698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finn, C.A.; Bedrosian, P.A.; Holbrook, W.S.; Auken, E.; Bloss, B.R.; Crosbie, J. Geophysical Imaging of the Yellowstone’s Hydrothermal Plumbing System. Nature 2022, 603, 643–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maclennan, K.; Li, Y.G. Denoising multicomponent CSEM data with equivalent source processing techniques. Geophysics 2013, 78, E125–E135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, M.; Tan, H.D.; Wang, K.P. 3D LBFGS inversion of controlled source extremely low frequency electromagnetic data. Appl. Geophys. 2017, 13, 689–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grayver, A.V.; Streich, R.; Ritter, O. 3D inversion and resolution analysis of land-based CSEM data from the Ketzin CO2 storage formation. Geophysics 2014, 79, E101–E114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Streich, R.; Becken, M.; Ritter, O. Robust processing of noisy land-based controlled-source electromagnetic data. Geophysics 2013, 78, E237–E247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constable, S.; Srnka, L.J. An introduction to marine controlled-source electromagnetic methods for hydrocarbon exploration. Geophysics 2007, 72, WA3–WA12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.S. Combined Application of Wide-Field Electromagnetic Method and Flow Field Fitting Method for High-Resolution Exploration: A Case Study of the Anjialing No. 1 Coal Mine. Engineering 2018, 4, 667–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reninger, P.A.; Martelet, G.; Deparis, J.; Perrin, J.; Chen, Y. Singular value decomposition as a denoising tool for airborne time domain electromagnetic data. J. Appl. Geophys. 2011, 75, 264–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen, S.; Nyboe, N.S.; Mai, S.; Larsen, J.J. Extraction and use of noise models from transient electromagnetic data. Geophysics 2018, 83, E37–E46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Li, D.Q.; Tong, T.G.; Zhang, D.; Zhou, Y.T.; Chen, Y.K. Denoising controlled-source electromagnetic data using least-squares inversion. Geophysics 2018, 83, E229–E244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barfod, A.S.; Levy, L.; Larsen, J.J. Automatic Processing of Time Domain Induced Polarization Data using Supervised Artificial Neural Networks. Geophys. J. Int. 2011, 224, 312–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Wu, S.L.; Cai, H.Z.; He, Z.S.; Liu, X.Q.; Zhou, C.; Tang, J.T. IncepTCN: A new deep temporal convolutional network combined with dictionary learning for strong cultural noise elimination of controlled-source electromagnetic data. Geophysics 2023, 88, E107–E122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Tang, J.T.; Xiao, X.; Jiang, Q.Y.; Huang, X.Y.; Hu, S.G. Application of powerline noise cancellation method in correlation identification of controlled source electromagnetic method. J. Geophys. Eng. 2021, 18, 339–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.Q.; Chen, R.J.; Cai, H.Z.; Luo, W.B.; Revil, A. Correlation analysis for spread-spectrum induced-polarization signal processing in electromagnetically noisy environments. Geophysics 2017, 82, E243–E256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.Q.; Lu, Q.T.; Chen, R.J.; Lin, P.R.; Chen, C.J.; Yang, L.Y.; Cai, H.Z. A modified empirical mode decomposition method for multiperiod time-series detrending and the application in full-waveform induced polarization data. Geophys. J. Int. 2019, 217, 1058–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.F.; Pan, X.P.; Guo, Z.W.; Liu, J.X.; Hou, Q.Y. Marine controlled-source electromagnetic data denoising while weak signal preserving based on jointly sparse model and dictionary learning. J. Appl. Geophys. 2023, 215, 105122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, S.Y.; Yin, C.C.; Su, Y.; Liu, Y.H.; Wang, Y.; Liu, C.H.; Xiong, B.; Sun, H.F. Airborne electromagnetic data denoising based on dictionary learning. Appl. Geophys. 2020, 17, 306–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; He, Z.S.; Tang, J.T.; Deng, J.Z.; Liu, X.Q.; Zhu, H.J. Dictionary learning and shift-invariant sparse coding denoising for controlled-source electromagnetic data combined with complementary ensemble empirical mode decomposition. Geophysics 2021, 86, E185–E198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.Y.; Cai, H.Z.; Liu, S.; Xie, J.T.; Hu, X.Y. Recovering 3D Basement Relief Using Gravity Data Through Convolutional Neural Networks. J. Geophys. Res.-Solid Earth 2021, 126, e2021JB022611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jifara, W.; Jiang, F.; Rho, S.; Chen, M.W.; Liu, S.H. Medical image denoising using convolutional neural network: A residual learning approach. J. Supercomput. 2019, 75, 704–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Zhao, J.; Xu, J. A Scene Images Diversity Improvement Generative Adversarial Network for Remote Sensing Image Scene Classification. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2020, 17, 1692–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grais, E.M.; Plumbley, M.D. Single channel audio source separation using convolutional denoising autoencoders. In Proceedings of the IEEE Global Conference on Signal and Information Processing, Montreal, QC, Canada, 14–16 November 2017; pp. 1265–1269. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.; Xue, G.Q.; Xiao, P.; Li, J.T.; Liu, L.H.; Fang, G.Y. The Removal of The High-Frequency Motion-Induced Noise in Helicopter-Borne Transient Electromagnetic Data Based on Wavelet Neural Network. Geophysics 2019, 84, K1–K9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, F.Q.; Chen, K.C.; Wang, X.B.; Cao, H.; Chen, D.L.; Chen, F.Z. Denoising stacked autoencoders for transient electromagnetic signal denoising. Nonlinear Proc. Geoph. 2019, 26, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.H.; Huang, Q.H.; Zhao, L. De-noising of transient electromagnetic data based on the long short-term memory-autoencoder. Geophys. J. Int. 2021, 224, 669–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.F.; Liu, Y.H.; Yin, C.C.; Ren, X.Y.; Su, Y. Fast imaging of time-domain airborne EM data using deep learning technology. Geophysics 2020, 85, E163–E170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bang, M.; Oh, S.; Noh, K.; Seol, S.J.; Byun, J. Imaging subsurface orebodies with airborne electromagnetic data using a recurrent neural network. Geophysics 2021, 86, E407–E419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.S.; Huang, S.H.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, J. Denoising of Transient Electromagnetic Data Based on the Minimum Noise Fraction-Deep Neural Network. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2022, 19, 8028405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Zuo, W.M.; Chen, Y.J.; Meng, D.Y.; Zhang, L. Beyond a gaussian denoiser: Residual Learning of deep cnn for image denoising. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2017, 26, 3142–3155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.M.; Zhang, X.Y.; Ren, S.Y.; Sun, J. Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, X.T.; Li, Y.; Yang, B.J. Desert low-frequency noise suppression by using adaptive DnCNNs based on the determination of high-order statistic. Geophys. J. Int. 2019, 219, 1281–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Zhou, X.; Chen, C.; Xu, L.; Zhou, F.; Shi, F.; Tang, J. Multi-type geomagnetic noise removal via an improved U-Net deep learning network. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 3307422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhu, Y.P.; Wang, Y.P. A Criminisi-DnCNN Model-Based Image Inpainting Method. Math. Probl. Eng. 2022, 2022, 9780668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, F.; Zhu, Z.H.; Zhou, H.; Tao, Z.; Jun, S.; Wu, X.J. Efficient automatically evolving convolutional neural network for image denoising. Memet. Comput. 2022, 15, 219–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthikeyan, V.; Raja, E.; Pradeep, D. Energy based denoising convolutional neural network for image enhancement. Imaging Sci. J. 2023, volume, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.J.; Zheng, Y.; Si, X. Attenuation of linear noise based on denoising convolutional neural network with asymmetric convolution blocks. Explor. Geophys. 2022, 53, 532–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.T.; Lin, J.; Lu, S.P.; Wang, H.Z.; Li, Y. Multiscale Spatial Attention Network for Seismic Data Denoising. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.B.; Zhang, W.X.; Su, X.Q.; Xu, Z.P. Optical Remote Sensing Image Denoising and Super-Resolution Reconstructing Using Optimized Generative Network in Wavelet Transform Domain. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, R.F.; Chen, Z.Y.; Zhang, H.T.; Wang, X.; Meng, W.; Sun, G.D. Dual Residual Denoising Autoencoder with Channel Attention Mechanism for Modulation of Signals. Sensors 2023, 23, 1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).