Long-Term Variability in Sea Surface Temperature and Chlorophyll a Concentration in the Gulf of California
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
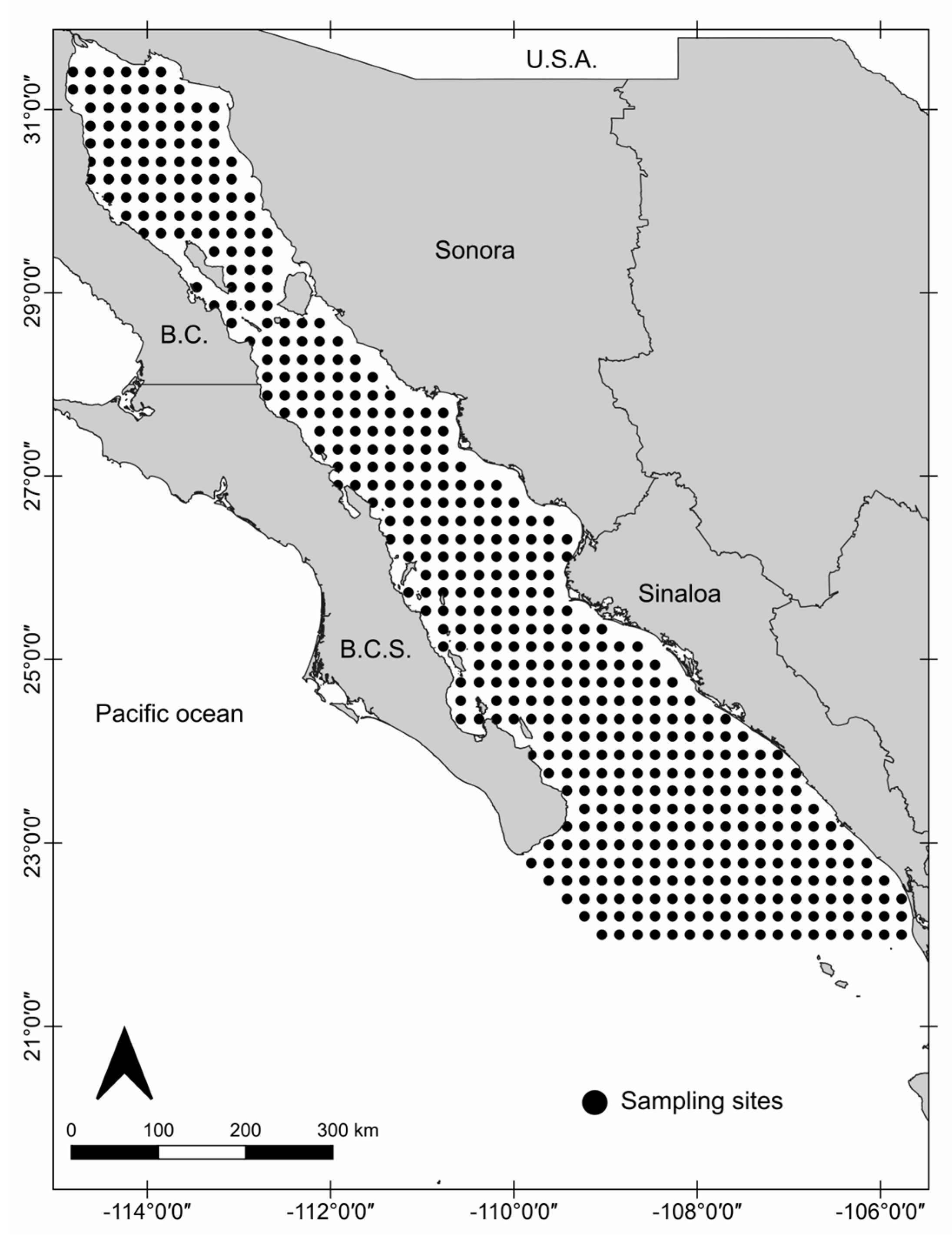
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Environmental and Oceanographic Characterization
- Initialize centroids by first shuffling the dataset and then randomly selecting K data points for the centroids without replacement;
- Keep iterating until there is no change to the centroids; i.e., the assignment of data points to clusters does not change;
- Compute the sum of the squared distance between data points and all centroids;
- Assign each data point to the closest cluster (centroid);
- Compute the centroids for the clusters by taking the average of the all data points that belong to each cluster.
3. Results
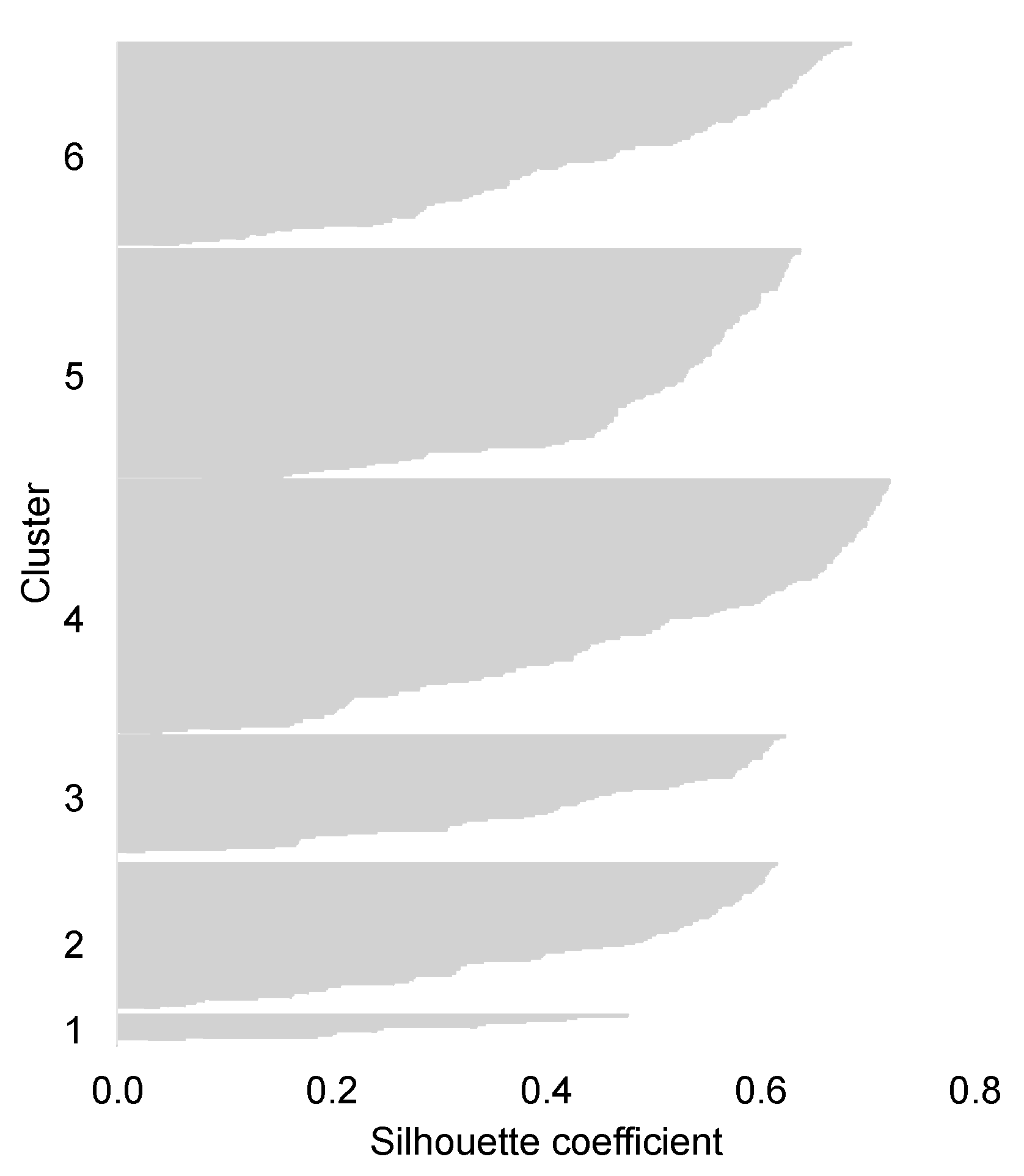
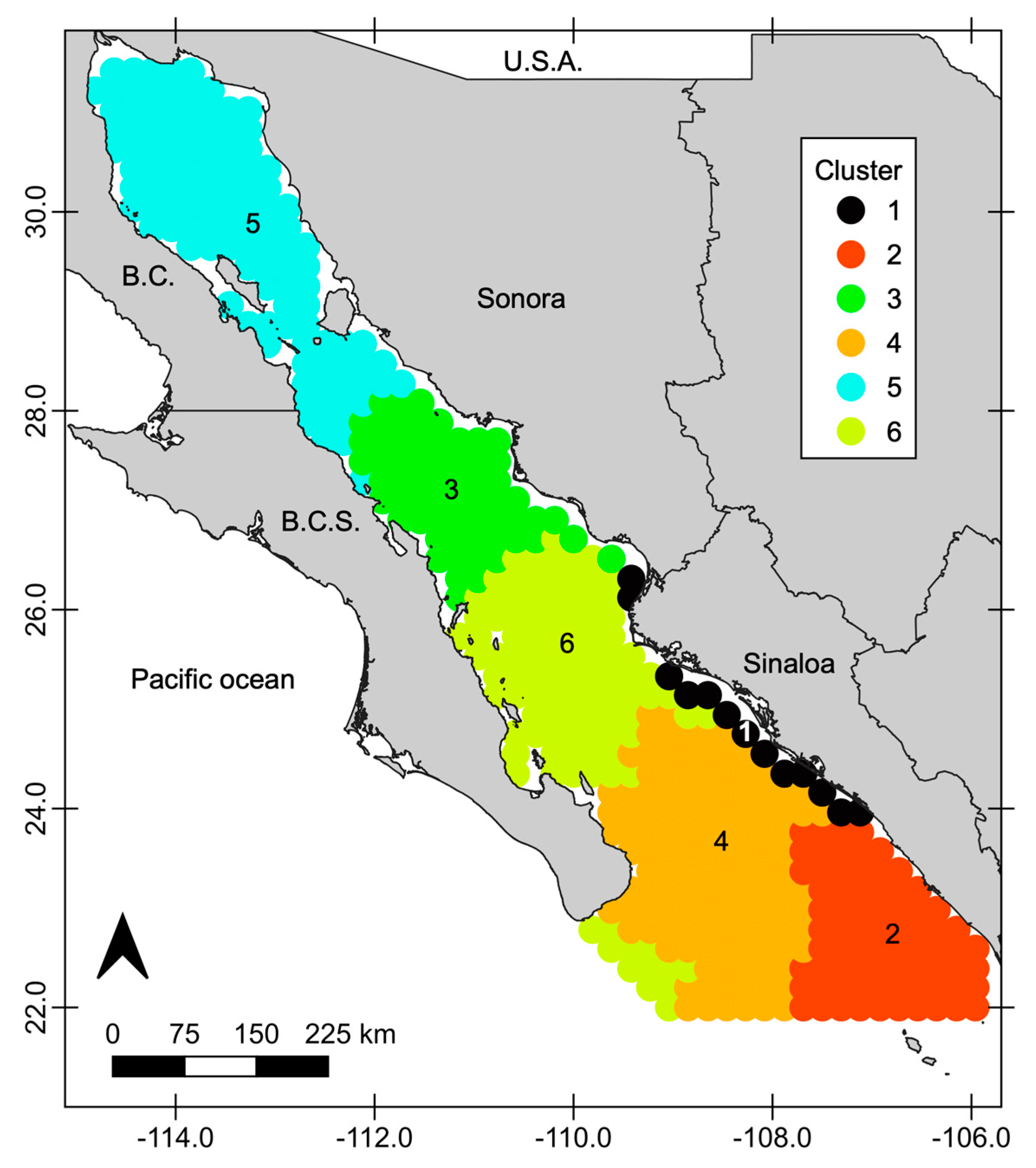
3.1. Cluster Analysis
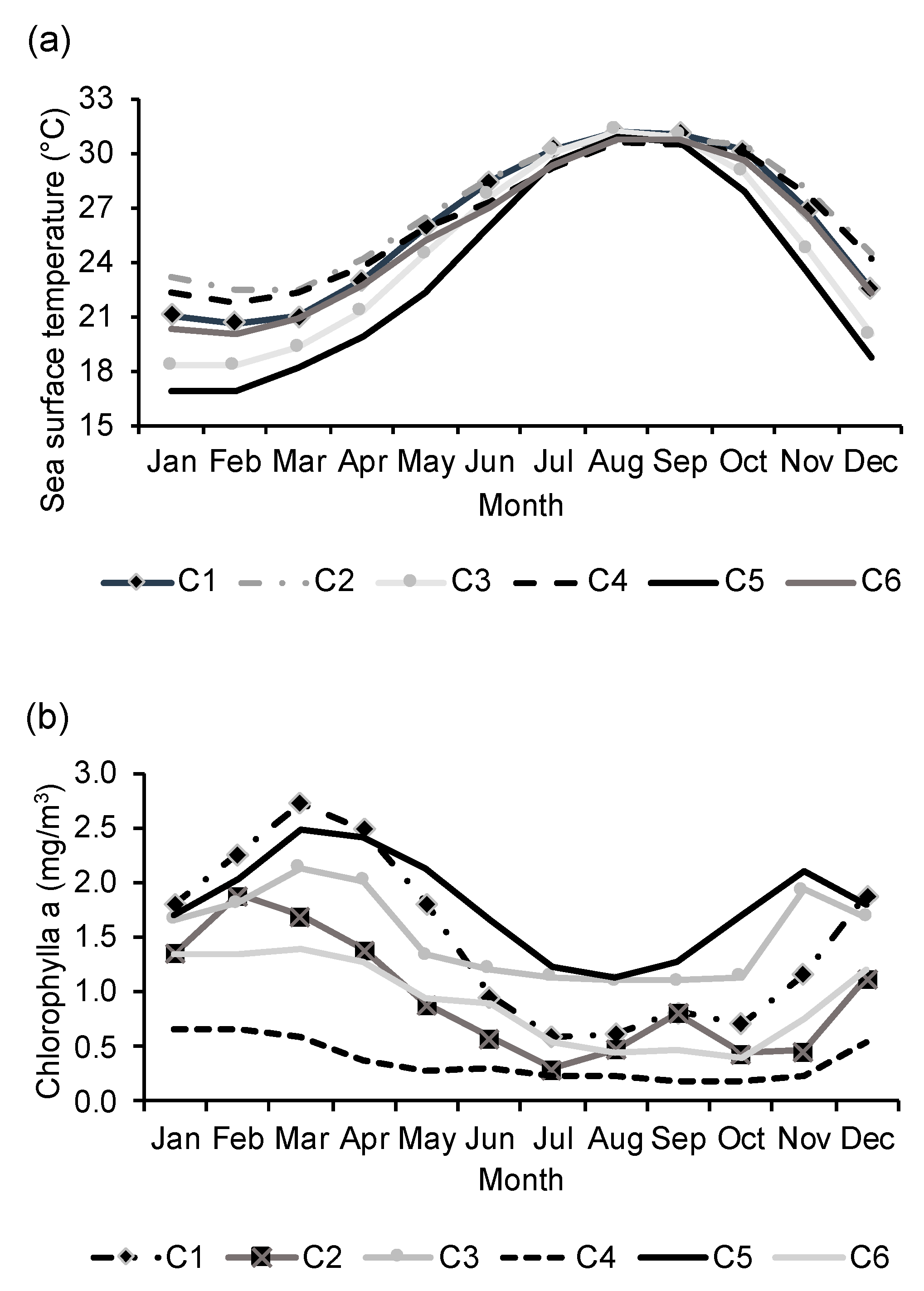
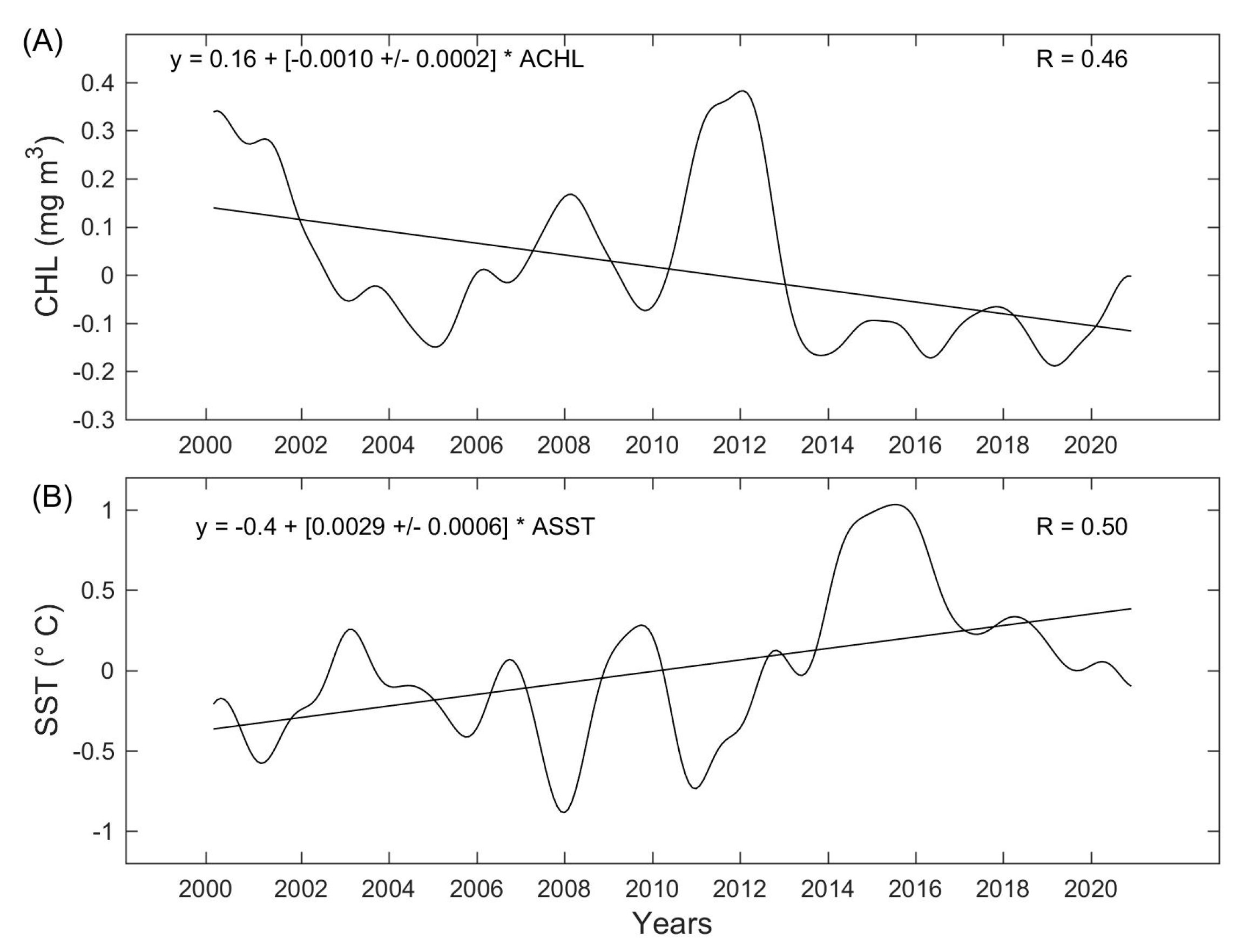
3.2. Time Series and Climatology
3.3. Interannual Variability
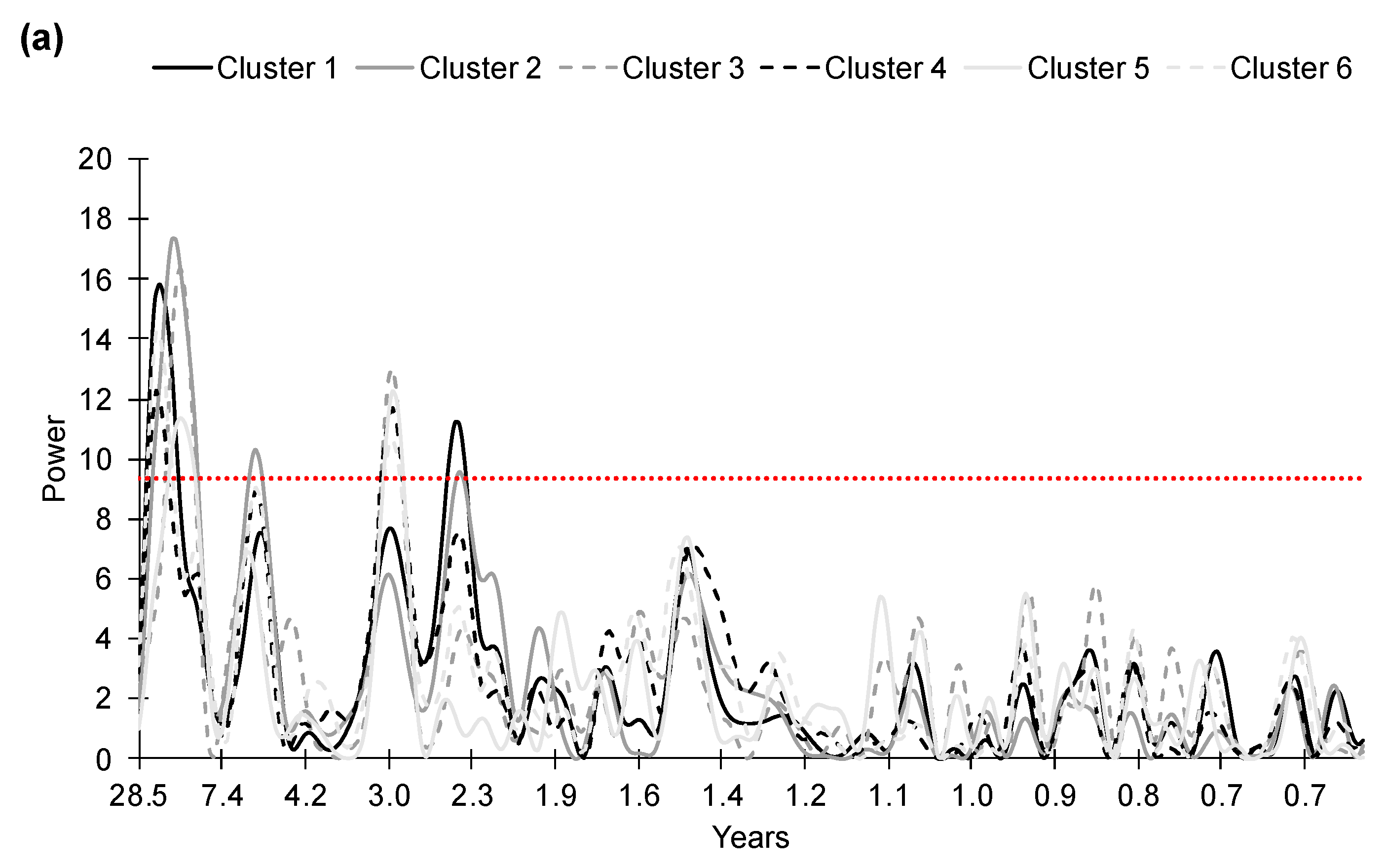
3.4. Fourier Analyses
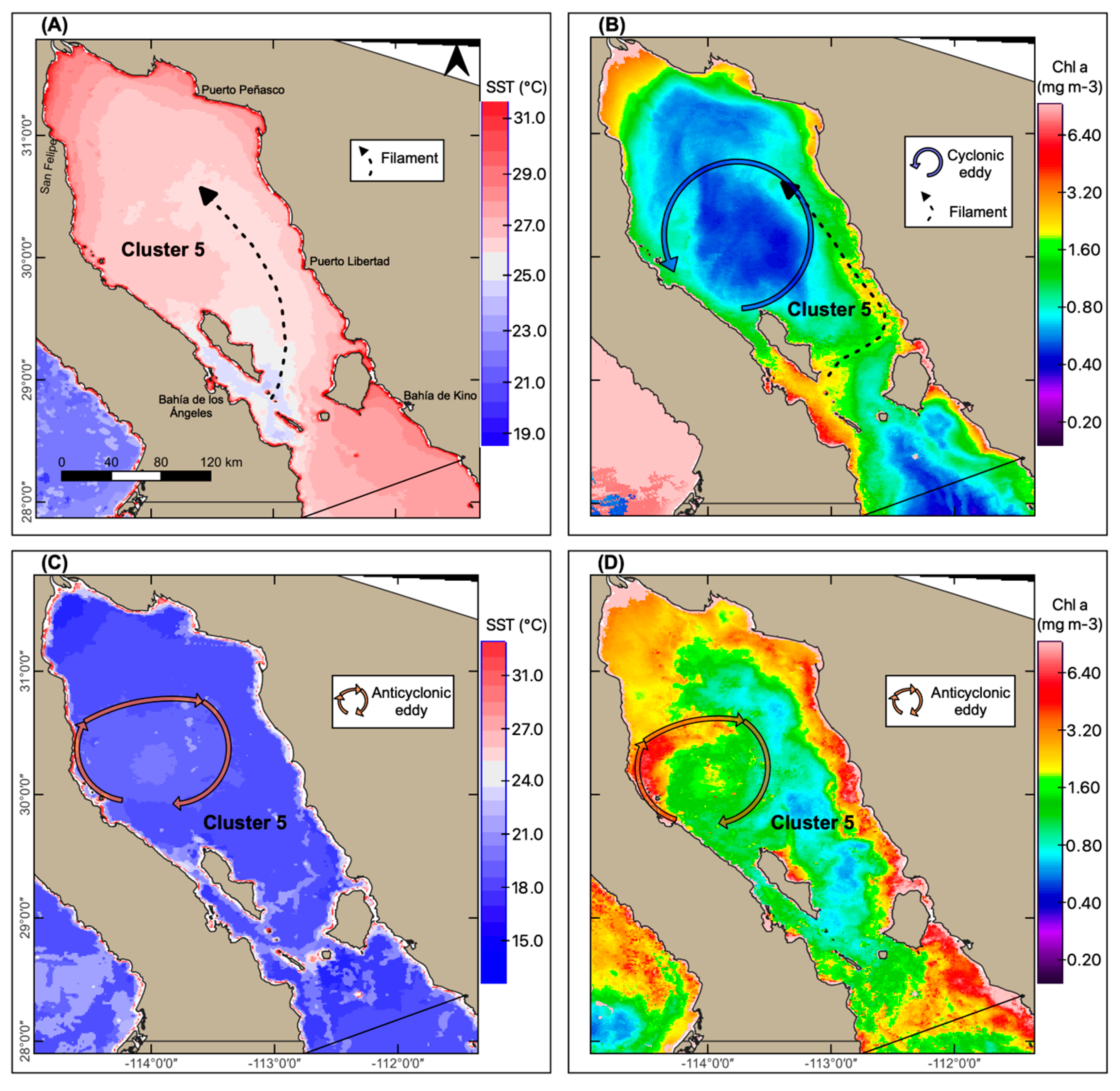
3.5. Mesoscale Processes, SST, and Chl-a Concentration
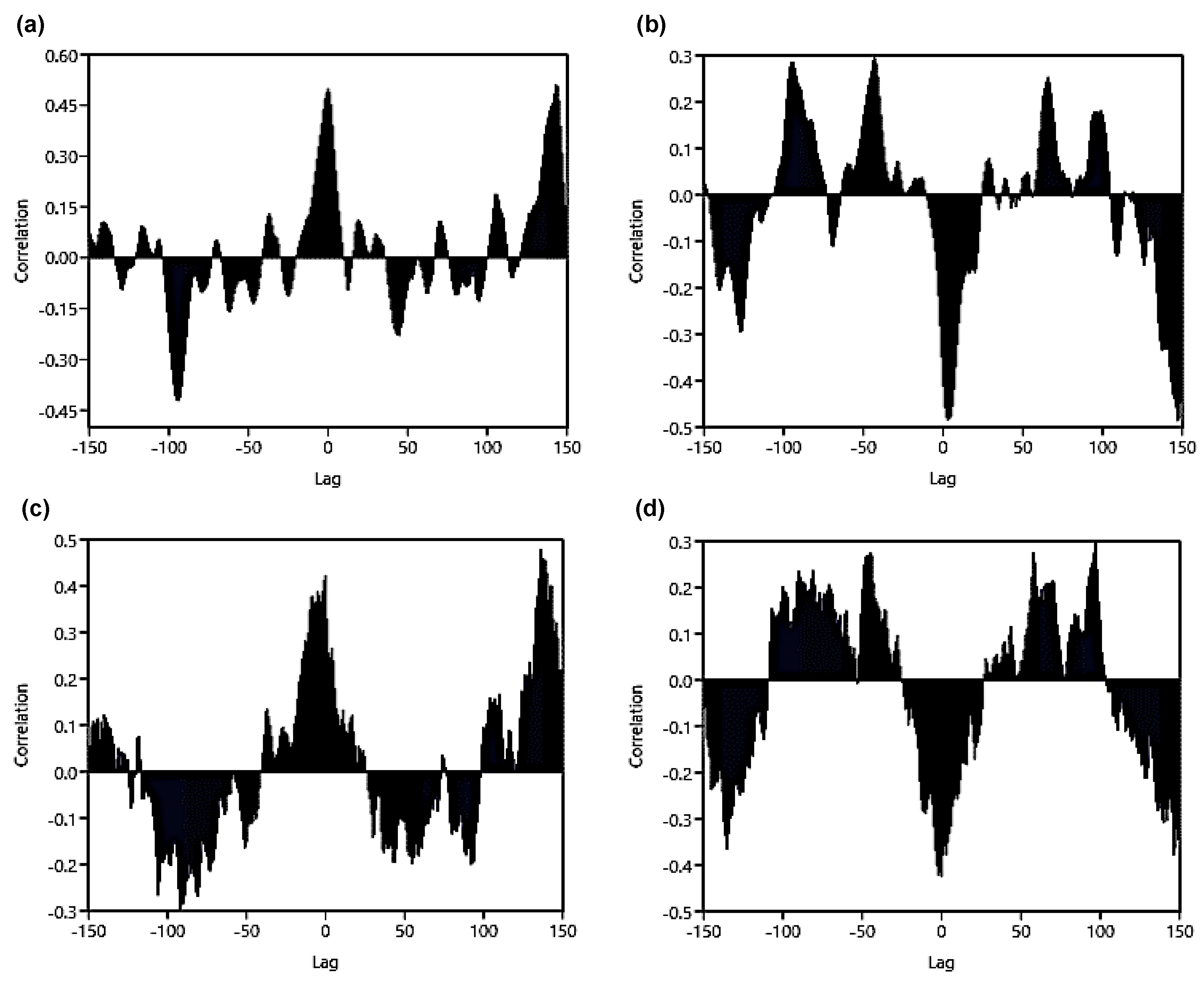
3.6. Association of the SST and Chl-a Concentration with Climate Indices (ONI and PDO)
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lluch-Cota, S.E.; Aragón-Noriega, E.A.; Arreguín-Sánchez, F.; Aurioles-Gambóa, D.; Bautista-Romero, J.J.; Brusca, R.C.; Cervantes-Duarte, R.; Cortés-Altamirano, R.; Del-Monte-Luna, P.; Esquivel-Herrera, A.; et al. The Gulf of California: Review of ecosystem status and sustainability challenges. Prog. Oceanogr. 2007, 73, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Páez-Osuna, F.; Sanchez-Cabeza, J.A.; Ruiz-Fernández, A.C.; Alonso-Rodríguez, R.; Piñón-Gimate, A.; Cardoso-Mohedano, J.G.; Flores-Verdugo, F.J.; Carballo, J.L.; Cisneros-Mata, M.A.; Álvarez-Borrego, S. Environmental status of the Gulf of California: A review of responses to climate change and climate variability. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2016, 162, 253–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duque-Herrera, A.F.; Helenes, J.; Flores-Trujillo, J.G.; Ruiz-Fernández, A.C.; Sánchez-Cabeza, J.A. Dinoflagellate cysts and ENSO-PDO climate forcing in the southern Gulf of California. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2020, 560, 110055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, R.; Durazo, R.; Mascarenhas, A.; Collins, C.A.; Trasviña, A. Thermohaline variability and geostrophic circulation in the southern portion of the Gulf of California. Deep-Sea Res. Pt. I. 2006, 53, 188–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Martínez, J.; Arreguín-Sánchez, F.; Hernández-Vázquez, S.; García-Juárez, A.R.; Valenzuela-Quiñonez, W. Interannual variation of growth of the brown shrimp Farfantepenaeus californiensis and its relation to temperature. Fish. Res. 2003, 61, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Martínez, J.; Rábago-Quiroz, C.; Nevárez-Martínez, M.O.; García-Juárez, A.R.; Rivera-Parra, G.; Chávez-Villalba, J. Growth, reproduction, and size at first maturity of blue shrimp, Litopenaeus stylirostris (Stimpson, 1874) along the east coast of the Gulf of California, Mexico. Fish. Res. 2005, 71, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Martínez, J. La Variabilidad Ambiental y las Pesquerías de México; Comisión Nacional de Acuacultura y Pesca: México D.F., México, 2008; pp. 1–200. [Google Scholar]
- Lanz, E.; López-Martínez, J.; Nevárez-Martínez, M.; Dworak, J.A. Small pelagic fish catches in the Gulf of California associated with sea surface temperature and chlorophyll. Calif. Coop. Ocean. Fish. Investig. Rep. 2009, 50, 134–146. [Google Scholar]
- Giron-Nava, A.; Ezcurra, E.; Brias, A.; Velarde, E.; Deyle, E.; Cisneros-Montemayor, A.M.; Munch, S.B.; Sugihara, G.; Aburto-Oropeza, O. Environmental variability and fishing effects on the Pacific sardine fisheries in the Gulf of California. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2021, 78, 623–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farach-Espinoza, E.B.; López-Martínez, J.; García-Morales, R.; Nevarez-Martínez, M.O.; Ortega-García, S.; Lluch-Cota, D.B. Coupling oceanic mesoscale events with catches of the Pacific sardine (Sardinops sagax) in the Gulf of California. Prog. Oceanogr. 2022, 206, 102858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, R.; Lavín, M.F.; Ripa, P. Seasonal heat balance in the Gulf of California. J. Geophys. Res-Ocean. 1994, 99, 3249–3261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lluch-Cota, S.E. Coastal upwelling in the eastern Gulf of California. Oceanol. Acta. 2000, 23, 731–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueroa, J.M.; Robles, J.M. Eddies in the Gulf of California. In Proceedings of the Oceanography Society Inaugural Meeting, Monterey, CA, USA, 27–30 August 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Oschlies, A.; Garçon, V. Eddy-induced enhancement of primary production in a model of the North Atlantic. Nature 1998, 394, 266–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Calderón, J.; Manzo-Monroy, H.; Santamaría-del-Ángel, E.; Castro, R.; González-Silvera, A.; Millán-Núñez, R. Mesoscale variability of the Mexican Tropical Pacific using TOPEX and SeaWiFS data. Cienc. Mar. 2006, 32, 539–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, L.-L.; Chelton, D.B.; Le Traon, P.-Y.; Morrow, R. Eddy Dynamics From Satellite Altimetry. Oceanography 2010, 23, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alpers, W.; Brandt, P.; Lazar, A.; Dagorne, D.; Sow, B.; Faye, S.; Hansen, M.W.; Rubino, A.; Poulain, P.-M.; Brehmer, P. A small-scale oceanic eddy off the coast of West Africa studied by multi-sensor satellite and surface drifter data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 129, 132–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz Gómez, R.C.; Monreal Gómez, M.A.; Nikolaevich Bulgakov, S. Efecto de los vórtices en sistemas acuáticos y su relación con la química, biología y geología. Interciencia 2008, 33, 741–746. [Google Scholar]
- Kahru, M.; Fiedler, P.C.; Gille, S.T.; Manzano, M.; Mitchell, B.G. Sea level anomalies control phytoplankton biomass in the Costa Rica Dome area. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahru, M.; Mitchell, B.G.; Gille, S.T.; Hewes, C.D.; Holm-Hansen, O. Eddies enhance biological production in the Weddell-Scotia Confluence of the Southern Ocean. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dufois, F.; Hardman-Mountford, N.J.; Greenwood, J.; Richardson, A.J.; Feng, M.; Matear, R.J. Anticyclonic eddies are more productive than cyclonic eddies in subtropical gyres because of winter mixing. Sci. Adv. 2016, 2, e1600282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaube, P.; Chelton, D.B.; Samelson, R.M.; Schlax, M.G.; O’Neill, L.W. Satellite Observations of Mesoscale Eddy-Induced Ekman Pumping. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2015, 45, 104–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, H.-R.; Chai, F.; Yuan, Y. Impact of mesoscale eddies on chlorophyll variability off the coast of Chile. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0203598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaigneau, A.; Eldin, G.; Dewitte, B. Eddy activity in the four major upwelling systems from satellite altimetry (1992–2007). Prog. Oceanogr. 2009, 83, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nan, F.; Xue, H.; Xiu, P.; Chai, F.; Shi, M.; Guo, P. Oceanic eddy formation and propagation southwest of Taiwan. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2011, 116, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ripa, P. Seasonal circulation in the Gulf of California. Ann. Geophys. 1990, 8, 559–563. [Google Scholar]
- Ripa, P. Toward a Physical Explanation of the Seasonal Dynamics and Thermodynamics of the Gulf of California. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 1997, 27, 597–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beier, E.; Ripa, P. Seasonal gyres in the northern Gulf of California. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 1999, 29, 305–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palacios-Hernández, E.; Beier, E.; Lavín, M.F.; Ripa, P. The effect of the seasonal variation of stratification on the circulation of the northern Gulf of California. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2002, 32, 705–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beron-Vera, F.J.; Ripa, P. Three-dimensional aspects of the seasonal heat balance in the Gulf of California. J. Geophys Res–Ocean. 2000, 105, 11441–11457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beron-Vera, F.J.; Ripa, P. Seasonal salinity balance in the Gulf of California. J. Geophys Res.–Ocean. 2002, 107, 15-1–15-15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, R.; Mascarenhas, A.S.; Durazo, R.; Collins, C.A. Seasonal variation of the temperature and salinity at the entrance to the Gulf of California, Mexico. Cienc. Mar. 2000, 26, 561–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavin, M.F.; Marinone, S.G. An Overview of the Physical Oceanography of the Gulf of California. In Nonlinear Processes in Geophysical Fluid Dynamics; Velasco Fuentes, O.U., Sheinbaum, J., Ochoa, J., Eds.; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2003; pp. 173–204. [Google Scholar]
- García-Morales, R.; López-Martínez, J.; Valdez-Holguin, J.E.; Herrera-Cervantes, H.; Espinosa-Chaurand, L.D. Environmental Variability and Oceanographic Dynamics of the Central and Southern Coastal Zone of Sonora in the Gulf of California. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farach-Espinoza, E.B.; López-Martínez, J.; García-Morales, R.; Nevárez-Martínez, M.O.; Lluch-Cota, D.B.; Ortega-García, S. Temporal variability of oceanic mesoscale events in the Gulf of California. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robles-Tamayo, C.M.; García-Morales, R.; Romo-León, J.R.; Figueroa-Preciado, G.; Peñalba-Garmendia, M.C.; Enríquez-Ocaña, L.F. Variability of Chl-a Concentration of Priority Marine Regions of the Northwest of Mexico. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badan-Dangon, A.; Dorman, C.E.; Merrifield, M.A.; Winant, C.D. The lower atmosphere over the Gulf of California. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 1991, 96, 16877–16896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turrent, C.; Zaitsev, O. Seasonal cycle of the near-surface diurnal wind field over the bay of La Paz, Mexico. Bound-Lay Meteorol. 2014, 151, 353–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robles-Tamayo, C.M.; García-Morales, R.; Valdez-Holguín, J.E.; Figueroa-Preciado, G.; Herrera-Cervantes, H.; López-Martínez, J.; Enríquez-Ocaña, L.F. Chlorophyll a concentration distribution on the mainland coast of the Gulf of California, Mexico. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robles-Tamayo, C.M.; Valdez-Holguín, J.E.; García-Morales, R.; Figueroa-Preciado, G.; Herrera-Cervantes, H.; López-Martínez, J.; Enríquez-Ocaña, L.F. Sea Surface Temperature (SST) Variability of the Eastern Coastal Zone of the Gulf of California. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lluch-Cota, S.E.; Parés-Sierra, A.; Magaña-Rueda, V.O.; Arreguín-Sánchez, F.; Bazzino, G.; Herrera-Cervantes, H.; Lluch-Belda, D. Changing climate in the Gulf of California. Prog. Oceanogr. 2010, 87, 114–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strub, P.T.; James, C. Altimeter-derived surface circulation in the large–scale NE Pacific Gyres.: Part 1. seasonal variability. Prog. Oceanogr. 2002, 53, 163–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latif, M.; Barnett, T.P. Causes of decadal climate variability over the North Pacific and North America. Science. 1994, 266, 634–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filonov, A.; Tereshchenko, I. El Niño 1997–98 monitoring in mixed layer at the Pacific Ocean near Mexico's west coast. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2000, 27, 705–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera-Cervantes, H.; Lluch-Cota, D.B.; Lluch-Cota, S.E.; Gutiérrez-de-Velasco, S. The ENSO signature in sea-surface temperature in the Gulf of California. J. Mar. Res. 2007, 65, 589–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavín, M.F.; Palacios-Hernández, E.; Cabrera, C. Sea surface temperature anomalies in the Gulf of California. Geofís. Int. 2003, 42, 363–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Cabeza, J.A.; Herrera-Becerril, C.A.; Carballo, J.L.; Yáñez, B.; Álvarez-Sánchez, L.F.; Cardoso-Mohedano, J.G.; Ruiz-Fernández, A.C. Rapid surface water warming and impact of the recent (2013–2016) temperature anomaly in shallow coastal waters at the eastern entrance of the Gulf of California. Prog. Oceanogr. 2022, 202, 102746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera-Cervantes, H.; Lluch-Cota, S.E.; Lluch-Cota, D.B.; Gutiérrez de Velasco Sanromán, G.; Lluch-Belda, D. ENSO influence on satellite-derived chlorophyll trends in the Gulf of California. Atmósfera 2010, 23, 253–262. [Google Scholar]
- Belda, D.L.; del Monte Luna, P.; Lluch-Cota, S.E. 20th century variability in Gulf of California SST. Cal. Coop. Ocean. Fish. 2009, 50, 147–154. [Google Scholar]
- Arias-Aréchiga, J.P. Regionalización del Golfo de California: Una Propuesta a Partir de Concentración de Pigmentos Fotosintéticos. Bachelor Thesis, Universidad Autónoma de Baja California Sur, La Paz, Bolivia, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Petatán-Ramírez, D. Propuesta de Zonación del Golfo de California con Base en Variables Oceanográficas y Distribución de Macroinvertebrados. Master thesis, Universidad Autónoma de Baja California Sur, La Paz, Bolivia, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Heras-Sánchez, M.d.C.; Valdez-Holguín, J.E.; Hazas-Izquierdo, R.G. Sea-Surface Temperature Spatiotemporal Analysis for the Gulf of California, 1998–2015: Regime Change Simulation. In Supercomputing. ISUM 2018. Communications in Computer and Information Science; Torres, M., Klapp, J., Gitler, I., Tchernykh, A., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; Volume 948, pp. 167–181. [Google Scholar]
- Allen, W.E. Plankton diatoms of the Gulf of California obtained by the G. Allan Hancock Expedition of 1936. Allan Hancock Pac. Exped. 1937, 3, 47–59. [Google Scholar]
- Flores-de-Santiago, F.J.; Santamaría-del-Ángel, E.; González-Silvera, A.; Martínez-Díaz-de-León, A.; Millán-Núñez, R.; Kovacs, J.M. Assessing dynamics micro-regions in the Great Islands of the Gulf of California based on MODIS aqua imagery products. In Proceedings of the Coastal Ocean Remote Sensing, San Diego, CA, USA, 5 October 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Lluch-Cota, S.E.; Arias-Aréchiga, J.P. Sobre la importancia de considerar la existencia de centros de actividad biológica para la regionalización del océano: El caso del Golfo de California. In Centros de Actividad Biológica del Pacífico Mexicano; Lluch-Belda, D., Elourduy-Garay, J.F., Lluch-Cota, S.E., Ponce-Díaz, G., Eds.; Centro de Investigaciones Biológicas del Noroeste, SC: La Paz, Mexico, 2000; pp. 255–263. ISBN 970-18-6285-6. [Google Scholar]
- Jiménez, A.; Marinone, S.G.; Parés-Sierra, A. Efecto de la variabilidad espacial y temporal del viento sobre la circulación en el Golfo de California. Ciencias Mar. 2005, 31, 357–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lavín, M.F.; Castro, R.; Beier, E.; Godínez, V.M.; Amador, A.; Guest, P. SST, thermohaline structure, and circulation in the southern Gulf of California in June 2004 during the North American Monsoon Experiment. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2009, 114, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahru, M. Windows Image Manager, WIM Software (Ver. 9.06) and User’s Manual. 2016, p. 125. Available online: http://www.wimsoft.com/ (accessed on 28 June 2017).
- Bitácora Ambiental Golfo de California. Available online: https://www.gob.mx/semarnat/acciones-y-programas/bitacora-ambiental-golfo-de-california (accessed on 23 July 2023).
- Ralambondrainy, H. A conceptual version of the k-means algorithm. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 1995, 16, 1147–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koren, O.; Hallin, C.A.; Perel, N.; Bendet, D. Decision-making enhancement in a big data environment: Application of the k-means algorithm to mixed data. J. Artif. Intell. Soft Comput. Res. 2019, 9, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Wang, J.; Li, X. Efficiency analysis of machine learning intelligent investment based on K-means algorithm. IEEE Access. 2020, 8, 147463–147470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacQueen, J. Some methods for classification and analysis of multivariate observations. In Proceedings of the Fifth Berkeley Symposium on Mathematical Statistics and Probability, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 21 June–18 July 1965; Cambridge University Press: London, UK, 1967; Volume 1, pp. 281–297. [Google Scholar]
- Mantua, N.J.; Hare, S.R.; Zhang, Y.; Wallace, J.M.; Francis, R.C. A Pacific interdecadal climate oscillation with impacts on salmon production. B. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1997, 78, 1069–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pegau, W.S.; Boss, E.; Martínez, A. Ocean color observations of eddies during the summer in the Gulf of California. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2002, 29, 6-1–6-3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cayula, J.-F.; Cornillon, P. Edge Detection Algorithm for SST Images. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 1992, 9, 67–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diehl, S.F.; Budd, J.W.; Ullman, D.; Cayula, J.-F. Geographic Window Sizes Applied to Remote Sensing Sea Surface Temperature Front Detection. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2002, 19, 1105–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinone, S.G.; Ulloa, M.J.; Parés-Sierra, A.; Lavín, M.F.; Cudney-Bueno, R. Connectivity in the northern Gulf of California from particle tracking in a three-dimensional numerical model. J. Mar. Syst. 2008, 71, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez-Borrego, S. Physical Oceanography in a New Island Biogeography of the Sea of Cortes; Case, T.J., Cody, M.L., Ezcurra, E., Eds.; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2002; pp. 41–59. [Google Scholar]
- López, M.; Candela, J.; García, J. Two overflows in the Northern Gulf of California. J. Geophys. Res.-Ocean. 2008, 113, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavín, M.F.; Castro, R.; Beier, E.; Godínez, V.M. Mesoscale eddies in the southern Gulf of California during summer: Characteristics and interaction with the wind stress. J. Geophys. Res.-Ocean. 2013, 118, 1367–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera-Cervantes, H. Sea surface temperature, ocean color and wind forcing patterns in the Bay of La Paz, Gulf of California: Seasonal variability. Atmósfera 2019, 32, 25–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, R.E. Predictability of sea surface temperature and sea level pressure anomalies over the North Pacific Ocean. J. Phys. Oceanog. 1976, 6, 249–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trenberth, K.E. What are the seasons? Bull. Am. Meteorol. 1983, 64, 1276–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, A.J.; Schneider, N. Interdecadal climate regime dynamics in the North Pacific Ocean: Theories, observations and ecosystem impacts. Prog. Oceanogr. 2000, 47, 355–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavín, M.F.; Durazo, R.; Palacios, E.; Argote, M.L.; Carrillo, L. Lagrangian Observations of the Circulation in the Northern Gulf of California. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 1997, 27, 2298–2305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanz-Sánchez, E.E. Análisis de la Variabilidad Espacio-Temporal en la Disponibilidad de las Especies de Pelágicos Menores en el Golfo de California y su Relación con el Medio Ambiente. Doctoral Thesis, Centro de Investigaciones Biológicas del Noroeste, La Paz, Bolivia, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Hernández-Padilla, J.C.; Zetina-Rejón, M.J.; Arreguín-Sánchez, F.; del Monte-Luna, P.; Nieto-Navarro, J.T.; Salcido-Guevara, L.A. Structure and function of the southeastern Gulf of California ecosystem during low and high sea surface temperature variability. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2021, 43, 101686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longhurst, A.; Sathyendranath, S.; Platt, T.; Caverhill, C. An estimate of global primary production in the ocean from satellite radiometer data. J. Plankton Res. 1995, 17, 1245–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reygondeau, G.; Longhurst, A.; Martinez, E.; Beaugrand, G.; Antoine, D.; Maury, O. Dynamic biogeochemical provinces in the global ocean. Global Biogeochem. Cycles. 2013, 27, 1046–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Round, F.E. The phytoplankton of the Gulf of California. Part I. Its composition, distribution and contribution to the sediments. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1967, 1, 76–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cupp, E.E.; Allen, W.A. Plankton diatoms of the Gulf of California. Allan Hancock Pac. Exped. 1938, 3, 61–99. [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert, J.Y.; Allen, W.E. The phytoplankton of the Gulf of California obtained by the E.W. Scripps in 1939 and 1940. J. Mar. Res. 1943, 5, 89–110. [Google Scholar]
- Sverdrup, H.U. The Gulf of California: Preliminary discussion of the cruise of the E.W. Scripps in February and March 1939. Pac. Sci. Cong. 1941, 3, 161–166. [Google Scholar]
- Santamaría-del-Angel, E.; Alvarez-Borrego, S.; Müller-Karger, F.E. Gulf of California biogeographic regions based on coastal zone color scanner imagery. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 1994, 99, 7411–7421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soto-Mardones, L.; Marinone, S.G.; Parés-Sierra, A. Time and spatial variability of sea surface temperature in the Gulf of California. Cienc. Mar. 1999, 25, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahru, M.; Marinone, S.G.; Lluch-Cota, S.E.; Parés-Sierra, A.; Mitchell, B.G. Ocean-color variability in the Gulf of California: Scales from days to ENSO. Deep Sea Res. 2 Top Stud. Oceanogr. 2004, 51, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lluch-Cota, D. El sector pesquero. In Cambio Climático: Una Visión Desde México; Martínez, J., Fernández, A., Eds.; Secretaria de Medio Ambiente y Recursos Naturales, Instituto Nacional de Ecología: México D.F., México, 2004; pp. 327–335. [Google Scholar]
- Escalante, F.; Valdez-Holguín, J.E.; Álvarez-Borrego, S.; Lara-Lara, J.R. Temporal and spatial variation of sea surface temperature, chlorophyll a, and primary productivity in the Gulf of California. Cienc. Mar. 2013, 39, 203–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez-Borrego, S. Gulf of California. In Estuaries and Enclosed Seas; Ketchum, B.H., Ed.; Elsevier: New York, NY, USA, 1983; pp. 427–449. [Google Scholar]
- Álvarez-Borrego, S.; Lara-Lara, J.R. The Physical environment and primary productivity of the Gulf of California. In The Gulf and Peninsular Province of the Californias; Dauphin, J.P., Simoneit, B.R.T., Eds.; AAPG Mem: Tulsa, OK, USA, 1991; pp. 555–567. [Google Scholar]
- Martínez-Díaz-de-León, A.; Pacheco-Ruíz, I.; Delgadillo-Hinojosa, F.; Zertuche-González, J.A.; Chee-Barragán, A.; Blanco-Betancourt, R.; Guzmán-Calderón, J.M.; Gálvez-Telles, A. Spatial and temporal variability of the sea surface temperature in the Ballenas-Salsipuedes Channel (central Gulf of California). J. Geophys. Res.-Ocean. 2006, 111, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, S.; Qin, D.; Manning, M.; Chen, Z.; Marquis, M.; Averyt, K.B.; Tignor, M.; Miller, H.L. (Eds.) Climate Change 2007: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2007; pp. 235–336. [Google Scholar]
- Gutiérrez, O.Q.; Marinone, S.G.; Parés-Sierra, A. Lagrangian surface circulation in the Gulf of California from a 3D numerical model. Deep. Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2004, 51, 659–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavín, M.F.; Castro, R.; Beier, E.; Cabrera, C.; Godínez, V.M.; Amador-Buenrostro, A. Surface circulation in the Gulf of California in summer from surface drifters and satellite images (2004–2006). J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2014, 119, 4278–4290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Orozco, E. Volumetric Analysis of the Water Masses of the Gulf of California. MSc. Thesis, Centro de Investigación Científica y de Educación Superior de Ensenada, Ensenada, México, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Hakspiel-Segura, C.; Martínez-López, A.; Delgado-Contreras, J.A.; Robinson, C.J.; Gómez-Gutiérrez, J. Temporal variability of satellite chlorophyll-a as an ecological resilience indicator in the central region of the Gulf of California. Prog. Oceanogr. 2022, 205, 102825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robles, J.M.; Marinone, S.G. Seasonal and interannual thermohaline variability in the Guaymas Basin of the Gulf of California. Cont. Shelf Res. 1987, 7, 715–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, M.; Candela, J.; Argote, M.L. Why does the Ballenas Channel have the coldest SST in the Gulf of California? Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez-Molina, L.L.; Álvarez-Borrego, S.; Lara-Lara, J.R.; Marinone, S.G. Annual and semiannual variations of phytoplankton biomass and production in the central Gulf of California estimated from satellite data. Cienc. Mar. 2013, 39, 217–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aadland, L.P. Stream habitat types: Their fish assemblages and relationship to flow. N. Am. J. Fish. Manag. 1993, 13, 790–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez, N.; Cochero, J. Un índice para evaluar la calidad del hábitat en la Franja Costera Sur del Río de la Plata y su vinculación con otros indicadores ambientales. Ecol. Austral. 2013, 23, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borja, A.; Bald, J.; Franco, J.; Larreta, J.; Muxika, I.; Revilla, M.; Germán Rodríguez, J.; Solaun, O.; Uriarte, A.; Valencia, V. Using multiple ecosystem components, in assessing ecological status in Spanish (Basque Country) Atlantic marine waters. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2009, 59, 54–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acevedo-Cervantes, A.; López-Martínez, J.; Herrera-Valdivia, E.; Rodríguez-Romero, J. Análisis de la abundancia, dominancia y diversidad de la comunidad de peces demersales de profundidad de 90 a540 metros en el Golfo de California, México. Interciencia 2009, 34, 660–665. [Google Scholar]
- Rábago-Quiroz, C.H.; López-Martínez, J.; Valdez-Holguín, J.E.; Nevárez-Martínez, M.O.; Acevedo-Cervantes, A. Fish assemblages in the bycatch of bottom shrimp trawls on the west side of the Gulf of California, Mexico. Mar. Biol. Res. 2012, 8, 865–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acevedo-Cervantes, A. Composición Espacial y Temporal de los Peces Acompañantes del Camarón de Profundidad del Golfo de California. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidad Autónoma de Nayarit, Nayarit, México, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez-Romero, J.; del Carmen López-González, L.; Galván-Magaña, F.; Sánchez-Gutiérrez, F.J.; Inohuye-Rivera, R.B.; Pérez-Urbiola, J.C. Seasonal changes in a fish assemblage associated with mangroves in a coastal lagoon of Baja California Sur, Mexico. Lat. Am. J. Aquat. Res. 2011, 39, 250–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McPhaden, M.J.; Zhang, D. Slowdown of the meridional overturning circulation in the upper Pacific Ocean. Nature 2002, 415, 603–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.; Yang, S.; Wang, C.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, G. Strengthening amplitude and impact of the Pacific meridional mode on ENSO in the warming climate depicted by CMIP6 models. J. Clim. 2022, 35, 5195–5213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, G.T.; Bliss, E.W. World Weather V. Mem. Roy. Met. Soc. 1932, 4, 53–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, J.C. The north Pacific oscillation. Int. J. Climatol. 1981, 1, 39–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linkin, M.E.; Nigam, S. The North Pacific Oscillation–west Pacific teleconnection pattern: Mature-phase structure and winter impacts. J. Clim. 2008, 21, 1979–1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ham, Y.G.; Kug, J.S.; Park, J.Y.; Jin, F.F. Sea surface temperature in the north tropical Atlantic as a trigger for El Niño/Southern Oscillation events. Nat. Geosci. 2013, 6, 112–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joh, Y.; Di Lorenzo, E. Interactions between Kuroshio Extension and Central Tropical Pacific lead to preferred decadal-timescale oscillations in Pacific climate. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 13558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.H.; Li, T.; Yeh, S.W.; Kim, H. Effect of recent Atlantic warming in strengthening Atlantic–Pacific teleconnection on interannual timescale via enhanced connection with the Pacific meridional mode. Clim. Dyn. 2019, 53, 371–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Xie, L.; Zheng, Q.; Zhou, L.; Wang, L.; Feng, B.; Yu, Z. Seasonal variability of mesoscale eddies in the Banda Sea inferred from altimeter data. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2020, 39, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; He, X.; Lu, Y.; Chu, Y. Application of Landsat time-series data in island ecological environment monitoring: A case study of Zhoushan Islands, China. J. Coast. Res. 2020, 108, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilly, W.; Markaida, U.; Daniel, P.; Frawley, T.; Robinson, C.; Gómez-Gutiérrez, J.; Hyun, D.; Soliman, J.; Pandey, P.; Rosenzweig, L. Long-term hydrographic changes in the Gulf of California and ecological impacts: A crack in the World’s Aquarium? Prog. Oceanogr. 2022, 206, 102857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, S.N.; Whitehead, H. Seasonal occurrence of sperm whales (Physeter macrocephalus) around Kelvin Seamount in the Sargasso Sea in relation to oceanographic processes. Deep-Sea Res. I Oceanogr. Res. Pap 2014, 91, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pörtner, H.O.; Karl, D.M.; Boyd, P.W.; Cheung, W.; Lluch-Cota, S.E.; Nojiri, Y.; Schmidt, D.N.; Zavialov, P.O.; Alheit, J.; Aristegui, J.; et al. Ocean Systems. In Climate Change 2014: Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability. Part A: Global and Sectoral Aspects. Contribution of Working Group II to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Field, C., Barros, V., Dokken, D., Mach, K., Mastrandrea, M., Bilir, T., Chatterjee, M., Ebi, K., Estrada, Y., Genova, R., et al., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 411–484. [Google Scholar]
- Behrenfeld, M.J.; Boss, E. Beam attenuation and chlorophyll concentration as alternative optical indices of phytoplankton biomass. J. Mar. Res. 2006, 64, 431–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinsky, M.L.; Worm, B.; Fogarty, M.J.; Sarmiento, J.L.; Levin, S.A. Marine taxa track local climate velocities. Science 2013, 341, 1239–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coll, M.; Bellido, J.M.; Pennino, M.G. Cómo Proteger las Sardinas y Anchoas Mediterráneas de la Sobrepesca y el Cambio Climático. Available online: https://digital.csic.es/handle/10261/261558 (accessed on 28 July 2023).
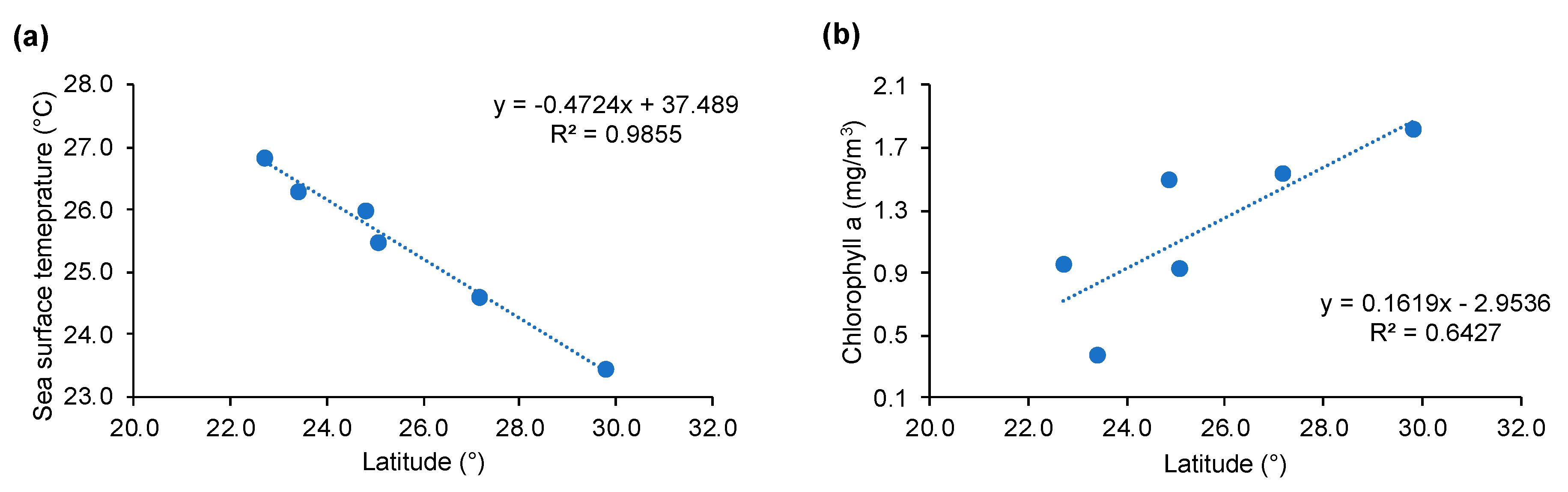
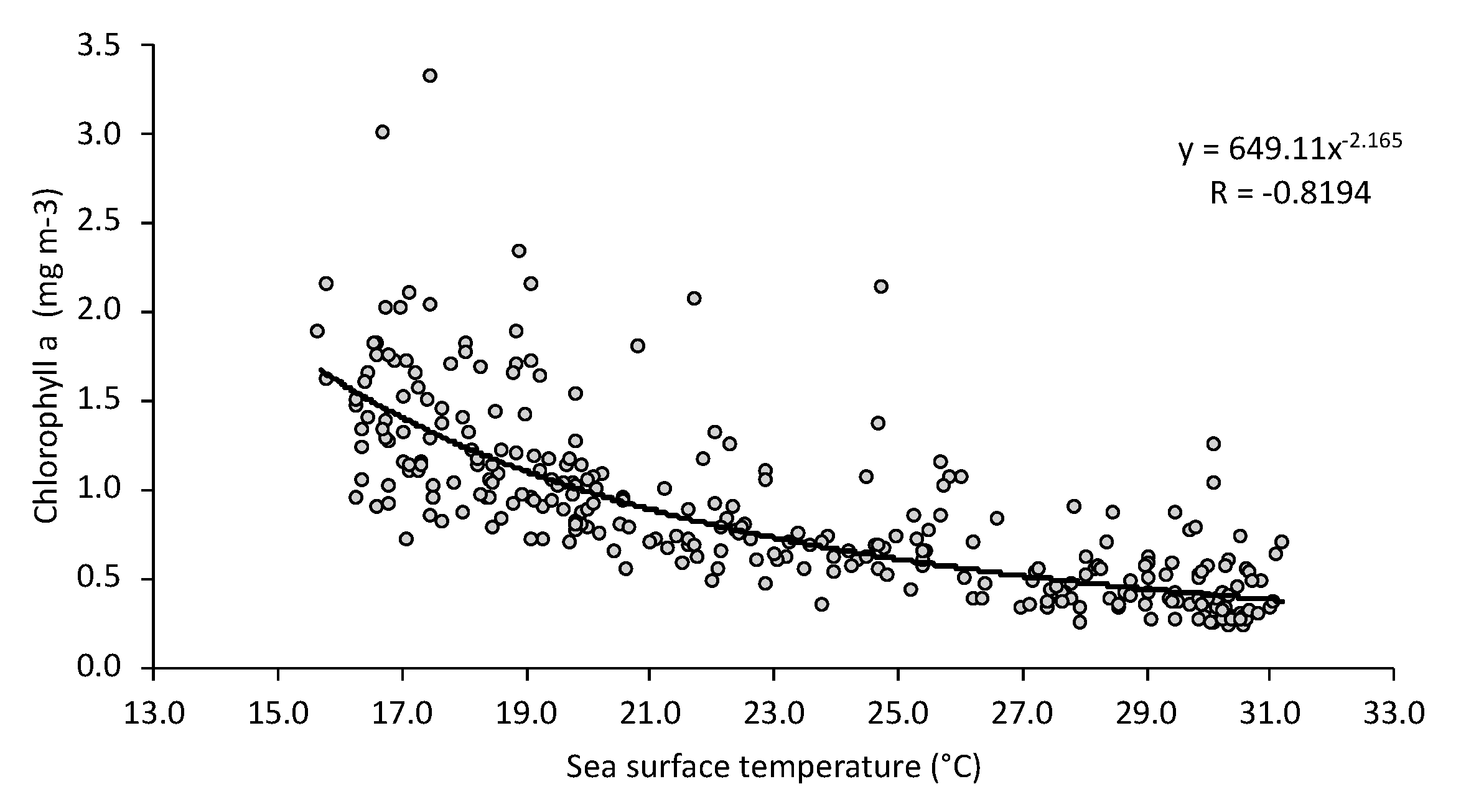
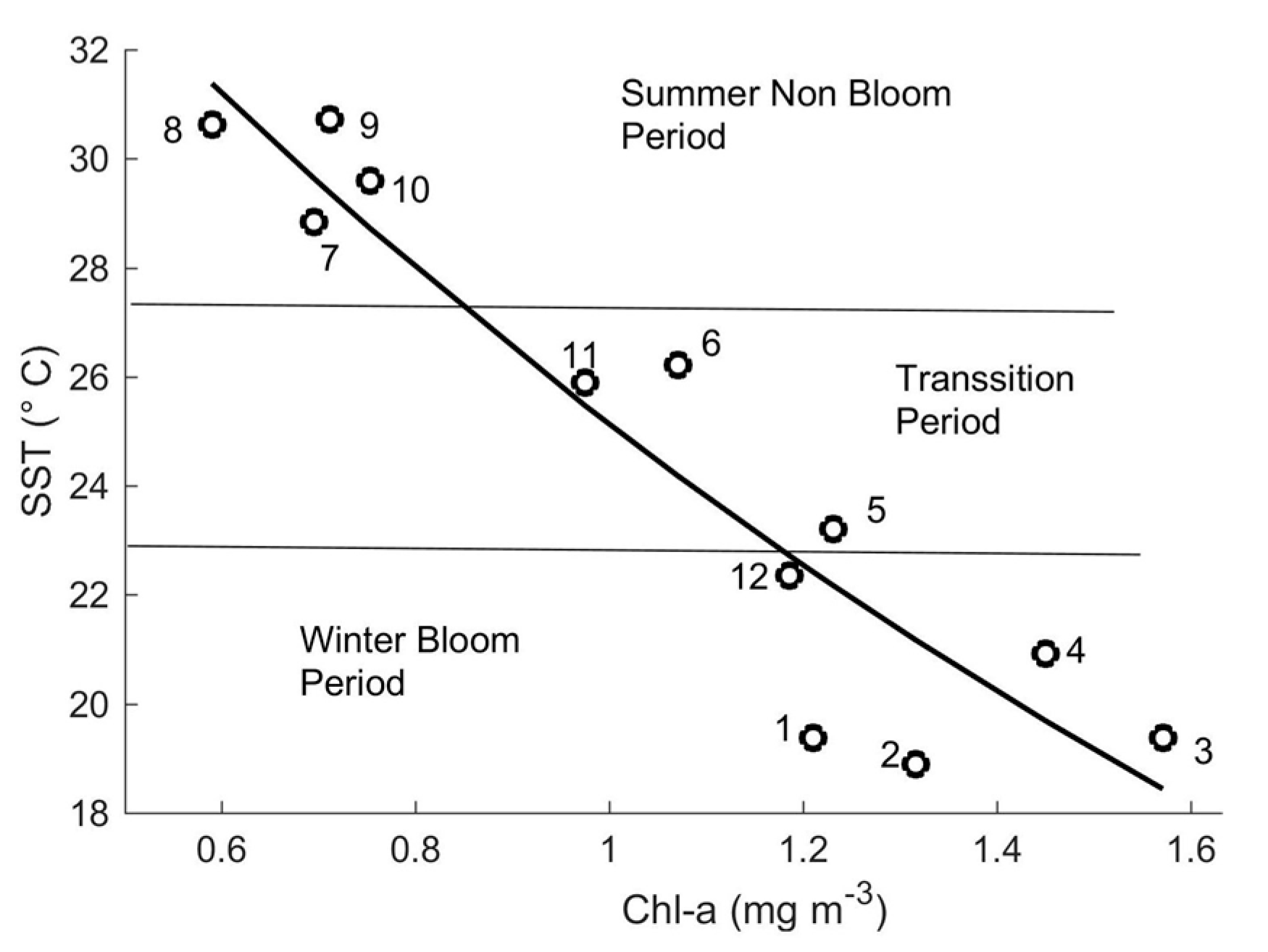
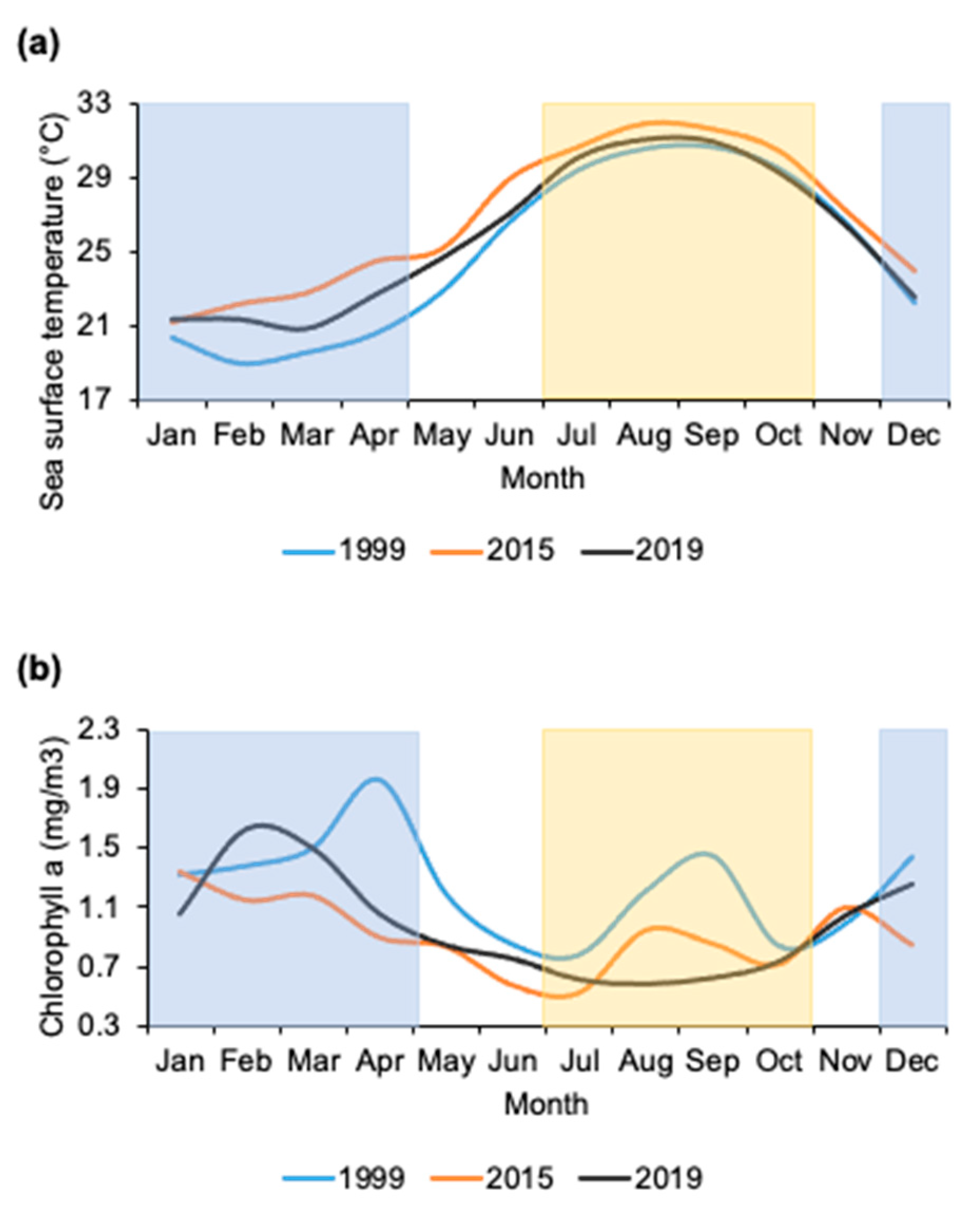


| Pearson’s Chi-Square Test | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | Chi-Square | Chi-Square (Critical) | d.f. | p-Value | |
| SST | 72 | 2.784 | 67.505 | 55 | 1 |
| Chl-a | 72 | 3.099 | 55 | 1 | |
| Region | Cluster | Sea Surface Water Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Upper GC–south of Midriff Islands | 5 | Cold water (23.43 °C), eutrophic (1.81 mg/m3) |
| Central gulf between 26° to 28°N | 3 | Intermediate water (24.59 °C), eutrophic (1.53 mg/m3) |
| Limit between Sonora and Sinaloa (24° to 26°N) | 6 | Intermediate water (25.46 °C), mesotrophic (0.92 mg/m3) |
| Northern and central coast of Sinaloa | 1 | Warm water (25.99 °C), eutrophic (1.49 mg/m3) |
| Oceanic region at the southern GC surrounding areas down to the southern tip of Baja California Peninsula | 4 | Warm water (26.29 °C), oligotrophic (0.37 mg/m3) |
| Around the entrance of the gulf, including the southern coastal region of Sinaloa | 2 | Warm water (26.83 °C), mesotrophic (0.95 mg/m3) |
| Cluster | SST | Chl-a | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean ± S.D. (°C) | Minimum (°C) | Maximum (°C) | Mean ± S.D. (mg/m3) | Minimum (mg/m3) | Maximum (mg/m3) | |
| 1 | 25.99 ± 4.17 | 16.98 | 31.96 | 1.49 ± 1.27 | 0.28 | 11.13 |
| 2 | 26.83 ± 3.40 | 18.58 | 31.98 | 0.95 ± 1.02 | 0.13 | 8.89 |
| 3 | 24.59 ± 4.94 | 16.17 | 32.43 | 1.53 ± 0.49 | 0.84 | 3.08 |
| 4 | 26.29 ± 3.32 | 19.62 | 31.66 | 0.37 ± 0.22 | 0.11 | 1.10 |
| 5 | 23.43 ± 5.21 | 15.27 | 31.60 | 1.81 ± 0.55 | 0.90 | 4.01 |
| 6 | 25.46 ± 4.04 | 17.89 | 31.99 | 0.92 ± 0.56 | 0.24 | 4.85 |
| Spearman Rank-Correlation (p < 0.05) | ||
|---|---|---|
| SST | Chl-a | |
| ONI | 0.440 | −0.448 |
| PDO | 0.379 | −0.445 |
| Pearson Linear Correlation (p < 0.05) | ||
| SST | Chl-a | |
| ONI | 0.498 | −0.411 |
| PDO | 0.422 | −0.424 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
López Martínez, J.; Farach Espinoza, E.B.; Herrera Cervantes, H.; García Morales, R. Long-Term Variability in Sea Surface Temperature and Chlorophyll a Concentration in the Gulf of California. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 4088. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15164088
López Martínez J, Farach Espinoza EB, Herrera Cervantes H, García Morales R. Long-Term Variability in Sea Surface Temperature and Chlorophyll a Concentration in the Gulf of California. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(16):4088. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15164088
Chicago/Turabian StyleLópez Martínez, Juana, Edgardo Basilio Farach Espinoza, Hugo Herrera Cervantes, and Ricardo García Morales. 2023. "Long-Term Variability in Sea Surface Temperature and Chlorophyll a Concentration in the Gulf of California" Remote Sensing 15, no. 16: 4088. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15164088
APA StyleLópez Martínez, J., Farach Espinoza, E. B., Herrera Cervantes, H., & García Morales, R. (2023). Long-Term Variability in Sea Surface Temperature and Chlorophyll a Concentration in the Gulf of California. Remote Sensing, 15(16), 4088. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15164088






