Target Recognition in SAR Images Using Complex-Valued Network Guided with Sub-Aperture Decomposition
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- A novel SAR target recognition method based on complex-valued networks with a multi-task learning strategy is proposed in this paper. The proposed method is not only a complex-valued network but also a multi-task learning-based SAR target recognition method. Multi-task learning can be used to improve the performance of the main task by learning and sharing useful information from the auxiliary task. Here, the main and auxiliary tasks are contained in the proposed method. Specifically, the main task is the target recognition task, which is used to obtain the recognition results. As an auxiliary task, the reconstruction task is used to guide the model to learn the separability characteristics of targets by reconstructing the sub-aperture image. Here, a complex-valued structure is used to obtain the features from SAR images because the original SAR images are complex-valued.
- (2)
- Multi-angle target information is mined for the SAR target recognition task using sub-aperture decomposition. Since different targets have different physical scattering characteristics at different angles, the sub-aperture images contain multi-angle target information, which increases the possibility of distinguishing different types of targets. Therefore, in this paper, sub-aperture decomposition is used to improve accuracy by guiding the model to learn the target separability characteristics.
2. Proposed Method
2.1. Overall CGS-Net Framework
2.2. Base Module
- (1)
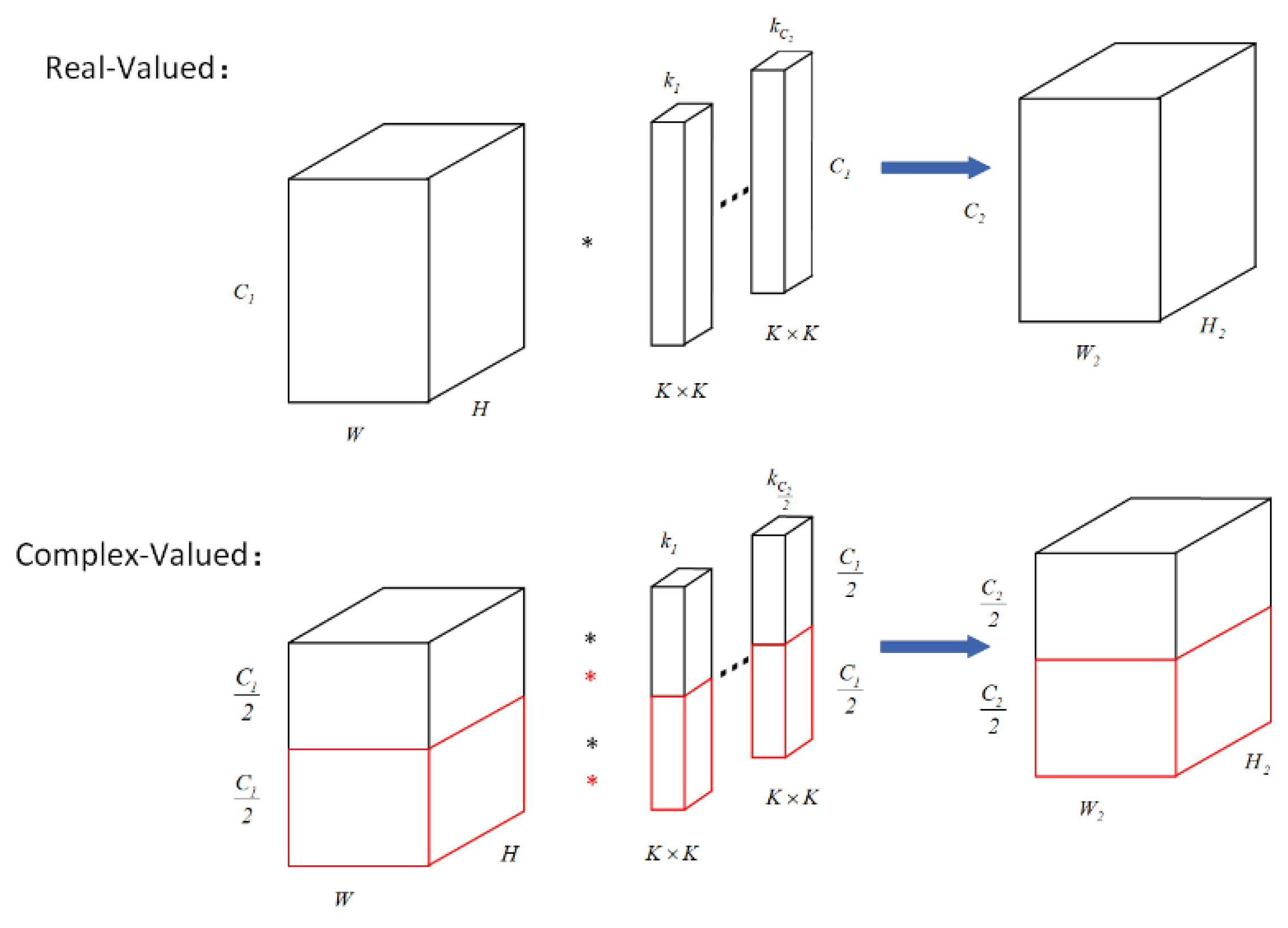
- Complex-Valued Convolutional Layer
- (2)
- Specific Structure of Base Module
2.3. Reconstruction Task
- (1)
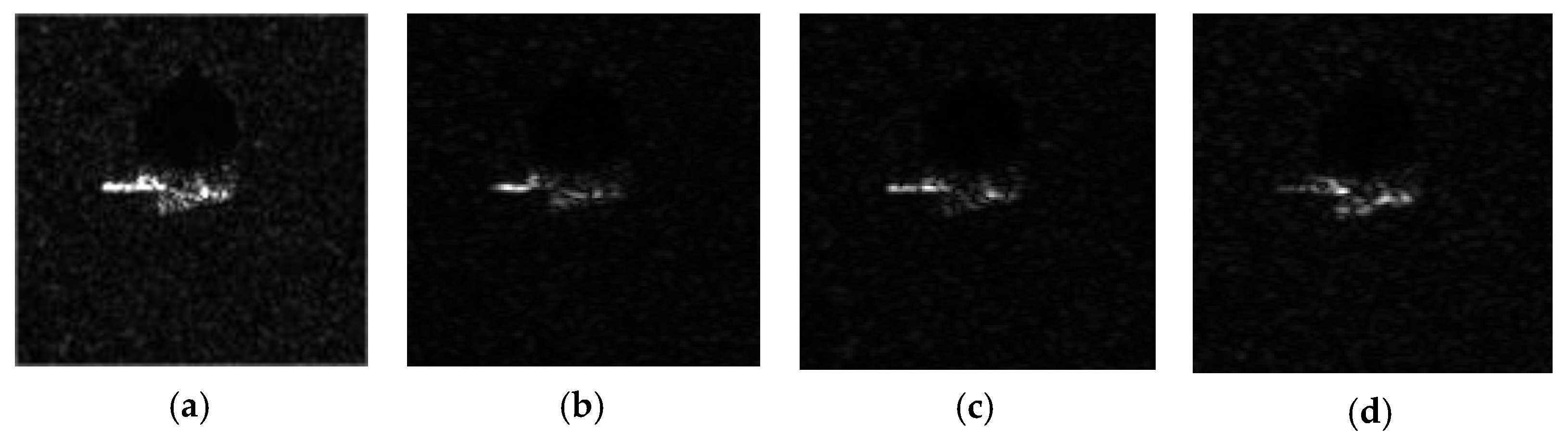
- Sub-Aperture Decomposition Algorithm
- (2)
- Guided Module
- (3)
- Reconstruction Loss Function
2.4. Recognition Task
- (1)
- Complex-Valued FC-Layer
- (2)
- Recognition Loss Function
2.5. Specific Loss Function in the Proposed Method
3. Experimental Results
3.1. Experimental Data
3.2. Experimental Details
3.3. Evaluation Criteria
3.4. Results under Ten-Class Targets
- A.
- Comparison with Classical Recognition Methods
- B. Comparison with Other Complex-Valued Networks
- C. Comparison with State-of-the-Art Methods
- D. Experimental Results with limited data
- E. Ablation Experiments
- F. Comparison with Different Numbers of Sub-Apertures
4. Discussion
- (1)
- The proposed method is only applicable to SAR images. The proposed method includes sub-aperture decomposition. This is the unique imaging mechanism in the SAR system. Therefore, it is impossible to extend the proposed method to other fields, such as optical remote sensing and natural images. Its application is limited.
- (2)
- The proposed method has not been verified using a large-scale dataset. In contrast to some state-of-the-art methods, such as LW-CMDANet [57] and so on, the dataset used in this paper is complex-valued SAR data. Although the SAR image itself is complex-valued data, there is currently no public large-scale complex-valued SAR dataset, such as ImageNet [58] in the natural image field. The complex-valued SAR data currently available are generally the MSATR and MiniSAR datasets. Therefore, we have not verified the proposed method with a large-scale dataset.
- (3)
- Whether the proposed method can be extended to other tasks in the SAR field has not been verified. We have not applied the proposed method to other tasks, such as target detection. Therefore, the extensibility of the proposed method has not been thoroughly explored.
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Z.; Wang, R.; Fu, X.; Xia, K. Unsupervised Ship Detection for Single-Channel SAR Images Based on Multiscale Saliency and Complex Signal Kurtosis. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2021, 19, 4011305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudgeon, D.E.; Lacoss, R.T. An overview of automatic target recognition. Linc. Lab. J. 1993, 6, 3–10. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, H.; Yu, X.; Zou, L.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, X.; Bruzzone, L. Extended convolutional capsule network with application on SAR automatic target recognition. Signal Process. 2021, 183, 108021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, J.; Tian, R.; Luo, Q.; Jin, J.; Tang, B. Multi-scale rotation-invariant haar-like feature integrated CNN based ship detection algorithm of multiple-target environment in SAR imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 10070–10087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, Y.; Shanwei, L.; Mingming, X.; Hui, S.; Hossain, M.S.; Colak, A.T.I.; Wang, D.; Jianhua, W.; Dang, K.B. Multi-scale ship target detection using SAR images based on improved Yolov5. Front. Mar. Sci. 2023, 9, 1086140. [Google Scholar]
- Novak, L.M.; Owirka, G.J.; Netishen, C.M. Performance of a high-resolution polarimetric SAR automatic target recognition system. Linc. Lab. J. 1993, 6, 1. [Google Scholar]
- O’Sullivan, J.A.; DeVore, M.D.; Kedia, V.; Miller, M.I. SAR ATR performance using a conditionally Gaussian model. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2001, 37, 91–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, G. Target Detection and Terrain Classification of Single-Channel SAR Images. In Characterization of SAR Clutter and Its Applications to Land and Ocean Observations; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 75–101. [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan, L.M. Analysis of multiplicative speckle models for template-based SAR ATR. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2001, 37, 1424–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeVore, M.D.; Lanterman, A.D.; O’Sullivan, J.A. ATR performance of a Rician model for SAR images. In Automatic Target Recognition X; SPIE: Orlando, FL, USA, 2000; Volume 4050. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Y.; Lv, X.; Qian, L.; Liu, X. An Optimal BP Neural Network Track Prediction Method Based on a GA– ACO Hybrid Algorithm. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 1399. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Y.; Liu, P.; Qian, L.; Qin, S.; Liu, X.; Ma, Y.; Cheng, G. Recognition and Depth Estimation of Ships Based on Binocular Stereo Vision. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, L.; Zheng, Y.; Li, L.; Ma, Y.; Zhou, C.; Zhang, D. A New Method of Inland Water Ship Trajectory Prediction Based on Long Short-Term Memory Network Optimized by Genetic Algorithm. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 4073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, S.; Li, B.; Zhu, S. DCGNN: A single-stage 3D object detection network based on density clustering and graph neural network. Complex Intell. Syst. 2022, 9, 3399–3408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.; Lin, J.; Xu, K.; Chen, P.; Ma, L.; Lau, R.W.H. Mirror Detection With the Visual Chirality Cue. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2023, 45, 3492–3504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, K.; Liu, L.; Lan, H.; Lin, L. TCGL: Temporal Contrastive Graph for Self-Supervised Video Representation Learning. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2022, 31, 1978–1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Ding, F.; Li, J.; Meng, X.; Liu, C.; Fang, H. Improved Detection of Buried Elongated Targets by Dual-Polarization GPR. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2023, 20, 3501705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Yue, Y.; Liu, C.; Spencer, B.F.; Cui, J. Automatic recognition and localization of underground pipelines in GPR B-scans using a deep learning model. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2023, 134, 0886–7798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Yu, X.; Dedman, S.; Rosso, M.; Zhu, J.; Yang, J.; Xia, Y.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, G.; Wang, J. UAV remote sensing applications in marine monitoring: Knowledge visualization and review. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 838, 0048–9697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Lv, Y.; Lei, J.; Yu, L. Global and Local-Contrast Guides Content-Aware Fusion for RGB-D Saliency Prediction. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 2021, 51, 3641–3649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Wang, H.; Hu, K.; Yin, G.; Wei, Z. IA-Net$:$ An Inception–Attention-Module-Based Network for Classifying Underwater Images From Others. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 2022, 47, 704–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Song, B.; Liang, P.; Xu, J.; Yue, T. Voids Filling of DEM with Multiattention Generative Adversarial Network Model. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Zhou, X.; Song, Y.; Xie, D.; Wang, L.; Yan, G.; Hu, M.; Liu, B.; Shang, W.; Gong, C.; et al. Design of supercontinuum laser hyperspectral light detection and ranging (LiDAR) (SCLaHS LiDAR). Int. J. Remote Sens. 2021, 42, 3731–3755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, D.; Chen, L.; Lv, C.; Guo, L.; Kou, Q. Light-Guided and Cross-Fusion U-Net for Anti-Illumination Image Super-Resolution. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2022, 32, 8436–8449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Ding, Y.; Liu, M.; Yin, Z.; Yin, L.; Zheng, W. Multiscale Feature Extraction and Fusion of Image and Text in VQA. International Journal of Computational Intelligence Systems. Int. J. Comput. Intell. Syst. 2023, 16, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Zhou, X.; Li, W.; Zhao, D.; Song, B.; Xu, C.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Z.; Xu, J.; Lin, G.; et al. Development of a Lightweight Single-Band Bathymetric LiDAR. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Chi, F.C.; Xu, P. High-efficiency sub-microscale uncertainty measurement method using pattern recognition. ISA Trans. 2020, 101, 503–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Luo, J.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Cai, X.; Yang, J. Resolution Enhancement for Large-Scale Real Beam Mapping Based on Adaptive Low-Rank Approximation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 5116921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Wang, H. SAR target recognition based on deep learning. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Data Science and Advanced Analytics (DSAA), Shanghai, China, 30 October–1 November 2014; pp. 541–547. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, L.; Ye, Y.; Tang, T.; Nan, K.; Qin, Y. Robust Matching for SAR and Optical Images Using Multiscale Conutional Gradient Features. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2022, 19, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, J.; Chen, B.; Liu, H.; Huang, M. Conutional Neural Network with Data Augmentation for SAR Target Recognition. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2016, 13, 364–368. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y.; Du, L.; Li, C.; Chen, J. SAR Automatic Target Recognition Based on Multi-Scale Conutional Factor Analysis Model with Max-Margin Constraint. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium IGARSS, Brussels, Belgium, 11–16 July 2021; pp. 3605–3608. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, G.; Liu, M.; Chen, S.; Li, Y.; Lu, F. Generation of SAR Images with Features for Target Recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Signal Processing, Communications and Computing (ICSPCC), Xi’an, China, 25–27 October 2022; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, J.; Liu, Z.; Ran, L.; Xie, R.; Tang, J.; Guo, Z. A Target SAR Image Expansion Method Based on Conditional Wasserstein Deep Conutional GAN for Automatic Target Recognition. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2022, 15, 7153–7170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Zhao, L.; Ji, K.; Kuang, G. SAR Target Recognition Based on Task-Driven Domain Adaptation Using Simulated Data. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2022, 19, 4019205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, S.; Qiu, X.; Lei, B.; Fu, K. A SAR Target Image Simulation Method With DNN Embedded to Calculate Electromagnetic Reflection. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2021, 14, 2593–2610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, W.; Zhang, C.; Xie, W.; Jin, X. Polarimetric SAR Image Classification Based on Ensemble Dual-Branch CNN and Superpixel Algorithm. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2022, 15, 2759–2772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Zhang, H.; Chen, Z.; Yu, N.; Kong, W.; Li, T.; Wang, E.; Wu, X.; Liu, Y. Denoising method of ground-penetrating radar signal based on independent component analysis with multifractal spectrum. Measurement 2022, 192, 110886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, D.; Du, Y.; Du, L.; Li, L. Target Detection Network for SAR Images Based on Semi-Supervised Learning and Attention Mechanism. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Xue, M.; Wang, Y.; Yuan, G.; Li, X. Fast Visual Tracking With Siamese Oriented Region Proposal Network. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2022, 29, 1437–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Sun, J.; Qi, P.; Yin, G.; Zhang, L. Multi-block mixed sample semi-supervised learning for SAR target recognition. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Du, L.; Mao, J.; Liu, B.; Yang, D. SAR target detection based on SSD with data augmentation and transfer learning. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2018, 16, 150–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Pan, Z.; Hu, Y. Multi-Aspect Conutional-Transformer Network for SAR Automatic Target Recognition. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marino, A.; Sanjuan-Ferrer, M.; Hajnsek, I.; Ouchi, K. Ship detection with spectral analysis of synthetic aperture radar: A comparison of new and well-known algorithms. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 5416–5439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cloude, S.R. Target decomposition theorems in radar scattering. Electron. Lett. 1985, 21, 22–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferro-Famil, L.; Reigber, A.; Pottier, E.; Boerner, W.M. Analysis of anisotropic behavior using sub-aperture polarimetric SAR data. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Toulouse, France, 21–25 July 2003; pp. 434–436. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Fu, X.; Xia, K. Target Classification for Single-Channel SAR Images Based on Transfer Learning With Subaperture Decomposition. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2022, 19, 4003205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trabelsi, C.; Olexa, B.; Ying, Z.; Dmitriy, S.; Christopher, J. Deep Complex Networks. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1705.09792. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, Z.; Sun, J.; Han, Z.; Hong, W. SAR Automatic Target Recognition Method Based on Multi-Stream Complex-Valued Networks. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 5228618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Wang, L.; Wen, Z.; Li, K.; Pan, Q. Multilevel Scattering Center and Deep Feature Fusion Learning Framework for SAR Target Recognition. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 5227914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilmanski, M.; Kreucher, C.; Hero, A. Complex input convolutional neural networks for wide angle SAR ATR. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Global Conference on Signal and Information Processing (GlobalSIP), Washington, DC, USA, 7–9 December 2016; pp. 1037–1041. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Karen, S.; Zisserman, A. Very deep conutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1409.1556. [Google Scholar]
- Scarnati, T.; Lewis, B. Complex-Valued Neural Networks for Synthetic Aperture Radar Image Classification. In Proceedings of the IEEE Radar Conference (RadarConf21), Atlanta, GA, USA, 7–14 May 2021; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Xing, M.; Xie, Y. FEC: A feature fusion framework for SAR target recognition based on electromagnetic scattering features and deep CNN features. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 59, 2174–2187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Wang, H.; Xu, F.; Jin, Y. Target classification using the deep conutional networks for SAR images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 54, 4806–4817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, P.; Fu, X.; Feng, C.; Dong, J.; Qin, R.; Martorella, M. LW-CMDANet: A Novel Attention Network for SAR Automatic Target Recognition. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2022, 15, 6615–6630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Dong, W.; Socher, R.; Li, L.-J.; Li, K.; Fei-Fei, L. ImageNet: A large-scale hierarchical image database. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Miami, FL, USA, 20–25 June 2009; pp. 248–255. [Google Scholar]
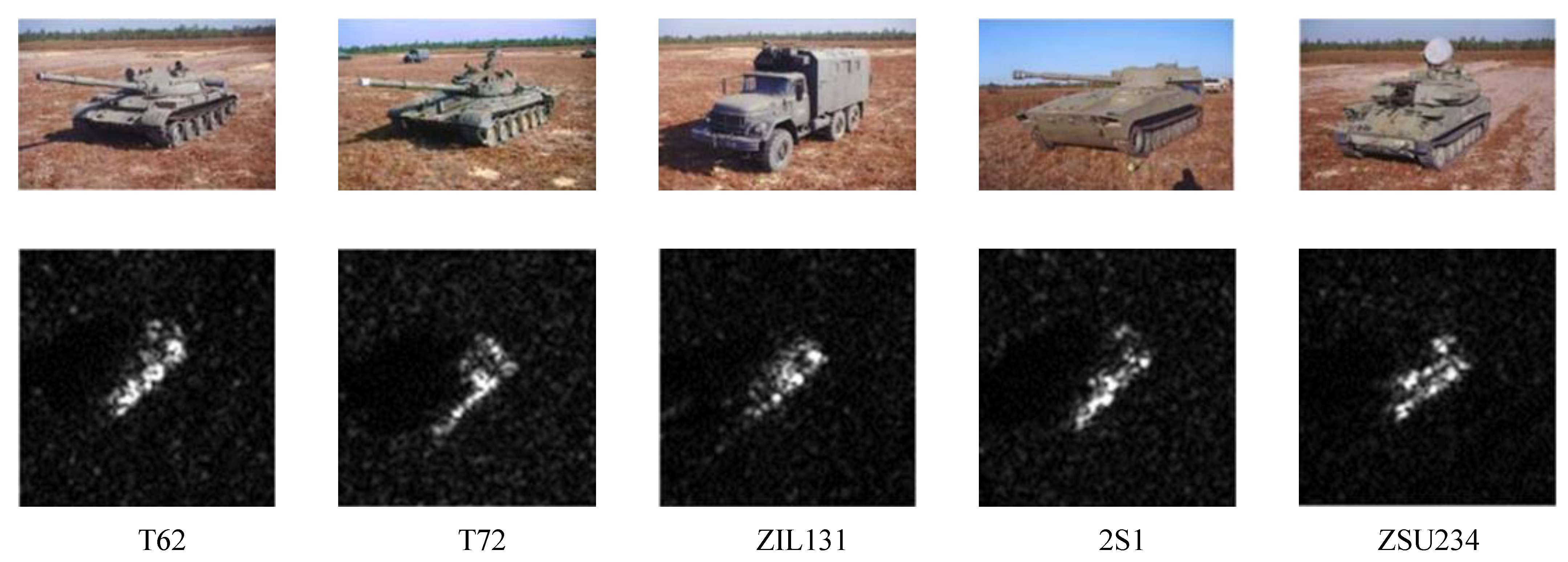





| Class | Test Set (Depression 15°) | Training Set (Depression 17°) | Serial Number | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BMP2 | 195 | 233 | 9563 | |
| BRDM2 | 274 | 298 | E-71 | |
| BTR70 | 196 | 233 | c71 | |
| BTR60 | 195 | 256 | k10yt7532 | |
| D7 | 274 | 299 | 9v13015 | |
| T62 | 273 | 299 | A51 | |
| T72 | 196 | 232 | 132 | |
| ZIL131 | 274 | 299 | E12 | |
| 2S1 | 274 | 299 | b01 | |
| 2SU234 | 274 | 299 | d08 | |
| Total | 2425 | 2747 | / | |
| Method | Accuracy | Parameters | Flops | Running Time (2425 Images) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ResNet18 | 97.69 | 11.2 M | 595.44 M | 3.20 s |
| ResNet10 | 97.28 | 4.93 M | 292.47 M | 2.67 s |
| VGG16 | 94.31 | 134.3 M | 5130.76 M | 4.47 s |
| Net-4 | 95.71 | 2.2 M | 10.94 M | 2.47 s |
| CGS-Net | 99.59 | 3.65 M | 277.37 M | 3.80 s |
| BMP2 | BTR70 | T72 | 2S1 | BRDM2 | BTR60 | D7 | T62 | ZIL131 | ZSU234 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Precision | 1.0 | 0.990 | 1.0 | 0.990 | 0.996 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 0.996 | 1.0 | 1.0 |
| Recall | 0.985 | 1.0 | 0.980 | 0.989 | 1.0 | 0.990 | 0.993 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 |
| F1-score | 0.992 | 0.995 | 0.990 | 0.989 | 0.998 | 0.995 | 0.996 | 0.998 | 1.0 | 1.0 |
| Method | Accuracy |
|---|---|
| DH-RCCNNs | 97.24 |
| Complex net | 98.56 |
| CGS-Net | 99.59 |
| Method | Accuracy |
|---|---|
| FEC | 99.27 |
| CAE | 97.86 |
| A-ConvNe | 99.13 |
| CGS-Net | 99.59 |
| Dataset Size | Accuracy (ResNet10) | Accuracy (Net4) | Accuracy (CGS-Net) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 40% | 94.88 | 88.80 | 97.44 |
| 50% | 95.04 | 90.19 | 97.90 |
| 60% | 96.04 | 92.25 | 98.72 |
| 70% | 96.88 | 94.40 | 99.09 |
| 100% | 97.28 | 95.71 | 99.59 |
| Method | Complex-Valued Based Module | Reconstruction Task | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|
| ResNet10 | × | × | 98.89 |
| Complex-ResNet10 | √ | × | 99.01 |
| Proposed Method | √ | √ | 99.59 |
| Number of Sub-Apertures | Accuracy |
|---|---|
| 0 | 98.89 |
| 2 | 99.26 |
| 3 | 99.59 |
| 4 | 99.38 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, R.; Wang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Kang, H.; Luo, F.; Liu, Y. Target Recognition in SAR Images Using Complex-Valued Network Guided with Sub-Aperture Decomposition. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 4031. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15164031
Wang R, Wang Z, Chen Y, Kang H, Luo F, Liu Y. Target Recognition in SAR Images Using Complex-Valued Network Guided with Sub-Aperture Decomposition. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(16):4031. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15164031
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Ruonan, Zhaocheng Wang, Yu Chen, Hailong Kang, Feng Luo, and Yingxi Liu. 2023. "Target Recognition in SAR Images Using Complex-Valued Network Guided with Sub-Aperture Decomposition" Remote Sensing 15, no. 16: 4031. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15164031
APA StyleWang, R., Wang, Z., Chen, Y., Kang, H., Luo, F., & Liu, Y. (2023). Target Recognition in SAR Images Using Complex-Valued Network Guided with Sub-Aperture Decomposition. Remote Sensing, 15(16), 4031. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15164031







