Abstract
Vision is an important way for unmanned mobile platforms to understand surrounding environmental information. For an unmanned mobile platform, quickly and accurately obtaining environmental information is a basic requirement for its subsequent visual tasks. Based on this, a unique convolution module called Multi-Scale Depthwise Separable Convolution module is proposed for real-time semantic segmentation. This module mainly consists of concatenation pointwise convolution and multi-scale depthwise convolution. Not only does the concatenation pointwise convolution change the number of channels, but it also combines the spatial features from the multi-scale depthwise convolution operations to produce additional features. The Multi-Scale Depthwise Separable Convolution module can strengthen the non-linear relationship between input and output. Specifically, the multi-scale depthwise convolution module extracts multi-scale spatial features while remaining lightweight. This fully uses multi-scale information to describe objects despite their different sizes. Here, Mean Intersection over Union (MIoU), parameters, and inference speed were used to describe the performance of the proposed network. On the Camvid, KITTI, and Cityscapes datasets, the proposed algorithm compromised between accuracy and memory in comparison to widely used and cutting-edge algorithms. In particular, the proposed algorithm acquired 61.02 MIoU with 2.68 M parameters on the Camvid test dataset.
1. Introduction
The major domains of application for semantic segmentation include embedded AI computer devices and self-driving systems, which have attracted a great deal of attention. These practical applications, however, must have rigorous memory requirements in addition to outstanding outcomes with high precision. The semantic segmentation algorithms that are now in use are widely used and generate competitive memory performance at the expense of segmentation accuracy [1,2]. Rtseg addresses computationally efficient solutions by presenting a real-time semantic segmentation benchmarking framework with a decoupled design for feature extraction and decoding methods [3]. Enet is a quick framework for semantically segmenting pixels. It is based on VGG16 and combines factorizing filters with conventional and dilated convolution to provide quicker inference [4]. Moreover, some algorithms result in a large number of parameters while achieving excellent segmentation accuracy [5]. To solve the problem of semantic segmentation and pixel-by-pixel classification based on the CNN, the existing CNN structure used for classification is converted into FCN. Local areas in the image are classified to obtain rough label maps; then, deconvolution (bilinear interpolation) is performed to obtain pixel-level labels. To achieve more accurate segmentation results, CRF can be used for post-processing [6]. Usually, the information in the last layers may be too spatially coarse to allow precise localization to be performed. On the contrary, earlier layers may be precise in localization but may not capture semantics. In order to solve this problem, the hypercolumn at the pixel is defined as an activation vector to obtain detailed semantic information [7]. Thus, it becomes a difficult task to build an efficient semantic segmentation network that balances memory and accuracy.
The output picture for semantic segmentation must have the same resolution as the input image, unlike the object detection [8,9], object identification [10,11], and image classification [3] tasks. Hence, corresponding networks must have the ability to classify pixels. Different objects need to be classified in terms of the semantic segmentation task in road scenes. This necessitates that the network comprehends spatial feature information among different classes, such as bicycles, autos, and pedestrians. In addition, the same class probably contains several instances that are located in different locations in the road image. This requires the network to understand spatial location information. Large categories such as roads, skies, and buildings contain a large number of pixels, while others, including pedestrians, lane lines, signs, and traffic lights, contain a small number of pixels. Specifically, it is possible for different instances in the same class to have different shapes due to their different distances, as shown in Figure 1. As a result, despite their various sizes, the network must be able to distinguish among classes or instances based on their shapes. Thus, it is crucial to keep boundary information in the extracted picture representation.
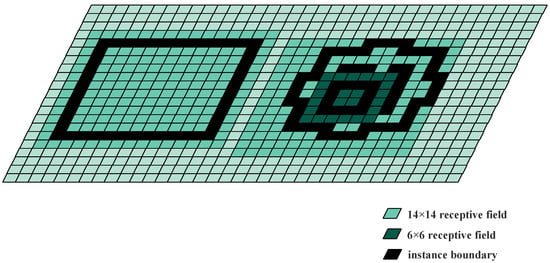
Figure 1.
Receptive field.
Several algorithms expand branches [3,12,13,14,15], combine various stages, or alter the network’s connection path based on standard convolution in order to extract multi-level information. However, since such algorithms only emphasize competitive performance with high precision, a wide range of parameters are introduced in practical applications, which presents a hard challenge for AI computer systems. In addition, some algorithms [4,6,16,17] use efficient convolution methods or simplify the network structure to reduce parameters. For example, Xception [18] makes three branches merge into one and use group convolution to reduce the parameters. In order to decrease the number of parameters, these algorithms usually ignore the extraction of multi-scale features, which greatly sacrifices the accuracy. We constructed a semantic segmentation module that balances accuracy and memory using Depthwise Separable Convolution [19] and emphasizes the extraction of multi-scale features to increase accuracy. Compared with standard convolution, deep separable convolution can achieve local feature extraction with less computational complexity, resulting in fast inference speed and local feature extraction ability. For unmanned sports platforms, this is very important. We provide a novel module called Multi-Scale Depthwise Separable Convolution based on Depthwise Separable Convolution, which is intended to be efficient in terms of feature extraction in various feature spaces while being lightweight. The two primary components of this module are concatenation pointwise convolution and multi-scale depthwise convolution. In order to extract multi-scale spatial information, multi-scale deep convolution uses deep convolution with different kernel sizes. To develop additional features, concatenation pointwise convolution filters input channels before combining them. This paper’s primary contributions are the following:
- A brand-new module called Multi-Scale Depthwise Separable Convolution is proposed in this paper. This module can extract multi-scale information while remaining lightweight.
- The proposed structure makes a trade-off between accuracy and memory. It significantly reduces the storage requirements of embedded AI computing devices, which is advantageous for real-world applications.
The rest of this essay is structured as follows: Related works, some of the current approaches used, and issues that need to be resolved are all described in Section 2. The evolution process is thoroughly explained in Section 3. The performance of the proposed algorithm and that of other algorithms involved are evaluated on different datasets in Section 4. Finally, we draw the final conclusion and discuss follow-up issues in Section 5.
2. Related Works
2.1. Semantic Segmentation Task
For picture segmentation, the OTSU algorithm and Maximum Entropy employ statistics of the color information, but they ignore local characteristics, making the segmentation results more susceptible to environmental change [20,21,22]. Moreover, the homogeneity of object color information is critically important for the aforementioned methods. Iteration is used by Genetic Algorithm and Simulated Annealing to find the global optimum. Even though they have low computing efficiency and are prone to becoming trapped in local optima, they can dynamically modify segmentation criteria [23]. Support Hyperplane is constructed using Vector Machine as an interval boundary, and the kernel function is added to increase non-linearity [24]. Nevertheless, the creation of non-linear and sample-dependent kernel functions often depends on a particular issue [25]. While such conventional algorithms produce decent segmentation results, they are very dependent on a certain environment and frequently fail when there are some aberrant spots in the picture. Because deep learning algorithms can automatically extract the object characteristics and have produced the greatest results in many situations, they can achieve superior segmentation results in those problems.
There are two typical models for segmentation networks: (1) An encoder network, interpolation, and pixel-wise classification layers make up the initial segmentation model. (2) The second segmentation model is made up of a pixel-wise classification layer, a related encoder network, and a decoder network. The encoder network generates sparse abstract spatial features, which are always convolved with trainable filters or extrapolated from the nearest neighbors to yield dense spatial features. Fully Convolutional Network (FCN) [26] upsampling employs bilinear interpolation [27] to restore full input resolution, and the encoder network is identical to the convolutional layers of VGG16. The FCN result is quite positive, although some of the details seem coarse. Then, skip connection is utilized to improve the description of details by copying high-resolution characteristics from the encoder network to the decoder network. Bilinear interpolation is replaced with deconvolution in the upsampling procedure in Unet [28], which is based on FCN. High-resolution features transferred from the encoder network are concatenated with features from deconvolution by Unet before being convolved with trainable filters to convey context information to higher-resolution layers. Segnet [29] is intended to be memory and computationally efficient during inference. By pooling indices, it takes the place of skip connection and obtains additional information. A pyramid pooling module and an encoder network make up PSPNet [30]. The encoder network is the same as ResNet’s [31] convolutional layers. By aggregating context based on multiple regions, the pyramid pooling module might collect more global context data. In terms of speed and segmentation performance, BiseNet [32] was made to be effective. In order to produce high-resolution features and achieve an adequate receptive field, it creates two routes. It also adds the new Feature Fusion Module to effectively merge features on top of the two existing pathways. To solve the basic challenge of significantly decreasing the amount of processing required for pixel-wise label inference, ICNet [33] comprises three branches with various resolutions operating under appropriate label guidance. The cascade feature fusion unit is also introduced in order to swiftly accomplish high-quality segmentation.
2.2. Multi-Scale Feature Extraction
Extracting multi-scale features is an excellent choice to widen the non-linear relationship between input and output. GoogLeNet [20] produces exciting results in image classification on the ImageNet dataset. It suggests a new structural module for Inception that can extract multi-scale features from various feature spaces. To increase the breadth of the network, Inception V1 combines three convolutional layers with various kernel sizes and a 3 × 3 max pooling layer. Inception V2 [34] also consists of four branches, similarly to Inception V1. In addition, Inception V2 introduces batch normalization [34] before the convolution operator and replaces 5 × 5 convolution with two 3 × 3 convolution operations. Compared with Inception V1, Inception V2 decreases the parameters. To accelerate computing speed, Inception V3 [35] incorporates factorization, which divides 7 × 7 convolution into 1 × 7 convolution and 7 × 1 convolution. Residual connection [31] and the Inception module are combined in Inception V4 [36] to speed up performance and cut down on training time. The aforementioned Inception structures are only used in image classification.
2.3. Computational Method in Convolution Operation
Standard convolution [37] is a common computational method of convolution operation that has wide applications in most network architectures [38,39,40,41,42,43]. This convolutional method is the operation of obtaining the dot product. For the given n × n convolution kernel, it needs to obtain the corresponding n × n area point-by-point dot product. Standard convolution extracts rich information, but it produces extensive parameters in a range of convolution operations; then, difficulties are encountered in training. Different from standard convolution, factorization [4] resolves n × n convolution into 1 × n and n × 1. So, it only obtains the dot product in the 1 × n or n × 1 region, and after that, it reduces the number of parameters and quickens training. It does, however, lose some feature data. Different from standard convolution, group convolution [44,45] is the first to divide lots of convolution operations into several groups; then, each group is independently trained. An efficient convolution technique called Depthwise Separable Convolution [16,19] combines pointwise and depthwise convolution. The number of groups is maximized in depthwise convolution, a special type of group convolution. Standard convolution with a 1 × 1 kernel is called pointwise convolution. It does not only filter input channels; it also combines them to provide new features. Both the number of parameters and the calculation time for Depthwise Separable Convolution are intended to be as efficient as possible.
3. Proposed Algorithms
A neural network must be able to distinguish among classes, despite their various sizes, based on their shapes. The majority of existing networks produce the same receptive field in a certain layer and are unsuitable to describe those classes that differ in size in the same class. In addition, standard convolution produces lots of parameters and is difficult to train. We suggest a Multi-Scale Depthwise Separable Convolution module based on Depthwise Separable Convolution. In terms of feature extraction in various feature spaces and parameters, this module is intended to be efficient.
Depthwise Separable Convolution changes the computational method by dividing n × n standard convolution into 2 convolution operations, as seen in Figure 2:
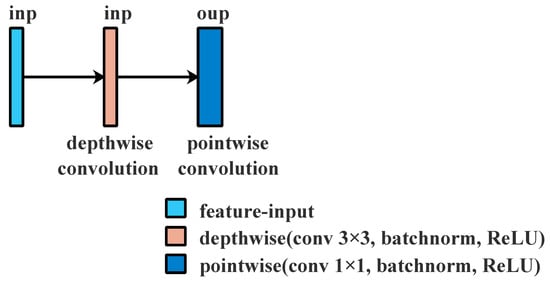
Figure 2.
Depthwise separable convolution; inp and oup are the channel numbers in different layers.
- To filter input channels, depthwise convolution is used, which is a group convolution operations with the same number of groups as input channels.
- To integrate features from a depthwise convolution operation to produce new features, pointwise convolution, a common convolution operation with a kernel size of 1 × 1, is used.
Comparing Depthwise Separable Convolution with normal convolution, one can see that it is able to both extract the features and minimize the number of parameters. However, it is unable to extract features in different feature spaces. This makes it challenging to distinguish among classes based on their forms and sizes. As illustrated in Figure 3, we utilize 1 × 1, 3 × 3, and 5 × 5 kernels, respectively, to filter the input channels and then concatenate them, thus overcoming this problem.
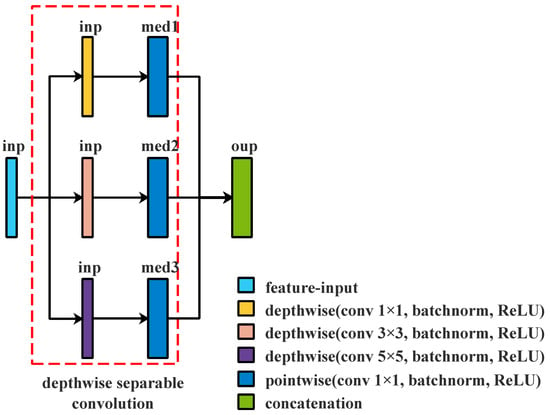
Figure 3.
Depthwise Separable Convolution with different kernels; inp, med1, med2, med3, and oup are the numbers of channels in different layers, where the sum of med1, med2, and med3 is equal to oup.
Figure 3 shows that the aforementioned module may extract multi-scale features from various feature spaces. Each branch in this module is an independent Depthwise Separable Convolution operation, and three branches, respectively, filter input channels in different feature spaces. The above module only filters input channels in different feature spaces. It does not combine those filtered input channels to produce new characteristics. As demonstrated in Figure 4, an additional layer is added to create new features before concatenation by computing a linear combination of features using 1 × 1 convolution.
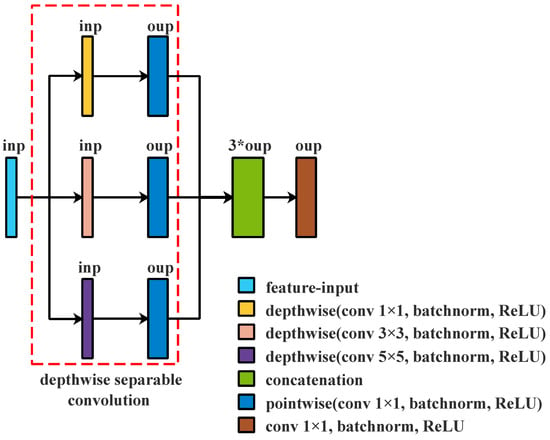
Figure 4.
Depthwise Separable Convolution with different kernels followed by additional layer; inp and oup are the numbers of channels in different layers.
Compared with the module in Figure 3, the module in Figure 4 widens the non-linear layers and adds a layer. The non-linear link between input and output is strengthened by enlarging the non-linear layers, adding a layer to combine features from different feature spaces to create new features. However, the pointwise convolution layer is an additional layer. We adjust the structure to eliminate the redundant layer, as shown in Figure 5.
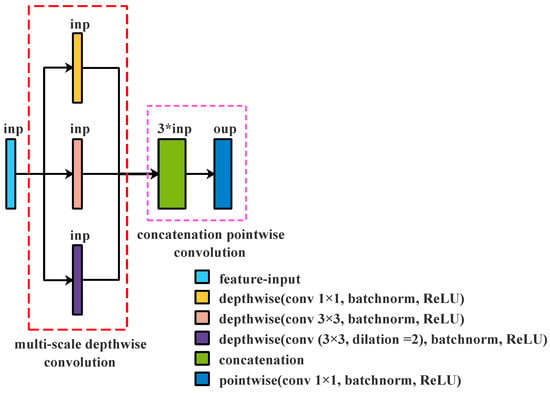
Figure 5.
Multi-Scale Depthwise Separable Convolution.
Different from the module in Figure 5, concatenation is placed before depthwise convolution and then concatenates the features; pointwise convolution merges with the additional layer; the 5 × 5 standard convolution is replaced with 3 × 3 dilated convolution (the dilation rate is 2). The combination of three depthwise convolution operations is called multi-scale depthwise convolution, and the combination of concatenation and pointwise convolution is called concatenation pointwise convolution. Figure 5 shows the proposed module, Multi-Scale Depthwise Separable Convolution. We can learn that this module consists of multi-scale depthwise convolution and concatenation pointwise convolution, which include convolution operation, batch normalization [34], and ReLU [46]. Multi-scale depthwise convolution is used to extract spatial features in different feature spaces. Concatenation pointwise convolution not only changes the number of channels but also combines those spatial features from multi-scale depthwise convolution to create new features. Compared with Depthwise Separable Convolution, Multi-Scale Depthwise Separable Convolution widens the non-linear layers to strengthen the non-linear relationship between input and output. However, the proposed module produces more parameters.
4. Experimental Results
The effectiveness on Camvid [47,48] and KITTI [49], which are often used in semantic segmentation tasks, is assessed in this section. The proposed network structure is similar to that of FCN-8s, but the channel numbers in every layer are different, as shown in Table 1. The network adopts Back Propagation [50]. First, we name the structure FCN-base when the convolution method is standard. Then, we respectively replace standard convolution with Depthwise Separable Convolution and Multi-Scale Depthwise Separable Convolution and then name them DS-FCN and MDS-FCN, respectively. To demonstrate the legitimacy and sanity of the suggested module, we first compared MDS-FCN and FCN-base, and MDS-FCN and DS-FCN. A second comparison was made between MDS-FCN and cutting-edge algorithms such as PSPNet, BiseNet, DeepLab, ICNet, and FSSNet, as well as the commonly used FCN-8s, Segnet, and Enet. All the performances were measured using MIoU and parameters. The whole proposed network structure is shown in Figure 6.

Table 1.
Detailed structure of network.
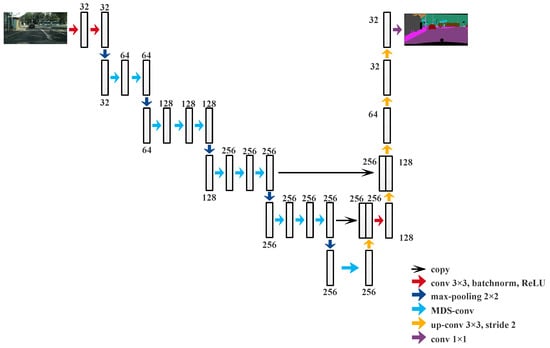
Figure 6.
Multi-Scale Depthwise Separable Convolution.
4.1. Parameter Setting
Before training, neural networks such as FCN and Segnet always use additional data for pre-training or are appended to a pre-trained architecture. Pre-training/trained and fine-tuning were not employed in this research. The parameters of the neural networks involved were randomly initialized and were only trained on the given dataset. In Camvid and KITTI, the figures were randomly cropped to 480 × 352 and then fed into neural networks. The parameters, such as the number of iterations, batch size, and learning rate, were set according to experimental experience and were finally set to 4, 1200, and 0.0025, respectively. All tests were run on a single GPU (GTX 1070ti).
4.2. Performance Evaluation on the Camvid Dataset
As seen in Figure 7, the Camvid dataset consists of 701 color-scale road photos that were taken in various places. We used the common split [51] to make comparisons with earlier works simple and fair. A total of 367 photos were utilized for training; a total of 101, for validation; and 233, for testing. Segmenting 11 classes in the Camvid dataset was used to verify performance. In this classification, automobiles were grouped with truck_bus; roads were grouped with lanes; and kids were grouped with pedestrians.

Figure 7.
Data from Camvid.
When the convolution method is standard convolution, Depthwise Separable Convolution, or Multi-Scale Depthwise Separable Convolution, we name the corresponding structure FCN-base, DS-FCN, or MDS-FCN. The problem of segmenting 11 classes on Camvid was completed using the aforementioned three network architectures, and MDS-FCN delivered results that are competitive in terms of MIoU and parameter count. Table 2 reveals that Depthwise Separable Convolution replacing standard convolution resulted in a small rise in MIoU from 52.58 to 54.71 and a sharp drop in parameters from 40.36 M to 1.68 M. The suggested module, Multi-Scale Depthwise Separable Convolution, builds on Depthwise Separable Convolution to increase the non-linear relationship between input and output in various feature spaces and can distinguish among classes that have varying sizes within a class. MIoU dramatically increased from 52.58 to 61.02 when Multi-Scale Depthwise Separable Convolution was used in place of conventional convolution. Compared with DS-FCN, the MIoU of MDS-FCN was more than 6, which was higher than that of DS-FCN. On the other hand, the parameters of MDS-FCN were only 1 M more than those of DS-FCN. In addition, the proposed module showed better performance in most classes, such as cars, roads, traffic lights, sidewalks, etc. In terms of large classes, such as trees, sky, and roads, standard convolution, Depthwise Separable Convolution, and Multi-Scale Depthwise Separable Convolution produced similar segmentation results. However, in terms of small classes, the per-class Intersection over Unions (per class IoU) obtained by the modules mentioned above was significantly different. The proposed module obviously produced better results than the other modules involved.

Table 2.
Comparison results of different convolution modules on Camvid.
We compared MDS-FCN with the commonly used FCN-8s [26], Segnet [29], and Enet [4], and cutting-edge algorithms such as PSPNet [30], BiseNet [32], Dilation8 [52], DeepLab [53], ICNet [33], and FSSNet [54] on Camvid. The results of our semantic segmentation job are quite promising, as demonstrated in Table 3 and Figure 8.

Table 3.
Result on Camvid.

Figure 8.
Semantic segmentation results on Camvid. (a) Original images. (b) The proposed structure. (c) Ground truth.
In semantic pixel-wise segmentation tasks on Camvid, MDS-FCN traded off accuracy and parameters, as shown in Table 3 and Figure 8. FCN-32 could finish the challenge of segmenting 11 classes, but the results are coarse, and many details could not be accurately delineated. Enet uses an efficient convolution method to decrease parameters but sacrifices accuracy. Compared with FSSNet, MDS-FCN adopts a parallel structure to extract spatial features in different feature spaces, producing more parameters; however, its MIoU increased from 58.6 to 61.02. Modern algorithms such as PSPNet and BiseNe multiply branches, combine many stages, or alter the network’s connection pattern to achieve competitive performance with excellent accuracy, but they also add numerous parameters and consume a lot of memory. Except ENet and FSSNet, the rest of the networks produced lots of parameters that were more than 20 M. In particular, although Dilation8 obtained 65.3 MIoU on Camvid, it produced 140.8 M parameters, about 138 M more than MDS-FCN. MDS-FCN only produced 2.68 M parameters, significantly less than most state-of-the-art algorithms, while reducing accuracy as little as possible, which is a benefit for synchronous operation with multiple algorithms under limited resources.
4.3. Performance Evaluation on KITTI Dataset
As seen in Figure 9, the KITTI pixel-level semantic segmentation benchmark comprises 400 color-scale pictures. As we could not collect the ground truth for 200 testing photos and wished to confirm the effectiveness of few-shot learning, 200 images were utilized for training, and 200 images, for testing. As a result, we randomly split the first 200 training pictures into two groups. The training portion included 140 photographs, while the testing portion included 60 images. The task at hand was to divide 19 classes into categories such as roads, buildings, pedestrians, trees, etc.

Figure 9.
Data from KITTI.
Then, we compared MDS-FCN, a neural network architecture related to Multi-Scale Depthwise Separable Convolution, with the commonly used FCN-8s, Unet, Segnet, and Enet. In a similar manner, we compared Multi-Scale Depthwise Separable Convolution with standard convolution and Depthwise Separable Convolution. In all experiments, pre-training/trained and fine-tuning were not used. The suggested approach generated competitive results that traded off accuracy and parameters, as shown in Tables “ref” Table 4 and Table 5, and Figure 10.

Table 4.
Comparison results of different convolution modules on KITTI.

Table 5.
Results on KITTI.
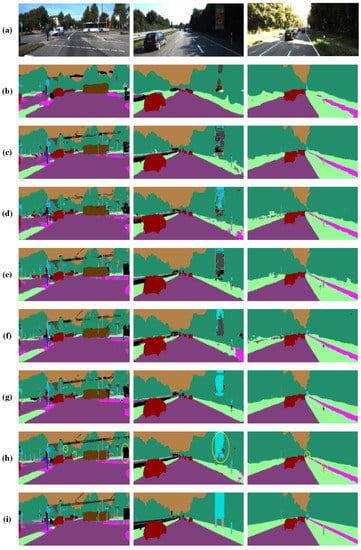
Figure 10.
Semantic segmentation results on KITTI. The yellow circles represent well segmented parts. (a) Original images. (b) FCN-32s. (c) FCN-8s. (d) DS-FCN. (e) Unet. (f) Segnet. (g) Enet. (h) MDS-FCN (the proposed module). (i) Ground truth.
The non-linear link between input and output is established by neural networks by extracting spatial characteristics. Studying those spatial features needs several data collected in all cases. For instance, just 140 photos were employed to train the neural network on the KITTI pixel-level semantic segmentation benchmark. Neural networks must be capable of few-shot learning for this to work.
We can learn from Table 4 that when standard convolution in FCN-8s was replaced with Multi-Scale Depthwise Separable Convolution, the MIoU significantly increased from 43.02 to 51.71. This demonstrates that extracting multi-scale features from diverse feature spaces appears to be quite effective for classifying entities in a variety of complicated environments. However, when standard convolution in FCN-8s was replaced with Depthwise Separable Convolution, the MIoU decreased from 43.02 to 41.26. From Table 5, we can learn that both MDS-FCN and Enet produced competitive results that are clearly superior to those of the algorithms mentioned above. In terms of MIoU, MDS-FCN outperformed the rest of the algorithms in Table 5. In terms of parameters, although MDS-FCN adopts a parallel structure to extract spatial features in different feature spaces, it produced 2.68 M parameters less than most other algorithms and occupied fewer storage resources. In addition, MDS-FCN could produce smooth segmentation results and delineate more details (see Figure 9) in instances based on their shapes despite their different sizes. FCN-32s, FCN-8s, Unet, and Segnet could not retain the boundary information and could not accurately delineate small classes.
4.4. Performance Evaluation on the Cityscapes Dataset
We compared MDSNet with the widely used FCN-8s, Segnet, and Enet, and state-of-the-art algorithms such as BiseNet, ICNet, Dilation10, DeepLab, and PSPNet on the Cityscapes dataset. Table 6 and Figure 11 show the competitive results.

Table 6.
Results on Cityscapes.
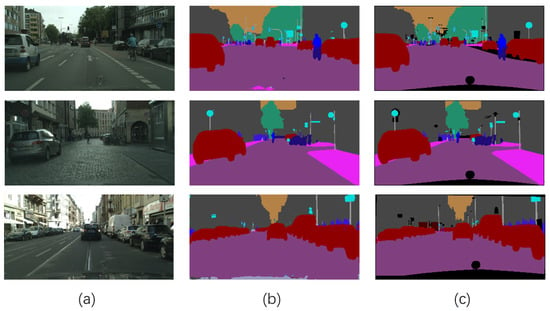
Figure 11.
Semantic segmentation results on Cityscapes. (a) Original images. (b) MDS-FCN. (c) Ground truth.
The algorithms aforementioned in Table 6 were able to finish the challenge of segmenting 19 classes on the Cityscapes dataset. Early widely used networks such as FCN and Segnet use standard convolution to extract object features, thus being easily affected by objects on multiple scales and different locations. This seemed to have a bad effect on segmentation accuracy. In addition, extensive standard convolution operations produced many parameters and slowed down the inference speed. Compared with those early algorithms, MDS-FCN showed a great advantage in terms of accuracy, parameters, and inference speed. Most lightweight networks, such as ESPNet, ENet, ERFNet, and BiseNet, used efficient convolution methods to accelerate the inference speed and decrease parameters. ESPNet and Enet only stressed inference speed and parameters. They significantly sacrificed segmentation accuracy. ERFNet, BiseNet, and ICNet balanced the relationship among segmentation accuracy, parameters, and inference speed and had similar segmentation accuracy. BiseNet had an obvious advantage in inference speed, and ERFNet had an advantage in parameters. Compared with ESPNet and ENet, MRDNet showed uncompetitive performance both in terms of parameters and inference speed, but it significantly improved segmentation accuracy from 60.3 to 68.5. MDS-FCN showed an acceptable inference speed that was slower than that of ERFNet, BiseNet, and ICNet. However, it had an advantage in accuracy and parameters. DeepLab and PSPNet showed high segmentation accuracy, which was higher than that of MDS-FCN by more than eight points, but they had extensive parameters and slow inference speed. This is not applicable to real-world applications that have a strict requirement on inference speed. MDS-FCN showed competitive performance, 68.5 MIoU with only 2.68 million parameters, while maintaining 13.4 fps on a single GTX 1070Ti card on Cityscapes, showing the ability to delineate objects based on their shape despite their small size and producing smooth segmentation results. In addition, due to mutual occlusion and blurry boundaries among objects, it is difficult to extract information such as boundaries. On the other hand, excessive downsampling results in the loss of some detailed information, especially for elongated objects with extensibility that cannot be recovered during subsequent upsampling, resulting in segmentation failure, as shown in Figure 12.
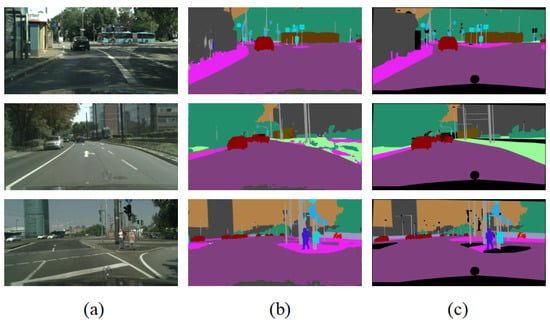
Figure 12.
Failed semantic segmentation results on Cityscapes. (a) Original images. (b) The proposed structure. (c) Ground truth.
5. Conclusions
We propose Multi-Scale Depthwise Separable Convolution, a novel convolution module made to balance accuracy and parameters. Concatenation pointwise convolution and multi-scale depthwise convolution make up this module. To produce new features, it filters the input channels and combines them. The suggested module, which is based on Depthwise Separable Convolution, can extract multi-scale spatial features in various feature spaces while preserving small parameter values. On the Camvid, KITTI, and Cityscapes datasets, MDS-FCN produced competitive results, i.e., MIoU of 61.02, 51.71, and 68.5, respectively, while producing 2.68 M parameters. Compared with FCN-8s, Unet, Segnet, and Enet, it can segment both small and large classes well due to the fact that this module may increase the non-linear interaction between input and output and broaden the non-linear layers. In addition, MDS-FCN is more efficient in terms of memory, since it moderately reduces parameters by changing the computational method of the convolution operation. However, MDS-FCN cannot effectively extract their spatial features for a few classes. Future work will mainly focus on a novel architecture based on Multi-Scale Depthwise Separable Convolution. Compared with MDS-FCN, the novel architecture will be designed to improve the computational time, reduce parameters, and improve accuracy.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.D. and J.L.; Data curation, C.L.; Formal analysis, C.L. and H.L.; Investigation, Y.D.; Project administration, J.L.; Resources, H.L.; Software, X.S.; Validation, X.S.; Writing—original draft, Y.D.; Writing—review and editing, J.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences Science and Technology Innovation Project grant number ASTIP-TRIC03 and National Natural Science Foundation of China grant number 62203176.
Data Availability Statement
Data sharing not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analysis, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Li, J.; Dai, Y.; Su, X.; Wu, W. Efficient Dual-Branch Bottleneck Networks of Semantic Segmentation Based on CCD Camera. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Dai, Y.; Wang, J.; Su, X.; Ma, R. Towards broad learning networks on unmanned mobile robot for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2022 International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Philadelphia, PA, USA, 23–27 May 2022; pp. 9228–9234. [Google Scholar]
- Siam, M.; Gamal, M.; Abdel-Razek, M.; Yogamani, S.; Jagersand, M. Rtseg: Real-time semantic segmentation comparative study. In Proceedings of the 2018 25th IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Athens, Greece, 7–10 October 2018; pp. 1603–1607. [Google Scholar]
- Paszke, A.; Chaurasia, A.; Kim, S.; Culurciello, E. Enet: A deep neural network architecture for real-time semantic segmentation. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1606.02147. [Google Scholar]
- Arsalan, M.; Kim, D.S.; Lee, M.B.; Owais, M.; Park, K.R. FRED-Net: Fully residual encoder–decoder network for accurate iris segmentation. Expert Syst. Appl. 2019, 122, 217–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noh, H.; Hong, S.; Han, B. Learning deconvolution network for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 1520–1528. [Google Scholar]
- Hariharan, B.; Arbelaez, P.; Girshick, R.; Malik, J. Object instance segmentation and fine-grained localization using hypercolumns. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2016, 39, 627–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, K.J.; Lin, Y.Y.; Chuang, Y.Y. Weakly supervised salient object detection by learning a classifier-driven map generator. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2019, 28, 5435–5449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.; He, K.; Girshick, R.; Sun, J. Faster r-cnn: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 39, 1137–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woźniak, M.; Połap, D. Object detection and recognition via clustered features. Neurocomputing 2018, 320, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szegedy, C.; Liu, W.; Jia, Y.; Sermanet, P.; Reed, S.; Anguelov, D.; Erhan, D.; Vanhoucke, V.; Rabinovich, A. Going deeper with convolutions. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Zhang, X.; Li, J.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J. Building and optimization of 3D semantic map based on Lidar and camera fusion. Neurocomputing 2020, 409, 394–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, S.; Kokkinos, I. Fast, exact and multi-scale inference for semantic image segmentation with deep gaussian crfs. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision–ECCV 2016: 14th European Conference, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 11–14 October 2016; Proceedings, Part VII 14. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 402–418. [Google Scholar]
- Hariharan, B.; Arbeláez, P.; Girshick, R.; Malik, J. Hypercolumns for object segmentation and fine-grained localization. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 447–456. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Wang, J.; Peng, H.; Hu, Y.; Su, H. Fuzzy-Torque Approximation-Enhanced Sliding Mode Control for Lateral Stability of Mobile Robot. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man, Cybern. Syst. 2022, 52, 2491–2500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, A.G.; Zhu, M.; Chen, B.; Kalenichenko, D.; Wang, W.; Weyand, T.; Andreetto, M.; Adam, H. Mobilenets: Efficient convolutional neural networks for mobile vision applications. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1704.04861. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Wang, J.; Peng, H.; Zhang, L.; Hu, Y.; Su, H. Neural fuzzy approximation enhanced autonomous tracking control of the wheel-legged robot under uncertain physical interaction. Neurocomputing 2020, 410, 342–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chollet, F. Xception: Deep learning with depthwise separable convolutions. In Proceedings of the EEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 1251–1258. [Google Scholar]
- Sandler, M.; Howard, A.; Zhu, M.; Zhmoginov, A.; Chen, L.C. Mobilenetv2: Inverted residuals and linear bottlenecks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 4510–4520. [Google Scholar]
- Sezgin, M.; Sankur, B.L. Survey over image thresholding techniques and quantitative performance evaluation. J. Electron. Imaging 2004, 13, 146–168. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, P.S.; Chen, T.S.; Chung, P.C. A fast algorithm for multilevel thresholding. J. Inf. Sci. Eng. 2001, 17, 713–727. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Dai, Y.; Xue, J.; Liu, B.; Ma, C.; Gao, Y. Research of segmentation method on color image of Lingwu long jujubes based on the maximum entropy. EURASIP J. Image Video Process. 2017, 2017, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinbrunn, M.; Moerkotte, G.; Kemper, A. Heuristic and randomized optimization for the join ordering problem. VLDB J. 1997, 6, 191–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortes, C.; Vapnik, V. Support-vector networks. Mach. Learn. 1995, 20, 273–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gönen, M.; Alpaydın, E. Multiple kernel learning algorithms. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2011, 12, 2211–2268. [Google Scholar]
- Long, J.; Shelhamer, E.; Darrell, T. Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 3431–3440. [Google Scholar]
- Keys, R. Cubic convolution interpolation for digital image processing. IEEE Trans. Acoust. Speech Signal Process. 1981, 29, 1153–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention–MICCAI 2015: 18th International Conference, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; Proceedings, Part III 18. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Badrinarayanan, V.; Kendall, A.; Cipolla, R. Segnet: A deep convolutional encoder-decoder architecture for image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 39, 2481–2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Shi, J.; Qi, X.; Wang, X.; Jia, J. Pyramid scene parsing network. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 2881–2890. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, C.; Wang, J.; Peng, C.; Gao, C.; Yu, G.; Sang, N. Bisenet: Bilateral segmentation network for real-time semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 325–341. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H.; Qi, X.; Shen, X.; Shi, J.; Jia, J. Icnet for real-time semantic segmentation on high-resolution images. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 405–420. [Google Scholar]
- Ioffe, S.; Szegedy, C. Batch normalization: Accelerating deep network training by reducing internal covariate shift. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, PMLR, Lille, France, 6–11 July 2015; pp. 448–456. [Google Scholar]
- Szegedy, C.; Vanhoucke, V.; Ioffe, S.; Shlens, J.; Wojna, Z. Rethinking the inception architecture for computer vision. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 2818–2826. [Google Scholar]
- Szegedy, C.; Ioffe, S.; Vanhoucke, V.; Alemi, A. Inception-v4, inception-resnet and the impact of residual connections on learning. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, San Francisco, CA, USA, 4–9 February 2017; Volume 31. [Google Scholar]
- LeCun, Y.; Boser, B.; Denker, J.S.; Henderson, D.; Howard, R.E.; Hubbard, W.; Jackel, L.D. Backpropagation applied to handwritten zip code recognition. Neural Comput. 1989, 1, 541–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeiler, M.D.; Fergus, R. Visualizing and understanding convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision–ECCV 2014: 13th European Conference, Zurich, Switzerland, 6–12 September 2014; Proceedings, Part I 13. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 818–833. [Google Scholar]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1409.1556. [Google Scholar]
- Girshick, R.; Donahue, J.; Darrell, T.; Malik, J. Rich feature hierarchies for accurate object detection and semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, OH, USA, 23–28 June 2014; pp. 580–587. [Google Scholar]
- Girshick, R. Fast r-cnn. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 1440–1448. [Google Scholar]
- Redmon, J.; Divvala, S.; Girshick, R.; Farhadi, A. You only look once: Unified, real-time object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 779–788. [Google Scholar]
- Mirza, M.; Osindero, S. Conditional generative adversarial nets. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1411.1784. [Google Scholar]
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Commun. ACM 2017, 60, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ting, Z.; Guo-Jun, Q.; Bin, X.; Jingdong, W. Interleaved group convolutions for deep neural networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Hahnloser, R.H.; Sarpeshkar, R.; Mahowald, M.A.; Douglas, R.J.; Seung, H.S. Digital selection and analogue amplification coexist in a cortex-inspired silicon circuit. Nature 2000, 405, 947–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brostow, G.J.; Shotton, J.; Fauqueur, J.; Cipolla, R. Segmentation and recognition using structure from motion point clouds. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision–ECCV 2008: 10th European Conference on Computer Vision, Marseille, France, 12–18 October 2008; Proceedings, Part I 10. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; pp. 44–57. [Google Scholar]
- Brostow, G.J.; Fauqueur, J.; Cipolla, R. Semantic object classes in video: A high-definition ground truth database. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2009, 30, 88–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geiger, A.; Lenz, P.; Urtasun, R. Are we ready for autonomous driving? the kitti vision benchmark suite. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Providence, RI, USA, 16–21 June 2012; pp. 3354–3361. [Google Scholar]
- Rumelhart, D.E.; Hinton, G.E.; Williams, R.J. Learning representations by back-propagating errors. Nature 1986, 323, 533–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sturgess, P.; Alahari, K.; Ladicky, L.; Torr, P.H. Combining appearance and structure from motion features for road scene understanding. In Proceedings of the BMVC-British Machine Vision Conference, London, UK, 7–10 September 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, F.; Koltun, V. Multi-scale context aggregation by dilated convolutions. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1511.07122. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.C.; Papandreou, G.; Kokkinos, I.; Murphy, K.; Yuille, A.L. Deeplab: Semantic image segmentation with deep convolutional nets, atrous convolution, and fully connected crfs. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 40, 834–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Chen, Z.; Wu, Q.J.; Cai, L.; Lu, D.; Li, X. Fast semantic segmentation for scene perception. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2018, 15, 1183–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).