Robust Feature-Guided Generative Adversarial Network for Aerial Image Semantic Segmentation against Backdoor Attacks
Abstract
1. Introduction
- To the best of our knowledge, we are the first to introduce the concept of backdoor attack into aerial image semantic segmentation. Our research comprehensively reveals the significance of the resistibility and robustness of DNNs models when addressing the safety-critical airborne earth observation tasks.
- We comprehensively analyze and summarize the characteristics of backdoor attacks in aerial images, and propose a robust feature guided generative adversarial network (RFGAN) against backdoor attacks. The constructed RFGAN can filter backdoor triggers by extracting different robust feature information.
- Based on the robust attributes of global and edge features, we construct robust global feature extractor (RobGF) and robust edge feature extractor (RobEF), respectively. In addition, the generative adversarial network (GAN) framework is used to generate benign samples and obtain semantic segmentation results.
- To verify the effectiveness and feasibility of the proposed defense framework, the extensive experiments are conducted on real-world aerial image datasets. The experimental results show the proposed method can against backdoor attacks while maintaining high semantic segmentation precision.
2. Related Works
2.1. Backdoor Attack
2.2. Backdoor Defense
2.3. Preliminary
3. Methodology
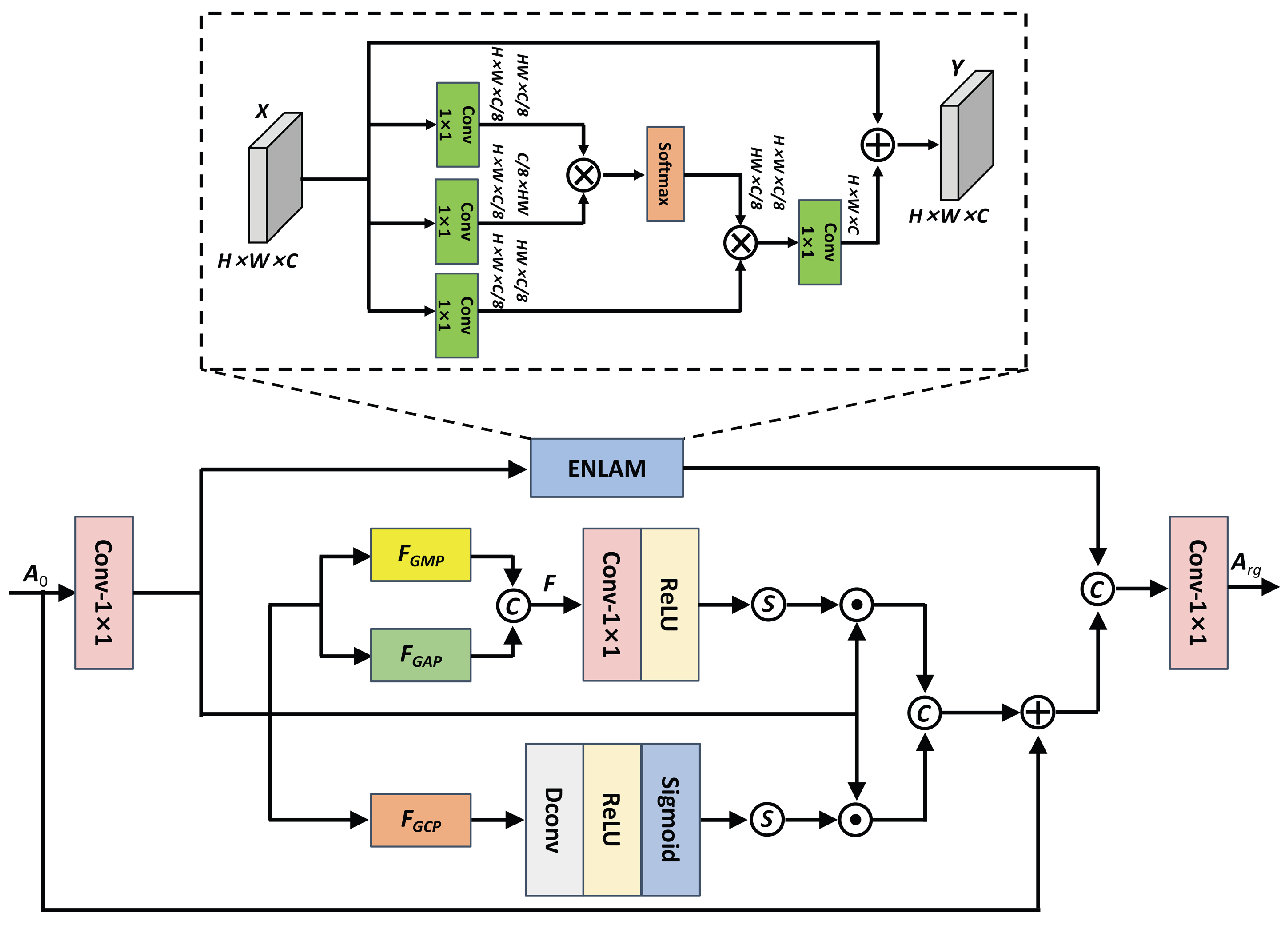
3.1. Robust Global Feature Extractor
3.2. Robust Edge Feature Extractor
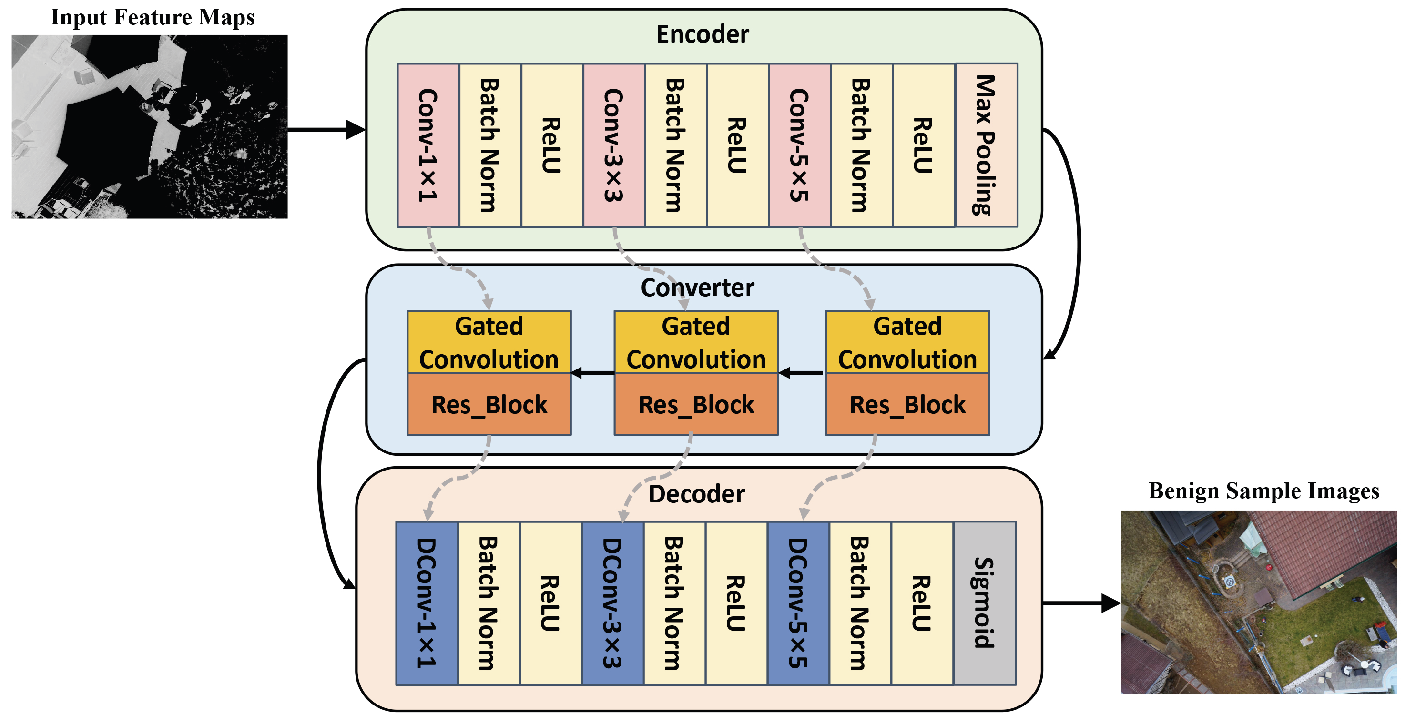
3.3. Benign Sample Generator
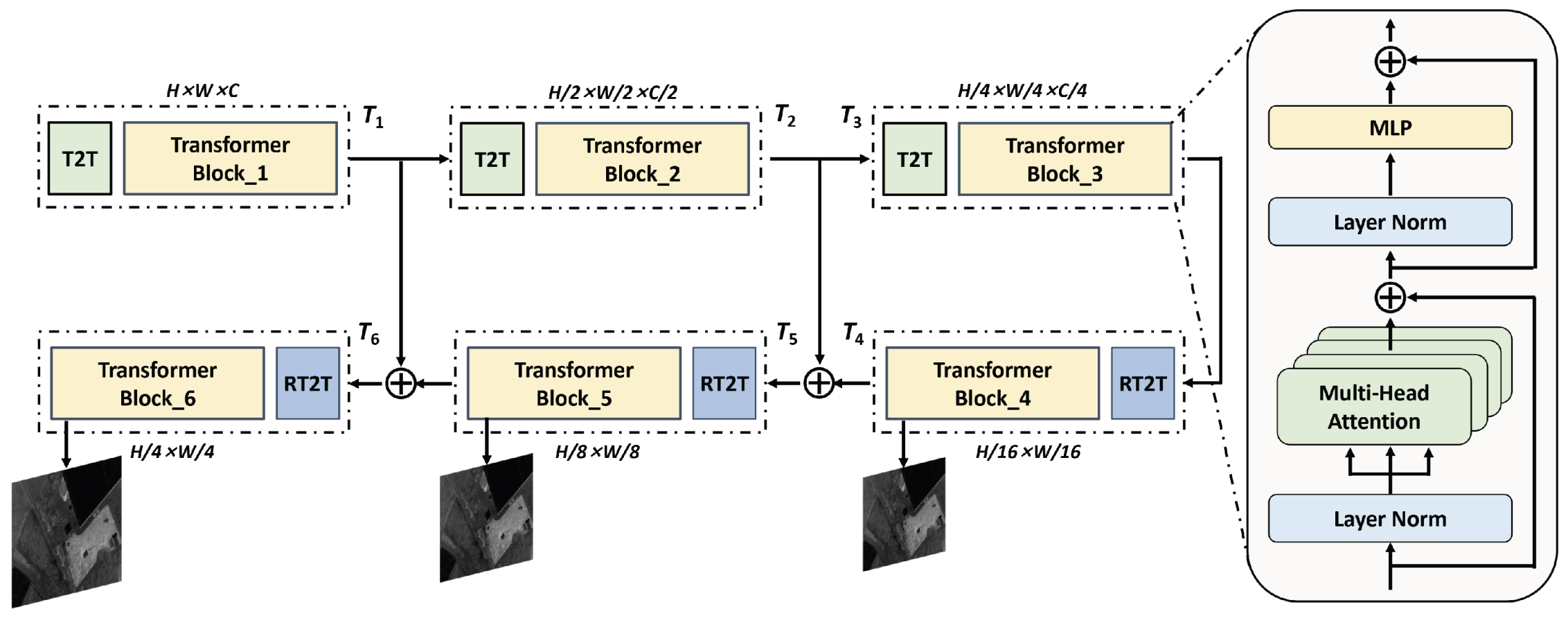
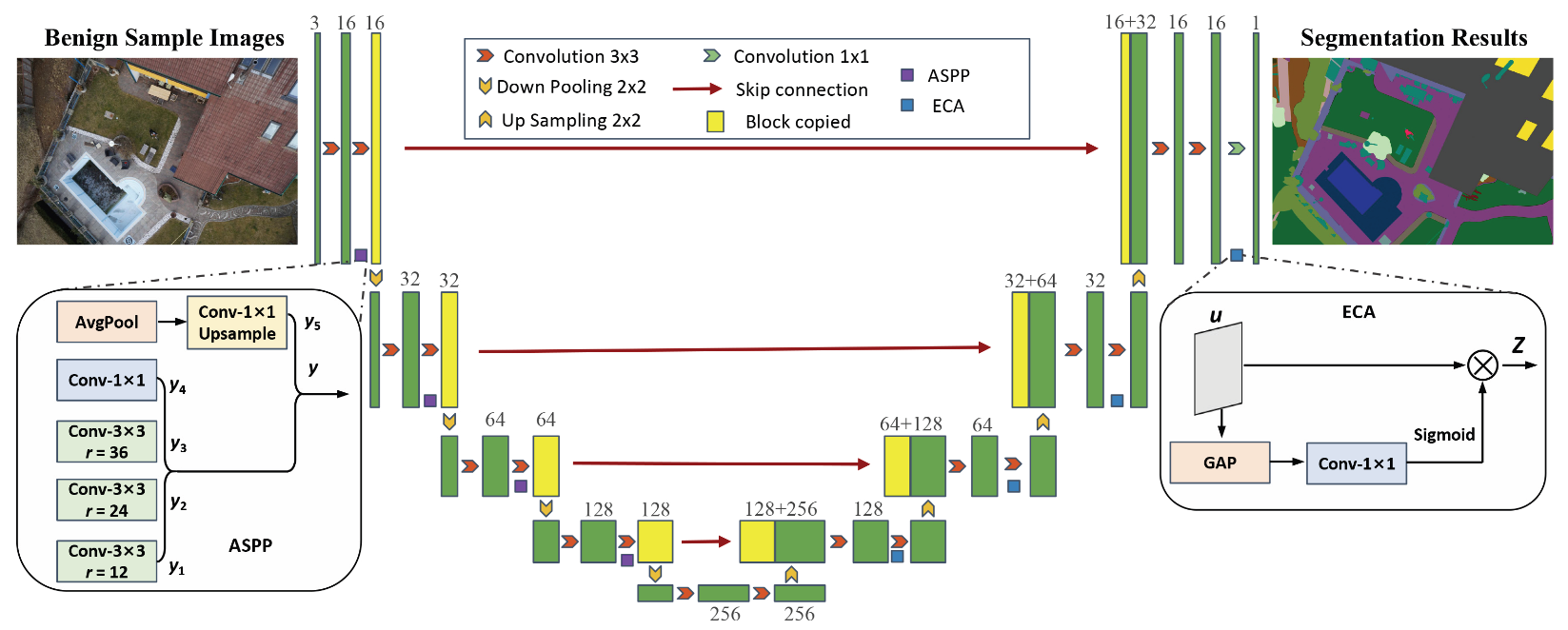
3.4. Discriminator
3.5. Loss Function
4. Experiments and Analysis
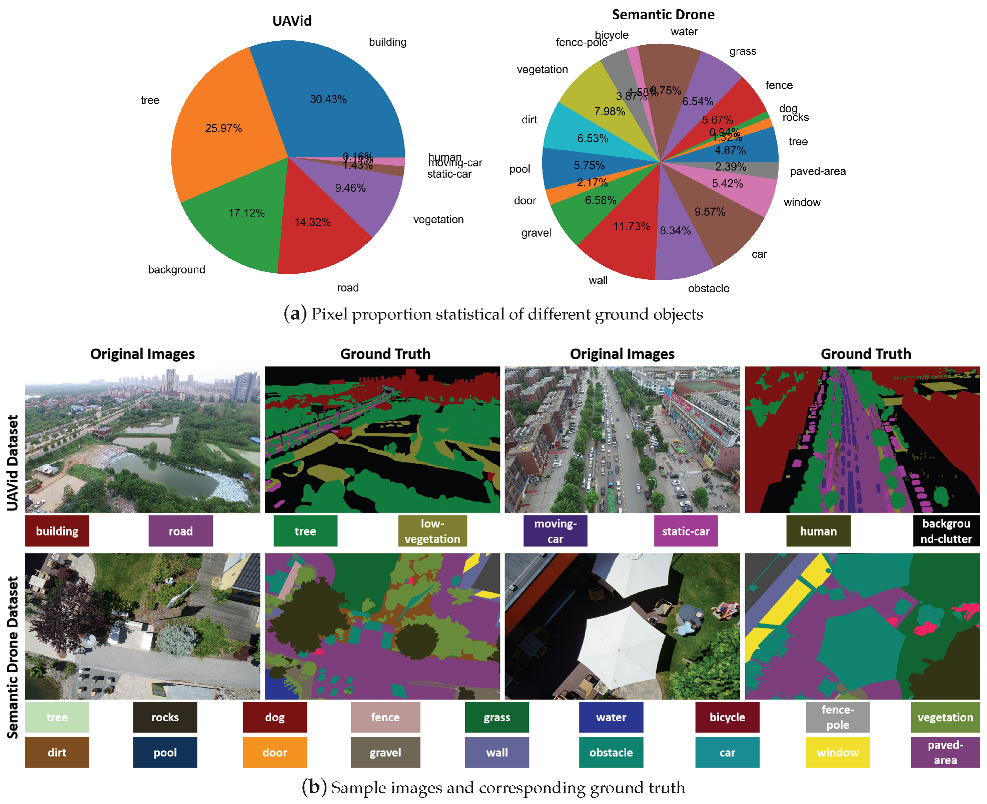
4.1. Dataset Information
4.2. Implementation Details and Evaluation Metrics
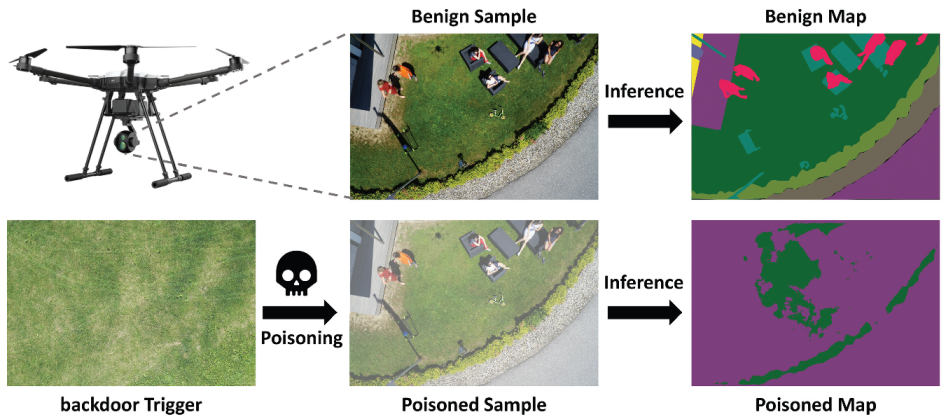
4.3. Backdoor Attack Settings
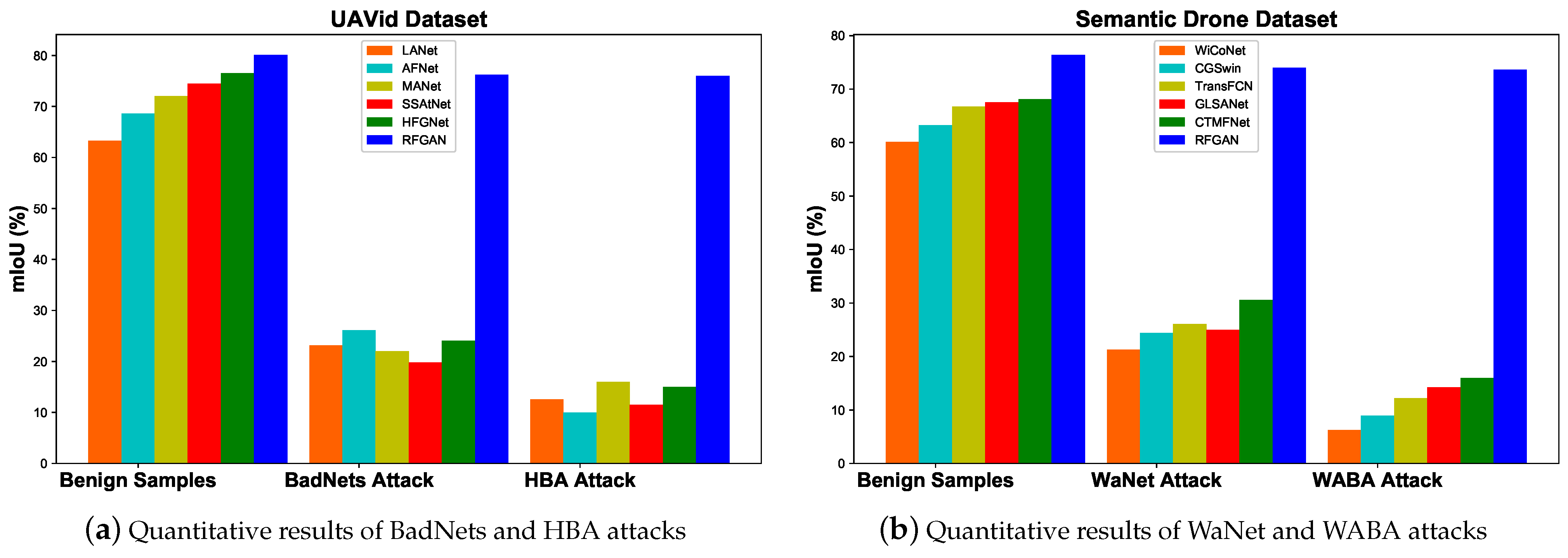
4.4. Defense Performance Analysis on UAVid Dataset
4.5. Defense Performance Analysis on Semantic Drone Dataset
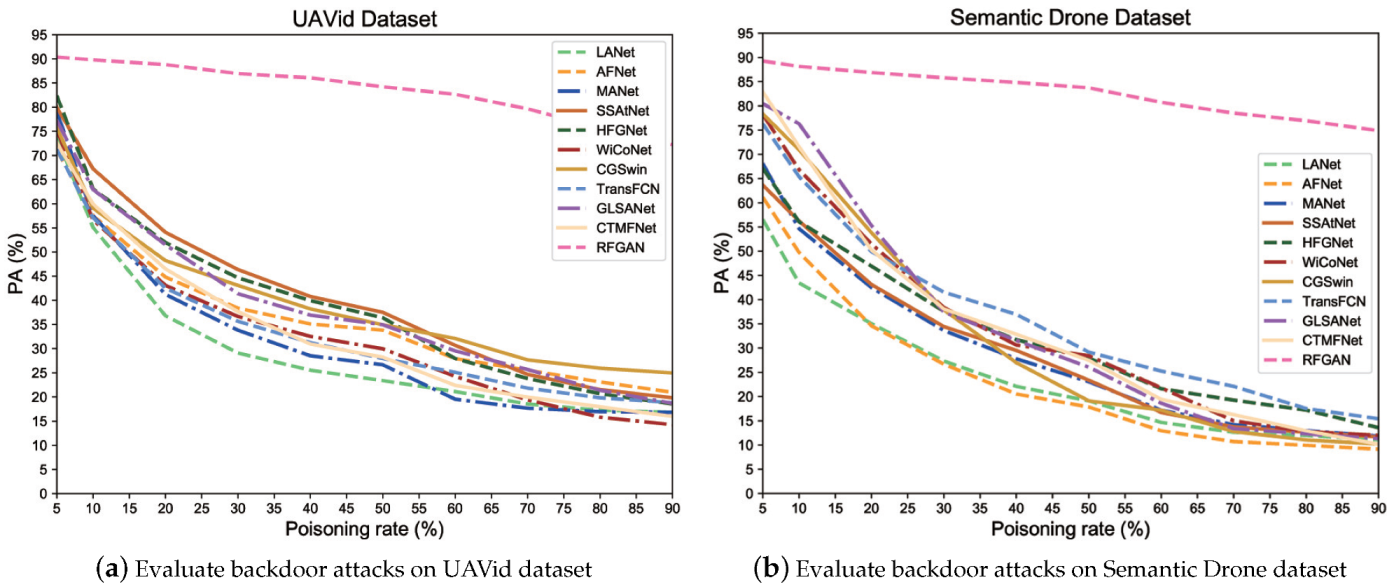
4.6. Ablation Studies
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Clabaut, É.; Lemelin, M.; Germain, M.; Bouroubi, Y.; St-Pierre, T. Model Specialization for the Use of ESRGAN on Satellite and Airborne Imagery. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maxwell, A.E.; Warner, T.A.; Guillén, L.A. Accuracy assessment in convolutional neural network-based deep learning remote sensing studies—Part 1: Literature review. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maxwell, A.E.; Warner, T.A.; Guillén, L.A. Accuracy assessment in convolutional neural network-based deep learning remote sensing studies—Part 2: Literature review. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, W.; Hu, Z.; Li, L.; Cao, J.; Jiang, J.; Li, Q.; Li, Q. Portraying urban functional zones by coupling remote sensing imagery and human sensing data. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdi, Z.M.; Brandmeier, M.; Straub, C. Forest damage assessment using deep learning on high resolution remote sensing data. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimoni, M.; Haelterman, R.; Perneel, C. Hypersectral imaging for military and security applications: Combining myriad processing and sensing techniques. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Mag. 2019, 7, 101–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Shi, J.; Gu, L. A review of deep learning methods for semantic segmentation of remote sensing imagery. Expert Syst. Appl. 2021, 169, 114417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldana-Martín, J.F.; García-Nieto, J.; del Mar Roldán-García, M.; Aldana-Montes, J.F. Semantic modelling of earth observation remote sensing. Expert Syst. Appl. 2022, 187, 115838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; He, P.; Zhu, Q.; Li, X. Adversarial examples: Attacks and defenses for deep learning. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2019, 30, 2805–2824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czaja, W.; Fendley, N.; Pekala, M.; Ratto, C.; Wang, I.J. Adversarial examples in remote sensing. In Proceedings of the 26th ACM SIGSPATIAL International Conference on Advances in Geographic Information Systems, Seattle, WA, USA, 6–9 November 2018; pp. 408–411. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Zhu, G.; Li, Q.; Li, H. Adversarial example in remote sensing image recognition. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1910.13222. [Google Scholar]
- Ai, S.; Koe, A.S.V.; Huang, T. Adversarial perturbation in remote sensing image recognition. Appl. Soft Comput. 2021, 105, 107252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, T.; Wang, H.; Wen, B. Targeted Universal Adversarial Examples for Remote Sensing. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.; Li, Q.; Chen, L.; Li, H. Scale-adaptive adversarial patch attack for remote sensing image aircraft detection. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Qi, J.; Bin, K.; Wen, H.; Tong, X.; Zhong, P. Adversarial Patch Attack on Multi-Scale Object Detection for UAV Remote Sensing Images. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Ghamisi, P. Universal adversarial examples in remote sensing: Methodology and benchmark. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, B.; Liu, Y.; Guo, J. Global Feature Attention Network: Addressing the Threat of Adversarial Attack for Aerial Image Semantic Segmentation. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Li, Z.; Xia, S.T. Backdoor learning: A survey. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2022, 11, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shokri, R.; Stronati, M.; Song, C.; Shmatikov, V. Membership inference attacks against machine learning models. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy (SP), San Jose, CA, USA, 22–26 May 2017; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 3–18. [Google Scholar]
- Juuti, M.; Szyller, S.; Marchal, S.; Asokan, N. PRADA: Protecting against DNN model stealing attacks. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE European Symposium on Security and Privacy (EuroS&P), Stockholm, Sweden, 17–19 June 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 512–527. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Zhai, T.; Wu, B.; Jiang, Y.; Li, Z.; Xia, S. Rethinking the trigger of backdoor attack. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2004.04692. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Liu, C.; Li, B.; Lu, K.; Song, D. Targeted backdoor attacks on deep learning systems using data poisoning. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1712.05526. [Google Scholar]
- Rakin, A.S.; He, Z.; Fan, D. Tbt: Targeted neural network attack with bit trojan. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 13198–13207. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, Z.; Wu, J.; Li, G.; Li, S.; Guizani, M. Deep neural backdoor in semi-supervised learning: Threats and countermeasures. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2021, 16, 4827–4842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brewer, E.; Lin, J.; Runfola, D. Susceptibility & defense of satellite image-trained convolutional networks to backdoor attacks. Inf. Sci. 2022, 603, 244–261. [Google Scholar]
- Dräger, N.; Xu, Y.; Ghamisi, P. Backdoor Attacks for Remote Sensing Data with Wavelet Transform. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2211.08044. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.C.; Papandreou, G.; Schroff, F.; Adam, H. Rethinking atrous convolution for semantic image segmentation. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1706.05587. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, M.; Li, Z.; Xiao, C.; Qiu, H.; Kailkhura, B.; Liu, M.; Li, B. Can shape structure features improve model robustness under diverse adversarial settings? In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 7526–7535. [Google Scholar]
- He, X.; Yang, S.; Li, G.; Li, H.; Chang, H.; Yu, Y. Non-local context encoder: Robust biomedical image segmentation against adversarial attacks. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Honolulu, HI, USA, 27 January–1 February 2019; Volume 33, pp. 8417–8424. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, J.; Wang, T.; Jiang, R.; Xu, J.; Zhao, L. Robust feature learning for adversarial defense via hierarchical feature alignment. Inf. Sci. 2021, 560, 256–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitas, S.; Chen, S.T.; Wang, Z.J.; Chau, D.H. Unmask: Adversarial detection and defense through robust feature alignment. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Big Data (Big Data), Atlanta, GA, USA, 10–13 December 2020; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 1081–1088. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, T.; Liu, K.; Dolan-Gavitt, B.; Garg, S. Badnets: Evaluating backdooring attacks on deep neural networks. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 47230–47244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafahi, A.; Huang, W.R.; Najibi, M.; Suciu, O.; Studer, C.; Dumitras, T.; Goldstein, T. Poison frogs! targeted clean-label poisoning attacks on neural networks. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2018, 31. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Lv, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Xia, S.T. Hidden backdoor attack against semantic segmentation models. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2103.04038. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, S.H.; Dong, Y.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, J. Baddet: Backdoor attacks on object detection. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision–ECCV 2022 Workshops, Tel Aviv, Israel, 23–27 October 2022; Proceedings, Part I. Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 396–412. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, X.; Zhang, M.; Sheng, B.; Zhu, J.; Yang, M. Hidden trigger backdoor attack on {NLP} models via linguistic style manipulation. In Proceedings of the 31st USENIX Security Symposium (USENIX Security 22), Boston, MA, USA, 10–12 August 2022; pp. 3611–3628. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Chen, X.; Wang, D.; Wen, S.; Ahmed, M.E.; Camtepe, S.; Xiang, Y. Backdoor attack on machine learning based android malware detectors. IEEE Trans. Dependable Secur. Comput. 2021, 19, 3357–3370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Shi, C.; Xie, Y.; Liu, J.; Yuan, B.; Chen, Y. Practical adversarial attacks against speaker recognition systems. In Proceedings of the 21st International Workshop on Mobile Computing Systems and Applications, Austin, TX, USA, 3 March 2020; pp. 9–14. [Google Scholar]
- Tran, B.; Li, J.; Madry, A. Spectral signatures in backdoor attacks. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2018, 31, 8000–8010. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, A.; Ong, Y.S. Poison as a cure: Detecting & neutralizing variable-sized backdoor attacks in deep neural networks. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1911.08040. [Google Scholar]
- Peri, N.; Gupta, N.; Huang, W.R.; Fowl, L.; Zhu, C.; Feizi, S.; Goldstein, T.; Dickerson, J.P. Deep k-nn defense against clean-label data poisoning attacks. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision–ECCV 2020 Workshops, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; Proceedings, Part I 16. Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 55–70. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Lee, W.C.; Tao, G.; Ma, S.; Aafer, Y.; Zhang, X. Abs: Scanning neural networks for back-doors by artificial brain stimulation. In Proceedings of the 2019 ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer and Communications Security, London, UK, 11–15 November 2019; pp. 1265–1282. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.; Yao, Y.; Shan, S.; Li, H.; Viswanath, B.; Zheng, H.; Zhao, B.Y. Neural cleanse: Identifying and mitigating backdoor attacks in neural networks. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy (SP), San Francisco, CA, USA, 19–23 May 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 707–723. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Xie, Y.; Srivastava, A. Neural trojans. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Design (ICCD), Boston, MA, USA, 5–8 November 2017; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 45–48. [Google Scholar]
- Doan, B.G.; Abbasnejad, E.; Ranasinghe, D.C. Februus: Input purification defense against trojan attacks on deep neural network systems. In Proceedings of the Annual Computer Security Applications Conference, Honolulu, HI, USA, 7–11 December 2020; pp. 897–912. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Zhai, T.; Jiang, Y.; Li, Z.; Xia, S.T. Backdoor attack in the physical world. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2104.02361. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.; Du, B.; Zhang, L. Self-attention context network: Addressing the threat of adversarial attacks for hyperspectral image classification. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2021, 30, 8671–8685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, T.; Cai, J.; Zhang, Y.; Xia, S.T.; Zhang, L. Second-order attention network for single image super-resolution. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 11065–11074. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, X.; Cheng, D.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, S.; Dai, J. An empirical study of spatial attention mechanisms in deep networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 6688–6697. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, J.; Liu, J.; Tian, H.; Li, Y.; Bao, Y.; Fang, Z.; Lu, H. Dual attention network for scene segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–20 June 2019; pp. 3146–3154. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Girshick, R.; Gupta, A.; He, K. Non-local neural networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 7794–7803. [Google Scholar]
- Vilnis, L.; McCallum, A. Word representations via gaussian embedding. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.6623. [Google Scholar]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, Ł.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is all you need. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2017, 30, 5998–6008. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, L.; Chen, Y.; Wang, T.; Yu, W.; Shi, Y.; Jiang, Z.H.; Tay, F.E.; Feng, J.; Yan, S. Tokens-to-token vit: Training vision transformers from scratch on imagenet. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 558–567. [Google Scholar]
- Longstaff, I.D.; Cross, J.F. A pattern recognition approach to understanding the multi-layer perception. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 1987, 5, 315–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.Y.; Park, T.; Isola, P.; Efros, A.A. Unpaired image-to-image translation using cycle-consistent adversarial networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2223–2232. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Xiang, S.; Pan, C. Gated convolutional neural network for semantic segmentation in high-resolution images. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention–MICCAI 2015: 18th International Conference, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; Proceedings, Part III 18. Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.C.; Papandreou, G.; Kokkinos, I.; Murphy, K.; Yuille, A.L. Deeplab: Semantic image segmentation with deep convolutional nets, atrous convolution, and fully connected crfs. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 40, 834–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isola, P.; Zhu, J.Y.; Zhou, T.; Efros, A.A. Image-to-image translation with conditional adversarial networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 1125–1134. [Google Scholar]
- Kanopoulos, N.; Vasanthavada, N.; Baker, R.L. Design of an image edge detection filter using the Sobel operator. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 1988, 23, 358–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirza, M.; Osindero, S. Conditional generative adversarial nets. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1411.1784. [Google Scholar]
- Lyu, Y.; Vosselman, G.; Xia, G.S.; Yilmaz, A.; Yang, M.Y. UAVid: A semantic segmentation dataset for UAV imagery. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2020, 165, 108–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Liu, F.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, W.; Yuan, X.; Zhu, J. Valid: A comprehensive virtual aerial image dataset. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Paris, France, 31 May–31 August 2020; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 2009–2016. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, A.; Tran, A. Wanet—Imperceptible warping-based backdoor attack. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2102.10369. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, L.; Tang, H.; Bruzzone, L. LANet: Local attention embedding to improve the semantic segmentation of remote sensing images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 59, 426–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Mi, L.; Chen, Z. AFNet: Adaptive fusion network for remote sensing image semantic segmentation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 59, 7871–7886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Zheng, S.; Zhang, C.; Duan, C.; Su, J.; Wang, L.; Atkinson, P.M. Multiattention network for semantic segmentation of fine-resolution remote sensing images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 60, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Liu, J.; Li, Y.; Zhang, H. Semantic segmentation with attention mechanism for remote sensing images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 60, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, C.; Wang, B. Hidden Feature-Guided Semantic Segmentation Network for Remote Sensing Images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.; Lin, D.; Lin, S.; Zhang, J.; Cui, X.; Wang, Y.; Tang, H.; Bruzzone, L. Looking outside the window: Wide-context transformer for the semantic segmentation of high-resolution remote sensing images. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2106.15754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Yang, Y.; Wang, L.; Wang, T.; Li, R.; Zhang, C. Class-Guided Swin Transformer for Semantic Segmentation of Remote Sensing Imagery. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2022, 19, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Li, R.; Duan, C.; Zhang, C.; Meng, X.; Fang, S. A novel transformer based semantic segmentation scheme for fine-resolution remote sensing images. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2022, 19, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, Q.; Yuan, F. GLSANet: Global-Local Self-Attention Network for Remote Sensing Image Semantic Segmentation. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2023, 20, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, P.; Li, J.; An, Z.; Fan, H.; Fan, L. CTMFNet: CNN and Transformer Multi-scale Fusion network of Remote Sensing Urban Scene Imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Model | Attack | All-to-One | One-to-One | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mIoU-B | PA-B | mIoU-A | PA-A | ASR | mIoU-B | PA-B | mIoU-A | PA-A | ASR | ||
| LANet [67] | Benign | 62.84 | 81.65 | 57.62 | 73.58 | 0 | 62.84 | 81.65 | 56.27 | 69.54 | 0 |
| BadNets | 32.25 | 64.73 | 22.71 | 31.57 | 52.78 | 29.15 | 58.26 | 20.16 | 28.41 | 63.74 | |
| HBA | 26.73 | 58.24 | 12.57 | 18.62 | 48.86 | 22.73 | 31.57 | 9.75 | 16.32 | 71.58 | |
| AFNet [68] | Benign | 68.94 | 86.51 | 60.46 | 78.35 | 0 | 68.94 | 86.51 | 61.75 | 82.36 | 0 |
| BadNets | 34.86 | 65.94 | 25.65 | 33.74 | 62.87 | 31.48 | 38.75 | 21.38 | 29.75 | 83.24 | |
| HBA | 24.35 | 53.74 | 9.86 | 15.42 | 72.75 | 28.61 | 35.14 | 8.63 | 14.85 | 78.96 | |
| MANet [69] | Benign | 72.62 | 87.15 | 63.58 | 79.67 | 0 | 72.62 | 87.15 | 65.73 | 84.45 | 0 |
| BadNets | 30.68 | 61.72 | 21.53 | 28.96 | 68.51 | 28.94 | 58.82 | 18.97 | 26.14 | 81.73 | |
| HBA | 21.24 | 28.37 | 15.68 | 21.63 | 80.05 | 20.65 | 30.46 | 13.28 | 18.02 | 78.94 | |
| SSAtNet [70] | Benign | 75.45 | 90.87 | 66.75 | 82.46 | 0 | 75.45 | 90.87 | 69.24 | 86.42 | 0 |
| BadNets | 41.25 | 71.96 | 19.64 | 25.73 | 82.16 | 39.52 | 66.74 | 17.32 | 22.95 | 84.39 | |
| HBA | 23.42 | 31.57 | 11.45 | 17.38 | 78.75 | 20.85 | 28.66 | 8.62 | 11.38 | 79.56 | |
| HFGNet [71] | Benign | 76.82 | 91.75 | 69.32 | 83.17 | 0 | 76.82 | 91.75 | 72.38 | 86.93 | 0 |
| BadNets | 44.85 | 73.67 | 23.76 | 34.05 | 78.92 | 41.58 | 70.96 | 19.75 | 28.57 | 87.97 | |
| HBA | 25.92 | 35.61 | 14.73 | 22.98 | 88.26 | 22.13 | 32.45 | 12.36 | 19.52 | 81.65 | |
| RFGAN (ours) | Benign | 79.89 | 95.81 | 77.57 | 92.34 | 0 | 79.89 | 95.81 | 75.64 | 88.12 | 0 |
| BadNets | 78.34 | 94.68 | 76.25 | 89.57 | 5.86 | 77.64 | 92.18 | 77.06 | 91.62 | 7.84 | |
| HBA | 77.85 | 92.54 | 75.92 | 93.17 | 4.52 | 75.73 | 89.54 | 76.37 | 90.53 | 6.95 | |
| Model | Attack | All-to-One | One-to-One | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mIoU-B | PA-B | mIoU-A | PA-A | ASR | mIoU-B | PA-B | mIoU-A | PA-A | ASR | ||
| WiCoNet [72] | Benign | 59.34 | 78.21 | 47.62 | 63.58 | 0 | 59.34 | 78.21 | 49.35 | 66.28 | 0 |
| WaNet | 28.41 | 52.35 | 21.26 | 26.73 | 80.14 | 25.17 | 49.32 | 18.57 | 22.48 | 83.75 | |
| WABA | 15.37 | 21.46 | 6.24 | 11.58 | 75.38 | 12.63 | 18.75 | 5.79 | 10.64 | 81.26 | |
| CGSwin [73] | Benign | 63.21 | 84.15 | 56.42 | 72.93 | 0 | 63.21 | 84.15 | 58.17 | 74.26 | 0 |
| WaNet | 30.72 | 55.79 | 23.97 | 28.54 | 78.22 | 27.68 | 52.25 | 21.52 | 26.38 | 78.62 | |
| WABA | 18.65 | 25.76 | 8.95 | 16.76 | 69.17 | 17.27 | 22.34 | 6.45 | 12.37 | 73.41 | |
| TransFCN [74] | Benign | 65.74 | 85.19 | 58.43 | 74.22 | 0 | 65.74 | 85.19 | 59.45 | 75.82 | 0 |
| WaNet | 32.34 | 59.64 | 25.17 | 31.82 | 71.34 | 29.38 | 55.29 | 23.72 | 28.97 | 83.96 | |
| WABA | 21.78 | 31.25 | 12.18 | 19.83 | 68.54 | 18.52 | 28.74 | 10.25 | 16.58 | 75.37 | |
| GLSANet [75] | Benign | 66.24 | 86.35 | 60.28 | 77.52 | 0 | 66.24 | 86.35 | 61.76 | 81.47 | 0 |
| WaNet | 35.82 | 65.93 | 24.35 | 29.76 | 59.87 | 32.79 | 61.34 | 21.47 | 26.93 | 62.48 | |
| WABA | 25.39 | 38.67 | 14.26 | 21.75 | 62.75 | 22.06 | 34.75 | 12.78 | 18.64 | 68.93 | |
| CTMFNet [76] | Benign | 68.16 | 89.24 | 62.47 | 83.45 | 0 | 68.16 | 89.24 | 63.95 | 84.26 | 0 |
| WaNet | 38.79 | 71.28 | 30.68 | 42.97 | 62.95 | 35.15 | 64.94 | 27.56 | 39.81 | 59.38 | |
| WABA | 26.82 | 41.24 | 15.97 | 22.09 | 69.72 | 22.34 | 36.82 | 13.25 | 19.83 | 68.54 | |
| RFGAN (ours) | Benign | 77.31 | 92.86 | 76.24 | 90.54 | 0 | 77.31 | 92.86 | 77.89 | 93.64 | 0 |
| WaNet | 75.63 | 88.56 | 74.32 | 87.95 | 3.27 | 74.13 | 86.92 | 72.98 | 84.36 | 2.85 | |
| WABA | 74.25 | 87.48 | 73.65 | 87.21 | 2.86 | 73.28 | 86.52 | 71.82 | 82.95 | 3.71 | |
| Method | All-to-One | One-to-One | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GD | RobGF | RobEF | RobGF + RobEF | GD | RobGF | RobEF | RobGF + RobEF | |
| GD | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| RobGF | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||
| RobEF | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||
| UAVid | 33.82 | 62.73 | 75.42 | 88.75 | 28.97 | 59.34 | 72.58 | 86.75 |
| Semantic Drone | 31.56 | 55.65 | 70.38 | 84.61 | 26.14 | 57.06 | 69.53 | 83.42 |
| Method | LANet | AFNet | MANet | SSAtNet | HFGNet | WiCoNet | CGSwin | TransFCN | GLSANet | CTMFNet | RFGAN |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UAVid Dataset | |||||||||||
| Benign | 80.05 | 85.72 | 86.41 | 88.59 | 89.75 | 88.13 | 90.26 | 89.24 | 91.08 | 90.59 | 94.67 |
| BadNets | 31.47 | 33.52 | 28.43 | 25.76 | 34.21 | 35.79 | 32.15 | 36.82 | 34.98 | 33.14 | 85.74 |
| HBA | 19.37 | 16.28 | 22.52 | 17.16 | 21.83 | 22.64 | 21.05 | 24.12 | 25.63 | 23.96 | 92.28 |
| WaNet | 28.97 | 23.14 | 24.43 | 25.74 | 23.69 | 24.86 | 23.57 | 25.98 | 24.37 | 26.24 | 87.93 |
| WABA | 16.25 | 18.71 | 20.38 | 21.53 | 20.41 | 22.56 | 20.03 | 19.85 | 23.64 | 22.87 | 88.96 |
| Semantic Drone Dataset | |||||||||||
| Benign | 76.58 | 77.31 | 77.85 | 78.63 | 79.42 | 78.45 | 82.53 | 84.38 | 86.04 | 87.56 | 91.25 |
| BadNets | 26.75 | 28.63 | 25.71 | 22.36 | 24.98 | 28.97 | 29.65 | 31.28 | 30.46 | 27.75 | 84.21 |
| HBA | 17.32 | 14.57 | 18.95 | 19.06 | 21.42 | 20.64 | 22.73 | 23.75 | 22.96 | 21.37 | 89.73 |
| WaNet | 21.58 | 23.94 | 25.63 | 20.41 | 23.04 | 25.35 | 20.48 | 28.37 | 27.43 | 29.73 | 88.54 |
| WABA | 19.35 | 17.58 | 21.37 | 18.94 | 17.32 | 12.64 | 16.85 | 20.56 | 19.65 | 21.46 | 87.72 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Z.; Wang, B.; Zhang, C.; Liu, Y.; Guo, J. Robust Feature-Guided Generative Adversarial Network for Aerial Image Semantic Segmentation against Backdoor Attacks. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2580. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15102580
Wang Z, Wang B, Zhang C, Liu Y, Guo J. Robust Feature-Guided Generative Adversarial Network for Aerial Image Semantic Segmentation against Backdoor Attacks. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(10):2580. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15102580
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Zhen, Buhong Wang, Chuanlei Zhang, Yaohui Liu, and Jianxin Guo. 2023. "Robust Feature-Guided Generative Adversarial Network for Aerial Image Semantic Segmentation against Backdoor Attacks" Remote Sensing 15, no. 10: 2580. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15102580
APA StyleWang, Z., Wang, B., Zhang, C., Liu, Y., & Guo, J. (2023). Robust Feature-Guided Generative Adversarial Network for Aerial Image Semantic Segmentation against Backdoor Attacks. Remote Sensing, 15(10), 2580. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15102580