Mapping Aquifer Recharge Potential Zones (ARPZ) Using Integrated Geospatial and Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP) in an Arid Region of Saudi Arabia
Abstract
1. Introduction
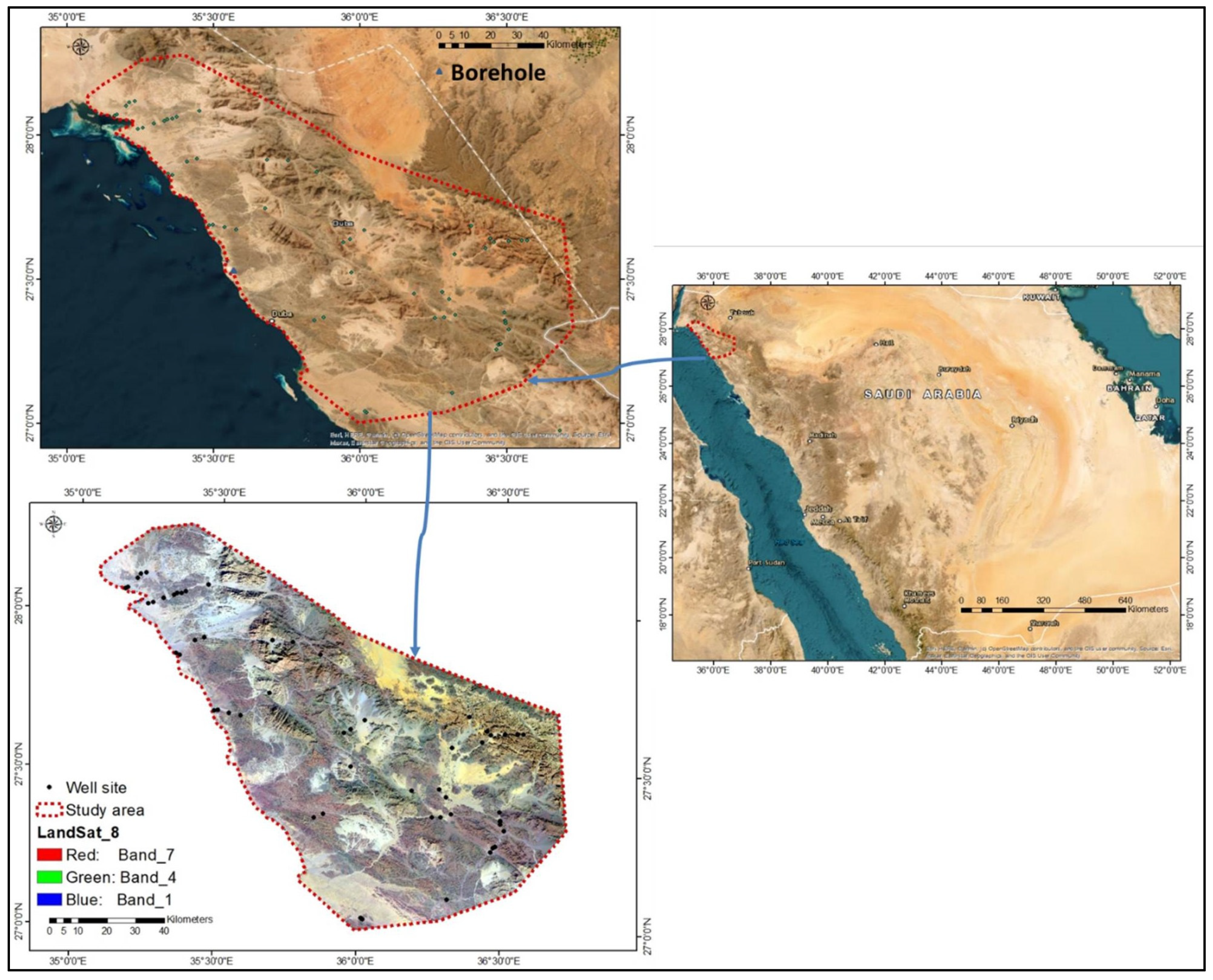
2. Study Area
2.1. SA Water Requirement
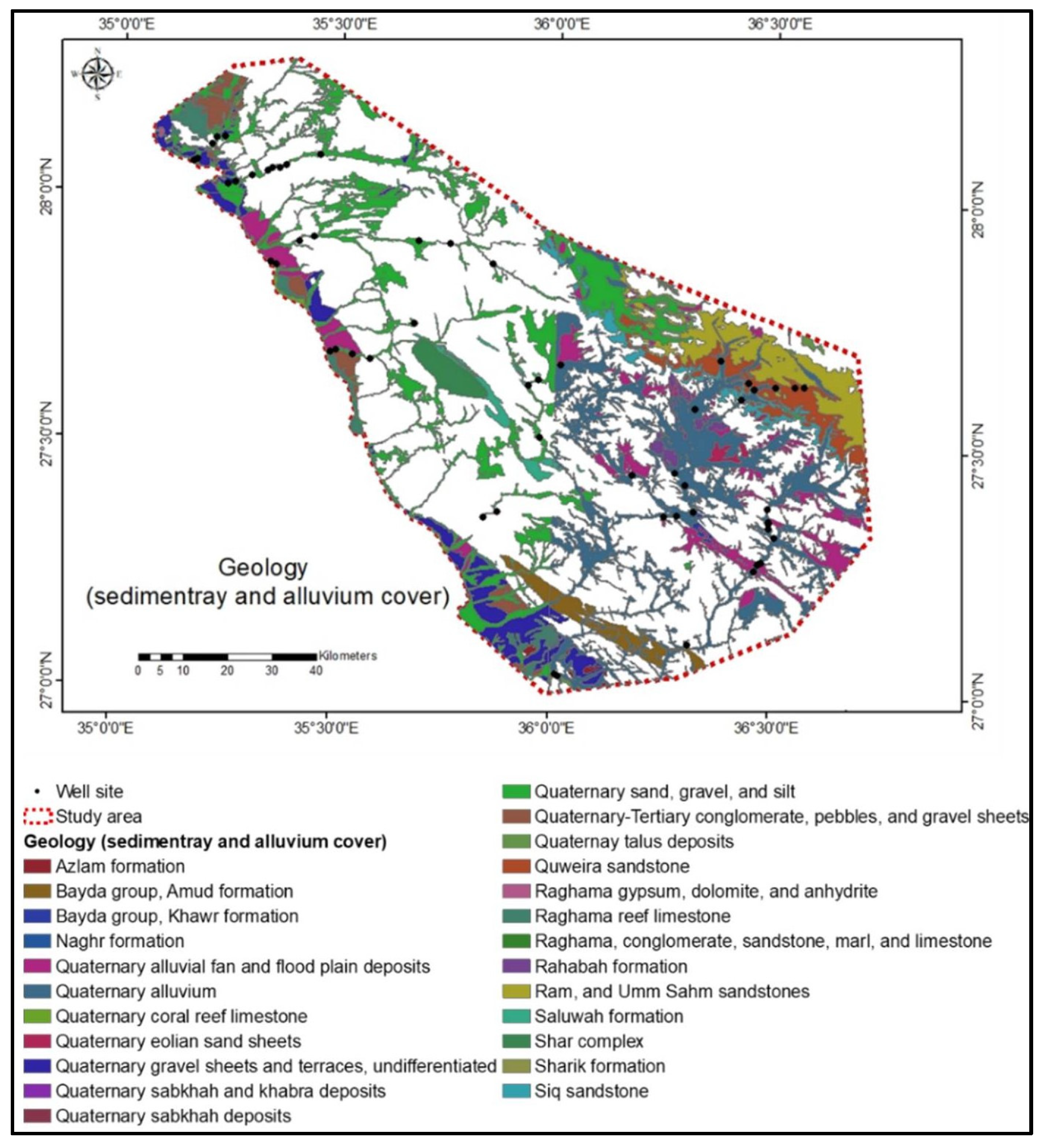
2.2. Geology
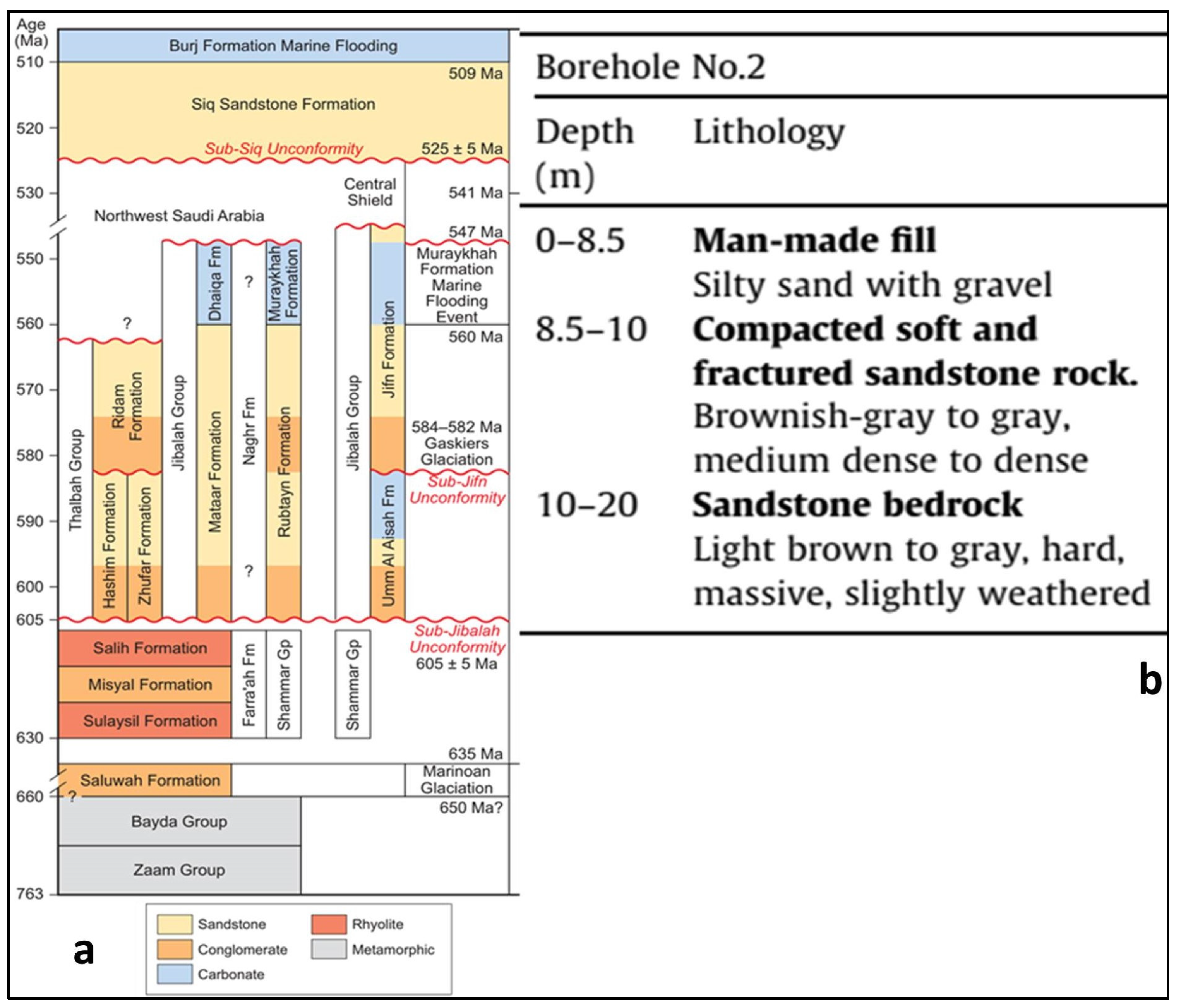
2.3. Hydrogeology
3. Methodology
3.1. Data Used
3.2. Procedures
3.3. Automatic Lineaments Extraction
3.4. Aquifer Potentiality Map and Verification
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Thematic Parameters
4.1.1. Surface Geology
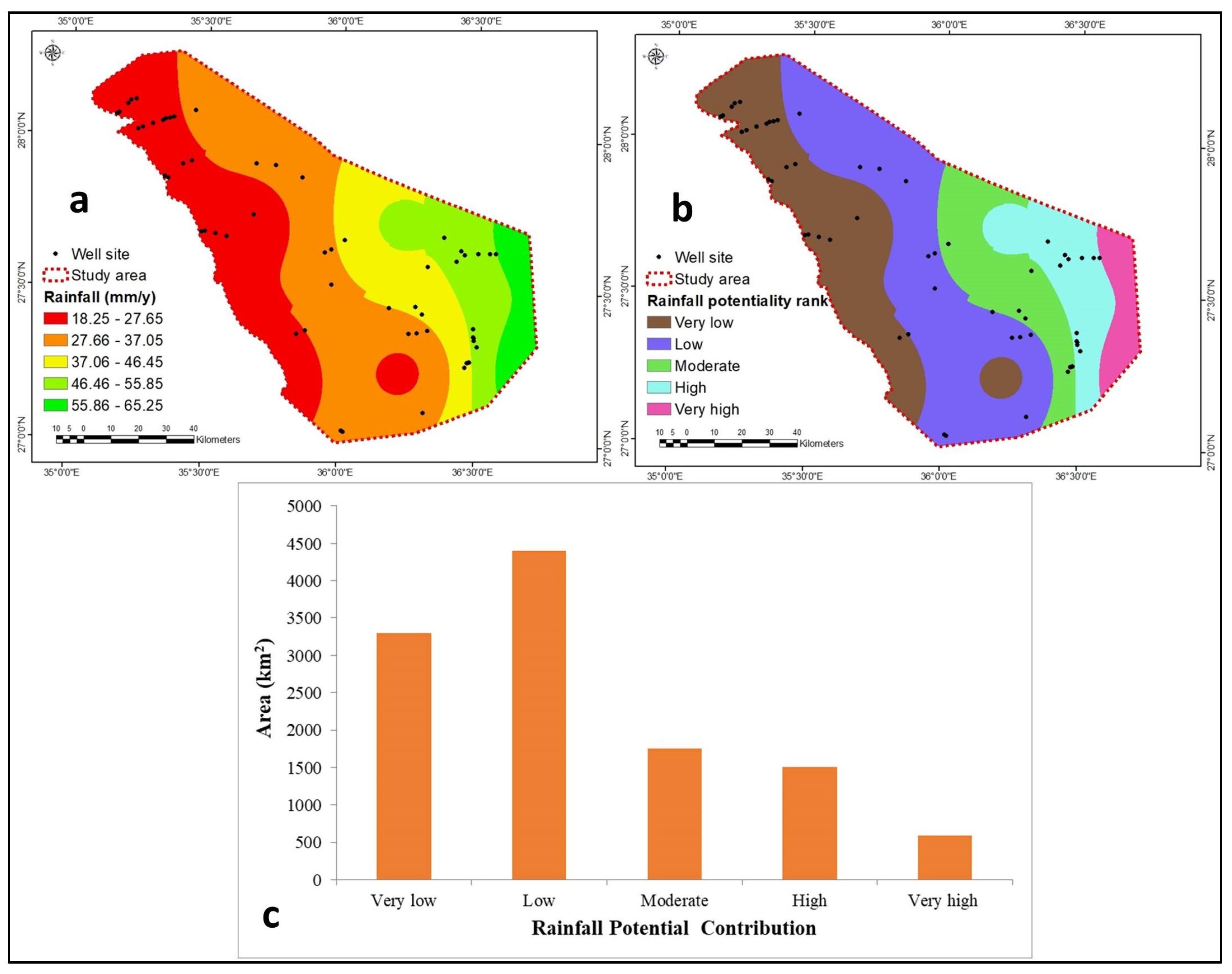
4.1.2. Rainfall
4.1.3. Lineaments Density
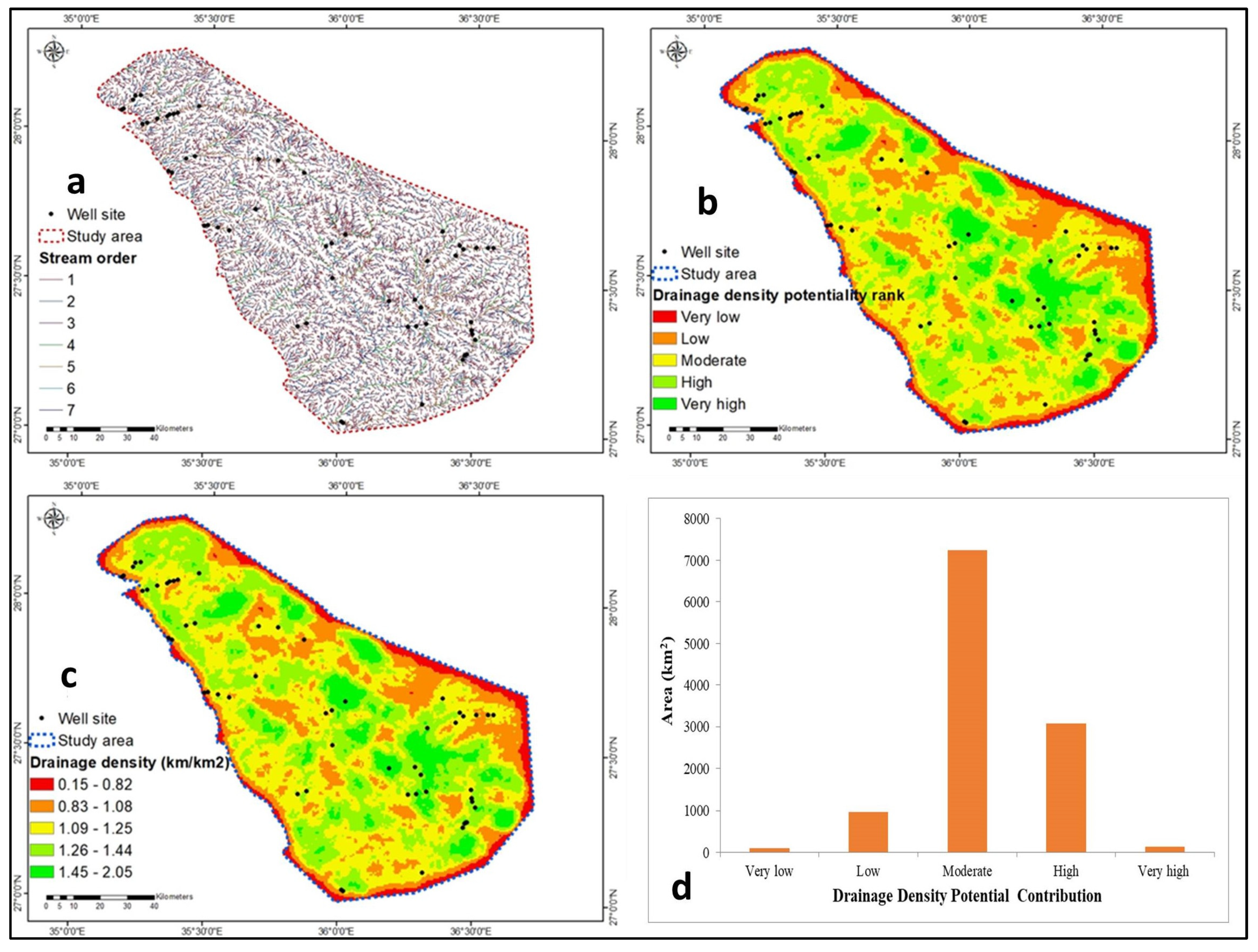
4.1.4. Drainage Density
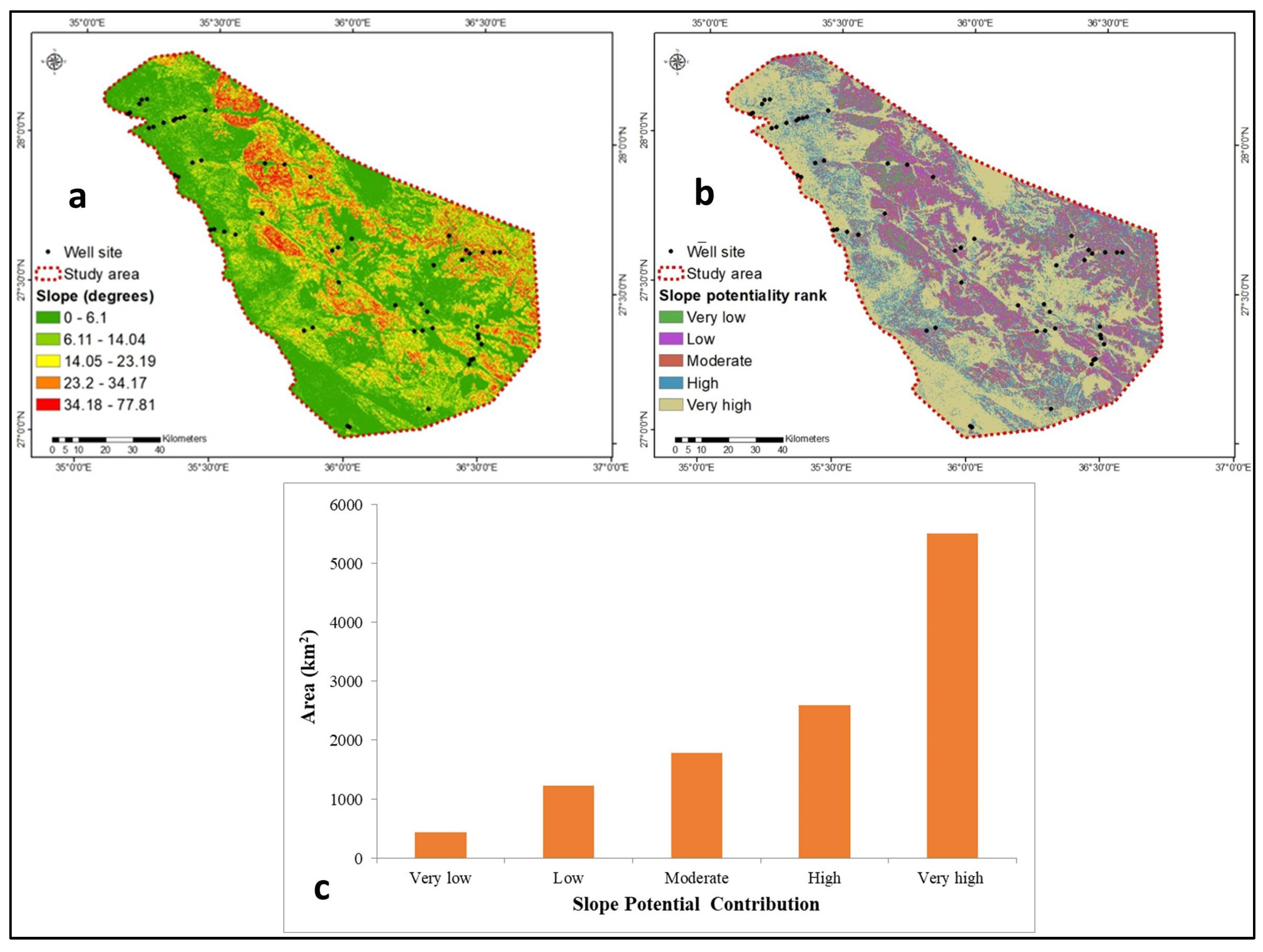
4.1.5. Slope
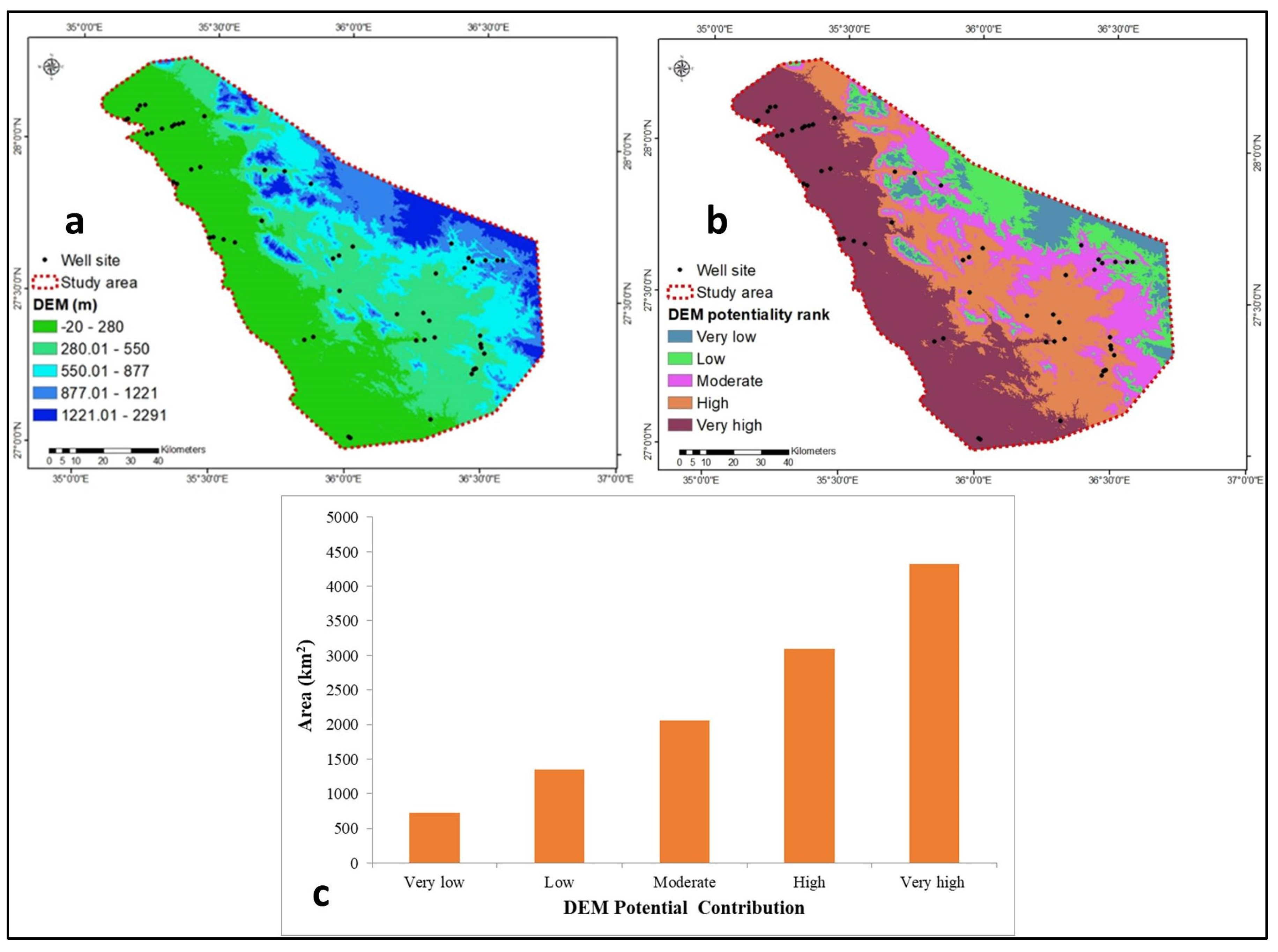
4.1.6. Elevation
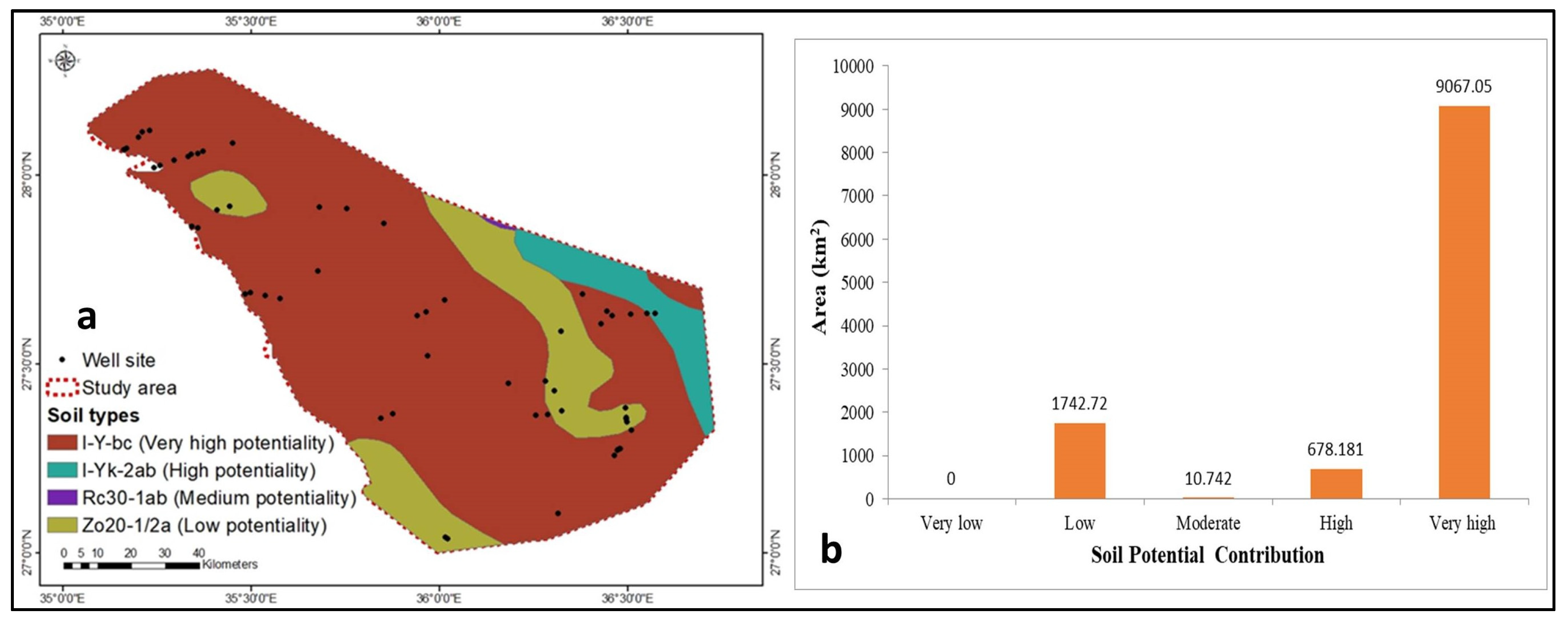
4.1.7. Soil
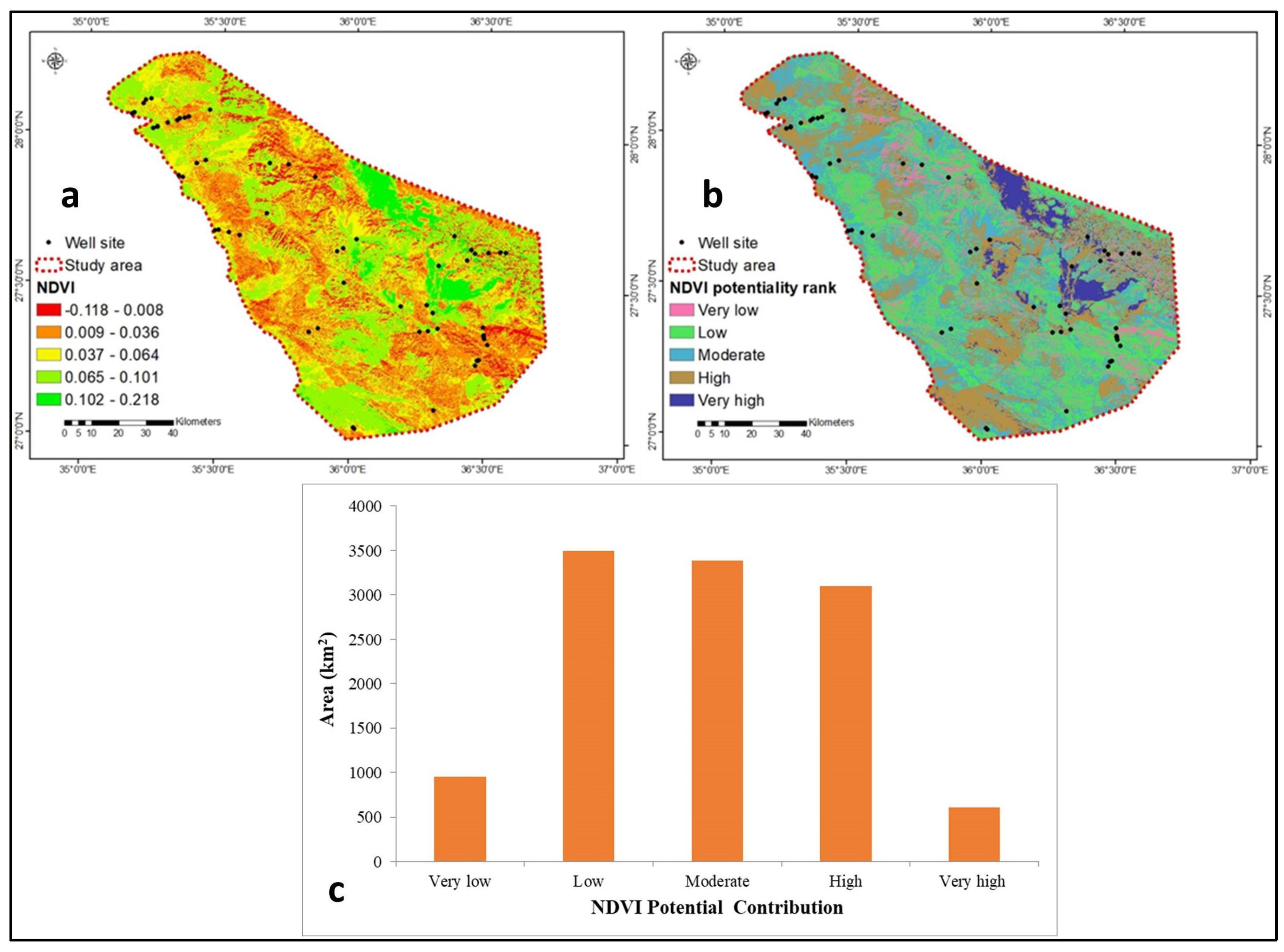
4.1.8. NDVI
4.2. Aquifer Potential Recharge Zones (ARPZs)
4.3. Verification
5. Conclusions and Recommendations
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Khan, M.Y.A.; ElKashouty, M.; Bob, M. Impact of rapid urbanization and tourism on the groundwater quality in Al Madinah city, Saudi Arabia: A monitoring and modeling approach. Arab. J. Geosci. 2020, 13, 922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.Y.A.; El Kashouty, M.; Gusti, W.; Kumar, A.; Subyani, A.M.; Alshehri, A. Geo-Temporal Signatures of Physicochemical and Heavy Metals Pollution in Groundwater of Khulais Region—Makkah Province, Saudi Arabia. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 9, 699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.Y.A.; ElKashouty, M.; Abdellattif, A.; Egbueri, J.C.; Taha, A.I.; Al Deep, M.; Shaaban, F. Influence of natural and anthropogenic factors on the hydrogeology and hydrogeochemistry of Wadi Itwad Aquifer, Saudi Arabia: Assessment using multivariate statistics and PMWIN simulation. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 110287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.Y.A.; Khan, B.; Chakrapani, G.J. Assessment of spatial variations in water quality of Garra River at Shahjahanpur, Ganga Basin, India. Arab. J. Geosci. 2016, 9, 516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.Y.A.; Gani, K.M.; Chakrapani, G.J. Assessment of surface water quality and its spatial variation. A case study of Ramganga River, Ganga Basin, India. Arab. J. Geosci. 2016, 9, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.Y.A.; Gani, K.M.; Chakrapani, G.J. Spatial and temporal variations of physicochemical and heavy metal pollution in Ramganga River—A tributary of River Ganges, India. Environ. Earth Sci. 2017, 76, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.Y.A.; Hu, H.; Tian, F.; Wen, J. Monitoring the spatio-temporal impact of small tributaries on the hydrochemical characteristics of Ramganga River, Ganges Basin, India. Int. J. River Basin Manag. 2020, 18, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panwar, S.; Yang, S.; Srivastava, P.; Khan, M.Y.A.; Sangode, S.J.; Chakrapani, G.J. Environmental magnetic characterization of the Alaknanda and Ramganga river sediments, Ganga basin, India. Catena 2020, 190, 104529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Yuan, Z.; Dai, J.; Zeng, Y.; Khan, M.Y.A. Analyzing the Water Pollution Control Cost-Sharing Mechanism in the Yellow River and Its Two Tributaries in the Context of Regional Differences. Water 2022, 14, 1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.Y.A.; Panwar, S.; Wen, J. Geochemistry of the dissolved load of the Ramganga River, Ganga Basin, India: Anthropogenic impacts and chemical weathering. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, M.K.; Kumar, R.; Banerjee, M.K.; Gupta, N.K.; Alam, T.; Eldin, S.M.; Khan, M.Y.A. Assessment of Chambal River Water Quality Parameters: A MATLAB Simulation Analysis. Water 2022, 14, 4040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haq, M.A.; Khan, M.Y.A. Crop Water Requirements with Changing Climate in an Arid Region of Saudi Arabia. Sustainability 2022, 14, 13554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agbasi, J.C.; Chukwu, C.N.; Nweke, N.D.; Uwajingba, H.C.; Khan, M.Y.A.; Egbueri, J.C. Water pollution indexing and health risk assessment due to PTE ingestion and dermal absorption for nine human populations in Southeast Nigeria. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2023, 21, 100921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Israil, M.; Al-Hadithi, M.; Singhal, D.C. Application of a resistivity survey and geographical information system (GIS) analysis for hydrogeological zoning of a piedmont area, Himalayan foothill region, India. Hydrogeol. J. 2006, 14, 753–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anbazhagan, S.; Ramasamy, S.M.; Edwin, J.M. Remote sensing and geophysical resistivity survey for groundwater exploration—A comparative analysis. In Proceedings of the Conference on Groundwater Exploration Techniques, Copenhagen, Denmark, 6–8 June 2000; pp. 177–181. [Google Scholar]
- Vaux, H. Groundwater under stress: The importance of management. Environ. Earth Sci. 2011, 62, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.L.; Berjamy, B.; Fakir, Y.; Bourgin, F.; Jarlan, J.; Abourida, A.; Benrhanem, M.; Jacob, G.; Huber, M.; Sghrer, F.; et al. An integrated DSS for groundwater management based on remote sensing. The case of a semi-arid aquifer in Morocco. Water Resour. Manag. 2012, 26, 3209–3230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adiat, K.; Nawawi, M.N.M.; Abdullah, K. Assessing the accuracy of GIS-based elementary multi criteria decision analysis as a spatial prediction tool—A case of predicting potential zones of sustainable groundwater resources. J. Hydrol. 2012, 440, 75–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manap, M.A.; Sulaiman, W.N.A.; Ramli, M.F.; Pradhan, B.; Surip, N. A knowledge-driven GIS modeling technique for groundwater potential mapping at the Upper Langat Basin, Malaysia. Arab J. Geosci. 2013, 6, 1621–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machireddy, S.R. Delineation of groundwater potential zones in South East part of Anantapur District using remote sensing and GIS applications. Sustain. Water Resour. Manag. 2019, 5, 1695–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, M.K.; Chowdary, V.M.; Chowdhury, A. Groundwater assessment in salboni block, West Bengal (India) using remote sensing, geographical information system and multi-criteria decision analysis techniques. Hydrogeol. J. 2010, 18, 1713–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meijerink, A.M.J. Groundwater. In Remote Sensing in Hydrology and Water Management; Schultz, G.A., Engman, E.T., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2000; pp. 305–325. [Google Scholar]
- Machiwal, D.; Jha, M.K.; Mal, B.C. Assessment of groundwater potential in a semi-arid region of India using remote sensing, GIS and MCDM techniques. Water Resour. Manag. 2011, 25, 1359–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waikar, M.L.; Nilawar, A.P. Identification of groundwater potential zone using remote sensing and GIS technique. Int. J. Innov. Res. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2014, 3, 12163–12174. [Google Scholar]
- Echogdali, F.Z.; Boutaleb, S.; Bendarma, A.; Saidi, M.E.; Aadraoui, M.; Abioui, M.; Ouchchen, M.; Abdelrahman, K.; Fnais, M.S.; Sajinkumar, K.S. Application of analytical hierarchy process and geophysical method for groundwater potential mapping in the Tata basin, Morocco. Water 2022, 14, 2393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saaty, T.L. The Analytic Hierarchy Process: Planning, Priority Setting, Resource Allocation; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Saranya, T.; Saravanan, S. Groundwater Potential Zone Mapping Using Analytical Hierarchy Process (Ahp) and Gis for Kancheepuram District, Tamilnadu, India. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2020, 6, 1105–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Krishna, A.P. Assessment of Groundwater Potential Zones in Coal Mining Impacted Hard-Rock Terrain of India by Integrating Geospatial and Analytic Hierarchy Process (Ahp) Approach. Geocarto Int. 2018, 33, 105–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanathan, R. A Note on the Use of the Analytic Hierarchy Process for Environmental Impact Assessment. J. Environ. Manag. 2001, 63, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesfamariam, S.; Sadiq, R. Risk-Based Environmental Decision-Making Using Fuzzy Analytic Hierarchy Process (F-Ahp). Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2006, 21, 35–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Memarbashi, E.; Azadi, H.; Barati, A.A.; Mohajeri, F.; Van Passel, S.; Witlox, F. Land-Use Suitability in Northeast Iran: Application of Ahp-Gis Hybrid Model. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2017, 6, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contreras, F.; Hanaki, K.; Aramaki, T.; Connors, S. Application of Analytical Hierarchy Process to Analyze Stakeholders Preferences for Municipal Solid Waste Management Plans, Boston, USA. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2008, 52, 979–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 20. Khoshand, A.; Kamalan, H.; Rezaei, H. Application of Analytical Hierarchy Process (Ahp) to Assess Options of Energy Recovery from Municipal Solid Waste: A Case Study in Tehran, Iran. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2018, 20, 1689–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrams, W.; Ghoneim, E.; Shew, R.; LaMaskin, T.; Al-Bloushi, K.; Hussein, S.; AbuBakr, M.; Al-Mulla, E.; Al-Awar, M.; El-Baz, F. Delineation of groundwater potential (GWP) in the northern United Arab Emirates and Oman using geospatial technologies in conjunction with Simple Additive Weight (SAW), Analytical Hierarchy Process (AHP), and Probabilistic Frequency Ratio (PFR) techniques. J. Arid Environ. 2018, 157, 77–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajasekhar, M.; Raju, G.S.; Sreenivasulu, Y.; Raju, R.S. Delineation of groundwater potential zones in semi-arid region of Jilledubanderu river basin, Anantapur District, Andhra Pradesh, India using fuzzy logic, AHP and integrated fuzzy-AHP approaches. HydroResearch 2019, 2, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dar, T.; Rai, N.; Bhat, A. Delineation of potential groundwater recharge zones using analytical hierarchy process (AHP). Geol. Ecol. Landsc. 2021, 5, 292–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.Y.A.; ElKashouty, M.; Tian, F. Mapping Groundwater Potential Zones Using Analytical Hierarchical Process and Multicriteria Evaluation in the Central Eastern Desert, Egypt. Water 2022, 14, 1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radulović, M.; Brdar, S.; Mesaroš, M.; Lukić, T.; Savić, S.; Basarin, B.; Crnojević, V.; Pavić, D. Assessment of Groundwater Potential Zones Using GIS and Fuzzy AHP Techniques—A Case Study of the Titel Municipality (Northern Serbia). ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2022, 11, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.Y.A.; ElKashouty, M.; Subyani, A.M.; Tian, F.; Gusti, W. GIS and RS intelligence in delineating the groundwater potential zones in Arid Regions: A case study of southern Aseer, southwestern Saudi Arabia. Appl. Water Sci. 2022, 12, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikirri, M.; Boutaleb, S.; Ibraheem, I.M.; Abioui, M.; Echogdali, F.Z.; Abdelrahman, K.; Id-Belqas, M.; Abu-Alam, T.; El Ayady, H.; Essoussi, S.; et al. Delineation of Groundwater Potential Area using an AHP, Remote Sensing, and GIS Techniques in the Ifni Basin, Western Anti-Atlas, Morocco. Water 2023, 15, 1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arumugam, M.; Kulandaisamy, P.; Karthikeyan, S.; Thangaraj, K.; Senapathi, V.; Chung, S.Y.; Muthuramalingam, S.; Rajendran, M.; Sugumaran, S.; Manimuthu, S. An Assessment of Geospatial Analysis Combined with AHP Techniques to Identify Groundwater Potential Zones in the Pudukkottai District, Tamil Nadu, India. Water 2023, 15, 1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Bank. A Water Sector Assessment Report on Countries of the Cooperation Council of the Arab State of the Gulf; Report No. 32539-MNA; World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives; Food and Agriculture Organization; World Health Organization. Safety Evaluation of Certain Food Additives (No. 56); World Health Organization: Geneva, Switxerland, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Rashed, M.F.; Sherif, M.M. Water resources in the GCC countries: An overview. Water Resour. Manag. 2000, 14, 59–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallick, J.; Singh, C.K.; AlMesfer, M.K.; Kumar, A.; Khan, R.A.; Islam, S.; Rahman, A. Hydro-Geochemical Assessment of Groundwater Quality in Aseer Region, Saudi Arabia. Water 2018, 10, 1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Laboun, A.A. Stratigraphy and hydrocarbon potential of the Paleozoic succession in both Tabuk and Widyan basins, Arabia. AAPG 1986, 373–397. [Google Scholar]
- Alamrani, N.A.; Almutairi, F.M.; Alatawi, N.M.; Mogharbel, A.T.; Al-Aoh, H.A.; Hajri, A.K.; Keshk, A.A. and Elsayed, N.H. Assessment and management of heavy metals pollution in Tabuk region Saudi Arabia, improvement for future development: A review. Wulfenia 2022, 29, 32–51. [Google Scholar]
- AQUASTAT Survey. Irrigation in the Middle East Region in Figures; AQUASTAT: North Somerset, UK, 2008; pp. 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Yahiaoui, B.; Agoubi, B.; Kharroubi, A. Groundwater potential recharge areas delineation using groundwater potential recharge index (GPRI) within arid areas: Ghomrassen, south Tunisia. Arab. J. Geosci. 2021, 14, 919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, R.K.; Mondal, N.C.; Banerjee, P.; Nandakumar, M.V.; Singh, V.S. Deciphering potential groundwater zone in hardrock through the application of GIS. Environ. Geol. 2008, 55, 467–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, B.; Pal, S.C. Assessment of groundwater recharge and its potential zone identification in groundwater- stressed Goghat-I block of Hugli District, West Bengal, India. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2019, 22, 5905–5923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajesh, J.; Pande, C.; Kadam, S.A.; Gorantiwar, S.D.; Shinde, M.G. Exploration of groundwater potential zones using analytical hierarchical process (AHP) approach in the Godavari river basin of Maharashtra in India. Appl. Water Sci. 2021, 11, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GASTAT. General Authority for Statistics. 2016. Available online: http://www.stats.gov.sa/en (accessed on 13 February 2023).
- MEWA. Ministry of Environment, Water and Agriculture. 2016. Available online: https://www.mewa.gov.sa/en/Pages/default.aspx (accessed on 14 January 2023).
- Ouda, O. Water demand versus supply in Saudi Arabia: Current and future challenges. Int. J. Water Resour. Dev. 2014, 30, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Omran, A.M.; Aly, A.A.; Al-Wabel, M.I.; Sallam, A.S.; Al-Shayaa, M.S. Hydrochemical characterization of groundwater under agricultural land in arid environment: A case study of Al-Kharj, Saudi Arabia. Arab. J. Geosci. 2016, 9, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, I.; Hasan, M.A.; Alharbi, O.M.L. Toxic metal ions contamination in the groundwater, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. J. Taibah Univ. Sci. 2020, 14, 1571–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallick, J.; Singh, C.K.; AlMesfer, M.K.; Singh, P.V.; Alsubih, M. Groundwater Quality Studies in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia: Prevalent Research and Management Dimensions. Water 2021, 13, 1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hikal, W.M.; Al Hawiti, A.K.; Atawi, M.M.A.; MF, M.; Al Qahttani, F.S.; Al Balawi, A.S. Determination of Iron in some Fish Species from the Red Sea, Duba Coast, Tabuk, Saudi Arabia. International Journal of Healthcare Sciences 2019, 7, 298–308. [Google Scholar]
- MWE. Supporting Documents for King Hassan II Great Water Prize. 2012. Available online: http://www.worldwatercouncil.org/fileadmin/wwc/Prizes/Hassan_II/Candidates_2011/16.Ministry_ (accessed on 30 November 2012).
- Alsaleh, M. Natural springs in northwest Saudi Arabia. Arab. J. Geosci. 2017, 10, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhumimidi, M.S. An integrated approach for identification of seawater intrusion in coastal region: A case study of northwestern Saudi Arabia. J. King Saud Univ.—Sci. 2020, 32, 3187–3194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jerais, A.A. Hydrogeology of Saq Aquifer in Hail Region. Master’s Thesis, Faculty of Earth Sciences, King Abdulaziz University, Jeddah, Saudi Arabia, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Ahmadi, M.E. Hydrogeology of the Saq Aquifer Northwest of Tabuk, Northern Saudi Arabia. Earth Sci. 2007, 20, 51–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King Fahd University Staff. Groundwater Resources Evaluation in Saudi Arabia and Long-term Strategic Plan for Fresh Groundwater Use, King Fahd University Petroleum and Minerals; KFUPM Press: Dhahran, Saudi Arabia, 1987; 168p. [Google Scholar]
- Edgell, H.S. Aquifers of Saudi Arabia and their Geological Framework. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 1997, 22, 5–31. [Google Scholar]
- Krishnamurthy, J.; Kumar, N.V.; Jayaraman, V.; Manivel, M. An approach to demarcate ground water potential zones through remote sensing and a geographical information system. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1996, 17, 1867–1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saraf, A.K.; Choudhury, P.R. Integrated remote sensing and GIS for groundwater exploration and identification of artificial recharge sites. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1998, 19, 1825–1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, M.; Wallace, J.; Lowe, M. Groundwater quality classification using GIS contouring methods for cedar valley, Iron County, Utah. Digit. Mapp. Technol. 2002, 2002, 207. [Google Scholar]
- Asadi, S.S.; Vuppala, P.; Reddy, M.A. Remote sensing and GIS techniques for evaluation of groundwater quality in municipal corporation of Hyderabad (Zone-V), India. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2007, 4, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yammani, S. Groundwater quality suitable zones identification: Application of GIS, Chittoor area, Andhra Pradesh, India. Environ. Geol. 2007, 53, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Hazra, S.; Chanda, A.; Das, S. Assessment of groundwater potential zones using multi-criteria decision-making technique: A micro-level case study from red and lateritic zone (RLZ) of West Bengal, India. Sustain. Water Resour. Manag. 2020, 6, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arefin, R. Groundwater potential zone identification at Plio-Pleistocene elevated tract, Bangladesh: AHP-GIS and remote sensing approach. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2020, 10, 100340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patra, S.; Mishra, P.; Mahapatra, S.C. Delineation of groundwater potential zone for sustainable development: A case study from Ganga Alluvial Plain covering Hooghly district of India using remote sensing, geographic information system and analytic hierarchy process. J. Clean Prod. 2018, 172, 2485–2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, S.; Mukhopadhyay, B.P.; Bera, A. Delineating groundwater potential zones of agriculture dominated landscapes using GIS based AHP techniques: A case study from Uttar Dinajpur district, West Bengal. Environ. Earth Sci. 2020, 79, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadam, A.K.; Umrikar, B.N.; Sankhua, R.N. Assessment of recharge potential zones for groundwater development and management using geospatial and MCDA technologies in semiarid region of Western India. Appl. Water Sci. 2020, 2, 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, P.K.; Bhattacharya, A.K. Groundwater assessment through an integrated approach using remote sensing, GIS and resistivity techniques: A case study from a hard rock terrain. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2006, 27, 4599–4620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Behera, S.C.; Kar, A.; Narendra, P.; Guha, S. Hydrogeomorphological mapping in groundwater exploration using remotely sensed data—A case study in keonjhar district, orissa. J. Ind. Soc. Remote Sens. 1997, 25, 247–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardcastle, K.C. Photolineament factor: A new computer-aided method for remotely sensing the degree to which bedrock is fractured. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 1995, 61, 739–746. [Google Scholar]
- Devi, S.P.; Srinivasulu, S.; Raju, K.K. Delineation of groundwater potential zones and electrical resistivity studies for groundwater exploration. Environ. Geol. 2001, 40, 1252–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magowe, M.; Carr, J.R. Relationship between lineaments and groundwater occurrence in western Botswana. Groundwater 1999, 37, 282–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, N.S.; Chakradhar, G.K.J.; Srinivas, V. Identification of groundwater potential zones using remote sensing techniques in and around Guntur town, Andhra Pradesh, India. J. Indian Soc. Remote Sens. 2001, 29, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razandi, Y.; Pourghasemi, H.R.; Neisani, N.S.; Rahmati, O. Application of analytical hierarchy process, frequency ratio, and certainty factor models for groundwater potential mapping using GIS. Earth Sci. Inform. 2015, 8, 867–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abijith, D.; Saravanan, S.; Singh, L.; Jennifer, J.J.; Saranya, T.; Parthasarathy, K.S.S. GIS-based multi-criteria analysis for identification of potential groundwater recharge zones–A case study from Ponnaniyaru watershed, Tamil Nadu, India. HydroResearch 2020, 3, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, N.; Mukhopadhyay, S. Application of multi-criteria decision making technique for the assessment of groundwater potential zones: A study on Birbhum district, West Bengal, India. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2018, 22, 931–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nithya, C.N.; Srinivas, Y.; Magesh, N.S.; Kaliraj, S. Assessment of groundwater potential zones in Chittar basin, Southern India using GIS based AHP technique. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2019, 15, 100248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godebo, T.R. Application of Remote Sensing and GIS for Geological Investigation and Groundwater Potential Zone Identification, Southeastern Ethiopian Plateau, Bale Mountains and the Surrounding Areas. Ph.D. Thesis, Addis Ababa University, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Doll, P.; Fiedler, K. Global-scale modeling of groundwater recharge. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2008, 12, 863–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Parameters | Lithology | Rainfall | Lineaments | Drainage | Slope | Elevation | Soil | NDVI | Weight |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lithology | 8 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0.37 |
| Rainfall | 8/2 | 7/2 | 6/2 | 5/2 | 4/2 | 3/2 | 2/2 | 1/2 | 0.18 |
| Lineaments | 8/3 | 7/3 | 6/3 | 5/3 | 4/3 | 3/3 | 2/3 | 1/3 | 0.12 |
| Drainage | 8/4 | 7/4 | 6/4 | 5/4 | 4/4 | 3/4 | 2/4 | 1/4 | 0.09 |
| Slope | 8/5 | 7/5 | 6/5 | 5/5 | 4/5 | 3/5 | 2/5 | 1/5 | 0.07 |
| Elevation | 8/6 | 7/6 | 6/6 | 5/6 | 4/6 | 3/6 | 2/6 | 1/6 | 0.06 |
| Soil | 8/7 | 7/7 | 6/7 | 5/7 | 4/7 | 3/7 | 2/7 | 1/7 | 0.05 |
| NDVI | 8/8 | 7/8 | 6/8 | 5/8 | 4/8 | 3/8 | 2/8 | 1/8 | 0.046 |
| Parameter | Classes | Weight | Influence (%) = Weight × 100 | Rank |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quaternary deposits | 0.37 | 37 | 5 | |
| Sedimentary succession | 5 | |||
| Lithology | Fractured and jointed hard rocks | 4 | ||
| Less fractured and jointed hard rocks | 2–3 | |||
| Nonfractured and jointed hard rocks | 1 | |||
| 18.25–27.65 | 0.18 | 18 | 1 | |
| 27.66–37.05 | 2 | |||
| Rainfall | 37.06–46.45 | 3 | ||
| (mm/year) | 46.46–55.86 | 4 | ||
| 55.86–65.25 | 5 | |||
| 0–0.22 | 0.12 | 12 | 1 | |
| 0.23–0.44 | 2 | |||
| Lineaments | 0.45–0.65 | 3 | ||
| (km/km2) | 0.66–0.87 | 4 | ||
| 0.88–1.09 | 5 | |||
| 0.15–0.82 | 0.09 | 9 | 1 | |
| 0.83–1.08 | 2 | |||
| Drainge | 1.09–1.25 | 3 | ||
| (km/km2) | 1.26–1.44 | 4 | ||
| 1.45–2.05 | 5 | |||
| 0–6.1 | 0.07 | 7 | 5 | |
| 6.11–14.04 | 4 | |||
| Slope | 14.05–23.19 | 3 | ||
| (Degrees) | 23.2–34.17 | 2 | ||
| 34.18–77.81 | 1 | |||
| −20–280 | 0.06 | 6 | 5 | |
| 280.01–550 | 4 | |||
| Elevation | 550.01–877 | 3 | ||
| (m) | 877.01–1221 | 2 | ||
| 1221.01–2291 | 1 | |||
| I-Y-bc | 0.05 | 5 | 4 | |
| I-YK-2ab | 3 | |||
| Soil | Rc30-1ab | 2 | ||
| Zo20-1/2a | 1 | |||
| −0.118–0.008 | 0.046 | 4.6 | 5 | |
| 0.009–0.036 | 4 | |||
| NDVI | 0.037–0.064 | 3 | ||
| 0.065–0.101 | 2 | |||
| 0.102–0.218 | 1 |
| NDVI | Features |
|---|---|
| ≤−1–0 | Snow, water, sand, and cloud |
| 0–0.1 | Bear rock, barren land, or built-up area |
| 0.1–0.2 | Shrub and grassland |
| 0.2–0.4 | Sparse vegetation or senescing crops |
| 0.4–0.8 | Vegetation |
| 0.8–1 | Very healthy dense vegetation |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khan, M.Y.A.; ElKashouty, M.; Zaidi, F.K.; Egbueri, J.C. Mapping Aquifer Recharge Potential Zones (ARPZ) Using Integrated Geospatial and Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP) in an Arid Region of Saudi Arabia. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2567. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15102567
Khan MYA, ElKashouty M, Zaidi FK, Egbueri JC. Mapping Aquifer Recharge Potential Zones (ARPZ) Using Integrated Geospatial and Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP) in an Arid Region of Saudi Arabia. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(10):2567. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15102567
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhan, Mohd Yawar Ali, Mohamed ElKashouty, Faisal K. Zaidi, and Johnbosco C. Egbueri. 2023. "Mapping Aquifer Recharge Potential Zones (ARPZ) Using Integrated Geospatial and Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP) in an Arid Region of Saudi Arabia" Remote Sensing 15, no. 10: 2567. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15102567
APA StyleKhan, M. Y. A., ElKashouty, M., Zaidi, F. K., & Egbueri, J. C. (2023). Mapping Aquifer Recharge Potential Zones (ARPZ) Using Integrated Geospatial and Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP) in an Arid Region of Saudi Arabia. Remote Sensing, 15(10), 2567. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15102567








