Abstract
The green tide caused by Ulva prolifera (U. prolifera) is becoming more severe as climate change and human activity accelerate, endangering tourism, aquaculture, and urban landscapes in coastal cities. In order to understand the spatio-temporal distribution of U. prolifera in response to the green tide disaster, this study used the Haiyang-1C (HY-1C) satellite accompanied by the Sentinel-2 and GaoFen-1 (GF-1) satellites to systematically monitor U. prolifera between 2020 and 2022. The consistency of U. prolifera distribution between the HY-1C and Sentinel-2 satellites, as well as the HY-1C and GF-1 satellites, was first investigated and the determination coefficients (R2) were 0.966 and 0.991, respectively, which supports the feasibility of China’s first ocean water color operational satellite, HY-1C, for U. prolifera monitoring. Therefore, the spatio-temporal distribution of U. prolifera is studied herein, along with the influence range, influence area, and drift paths. From 2020 to 2022, U. prolifera appeared in late May and lasted for 61, 88, and 73 days. Additionally, the in influence area continuously decreased in 2020 and 2022, while it generally increased and then decreased in 2021. It is an interesting phenomenon that when the maximum influence area occurred at the early stage of U. prolifera in both 2020 and 2022, the drift paths tended to move southward after traveling northward. The overall trend of the drift path in 2021 was to head northward. Thus, the study of the dynamic evolution, influence range, influence area, and drift paths of U. prolifera is helpful to promote the systematic development of emergency response mechanisms for U. prolifera.
1. Introduction
The green tide is an ecological anomaly that occurs when large green algae bloom appears in the ocean, causing water column discoloration [1,2]. In recent years, the natural environment has become more polluted in China’s coastal areas due to climate change and unreasonable human activities. Since 2007, large-scale green algae blooms have occurred on a regular basis [3], producing massive disasters in the Yellow Sea and its surrounding coasts. Furthermore, large-scale accumulations of green algae can prevent the penetration of sunlight, reduce the oxygen content in water, and adversely affect the survival and reproduction of other marine life [4,5]. In addition, sulfide compounds decomposed by the sheet of green algae can lead to the deterioration of water quality, which is harmful to the environment [6,7,8]. Meanwhile, the green tide can have a considerable impact on tourism and aquaculture in coastal cities, as well as on the economic development of the affected regions [9,10,11,12,13,14]. According to Wang et al. [15], in order to maintain an area free of large green algae for the 2008 Olympic sailing competition, the government of Tsingtao trialed a variety of tactics and spent more than USD 100 million on the problem. The green tide has become a critical marine environmental disaster in China, and it is of theoretical and practical importance to further prevent and mitigate it [4,16]. Figure 1 shows the green tide floating near the coast after extensive fishing.
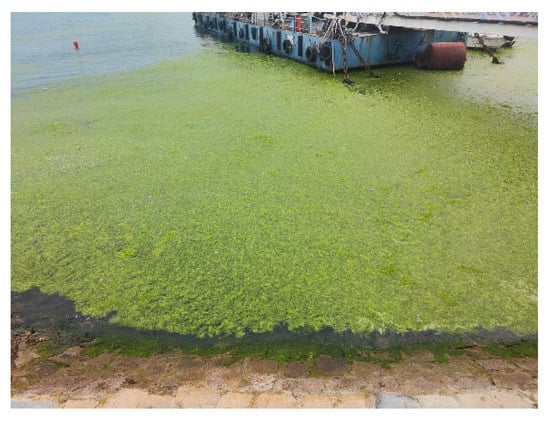

Figure 1.
Green tide floating near the coast of Tsingtao on 24 June 2022.
There are three main reasons for large-scale green algae blooms in the Yellow Sea. Firstly, due to the abundant coastal aquaculture activities, a large amount of nitrogen and phosphate is discharged into the sea, causing widespread seawater eutrophication [17,18]. Pang et al. [19] discovered that coastal aquaculture activities in Jiangsu province provided adequate conditions for green algae proliferation in the Yellow Sea. Secondly, green algae are opportunistic, with a high capacity for nutrient absorption, rapid propagation, strong light use efficiency (LUE), and extreme stress resistance [20,21,22]. As a consequence, Ulva prolifera outcompete other species to become dominant during the green tide in the Yellow Sea. Lastly, the aquaculture rafts of Porphyra yezoensis (P. yezoensis) along the Jiangsu Shoal offer a favorable habitat for U. prolifera attachment and sprouting, thus promoting the reproduction of U. prolifera [23,24]. Xing et al. [25] discovered that prolonging the recycling of P. yezoensis facilities in April and May could delay the onset of U. prolifera and thus decrease its annual biomass.
Currently, there are two types of widely adopted U. prolifera monitoring strategies: traditional observation and remote sensing monitoring. Traditional observation using ships and aircraft as the platform cannot achieve adequate real-time monitoring on a large scale. Remote sensing monitoring is a highly automated technique for gathering data on a specific target, which can then be identified and analyzed without the need for physical interaction. Owing to the variable drift trajectories and the extensive distribution range of U. prolifera, remote sensing monitoring can save a substantial amount of labor, material resources, and time when compared with the traditional observation strategy [26,27,28,29]. Utilizing multi-source remote sensing data, scholars concluded that P. yezoensis cultivation is positively correlated with the annual maximum biomass of U. prolifera and the level of early U. prolifera can be effectively controlled by macroalgae collection efforts [30,31]. In order to accomplish real-time U. prolifera biomass estimation, Hu et al. [3] developed a model on the basis of Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectrometer (MODIS) data, which can provide technical support for U. prolifera collection. Using multiple satellite data can provide not only the rapid and thorough monitoring of U. prolifera but also quick and precise spatial information assistance for U. prolifera prevention, control, and collection [32,33,34]. Wang et al. [35] studied the influence of different spatial resolutions on U. prolifera observation by using Sentinel-2, GF-1, Landsat-5, Haiyang-1C (HY-1C), Tiangong-2, and MODIS and found that satellite remote sensing based on low-resolution images tended to overestimate the coverage of U. prolifera and ignore small patches in the affected area. In order to reduce the influence of overestimation and omission, the use of high-resolution images is recommended for green tide observation and research. The HY-1C, China’s first operational ocean water color satellite, has significant advantages in terms of temporal and spatial resolution and range coverage for the monitoring of U. prolifera [36]. Therefore, we considered the high spatial and temporal resolutions of HY-1C and high spatial resolutions of GF-1 and Sentinel-2 A/B and thus investigated the feasibility of HY-1C for U. prolifera monitoring using GF-1 and Sentinel-2 A/B as benchmarks. Based on multi-source data, domestic and foreign researchers have conducted systematic studies on U. prolifera, which usually comprise a five-stage process of “appearance–development–outbreak–decline–disappearance” [8]. In the middle and end of May, U. prolifera is generally apparent in remote sensing images surrounding the northern Jiangsu Shoal waters. Notably, the crucial period for U. prolifera breakout is from mid-May to mid-June. From late June to early July, U. prolifera starts to enter the decline stage, during which U. prolifera decreases sharply and is challenging to track. The decline period is typically between early and mid-August. Thus, studying the growing trends, influence area, and drift path of U. prolifera is helpful for preventing and controlling U. prolifera successfully and even for improving U. prolifera management mechanisms [37,38].
Recently, U. prolifera monitoring and quantitative analysis have been hindered due to limited reports on the consistency of U. prolifera distribution from high-resolution remote sensing platforms on the same dates, the low resolution of contemporary remote sensing satellites, the serious interference of mixed pixels, and the unclear uniformity of monitoring results from multiple remote sensing platforms. Hence, this paper evaluates the consistency of U. prolifera information based on the high-resolution remote sensing data of HY-1C, Sentinel-2, and GF-1, as well as supporting the feasibility of HY-1C for U. prolifera monitoring. We studied the spatio-temporal distribution of U. prolifera based mainly on the data from the HY-1C satellite and utilized data from the Sentinel-2 and GF-1 satellites complementarily; the influence range of U. prolifera was analyzed, the influence area of U. prolifera was quantitatively studied, and the drift trajectory was thereby systematically investigated. This study will serve as a reference for the prevention and control of U. prolifera in order to advance the development of U. prolifera prevention and management technology, which will promote the growth of marine-related enterprises in coastal areas.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
The Yellow Sea (31°40′N ~ 39°50′N and 119°10′E ~ 126°50′E), which is located between the Chinese mainland and the Korean Peninsula, is a continental shelf sea in the western Pacific Ocean [39], linking the Bohai Sea in the northwest with the East China Sea in the south. By the line running from Chengshantou on the Shandong Peninsula to Changshan on the Korean Peninsula, the Yellow Sea is separated into the North Yellow Sea and the South Yellow Sea. Recently, the South Yellow Sea has seen economic growth along its coastline; its saltwater is fairly eutrophic and ideal for algae development. Since 2007, U. prolifera has occurred in the South Yellow Sea from May to August [40,41]. The study area for this paper is within the range of 31°30′N ~ 37°30′N and 119°E ~ 124°30′E (Figure 2), which saw U. prolifera outbreaks for 16 years up to 2022.
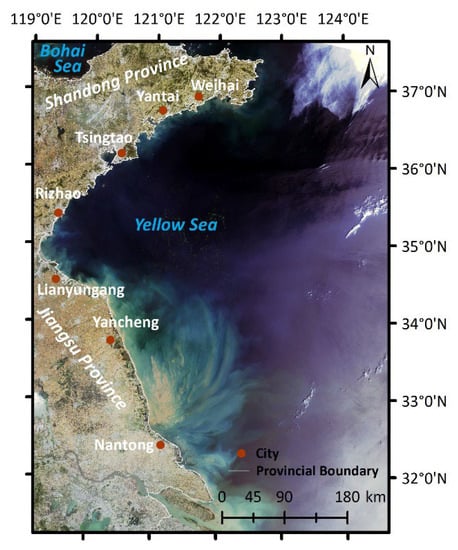
Figure 2.
Map of the study area and major coastal cities. The background image is an HY-1C true color image from 6 June 2021.
2.2. Data Sources Information and Processing
The research data are remote sensing images selected from HY-1C, GF-1, and Sentinel-2 between 2020 and 2022. HY-1C is equipped with a Coastal Zone Imager (CZI) sensor that can acquire real-time image data of the sea–land interaction area, which is a significant advantage in marine environment monitoring. GF-1 is equipped with a Wide Field of View (WFV) sensor to ensure a high resolution and a wide range of width, and Sentinel-2 is equipped with a MultiSpectral Instrument (MSI) sensor with a high resolution and wide application characteristics. We chose the data from HY-1C CZI with low cloud coverage from May to August, which encompasses a width of 950 km, a resolution of 50 m, a revisit time of 3 days, and four bands, including visible and near-infrared bands [42]. The HY-1C satellite is in a sun-synchronous orbit, with an average height of 782 km, and its data can be downloaded from the National Satellite Ocean Application Service (NSOAS, https://osdds.nsoas.org.cn (accessed on 10 October 2022)). At a height of 645 km and a 4-day revisit interval, the GF-1 satellite also circles the Earth in a sun-synchronous orbit. Images from GF-1 WFV are available from the Chinese Center for Resources Satellite Data and Application (CRESDA, http://www.cresddataa.com/CN/index.shtml (accessed on 10 October 2022)) and contain four bands, covering visible and near-infrared bands with a width of 800 km and a resolution of 16 m [43]. Sentinel-2 is made up of two satellites, 2A and 2B, which are also in a sun-synchronous orbit, with an average height of 786 km, and that synchronize with one another at 180 degrees. For one satellite, the revisit period is 10 days. However, the two satellites complement each other and have a 5-day revisit time [44]. The European Space Agency (ESA, https://scihub.copernicus.eu (accessed on 10 October 2022)) provides Sentinel-2 MSI data, which include a 290 km observation width and thirteen bands with 10, 20, and 60 m spatial resolution. According to the difference vegetation index (DVI, detailed in Section 2.3), we selected visible and near-infrared bands with a resolution of 10 m to conduct our research. The data of GF-1 WFV and Sentinel-2 MSI were applied to support and validate the information on U. prolifera obtained from HY-1C CZI. All of the data sources shared the advantages of high resolution, wide width, and high timeliness. Table 1 displays the dates for the remote sensing images discussed in this paper.

Table 1.
The dates of remote sensing images.
The data from HY-1C CZI and GF-1 WFV are Level 1 products with radiation correction, and they were corrected using QUAC (quick atmospheric correction) and FLAASH (fast line-of-sight atmospheric analysis of spectral hypercubes) in ENVI 5.3, respectively. The images from Sentinel-2 are Level 2 products with geometric correction and atmospheric correction. The red, green, blue, and near-infrared band data were processed through layer stacking. All images were converted into the WGS_1984_UTM_Zone_51N coordinate system and clipped according to the study area.
2.3. U. prolifera Extraction Process
According to the presence of reflecting troughs in the red band and significant reflective peaks in the near-infrared band, respectively, the red band and the near-infrared band can be used as sensitive bands for U. prolifera monitoring [45]. Therefore, scholars have recently proposed many different index algorithms for U. prolifera detection, such as the DVI, the floating algae index (FAI), and the virtual–baseline floating macroalgae height index (VB-FAH), which are able to resist interference from sunlight and aerosol changes to a great extent [46]. Since the HY-1C CZI and GF-1 WFV data are only available in the visible and near-infrared bands, the DVI, which is linearly correlated with U. prolifera coverage, was selected for extraction [47,48]. Equation (1) demonstrates how DVI is calculated.
where Mdvi represents the value of DVI, Rnir represents the reflectance in the near-infrared band, and Rred represents the reflectance in the red band.
U. prolifera, with a higher DVI value than saltwater, may be distinguished from seawater by setting an appropriate threshold. One image covers a wide area, and objective conditions, such as clouds, fog, seawater color, and sun glint, can have a significant influence on the selection of the threshold value. The dynamic threshold approach is extremely useful and can improve the extraction accuracy of U. prolifera [49]. The DVI image is first divided into several small windows to ensure that the objective conditions vary as little as possible in each window, so that the size of the image in the window ranges from 300 * 300 pixels to 600 * 600 pixels. Then, a DVI threshold is set for each window to extract U. prolifera. Regarding the thresholds, they are determined by the difference between seawater and U. prolifera and usually range from −0.02 to 0.01 [46]. Moreover, the extracted U. prolifera should coincide with the U. prolifera region in the false color images. Through visual judgement and the assistance of the Cursor Value and Quick Stats function of ENVI 5.3, the individual level of the threshold can be obtained, which may undergo repeated comparison.
2.4. Drift Path and Influence Area
Considering the various densities and patch sizes of the U. prolifera in different locations, the weighted average center method was chosen to calculate the drift centers, which utilizes the area of various patches as the weight. Equations (2) and (3) illustrate how to calculate the drift center [50]. Then, joining the drift centers in chronological order, the drift path of U. prolifera can be identified.
where represents the abscissa of the element , represents the ordinate of the element , represents the total number of all elements, represents the area of the element , represents the abscissa of the weighted average center, and represents the ordinate of the weighted average center.
where represents the abscissa of the U. prolifera drift center and represents the ordinate of the U. prolifera drift center.
Any image with a spatial resolution has mixed pixels, which has an effect on the U. prolifera area [35]. In this study, we used Sentinel-2 with a 10 m resolution, GF-1 with a 16 m resolution, and HY-1C with a 50 m resolution for monitoring U. prolifera. We applied Euclidean distance analysis to compute the influence range of U. prolifera in ArcMap 10.7 and set the maximum distance to 5000 m, which may allow the area of U. prolifera to be compared on the same level and better portray the spatio-temporal variations of U. prolifera [51]. After that, the U. prolifera influence area was calculated.
2.5. Investigation of the Consistency between High-Resolution Images
Information on the images of the same date from the HY-1C and Sentinel-2 satellites with almost identical acquisition times is displayed in Table 2. It is clear that there were the fewest clouds and the largest green algae distribution on 2 July 2021, which indicates that the images are of superb quality. Thus, images taken on 2 July 2021 were preferred for modeling. When selecting the appropriate threshold of the corresponding DVI images, the distribution information of U. prolifera was obtained, and experimental batches of various sizes showed the consistency of the monitoring data from the HY-1C and Sentinel-2 satellites. Based on the distribution information of U. prolifera, experimental batches of various sizes were able to display the consistency of the monitoring data from HY-1C and Sentinel-2 satellites. The experimental batches were dispersed over the U. prolifera coverage range and were chosen based on U. prolifera with comparable shapes and distribution patterns. The verification images were taken on 17 July and 11 August 2021 to attest to the reliability of the model built using the images taken on 2 July 2021. In addition, 25 pairs, 15 pairs, and 14 pairs of experimental batches from the images taken on 2 July, 17 July, and 11 August 2021, respectively, were chosen to analyze the consistency of HY-1C CZI and Sentinel-2 MSI monitoring. The specific patterns of the experimental batches are displayed in Figure 3. Then, the consistency model of HY-1C and Sentinel-2 (MHS) was established using the experimental batches selected from the modeling image.

Table 2.
Information of the near-coincident HY-1C and Sentinel-2 satellite images.
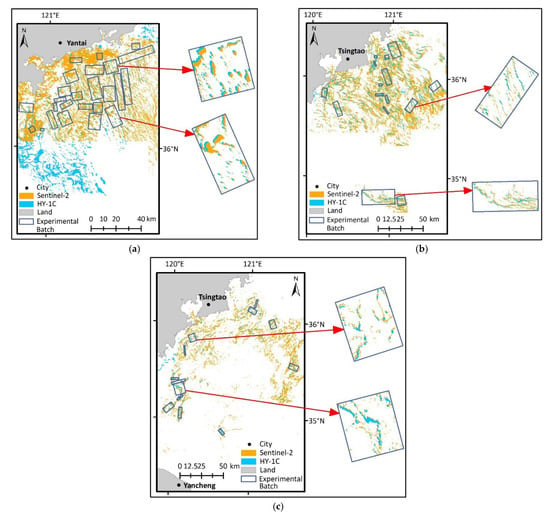
Figure 3.
Experimental patch distribution for MHS establishment and verification. (a) Distribution of modeling patches on 2 July 2021. (b) Distribution of verifying patches on 17 July 2021. (c) Distribution of verifying patches on 11 August 2021.
Adhering to the same experimental batch selection strategy and U. prolifera extraction method, the images taken on the same date from the HY-1C and GF-1 satellites with relatively similar acquisition times were selected for this research. Table 3 displays the image information. The images taken on 20 June 2021 have fewer clouds and huge patches of U. prolifera and thus were chosen as the modeling images. Moreover, images taken on 25 May and 21 June 2021 were used for validation, which were able to determine the reliability of the model built by the images taken on 20 June 2021. In the process of experimental batch selection, 15 pairs, 25 pairs, and 17 pairs of the batches on 25 May, 20 June, and 21 June 2021, respectively, were selected. The specific patterns of the experimental batches are displayed in Figure 4. By utilizing the batches picked from the modeling images, the consistency model of HY-1C and GF-1 (MHG) was established.

Table 3.
Information of near-coincident GF-1 and HY-1C satellite images.
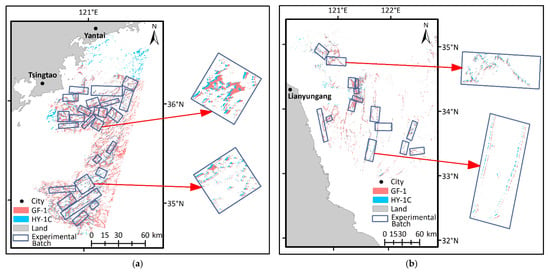
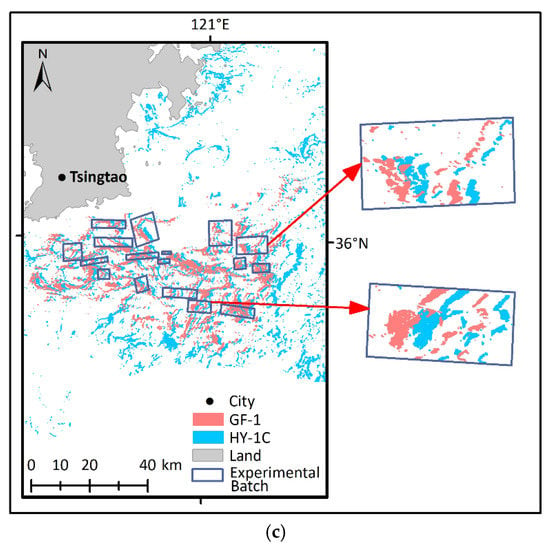
Figure 4.
Experimental patch distribution for MHG establishment and verification. (a) Distribution of modeling patches on 20 June 2021. (b) Distribution of verifying patches on 25 May 2021. (c) Distribution of verifying patches on 21 July 2021.
3. Results
3.1. Consistency Models between High-Resolution Images
The consistency models and verification results between high-resolution images are shown in Figure 5, and the ratio of data for model construction and validation is around 1:1. The determination coefficient (R2) of the model is between 0 and 1. The larger the R2, the better the fit of the model. The relative error (RE) is between 0 and 1, and the smaller the RE, the more reliable the model. On the basis of the images from HY-1C and Sentinel-2, the model MHS was created with linear characteristics and an R2 of 0.966 (Figure 5a). The experimental patches in verification images verify the model MHS with an RE of 16.179% (Figure 5b). U. prolifera in the verifying images is in the stage of decline, with its distribution and density as less than is seen in the modeling image. The model MHS fits well since there is a high R2 in the consistency model and a low RE in the validation. Meanwhile, the model MHG based on the images from HY-1C and GF-1 is in a linear relationship with an R2 value of 0.991 (Figure 5c). Verifying the model MHG, the RE value of this model is 14.885% (Figure 5d). Hence, the high R2 and low RE indicate that the consistency model MHG fits well. The models MHS and MHG remain consistent with the study by An et al. [46]. Therefore, the consistency models have high applicability, and the feasibility of HY-1C in U. prolifera monitoring is reliable, with outstanding spectral ranges.
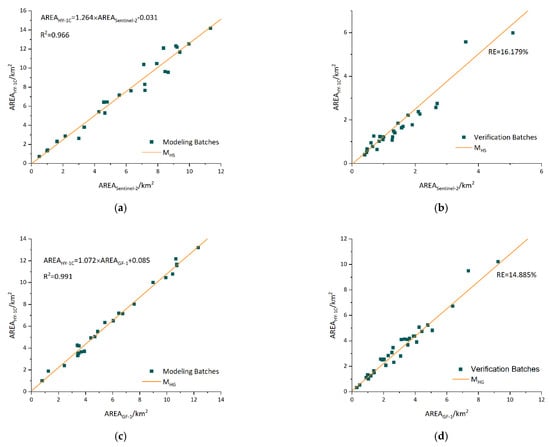
Figure 5.
Consistency models and verification. (a) Consistency model between HY-1C and Sentinel-2 images. (b) Verification result between HY-1C and Sentinel-2 images. (c) Consistency model between HY-1C and GF-1 images. (d) Verification result between HY-1C and GF-1 images.
3.2. Spatio-Temporal Distribution of U. prolifera
The dynamic evolution of U. prolifera from 2020 to 2022 is depicted in Figure 6, Figure 7 and Figure 8, mainly using the images from the HY-1C satellite and using the images from the Sentinel-2 and GF-1 satellites complementarily.
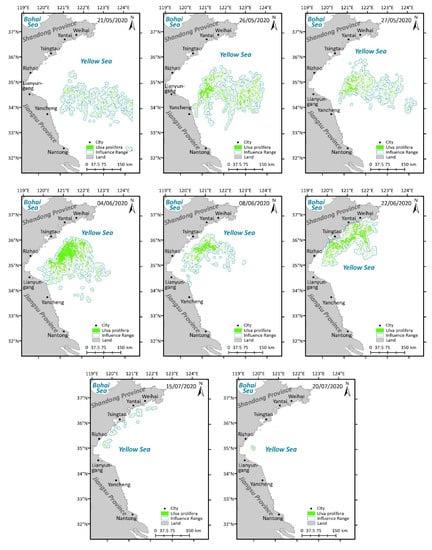
Figure 6.
Spatio-temporal distribution of U. prolifera in the Yellow Sea in 2020.
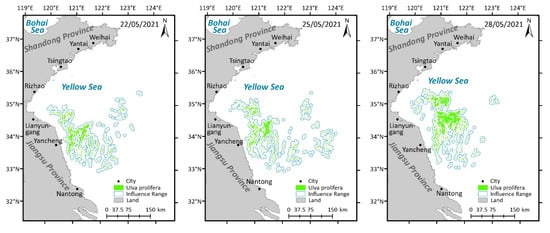
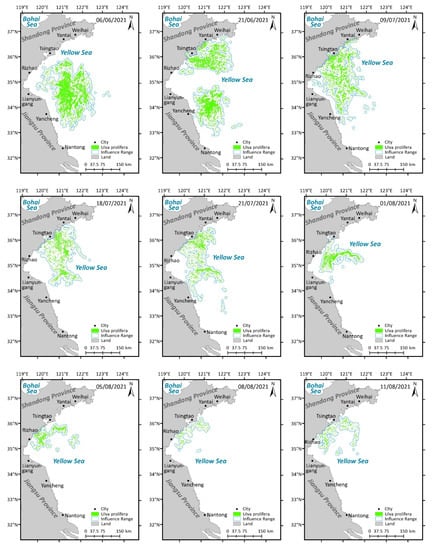
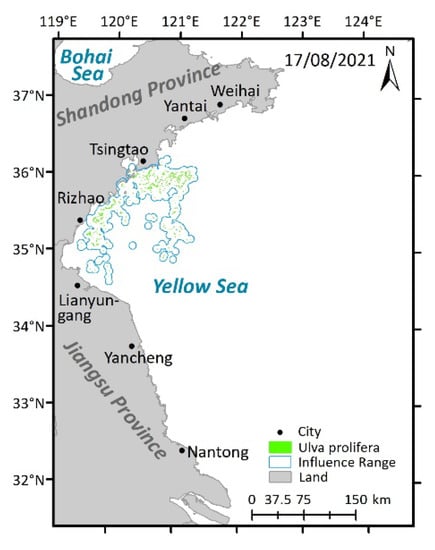
Figure 7.
Spatio-temporal distribution of U. prolifera in the Yellow Sea in 2021.
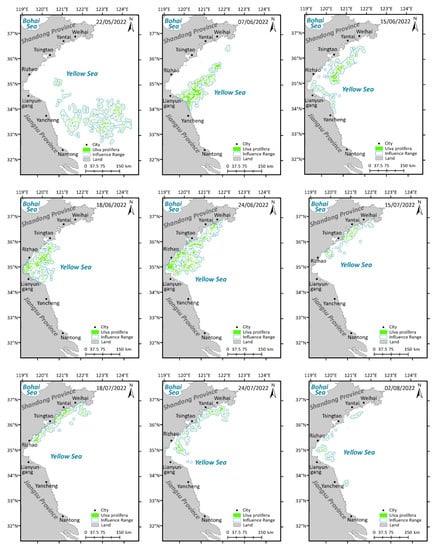
Figure 8.
Spatio-temporal distribution of U. prolifera in the Yellow Sea in 2022.
The distribution and influence range of U. prolifera in 2020 can be observed in Figure 6. In 2020, it is clear that U. prolifera was first found late in May along the Jiangsu Shoal, where it gradually floated northward. Then, it accelerated and reached the Shandong coast in June, taking the shape of large and striped patches with higher density. In July, the patches and density were both reduced, along with the shrinking distribution range. Accordingly, U. prolifera was seen for the first and final times on 21 May and 20 July 2020, a period of 61 days.
On 21 May 2020, U. prolifera, at the initial stage of appearance, was monitored for the first time. On 27 May, U. prolifera was concentrated in the middle of the Yellow Sea in the open water, when it began to affect the sea area near Yancheng and Lianyungang. On 4 June, the entire biomass spread in a northeasterly direction, with an increasing impact on the sea area near Lianyungang. On 8 June, U. prolifera was close to the coastline of Rizhao and Tsingtao, with a reduced influence in Lianyungang. Meanwhile, there was a tendency for the influence range of U. prolifera to narrow in both the north–south and east–west directions. On 22 June, U. prolifera threatened the sea near Rizhao, Tsingtao, Yantai, and Weihai. At this time, the influence range was primarily located along the coast of Shandong Province, with a distribution trend moving from the southwest and northeast. On 15 July, the influence range was substantially smaller and dispersed in the sea areas of Rizhao, Qingdao, Yantai, and Weihai. On 20 July, the final day when the dispersion of U. prolifera was detected, only the sea area around Rizhao was affected.
The distribution and influence range of U. prolifera in 2021 can be observed in Figure 7. It is evident that U. prolifera was initially observed late in May along the Jiangsu Shoal. In May and June, U. prolifera gradually moved northward while spreading out, changing shape from small and scattered clusters to large and striped patches. Simultaneously, the density and coverage area of U. prolifera increased. In addition, the affected range of U. prolifera extended from the Jiangsu Shoal to the Shandong coast and neighboring sea areas, eventually reaching the coastline of Tsingtao. Then, the patches and density of U. prolifera all gradually shrank in July and August. In total, the first and final occasions of U. prolifera identification were on 22 May and 17 August 2021, which encompasses a span of 88 days.
On 22 May 2021, U. prolifera, at the initial stage of appearance, was monitored for the first time. On 25 May, U. prolifera started to spread from the Jiangsu Shoal to the sea far offshore, which led to sporadic U. prolifera floating in the open water. On 28 May, the impact of U. prolifera on the waterways surrounding Lianyungang and Yancheng worsened. At the same time, U. prolifera drifted northward, threatening the seas close to Rizhao. Between 28 May and 6 June, the influence range of U. prolifera spread westward, eastward, and northward towards the sea near Tsingtao. On 21 June, with the trend of U. prolifera heading northward, the north–south range of U. prolifera extended from the sea near Yancheng to the waters close to Weihai, traveling through the sea areas at Lianyungang, Rizhao, Tsingtao, and Yantai, while the east–west range essentially stayed the same. Between the dates of 21 June and 9 July, the east–west influence range of U. prolifera was greatly diminished, and the impact on the sea around Weihai and Yancheng also began to decrease. From 9 July to 18 July, the impacted area declined in the waters of Yancheng and the sea north of Yancheng. On 21 July, the patches and density of U. prolifera were significantly smaller. On 1 August, U. prolifera posed no threat to Yantai. However, Lianyungang, Tsingtao, and Rizhao were still under threat. On 5 August, the U. prolifera on the Jiangsu Shoal almost disappeared, and the aging U. prolifera could be observed only in the sea area close to Tsingtao and Rizhao. 17 August was the last time that the HY-1C satellite was able to detect U. prolifera.
The distribution and influence range of U. prolifera in 2022 can be observed in Figure 8. In mid–late May 2022, it was apparent that U. prolifera was scattered throughout the sea close to Nantong. Additionally, it expanded northward in late May, approaching the Jiangsu Shoal. In June, it continued traveling northward until it arrived at the Shandong coast, during which its influence range narrowed. In July, it encompassed only a sporadic distribution of biomass on the Shandong coast, with the density and influence range decreasing. At the beginning of August, it disappeared. U. prolifera was detected for the first and last time on 22 May and 2 August 2022, a span of 73 days.
On 22 May 2022, U. prolifera at the stage of appearance was monitored for the first time. On 7 June, the influence range narrowed and traveled northwest, showing a trend towards strip shapes from the southwest to northeast, which had a significant impact on the sea areas near Lianyungang and Yancheng. On 15 June, the influence range continued spreading northwest in the strip shape and reached the coastline of Shandong. Meanwhile, several cities were threatened, including Yancheng, Lianyungang, Rizhao, Tsingtao, Yantai, and Weihai. On 18 June, the influence range narrowed and concentrated around the sea of Lianyungang, Rizhao, and Tsingtao. On 24 June, the shore of the Shandong Peninsula was once more within the influence range, and it threatened the coastline of Lianyungang, Rizhao, Tsingtao, Yantai, and Weihai. On 18 July, the sea areas close to Rizhao, Tsingtao, Yantai, and Weihai were still being impacted. On 24 July, the influence range was distributed from Weihai to Lianyungang along the mainland, with a southward-moving trend. On 2 August, the last day of U. prolifera identification, the influence range was obviously smaller along the coast of the mainland from Yantai to Yancheng.
3.2.1. Influence Area
In terms of the influence area of U. prolifera, Figure 9 displays the changing trends. On 21 May 2020, when U. prolifera initially appeared, the influence area was noted, and the maximum influence area for U. prolifera occurred on 26 May. During the time between 26 May and 8 June, the area actually decreased slightly. The areas of influence that were recorded on 27 May and 8 June were based on the HY-1C satellite, whereas the areas that were acquired on 26 May and 4 June were based on the GF-1 satellite. Meanwhile, U. prolifera was at the stage of development and was composed of various small batches. Since the GF-1 images with a 16 m resolution were better able to capture tiny batches of U. prolifera, the area collected from the GF-1 satellite is larger than that seen in the data from the HY-1C satellite. However, when viewed independently, the data from the HY-1C satellite and the GF-1 satellite both exhibited a decreasing trend. With the outbreak of U. prolifera from 8 June to 22 June, the distribution density and patches of U. prolifera grew larger, and its influence area also showed a substantial increasing tendency. As U. prolifera entered the decline stage after 22 June, its influence area began to shrink, and after 20 July, U. prolifera had completely vanished.
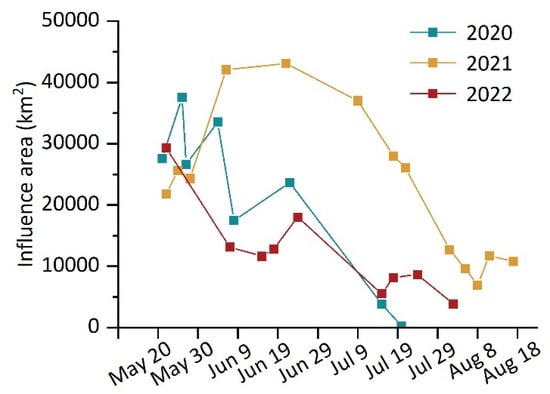
Figure 9.
Statistics of the influence area of U. prolifera from 2020 to 2022.
In 2021, the influence area of U. prolifera was recorded for the first time on 22 May when U. prolifera first appeared. Then, there was an increasing trend in the influence area from 22 May to 6 June. Although clouds on 21 June concealed around one fifth of the U. prolifera, making it difficult to collect the influence area of U. prolifera, the maximum influence area of U. prolifera was observed on 21 June, according to the data, when the influence area was more than 1000 km2 larger than on 6 June. Until 9 July, the coverage area of U. prolifera saw a sharp drop, which indicates the decline stage of U. prolifera. During the time between 9 July and 8 August, the decline rate of U. prolifera was fairly quick; however, the rate slowed down after 8 August. Eventually, U. prolifera vanished after 17 August.
In 2022, the influence area of U. prolifera was first noted on 21 May, when U. prolifera displayed maximum coverage of the influence area. From 22 May to 15 June, a declining trend was apparent. During the time between 15 June and 24 June, the influence area showed an upward trend, with an outbreak of U. prolifera. Then, the overall influence area showed a downward trend, with U. prolifera dissipating from 24 June to 2 August, although it fluctuated slightly on 18 July and 24 July.
3.2.2. Drift Path
Using to the weighted average centers of U. prolifera, the drift centers of U. prolifera can be determined. Then, connecting the drift centers in chronological order, the drift paths of U. prolifera for 2020, 2021, and 2022 can be obtained (Figure 10).
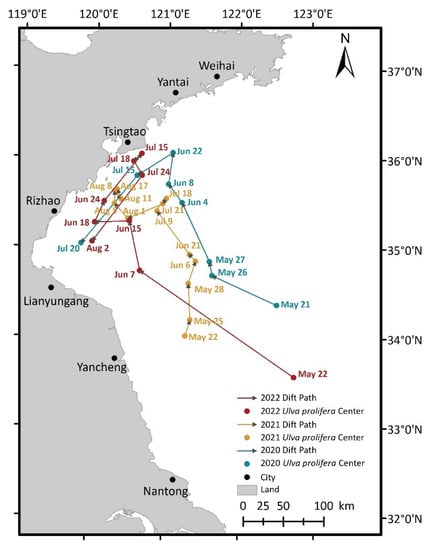
Figure 10.
The drift path of U. prolifera in 2021.
In 2020, U. prolifera was observed on 21 May in the open sea east of Yancheng. Then, U. prolifera traveled northwest to the waters around Tsingtao between 21 May and 8 June. From 8 June to 22 June, the entire biomass moved in a northeasterly direction but was still present in the waters near Tsingtao. Thereafter, U. prolifera drifted southwest between 22 June to 20 July to the sea waters near Rizhao. The overall trend of the drift path in 2020 was to head northwest initially, then turn southwest, which is in line with the study of Li et al. [52].
In 2021, U. prolifera was discovered on 22 May in the northern waters of Yancheng. Then, from 22 May to 6 June, U. prolifera floated in a northeasterly direction farther offshore towards the open sea. Later, the entire biomass drifted northwest between 6 June and 9 July to the open water east of Rizhao. Afterward, U. prolifera almost stayed in the same position from 9 July to 21 July. Then, it floated southwest between 21 July and 1 August and was still present in the open sea east of Rizhao. Thereafter, U. prolifera drifted northwest between 1 August and August 8 to the waters around Tsingtao. After August 8, U. prolifera continued to be identified in the sea waters near Tsingtao, with 17 August being the final instance when U. prolifera was detected in 2021. The overall trend of the drift path in 2021 was to travel northward, which is consistent with the results of Ma et al. [51].
In 2022, U. prolifera was detected on 22 May in the open sea east of Yancheng. From 22 May to 15 June, U. prolifera drifted in a northwesterly direction to the open sea east of Rizhao. Then, it traveled westward to the sea waters around Rizhao between 15 June and 18 June. Later, the entire biomass floated northeast between 18 June and 15 July to the waters near Tsingtao. However, U. prolifera moved southwest and returned to the waters around Rizhao between 15 July and 2 August. The overall trend of the drift path in 2022 was an initial movement north and then a turn back south.
4. Discussion
Comparing the consistency models MHS and MHG in Figure 5, it is apparent that the monitoring area of U. prolifera is smaller at higher resolutions. Throughout the data used in the study, Sentinel-2 MSI detected the smallest area of U. prolifera at the highest resolution, whereas HY-1C CZI observed the largest area of U. prolifera at the lowest resolution. Similarly to the former, GF-1 WFV obtained a larger area of U. prolifera at a higher resolution. This led to the conclusion that the higher the resolution of the satellites’ sensors, the smaller the area of U. prolifera monitored, which agrees with the results of Xing et al. [25] and strongly confirms the consistency models between HY-1C and GF-1 and HY-1C and Sentinel-2, corresponding to the overall trend of the research. Moreover, there are always green algae patches smaller than the resolution of the image. In reality, the lack of measured data on U. prolifera, which is a result of the dynamic process of U. prolifera on the sea, still represents a challenge. All these phenomena make it challenging to monitor U. prolifera accurately, even if the images are all of a high resolution.
While investigating the temporal and spatial alterations of U. prolifera, we employed HY-1C, Sentinel-2, and GF-1 data to analyze the five-stage process of “appearance–development–outbreak–decline–disappearance”. It can be seen that the distribution of U. prolifera on 21 June 2021 differed from the others, and the statistical results of its influence area and path varied greatly. On the one hand, this is due to the occurrence of cloud occlusion, which interferes with our extraction of U. prolifera. On the other hand, changes in sea surface temperature, photosynthetically active radiation, precipitation, and wind and seawater eutrophication may have certain effects on U. prolifera [53], which in turn have a greater impact on the area and drift path of U. prolifera. We examined the images before and after 21 June, but the quality was poor and there were far more clouds in the images. To ensure the accuracy of the study, it was important to include the images taken on 21 June due to objective factors. The distribution of U. prolifera in the sea is regular, so it was reasonable for us to use the area of the U. prolifera patches on 21 June as the weight and then calculate the weighted mean center to obtain the drift center.
Interestingly, there are similarities between the spatio-temporal distribution of U. prolifera in 2020 and 2022. In 2020, the drift path headed northwest first, then southwest. Similarly, in 2022, the drift path traveled north first, then south. Both displayed a trend of heading southward after heading northward. Moreover, in 2020 and 2022 the maximum influence area occurred during the early stage of U. prolifera. This occurrence may have been caused by a variety of factors, including ocean currents, sea surface wind fields, and so on. Further studies are needed to investigate this phenomenon.
Monitoring marine life is different from monitoring creatures on land, since the sea is a complex and varied environment. As a marine species, U. prolifera adapts to changes in the marine environment through changes in its growth, reproduction, death, and other physiological traits. Different variables have different impacts on the appearance, development, breakout, decline, and disappearance of U. prolifera, including the ocean current, oxygen enrichment of seawater, the degree of eutrophication of coastal waters, sea surface wind field, natural enemies, human activities in coastal waters, and global warming. Today, in the context of multiple disciplines being closely connected and instruments representing diverse tools, we can combine marine science and technology, such as marine physics and marine chemistry, to improve instrument representation accuracy, increase the ability of U. prolifera monitoring from multiple perspectives, and achieve interdisciplinarity, which is a fundamental means to achieving better U. prolifera monitoring and control mechanisms.
5. Conclusions
Threats posed by U. prolifera are some of the most critical challenges in the maritime environment and must be addressed and managed as soon as possible. The unique feature of this study is the verification of the feasibility of China’s first ocean water color operational satellite HY-1C for U. prolifera monitoring based on the models MHS and MHS. Then, using mainly the HY-1C satellite and using the Sentinel-2 and GF-1 satellites complementarily, we recorded the spatio-temporal change in U. prolifera in the Yellow Sea from 2020 to 2022, analyzed the influence range, quantitatively studied the influence area, and then carried out a systematic analysis of the drift paths, which are beneficial in the systematic development of emergency response mechanisms for U. prolifera. The results show the following:
- (1)
- The feasibility of China’s first ocean water color operational satellite HY-1C for U. prolifera monitoring is reliable, with excellent spectral ranges, which were examined using the consistency models MHS and MHG, with R2 of 0.966 and 0.991, respectively.
- (2)
- In 2020, U. prolifera was detected for the first and final times on 21 May and 20 July, a period of 61 days. In 2021, U. prolifera was observed on 22 May for the first time and 17 August for the last time, a span of 88 days. In 2022, U. prolifera was initially discovered on 22 May and disappeared after 2 August, a 73-day duration.
- (3)
- In terms of the influence area, the trends were essentially identical in 2020 and 2022, with the maximum influence area occurring during the early stages, followed by a general decline. In 2021, the influence area generally increased and then decreased.
- (4)
- Regarding the drift path in 2020, the general pattern saw an initial move northwest before turning southwest. In 2021, the overall trend of the drift path was the northward accumulation, development, and extension. Additionally, the general trend for the drift path in 2022 began with movement in a northward direction before turning south.
In the process of studying the spatio-temporal changes in U. prolifera, there were certain deviations in the research results due to the limitation of the satellite time, spatial resolutions, and the interference of external factors, such as weather. Meanwhile, a single study approach or model cannot reliably yield high-quality research findings, since a large variety of factors impact the development of U. prolifera. In future research, a simulation model of U. prolifera suspended on the water surface and in the water should be developed through the cross-combination of multiple disciplines and the careful consideration of various factors. Moreover, measured data are crucial for monitoring the spatio-temporal distribution of U. prolifera, which can quantitatively estimate the accuracy of detecting U. prolifera. Based on the location and time information of U. prolifera in this work, it is of vital significance to utilize a deep learning algorithm of high intelligence to enhance U. prolifera predictive performance. This will contribute to the upgrading of the disaster emergency response system of coastal cities, the lowering of the resource investment of U. prolifera fishing, and the promotion of the positive perception of coastal cities.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Z.W. and B.F.; methodology, Z.W., B.F. and D.A.; software, Z.W. and D.A.; validation, Z.W., B.F. and D.Y.; formal analysis, Z.W. and B.F.; data curation, Z.W. and D.A.; writing—original draft preparation, Z.W. and B.F.; writing—review and editing, Z.W., D.Y., Y.F. and S.P.; supervision, D.Y. and Y.F.; project administration, B.F., D.Y. and Y.F.; funding acquisition, D.Y. and Y.F. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (no. 42106172), the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province (no. ZR2021QD135), University-Industry Collaborative Education Program (nos. 202102245036 and 202101044002), the Open Research Fund of State Key Laboratory of Estuarine and Coastal Research under Project (no. SKLEC-KF202001), and the Project Plan of Pilot Project of Integration of Science, Education and Industry (nos. 2022GH004 and 2022PY041).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data used in this study are available on request from the first author.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to the National Satellite Ocean Application Service for providing HY-1C data, to China Center for Resources Satellite Data and Application for GF-1 data, and to NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center and the European Space Agency for Sentinel-2 data.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Fletcher, R.L. The Occurrence of “Green Tides”—A Review; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1996; pp. 7–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smetacek, V.; Zingone, A. Green and golden seaweed tides on the rise. Nature 2013, 504, 84–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, L.B.; Hu, C.M.; He, M.X. Remote estimation of biomass of Ulva prolifera macroalgae in the Yellow Sea. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 192, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.Y.; He, P.M.; Li, H.M.; Li, G.; Liu, J.H.; Jiao, F.L.; Zhang, J.H.; Huo, Y.Z.; Shi, X.Y.; Su, R.G.; et al. Ulva prolifera green-tide outbreaks and their environmental impact in the Yellow Sea, China. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2019, 6, 825–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.Y.; Fang, Z.X.; Liang, J.F.; Song, X. Assessment of global habitat suitability and risk of ocean green tides. Harmful Algae 2022, 119, 102324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Yu, R.C.; Zhou, M.J. Effects of the decomposing green macroalga Ulva (Enteromorpha) prolifera on the growth of four red-tide species. Harmful Algae 2012, 16, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.Y.; Keesing, J.K.; He, P.M.; Wang, Z.L.; Shi, Y.J.; Wang, Y.J. The world’s largest macroalgal bloom in the Yellow Sea, China: Formation and implications. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2013, 129, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Wu, M.Q.; Xing, Q.G.; Song, X.D.; Zhao, D.H.; Han, Q.Q.; Zhang, G.Z. Spatio-temporal patterns of Ulva prolifera blooms and the corresponding influence on chlorophyll-a concentration in the Southern Yellow Sea, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 640–641, 807–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Z.Y.; Yuan, H.Q.; Liu, J.L.; Sun, Y.Q.; Tong, Y.C.; Zhao, S.; Xia, J.; Li, S.; Hu, M.J.; Cao, J.X.; et al. A review of physical, chemical, and biological green tide prevention methods in the Southern Yellow Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 180, 113772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasson, K.; Jeppesen, R.; Endris, C.; Perry, D.C.; Woolfolk, A.; Beheshti, K.; Rodriguez, M.; Eby, R.; Watson, E.B.; Rahman, F.; et al. Eutrophication decreases salt marsh resilience through proliferation of algal mats. Biol. Conserv. 2017, 212, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.H.; Huo, Y.Z.; Zhang, Z.L.; Yu, K.F.; He, Q.; Zhang, L.H.; Yang, L.L.; Xu, R.; He, P.M. Variations of morphology and photosynthetic performances of Ulva prolifera during the whole green tide blooming process in the Yellow Sea. Mar. Environ. Res. 2013, 92, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.Q.; Yao, L.L.; Liu, J.L.; Tong, Y.C.; Xia, J.; Zhao, X.H.; Zhao, S.; Fu, M.L.; Zhuang, M.M.; He, P.M.; et al. Prevention strategies for green tides at source in the Southern Yellow Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 178, 113646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.X.; Gao, Z.Q.; Wang, Z.C. Analysis of the reasons for the outbreak of Yellow Sea green tide in 2021 based on long-term multi-source data. Mar. Environ. Res. 2022, 178, 105649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.N.; Zhu, A.; Chen, R.S. China’ s algal bloom suffocates marine life. Science 2021, 373, 751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.H.; Li, L.; Bao, X.; Zhao, L.D. Economic cost of an algae bloom cleanup in China’s 2008 Olympic sailing venue. Eos Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 2009, 90, 238–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.L.; Xia, J.; Zhuang, M.M.; Zhang, J.H.; Yu, K.F.; Zhao, S.; Sun, Y.Q.; Tong, Y.C.; Xia, L.H.; Qin, Y.T.; et al. Controlling the source of green tides in the Yellow Sea: NaClO treatment of Ulva attached on Pyropia aquaculture rafts. Aquaculture 2021, 535, 736378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.Y.; Qi, M.Y.; Tang, H.J.; Han, X.R. Spatial and temporal nutrient variations in the Yellow Sea and their effects on Ulva prolifera blooms. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2015, 163, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Q.G.; Tosi, L.G.; Braga, F.; Gao, X.L.; Gao, M. Interpreting the progressive eutrophication behind the world’s largest macroalgal blooms with water quality and ocean color data. Nat. Hazards 2015, 78, 7–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, S.J.; Liu, F.; Shan, T.F.; Xu, N.; Zhang, Z.H.; Gao, S.Q.; Chopin, T.; Sun, S. Tracking the algal origin of the Ulva bloom in the Yellow Sea by a combination of molecular, morphological and physiological analyses. Mar. Environ. Res. 2010, 69, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, F.; Liu, X.F.; Shi, S.T.; Bi, Y.P.; Moejes, F.W. Comparative transcriptome analysis of four co-occurring Ulva species for understanding the dominance of Ulva prolifera in the Yellow Sea green tides. J. Appl. Phycol. 2019, 31, 3303–3316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Xu, D.; Wang, Y.T.; Zhang, X.W.; Cao, S.N.; Mou, S.L.; Ye, N.H. The effect of nutrient concentrations, nutrient ratios and temperature on photosynthesis and nutrient uptake by Ulva prolifera: Implications for the explosion in green tides. J. Appl. Phycol. 2014, 26, 537–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, L.; Zhou, B.; Tang, X.X. Comparative studies on the ecophysiological differences of two green tide macroalgae under controlled laboratory conditions. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e38245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, X.X.; Xiao, J.; Pang, M.; Zhang, X.L.; Wang, Z.L.; Miao, J.W.; Li, Y. Effect of the large-scale green tide on the species succession of green macroalgal micro-propagules in the coastal waters of Qingdao, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 126, 549–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keesing, J.K.; Liu, D.Y.; Fearns, P.; Garcia, R. Inter- and intra-annual patterns of Ulva prolifera green tides in the Yellow Sea during 2007–2009, their origin and relationship to the expansion of coastal seaweed aquaculture in China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2011, 62, 1169–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, Q.G.; An, D.Y.; Zheng, X.Y.; Wei, Z.N.; Wang, X.H.; Li, L.; Tian, L.Q.; Chen, J. Monitoring seaweed aquaculture in the Yellow Sea with multiple sensors for managing the disaster of macroalgal blooms. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 231, 111279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Zhang, H.Y.; Cheng, Y.C.; Zhang, S.S.; Zhang, W. Monitoring and tracking the green tide in the Yellow Sea with satellite imagery and trajectory model. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Observ. Remote Sens. 2016, 9, 5172–5181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.Y.; Fang, Z.X.; Wu, Y.C.; Liang, J.F.; Song, X. Multi-source evidence data fusion approach to detect daily distribution and coverage of Ulva prolifera in the Yellow Sea, China. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 115214–115228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Q.G.; Hu, C.M.; Tang, D.L.; Tian, L.Q.; Tang, S.L.; Wang, X.H.; Lou, M.J.; Gao, X.L. World’s largest macroalgal blooms altered phytoplankton biomass in Summer in the Yellow Sea: Satellite observations. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 12297–12313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Yu, D.F.; Cheng, W.T.; Gai, Y.Y.; Yao, H.P.; Yang, L. Monitoring multi-temporal and spatial variations of water transparency in the Jiaozhou Bay using GOCI data. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 180, 113815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.F.; Zhang, J.; Cui, T.W.; Gong, J.L.; Liu, R.J.; Chen, X.Y.; Liang, X.J. Remote sensing estimation of the biomass of floating Ulva prolifera and analysis of the main factors driving the interannual variability of the biomass in the Yellow Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 140, 330–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Q.G.; Wu, L.L.; Tian, L.Q.; Cui, T.W.; Li, L.; Kong, F.Z.; Gao, X.L.; Wu, M.Q. Remote sensing of early-stage green tide in the Yellow Sea for floating-macroalgae collecting campaign. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 133, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, T.T.; Ke, L.N.; Fan, J.C.; Zhao, J.H. Green tide information extraction based on multi-source remote sensing data. In Proceedings of the 2020 12th International Conference on Advanced Computational Intelligence (ICACI), Dali, China, 14–16 August 2020; pp. 460–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.F.; Wan, J.H.; Hu, W.; Song, Y.; Lu, B. Retrieval of green tide concentration and interannual variation analysis in Yellow Sea based on multi-source remote sensing monitoring. In Proceedings of the 2020 Global OCEANS Singapore—U.S. Gulf Coast Conference, Biloxi, MS, USA, 5–30 October 2020; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.T.; Ma, Q.; Huang, J.X.; Feng, Q.L.; Zhao, Y.Y.; Guo, H.; Chen, B.A.; Li, C.X.; Zhang, Y.X. Remote sensing monitoring of grasslands based on adaptive feature fusion with multi-source data. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.H.; Xing, Q.G.; An, D.Y.; Meng, L.; Zhang, X.Y.; Jiang, B.; Liu, H.L. Effects of spatial resolution on the satellite observation of floating macroalgae blooms. Water 2021, 13, 1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.C.; Liu, J.Q.; Ding, J.; Lu, Y.C. A refined imagery algorithm to extract green tide in the Yellow Sea from HY-1C satellite CZI measurements. Haiyang Xuebao 2022, 44, 1–11. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Gao, L.; Li, X.F.; Kong, F.Z.; Yu, R.C.; Guo, Y.; Ren, Y.B. AlgaeNet: A deep-learning framework to detect floating green algae from optical and SAR imagery. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Observ. Remote Sens. 2022, 15, 2782–2796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.Y.; Fang, Z.X.; Zhang, Y.; Song, Z.L. Bidirectional spatio-temporal association between the observed results of Ulva prolifera green tides in the Yellow Sea and the social response in Sina Weibo. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Observ. Remote Sens. 2021, 14, 5988–6008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Wu, L. Numerical study on the massive outbreak of the Ulva prolifera green tides in the southwestern Yellow Sea in 2021. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.F.; Wang, C.Y.; Li, J.H.; Sui, Y. Automatic extraction of green tide from GF-3 SAR images based on feature selection and deep learning. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Observ. Remote Sens. 2021, 14, 10598–10613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.Y.; Chu, J.L.; Tan, M.; Shao, F.J.; Sui, Y.; Li, S.J. An automatic detection of green tide using multi-windows with their adaptive threshold from landsat TM/ETM plus image. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2017, 36, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, H.R.; Tian, L.Q.; Li, J.; Tong, R.Q.; Guo, Y.L.; Zeng, Q. Spatial–spectral fusion of HY-1C COCTS/CZI data for coastal water remote sensing using deep belief network. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Observ. Remote Sens. 2021, 14, 1693–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, P.Q.; Fu, B.L.; He, H.C.; Chen, J.J.; Wu, T.H.; Lin, X.C.; Liu, L.L.; Fan, D.L.; Deng, T.F. An effective method for canopy chlorophyll content estimation of marsh vegetation based on multiscale remote sensing data. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Observ. Remote Sens. 2021, 14, 5311–5325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helber, P.; Bischke, B.; Dengel, A.; Borth, D. EuroSAT: A novel dataset and deep learning benchmark for land use and land cover classification. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Observ. Remote Sens. 2019, 12, 2217–2226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.G.; Bai, Y.; Chen, P.P.; Ding, Z.H.; Xu, L. Research of spectrum characteristics of enteromorpha in Qingdao offshore. Mar. Sci. 2015, 37, 87–91. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- An, D.Y.; Yu, D.F.; Zheng, X.Y.; Zhou, Y.; Meng, L.; Xing, Q.G. Monitoring the dissipation of the floating green macroalgae blooms in the Yellow Sea (2007–2020) on the basis of satellite remote sensing. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zheng, X.Y.; Wei, Z.N.; Zou, J.Q.; Xing, Q.G. A spectral-mixing model for estimating sub-pixel coverage of sea-surface floating macroalgae. Atmos. Ocean 2018, 56, 296–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, T.W.; Liang, X.J.; Gong, J.L.; Tong, C.; Xiao, Y.F.; Liu, R.J.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, J. Assessing and refining the satellite-derived massive green macro-algal coverage in the Yellow Sea with high resolution images. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2018, 144, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, D.Y.; Xing, Q.G.; Yu, D.F.; Pan, S.Q. A simple method for estimating macroalgae area under clouds on MODIS imagery. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 995731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, D.B.; Gao, Z.Q.; Xu, F.X.; Zheng, X.Y.; Ai, J.Q.; Chen, M.S. Remote sensing of the Yellow Sea green tide in 2014 based on GOCI. In Proceedings of the 2017 Conference on Remote Sensing and Modeling of Ecosystems for Sustainability XIV, San Diego, CA, USA, 9 August 2017; p. 104050R. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.F.; Wong, K.P.; Tsou, J.Y.; Zhang, Y.Z. Investigating spatial distribution of green-tide in the Yellow Sea in 2021 using combined optical and SAR images. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.X.; Gao, Z.Q.; Xu, F.X. Research on the dissipation of green tide and its influencing factors in the Yellow Sea based on Google Earth Engine. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 172, 112801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.X.; Wu, M.Q.; Cui, Y.T.; Tian, L.; Yang, P.S.; Zhao, L.J.; Xue, M.Y.; Liu, J.Y. What causes the great green tide disaster in the South Yellow Sea of China in 2021? Ecol. Indic. 2022, 140, 108988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).