Development of Chaos Terrain as Subaqueous Slide Blocks in Galilaei Crater, Mars
Abstract
:1. Introduction
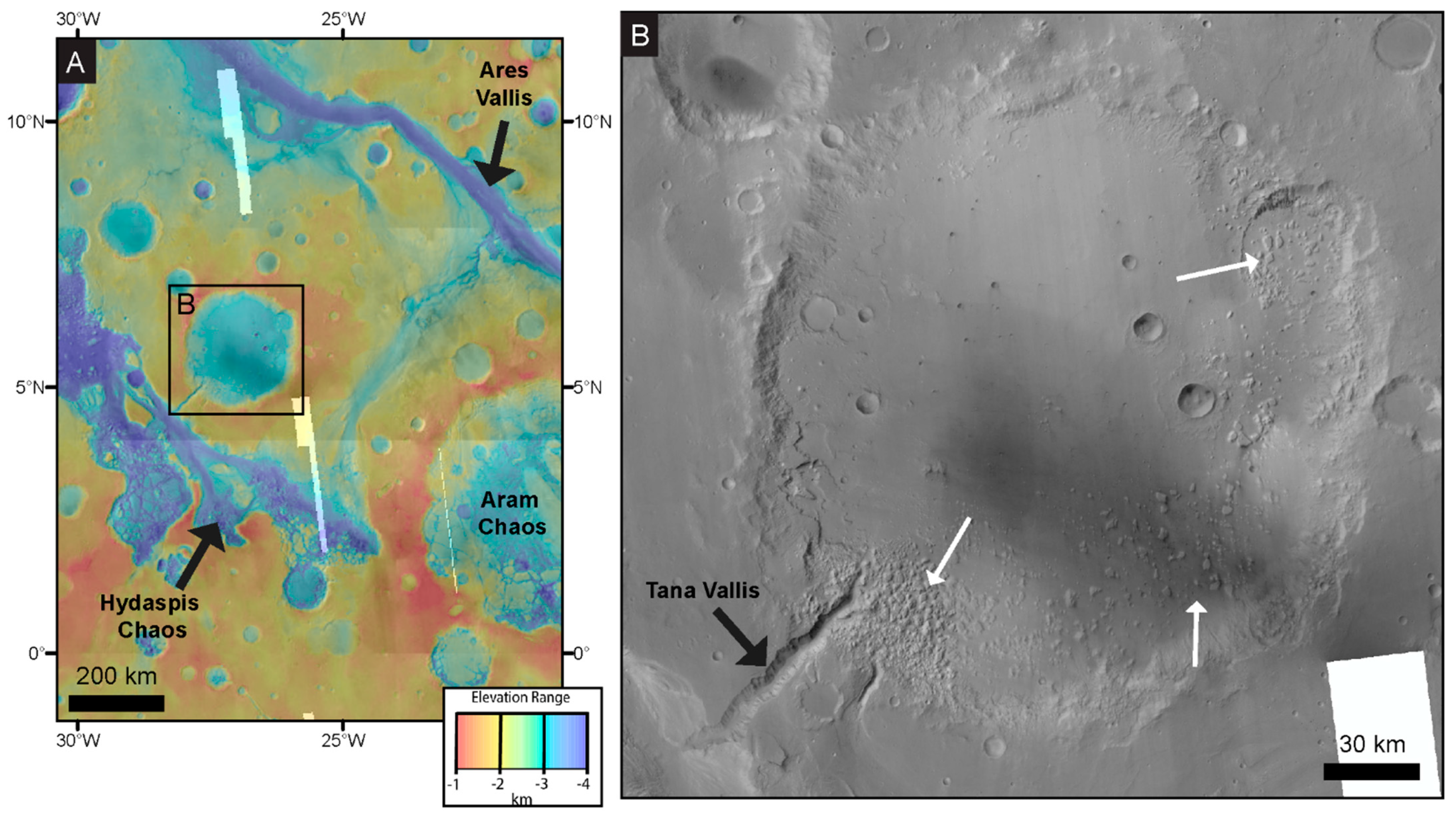
2. Study Area
3. Data and Methods
4. Observations and Results
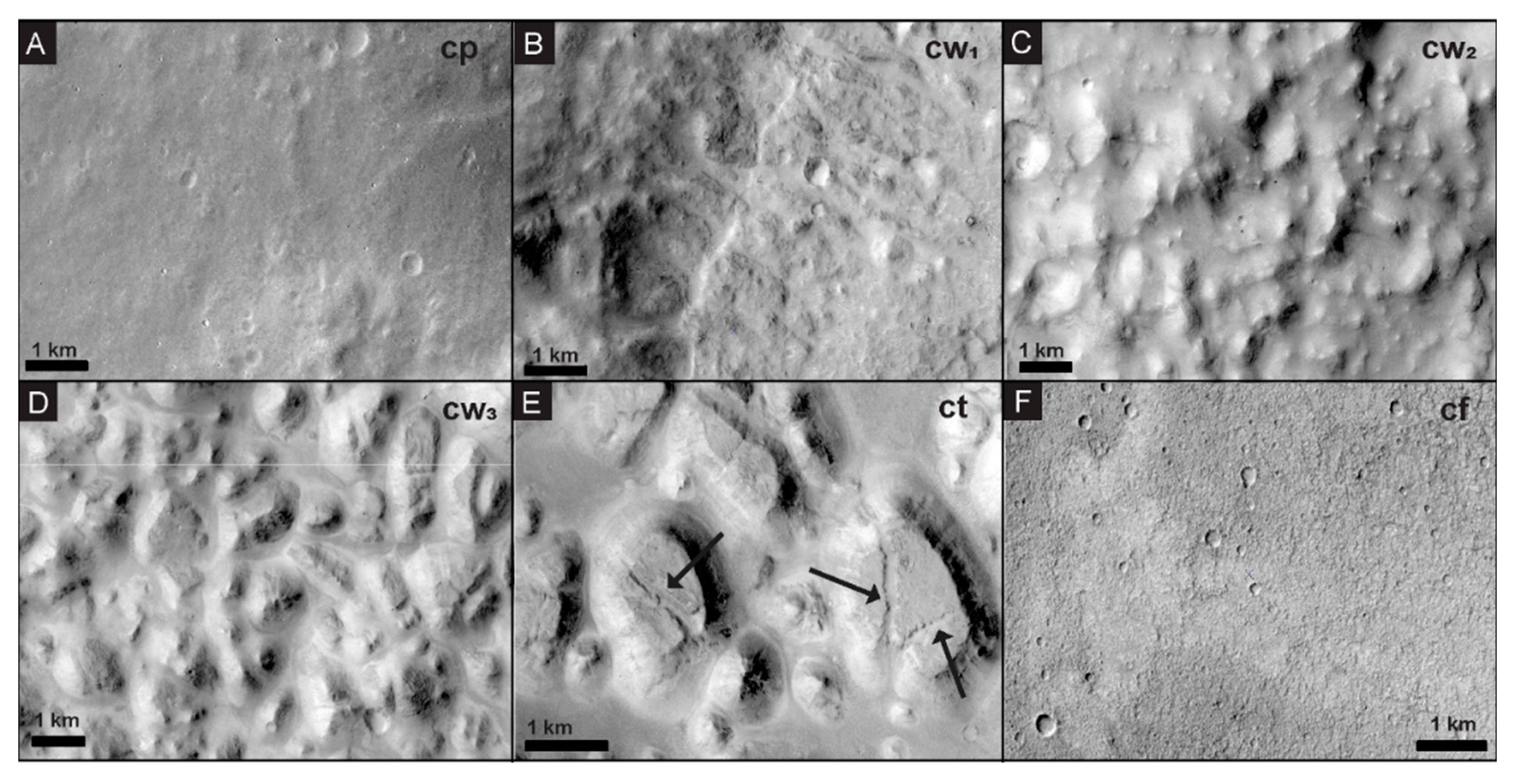
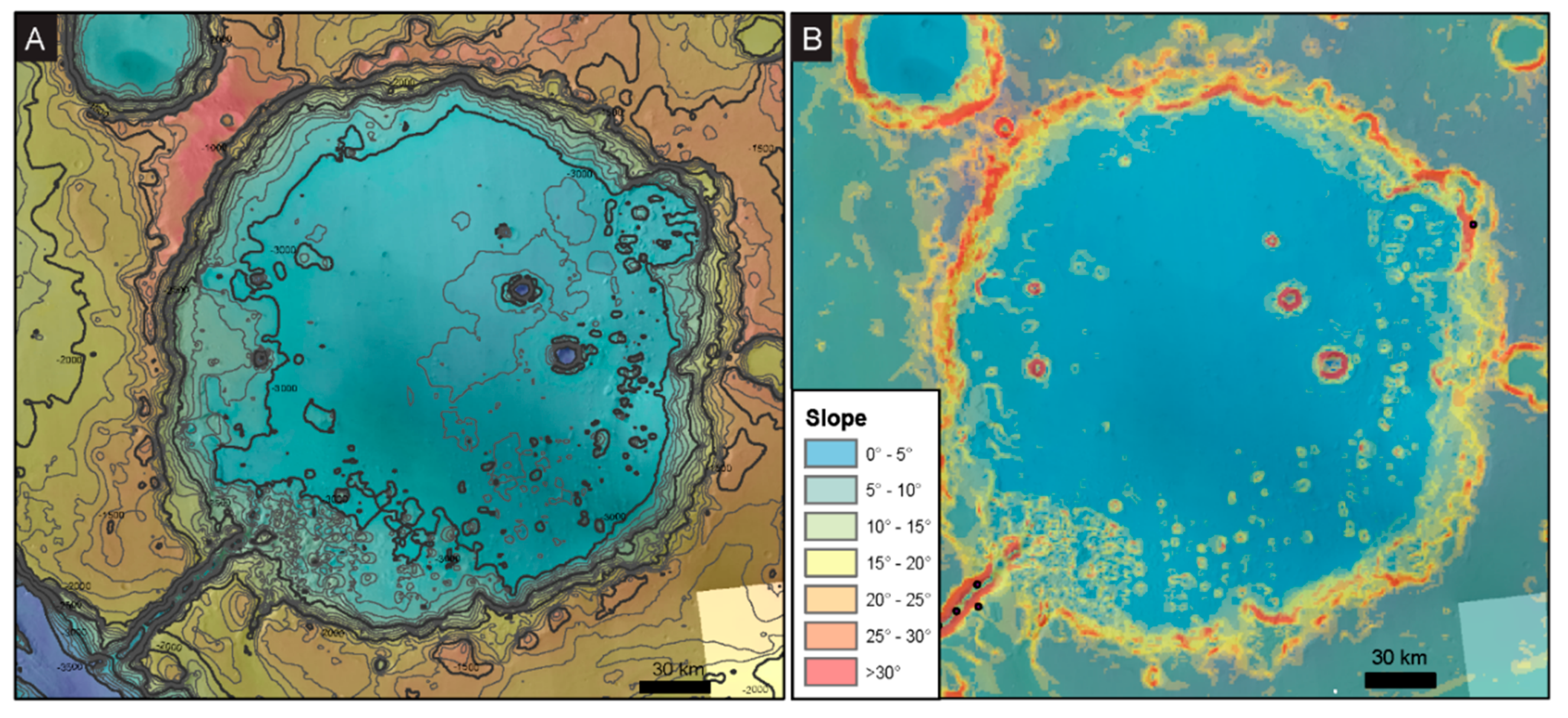
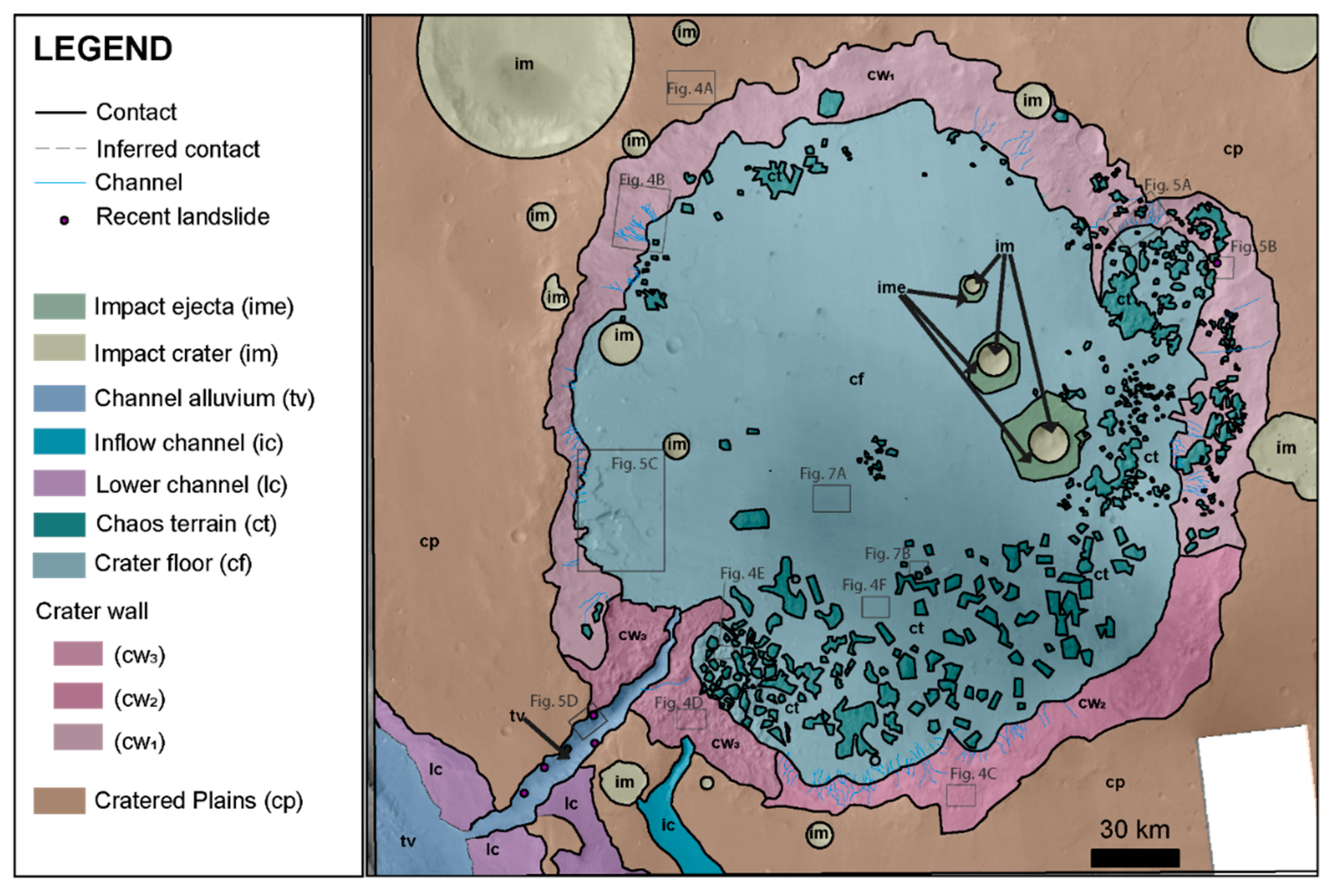
4.1. Contextual Geomorphic Mapping and Crater Interior Geomorphology
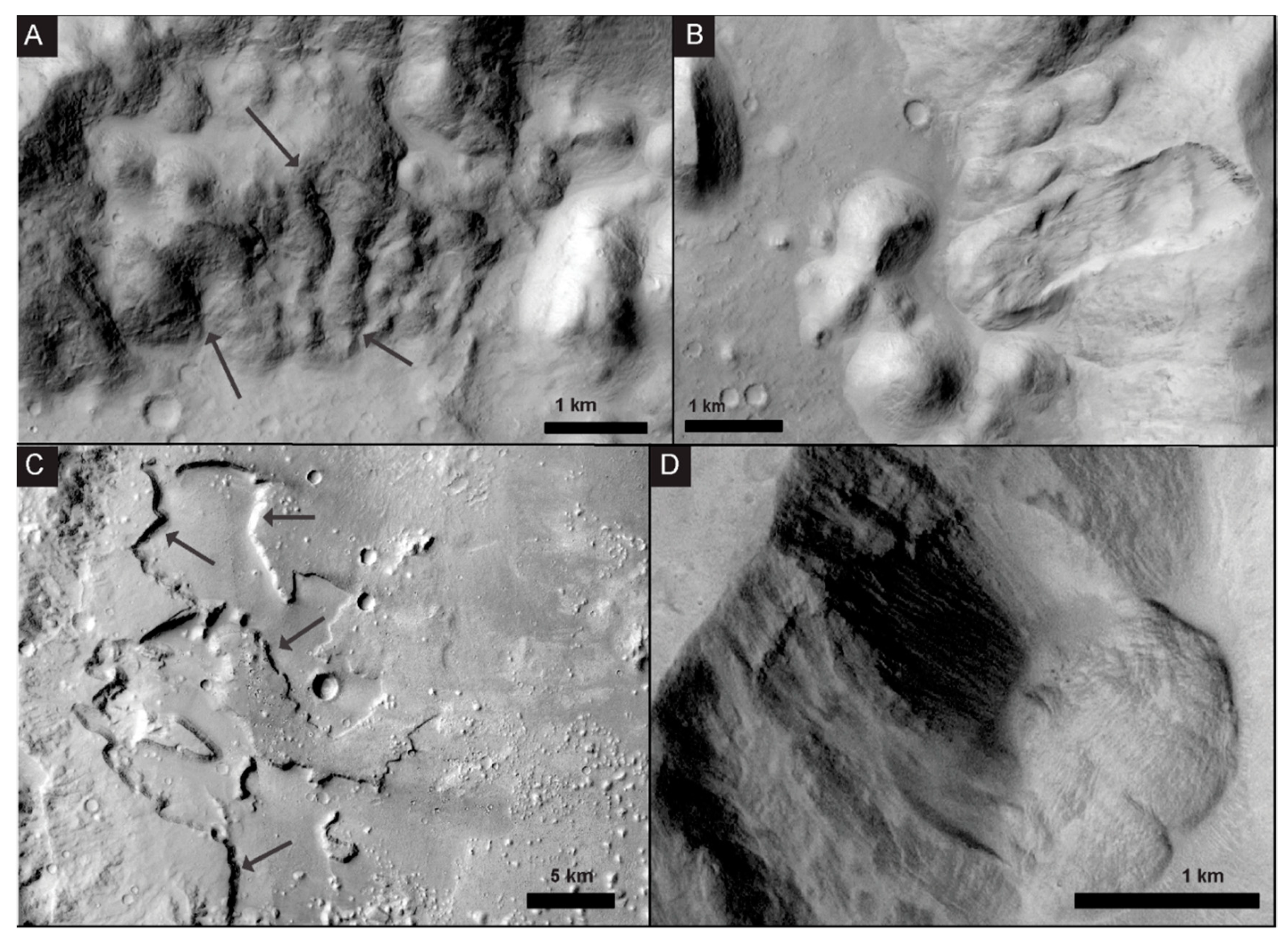
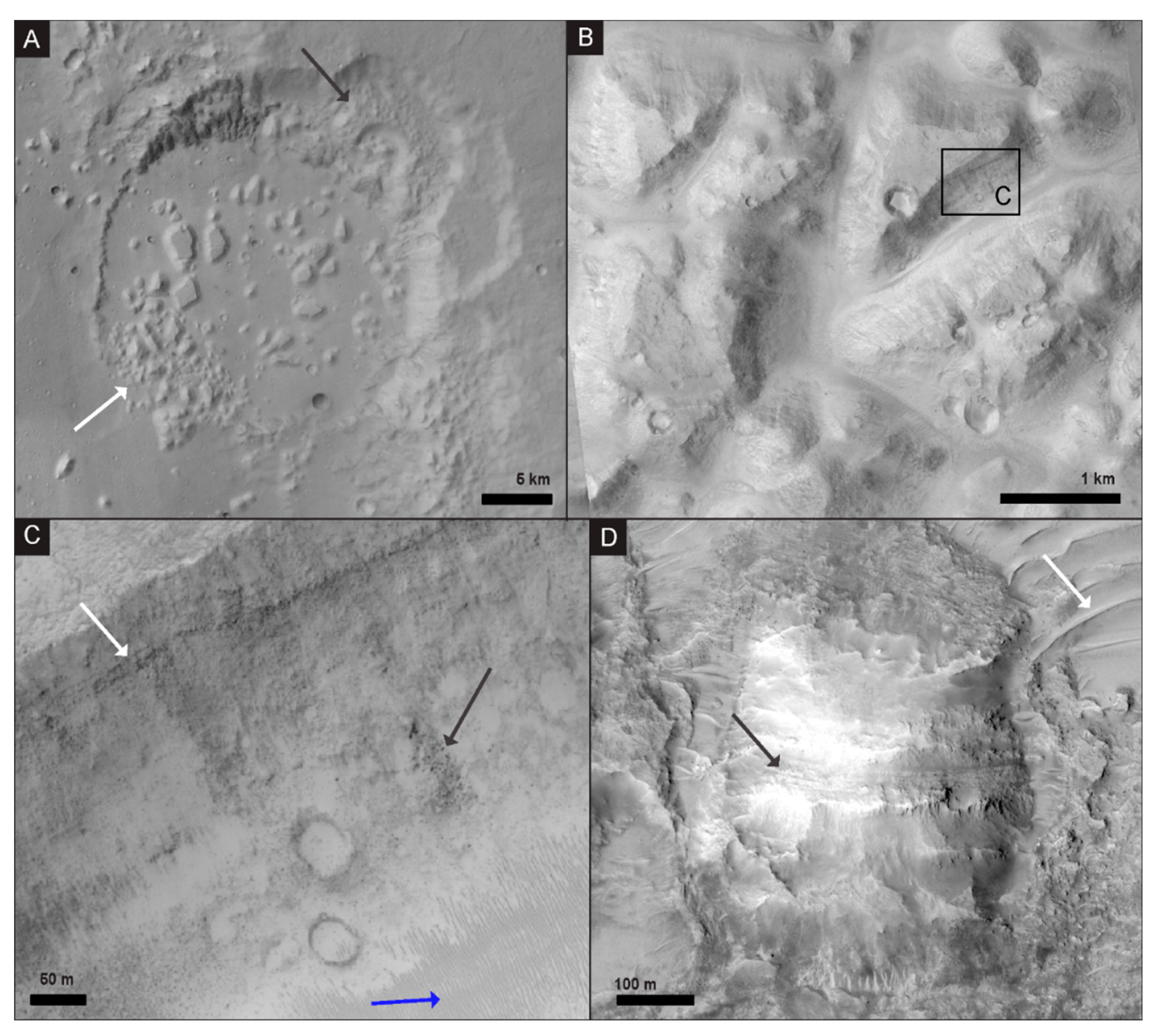
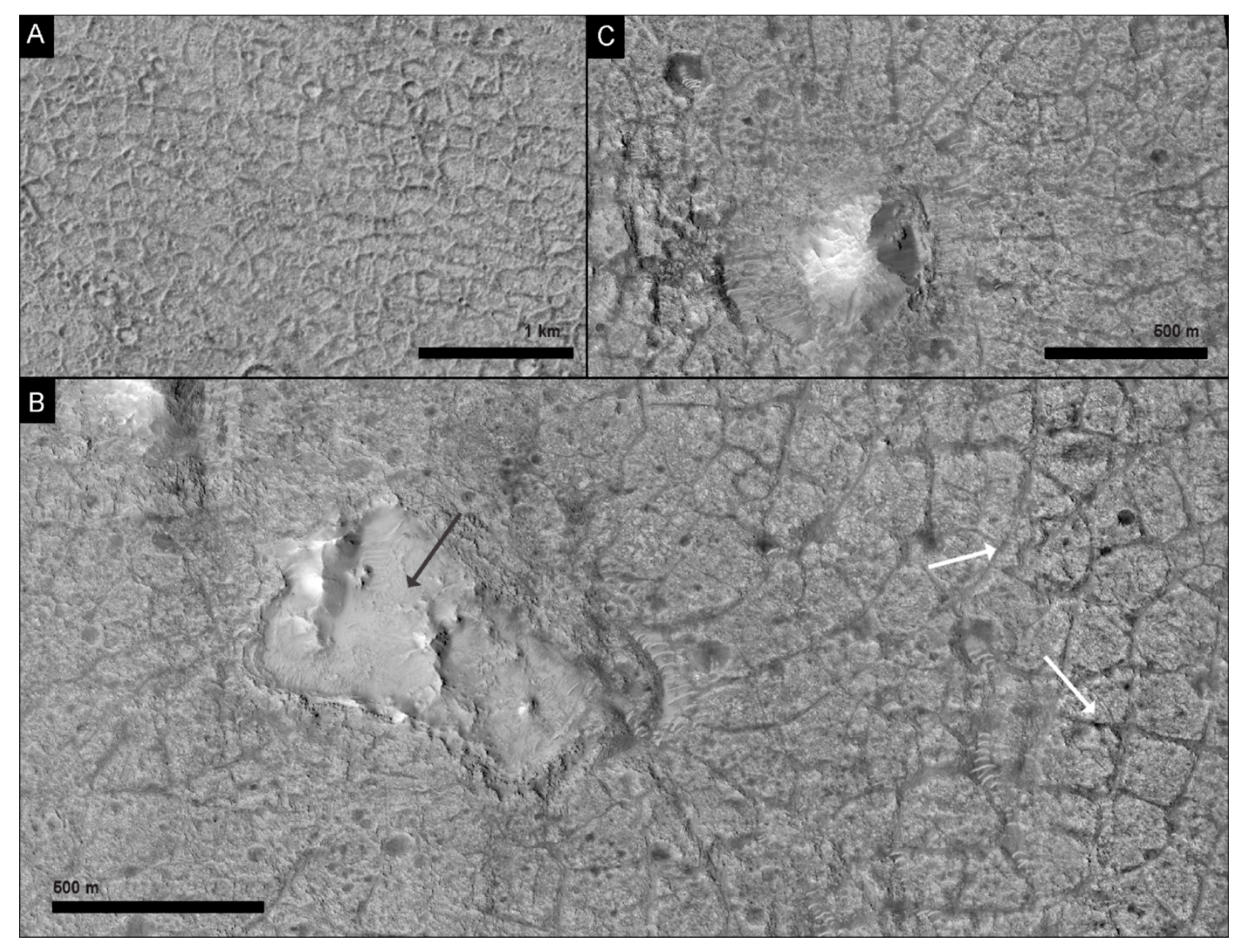
4.2. Chaos Terrain
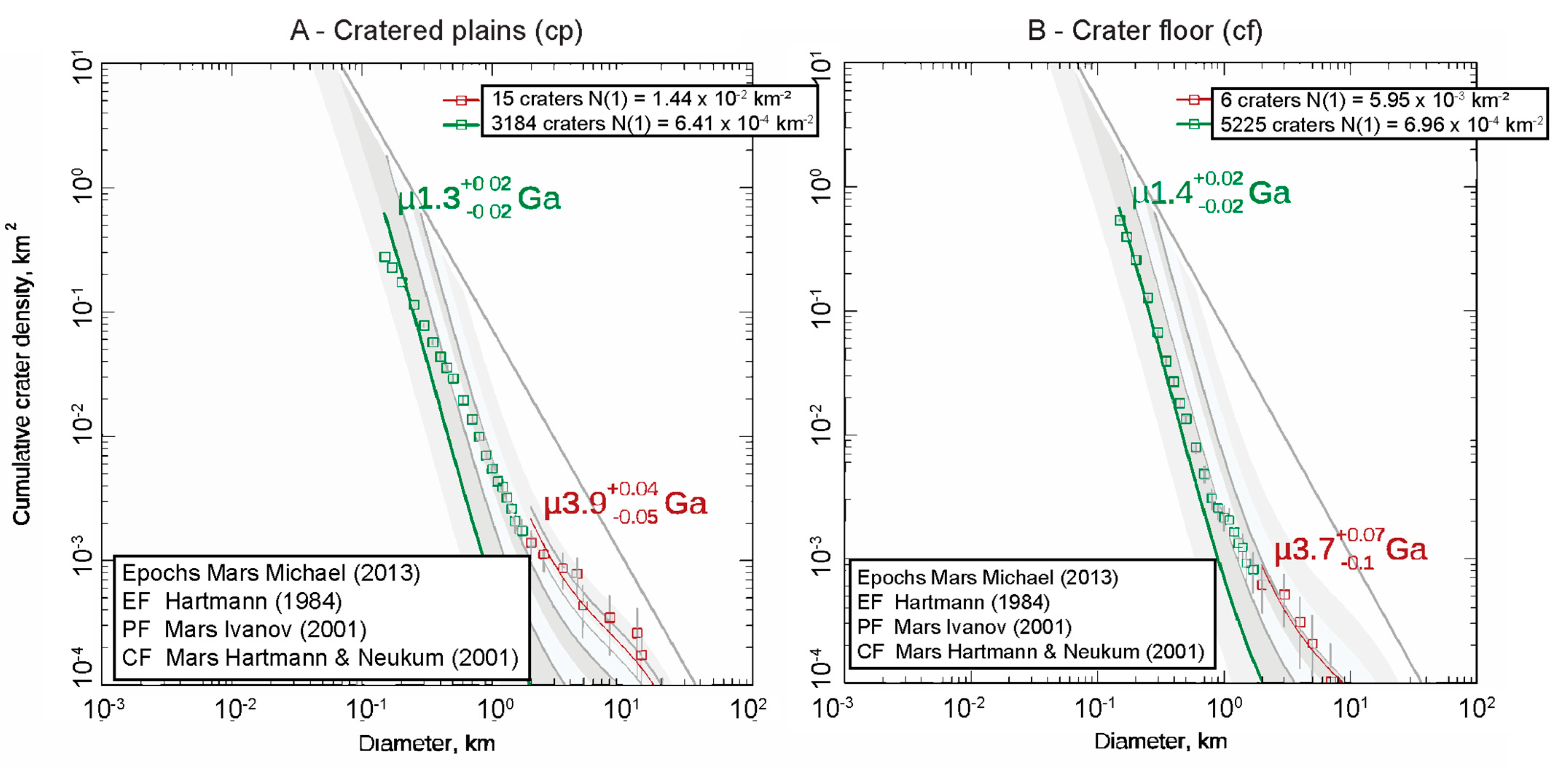
4.3. Impact Crater Chronology
5. Discussion
5.1. Inconsistency with Previously Proposed Chaos Formation Mechanisms
5.2. Subaqueous Mass Flow Analogs for Chaos Terrain on Earth
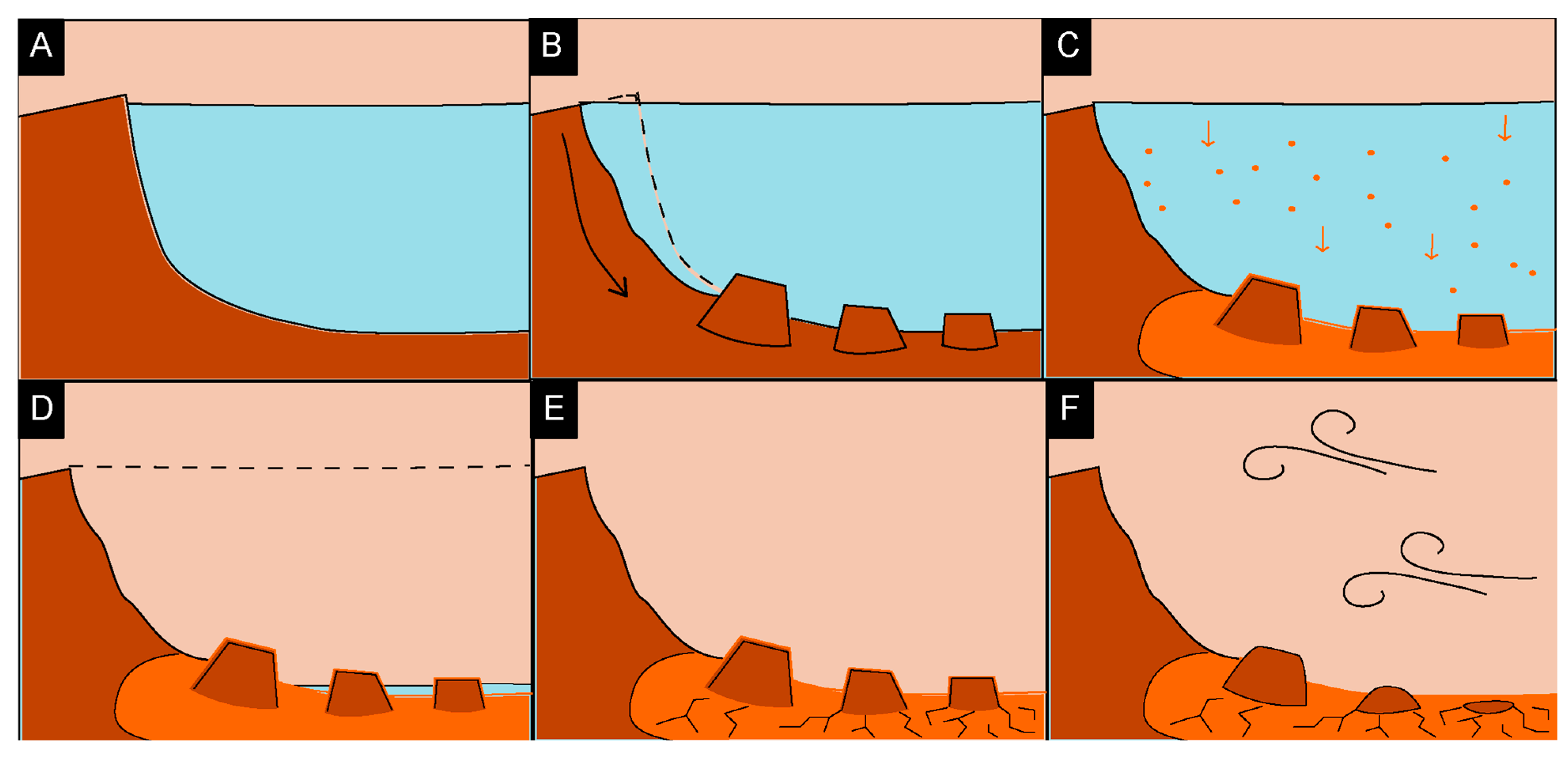
5.3. History of Formation
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Breed, C.S.; Grolier, M.J.; McCauley, J.F. Morphology and distribution of common “sand” dunes on Mars—Comparison with the earth. J. Geophys. Res. 1979, 84, 8183–8204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newsom, H.E.; Brittelle, G.E.; Hibbitts, C.A.; Crossey, L.J.; Kudo, A.M. Impact crater lakes on Mars. J. Geophys. Res. Planets 1996, 101, 14951–14955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, M.A.; Netoff, D.I. A terrestrial weathering and wind abrasion analog for mound and moat morphology of Gale crater, Mars. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2017, 44, 4000–4007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharp, R.P.; Soderblom, L.A.; Murray, B.C.; Cutts, J.A. The surface of Mars 2. Uncratered terrains. J. Geophys. Res. 1971, 76, 331–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sharp, R.P. Mars: Fretted and chaotic terrains. J. Geophys. Res. 1973, 78, 4073–4083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Glotch, T.D.; Christensen, P.R. Geologic and mineralogic mapping of Aram Chaos: Evidence for a water-rich history. J. Geophys. Res. Planets 2005, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meresse, S.; Costard, F.; Mangold, N.; Masson, P.; Neukum, G. Formation and evolution of the chaotic terrains by subsidence and magmatism: Hydraotes Chaos, Mars. Icarus 2008, 194, 487–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nummedal, D.; Prior, D.B. Generation of Martian chaos and channels by debris flows. Icarus 1981, 45, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, J.A.P.; Sasaki, S.; Kuzmin, R.O.; Dohm, J.M.; Tanaka, K.L.; Miyamoto, H.; Kurita, K.; Komatsu, G.; Fairén, A.G.; Ferris, J.C. Outflow channel sources, reactivation, and chaos formation, Xanthe Terra, Mars. Icarus 2005, 175, 36–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carr, M.H. Formation of Martian flood features by release of water from confined aquifers. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 1979, 84, 2995–3007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, G.B.M.; Head III, J.W. Chaos formation by sublimation of volatile-rich substrate: Evidence from Galaxias Chaos, Mars. Icarus 2011, 211, 316–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warner, N.H.; Gupta, S.; Kim, J.-R.; Muller, J.-P.; Le Corre, L.; Morley, J.; Lin, S.-Y.; McGonigle, C. Constraints on the origin and evolution of Iani Chaos, Mars. J. Geophys. Res. Planets 2011, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leask, H.J.; Wilson, L.; Mitchell, K.L. Formation of Aromatum Chaos, Mars: Morphological development as a result of volcano-ice interactions. J. Geophys. Res. Planets 2006, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rodriguez, J.A.P.; Sasaki, S.; Miyamoto, H. Nature and hydrological relevance of the Shalbatana complex underground cavernous system. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2003, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Manga, M.; Wong, A. Floods on Mars released from groundwater by impact. Icarus 2005, 175, 551–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luzzi, E.; Rossi, A.P.; Massironi, M.; Pozzobon, R.; Maestrelli, D.; Corti, G. Chaotic Caldera collapse: A new interpretation for the origin of Chaotic terrains on Mars. In EGU General Assembly Conference Abstracts; European Geophysical Union: Vienna Austria, 2020; p. 11071. [Google Scholar]
- Zegers, T.E.; Oosthoek, J.H.P.; Rossi, A.P.; Blom, J.K.; Schumacher, S. Melt and collapse of buried water ice: An alternative hypothesis for the formation of chaotic terrains on Mars. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2010, 297, 496–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, M.G.; Tanaka, K.L. Related Magma–Ice Interactions: Possible Origins of Chasmata, Chaos, and Surface Materials in Xanthe, Margaritifer, and Meridiani Terrae, Mars. Icarus 2002, 155, 324–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kargel, J.S.; Furfaro, R.; Prieto-Ballesteros, O.; Rodriguez, J.A.P.; Montgomery, D.R.; Gillespie, A.R.; Marion, G.M.; Wood, S.E. Martian hydrogeology sustained by thermally insulating gas and salt hydrates. Geology 2007, 35, 975–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melosh, H.J.; Ivanov, B.A. Impact Crater Collapse. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 1999, 27, 385–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barlow, N.G.; Boyce, J.M.; Costard, F.M.; Craddock, R.A.; Garvin, J.B.; Sakimoto, S.E.H.; Kuzmin, R.O.; Roddy, D.J.; Soderblom, L.A. Standardizing the nomenclature of Martian impact crater ejecta morphologies. J. Geophys. Res. Planets 2000, 105, 26733–26738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tanaka, K.L.; Skinner, J.A., Jr.; Dohm, J.M.; Irwin, R.P., III; Kolb, E.J.; Fortezzo, C.M.; Platz, T.; Michael, G.G.; Hare, T.M. Geologic Map of Mars: U.S. Geological Survey Scientific Investigations Map 3292, Scale 1:20,000,000, Pamphlet 43 p; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2014.
- Coleman, N. Hydrographs of a Martian flood from the breach of Galilaei Crater. Geomorphology 2015, 236, 90–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malin, M.C.; Bell, J.F.; Cantor, B.A.; Caplinger, M.A.; Calvin, W.M.; Clancy, R.T.; Edgett, K.S.; Edwards, L.; Haberle, R.M.; James, P.B.; et al. Context Camera Investigation on board the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter. J. Geophys. Res. Planets 2007, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dickson, J.L.; Kerber, L.A.; Fassett, C.I.; Ehlmann, B.L. A Global, Blended CTX Mosaic of Mars with Vectorized Seam Mapping: A New Mosaicking Pipeline Using Principles of Non-Destructive Image Editing. In Lunar and Planetary Science Conference; Lunar and Planetary Institute: The Woodlands, TX, USA, 2018; Volume 49, pp. 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- McEwen, A.S.; Eliason, E.M.; Bergstrom, J.W.; Bridges, N.T.; Hansen, C.J.; Delamere, W.A.; Grant, J.A.; Gulick, V.C.; Herkenhoff, K.E.; Keszthelyi, L.; et al. Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter’s High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment (HiRISE). J. Geophys. Res. Planets 2007, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smith, D.E.; Zuber, M.T.; Frey, H.V.; Garvin, J.B.; Head, J.W.; Muhleman, D.O.; Pettengill, G.H.; Phillips, R.J.; Solomon, S.C.; Zwally, H.J. Mars Orbiter Laser Altimeter: Experiment summary after the first year of global mapping of Mars. J. Geophys. Res. Planets 2001, 106, 23689–23722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neukum, G.; Jaumann, R. HRSC: The high resolution stereo camera of Mars Express. In Mars Express: The Scientific Payload; Andrew Wilson, A., Ed.; ESA Publications Division: Noordwijk, The Netherlands, 2004; Volume 1240, pp. 17–35. [Google Scholar]
- Murchie, S.; Arvidson, R.; Bedini, P.; Beisser, K.; Bibring, J.; Bishop, J.; Boldt, J.; Cavender, P.; Choo, T.; Clancy, R.T. Compact reconnaissance imaging spectrometer for Mars (CRISM) on Mars reconnaissance orbiter (MRO). J. Geophys. Res. Planets 2007, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michael, G.G.; Neukum, G. Planetary surface dating from crater size–frequency distribution measurements: Partial resurfacing events and statistical age uncertainty. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2010, 294, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michael, G.G.; Platz, T.; Kneissl, T.; Schmedemann, N. Planetary surface dating from crater size–frequency distribution measurements: Spatial randomness and clustering. Icarus 2012, 218, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michael, G.G. Planetary surface dating from crater size–frequency distribution measurements: Multiple resurfacing episodes and differential isochron fitting. Icarus 2013, 226, 885–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neukum, G.; Ivanov, B.A. Crater production function for Mars. In Lunar and Planetary Science Conference; Lunarand Planetary Institute: Woodlands, TX, USA, 2001; Volume 32. [Google Scholar]
- Hartmann, W.K.; Neukum, G. Cratering chronology and the evolution of Mars. Space Sci. Rev. 2001, 96, 165–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, B.A. Mars/Moon Cratering Rate Ratio Estimates BT—Chronology and Evolution of Mars; Kallenbach, R., Geiss, J., Hartmann, W.K., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2001; pp. 87–104. [Google Scholar]
- Hartmann, W.K. Does crater “saturation equilibrium” occur in the solar system? Icarus 1984, 60, 56–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platz, T.; Michael, G.; Tanaka, K.L.; Skinner, J.A.; Fortezzo, C.M. Crater-based dating of geological units on Mars: Methods and application for the new global geological map. Icarus 2013, 225, 806–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, W.K.; Daubar, I.J. Martian cratering 11. Utilizing decameter scale crater populations to study Martian history. Meteorit. Planet. Sci. 2017, 52, 493–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustard, J.F.; Murchie, S.L.; Pelkey, S.M.; Ehlmann, B.L.; Milliken, R.E.; Grant, J.A.; Bibring, J.P.; Poulet, F.; Bishop, J.; Dobrea, E.N.; et al. Hydrated silicate minerals on mars observed by the Mars reconnaissance orbiter CRISM instrument. Nature 2008, 454, 305–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fraeman, A.A.; Johnson, J.R.; Arvidson, R.E.; Rice, M.S.; Wellington, D.F.; Morris, R.V.; Fox, V.K.; Horgan, B.H.N.; Jacob, S.R.; Salvatore, M.R. Synergistic ground and orbital observations of iron oxides on Mt. Sharp and Vera Rubin ridge. J. Geophys. Res. Planets 2020, 125, e2019JE006294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ceamanos, X.; Douté, S.; Fernando, J.; Schmidt, F.; Pinet, P.; Lyapustin, A. Surface reflectance of Mars observed by CRISM/MRO: 1. Multi-angle Approach for Retrieval of Surface Reflectance from CRISM observations (MARS-ReCO). J. Geophys. Res. Planets 2013, 118, 514–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Balme, M.; Berman, D.C.; Bourke, M.C.; Zimbelman, J.R. Transverse Aeolian Ridges (TARs) on Mars. Geomorphology 2008, 101, 703–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Berman, D.C.; Balme, M.R.; Rafkin, S.C.R.; Zimbelman, J.R. Transverse aeolian ridges (TARs) on Mars II: Distributions, orientations, and ages. Icarus 2011, 213, 116–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, W.K. Martian cratering III: Theory of crater obliteration. Icarus 1971, 15, 410–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, C.R.; Jones, K.L. Cratering and obliteration history of Mars. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 1977, 5, 515–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.R.; Gillespie, D.R.; Montgomery, M.R. Efect of obliteration on crater-count chronologies for Martian surfaces. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Daubar, I.J.; McEwen, A.S.; Byrne, S.; Kennedy, M.R.; Ivanov, B. The current martian cratering rate. Icarus 2013, 225, 506–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hampton, M.A.; Lee, H.J.; Locat, J. Submarine landslides. Rev. Geophys. 1996, 34, 33–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Locat, J.; Lee, H.J. Submarine landslides: Advances and challenges. Can. Geotech. J. 2002, 39, 193–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Locat, J.; Lee, H.J.; Locat, P.; Imran, J. Numerical analysis of the mobility of the Palos Verdes debris avalanche, California, and its implication for the generation of tsunamis. Mar. Geol. 2004, 203, 269–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.J.; Kayen, R.E.; Gardner, J.V.; Locat, J. Characteristics of several tsunamigenic submarine landslides. In Submarine Mass Movements and Their Consequences; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2003; pp. 357–366. [Google Scholar]
- Clague, D.A.; Moore, J.G. The proximal part of the giant submarine Wailau landslide, Molokai, Hawaii. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 2002, 113, 259–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, J.G.; Clague, D.A. Mapping the Nuuanu and Wailau landslides in Hawaii. Washingt. DC Am. Geophys. Union Geophys. Monogr. Ser. 2002, 128, 223–244. [Google Scholar]
- Satake, K.; Smith, J.R.; Shinozaki, K. Three-Dimensional Reconstruction and Tsunami Model of the Nuuanu and Wailau Giant Landslides, Hawaii. Hawaii Volcanoes Deep Underw. Perspect. 2002, 128, 333–346. [Google Scholar]
- Moore, J.G.; Normark, W.R.; Holcomb, R.T. Giant hawaiian landslides. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 1994, 22, 119–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Normark, W.R.; Moore, J.G.; Torresan, M.E. Giant volcano-related landslides and the development of the Hawaiian Islands. In Submarine Landslides: Selected Studies in the US Exclusive Economic Zone; Geological Survey Bulletin US: Denver, CO, USA, 1993; Volume 2002, pp. 184–196. [Google Scholar]
- Wessel, P.; Luis, J.F.; Uieda, L.; Scharroo, R.; Wobbe, F.; Smith, W.H.F.; Tian, D. The generic mapping tools version 6. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 2019, 20, 5556–5564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carlson, P.R. Holocene slump on continental shelf off Malaspina Glacier, Gulf of Alaska. Am. Assoc. Pet. Geol. Bull. 1978, 62, 2412–2426. [Google Scholar]
- Coleman, J.M.; Prior, D.B.; Garrison, L.E. Submarine landslides in the Mississippi River delta. In Offshore Technology Conference; OnePetro: Houston, TX, USA, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- McAdoo, B.G.; Pratson, L.F.; Orange, D.L. Submarine landslide geomorphology, US continental slope. Mar. Geol. 2000, 169, 103–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craddock, R.A.; Maxwell, T.A.; Howard, A.D. Crater morphometry and modification in the Sinus Sabaeus and Margaritifer Sinus regions of Mars. J. Geophys. Res. Planets 1997, 102, 13321–13340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Forsberg-Taylor, N.K.; Howard, A.D.; Craddock, R.A. Crater degradation in the Martian highlands: Morphometric analysis of the Sinus Sabaeus region and simulation modeling suggest fluvial processes. J. Geophys. Res. Planets 2004, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipman, P.W.; Normark, W.R.; Moore, J.G.; Wilson, J.B.; Gutmacher, C.E. The giant submarine alika debris slide, Mauna Loa, Hawaii. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 1988, 93, 4279–4299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Masson, D.G.; Harbitz, C.B.; Wynn, R.B.; Pedersen, G.; Løvholt, F. Submarine landslides: Processes, triggers and hazard prediction. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2006, 364, 2009–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nizam, N.; Divola, C.; Day, M.; Yin, A.; Moon, S. Development of Chaos Terrain as Subaqueous Slide Blocks in Galilaei Crater, Mars. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1998. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14091998
Nizam N, Divola C, Day M, Yin A, Moon S. Development of Chaos Terrain as Subaqueous Slide Blocks in Galilaei Crater, Mars. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(9):1998. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14091998
Chicago/Turabian StyleNizam, Nabila, Claire Divola, Mackenzie Day, An Yin, and Seulgi Moon. 2022. "Development of Chaos Terrain as Subaqueous Slide Blocks in Galilaei Crater, Mars" Remote Sensing 14, no. 9: 1998. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14091998
APA StyleNizam, N., Divola, C., Day, M., Yin, A., & Moon, S. (2022). Development of Chaos Terrain as Subaqueous Slide Blocks in Galilaei Crater, Mars. Remote Sensing, 14(9), 1998. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14091998





