Spatiotemporal Analysis of NO2 Production Using TROPOMI Time-Series Images and Google Earth Engine in a Middle Eastern Country
Abstract
1. Introduction
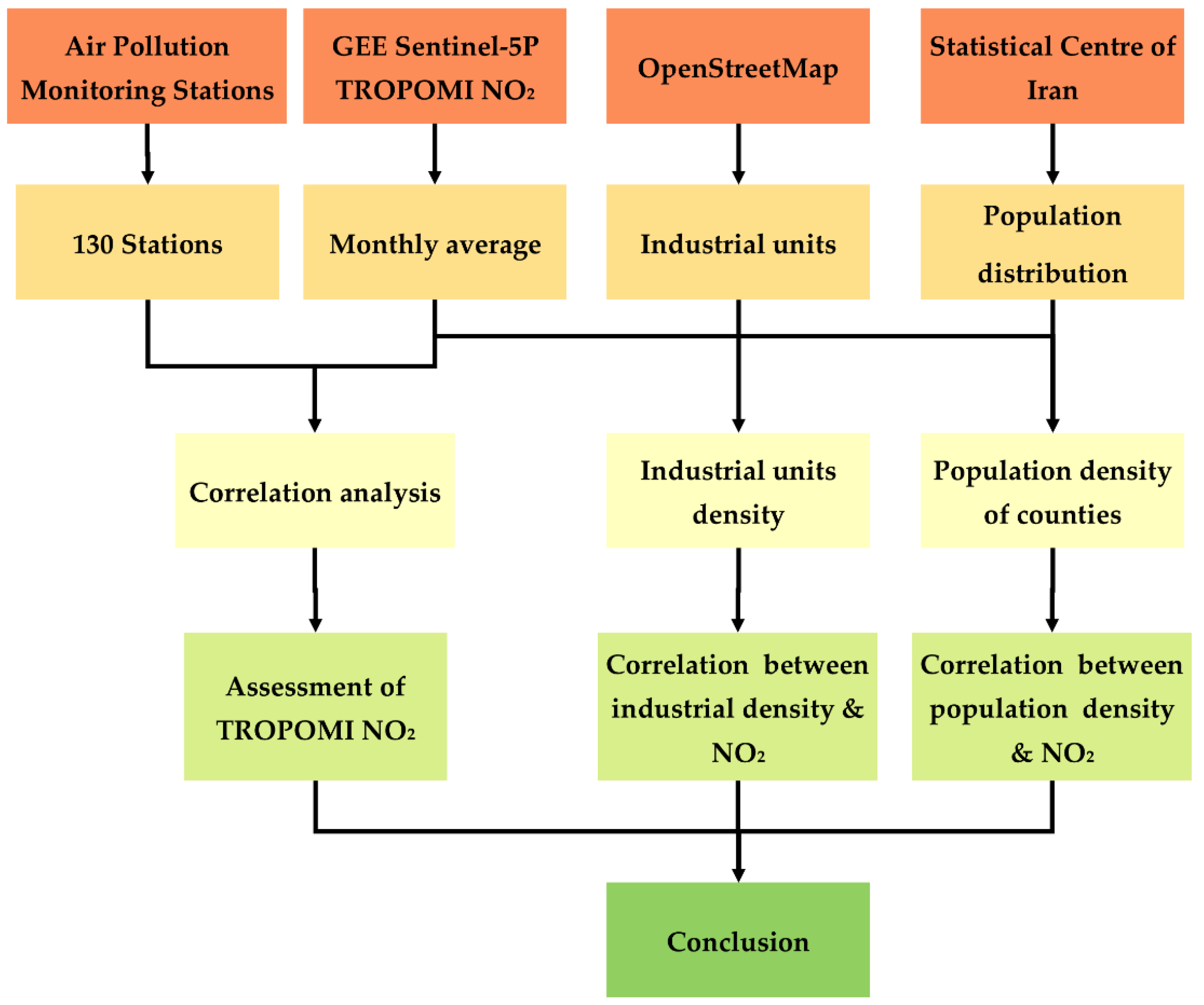
2. Materials and Methods
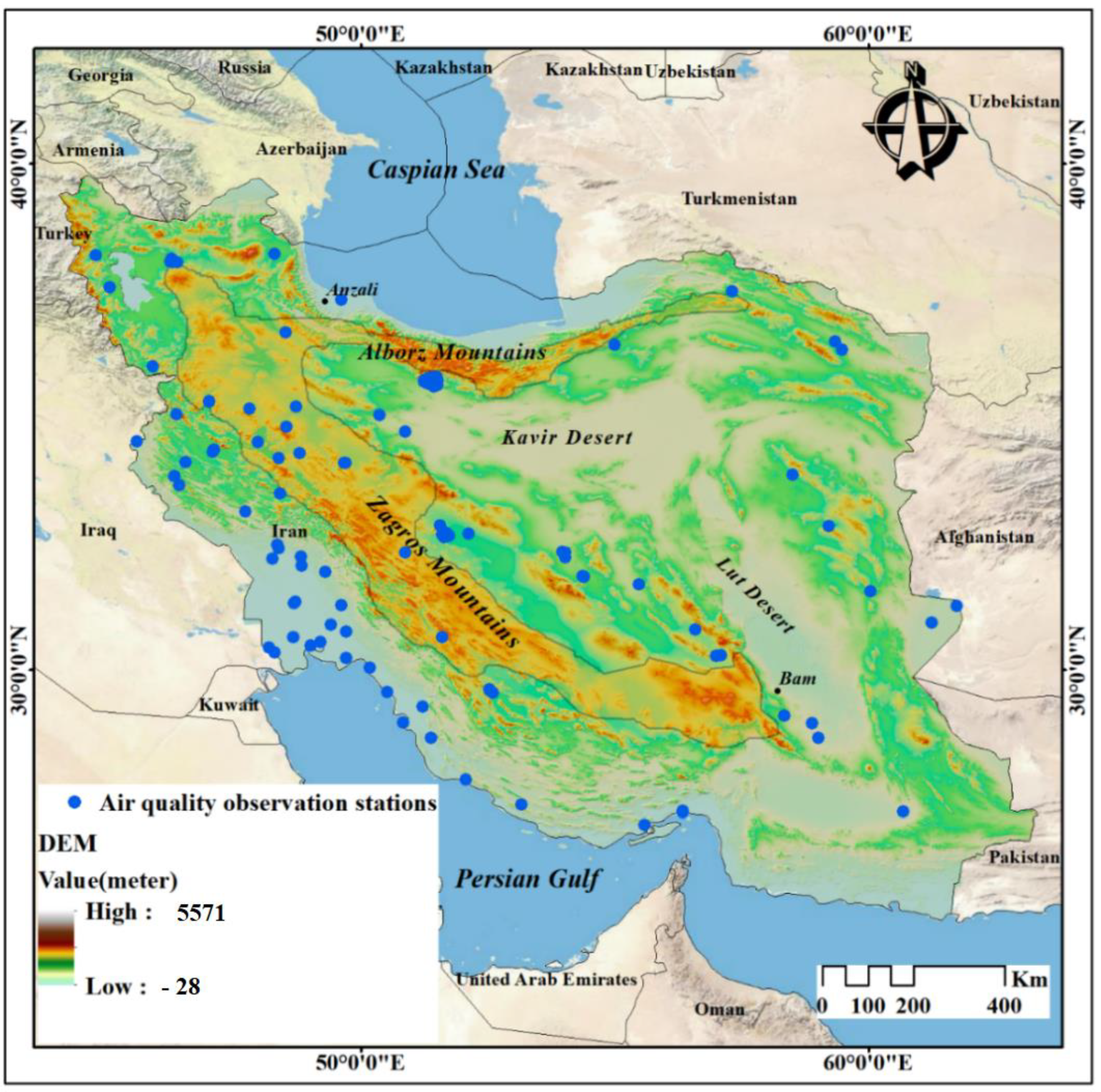
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Description
2.2.1. TROPOMI (S5P)
2.2.2. Ground Air Quality Data
2.3. NO2 Retrieval Using TROPOMI
2.4. Accuracy Assessment
3. Results
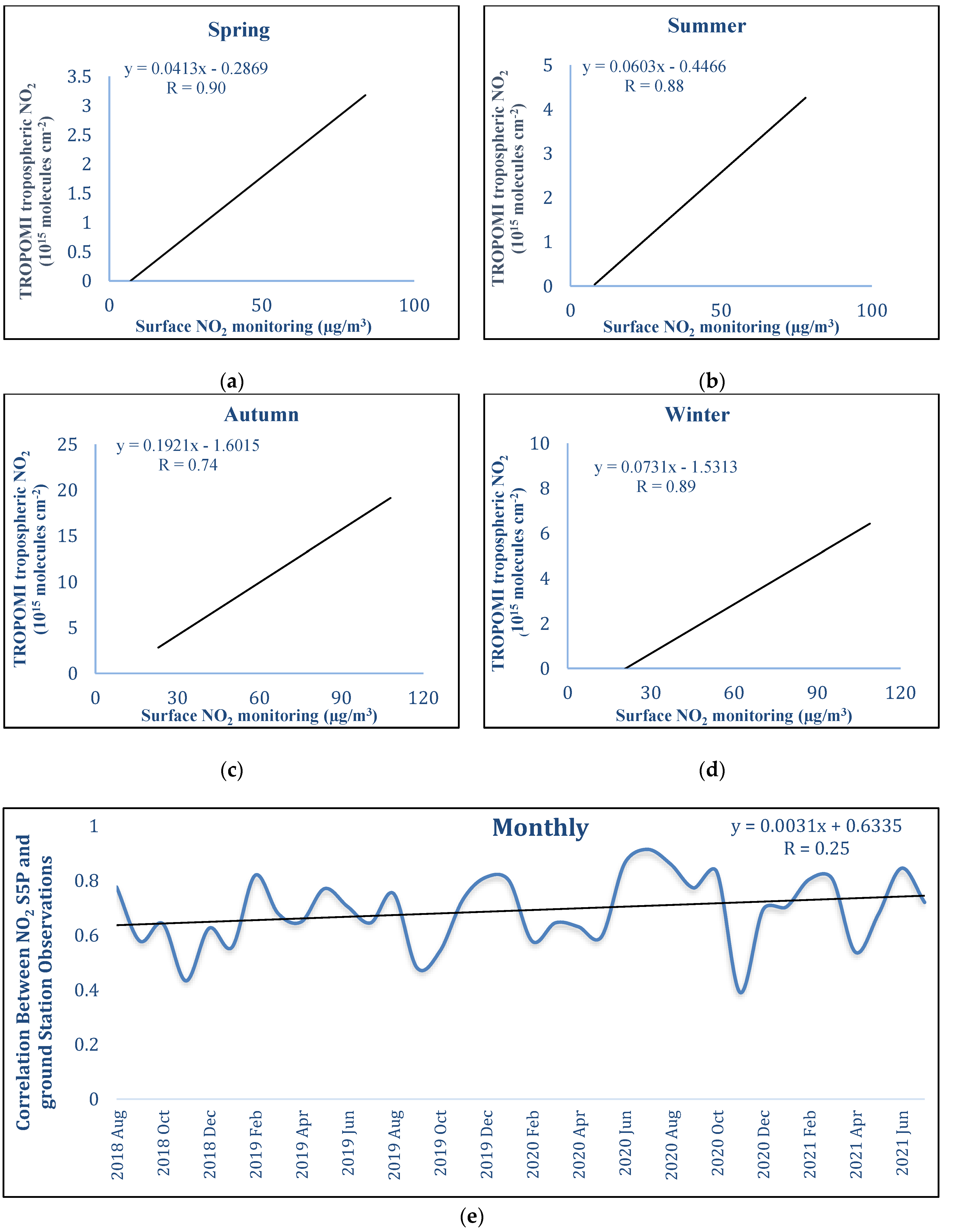
3.1. Correlation between NO2 Surface Concentration (APMS) and TROPOMI NO2
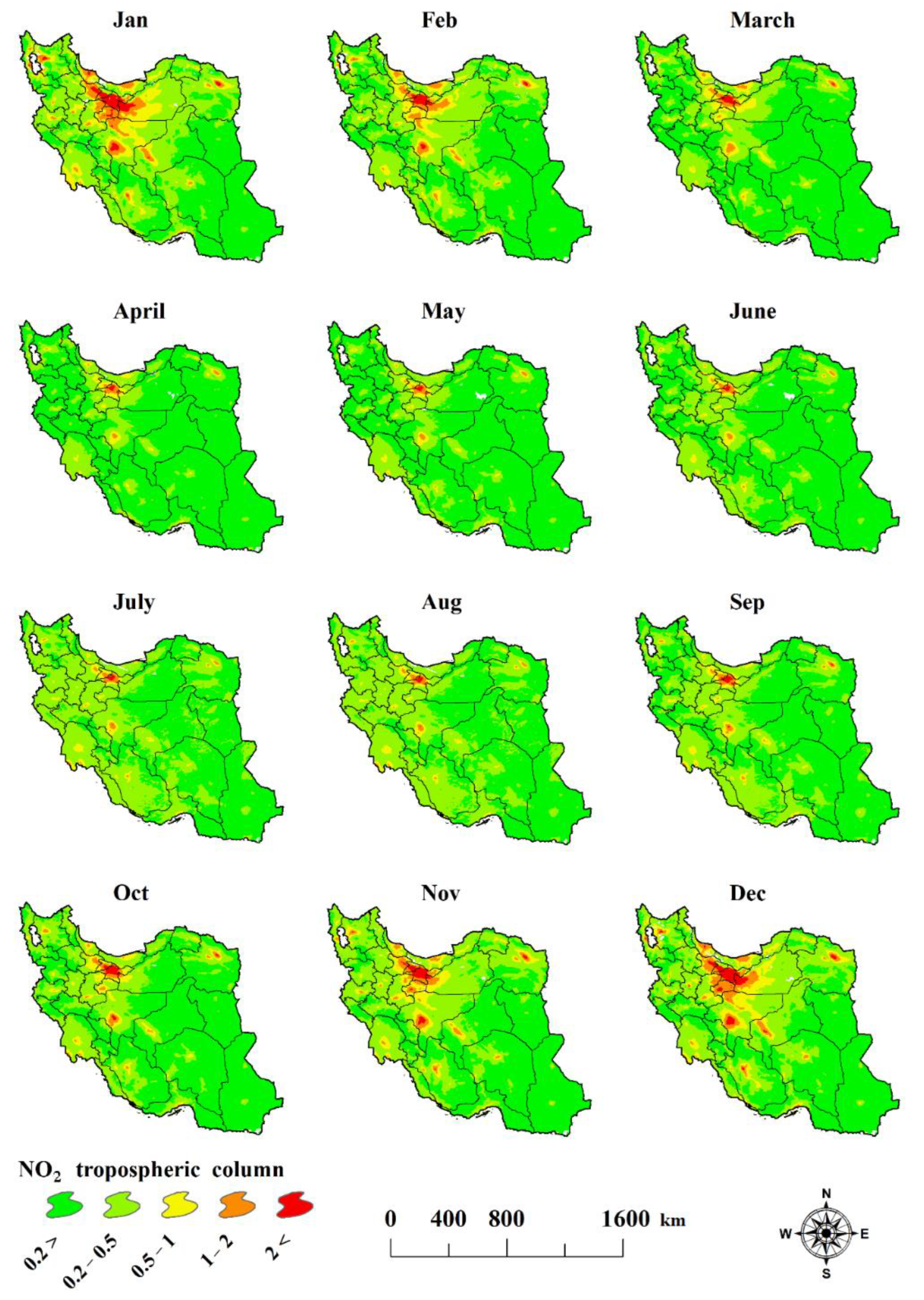
3.2. Spatiotemporal Characteristics of Tropospheric NO2 Columns
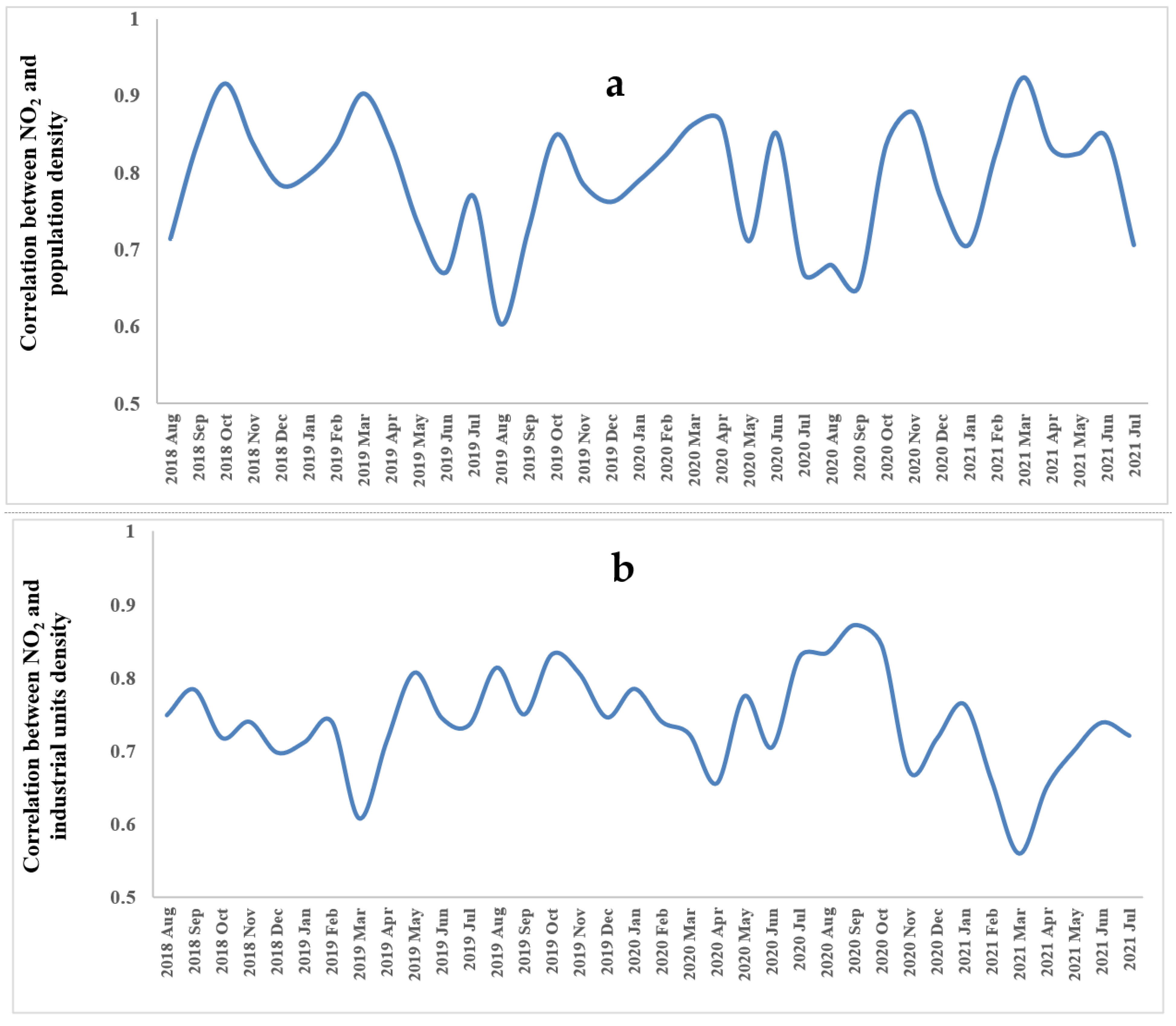
3.3. Correlation Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- (a)
- Monthly fluctuations of the tropospheric NO2 column concentration over the study area are significant;
- (b)
- The pattern of spatial changes in NO2 concentration in the troposphere shows that the amount of NO2 gaseous air pollutants in the study area’s northern part is more than in the central and southern regions;
- (c)
- The results show that about 15% of the population of Iran (about 13 million people) who live in 0.5% of the total area of Iran live in areas with severe air pollution.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AQG | Air quality guideline |
| AQMO | Air quality monitoring organization |
| APEX | Airborne PRISM experiment |
| CO2 | Carbon dioxide |
| CO | Carbon monoxide |
| DEM | Digital elevation model |
| ESA | European Space Agency |
| GEE | Google Earth Engine |
| GOME | Global Ozone Monitoring Experiment |
| HCHO | Formaldehyde |
| HNO3 | Nitric acid |
| NO2 | Nitrogen dioxide |
| O3 | Ozone |
| OMI | Ozone Monitoring Instrument |
| OSM | OpenStreetMap |
| RS | Remote sensing |
| SCIAMACHY | Scanning Imaging Absorption Spectrometer for Atmospheric Cartography |
| S5P | Sentinel-5P |
| SNR | Signal-to-noise-ratio |
| SO2 | Sulfur dioxide |
| TROPOMI | Tropospheric Monitoring Instrument |
| VOCS | Volatile organic compounds |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
References
- World Health Organization. Report of the Regional Director: The Work of WHO/Europe in 2019–2020; World Health Organization, Regional Office for Europe: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020.
- Begum, A.; Ramaiah, M.; Khan, I.; Veena, K. Analysis of heavy metals concentration in soil and litchens from various localities of Hosur road, Bangalore, India. E-J. Chem. 2009, 6, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitas, M.; Costa, N.; Rodrigues, M.; Marques, J.; Da Silva, M.V. Lichens as bio indicators of atmospheric pollution in Porto, Portugal. J. Biodivers. Ecol. Sci. 2011, 1, 29–39. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, A.J.; Anderson, H.R.; Ostro, B.; Pandey, K.D.; Krzyzanowski, M.; Künzli, N.; Gutschmidt, K.; Pope III, C.A.; Romieu, I.; Samet, J.M. Urban air pollution. In Comparative Quantification of Health Risks: Global and Regional Burden of Disease Attributable to Selected Major Risk Factors; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2004; Volume 2, pp. 1353–1433. [Google Scholar]
- Bernard, S.M.; Samet, J.M.; Grambsch, A.; Ebi, K.L.; Romieu, I. The potential impacts of climate variability and change on air pollution-related health effects in the United States. Environ. Health Perspect. 2001, 109, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hou, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, S.; Liu, W.; Zhu, J. Analysis of the tropospheric column nitrogen dioxide over China based on satellite observations during 2008–2017. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2019, 10, 651–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diao, B.; Ding, L.; Su, P.; Cheng, J. The spatial-temporal characteristics and influential factors of NOx emissions in China: A spatial econometric analysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bell, J.N.B.; Treshow, M. Air Pollution and Plant Life; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2002; ISBN 0471490911. [Google Scholar]
- Brunekreef, B.; Holgate, S.T. Air pollution and health. Lancet 2002, 360, 1233–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boersma, K.F.; Eskes, H.J.; Brinksma, E.J. Error analysis for tropospheric NO2 retrieval from space. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2004, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucsela, E.J.; Perring, A.E.; Cohen, R.C.; Boersma, K.F.; Celarier, E.A.; Gleason, J.F.; Wenig, M.O.; Bertram, T.H.; Wooldridge, P.J.; Dirksen, R. Comparison of tropospheric NO2 from in situ aircraft measurements with near-real-time and standard product data from OMI. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2008, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heue, K.-P.; Richter, A.; Bruns, M.; Burrows, J.P.; Friedeburg, C.v; Platt, U.; Pundt, I.; Wang, P.; Wagner, T. Validation of SCIAMACHY tropospheric NO2-columns with AMAXDOAS measurements. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2005, 5, 1039–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krotkov, N.A.; McLinden, C.A.; Li, C.; Lamsal, L.N.; Celarier, E.A.; Marchenko, S.V.; Swartz, W.H.; Bucsela, E.J.; Joiner, J.; Duncan, B.N. Aura OMI observations of regional SO2 and NO2 pollution changes from 2005 to 2015. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 4605–4629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, P.; Lahoz, W.A.; van der A, R. Recent satellite-based trends of tropospheric nitrogen dioxide over large urban agglomerations worldwide. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 1205–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Streets, D.G.; Yarber, K.F.; Woo, J.; Carmichael, G.R. Biomass burning in Asia: Annual and seasonal estimates and atmospheric emissions. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2003, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matos, E.P.; Reisen, V.A.; Serpa, F.S.; Filho, P.R.P.; De Fátima Silva Leite, M. Space-time analysis of the effect of air pollution on children’s health. Cad. Saude Publica 2019, 35, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viatte, C.; Petit, J.E.; Yamanouchi, S.; Van Damme, M.; Doucerain, C.; Germain-Piaulenne, E.; Gros, V.; Favez, O.; Clarisse, L.; Coheur, P.F.; et al. Ammonia and pm2.5 air pollution in paris during the 2020 covid lockdown. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadian, A.; Mobasheri, M.R.; Matkan, A.A. Distribution of atmospheric NO2 in the industrial cities using OMI and MODIS images (Case study: Tehran metropolis). Eng. J. Geospat. Inf. Technol. 2018, 6, 171–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mohammadi, S.; Balouei, F.; Haji, K.; Khaledi Darvishan, A.; Karydas, C.G. Country-scale spatio-temporal monitoring of soil erosion in Iran using the G2 model. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2021, 14, 1019–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alimohammadi, A.; Rabiei, H.R.; Firouzabadi, P.Z. A new approach for modeling uncertainty in remote sensing change detection process. In Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Geomatics, Gävle, Sweden, 7–9 June 2004; pp. 503–508. [Google Scholar]
- Alqurashi, A.F.; Kumar, L. Investigating the Use of Remote Sensing and GIS Techniques to Detect Land Use and Land Cover Change: A Review. Adv. Remote Sens. 2013, 2, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, A.; Bhat, M.S.; Maheen, M. Using Landsat satellite data for assessing the land use and land cover change in Kashmir valley. GeoJournal 2020, 85, 1529–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatta, B.; Saraswati, S.; Bandyopadhyay, D. Urban sprawl measurement from remote sensing data. Appl. Geogr. 2010, 30, 731–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabiei-Dastjerdi, H.; Amini, S.; McArdle, G.; Homayouni, S. City-region or city? That is the question: Modelling sprawl in Isfahan using geospatial data and technology. GeoJournal 2022, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabiei-Dastjerdi, H.; Matthews, S.A. Who gets what, where, and how much? Composite index of spatial inequality for small areas in Tehran. Reg. Sci. Policy Pract. 2021, 13, 191–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, R. V Satellite remote sensing of surface air quality. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 7823–7843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, J.; Sun, Y.; Zheng, F.; Ni, C.; Gui, K.; Zhang, X.; Jiang, W.; Liao, T. The spatial temporal variation and factor analysis of the tropospheric NO2 columns in the Sichuan Basin from 2005 to 2016. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2018, 9, 1157–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bechle, M.J.; Millet, D.B.; Marshall, J.D. Remote sensing of exposure to NO2: Satellite versus ground-based measurement in a large urban area. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 69, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, K.; Zhang, Q.; Li, S.; Li, Y.; Ge, W. Spatial–Temporal variations in NO2 and PM2. 5 over the Chengdu–Chongqing economic zone in china during 2005–2015 based on satellite remote sensing. Sensors 2018, 18, 3950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popp, C.; Brunner, D.; Damm, A.; Buchmann, B. Mapping of high resolution nitrogen dioxide vertical column densities with the Airborne Prism EXperiment (APEX) imaging spectrometer over Zurich, Switzerland. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Munich, Germany, 22–27 July 2012; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 3646–3649. [Google Scholar]
- Ting, W.; Pu-Cai, W.; Hendrick, F.; Huan, Y.U.; Van Roozendael, M. The spatial and temporal variability of tropospheric NO2 during 2005–14 over China observed by the OMI. Atmos. Ocean. Sci. Lett. 2015, 8, 392–396. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, C.; Ju, T.; Wang, Q.; Li, F.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, G. Spatiotemporal variations of tropospheric NO2 in Lanzhou for the period 2009–2018 based on satellite remote sensing. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Judd, L.M.; Al-Saadi, J.A.; Szykman, J.J.; Valin, L.C.; Janz, S.J.; Kowalewski, M.G.; Eskes, H.J.; Pepijn Veefkind, J.; Cede, A.; Mueller, M.; et al. Evaluating Sentinel-5P TROPOMI tropospheric NO2 column densities with airborne and Pandora spectrometers near New York City and Long Island Sound. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2020, 13, 6113–6140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharytonov, M.M.; Khlopova, V.M.; Stankevich, S.A.; Titarenko, O.V. Remote and ground-based sensing of air polluted by nitrogen dioxide in the Dnepropetrovsk region (Ukraine). In Disposal of Dangerous Chemicals in Urban Areas and Mega Cities; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 291–298. [Google Scholar]
- Popp, C.; Brunner, D.; Damm, A.; Van Roozendael, M.; Fayt, C.; Buchmann, B. High-resolution NO2 remote sensing from the Airborne Prism EXperiment (APEX) imaging spectrometer. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2012, 5, 2211–2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Liu, H.; Geng, G.; Hong, C.; Liu, F.; Song, Y.; Tong, D.; Zheng, B.; Cui, H.; Man, H. Anthropogenic emission inventories in China: A review. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2017, 4, 834–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der A, R.J.; Peters, D.; Eskes, H.; Boersma, K.F.; Van Roozendael, M.; De Smedt, I.; Kelder, H.M. Detection of the trend and seasonal variation in tropospheric NO2 over China. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2006, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, V.; Shahbazi, H. Urban air pollution in Iran. Iran. Stud. 2016, 49, 1029–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorani-Azam, A.; Riahi-Zanjani, B.; Balali-Mood, M. Effects of air pollution on human health and practical measures for prevention in Iran. J. Res. Med. Sci. Off. J. Isfahan Univ. Med. Sci. 2016, 21, 65. [Google Scholar]
- Shahsavani, A.; Naddafi, K.; Haghighifard, N.J.; Mesdaghinia, A.; Yunesian, M.; Nabizadeh, R.; Arahami, M.; Sowlat, M.H.; Yarahmadi, M.; Saki, H. The evaluation of PM10, PM2. 5, and PM1 concentrations during the Middle Eastern Dust (MED) events in Ahvaz, Iran, from April through September 2010. J. Arid. Environ. 2012, 77, 72–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Showstack, R. Sentinel satellites initiate new era in earth observation. EOS 2014, 95, 239–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, M.; Moreno, J.; Johannessen, J.A.; Levelt, P.F.; Hanssen, R.F. ESA’s sentinel missions in support of Earth system science. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 120, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guanter, L.; Aben, I.; Tol, P.; Krijger, J.M.; Hollstein, A.; Köhler, P.; Damm, A.; Joiner, J.; Frankenberg, C.; Landgraf, J. Potential of the TROPOspheric Monitoring Instrument (TROPOMI) onboard the Sentinel-5 Precursor for the monitoring of terrestrial chlorophyll fluorescence. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2015, 8, 1337–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansouri Daneshvar, M.R.; Ebrahimi, M.; Nejadsoleymani, H. An overview of climate change in Iran: Facts and statistics. Environ. Syst. Res. 2019, 8, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köhler, P.; Frankenberg, C.; Magney, T.S.; Guanter, L.; Joiner, J.; Landgraf, J. Global retrievals of solar-induced chlorophyll fluorescence with TROPOMI: First results and intersensor comparison to OCO-2. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2018, 45, 10–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, J.; Vollmer, B.; Ostrenga, D.; Gerasimov, I. Air quality satellite monitoring by TROPOMI on Sentinel-5P. In Proceedings of the AGU Fall Meeting 2018, Washington, DC, USA, 10–14 December 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Borsdorff, T.; Pandey, S.; Hasekamp, O.; Aben, I.; Houweling, S.; Landgraf, J. Carbon monoxide air pollution on sub-city scales and along arterial roads detected by the Tropospheric Monitoring Instrument. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 3579–3588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veefkind, J.P.; Aben, I.; McMullan, K.; Förster, H.; De Vries, J.; Otter, G.; Claas, J.; Eskes, H.J.; De Haan, J.F.; Kleipool, Q. TROPOMI on the ESA Sentinel-5 Precursor: A GMES mission for global observations of the atmospheric composition for climate, air quality and ozone layer applications. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 120, 70–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zhang, X.; Xu, W.; Liu, X.; Lu, X.; Wei, J.; Li, Y.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Wong, A.Y.H. Reviewing global estimates of surface reactive nitrogen concentration and deposition using satellite retrievals. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 8641–8658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Geffen, J.; Folkert Boersma, K.; Eskes, H.; Sneep, M.; Ter Linden, M.; Zara, M.; Pepijn Veefkind, J. S5P TROPOMI NO2 slant column retrieval: Method, stability, uncertainties and comparisons with OMI. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2020, 13, 1315–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Congalton, R.G. Accuracy assessment and validation of remotely sensed and other spatial information. Int. J. Wildland Fire 2001, 10, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Fei, F.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, B.; Jiao, H.; Zhang, L. SatCNN: Satellite image dataset classification using agile convolutional neural networks. Remote Sens. Lett. 2016, 8, 136–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huijnen, V.; Eskes, H.J.; Poupkou, A.; Elbern, H.; Boersma, K.F.; Foret, G.; Sofiev, M.; Valdebenito, A.; Flemming, J.; Stein, O. Comparison of OMI NO2 tropospheric columns with an ensemble of global and European regional air quality models. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 3273–3296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramer, L.J.; Leigh, R.J.; Remedios, J.J.; Monks, P.S. Comparison of OMI and ground-based in situ and MAX-DOAS measurements of tropospheric nitrogen dioxide in an urban area. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2008, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.-H.K.; Qiu, C.; Schmitt, M.; Zhu, X.X.; Sabel, C.E.; Prishchepov, A.V. Mapping horizontal and vertical urban densification in Denmark with Landsat time-series from 1985 to 2018: A semantic segmentation solution. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 251, 112096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Lindqvist, H.; Liu, Q.; Wang, K.; Wang, L. Estimating the spatial and temporal variability of the ground-level NO2 concentration in China during 2005–2019 based on satellite remote sensing. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2020, 12, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Yang, Z.; Wu, Z.; Marinello, F. Spatial variation of NO2 and its impact factors in China: An application of sentinel-5P products. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Zhan, Y.; Wang, B.; Li, Z.; Qin, Y.; Zhang, K. Spatiotemporally mapping of the relationship between NO2 pollution and urbanization for a megacity in Southwest China during 2005–2016. Chemosphere 2019, 220, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Wang, T.; Wang, P. The spatial–temporal variation of tropospheric no2 over china during 2005 to 2018. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Luo, Y.; Li, J. Urban traffic infrastructure investment and air pollution: Evidence from the 83 cities in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 172, 488–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shariepour, Z.; Aliakbari Bidokhti, A. An Investigation on the status of troposphere NO2 over Iran during 2004 to 2012. J. Environ. Stud. 2014, 40, 65–78. [Google Scholar]
- Borsdorff, T.; Hu, H.; Hasekamp, O.; Sussmann, R.; Rettinger, M.; Hase, F.; Gross, J.; Schneider, M.; Garcia, O.; Stremme, W. Mapping carbon monoxide pollution from space down to city scales with daily global coverage. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2018, 11, 5507–5518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maroufnejad, A.; Reis Ghanavati, K. The Effect of Urban Management on Reducing Industrial Pollutants in the City of Mahshahr. J. Urban Econ. Manag. 2014, 2, 19–35. [Google Scholar]





| Name | Dataset Provider | Dataset Availability | Range |
|---|---|---|---|
| Copernicus Sentinel-5P OFFL NO2 | European Union/ESA/Copernicus | 2018 to 2021 | 0 to 20 (1015 molecules cm−2) |
| Ground air quality data | Air Quality Control Monitoring Organization | 2018–2021 | 0 to 120 µg/m3 |
| Population | Statistical Center of Iran | 2016 | 7402 to 8,737,510 persons per county |
| Industry | OpenStreetMap (OSM) | 2020 | 0 to 114 industrial units in the counties |
| City Name | Number of Stations | Number of Observations (2018 to 2021) | Average NO2 (µg/m3) | Standard Deviation (µg/m3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tehran | 23 | 478 | 59 | 25 |
| Isfahan | 16 | 22 | 13 | 9 |
| Tabriz | 8 | 36 | 31 | 13 |
| Ahvaz | 5 | 15 | 22 | 21 |
| Total | 52 | 551 | 31 | 17 |
| Month | July | August | September | October | November | December | January | February | March | April | May | June |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Min | 0.01 | 0.04 | 0.05 | 0.19 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Max | 2.97 | 2.90 | 4.80 | 7.95 | 15.00 | 19.00 | 15.80 | 12.04 | 9.00 | 3.87 | 4.00 | 3.20 |
| Mean | 0.20 | 0.23 | 0.22 | 0.19 | 0.25 | 0.28 | 0.30 | 0.24 | 0.18 | 0.16 | 0.17 | 0.18 |
| STD | 0.11 | 0.11 | 0.15 | 0.20 | 0.33 | 0.40 | 0.41 | 0.28 | 0.24 | 0.11 | 0.12 | 0.11 |
| Pollution Class | Value (1015 Molecules cm−2) | Cities Count | Area (km2) | Percentage of Area | Population | Percentage of Population |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Very Low | <0.2 | 194 | 1,048,152.2 | 64.3 | 18,948,295 | 23.7 |
| Low | 0.2–0.5 | 193 | 544,494.7 | 33.4 | 39,106,088 | 48.9 |
| Moderate | 0.5–1 | 27 | 28,341.2 | 1.74 | 8,582,952 | 10.7 |
| High | 1–2 | 9 | 5102.4 | 0.31 | 2,894,314 | 3.6 |
| Very High | >2 | 6 | 2704.9 | 0.16 | 10,394,621 | 13.1 |
| Sum | 429 | 1,628,795 | 100 | 79,926,270 | 100 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rabiei-Dastjerdi, H.; Mohammadi, S.; Saber, M.; Amini, S.; McArdle, G. Spatiotemporal Analysis of NO2 Production Using TROPOMI Time-Series Images and Google Earth Engine in a Middle Eastern Country. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1725. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14071725
Rabiei-Dastjerdi H, Mohammadi S, Saber M, Amini S, McArdle G. Spatiotemporal Analysis of NO2 Production Using TROPOMI Time-Series Images and Google Earth Engine in a Middle Eastern Country. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(7):1725. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14071725
Chicago/Turabian StyleRabiei-Dastjerdi, Hamidreza, Shahin Mohammadi, Mohsen Saber, Saeid Amini, and Gavin McArdle. 2022. "Spatiotemporal Analysis of NO2 Production Using TROPOMI Time-Series Images and Google Earth Engine in a Middle Eastern Country" Remote Sensing 14, no. 7: 1725. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14071725
APA StyleRabiei-Dastjerdi, H., Mohammadi, S., Saber, M., Amini, S., & McArdle, G. (2022). Spatiotemporal Analysis of NO2 Production Using TROPOMI Time-Series Images and Google Earth Engine in a Middle Eastern Country. Remote Sensing, 14(7), 1725. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14071725








