Aloft Transport of Haze Aerosols to Xuzhou, Eastern China: Optical Properties, Sources, Type, and Components
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Observations and Model
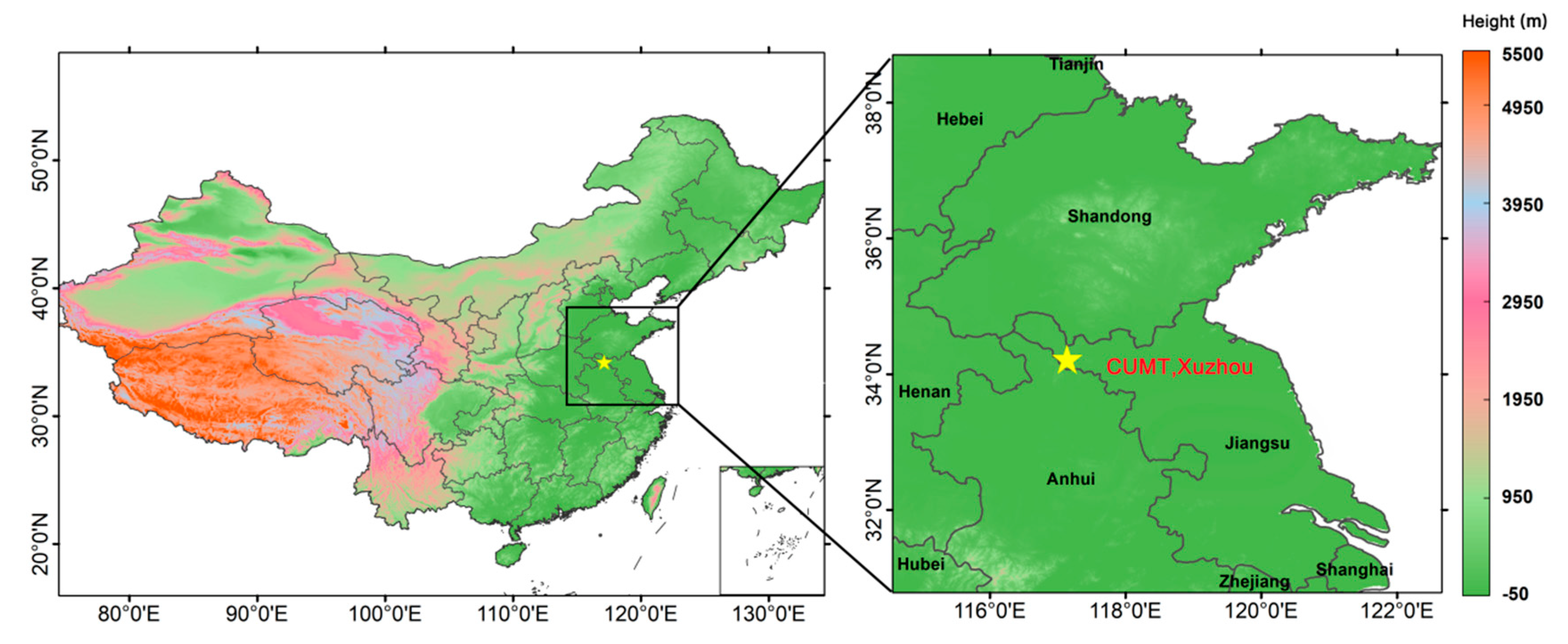
2.1. Ground-Based Observations
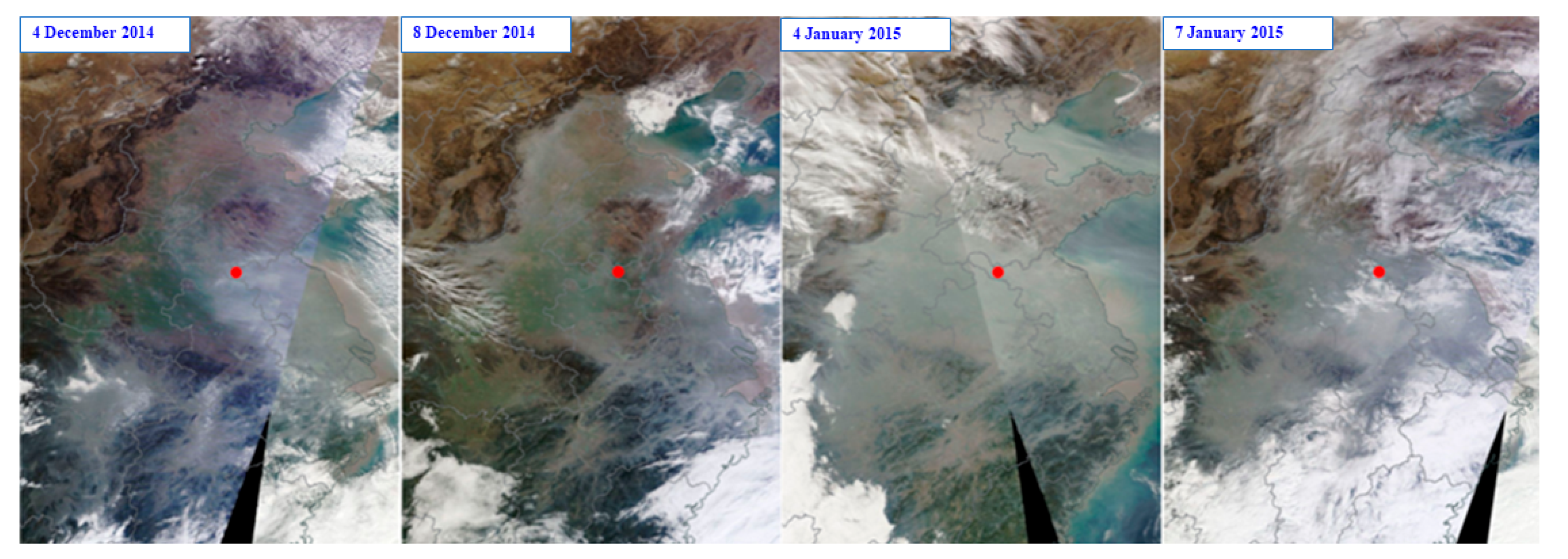
2.2. Satellite Observations
2.3. WRF-Chem Simulations
3. Results
3.1. Identifying Aloft Haze Plumes Using Ground-Based Lidar Measurements
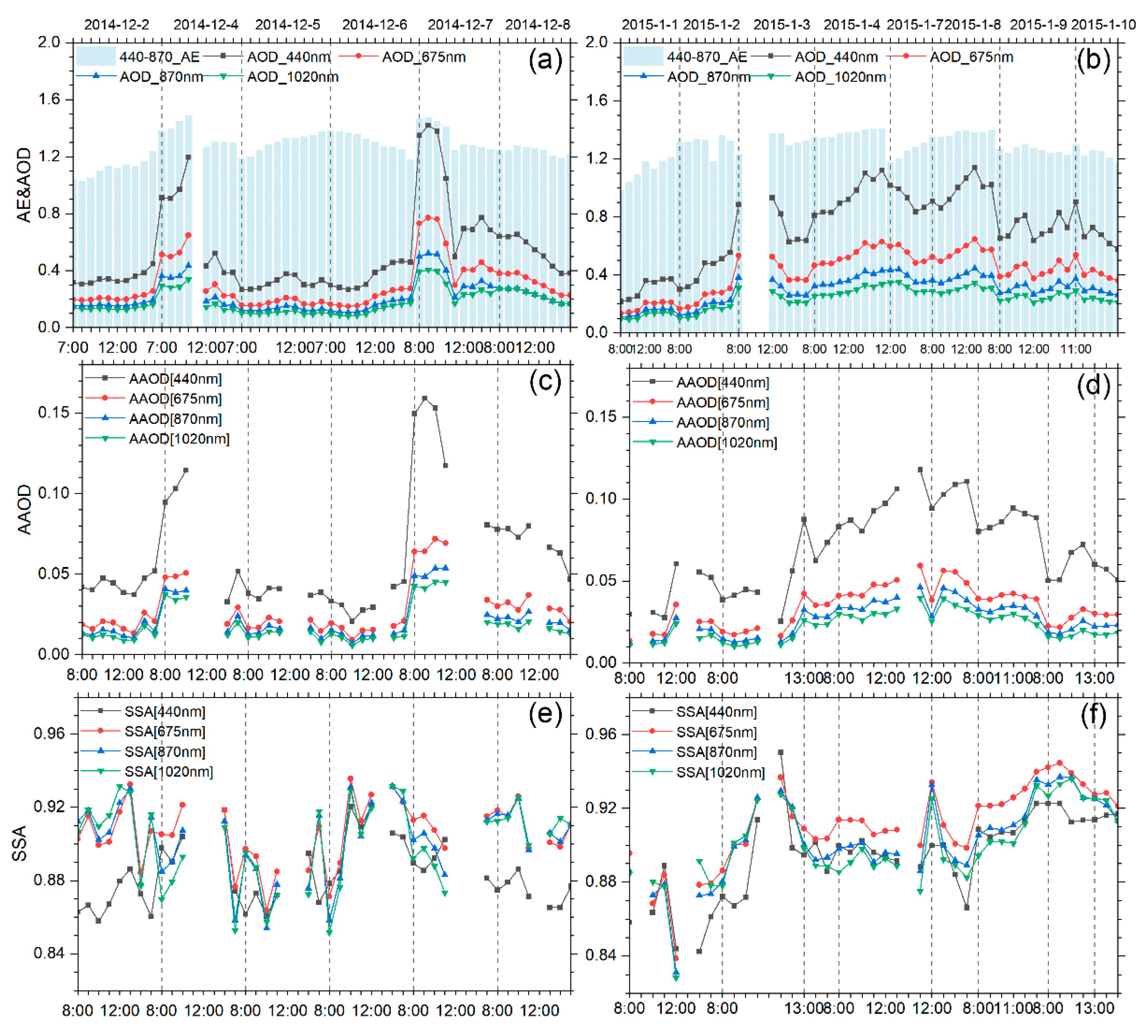
3.2. Optical Properties of the Plumes
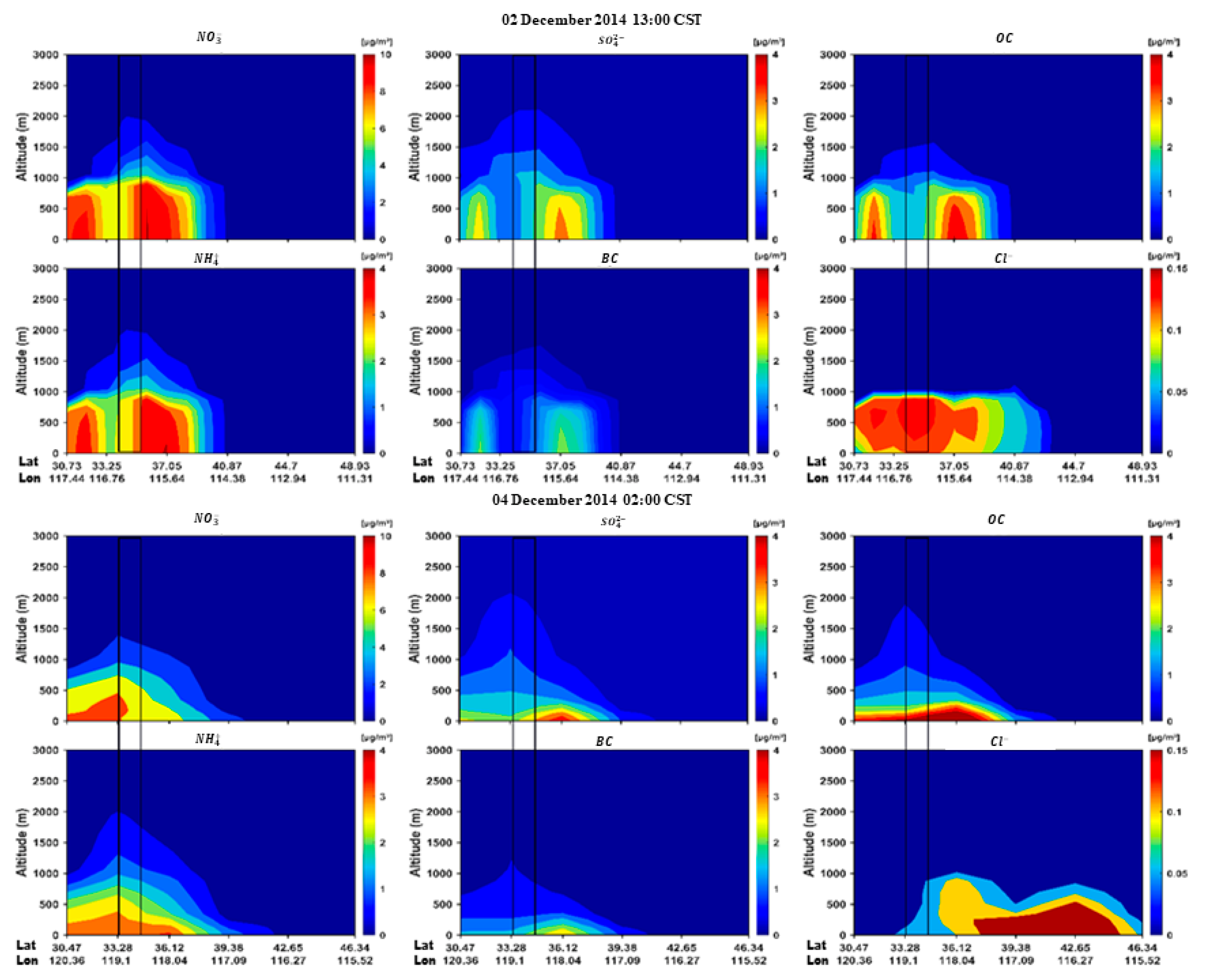
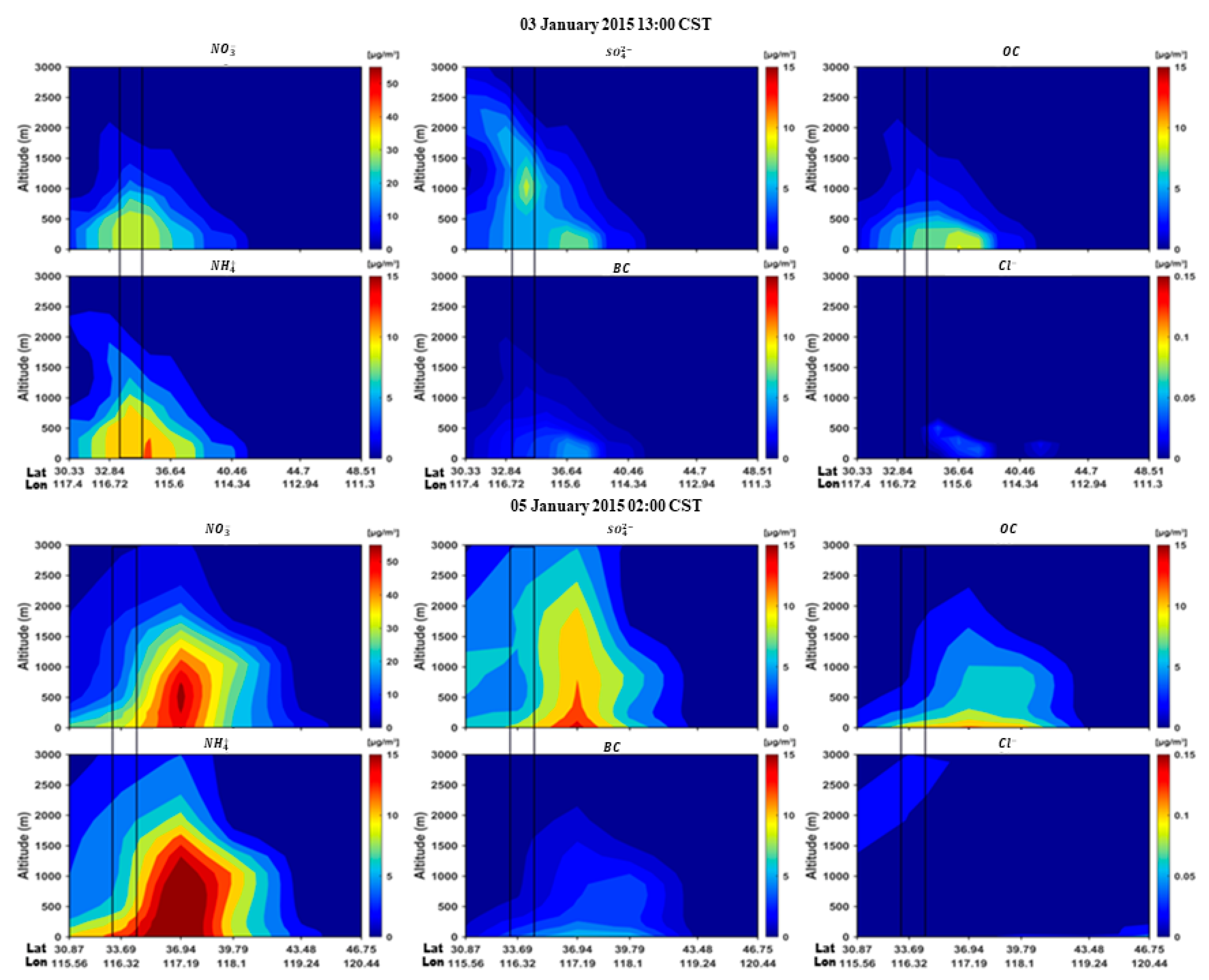
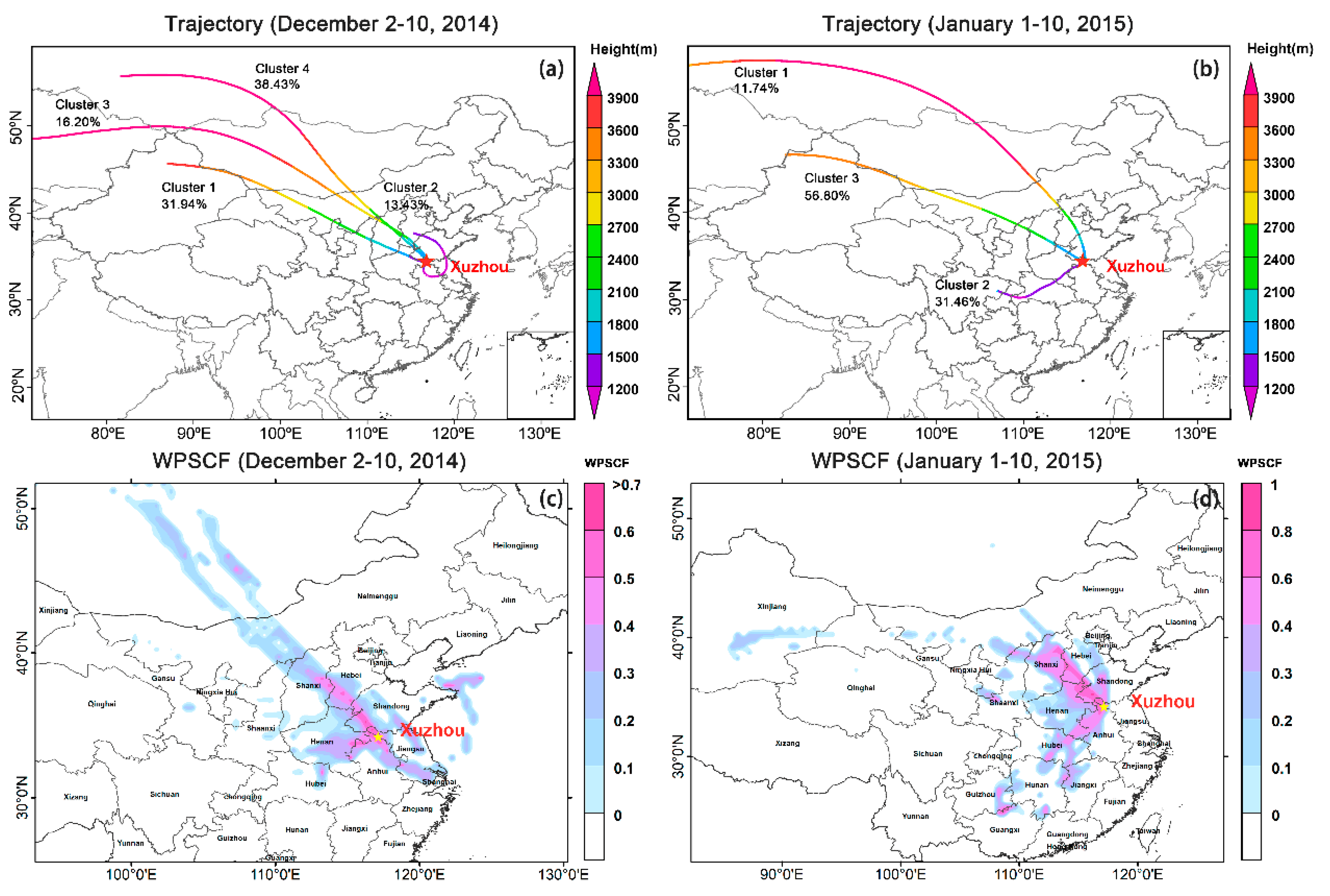
3.3. Compositions, Aerosol Type, and Sources
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guo, J.; Liu, H.; Wang, F.; Huang, J.; Xia, F.; Lou, M.; Wu, Y.; Jiang, J.H.; Xie, T.; Zhaxi, Y.; et al. Three-Dimensional Structure of Aerosol in China: A Perspective from Multi-Satellite Observations. Atmos. Res. 2016, 178–179, 580–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lolli, S.; Khor, W.Y.; Matjafri, M.Z.; Lim, H.S. Monsoon Season Quantitative Assessment of Biomass Burning Clear-Sky Aerosol Radiative Effect at Surface by Ground-Based Lidar Observations in Pulau Pinang, Malaysia in 2014. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.; Li, Y.; Guang, J.; Tugui, A.; She, L.; Qin, K.; Fan, C.; Che, Y.; Xie, Y.; Wen, Y.; et al. Hourly PM2.5 Estimation over Central and Eastern China Based on Himawari-8 Data. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niranjan, K.; Madhavan, B.L.; Sreekanth, V. Micro Pulse Lidar Observation of High Altitude Aerosol Layers at Visakhapatnam Located on the East Coast of India. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salinas, S.V.; Chew, B.N.; Miettinen, J.; Campbell, J.R.; Welton, E.J.; Reid, J.S.; Yu, L.E.; Liew, S.C. Physical and Optical Characteristics of the October 2010 Haze Event over Singapore: A Photometric and Lidar Analysis. Atmos. Res. 2013, 122, 555–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciofini, M.; Lapucci, A.; Lolli, S. Diffractive Optical Components for High Power Laser Beam Sampling. J. Opt. A Pure Appl. Opt. 2003, 5, 186–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lolli, S.; Madonna, F.; Rosoldi, M.; Campbell, J.R.; Welton, E.J.; Lewis, J.R.; Gu, Y.; Pappalardo, G. Impact of Varying Lidar Measurement and Data Processing Techniques in Evaluating Cirrus Cloud and Aerosol Direct Radiative Effects. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2018, 11, 1639–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cottle, P.; Strawbridge, K.; McKendry, I. Long-Range Transport of Siberian Wildfire Smoke to British Columbia: Lidar Observations and Air Quality Impacts. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 90, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kar, J.; Vaughan, M.A.; Liu, Z.; Omar, A.H.; Trepte, C.R.; Tackett, J.; Fairlie, T.D.; Kowch, R. Detection of Pollution Outflow from Mexico City Using CALIPSO Lidar Measurements. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 169, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Wu, Y.; Wang, T.; Zhuang, B.; Li, S.; Zhao, K. Impacts of Elevated-Aerosol-Layer and Aerosol Type on the Correlation of AOD and Particulate Matter with Ground-Based and Satellite Measurements in Nanjing, Southeast China. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 532, 195–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, L.K.; Fast, J.D.; Barnard, J.C.; Burton, S.P.; Cairns, B.; Chand, D.; Comstock, J.M.; Dunagan, S.; Ferrare, R.A.; Flynn, C.J.; et al. The Two-Column Aerosol Project: Phase I—Overview and Impact of Elevated Aerosol Layers on Aerosol Optical Depth. J. Geophys. Res. 2016, 121, 336–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarangi, C.; Tripathi, S.N.; Mishra, A.K.; Goel, A.; Welton, E.J. Elevated Aerosol Layers and Their Radiative Impact over Kanpur during Monsoon Onset Period. J. Geophys. Res. 2016, 121, 7936–7957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J.B.; Ng, D.H.L.; Lim, A.W.L.; Chua, X.R. Vertical Distribution of Aerosols over the Maritime Continent during El Niño. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 7095–7108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Blake Cohen, J.; Lin, C.; Deng, W. Constraining the Relationships between Aerosol Height, Aerosol Optical Depth and Total Column Trace Gas Measurements Using Remote Sensing and Models. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 15401–15426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Cohen, J.B.; Deng, W.; Qin, K.; Guo, J. Using a New Top-Down Constrained Emissions Inventory to Attribute the Previously Unknown Source of Extreme Aerosol Loadings Observed Annually in the Monsoon Asia Free Troposphere. Earth’s Futur. 2021, 9, e2021EF002167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lolli, S. Is the Air Too Polluted for Outdoor Activities? Check by Using Your Photovoltaic System as an Air-Quality Monitoring Device. Sensors 2021, 21, 6342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, J.; Huang, J.; Hu, Z.; Holben, B.N.; Guo, Z. Investigating the Aerosol Optical and Radiative Characteristics of Heavy Haze Episodes in Beijing during January of 2013. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 9884–9900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Jiang, Q.; Wang, Z.; Fu, P.; Li, J.; Yang, T.; Yin, Y. Investigation of the Sources and Evolution Processes of Severe Haze Pollution in Beijing in January 2013. J. Geophys. Res. 2014, 119, 4380–4398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, M.; Chen, L.; Xiong, X.; Zhang, M.; Ma, P.; Tao, J.; Wang, Z. Formation Process of the Widespread Extreme Haze Pollution over Northern China in January 2013: Implications for Regional Air Quality and Climate. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 98, 417–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, K.; Liu, H.; Ding, A.; Wang, X. WRF-Chem Simulation of a Severe Haze Episode in the Yangtze River Delta, China. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2016, 16, 1268–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, M.; Chen, L.; Wang, Z.; Wang, J.; Tao, J.; Wang, X. Did the Widespread Haze Pollution over China Increase during the Last Decade? A Satellite View from Space. Environ. Res. Lett. 2016, 11, 54019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, G.J.; Duan, F.K.; Su, H.; Ma, Y.L.; Cheng, Y.; Zheng, B.; Zhang, Q.; Huang, T.; Kimoto, T.; Chang, D.; et al. Exploring the Severe Winter Haze in Beijing: The Impact of Synoptic Weather, Regional Transport and Heterogeneous Reactions. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 2969–2983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.-J.; Zhang, Y.; Bozzetti, C.; Ho, K.-F.; Cao, J.-J.; Han, Y.; Daellenbach, K.R.; Slowik, J.G.; Platt, S.M.; Canonaco, F.; et al. High Secondary Aerosol Contribution to Particulate Pollution during Haze Events in China. Nature 2014, 514, 218–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J.B.; Prinn, R.G. Development of a Fast, Urban Chemistry Metamodel for Inclusion in Global Models. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 7629–7656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J.B.; Prinn, R.G.; Wang, C. The Impact of Detailed Urban-Scale Processing on the Composition, Distribution, and Radiative Forcing of Anthropogenic Aerosols. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2011, 38, L10808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, A.; Huang, X.; Nie, W.; Chi, X.; Xu, Z.; Zheng, L.; Xu, Z.; Xie, Y.; Qi, X.; Shen, Y.; et al. Significant Reduction of PM2.5 in Eastern China Due to Regional-Scale Emission Control: Evidence from SORPES in 2011–2018. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 11791–11801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Ding, A.; Wang, Z.; Ding, K.; Gao, J.; Chai, F.; Fu, C. Amplified Transboundary Transport of Haze by Aerosol–Boundary Layer Interaction in China. Nat. Geosci. 2020, 13, 428–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhao, B.; Wang, S.; Yang, F.; Xing, J.; Morawska, L.; Ding, A.; Kulmala, M.; Kerminen, V.M.; Kujansuu, J.; et al. Particulate Matter Pollution over China and the Effects of Control Policies. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 584–585, 426–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, A.J.; Huang, X.; Nie, W.; Sun, J.N.; Kerminen, V.M.; Petäjä, T.; Su, H.; Cheng, Y.F.; Yang, X.Q.; Wang, M.H.; et al. Enhanced Haze Pollution by Black Carbon in Megacities in China. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2016, 43, 2873–2879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Wang, Z.; Ding, A. Impact of Aerosol-PBL Interaction on Haze Pollution: Multiyear Observational Evidences in North China. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2018, 45, 8596–8603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Wang, X.; Wang, Z.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, B.; Du, Y. Gravity-Current Driven Transport of Haze from North China Plain to Northeast China in Winter 2010-Part I: Observations. SOLA 2012, 8, 13–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Li, H.; Cheng, J.; Zhang, Q.; Zheng, B.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, G.; He, K. Rapid Transition in Winter Aerosol Composition in Beijing from 2014 to 2017: Response to Clean Air Actions. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 11485–11499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ding, A.; Mao, H.; Nie, W.; Zhou, D.; Liu, L.; Huang, X.; Fu, C. Impact of Synoptic Weather Patterns and Inter-Decadal Climate Variability on Air Quality in the North China Plain during 1980–2013. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 124, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Tian, H.; Qin, K. Black Carbon Aerosol in the Industrial City of Xuzhou, China: Temporal Characteristics and Source Appointment. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2019, 19, 794–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Tian, H.; Zhao, H.; Qin, K. Multichannel Characteristics of Absorbing Aerosols in Xuzhou and Implication of Black Carbon. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 714, 136820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.; Xie, X.; Zhou, Y.; Lang, J.; Xu, T.; Yang, N.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, X. Performance Evaluation of the {WRF}-Chem Model with Different Physical Parameterization Schemes during an Extremely High {PM}2.5 Pollution Episode in Beijing. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2017, 17, 262–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Gao, X. A New Study on Air Quality Standards: Air Quality Measurement and Evaluation for Jiangsu Province Based on Six Major Air Pollutants. Sustainability 2018, 10, 3561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, K.; Wang, L.; Xu, J.; Letu, H.; Zhang, K.; Li, D.; Zou, J.; Fan, W. Haze Optical Properties from Long-Term Ground- Based Remote Sensing over Beijing and Xuzhou, China. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, K.; Wu, L.; Wong, M.S.; Letu, H.; Hu, M.; Lang, H.; Sheng, S.; Teng, J.; Xiao, X.; Yuan, L. Trans-Boundary Aerosol Transport during a Winter Haze Episode in China Revealed by Ground-Based Lidar and CALIPSO Satellite. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 141, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holben, B.N.; Eck, T.F.; Slutsker, I.; Tanré, D.; Buis, J.P.; Setzer, A.; Vermote, E.; Reagan, J.A.; Kaufman, Y.J.; Nakajima, T.; et al. AERONET—A Federated Instrument Network and Data Archive for Aerosol Characterization. Remote Sens. Environ. 1998, 66, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, J.R.; Hlavka, D.L.; Welton, E.J.; Flynn, C.J.; Turner, D.D.; Spinhirne, J.D.; Scott, V.S.; Hwang, I.H. Full-Time, Eye-Safe Cloud and Aerosol Lidar Observation at Atmospheric Radiation Measurement Program Sites: Instruments and Data Processing. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2002, 19, 431–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welton, E.J.; Campbell, J.R.; Spinhirne, J.D.; Scott, V.S., III. Global Monitoring of Clouds and Aerosols Using a Network of Micropulse Lidar Systems. In Proceedings of the Lidar Remote Sensing for Industry and Environment Monitoring; Singh, U.N., Asai, K., Ogawa, T., Singh, U.N., Itabe, T., Sugimoto, N., Eds.; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2001; Volume 4153, p. 151. [Google Scholar]
- Flynn, C.; Mendoza, A.; Zheng, Y.; Mathur, S. Novel Polarization-Sensitive Micropulse Lidar Measurement Technique. Opt. Express 2007, 15, 2785–2790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernald, F.G. Analysis of Atmospheric Lidar Observations: Some Comments. Appl. Opt. 1984, 23, 652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welton, E.; Voss, K.; Gordon, H.; Maring, H.; Smirnov, A.; Holben, B.; Schmid, B.; Livingston, J.; Russell, P.; Durkee, P.; et al. Ground-Based Lidar Measurements of Aerosols during ACE-2: Instrument Description, Results, and Comparisons with Other Ground-Based and Airborne Measurements. Tellus 2000, 52, 635–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Eck, T.F.; Holben, B.N.; Reid, J.S.; Dubovik, O.; Smirnov, A.; O’Neill, N.T.; Slutsker, I.; Kinne, S. Wavelength Dependence of the Optical Depth of Biomass Burning, Urban, and Desert Dust Aerosols. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1999, 104, 31333–31349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, N.T.; Eck, T.F.; Smirnov, A.; Holben, B.N.; Thulasiraman, S. Spectral Discrimination of Coarse and Fine Mode Optical Depth. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2003, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winker, D.M.; Hunt, W.H.; McGill, M.J. Initial Performance Assessment of CALIOP. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mielonen, T.; Arola, A.; Komppula, M.; Kukkonen, J.; Koskinen, J.; De Leeuw, G.; Lehtinen, K.E.J. Comparison of CALIOP Level 2 Aerosol Subtypes to Aerosol Types Derived from AERONET Inversion Data. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2009, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burton, S.P.; Ferrare, R.A.; Vaughan, M.A.; Omar, A.H.; Rogers, R.R.; Hostetler, C.A.; Hair, J.W. Aerosol Classification from Airborne HSRL and Comparisons with the CALIPSO Vertical Feature Mask. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2013, 6, 1397–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grell, G.A.; Peckham, S.E.; Schmitz, R.; McKeen, S.A.; Frost, G.; Skamarock, W.C.; Eder, B. Fully Coupled “Online” Chemistry within the WRF Model. Atmos. Environ. 2005, 39, 6957–6975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Liu, H.; Geng, G.; Hong, C.; Liu, F.; Song, Y.; Tong, D.; Zheng, B.; Cui, H.; Man, H.; et al. Anthropogenic Emission Inventories in China: A Review. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2017, 4, 834–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Nazmi, C.; Han, Z.; Li, C.; Gross, B.; Moshary, F. Integrated Observation of Aerosol Plumes Transport and Impacts on the Air Quality Remote Sensing in the Northeast U.S. EPJ Web Conf. 2016, 119, 18004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strong, S.B.; Brown, A.M. Developing a Broad Spectrum Atmospheric Aerosol Characterization for Remote Sensing Platforms over Desert Regions. In Proceedings of the Infrared Imaging Systems: Design, Analysis, Modeling, and Testing XXV; Holst, G.C., Krapels, K.A., Ballard, G.H., Jr., Murrer, R.L., Jr., Eds.; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2014; Volume 9071, pp. 376–386. [Google Scholar]
- Lolli, S.; Campbell, J.R.; Lewis, J.R.; Gu, Y.; Marquis, J.W.; Chew, B.N.; Liew, S.C.; Salinas, S.V.; Welton, E.J. Daytime Top-of-the-Atmosphere Cirrus Cloud Radiative Forcing Properties at Singapore. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2017, 56, 1249–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wang, X.; Cohen, J.B.; Qin, K. Inferring Polluted Asian Absorbing Aerosol Properties Using Decadal Scale AERONET Measurements and a MIE Model. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2021, 48, e2021GL094300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ångström, A. On the Atmospheric Transmission of Sun Radiation and on Dust in the Air. Geogr. Ann. 1929, 11, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westphal, D.L.; Toon, O.B. The Short-term Temperature Response to Smoke from Oil Fires. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1991, 18, 1873–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuster, G.L.; Dubovik, O.; Holben, B.N. Angstrom Exponent and Bimodal Aerosol Size Distributions. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2006, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cazorla, A.; Bahadur, R.; Suski, K.J.; Cahill, J.F.; Chand, D.; Schmid, B.; Ramanathan, V.; Prather, K.A. Relating Aerosol Absorption Due to Soot, Organic Carbon, and Dust to Emission Sources Determined from in-Situ Chemical Measurements. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 9337–9350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moosmüller, H.; Chakrabarty, R.K.; Arnott, W.P. Aerosol Light Absorption and Its Measurement: A Review. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2009, 110, 844–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J.B.; Wang, C. Estimating Global Black Carbon Emissions Using a Top-down Kalman Filter Approach. J. Geophys. Res. 2014, 119, 307–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngan, F.; Stein, A.; Draxler, R. Inline Coupling of WRF–HYSPLIT: Model Development and Evaluation Using Tracer Experiments. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2015, 54, 1162–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.Q.; Zhang, X.Y.; Draxler, R.R. TrajStat: GIS-Based Software That Uses Various Trajectory Statistical Analysis Methods to Identify Potential Sources from Long-Term Air Pollution Measurement Data. Environ. Model. Softw. 2009, 24, 938–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.Y.; Arimoto, R.; Cao, J.J.; Shen, Z.X. The Transport Pathways and Sources of PM10 Pollution in Beijing during Spring 2001, 2002 and 2003. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.; Zhang, R.; Yang, W.; Bai, Z.; Ma, Z.; Zhang, W. Heavy Haze Episodes in Beijing during January 2013: Inorganic Ion Chemistry and Source Analysis Using Highly Time-Resolved Measurements from an Urban Site. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 544, 319–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lolli, S.; Delaval, A.; Loth, C.; Garnier, A.; Flamant, P.H. 0.355-Micrometer Direct Detection Wind Lidar under Testing during a Field Campaign in Consideration of ESA’s ADM-Aeolus Mission. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2013, 6, 3349–3358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, W.W.Y.; Steenburgh, W.J. Evaluation of Surface Sensible Weather Forecasts by the WRF and the Eta Models over the Western United States. Weather Forecast. 2005, 20, 812–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Module | Parameter Scheme |
|---|---|
| Microphysics | WSM 6 |
| Surface layer | Monin–Obukhov |
| Boundary layer | YSU |
| Longwave radiation | Rrtmg |
| Shortwave radiation | Rrtmg |
| Cumulus convection | New Grell |
| Land surface process | Noah |
| Aerosol | MOSAIC (4 bins) |
| Photolysis | Fast-J |
| Biogenic emission | Gunther |
| data | Data |
| AOD | AE | FMF | |
|---|---|---|---|
| No upper layer | 0.40 ± 0.23 | 1.17 ± 0.29 | 0.70 ± 0.17 |
| Upper layer | 0.68 ± 0.26 | 1.30 ± 0.12 | 0.81 ± 0.09 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qin, K.; He, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Cohen, J.B.; Tiwari, P.; Lolli, S. Aloft Transport of Haze Aerosols to Xuzhou, Eastern China: Optical Properties, Sources, Type, and Components. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1589. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14071589
Qin K, He Q, Zhang Y, Cohen JB, Tiwari P, Lolli S. Aloft Transport of Haze Aerosols to Xuzhou, Eastern China: Optical Properties, Sources, Type, and Components. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(7):1589. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14071589
Chicago/Turabian StyleQin, Kai, Qin He, Yishu Zhang, Jason Blake Cohen, Pravash Tiwari, and Simone Lolli. 2022. "Aloft Transport of Haze Aerosols to Xuzhou, Eastern China: Optical Properties, Sources, Type, and Components" Remote Sensing 14, no. 7: 1589. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14071589
APA StyleQin, K., He, Q., Zhang, Y., Cohen, J. B., Tiwari, P., & Lolli, S. (2022). Aloft Transport of Haze Aerosols to Xuzhou, Eastern China: Optical Properties, Sources, Type, and Components. Remote Sensing, 14(7), 1589. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14071589










