Monitoring Short-Term Morphobathymetric Change of Nearshore Seafloor Using Drone-Based Multispectral Imagery
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
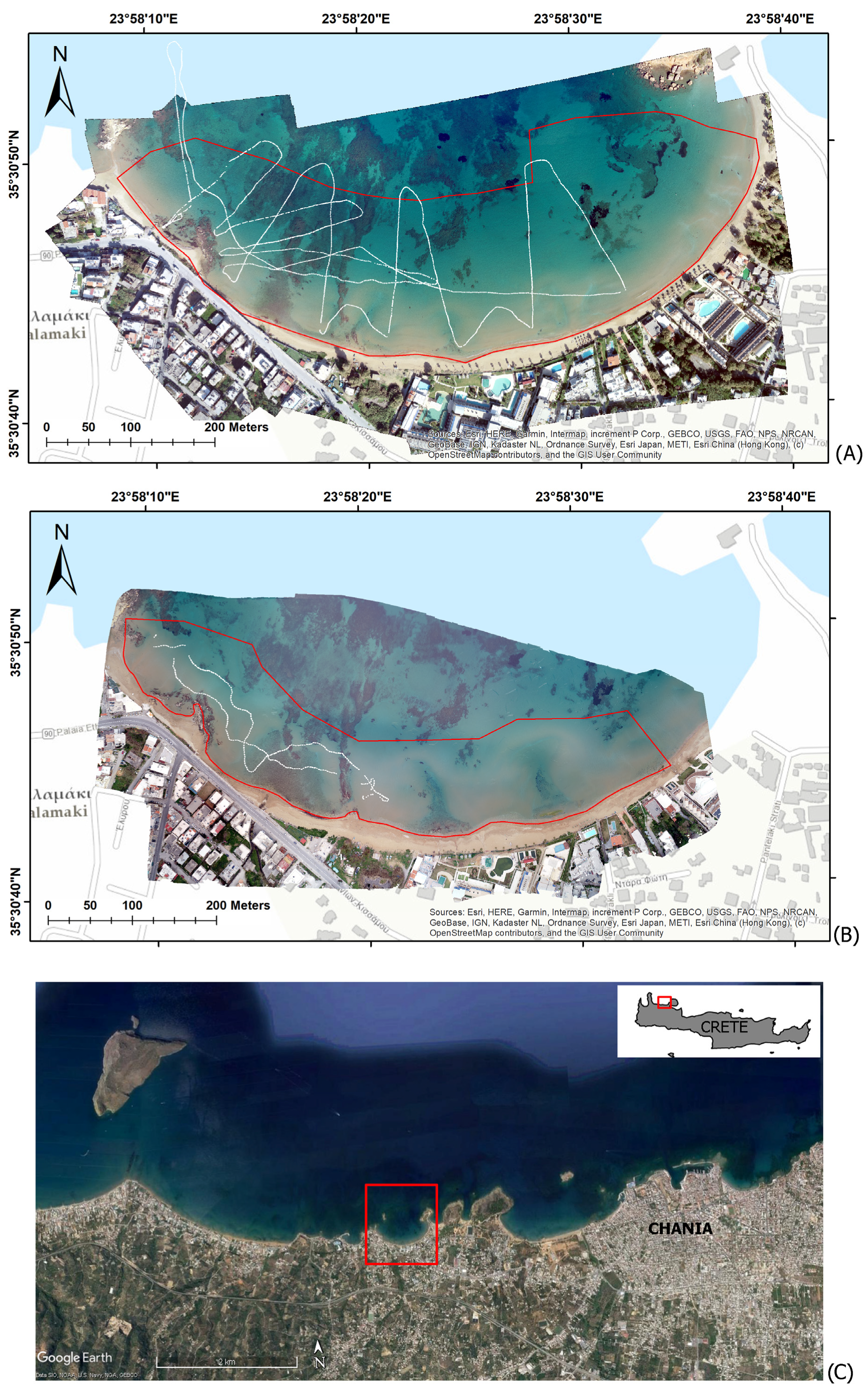
2.1. Study Area and Fieldwork
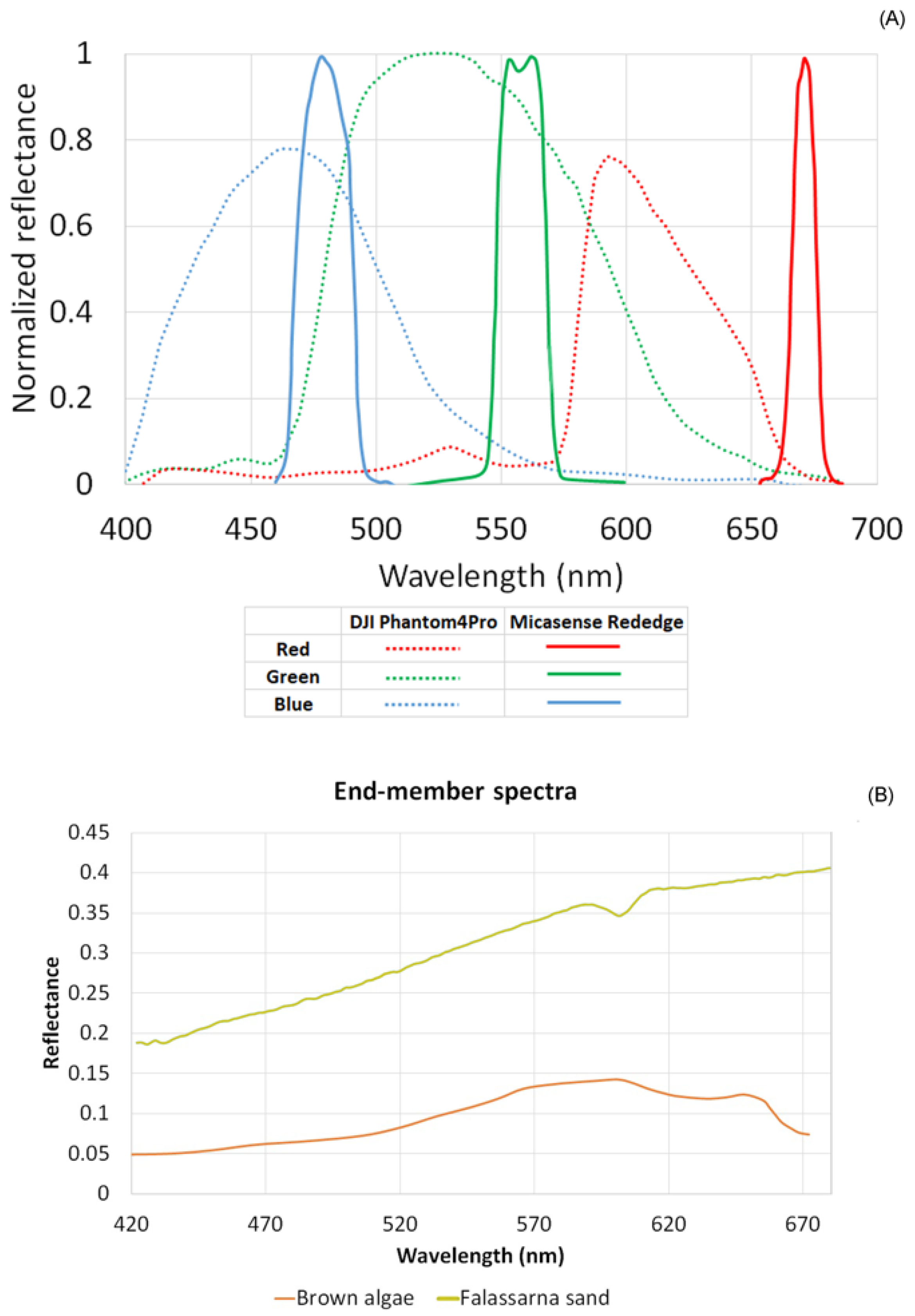
2.2. Pre-Processing of Drone-Based Imagery
2.3. Shallow Bathymetry Inversion in WASI-2D
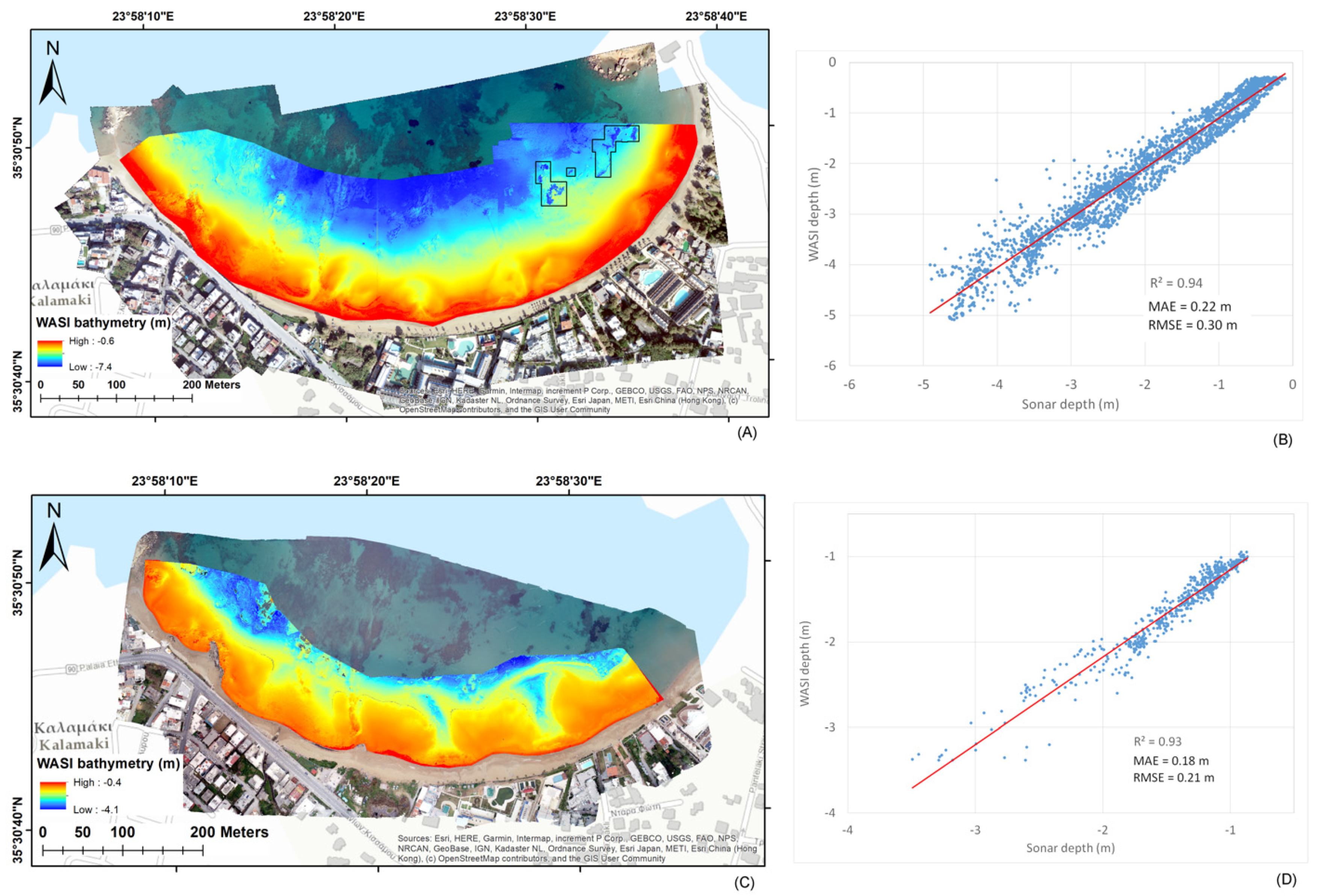
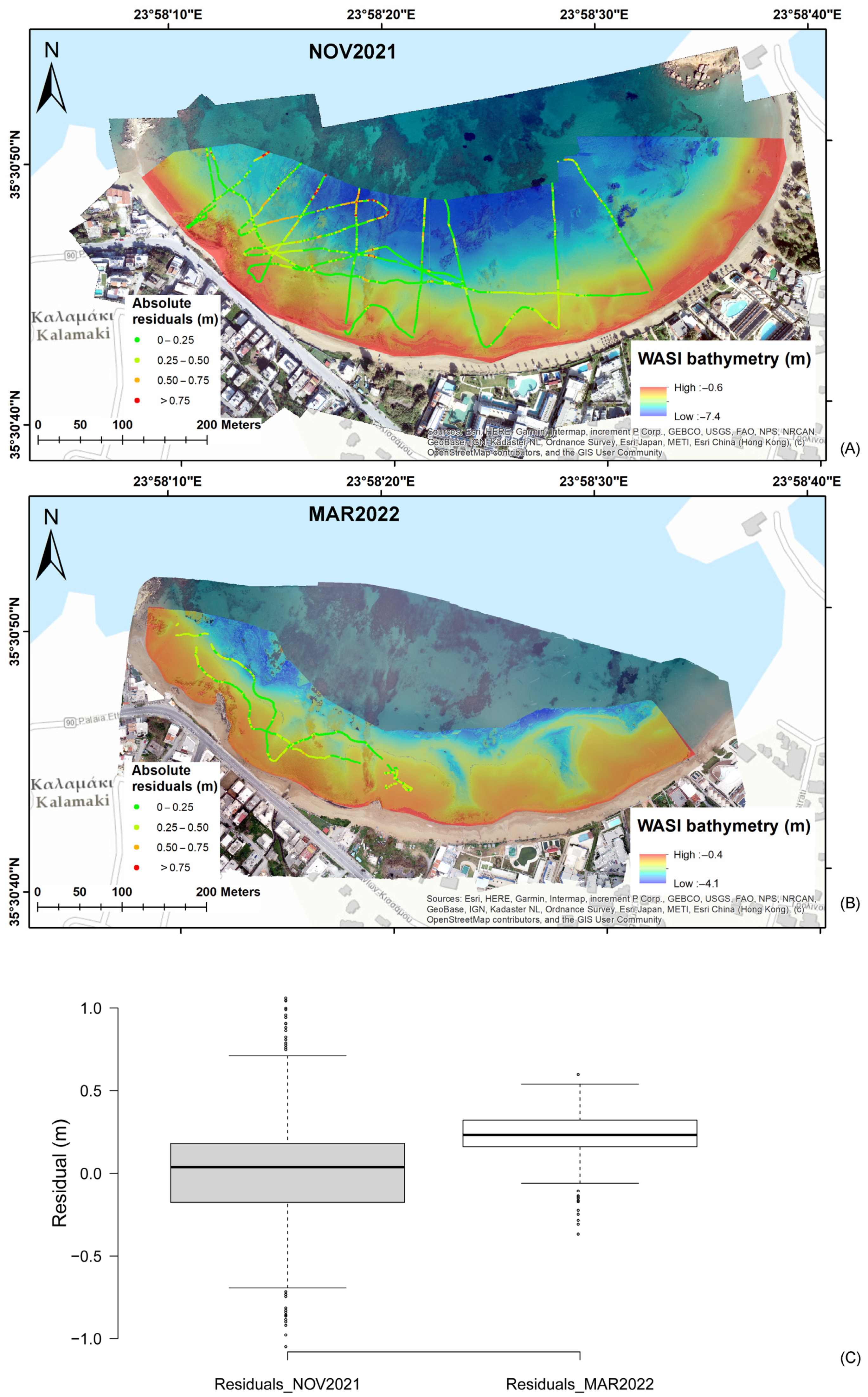
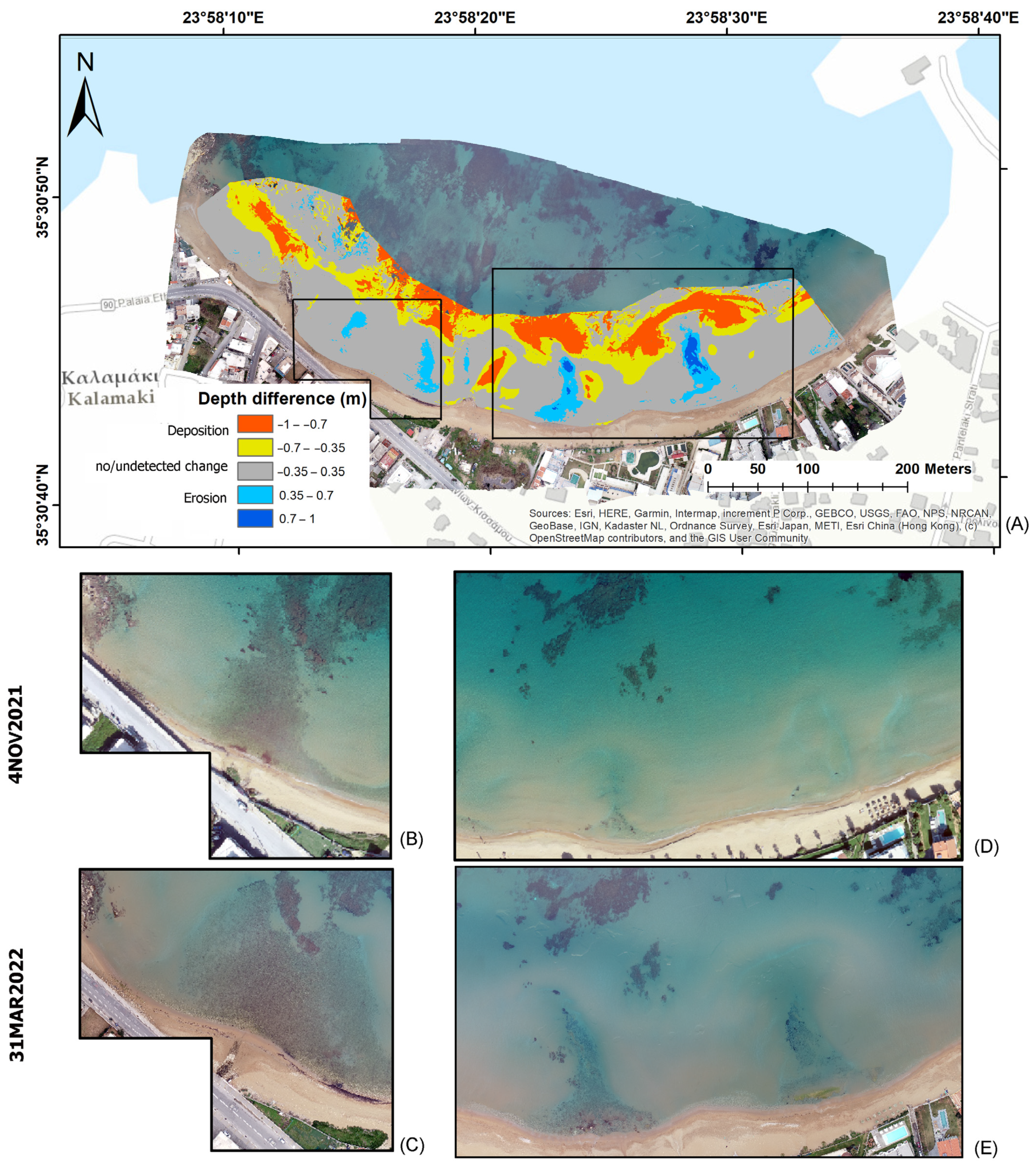
3. Results
3.1. Bathymetry Validation
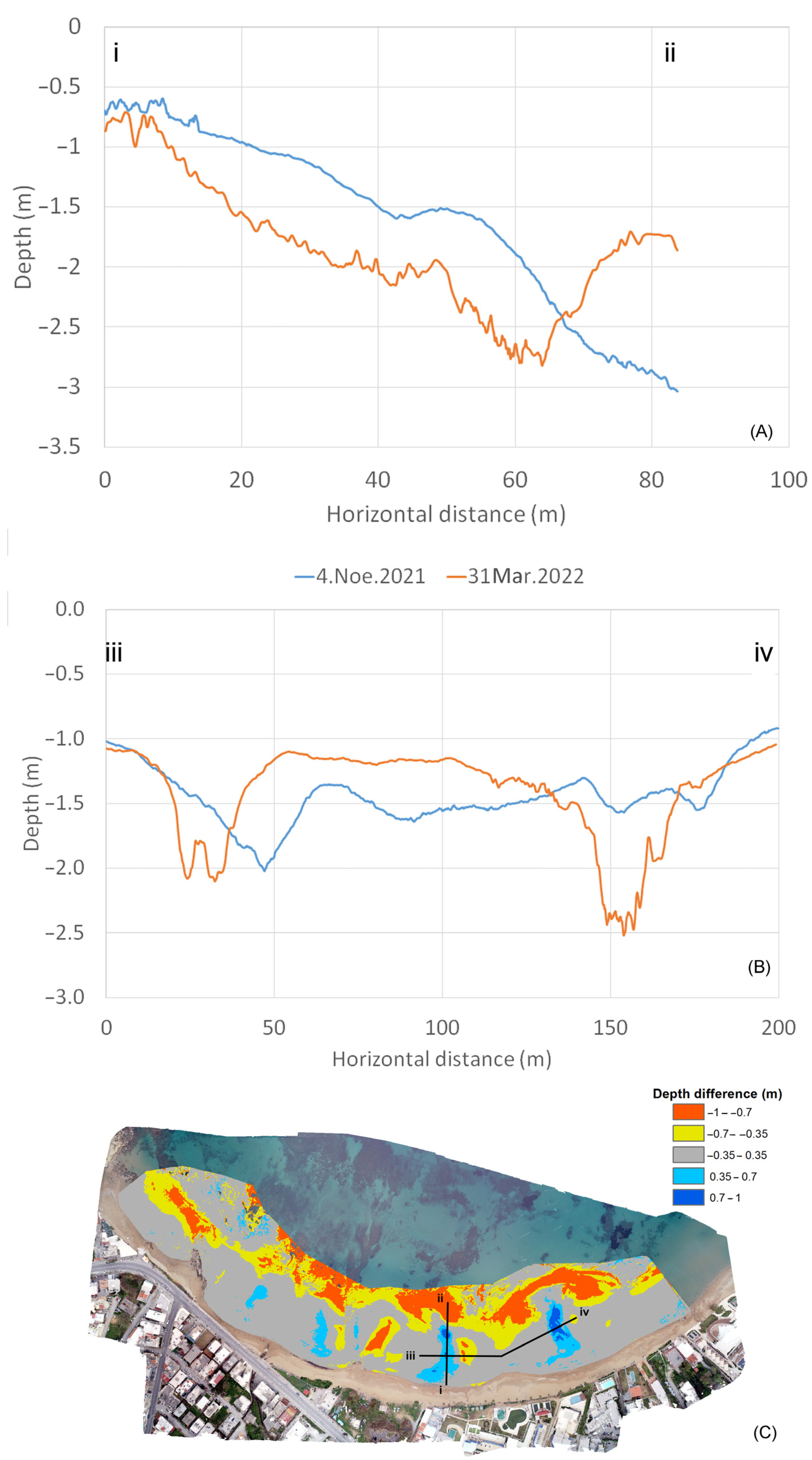
3.2. Short-Term Bathymetric Changes
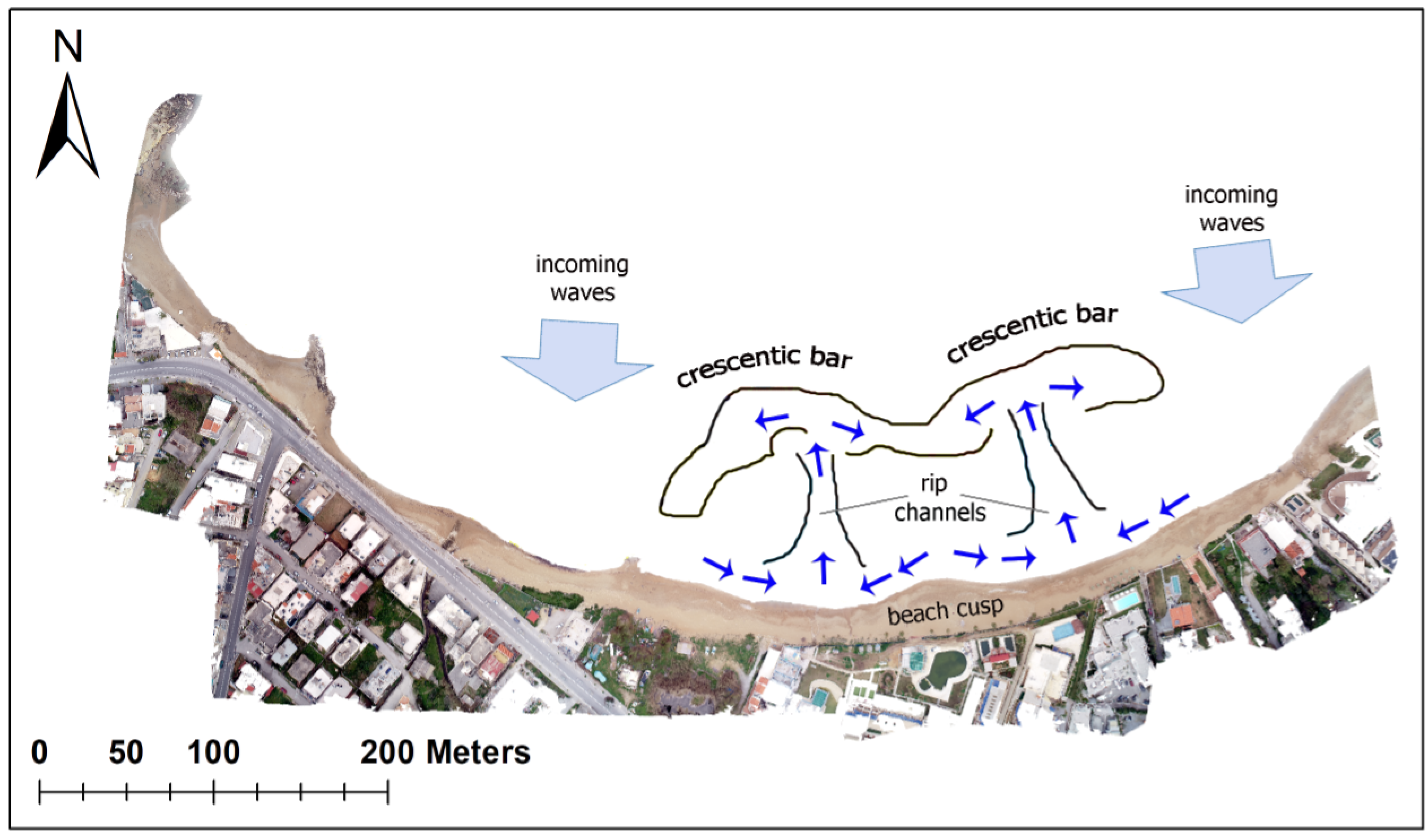
4. Discussion
4.1. Interpretation of Nearshore Bathymetry Change
4.2. Implications in Coastal Seafloor Monitoring
4.3. Sources of Error and Method Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Band Name | Central Wavelength (nm) | Fwhm * (nm) |
|---|---|---|
| Blue | 462 | 40 |
| Green | 525 | 50 |
| Red | 592 | 25 |
| MS-Blue | 480 | 10 |
| MS-Green | 560 | 10 |
| MS-Red | 671 | 5 |

References
- Davidson, M.; Van Koningsveld, M.; de Kruif, A.; Rawson, J.; Holman, R.; Lamberti, A.; Medina, R.; Kroon, A.; Aarninkhof, S. The CoastView Project: Developing Video-Derived Coastal State Indicators in Support of Coastal Zone Management. Coast. Eng. 2007, 54, 463–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Swart, H.E.; Zimmerman, J.T.F. Morphodynamics of Tidal Inlet Systems. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 2009, 41, 203–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Dongeren, A.; Plant, N.; Cohen, A.; Roelvink, D.; Haller, M.C.; Catalán, P. Beach Wizard: Nearshore Bathymetry Estimation through Assimilation of Model Computations and Remote Observations. Coast. Eng. 2008, 55, 1016–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, D.W.T.; Short, A.D.; Loureiro, C.; Cooper, J.A.G. Beach Morphodynamic Classification Using High-Resolution Nearshore Bathymetry and Process-Based Wave Modelling. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2022, 268, 107812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misra, A.; Ramakrishnan, B. Assessment of Coastal Geomorphological Changes Using Multi-Temporal Satellite-Derived Bathymetry. Cont. Shelf Res. 2020, 207, 104213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toodesh, R.; Verhagen, S.; Dagla, A. Prediction of Changes in Seafloor Depths Based on Time Series of Bathymetry Observations: Dutch North Sea Case. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrafiotis, P.; Karantzalos, K.; Georgopoulos, A.; Skarlatos, D. Correcting Image Refraction: Towards Accurate Aerial Image-Based Bathymetry Mapping in Shallow Waters. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J. Bathymetric Mapping by Means of Remote Sensing: Methods, Accuracy and Limitations. Prog. Phys. Geogr. Earth Environ. 2009, 33, 103–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salameh, E.; Frappart, F.; Almar, R.; Baptista, P.; Heygster, G.; Lubac, B.; Raucoules, D.; Almeida, L.P.; Bergsma, E.W.J.; Capo, S.; et al. Monitoring Beach Topography and Nearshore Bathymetry Using Spaceborne Remote Sensing: A Review. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Z.; Casey, B.; Arnone, R.A.; Weidemann, A.D.; Parsons, R.; Montes, M.J.; Gao, B.-C.; Goode, W.; Davis, C.O.; Dye, J. Water and Bottom Properties of a Coastal Environment Derived from Hyperion Data Measured from the EO-1 Spacecraft Platform. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2007, 1, 011502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergsma, E.W.J.; Almar, R. Video-Based Depth Inversion Techniques, a Method Comparison with Synthetic Cases. Coast. Eng. 2018, 138, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, A.M.; Geheran, M.P.; Hesser, T.J.; Bak, A.S.; Brodie, K.L.; Farthing, M.W. Development of a Fully Convolutional Neural Network to Derive Surf-Zone Bathymetry from Close-Range Imagery of Waves in Duck, NC. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, B.M.; Battista, T.A.; Pittman, S.J. Comparative Evaluation of Airborne LiDAR and Ship-Based Multibeam SoNAR Bathymetry and Intensity for Mapping Coral Reef Ecosystems. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 1082–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janowski, L.; Wroblewski, R.; Rucinska, M.; Kubowicz-Grajewska, A.; Tysiac, P. Automatic Classification and Mapping of the Seabed Using Airborne LiDAR Bathymetry. Eng. Geol. 2022, 301, 106615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klemas, V. Beach Profiling and LIDAR Bathymetry: An Overview with Case Studies. J. Coast. Res. 2011, 277, 1019–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taramelli, A.; Cappucci, S.; Valentini, E.; Rossi, L.; Lisi, I. Nearshore Sandbar Classification of Sabaudia (Italy) with LiDAR Data: The FHyL Approach. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brock, J.C.; Purkis, S.J. The Emerging Role of Lidar Remote Sensing in Coastal Research and Resource Management. J. Coast. Res. 2009, 53, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freire, R.; Pe’eri, S.; Madore, B.; Rzhanov, Y.; Alexander, L.; Parrish, C.; Lippmann, T. Monitoring Near-Shore Bathymetry Using a Multi-Image Satellite-Derived Bathymetry Approach. In Proceedings of the US Hydrographic Conference 2015, National Harbor, MD, USA, 16–19 March 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Lyzenga, D.R. Passive Remote Sensing Techniques for Mapping Water Depth and Bottom Features. Appl. Opt. 1978, 17, 379–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stumpf, R.P.; Holderied, K.; Sinclair, M. Determination of Water Depth with High-Resolution Satellite Imagery over Variable Bottom Types. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2003, 48, 547–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geyman, E.C.; Maloof, A.C. A Simple Method for Extracting Water Depth from Multispectral Satellite Imagery in Regions of Variable Bottom Type. Earth Space Sci. 2019, 6, 527–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholamalifard, M.; Kutser, T.; Esmaili-Sari, A.; Abkar, A.A.; Naimi, B. Remotely Sensed Empirical Modeling of Bathymetry in the Southeastern Caspian Sea. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 2746–2762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Tao, Z.; Yang, X.; Yu, Y.; Zhou, X.; Li, Z. Bathymetry Retrieval from Hyperspectral Remote Sensing Data in Optical-Shallow Water. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 1205–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traganos, D.; Poursanidis, D.; Aggarwal, B.; Chrysoulakis, N.; Reinartz, P. Estimating Satellite-Derived Bathymetry (SDB) with the Google Earth Engine and Sentinel-2. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.; Zhao, Q.; Lu, Y.; Fu, D. Assessment of Empirical Algorithms for Shallow Water Bathymetry Using Multi-Spectral Imagery of Pearl River Delta Coast, China. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kibele, J.; Shears, N.T. Nonparametric Empirical Depth Regression for Bathymetric Mapping in Coastal Waters. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2016, 9, 5130–5138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caballero, I.; Stumpf, R.P. Retrieval of Nearshore Bathymetry from Sentinel-2A and 2B Satellites in South Florida Coastal Waters. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2019, 226, 106277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dekker, A.G.; Phinn, S.R.; Anstee, J.; Bissett, P.; Brando, V.E.; Casey, B.; Fearns, P.; Hedley, J.; Klonowski, W.; Lee, Z.P.; et al. Intercomparison of Shallow Water Bathymetry, Hydro-Optics, and Benthos Mapping Techniques in Australian and Caribbean Coastal Environments. Limnol. Oceanogr. Methods 2011, 9, 396–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klonowski, W.M. Retrieving Key Benthic Cover Types and Bathymetry from Hyperspectral Imagery. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2007, 1, 011505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutser, T.; Hedley, J.; Giardino, C.; Roelfsema, C.; Brando, V.E. Remote Sensing of Shallow Waters—A 50 Year Retrospective and Future Directions. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 240, 111619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leiper, I.A.; Phinn, S.R.; Roelfsema, C.M.; Joyce, K.E.; Dekker, A.G. Mapping Coral Reef Benthos, Substrates, and Bathymetry, Using Compact Airborne Spectrographic Imager (CASI) Data. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 6423–6445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Z.; Carder, K.L.; Mobley, C.D.; Steward, R.G.; Patch, J.S. Hyperspectral Remote Sensing for Shallow Waters: 2. Deriving Bottom Depths and Water Properties by Optimization. Appl. Opt. 1999, 38, 3831–3843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mobley, C.D.; Sundman, L.K.; Davis, C.O.; Bowles, J.H.; Downes, T.V.; Leathers, R.A.; Montes, M.J.; Bissett, W.P.; Kohler, D.D.R.; Reid, R.P.; et al. Interpretation of Hyperspectral Remote-Sensing Imagery by Spectrum Matching and Look-up Tables. Appl. Opt. 2005, 44, 3576–3592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capo, S.; Lubac, B.; Marieu, V.; Robinet, A.; Bru, D.; Bonneton, P. Assessment of the Decadal Morphodynamic Evolution of a Mixed Energy Inlet Using Ocean Color Remote Sensing. Ocean Dyn. 2014, 64, 1517–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolaños, R.; Hansen, L.B.; Rasmussen, M.L.; Golestani, M.; Mariegaard, J.S.; Nielsen, L.T. Coastal Bathymetry from Satellite and Its Use on Coastal Modelling. Coast. Eng. Proc. 2018, 1, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alevizos, E.; Roussos, A.; Alexakis, D. Geomorphometric Analysis of Nearshore Sedimentary Bedforms from High-Resolution Multi-Temporal Satellite-Derived Bathymetry. Geocarto Int. 2021, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacheco, A.; Horta, J.; Loureiro, C.; Ferreira, Ó. Retrieval of Nearshore Bathymetry from Landsat 8 Images: A Tool for Coastal Monitoring in Shallow Waters. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 159, 102–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alevizos, E. How to Create High Resolution Digital Elevation Models of Terrestrial Landscape Using Uav Imagery and Open-Source Software; Research Gate: Berlin, Germany, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Román, A.; Tovar-Sánchez, A.; Olivé, I.; Navarro, G. Using a UAV-Mounted Multispectral Camera for the Monitoring of Marine Macrophytes. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 722698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, L.; Mammi, I.; Pelliccia, F. UAV-Derived Multispectral Bathymetry. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alevizos, E.; Oikonomou, D.; Argyriou, A.V.; Alexakis, D.D. Fusion of Drone-Based RGB and Multi-Spectral Imagery for Shallow Water Bathymetry Inversion. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabiri, K.; Rezai, H.; Moradi, M. A Drone-Based Method for Mapping the Coral Reefs in the Shallow Coastal Waters—Case Study: Kish Island, Persian Gulf. Earth Sci. Inform. 2020, 13, 1265–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsons, M.; Bratanov, D.; Gaston, K.; Gonzalez, F. UAVs, Hyperspectral Remote Sensing, and Machine Learning Revolutionizing Reef Monitoring. Sensors 2018, 18, 2026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slocum, R.K.; Parrish, C.E.; Simpson, C.H. Combined Geometric-Radiometric and Neural Network Approach to Shallow Bathymetric Mapping with UAS Imagery. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2020, 169, 351–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starek, M.J.; Giessel, J. Fusion of Uas-Based Structure-from-Motion and Optical Inversion for Seamless Topo-Bathymetric Mapping. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Fort Worth, TX, USA, 23–28 July 2017; pp. 2999–3002. [Google Scholar]
- Agrafiotis, P.; Skarlatos, D.; Georgopoulos, A.; Karantzalos, K. Shallow water bathymetry mapping from uav imagery based on machine learning. ISPRS Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2019, XLII-2/W10, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietrich, J.T. Bathymetric Structure-from-Motion: Extracting Shallow Stream Bathymetry from Multi-View Stereo Photogrammetry. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2017, 42, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biausque, M.; Guisado-Pintado, E.; Grottoli, E.; Jackson, D.W.T.; Cooper, J.A.G. Seasonal Morphodynamics of Multiple Intertidal Bars (MITBs) on a Meso- to Macrotidal Beach. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2022, 47, 839–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foteinis, S.; Synolakis, C.; Tsoutsos, T. Numerical Modelling for Coastal Structures Design and Planning. A Case Study of the Venetian Harbour of Chania, Greece. Int. J. Geoengin. Case Hist 2018, 4, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsoukala, V.K.; Katsardi, V.; Hadjibiros, K.; Moutzouris, C.I. Beach Erosion and Consequential Impacts Due to the Presence of Harbours in Sandy Beaches in Greece and Cyprus. Environ. Process. 2015, 2, 55–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ignatiades, L. The Productive and Optical Status of the Oligotrophic Waters of the Southern Aegean Sea (Cretan Sea), Eastern Mediterranean. J. Plankton Res. 1998, 20, 985–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albert, A. Inversion Technique for Optical Remote Sensing in Shallow Water. Optische Fernerkundung von Flachwasserzonen. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Hamburg, Hamburg, Germany, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Marcello, J.; Eugenio, F.; Martín, J.; Marqués, F. Seabed Mapping in Coastal Shallow Waters Using High Resolution Multispectral and Hyperspectral Imagery. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alevizos, E.; Alexakis, D.D. Evaluation of Radiometric Calibration of Drone-Based Imagery for Improving Shallow Bathymetry Retrieval. Remote Sens. Lett. 2022, 13, 311–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poseidon System. Available online: https://poseidon.hcmr.gr/ (accessed on 1 April 2022).
- Gege, P. A Case Study at Starnberger See for Hyperspectral Bathymetry Mapping Using Inverse Modeling. In Proceedings of the 2014 6th Workshop on Hyperspectral Image and Signal Processing: Evolution in Remote Sensing (WHISPERS), Lausanne, Switzerland, 24–27 June 2014; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Dörnhöfer, K.; Göritz, A.; Gege, P.; Pflug, B.; Oppelt, N. Water Constituents and Water Depth Retrieval from Sentinel-2A—A First Evaluation in an Oligotrophic Lake. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niroumand-Jadidi, M.; Bovolo, F.; Bruzzone, L.; Gege, P. Physics-Based Bathymetry and Water Quality Retrieval Using PlanetScope Imagery: Impacts of 2020 COVID-19 Lockdown and 2019 Extreme Flood in the Venice Lagoon. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alevizos, E.; Le Bas, T.; Alexakis, D. Assessment of PRISMA Level-2 Hyperspectral Imagery for Large Scale Satellite-Derived Bathymetry Retrieval. Mar. Geod. 2022, 45, 251–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albert, A.; Mobley, C.D. An Analytical Model for Subsurface Irradiance and Remote Sensing Reflectance in Deep and Shallow Case-2 Waters. Opt. Express 2003, 11, 2873–2890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gege, P.; Albert, A. A tool for inverse modeling of spectral measurements in deep and shallow waters. In Remote Sensing of Aquatic Coastal Ecosystem Processes; Remote Sensing and Digital Image Processing; Richardson, L.L., Ledrew, E.F., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2006; pp. 81–109. ISBN 978-1-4020-3968-3. [Google Scholar]
- Gege, P. WASI-2D: A Software Tool for Regionally Optimized Analysis of Imaging Spectrometer Data from Deep and Shallow Waters. Comput. Geosci. 2014, 62, 208–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouquet, P.; Quod, J.-P. Spectrhabent-OI-Acquisition et Analyse de la Librairie Spectrale Sous-Marine; Archimer: Plouzane, France, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Castelle, B.; Ruessink, B.G.; Bonneton, P.; Marieu, V.; Bruneau, N.; Price, T.D. Coupling Mechanisms in Double Sandbar Systems. Part 1: Patterns and Physical Explanation. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2010, 35, 476–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribas, F.; Falqués, A.; de Swart, H.E.; Dodd, N.; Garnier, R.; Calvete, D. Understanding Coastal Morphodynamic Patterns from Depth-Averaged Sediment Concentration. Rev. Geophys. 2015, 53, 362–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castelle, B.; Scott, T.; Brander, R.W.; McCarroll, R.J. Rip Current Types, Circulation and Hazard. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2016, 163, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreeva, N.; Saprykina, Y.; Valchev, N.; Eftimova, P.; Kuznetsov, S. Influence of Wave Climate on Intra and Inter-Annual Nearshore Bar Dynamics for a Sandy Beach. Geosciences 2021, 11, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holman, R.A.; Symonds, G.; Thornton, E.B.; Ranasinghe, R. Rip Spacing and Persistence on an Embayed Beach. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2006, 111, C01006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garnier, R.; Falqués, A.; Calvete, D.; Thiébot, J.; Ribas, F. A Mechanism for Sandbar Straightening by Oblique Wave Incidence. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2013, 40, 2726–2730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, T.D.; Ruessink, B.G. State Dynamics of a Double Sandbar System. Cont. Shelf Res. 2011, 31, 659–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Splinter, K.D.; Holman, R.A.; Plant, N.G. A Behavior-Oriented Dynamic Model for Sandbar Migration and 2DH Evolution. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2011, 116, C01020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thornton, E.B.; MacMahan, J.; Sallenger, A.H. Rip Currents, Mega-Cusps, and Eroding Dunes. Mar. Geol. 2007, 240, 151–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dean, R. Equilibrium Beach Profiles: Characteristics and Applications. J. Coast. Res. 1991, 7, 53–84. [Google Scholar]
- Suomalainen, J.; Oliveira, R.A.; Hakala, T.; Koivumäki, N.; Markelin, L.; Näsi, R.; Honkavaara, E. Direct Reflectance Transformation Methodology for Drone-Based Hyperspectral Imaging. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 266, 112691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedley, J.D.; Roelfsema, C.; Brando, V.; Giardino, C.; Kutser, T.; Phinn, S.; Mumby, P.J.; Barrilero, O.; Laporte, J.; Koetz, B. Coral Reef Applications of Sentinel-2: Coverage, Characteristics, Bathymetry and Benthic Mapping with Comparison to Landsat 8. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 216, 598–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holman, R.; Haller, M.C. Remote Sensing of the Nearshore. Annu. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2013, 5, 95–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dierssen, H.M.; Ackleson, S.G.; Joyce, K.E.; Hestir, E.L.; Castagna, A.; Lavender, S.; McManus, M.A. Living up to the Hype of Hyperspectral Aquatic Remote Sensing: Science, Resources and Outlook. Front. Environ. Sci. 2021, 9, 649528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hovis, W.A.; Clark, D.K.; Anderson, F.; Austin, R.W.; Wilson, W.H.; Baker, E.T.; Ball, D.; Gordon, H.R.; Mueller, J.L.; El-Sayed, S.Z.; et al. Nimbus-7 Coastal Zone Color Scanner: System Description and Initial Imagery. Science 1980, 210, 60–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| 4 November 21 | 0–1 m | 1–2 m | 2–3 m | 3–4 m | 4–5 m |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Samples | 498 | 573 | 597 | 423 | 177 |
| MAE (m) | 0.13 | 0.22 | 0.21 | 0.29 | 0.38 |
| RMSE (m) | 0.16 | 0.27 | 0.29 | 0.37 | 0.45 |
| St.dev. (m) | 0.16 | 0.26 | 0.28 | 0.35 | 0.40 |
| 31 March 22 | 1–2 m | 2–3 m | 3–4 m | ||
| Samples | 434 | 113 | 14 | ||
| MAE (m) | 0.16 | 0.24 | 0.29 | ||
| RMSE (m) | 0.18 | 0.29 | 0.39 | ||
| St.dev. (m) | 0.10 | 0.19 | 0.30 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alevizos, E.; Alexakis, D.D. Monitoring Short-Term Morphobathymetric Change of Nearshore Seafloor Using Drone-Based Multispectral Imagery. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 6035. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14236035
Alevizos E, Alexakis DD. Monitoring Short-Term Morphobathymetric Change of Nearshore Seafloor Using Drone-Based Multispectral Imagery. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(23):6035. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14236035
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlevizos, Evangelos, and Dimitrios D. Alexakis. 2022. "Monitoring Short-Term Morphobathymetric Change of Nearshore Seafloor Using Drone-Based Multispectral Imagery" Remote Sensing 14, no. 23: 6035. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14236035
APA StyleAlevizos, E., & Alexakis, D. D. (2022). Monitoring Short-Term Morphobathymetric Change of Nearshore Seafloor Using Drone-Based Multispectral Imagery. Remote Sensing, 14(23), 6035. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14236035







