Reverse Thinking: The Logical System Research Method of Urban Thermal Safety Pattern Construction, Evaluation, and Optimization
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Research Overview
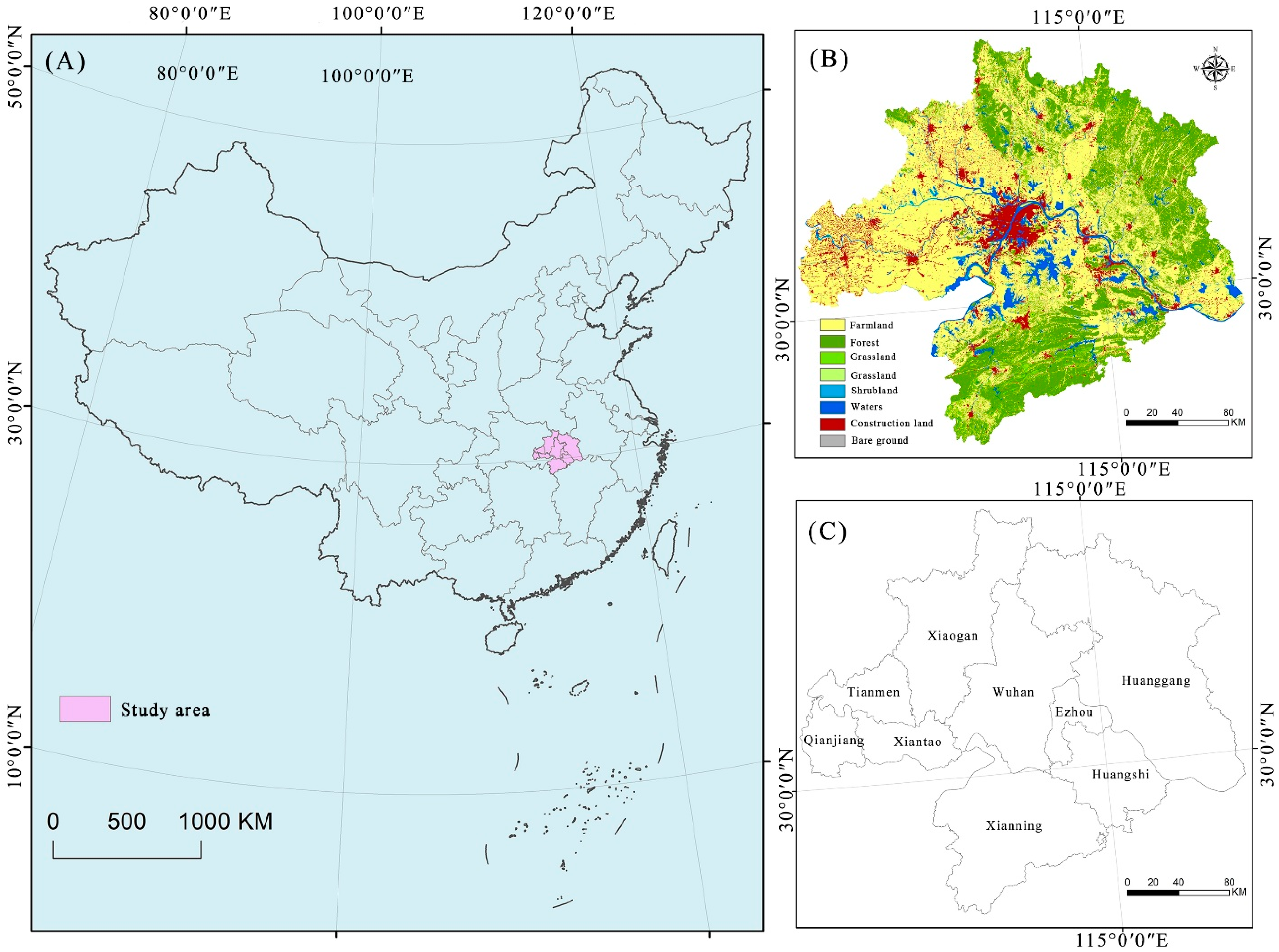
2.1. Research Area
2.2. Research Framework and Data Sources
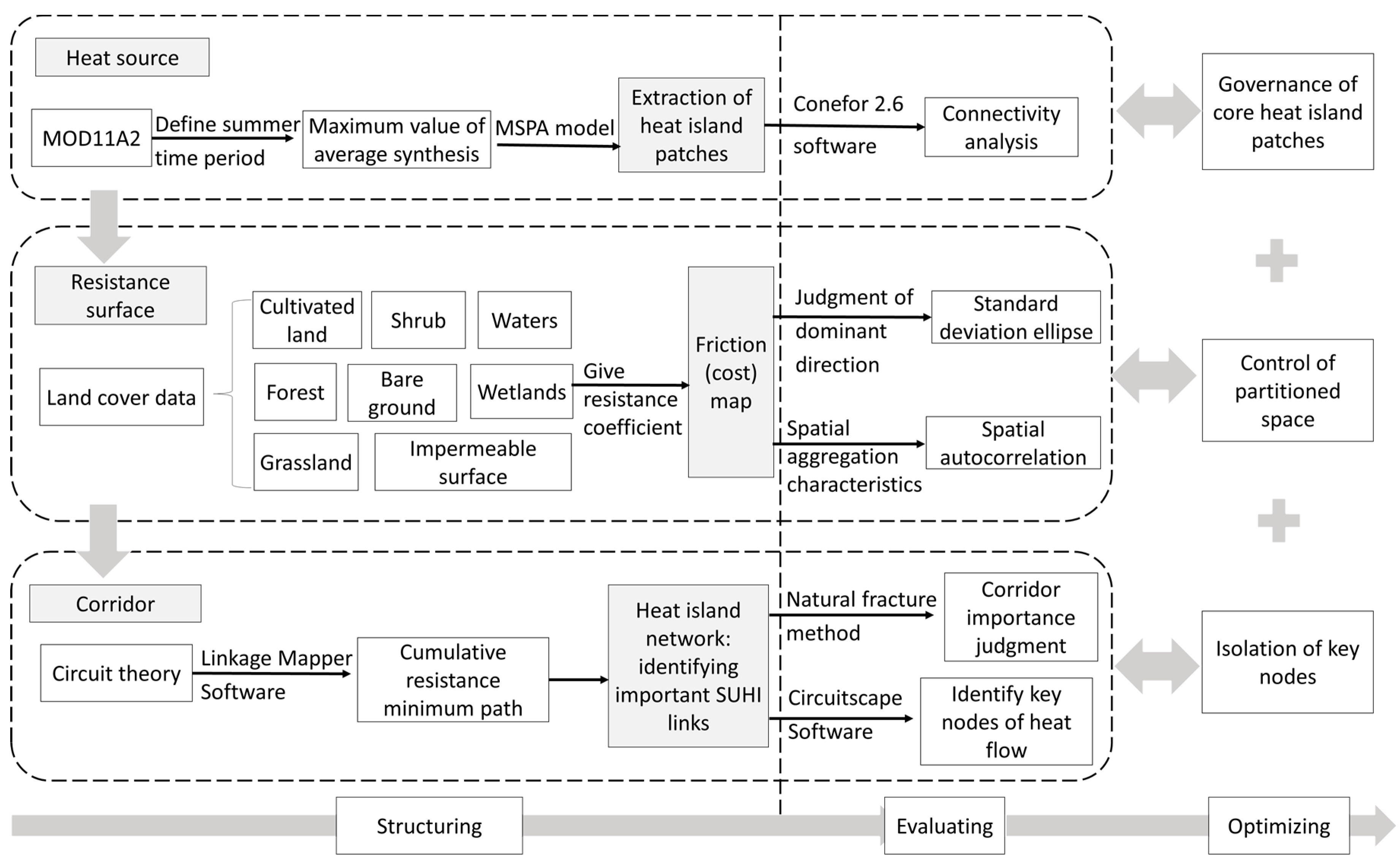
2.2.1. Research Framework
2.2.2. Data Sources
3. Method
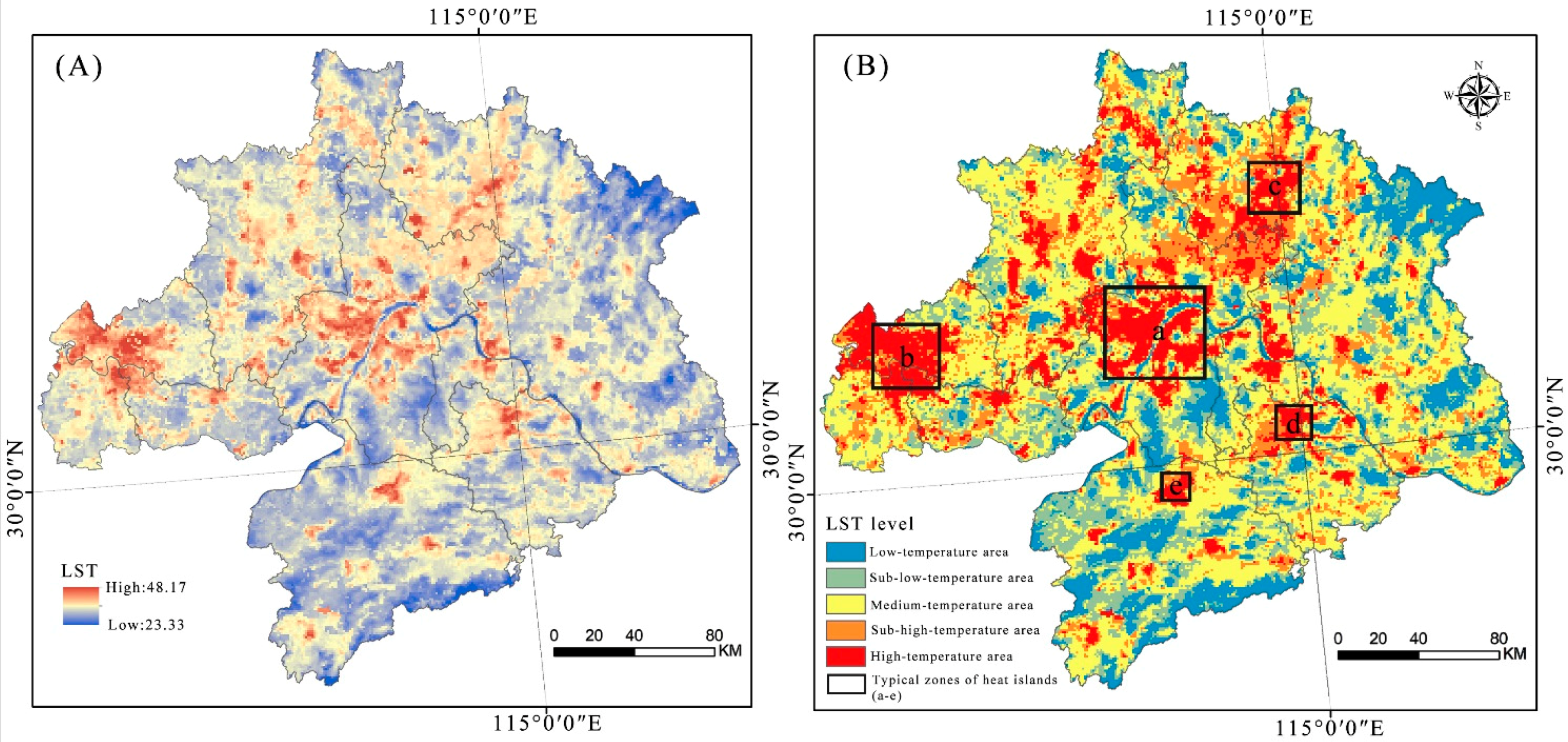
3.1. Seasonal Division and Calculation of Land Surface Temperature (LST)
3.2. Division of Urban Heat Island Intensity
3.3. MSPA-Based SUHI Mode
3.4. Connectivity Analysis
3.5. Building the Friction (Cost) Map
3.6. Standard Deviation Ellipse and Spatial Autocorrelation Analysis
3.7. Construction of a Heat Island Network Based on Circuit Theory
4. Results
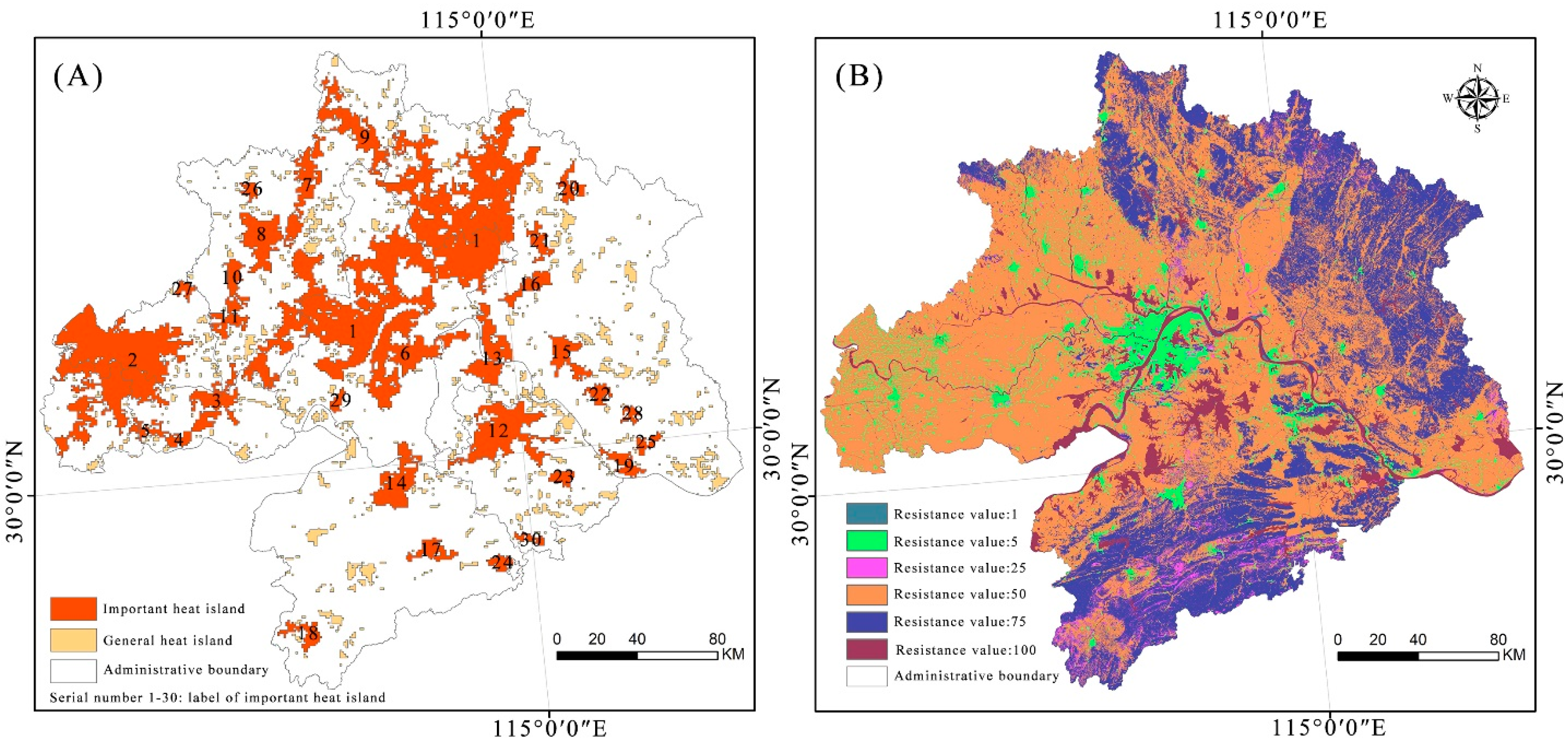
4.1. Construction of the Urban Thermal Security Pattern
4.2. Evaluation of the Urban Thermal Safety Pattern
5. Discussion
5.1. Characteristics of the Urban Thermal Safety Pattern
5.2. Optimization of the Urban Thermal Safety Pattern
5.2.1. Comprehensive “Destruction” of Patches and Corridors
5.2.2. Effective “Barrier” Based on Key Point Analysis
5.3. Limitations and Deficiencies
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lo, C.P.; Quattrochi, D.A.; Luvall, J.C. Application of High-Resolution Thermal Infrared Remote Sensing and GIS to Assess the Urban Heat Island Effect. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1997, 18, 287–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Malley, C.; Piroozfar, P.; Farr, E.R.; Pomponi, F. Urban Heat Island (UHI) Mitigating Strategies: A Case-Based Comparative Analysis. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2015, 19, 222–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, L. The Climate of London: Deduced from Meteorological Observations Made in the Metropolis and at Various Places around It; Harvey and Darton: London, UK, 1833; Volume 3. [Google Scholar]
- Stone Jr, B.; Rodgers, M.O. Urban Form and Thermal Efficiency: How the Design of Cities Influences the Urban Heat Island Effect. Am. Plan. Assoc. J. Am. Plan. Assoc. 2001, 67, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizwan, A.M.; Dennis, L.Y.; Chunho, L.I.U. A Review on the Generation, Determination and Mitigation of Urban Heat Island. J. Environ. Sci. 2008, 20, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Xiao, J.; Bonafoni, S.; Berger, C.; Deilami, K.; Zhou, Y.; Frolking, S.; Yao, R.; Qiao, Z.; Sobrino, J. Satellite Remote Sensing of Surface Urban Heat Islands: Progress, Challenges, and Perspectives. Remote Sens. 2018, 11, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.-L.; Zhao, H.-M.; Li, P.-X.; Yin, Z.-Y. Remote Sensing Image-Based Analysis of the Relationship between Urban Heat Island and Land Use/Cover Changes. Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 104, 133–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, H.; Sodoudi, S. Quantifying Urban Heat Island Intensity and Its Physical Mechanism Using WRF/UCM. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 650, 3110–3119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corburn, J. Cities, Climate Change and Urban Heat Island Mitigation: Localising Global Environmental Science. Urban Stud. 2009, 46, 413–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Yu, Z.; Wang, L.; Vejre, H. Suitability of Regional Development Based on Ecosystem Service Benefits and Losses: A Case Study of the Yangtze River Delta Urban Agglomeration, China. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 107, 105579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Hu, C.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, J. Examining Spatio-Temporal Characteristics of Urban Heat Islands and Factors Driving Them in Hangzhou, China. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2021, 14, 8316–8325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Sun, D.; Hu, C.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J. Seasonal Contrast and Interactive Effects of Potential Drivers on Land Surface Temperature in the Sichuan Basin, China. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbari, H.; Kolokotsa, D. Three Decades of Urban Heat Islands and Mitigation Technologies Research. Energy Build. 2016, 133, 834–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J. Urban Ecology and Sustainability: The State-of-the-Science and Future Directions. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2014, 125, 209–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimm, N.B.; Faeth, S.H.; Golubiewski, N.E.; Redman, C.L.; Wu, J.; Bai, X.; Briggs, J.M. Global Change and the Ecology of Cities. Science 2008, 319, 756–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oke, T.R.; Mills, G.; Christen, A.; Voogt, J.A. Urban Climates; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2017; ISBN 0-521-84950-0. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Zhou, Y.; Asrar, G.R.; Imhoff, M.; Li, X. The Surface Urban Heat Island Response to Urban Expansion: A Panel Analysis for the Conterminous United States. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 605, 426–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Zhao, S.; Liu, S.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, C. Surface Urban Heat Island in China’s 32 Major Cities: Spatial Patterns and Drivers. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 152, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saaroni, H.; Amorim, J.H.; Hiemstra, J.A.; Pearlmutter, D. Urban Green Infrastructure as a Tool for Urban Heat Mitigation: Survey of Research Methodologies and Findings across Different Climatic Regions. Urban Clim. 2018, 24, 94–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowler, D.E.; Buyung-Ali, L.; Knight, T.M.; Pullin, A.S. Urban Greening to Cool Towns and Cities: A Systematic Review of the Empirical Evidence. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2010, 97, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Wang, J.; Cadenasso, M.L. Effects of the Spatial Configuration of Trees on Urban Heat Mitigation: A Comparative Study. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 195, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Sun, R.; Lu, Y. A Conceptual Model for a Process-Oriented Landscape Pattern Analysis. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2019, 62, 2050–2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Yang, G.; Schlaberg, J. Reverse Thinking: A New Method from the Graph Perspective for Evaluating and Mitigating Regional Surface Heat Islands. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Bonafoni, S.; Zhang, L.; Wang, R. Remote Sensing of the Urban Heat Island Effect in a Highly Populated Urban Agglomeration Area in East China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 628–629, 415–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Z.; Yao, Y.; Yang, G.; Wang, X.; Vejre, H. Spatiotemporal Patterns and Characteristics of Remotely Sensed Region Heat Islands during the Rapid Urbanization (1995–2015) of Southern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 674, 242–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, J. Area Delineation and Spatial-Temporal Dynamics of Urban Heat Island in Lanzhou City, China Using Remote Sensing Imagery. J. Indian Soc. Remote Sens. 2016, 44, 111–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santamouris, M. Cooling the Cities–a Review of Reflective and Green Roof Mitigation Technologies to Fight Heat Island and Improve Comfort in Urban Environments. Sol. Energy 2014, 103, 682–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meerow, S.; Newell, J.P. Spatial Planning for Multifunctional Green Infrastructure: Growing Resilience in Detroit. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2017, 159, 62–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, R.; Xie, W.; Chen, L. A Landscape Connectivity Model to Quantify Contributions of Heat Sources and Sinks in Urban Regions. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2018, 178, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Cheng, X.; Hu, Y.; Corcoran, J. A Landscape Connectivity Approach to Mitigating the Urban Heat Island Effect. Landsc. Ecol. 2022, 37, 1707–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Hu, Y.; Dong, J.; Liu, Q.; Liu, Y. Quantifying Spatial Morphology and Connectivity of Urban Heat Islands in a Megacity: A Radius Approach. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 714, 136792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Yang, G. How to Build a Heat Network to Alleviate Surface Heat Island Effect? Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 74, 103135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y. A Review on the Development of Cool Pavements to Mitigate Urban Heat Island Effect. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 52, 445–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, G.; Wu, Z.; Cao, Z.; Chen, Y.; Zheng, Z. Location of Greenspace Matters: A New Approach to Investigating the Effect of the Greenspace Spatial Pattern on Urban Heat Environment. Landsc. Ecol. 2021, 36, 1533–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Odeh, I.O.; Ramadan, E. Assessment of Land Surface Temperature in Relation to Landscape Metrics and Fractional Vegetation Cover in an Urban/Peri-Urban Region Using Landsat Data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2013, 34, 168–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunawardena, K.R.; Wells, M.J.; Kershaw, T. Utilising Green and Bluespace to Mitigate Urban Heat Island Intensity. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 584, 1040–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Sun, D.; Zhang, J. Combining MSPA-MCR Model to Evaluate the Ecological Network in Wuhan, China. Land 2022, 11, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Fang, X.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, S.; Luan, Q. Assessment of Surface Urban Heat Island across China’s Three Main Urban Agglomerations. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2018, 133, 473–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saura, S.; Pascual-Hortal, L. A New Habitat Availability Index to Integrate Connectivity in Landscape Conservation Planning: Comparison with Existing Indices and Application to a Case Study. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2007, 83, 91–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Y.; Liu, S.; Sun, Y.; Shi, F.; Beazley, R. Construction and Optimization of an Ecological Network Based on Morphological Spatial Pattern Analysis and Circuit Theory. Landsc. Ecol. 2021, 36, 2059–2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McRae, B.H.; Dickson, B.G.; Keitt, T.H.; Shah, V.B. Using Circuit Theory to Model Connectivity in Ecology, Evolution, and Conservation. Ecology 2008, 89, 2712–2724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickson, B.G.; Albano, C.M.; Anantharaman, R.; Beier, P.; Fargione, J.; Graves, T.A.; Gray, M.E.; Hall, K.R.; Lawler, J.J.; Leonard, P.B. Circuit-theory Applications to Connectivity Science and Conservation. Conserv. Biol. 2019, 33, 239–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wu, M.; Hu, M.; Fan, C.; Wang, T.; Xia, B. Promoting Landscape Connectivity of Highly Urbanized Area: An Ecological Network Approach. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 125, 107487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Wang, H.; Shan, L.; Xiao, F. Constructing and Optimizing Urban Ecological Network in the Context of Rapid Urbanization for Improving Landscape Connectivity. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 132, 108319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Li, H.; Huang, Y. The Complex Ecological Network’s Resilience of the Wuhan Metropolitan Area. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 130, 108101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Ma, Y.; Wang, J.; You, X. Landscape Pattern Analysis and Ecological Network Planning of Tianjin City. Urban For. Urban Green. 2019, 46, 126479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buyantuyev, A.; Wu, J. Urban Heat Islands and Landscape Heterogeneity: Linking Spatiotemporal Variations in Surface Temperatures to Land-Cover and Socioeconomic Patterns. Landsc. Ecol. 2010, 25, 17–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coutts, A.M.; Tapper, N.J.; Beringer, J.; Loughnan, M.; Demuzere, M. Watering Our Cities: The Capacity for Water Sensitive Urban Design to Support Urban Cooling and Improve Human Thermal Comfort in the Australian Context. Prog. Phys. Geogr. 2013, 37, 2–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.Y.; Jim, C.Y. Assessment and Valuation of the Ecosystem Services Provided by Urban Forests. In Ecology, Planning, and Management of Urban Forests; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; pp. 53–83. [Google Scholar]
- Sacks, W.J.; Cook, B.I.; Buenning, N.; Levis, S.; Helkowski, J.H. Effects of Global Irrigation on the Near-Surface Climate. Clim. Dyn. 2009, 33, 159–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Tao, F.; Liu, J. Regional Temperature Change over the Huang-Huai-Hai Plain of China: The Roles of Irrigation versus Urbanization. Int. J. Climatol. 2014, 34, 1181–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Z.; Yan, C.; Yu, L.; Jiang, X.; Ding, J.; Qin, L.; Wang, B.; Qiu, G. Impacts of Land Use/Land Cover Types on Interactions between Urban Heat Island Effects and Heat Waves. Build. Environ. 2021, 204, 108138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Jia, J.; Liu, Y.; Li, H.; Wu, J. Seasonal Contrast of the Dominant Factors for Spatial Distribution of Land Surface Temperature in Urban Areas. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 215, 255–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verbeke, S.; Audenaert, A. Thermal Inertia in Buildings: A Review of Impacts across Climate and Building Use. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 82, 2300–2318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Tian, G. Analysis of the Impact of Land Use/Land Cover Change on Land Surface Temperature with Remote Sensing. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2010, 2, 571–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, D.X.; Pla, F.; Latorre-Carmona, P.; Myint, S.W.; Caetano, M.; Kieu, H.V. Characterizing the Relationship between Land Use Land Cover Change and Land Surface Temperature. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2017, 124, 119–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuill, R.S. The Standard Deviational Ellipse; an Updated Tool for Spatial Description. Geogr. Ann. Ser. B Hum. Geogr. 1971, 53, 28–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefever, D.W. Measuring Geographic Concentration by Means of the Standard Deviational Ellipse. Am. J. Sociol. 1926, 32, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, C.; Myint, S. A Comparison of Spatial Autocorrelation Indices and Landscape Metrics in Measuring Urban Landscape Fragmentation. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2014, 121, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Tian, J.; Zheng, W.; Yin, L. Spatial and Temporal Distribution Characteristics of Haze and Pollution Particles in China Based on Spatial Statistics. Urban Clim. 2022, 41, 101031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Fang, C.; Wang, S. Exploring Spatiotemporal Changes in Ecosystem-Service Values and Hotspots in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 545, 609–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, P.; Yang, J.; Wang, H.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y. A New Method of Simulating Urban Ventilation Corridors Using Circuit Theory. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2020, 59, 102162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Hu, Y.; Zheng, F. Research on Recognition and Protection of Ecological Security Patterns Based on Circuit Theory: A Case Study of Jinan City. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 12414–12427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Huang, T.-T.; Zheng, X. A Method of Linking Functional and Structural Connectivity Analysis in Urban Green Infrastructure Network Construction. Urban Ecosyst. 2022, 25, 909–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hathway, E.A.; Sharples, S. The Interaction of Rivers and Urban Form in Mitigating the Urban Heat Island Effect: A UK Case Study. Build. Environ. 2012, 58, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Zhang, Y. Water Bodies’ Cooling Effects on Urban Land Daytime Surface Temperature: Ecosystem Service Reducing Heat Island Effect. Sustainability 2019, 11, 787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Zhang, F. Effect of Human Settlements on Urban Thermal Environment and Factor Analysis Based on Multi-Source Data: A Case Study of Changsha City. J. Geogr. Sci. 2021, 31, 819–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Q.; Zhang, L.; Sun, Z.; Meng, F.; Wang, L.; Sun, Y. Characterizing Spatial and Temporal Trends of Surface Urban Heat Island Effect in an Urban Main Built-up Area: A 12-Year Case Study in Beijing, China. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 204, 826–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.D.; Dong, L.; Yan, H.; Yang, N.; Xiong, Y. The Influence of the Spatial Characteristics of Urban Green Space on the Urban Heat Island Effect in Suzhou Industrial Park. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2018, 40, 428–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarrat, C.; Lemonsu, A.; Masson, V.; Guédalia, D. Impact of Urban Heat Island on Regional Atmospheric Pollution. Atmos. Environ. 2006, 40, 1743–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oke, T.R.; Johnson, G.T.; Steyn, D.G.; Watson, I.D. Simulation of Surface Urban Heat Islands under ‘Ideal’Conditions at Night Part 2: Diagnosis of Causation. Bound.-Layer Meteorol. 1991, 56, 339–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulpiani, G. On the Linkage between Urban Heat Island and Urban Pollution Island: Three-Decade Literature Review towards a Conceptual Framework. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 751, 141727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Meng, Q.; Allam, M.; Hu, D.; Zhang, L.; Menenti, M. Environmental and Anthropogenic Drivers of Surface Urban Heat Island Intensity: A Case-Study in the Yangtze River Delta, China. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 128, 107845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Temperature Class | Division Method of Thermal Field |
|---|---|
| High-temperature zone | Ts > μ + std |
| Medium-high temperature zone | μ + 0.5 std ≤ Ts ≤ μ + std |
| Middle-temperature zone | μ − 0.5 std ≤ Ts ≤ μ + 0.5 std |
| Medium-low temperature zone | μ − std ≤ Ts ≤ μ − 0.5 std |
| Low-temperature zone | Ts ≤ μ − std |
| Types | Area/km2 | Percent in Foreground Area/% | Percent in Total Area/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| Core | 15,845.5323 | 97.59243% | 27.325795% |
| Loop | 0.1377 | 0.00085% | 0.000237% |
| Bridge | 0.4896 | 0.00302% | 0.000844% |
| Edge | 366.5637 | 2.25766% | 0.632143% |
| Islet | 0.0027 | 0.00002% | 0.000005% |
| Branch | 0.0324 | 0.00020% | 0.000056% |
| Perforation | 23.6772 | 0.14583% | 0.040832% |
| Serial Number | Area/km2 | dPC Value |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 5227.9668 | 87.1181 |
| 2 | 2124.2952 | 23.8945 |
| 3 | 314.8272 | 22.0948 |
| 4 | 68.1552 | 18.6799 |
| 5 | 90.6255 | 18.2483 |
| 6 | 793.9566 | 17.1256 |
| 7 | 352.3500 | 10.6279 |
| 8 | 366.7203 | 6.7918 |
| 9 | 434.9169 | 6.6787 |
| 10 | 120.9843 | 2.2007 |
| 11 | 163.9728 | 1.3063 |
| 12 | 713.1960 | 0.7596 |
| 13 | 384.5322 | 0.2208 |
| 14 | 373.0311 | 0.2078 |
| 15 | 207.6714 | 0.0644 |
| 16 | 149.6457 | 0.0334 |
| 17 | 136.6938 | 0.0279 |
| 18 | 124.4772 | 0.0231 |
| 19 | 120.0708 | 0.0215 |
| 20 | 116.4915 | 0.0203 |
| 21 | 108.6786 | 0.0176 |
| 22 | 85.7034 | 0.0110 |
| 23 | 69.7050 | 0.0073 |
| 24 | 68.1696 | 0.0069 |
| 25 | 62.8362 | 0.0059 |
| 26 | 51.4611 | 0.0040 |
| 27 | 51.1101 | 0.0039 |
| 28 | 48.0726 | 0.0035 |
| 29 | 46.6524 | 0.0033 |
| 30 | 46.2600 | 0.0032 |
| The Circumference of an Ellipse/km | The Area of an Ellipse/km2 | Center Point X Coordinates | Center Point Y Coordinates | The Length of the X-Axis of an Ellipse/km | The Length of the Y-Axis of the Ellipse/km | Azimuth/(°) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 635.32 | 27,922.31 | 114°6′33″ | 30°24′4″ | 114.54 | 77.60 | 92.13 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, C.; Li, H. Reverse Thinking: The Logical System Research Method of Urban Thermal Safety Pattern Construction, Evaluation, and Optimization. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 6036. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14236036
Hu C, Li H. Reverse Thinking: The Logical System Research Method of Urban Thermal Safety Pattern Construction, Evaluation, and Optimization. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(23):6036. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14236036
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Chunguang, and He Li. 2022. "Reverse Thinking: The Logical System Research Method of Urban Thermal Safety Pattern Construction, Evaluation, and Optimization" Remote Sensing 14, no. 23: 6036. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14236036
APA StyleHu, C., & Li, H. (2022). Reverse Thinking: The Logical System Research Method of Urban Thermal Safety Pattern Construction, Evaluation, and Optimization. Remote Sensing, 14(23), 6036. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14236036





