Entropy Approximation by Machine Learning Regression: Application for Irregularity Evaluation of Images in Remote Sensing
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods and Datasets
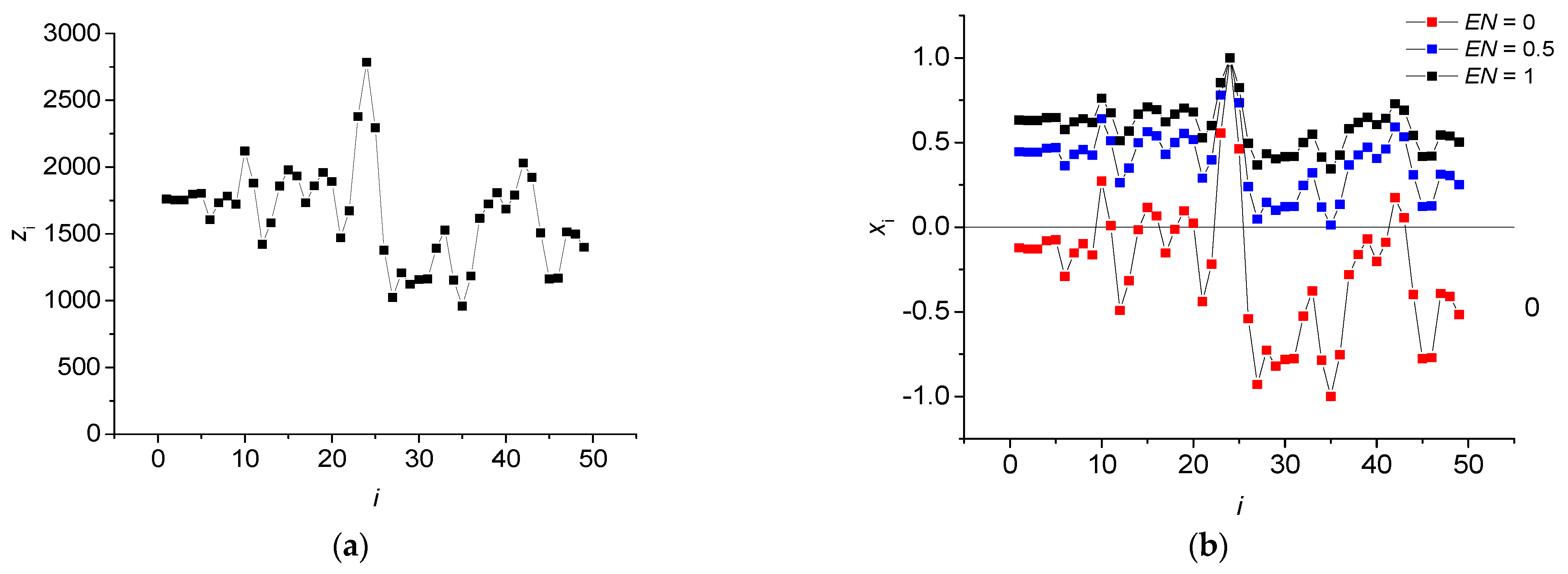
2.1. Time Series Normalization Method
2.2. Methods for Entropy Evaluation with Standard Methods
2.2.1. Singular Value Decomposition Entropy
2.2.2. Permutation Entropy
2.2.3. Sample Entropy
2.2.4. Neural Network Entropy
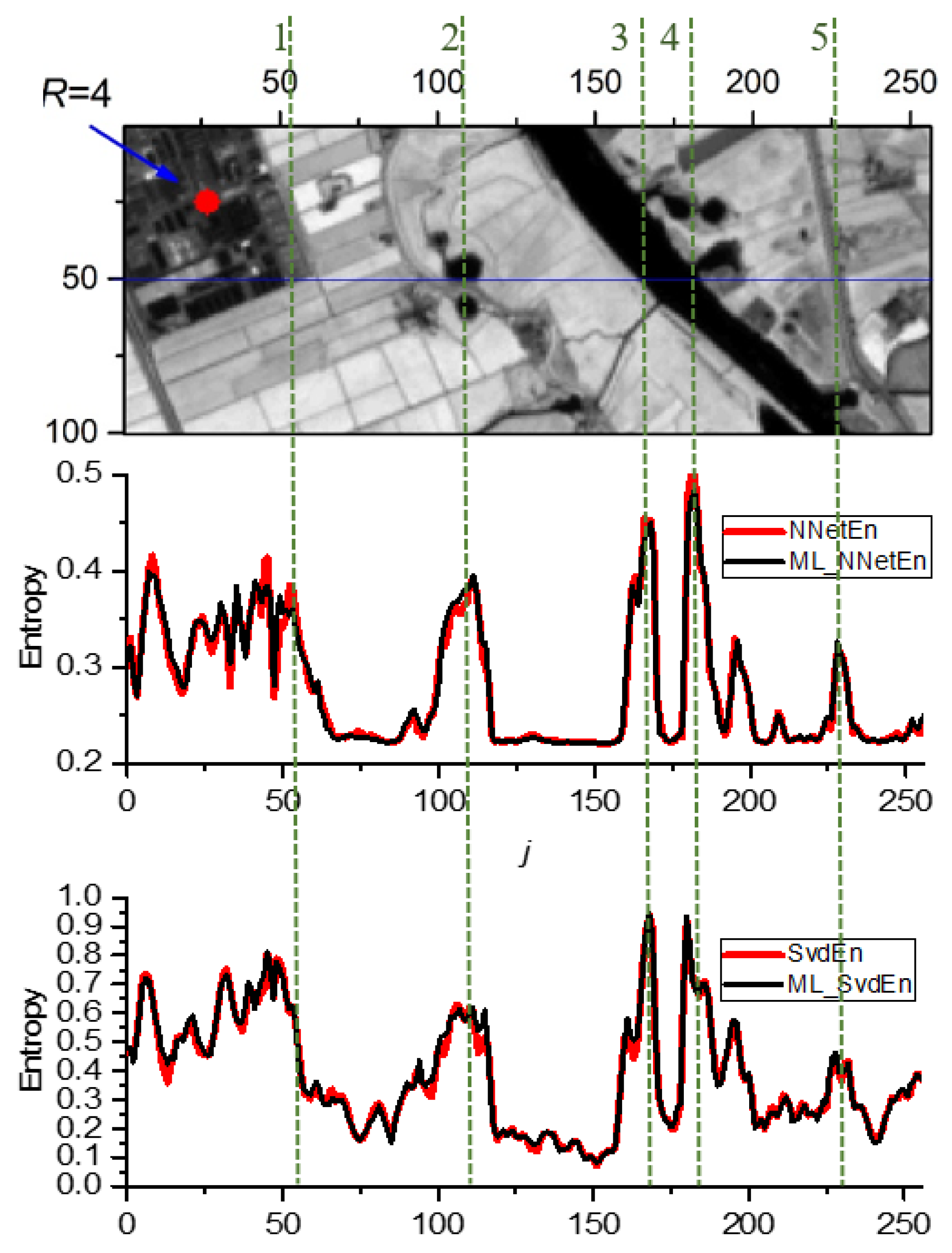
2.2.5. Method for 2D Entropy Calculation with Circular Kernels
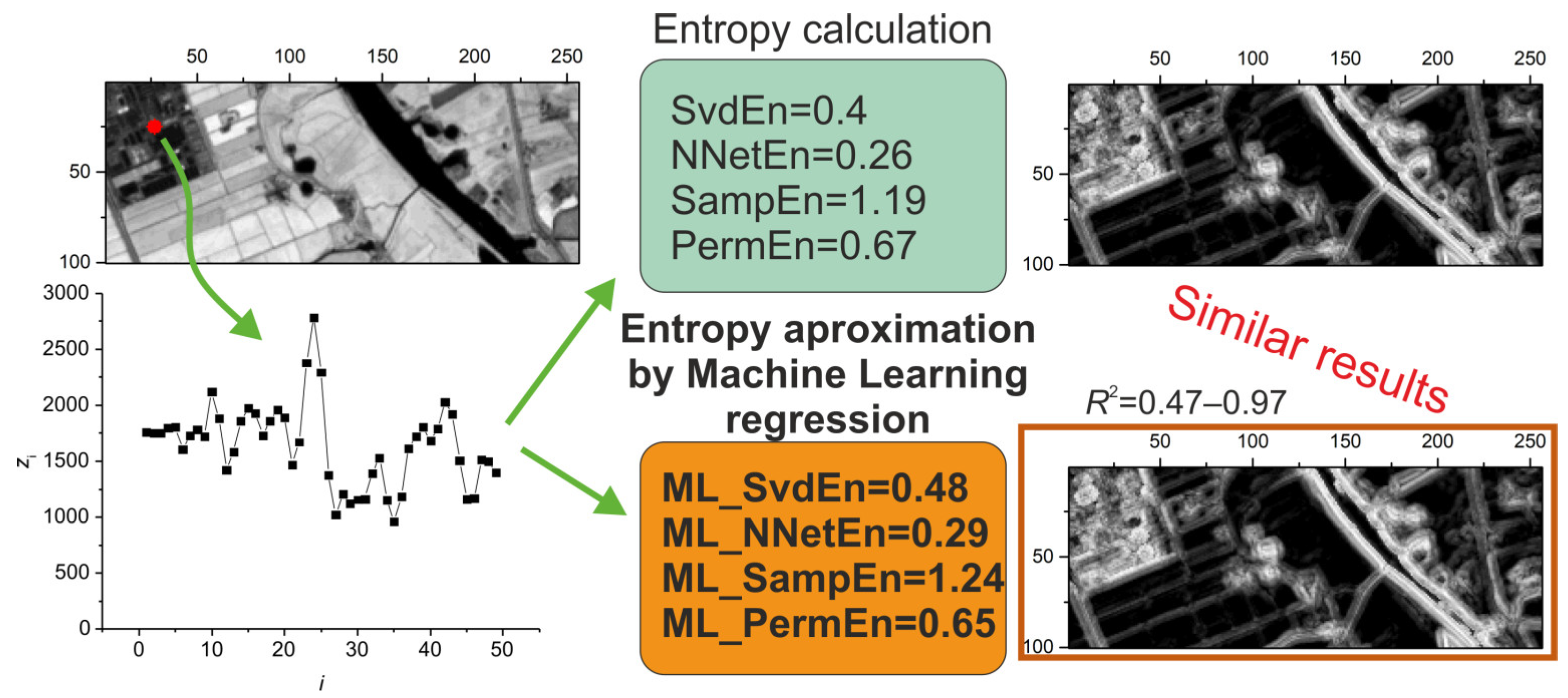
2.3. Entropy Approximation by ML Regression Models
- Setting the entropy type. We used 4 types of entropy: SvdEn, SampEn, PermEn and NNetEn. We denoted their approximations using ML regression as ML_SvdEn, ML_SampEn, ML_PermEn and ML_NNetEn, respectively.
- Setting the ML algorithm for regression: a gradient boosting algorithm was used as the main method.
- Setting the length of the time series N. In this research, we tested several lengths of short time series N = 5, 13, 29, 49, 81 and 113 (see Table 1).
- Generation of training dataset using two images. Each element of the training set consisted of a time series of length N and an output entropy value.
- Hyperparameter optimization and training of the regression model using training dataset.
- Generation of a test dataset based on 198 sample images from Sentinel-2. One element of the test set consisted of a time series of length N and the output entropy value.
- Testing the regression model on a test dataset and determining the error using R2 metric. At the input of the ML algorithm, it is necessary to supply a vector of a time series of a certain length on which the algorithm was trained.
- Calculation of 2D entropies using circular kernels: SvdEn2D, SampEn2D, PermEn2D and NNetEn2D.
2.3.1. Dataset Description
2.3.2. Training Dataset
2.3.3. Hyperparameter Optimization and Training the Regression Model
2.3.4. Test Dataset Generation
2.3.5. Estimation the Accuracy of the ML Model
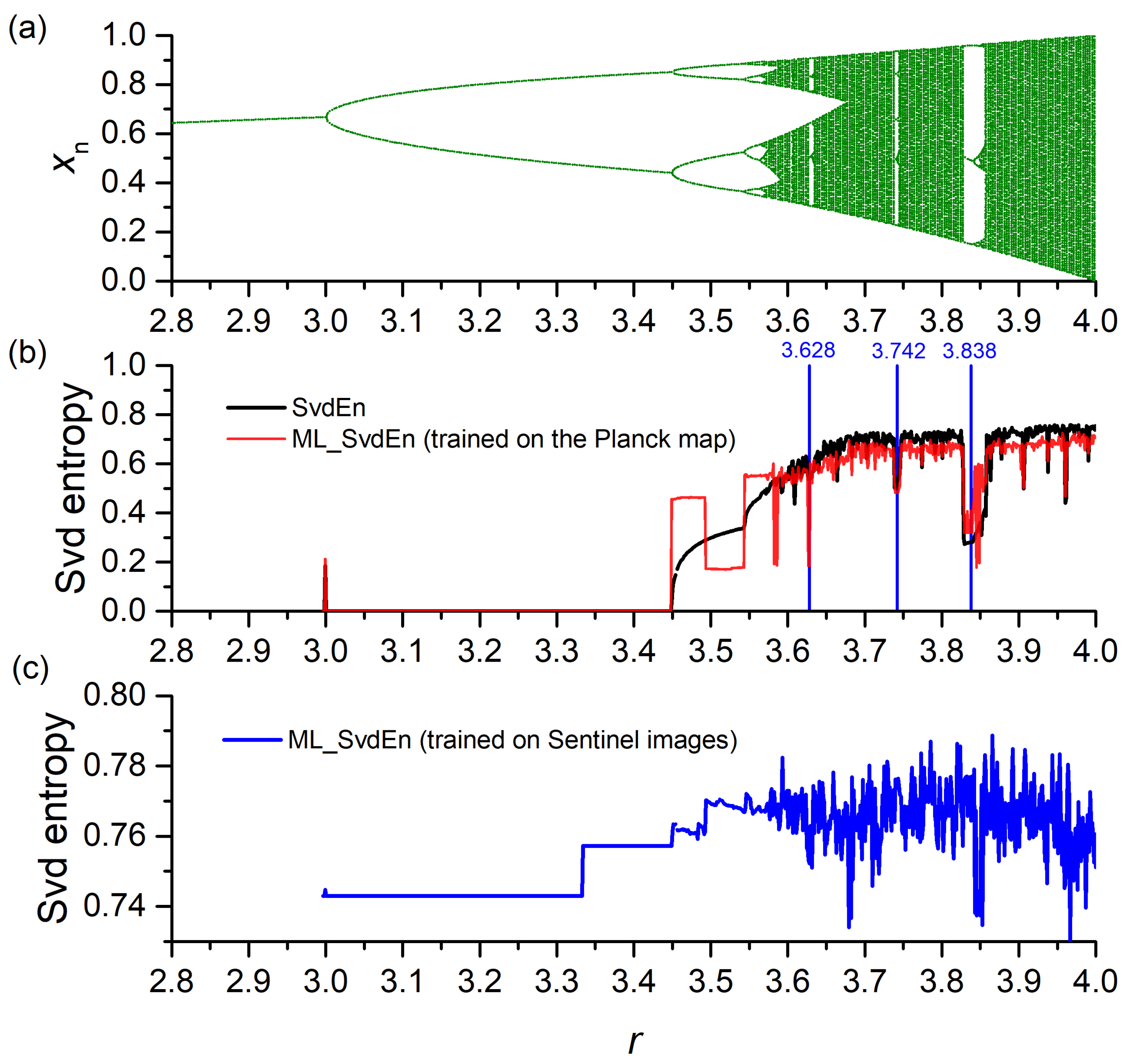
2.3.6. Synthetic Time Series Approximation Method
3. Results
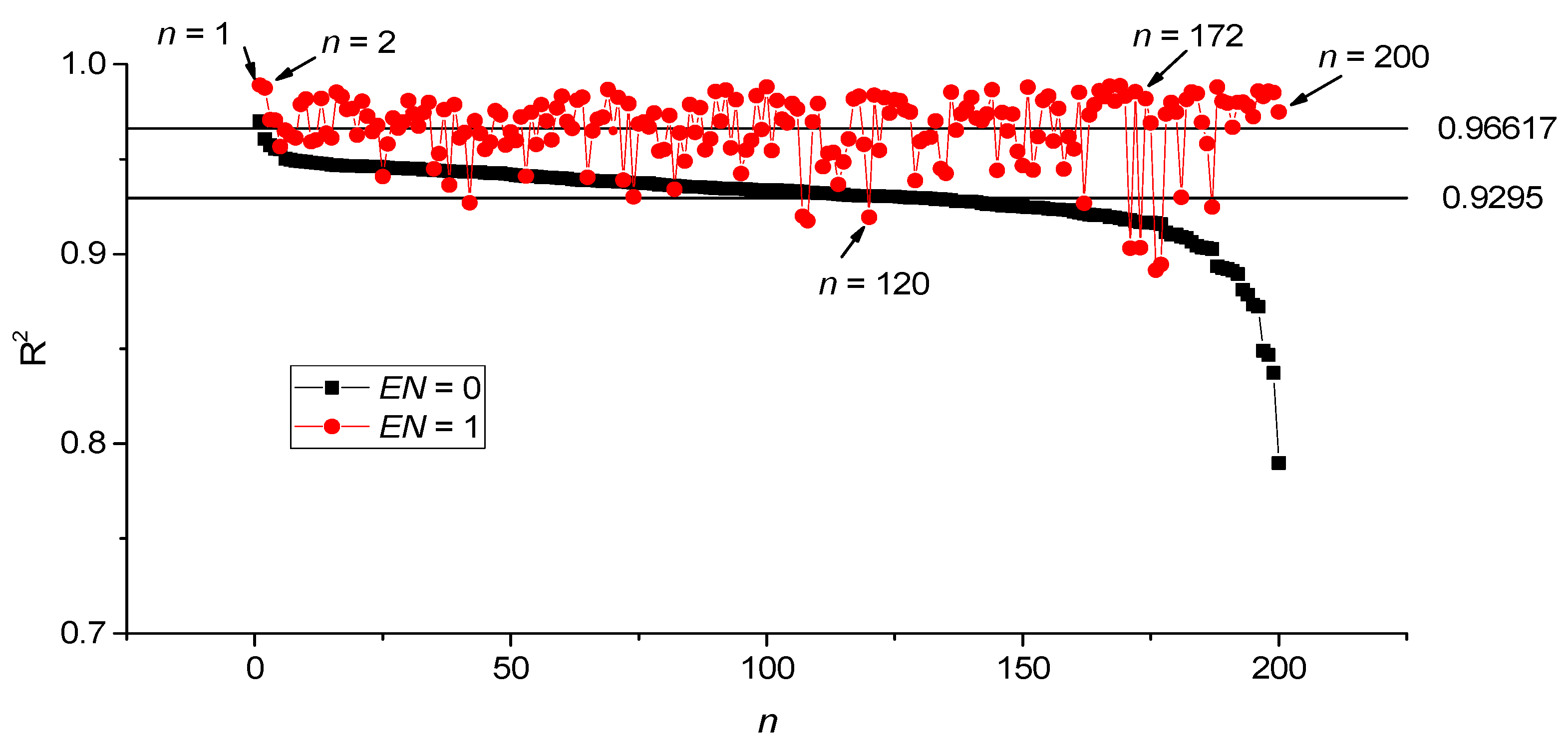
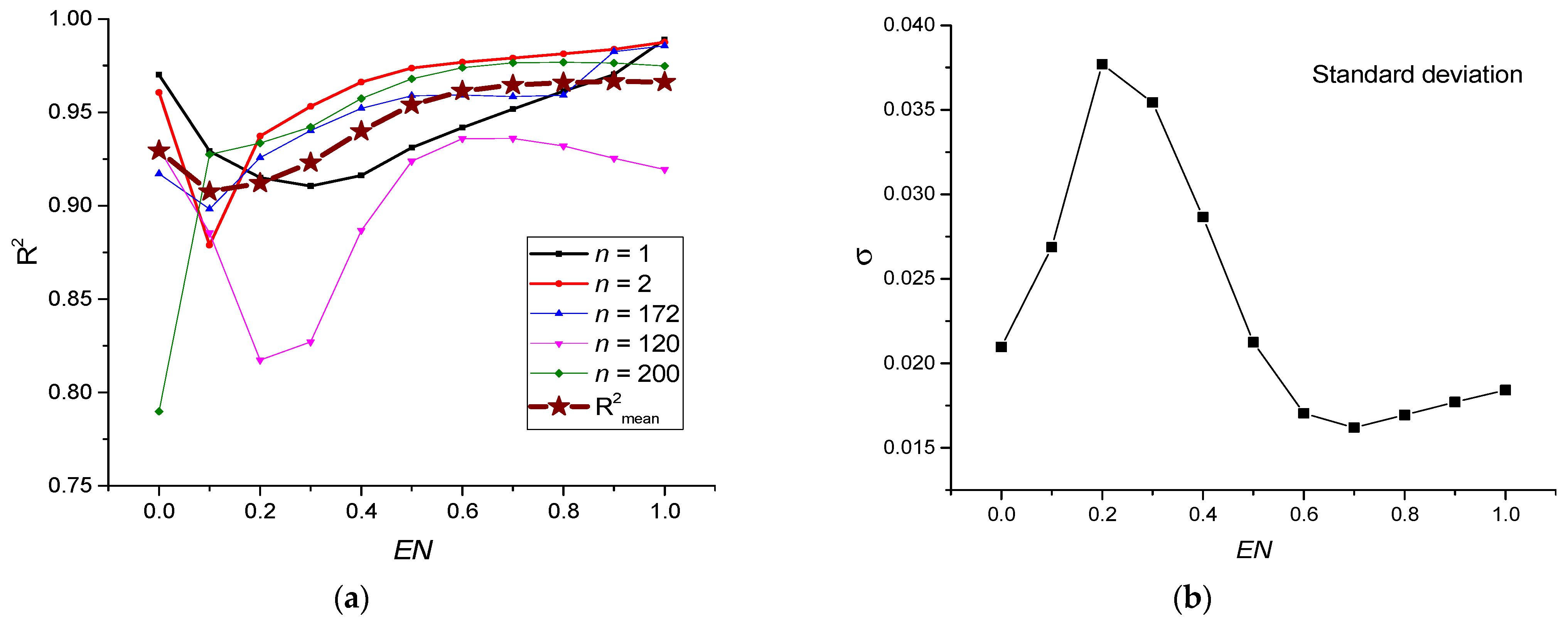
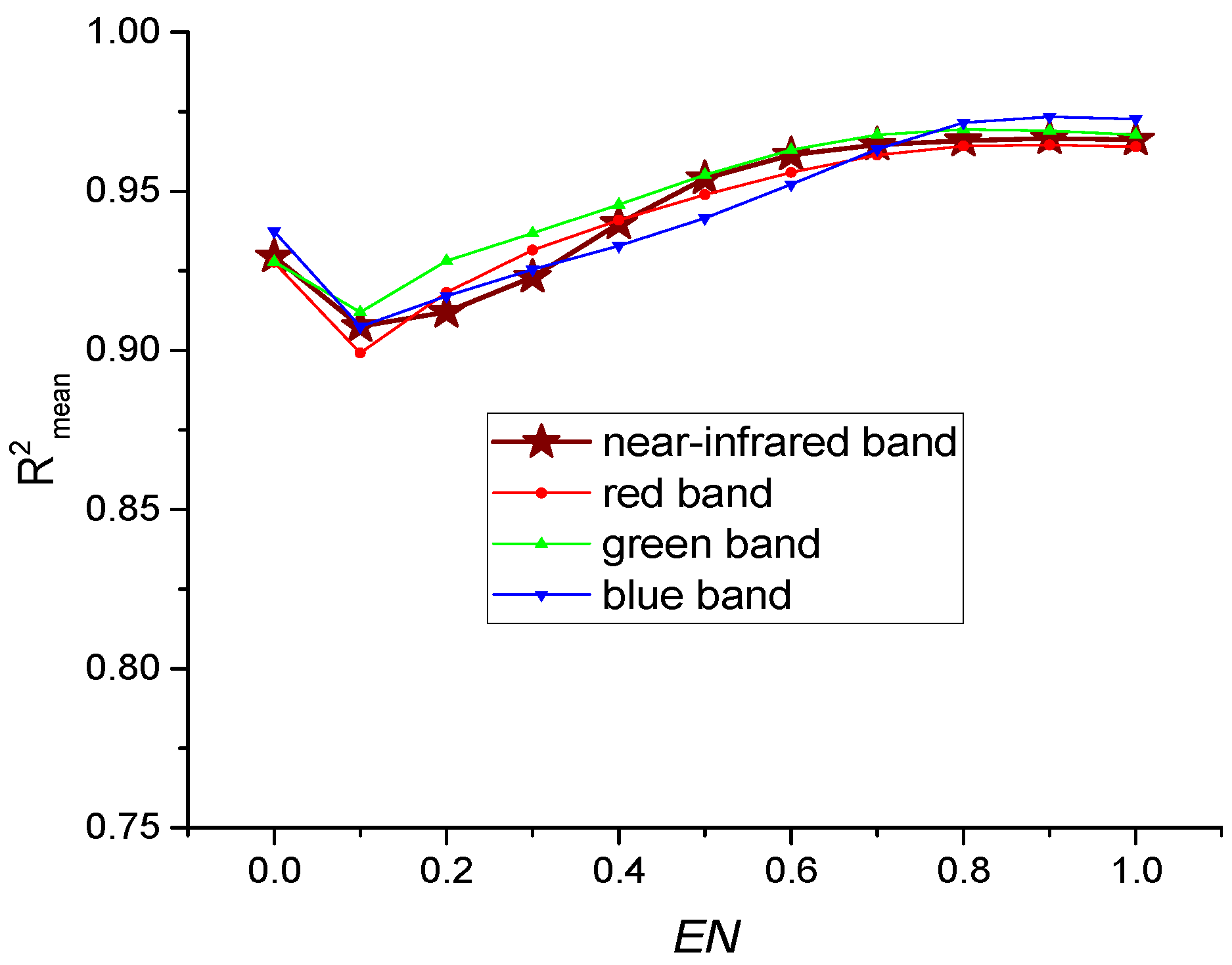
3.1. Calculation of 2D Entropy with Variation of the Normalization Parameter EN
3.2. Comparison of Regression Algorithms Using Training Set
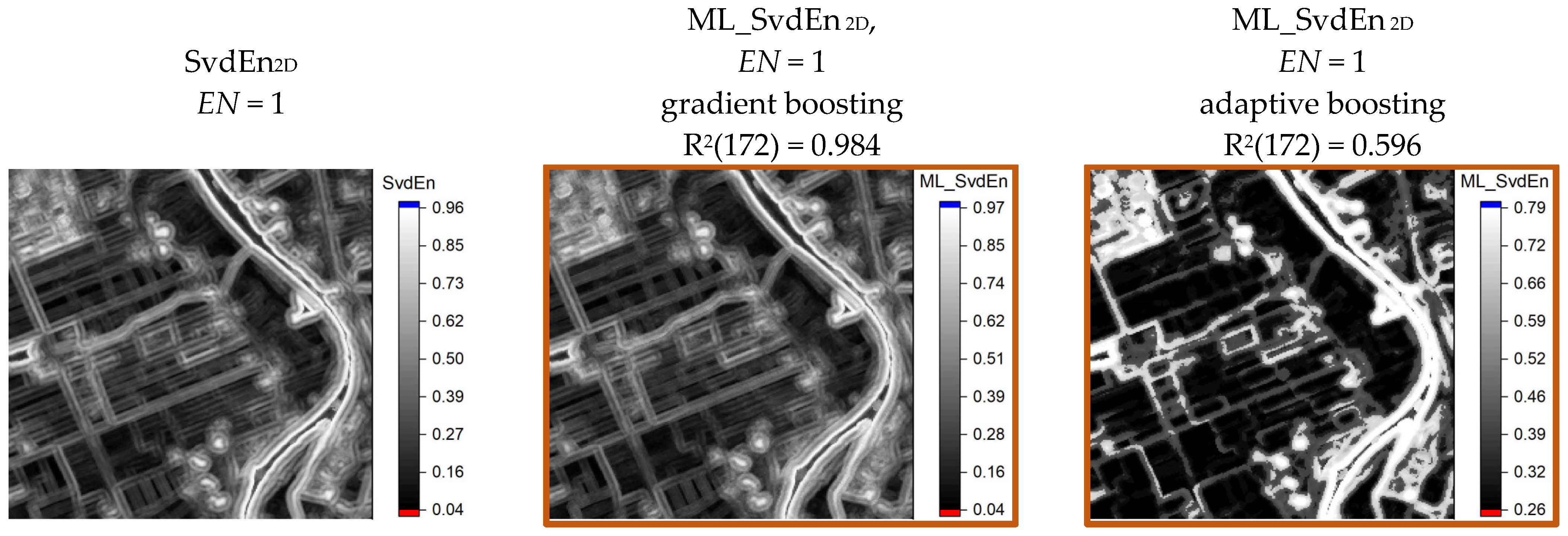
3.3. Results of Approximation SvdEn2D Using GB Regression and Test Set
3.4. Results of Fitting SampEn2D, PermEn2D and NNetEn2D Entropy Using GB Regression and Test Set
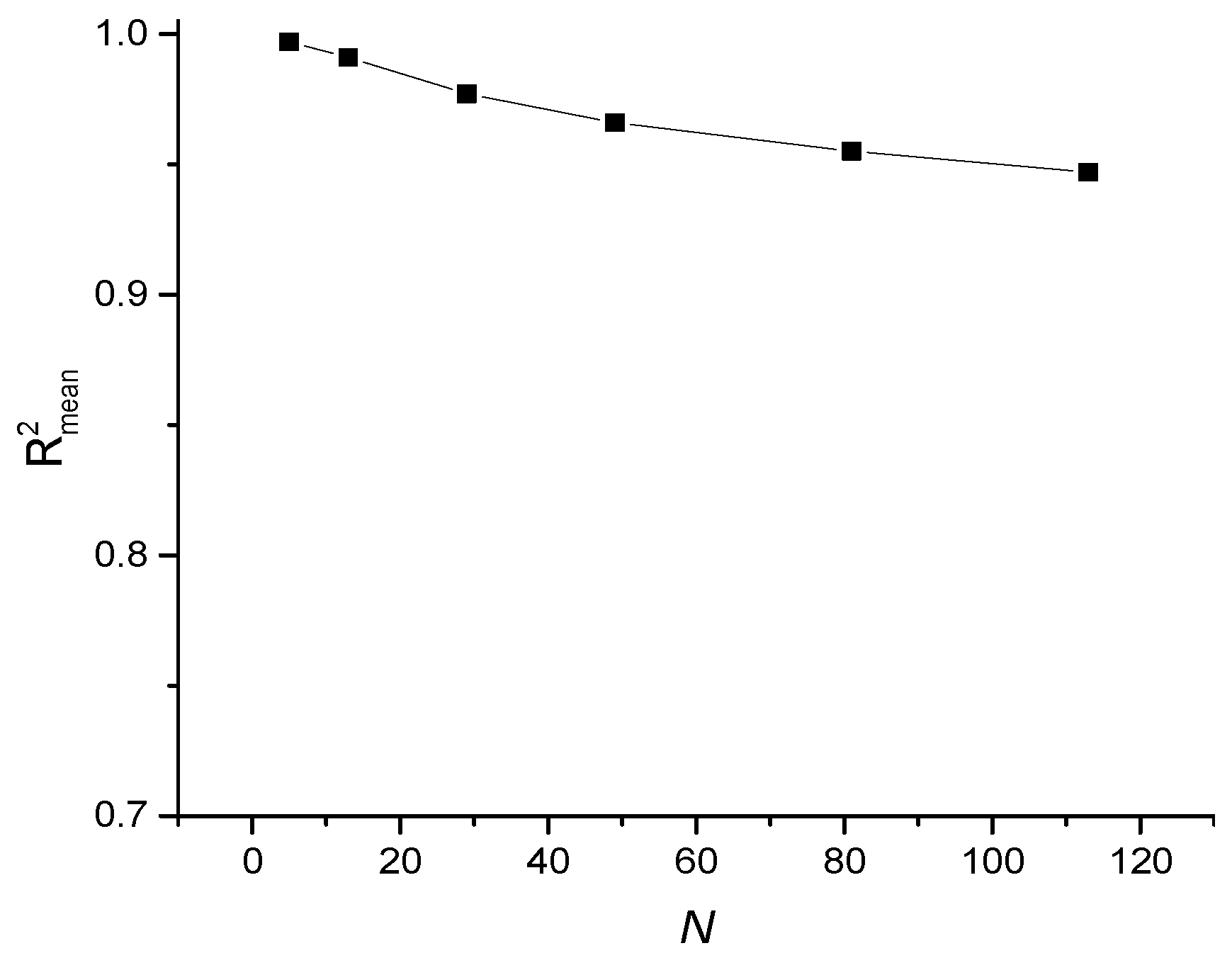
3.5. Comparative Characteristics of GB Regression for Approximating Entropies of Various Types and Lengths of the Time Series
3.6. Results of Approximation of Synthetic Time Series
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- History of Entropy—Wikipedia. Available online: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/History_of_entropy (accessed on 6 September 2022).
- Boltzmann’s Entropy Formula—Wikipedia. Available online: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Boltzmann%27s_entropy_formula#cite_note-2 (accessed on 6 September 2022).
- Shannon, C.E. A Mathematical Theory of Communication. Bell Syst. Tech. J. 1948, 27, 379–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolmogorov, A.N. On Tables of Random Numbers. Theor. Comput. Sci. 1998, 207, 387–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Neumann Entropy—Wikipedia. Available online: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Von_Neumann_entropy (accessed on 6 September 2022).
- Baez, J.C. Rényi Entropy and Free Energy. Entropy 2022, 24, 706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koutsoyiannis, D.; Sargentis, G.-F. Entropy and Wealth. Entropy 2021, 23, 1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.X.; Tuia, D.; Mou, L.; Xia, G.-S.; Zhang, L.; Xu, F.; Fraundorfer, F. Deep Learning in Remote Sensing: A Comprehensive Review and List of Resources. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Mag. 2017, 5, 8–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Ma, J. Deep Learning for Geophysics: Current and Future Trends. Rev. Geophys. 2021, 59, e2021RG000742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yulianto, F.; Fitriana, H.L.; Sukowati, K.A.D. Integration of Remote Sensing, GIS, and Shannon’s Entropy Approach to Conduct Trend Analysis of the Dynamics Change in Urban/Built-up Areas in the Upper Citarum River Basin, West Java, Indonesia. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2020, 6, 383–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Mashagbah, A.F. The Use of GIS, Remote Sensing and Shannon’s Entropy Statistical Techniques to Analyze and Monitor the Spatial and Temporal Patterns of Urbanization and Sprawl in Zarqa City, Jordan. J. Geogr. Inf. Syst. 2016, 8, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, C. Maximum Entropy for Image Segmentation Based on an Adaptive Particle Swarm Optimization. Appl. Math. Inf. Sci. 2014, 8, 3129–3135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haralick, R.M.; Shanmugam, K.; Dinstein, I. Textural Features for Image Classification. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man. Cybern. 1973, SMC-3, 610–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, T.; Zheng, L.; Xu, W.; Piao, Y.; Feng, R.; Chen, X.; Zhou, T. An Automatic Exposure Method of Plane Array Remote Sensing Image Based on Two-Dimensional Entropy. Sensors 2021, 21, 3306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, M.T.; Kehtarnavaz, N.; Razlighi, Q.R. Using Image Entropy Maximum for Auto Exposure. J. Electron. Imaging 2011, 20, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Chen, H.; Tang, H.; Liu, Y. Unsupervised Image Change Detection Means Based on 2-D Entropy. In Proceedings of the the 2nd International Conference on Information Science and Engineering, Hangzhou, China, 4–6 December 2010; pp. 4199–4202. [Google Scholar]
- Azami, H.; da Silva, L.E.V.; Omoto, A.C.M.; Humeau-Heurtier, A. Two-Dimensional Dispersion Entropy: An Information-Theoretic Method for Irregularity Analysis of Images. Signal Process. Image Commun. 2019, 75, 178–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, L.E.V.; Filho, A.C.S.S.; Fazan, V.P.S.; Felipe, J.C.; Junior, L.O.M. Two-Dimensional Sample Entropy: Assessing Image Texture through Irregularity. Biomed. Phys. Eng. Express 2016, 2, 45002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, H.V.; Zunino, L.; Lenzi, E.K.; Santoro, P.A.; Mendes, R.S. Complexity-Entropy Causality Plane as a Complexity Measure for Two-Dimensional Patterns. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e40689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, C.; Marchant, T. The Approximate Entropy Concept Extended to Three Dimensions for Calibrated, Single Parameter Structural Complexity Interrogation of Volumetric Images. Phys. Med. Biol. 2017, 62, 6092–6107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velichko, A.; Wagner, M.P.; Taravat, A.; Hobbs, B.; Ord, A. NNetEn2D: Two-Dimensional Neural Network Entropy in Remote Sensing Imagery and Geophysical Mapping. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chagas, E.T.C.; Frery, A.C.; Rosso, O.A.; Ramos, H.S. Analysis and Classification of SAR Textures Using Information Theory. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2021, 14, 663–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carincotte, C.; Derrode, S.; Bourennane, S. Unsupervised Change Detection on SAR Images Using Fuzzy Hidden Markov Chains. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2006, 44, 432–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouyahia, Z.; Benyoussef, L.; Derrode, S. Change Detection in Synthetic Aperture Radar Images with a Sliding Hidden Markov Chain Model. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2008, 2, 23526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallat, R. AntroPy: Entropy and Complexity of (EEG) Time-Series in Python. Available online: https://github.com/raphaelvallat/antropy (accessed on 20 November 2022).
- Stewart, G.W. On the Early History of the Singular Value Decomposition. SIAM Rev. 1993, 35, 551–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Yang, M.; Li, C.; Cai, P. Analysis of Heart Rate Variability Based on Singular Value Decomposition Entropy. J. Shanghai Univ. Engl. Ed. 2008, 12, 433–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jelinek, H.F.; Donnan, L.; Khandoker, A.H. Singular Value Decomposition Entropy as a Measure of Ankle Dynamics Efficacy in a Y-Balance Test Following Supportive Lower Limb Taping. In Proceedings of the 2019 41st Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), IEEE, Berlin, Germany, 23–27 July 2019; pp. 2439–2442. [Google Scholar]
- Anagnoste, S.; Caraiani, P. The Impact of Financial and Macroeconomic Shocks on the Entropy of Financial Markets. Entropy 2019, 21, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarez-Ramirez, J.; Rodriguez, E. A Singular Value Decomposition Entropy Approach for Testing Stock Market Efficiency. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2021, 583, 126337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strydom, T.; Dalla Riva, G.V.; Poisot, T. SVD Entropy Reveals the High Complexity of Ecological Networks. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2021, 9, 623141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buisine, J.; Bigand, A.; Synave, R.; Delepoulle, S.; Renaud, C. Stopping Criterion during Rendering of Computer-Generated Images Based on SVD-Entropy. Entropy 2021, 23, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velichko, A.; Heidari, H. A Method for Estimating the Entropy of Time Series Using Artificial Neural Networks. Entropy 2021, 23, 1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velichko, A. Neural Network for Low-Memory IoT Devices and MNIST Image Recognition Using Kernels Based on Logistic Map. Electronics 2020, 9, 1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeCun, Y.; Cortes, C.; Burges, C. MNIST Handwritten Digit Database. Available online: http://yann.lecun.com/exdb/mnist/ (accessed on 9 November 2018).
- Feurer, M.; Eggensperger, K.; Falkner, S.; Lindauer, M.; Hutter, F. Auto-Sklearn 2.0: Hands-Free AutoML via Meta-Learning. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2007.04074. [Google Scholar]
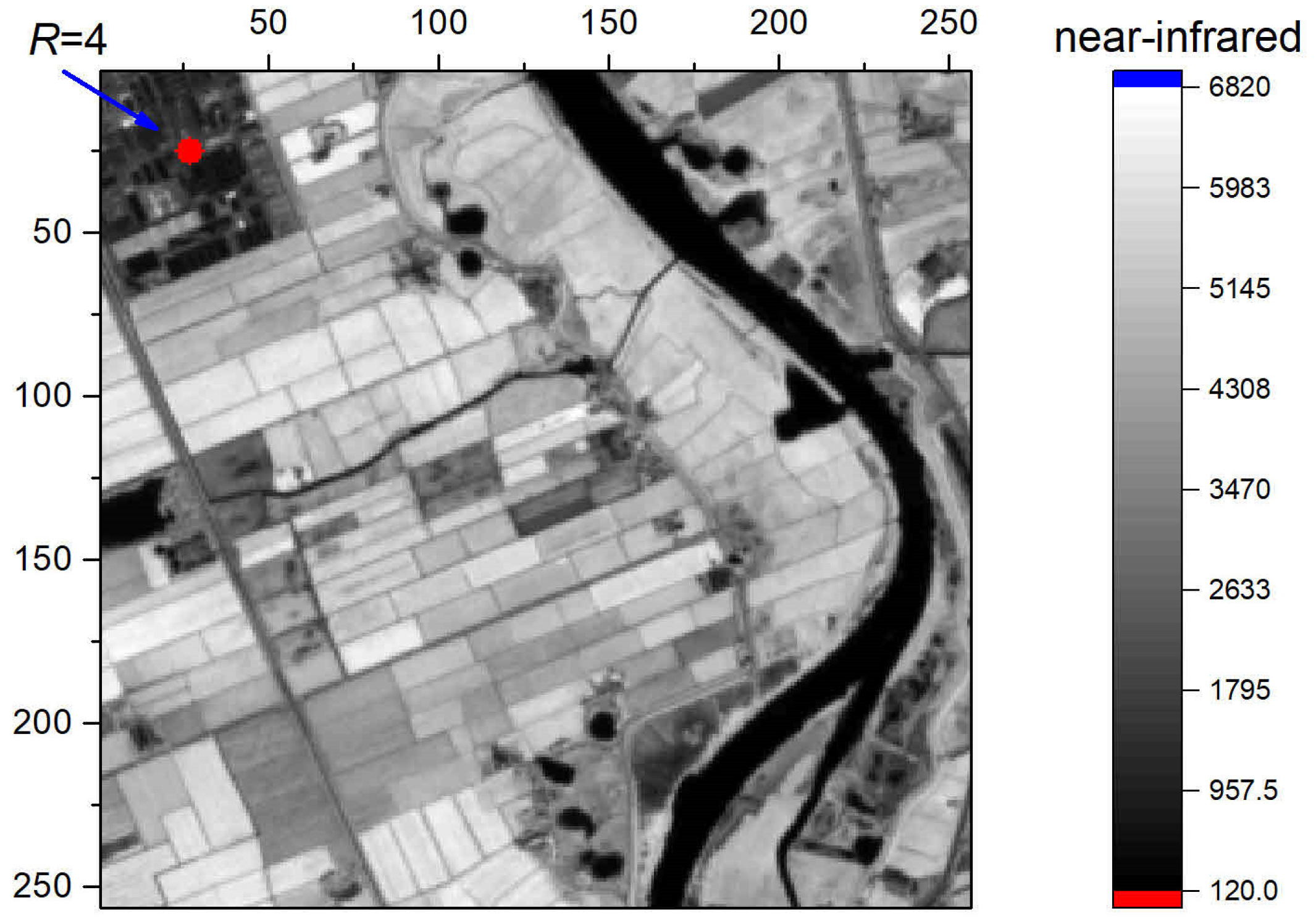

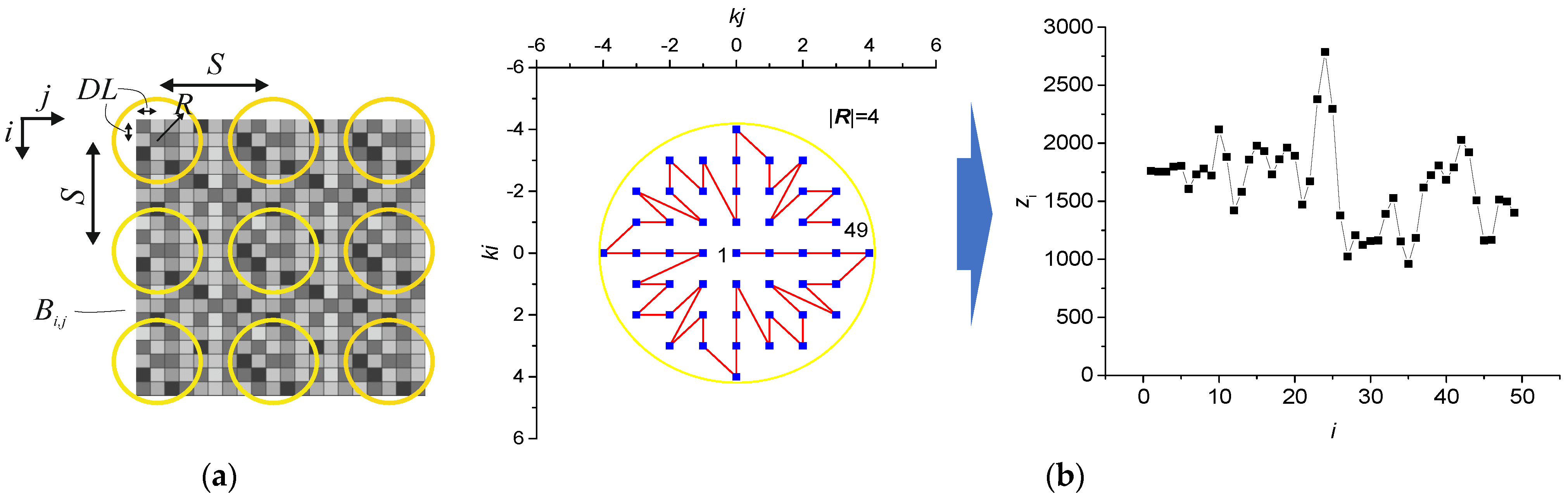
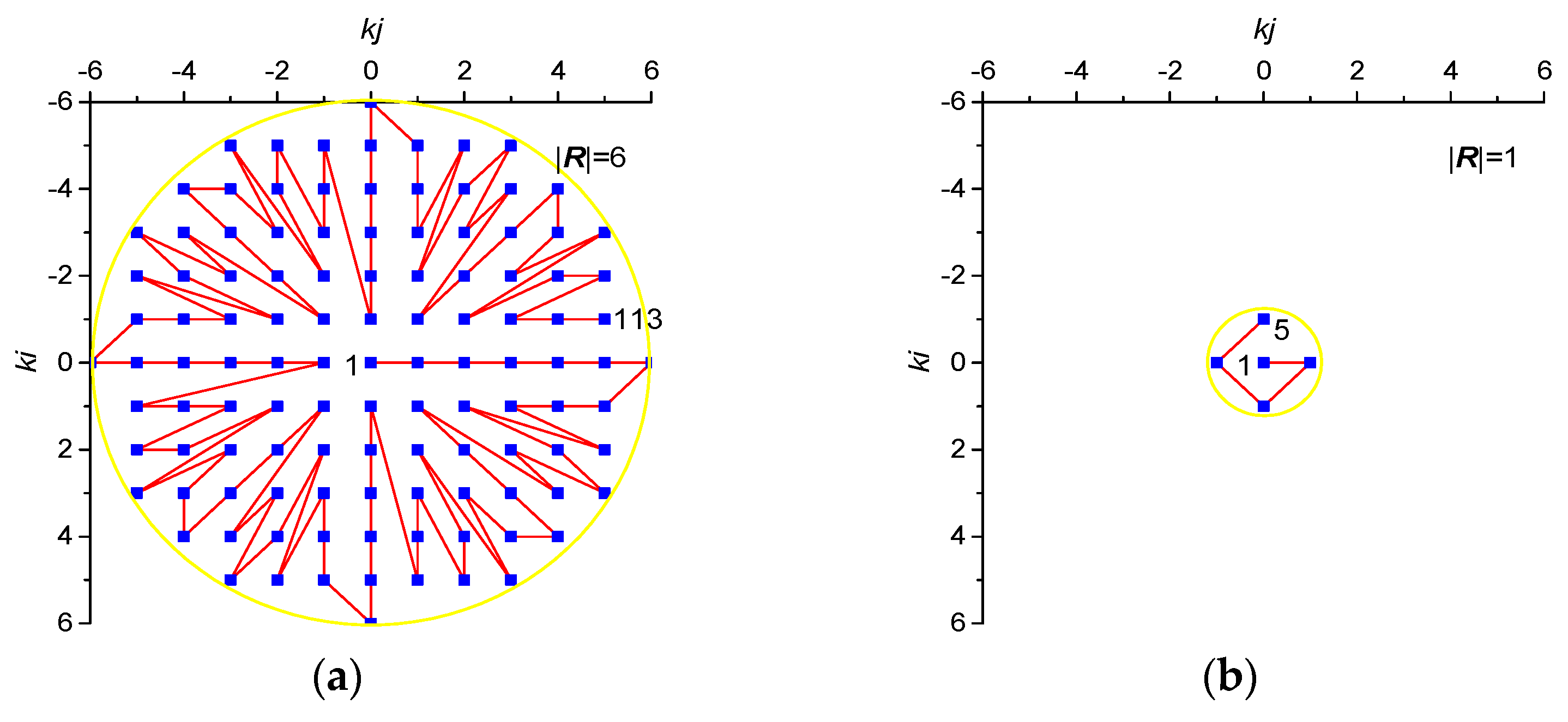
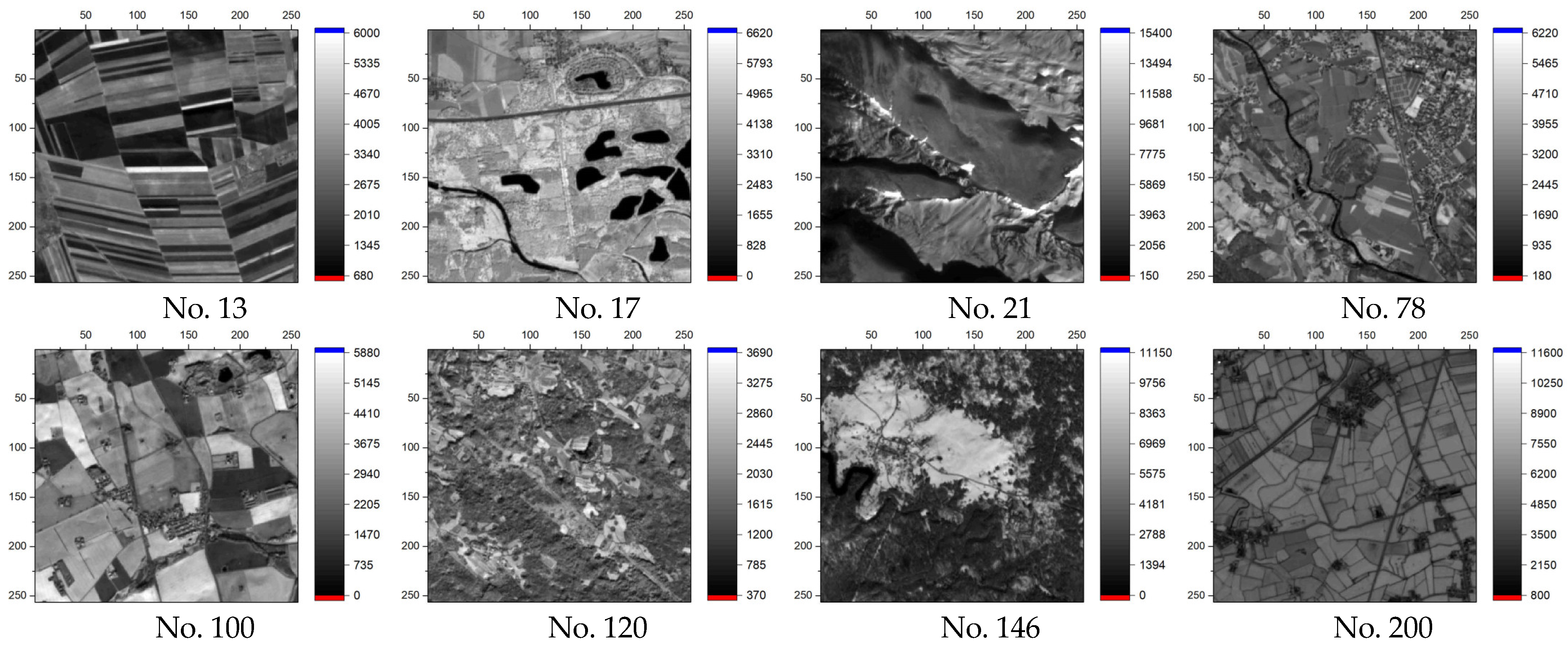
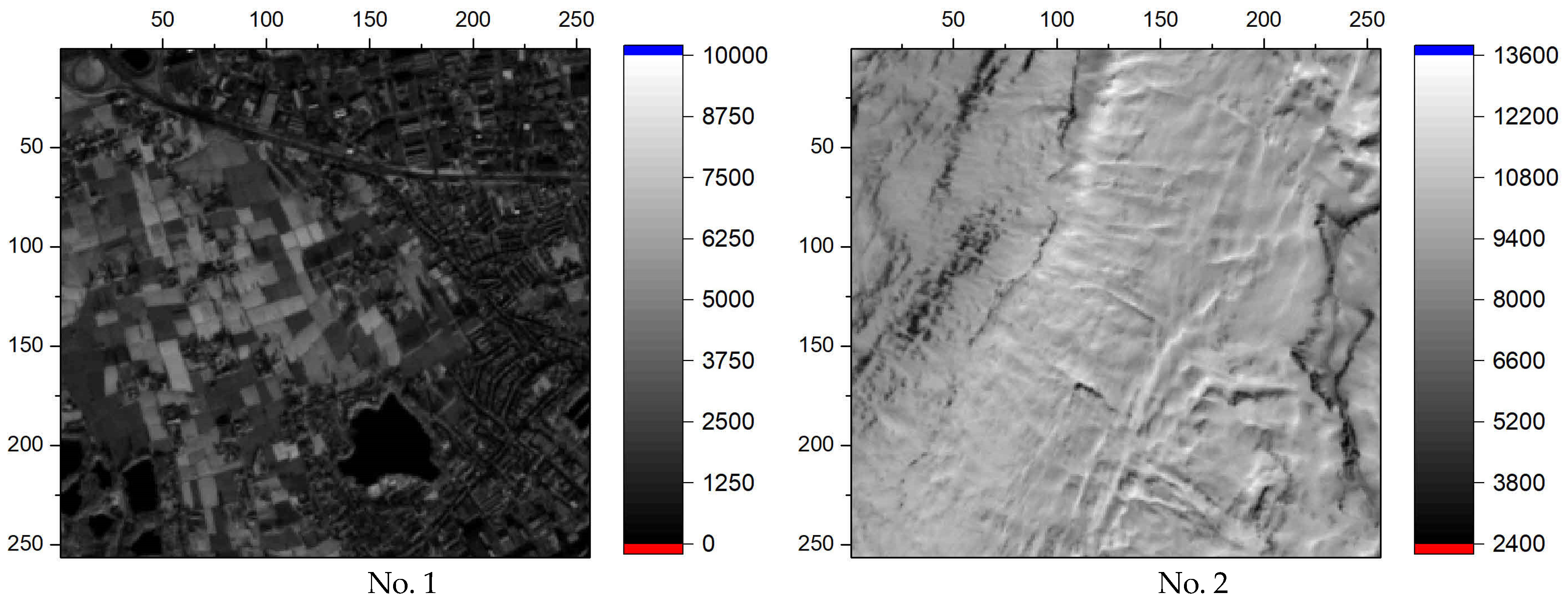
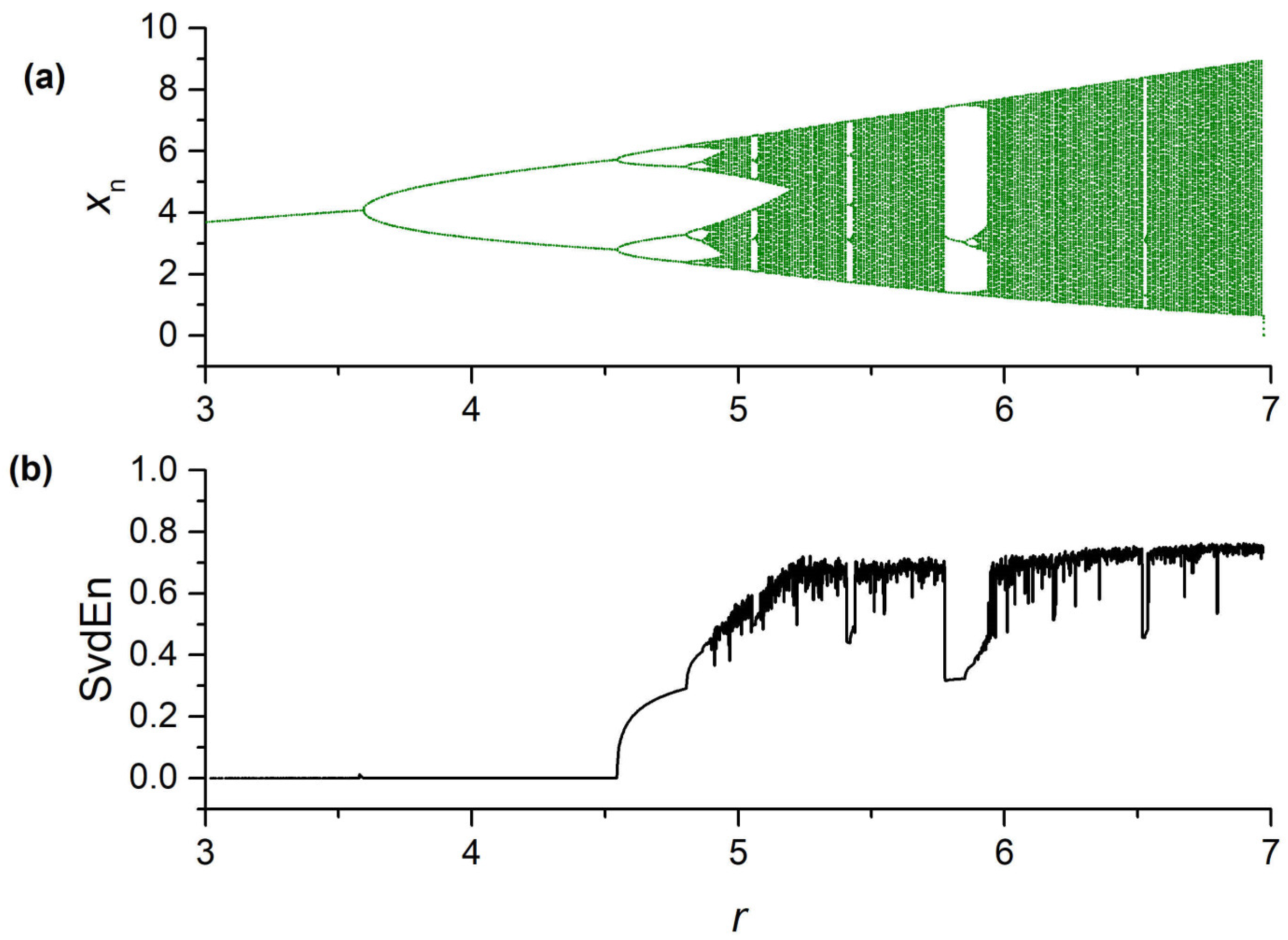


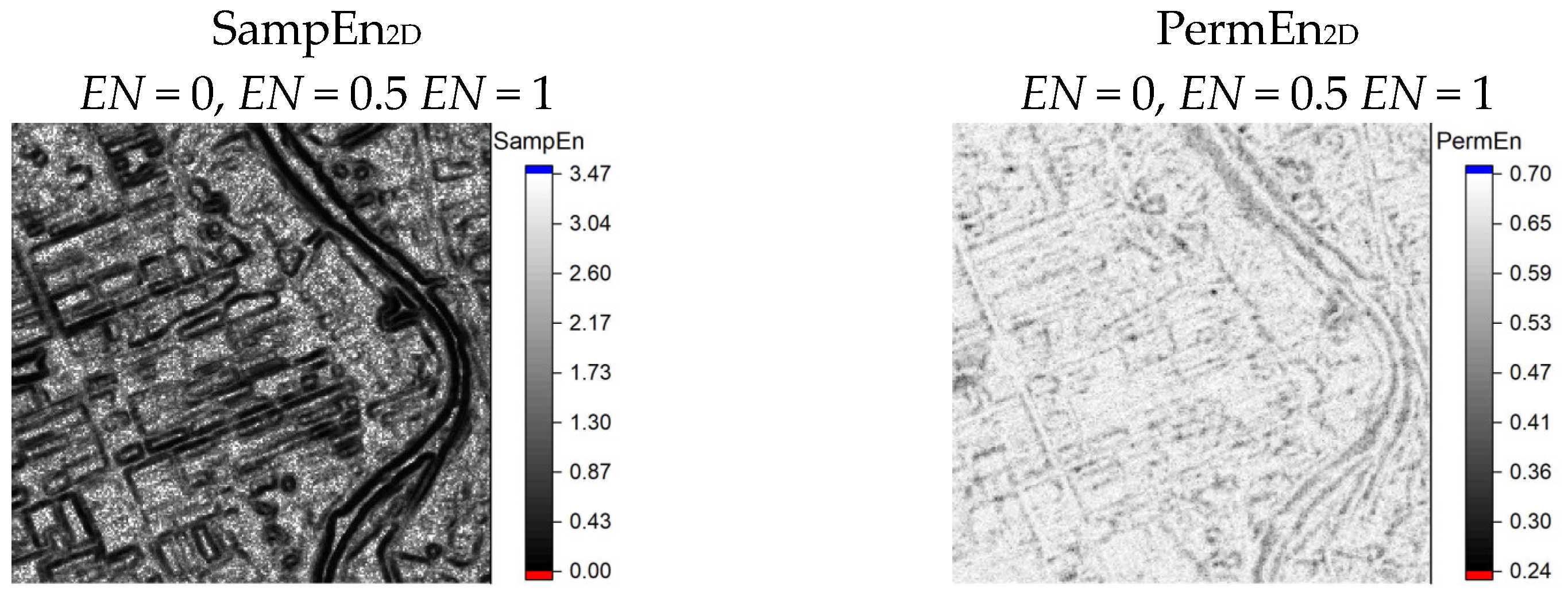

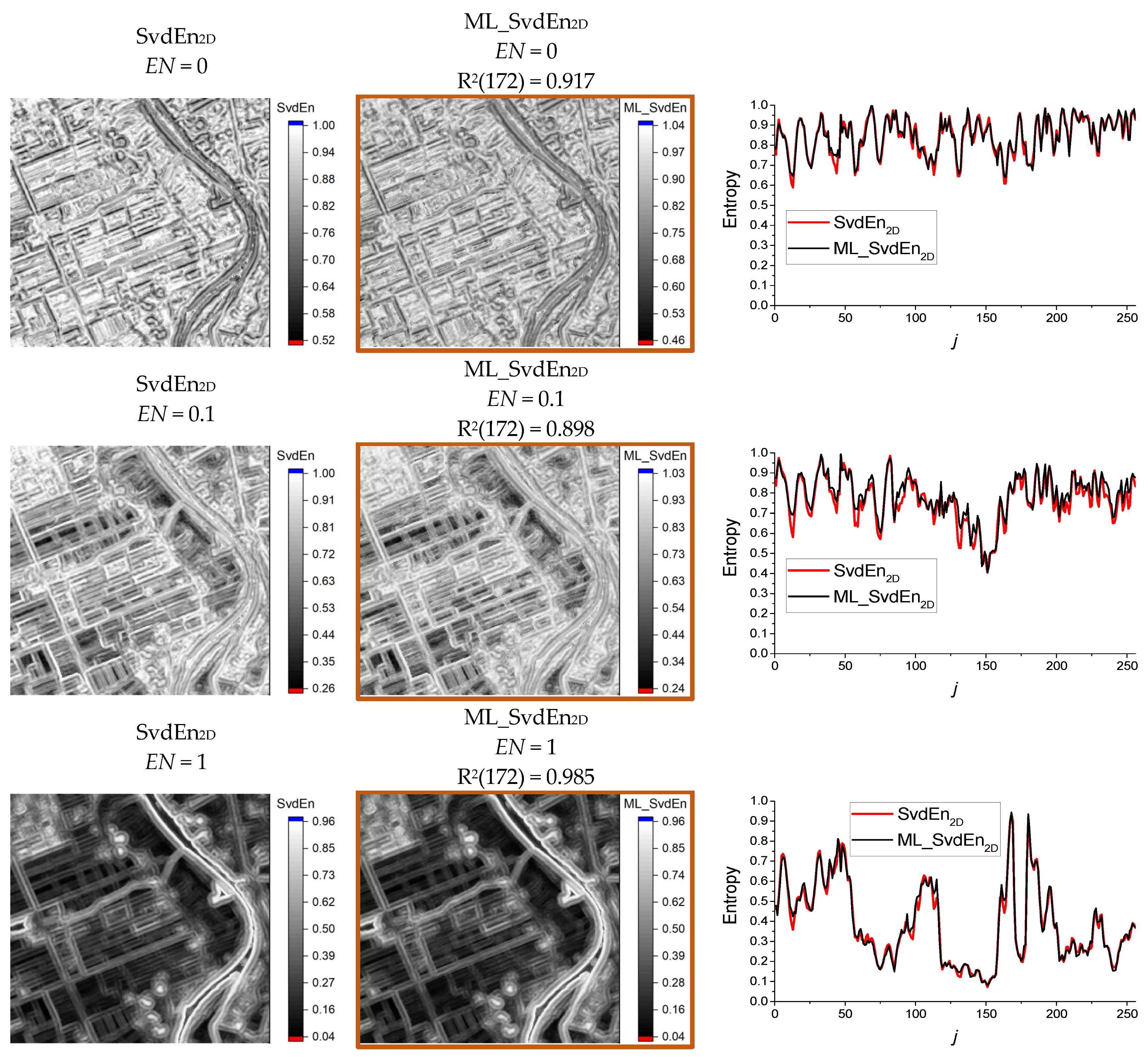


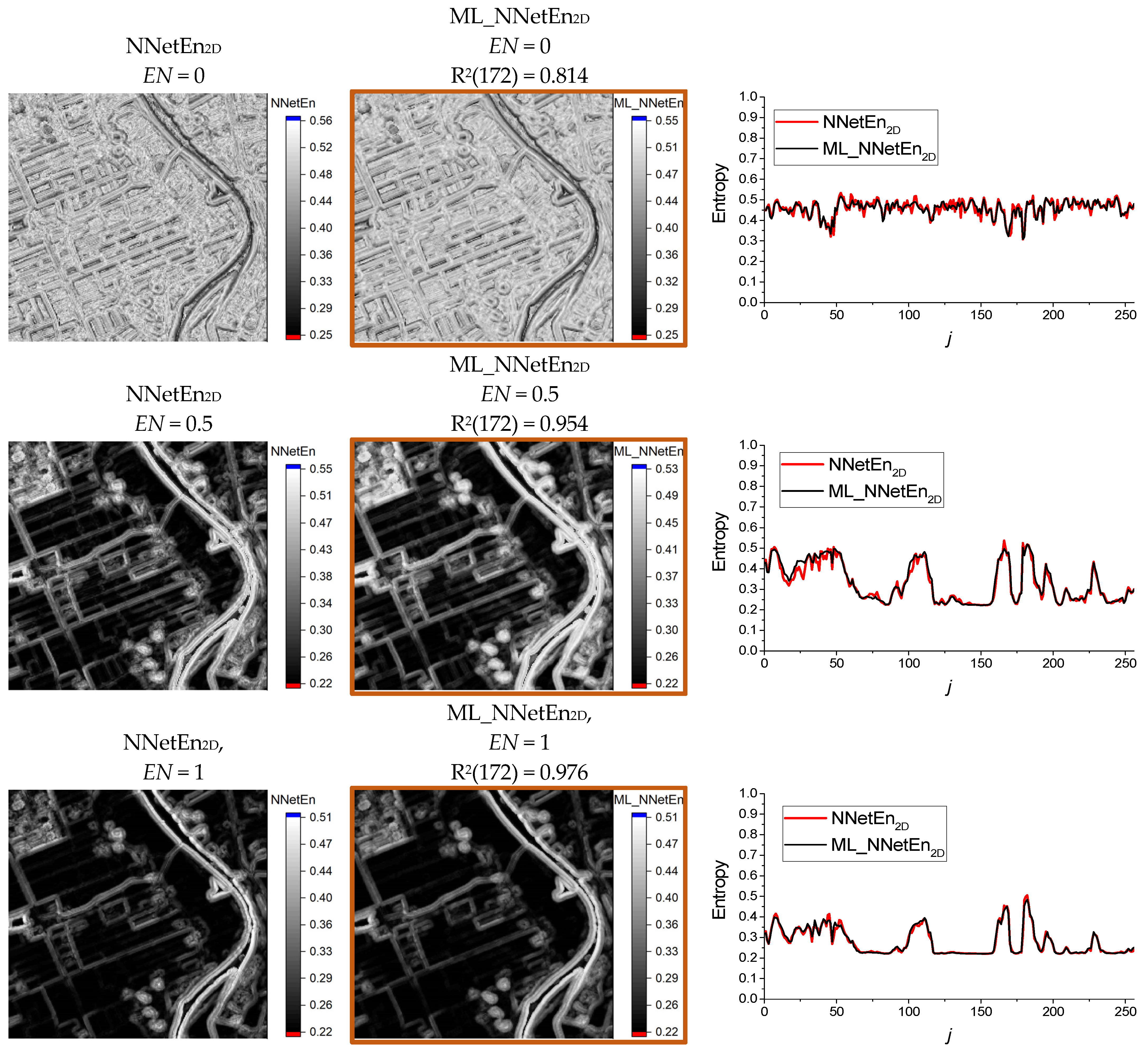
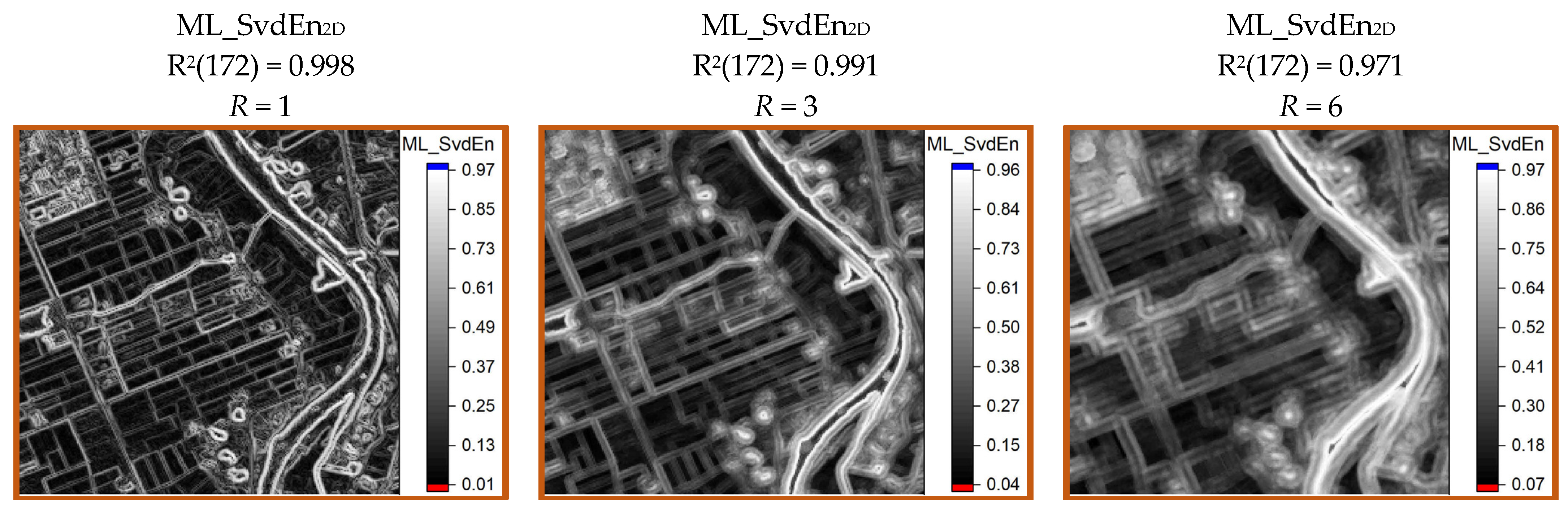
| R | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
| N | 5 | 13 | 29 | 49 | 81 | 113 |
| Algorithm | R2(1,2) | R2(172) |
|---|---|---|
| gradient boosting | 0.996 | 0.984 |
| support vector regression | 0.982 | 0.891 |
| k-nearest neighbors | 0.982 | 0.889 |
| multi-layer perceptron | 0.972 | 0.864 |
| stochastic gradient descent | 0.970 | 0.848 |
| decision tree | 0.968 | 0.908 |
| automatic relevance determination | 0.872 | 0.840 |
| adaptive boosting | 0.836 | 0.596 |
| Entropy | ML Model | R2mean | σ | R2(172) | Entropy Calculation Time, s | ML Model Calculation Time, s | Calculation Acceleration |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SvdEn2D | ML_SvdEn2D (EN = 1) | 0.966 | 0.018 | 0.985 | 2.14 | 3.31 | 0.64 |
| SampEn2D | ML_SampEn2D | 0.472 | 0.113 | 0.628 | 2.35 | 1.26 | 1.86 |
| PermEn2D | ML_PermEn2D | 0.553 | 0.075 | 0.535 | 3.68 | 1.51 | 2.44 |
| NNetEn2D | ML_NNetEn2D (EN = 1) | 0.942 | 0.02 | 0.976 | 684195 | 2.01 | 340395 |
| R | N | R2mean | σ | R2 Minimum | R2 Maximum | R2(172) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 5 | 0.997 | 0.00094 | 0.99452 | 0.99764 | 0.99881 |
| 2 | 13 | 0.991 | 0.0051 | 0.97063 | 0.99836 | 0.99641 |
| 3 | 29 | 0.977 | 0.012 | 0.92733 | 0.99258 | 0.99129 |
| 4 | 49 | 0.966 | 0.018 | 0.89146 | 0.97029 | 0.98559 |
| 5 | 81 | 0.955 | 0.023 | 0.85312 | 0.99005 | 0.9793 |
| 6 | 113 | 0.947 | 0.026 | 0.82805 | 0.99004 | 0.97186 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Velichko, A.; Belyaev, M.; Wagner, M.P.; Taravat, A. Entropy Approximation by Machine Learning Regression: Application for Irregularity Evaluation of Images in Remote Sensing. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5983. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14235983
Velichko A, Belyaev M, Wagner MP, Taravat A. Entropy Approximation by Machine Learning Regression: Application for Irregularity Evaluation of Images in Remote Sensing. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(23):5983. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14235983
Chicago/Turabian StyleVelichko, Andrei, Maksim Belyaev, Matthias P. Wagner, and Alireza Taravat. 2022. "Entropy Approximation by Machine Learning Regression: Application for Irregularity Evaluation of Images in Remote Sensing" Remote Sensing 14, no. 23: 5983. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14235983
APA StyleVelichko, A., Belyaev, M., Wagner, M. P., & Taravat, A. (2022). Entropy Approximation by Machine Learning Regression: Application for Irregularity Evaluation of Images in Remote Sensing. Remote Sensing, 14(23), 5983. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14235983









