Abstract
Water availability in lakes must be studied in order to better manage ecosystems within lake basins and meet economic development needs. Despite being Iran’s largest lake, Lake Urmia’s water level and surface area have declined dramatically over the past two decades. During the same period, Lake Van in Turkey maintained a relatively stable water level and surface area. As a result, comparing factors related to water level and surface area in these lakes, which have similar geographical and climate conditions but different management policies, can be an appropriate way to identify the causes of water declines in Lake Urmia. Comparing these variables may help explain observed differences in lake behavior between 2000 and 2016. Hydrometric and climatic parameters, as well as the Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) and the Normalized Difference Water Index (NDWI), were used to achieve this goal. Changes in precipitation, temperature, and evapotranspiration in both lakes show essentially identical trends, but this is not a convincing explanation for Lake Urmia’s water surface changes. The results revealed that dam construction and water diversion projects, the expansion of irrigated agriculture, and the lake’s shallow depth in most parts were the primary causes of Lake Urmia’s shrinkage compared to Lake Van.
1. Introduction
Lakes cover about 2% of the Earth’s land surface, with the vast majority centered in the Northern Hemisphere [1]. They provide water resources for anthropological activities, particularly in arid regions where water scarcity severely limits local development [2]. Lakes also promote species biodiversity by providing various ecosystem services [3]. Water volume in lakes in primarily arid areas is declining globally [4,5], causing ecological crises [6]. Human activities and over-extraction of water have increased localized dryness in many parts of the world, resulting in anthropogenic dryness [7]. Variations in lake level can impact human activities, coastal structures, and ecosystems [8].
Research in diverse places has been conducted to model and statistically assess variations in lake water levels. Yin and Yang [9] proposed a method for analyzing changes in the patterns of water level fluctuation in China’s Lake Baiyangdian. Their findings demonstrated that the new method’s estimation of water level variations corresponded to the lake’s level of environmental degradation. Kakahaji et al. [10] predicted water level changes in Iran’s Lake Urmia using analytical, linear statistics, and intelligent approaches.
According to this study, intelligent approaches are preferable to traditional methods for modeling water level variations. La Valle et al. [11] looked into the relationship between Lake Erie water level changes and the El Nino/Southern Oscillation (ENSO). According to their findings, Lake Erie water levels fluctuated in reaction to the two ENSO phases, El Nino (warming phase) and La Nina (cold phase) (cooling phase).
In another study, Ouarda et al. [12] examined variations in water levels in the Great Lakes between the Canada–U.S. border using the Mann–Kendall (MK) trend test under the independence, short-term, and long-term persistence hypotheses. For monthly and annual time series, water levels in Lake St. Clair and Lake Erie showed strong rising tendencies. In contrast, no significant trends in monthly or yearly water levels were identified in Lake Superior, Lake Michigan–Huron, or Georgian Bay, whereas annual and certain monthly water levels increased dramatically in Lake Ontario. Sellinge et al. [13] investigated water level data from Lake Michigan and Lake Huron to assess seasonal and long-term patterns. Seasonal trend decomposition utilizing Loess results revealed a 30-year, long-term periodic decline in water level since about 1900. Over a 3-year time lag, the outputs of a dynamic linear model were directly associated with precipitation. In Turkey, Ülgen et al. [14] conducted a statistical investigation of changes in watershed climate and Lake Iznik’s level. The data revealed that the long-term climate trend at Lake Izink has been toward drier conditions in the past 4700 years.
Lake Urmia (LU) is the world’s second-largest hypersaline lake, with its shores home to a population of approximately 6 million people. Numerous studies have been conducted to address issues related to changes in Lake Urmia, using either statistical methods or satellite image processing. Jalili et al. [15], for example, examined the lake’s water level change in relation to climate indicators and observed a high association before 1995, when the basin was heavily dammed. They gradually raised the water level of LU to that of Turkey’s Lake Van (LV), discovering a negative trend in LU and a positive trend in LV. Shadkam et al. [16] used a variable infiltration model to explore the impact of climate change and water resource development on inflow into LU. This study found a 40% decrease in inflow during a few dry years. AghaKouchak et al. [17] also looked at the change in water level in LU and discovered that it had dropped by 88% in the past two decades. As a result, according to these reports, the lake’s water level and surface area have dropped substantially over the past two decades, as has been widely recorded [7,17,18].
Similarly, other research [19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28] explored the association between water level variation in LV, Turkey’s largest lake, and climate characteristics. As a result of combining these complementary methodologies, statistical analysis, and satellite data processing, lake planning can gain new insight into changes in water level and surface area. Given this, the primary objectives of this study are to investigate and compare potential factors influencing water level and surface area changes in LU (Iran) and LV (Turkey) over seventeen years (2000–2016) using Landsat Enhanced Thematic Mapper (ETM), Landsat Operational Land Imager (OLI), and Thermal Infrared Sensor (TIRS) images in conjunction with some statistical methods. The most essential parameters influencing water level and surface area in both lakes should be identified by comparing geographical and climate circumstances, as well as basin management practices. Knowing such characteristics is essential for regulating future lake levels when planning, designing, building, and operating shoreline projects [19].
The rest of this paper is organized as follows. Section 2 demonstrates how to extract surface area changes and assess water level oscillations using Landsat data and climatic parameters. Section 3 addresses the impact of evapotranspiration, agricultural growth, dam construction, and other variables on water level fluctuations. Section 4 closes the paper with the study’s conclusions and findings.
2. Study Area and Methods
2.1. Study Area—LU
LU is located in northwest Iran. It is the largest lake in the country and one of the saltiest bodies of water in the world. The basin is delimited to the west by Turkey and to the southwest by Iraq. The basin’s northern, eastern, and southern boundaries are entirely within Iran (Figure 1). It has a surface elevation of 1274.1 m above sea level and an average depth of 2 m. The basin is separated into 14 distinct sub-basins that surround the lake and range in size from 431 to 11,759 km2. The basin’s elevation ranges from 1270 m above sea level at the lake’s surface to 3710 m in the Sahand Mountains. Several dams and diversion projects in the basin regulate river flow, some limiting surface water input into the lake.
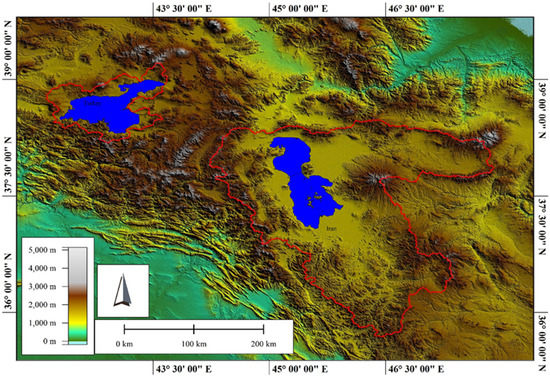
Figure 1.
Location of LU in Iran and LV in Turkey and their basins.
2.2. Study Area—LV
LV is the world’s fourth-largest hydrologically closed (terminal) lake in terms of volume and the world’s largest saline lake in terms of area. It is located in Eastern Turkey (Figure 1). It has a surface elevation of 1640 m above sea level and a depth of 171 m on average. LV covers an area of 3755 km2 and has a volume of 607 km3. The LV basin has a regional climate comparable to the LU basin, with extreme seasonality: frigid winters with mean temperatures below 0 °C from December to February, and warm, dry summers with mean temperatures above 20 °C in July and August. The height of the basin increases from the lake’s surface to approximately 4000 m at Mount Suphan’s peak.
2.3. Methods
The following are the main steps in this research: (1) gathering precipitation, temperature, lake water levels, dam construction, and hydrometric data; (2) processing satellite images and extracting water bodies and surface area changes; (3) calculating vegetation index, water depth, and evapotranspiration; and (4) comparing the results of the preceding steps within each lake and between the two lakes (Figure 2).
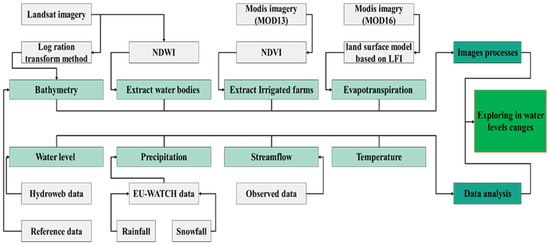
Figure 2.
Data processing diagram.
2.3.1. Data Collection and Analysis
Precipitation
Our data were obtained from different sources. As shown in Figure 3, the precipitation data were based on the European Union’s (EU) Integrated Project Water and Global Change (WATCH) [20] with a spatial resolution of 0.5 degrees (55 km). WATCH is a European Union project that investigates the Earth’s water cycle using land surface models and general hydrological models to assess the impact of significant hydrological variables [21]. Previous studies in other parts of the world have widely used these datasets to evaluate the effect of precipitation, evaporation, and hydrological parameters on streamflow [21,22]. Furthermore, long-term precipitation gauge data from eleven LU basin stations were used to evaluate and validate WATCH data in the basin. As a result, the correlation coefficient estimated for the two datasets was 0.88%.
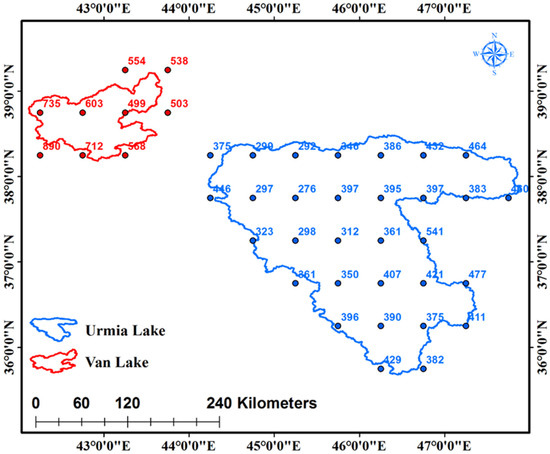
Figure 3.
Gridded EU-WATCH data covering LU and LV (mm).
Temperature
We calculated the surface temperature of each lake using Landsat images. Six steps were taken to accomplish this:
- 1.
- Conversion of DN to BT
Lλ is the spectral radiance and was calculated by Equation (1):
where RM (RADIANCE_MULT_BAND_x) and RA (RADIANCE_ADD_BAND_x) are band-specific multiplicative rescaling factor and band-specific additive rescaling factor, respectively. DN (QUANTIZE_CAL_MIN_BAND_x) is the digital number extracted from metadata.
- 2.
- Brightness Temperature (BT)
BT is microwave radiation that travels from the top of the Earth’s atmosphere upward. The conversion process was used to convert the thermal DN values of bands 10 and 11 to BT. BT for both TIR bands were estimated as follows (Equation (2)):
where BT = satellite brightness temperature in Kelvin (K), Lλ = spectral radiance at the sensor, K1 = thermal conversion values (774.89 for band 10 and 480.89 for band 11), and K2 = thermal conversion values (1321.08 for band 10 and 1201.14 for band 11).
- 3.
- Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI)
NDVI is calculated by Equation (3):
where ρNIR and ρRed represent the reflectance of the near-infrared (NIR) (band 5) and red bands (band 4), respectively. The value of this index ranges from −1 to 1, where a value closer to 1 indicates vegetation cover and a value closer to −1 represents water or soil.
- 4.
- Fractional Vegetation Cover (FVC)
FVC is calculated by the following equation:
where NDVI = Normalized Vegetation Difference Index, NDVIvegetation = NDVI for vegetation (maximum), and NDVIsoil = NDVI for soil (minimum).
This index has a value ranging from 0 to 1, with a value closer to 1 representing more vegetation cover and a value closer to 0 representing built-up and bare land (soil). Water bodies for this index are in the median range (0.3–0.7).
- 5.
- Land Surface Emissivity (LSE)
According to Plank’s law [23], before estimating LST, it is necessary to estimate LSE for more accuracy in the results. Thus, LSE can be calculated based on Equation (5):
where εsoil and εvegetation are emissivity values of soil and vegetation in the corresponding bands, respectively.
- 6.
- Land Surface Temperature (LST)
LST is obtained based on the following equation [24]:
where λ = effective wavelength, , , , , and = emissivity.
Water Level Data
This step’s data were obtained from the Data and Services Center for Continental Surfaces [25]. The monthly water levels of both lakes are available from 1995 to 2020.
Dam Constriction and Hydrometric Data
These data were obtained from the Iranian Ministry of Energy between 1985 and 2015. To present the annual time series of daily streamflow, we used the HydroTSM package in RStudio [26].
2.3.2. Water Body Extraction
Landsat images from 2000 to 2016 were used to extract water bodies and show changes in water surface areas in September, with a resolution of 900 m2 and path/row of 168/34, 169/33, and 169/34 for LU, and 170/33, and 171/33 for LV. The primary reasons for selecting this month are because it is the end of the agricultural season, the end of the rainy season, and, more importantly, the date when the water level is at its lowest level to show the most remarkable surface area changes. Detailed data are shown in Table 1. Atmospheric correction is a significant part of satellite remotely sensed data pre-processing. To control sensor, atmospheric, solar, and topographic impacts, these data typically require pre-processing before analysis. As a result, the images for Landsat 7 were rectified and the noise was removed. Due to discrepancies in thematic mapper and OLI sensors, the year 2000’s geometric correction was based on digital elevation model data from the research areas. As a result, images were georeferenced to the 2000 image from 2001 to 2016. Eventually, filtered pixels were used to delineate and extract water bodies based on the Normalized Difference Water Index (NDWI) that is calculated based on Equation (7) [27],
where Green and NIR are values per pixel for the green (0.533–0.59 mm) and near-infrared (0.851–0.879 mm) bands, respectively. The NDWI ranges from −1 to +1, where <0 represents no vegetation or water content and >0 represents water content.

Table 1.
Landsat image data.
Vegetation Index
Vegetation indices enable reliable geographical and temporal comparisons of vegetation canopy greenness, a composite feature of leaf area, canopy cover, and structure. MODIS produced vegetation indices at 8- and 16-day intervals and multiple spatial resolutions. The Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) was employed in this investigation. The MODIS NDVI dataset was based on a 16-day period with a resolution of 250 m. The MOD13Q1 product was obtained from [29].
Water Depth
Landsat images from 2000 were used in both lakes to determine relative water depth and demonstrate its variations. Previous research [30,31,32] used the green band to estimate water depth. A correlation study was performed to improve accuracy between the relative water depth and the reflectance of other bands (blue, green, red, and near-infrared). As a result, for a single-band model, the green band had the highest correlation coefficient, and for a multi-band combination model, the red and blue band combination had the highest correlation coefficient. Table 2 shows the findings. ENVI 5.1 was used to perform all these tasks.

Table 2.
Correlation analysis between water depth, band reflectance, and combined bands.
Evapotranspiration
ET was estimated using MODIS at 8- and 16-day intervals at multiple spatial resolutions. In this study, the MODIS ET dataset was based on the 16-day interval with a resolution of 500 m. The MOD16A2 was collected from [29], named “MODIS/Terra Net Evapotranspiration 8-Day L4 Global 500 m SIN Grid V006”. Because the most recent update to these images was in 2014, the ET estimate was calculated from 2000 to 2014.
3. Results
3.1. Analysis of Lake Extents and Water Levels
We analyzed LU and LV aerial changes from 2000 to 2016. Enhanced Thematic Mapper Plus (ETM+) was used from 2000 to 2012, and Operational Land Imager (OLI) sensor was used from 2013 to 2016. A series of 85 Landsat images acquired from 2000 to 2016 were used to investigate changes in the surface area of the lakes. The lake extents for each year, together with the 17-year trends for each lake, are shown in Figure 4. Generally, the surface area of LU showed a decreasing trend from 2000 to 2016. In contrast, the surface area of LV remained relatively constant during the same period. As seen in Figure 4, LU’s largest decrease in surface area occurred from 2011 to 2014.
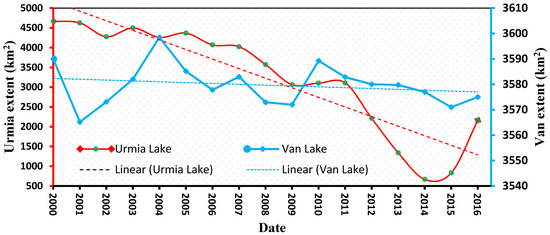
Figure 4.
Annual changes in surface area of LU and LV and the trend in surface area change for the 17-year period from 2000 to 2016.
The LU surface area was at its lowest in 2014, about 14% of what it was in 2000. In comparison, the surface area of LV was relatively steady during this period.
From 2000 to 2016, the maximum water level of LU (1273.8 m) was in 2000, while the highest in LV (1647.8 m) was in 2007 (Figure 5). The lowest water levels in 2014 were 1270.1 m in LU (a loss of roughly 3.75 m) and 1647.0 m in LV (a loss of approximately 0.8 m) in 2002. In general, a decreasing tendency in water level (average of around 0.21 m/year) was recorded for LU. On the other hand, from 2000 to 2016, the overall change in water level for LV was close to zero or slightly positive (10 cm/year) (Figure 5).
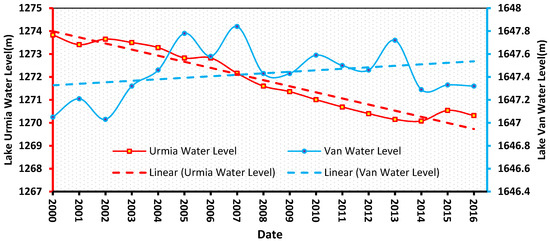
Figure 5.
Annual changes in water levels in LU and LV and the trend in its changes for the 17-year period 2000 to 2016 based on [25].
The general decrease in the surface area of LU by the annual maps of the surface area from 2000 to 2016 is shown in Figure 6, and the rather constant surface area of LV during the same period is illustrated in Figure 7. As shown in Figure 6, the surface area at the southern shore of LU was the first to recede, followed by the surface area at the eastern and then the northern shores. The surface area along the western shore was the least sensitive to recession. The average surface area of LU from 2000 to 2016 was approximately 3138 km2, with maximum surface areas of 4666, 4624, and 4496 km2 recorded in 2000 (Figure 6), 2001, and 2003, respectively. The corresponding average surface area of LV was approximately 3579 km2, with maximum surface areas of 3598, 3590, and 3589 km2 recorded in 2004, 2000, and 2010, respectively (Figure 7). Minimum water surface areas for LU were approximately 700 and 800 km2 and were recorded in September 2014 (Figure 6) and 2015, respectively.
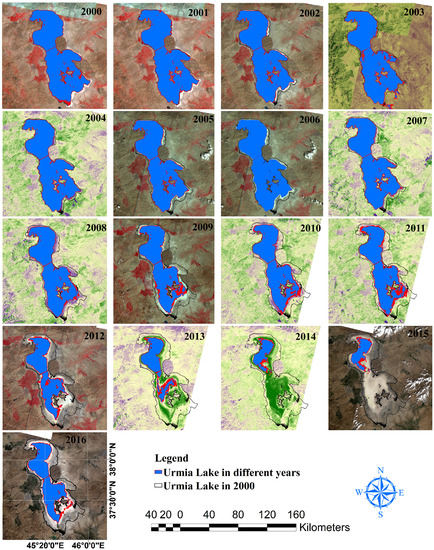
Figure 6.
Maps illustrating surface area changes in LU as extracted from Landsat satellite images.
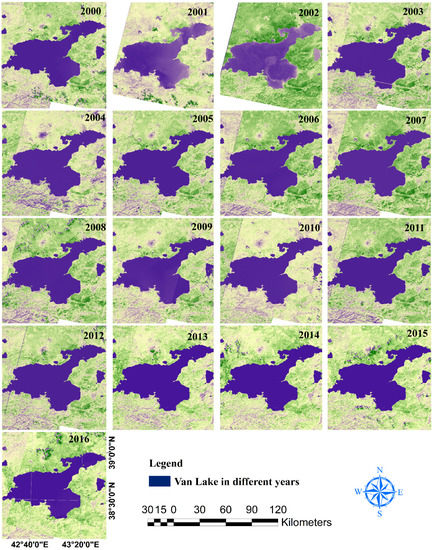
Figure 7.
Maps illustrating surface area changes in LV as extracted from Landsat satellite images.
3.2. NDVI
NDVI data were utilized to investigate long-term changes in the area of irrigated lands in both LU and LV basins. The July to August period from 2000 to 2016 was selected to represent maximum irrigation on farms and minimum vegetation in the remainder of the basins. Because of the limited timespan of MODIS imagery, the NDVI in 2000 was selected as a baseline for change detection. Based on our analysis, an increase in NDVI values from 2000 to 2016 was observed in most years in both lake basins (Figure 8). The greatest annual increase for the LU basin occurred in 2007, with other maxima occurring in 2003, 2004, and 2005. Generally, the satellite images showed an increasing trend in NDVI values from 2000 to 2016 for both basins. However, the increase in NDVI values was greater in the LU basin, as evidenced by the steeper slope of its linear trend plot relative to that of the LV basin.
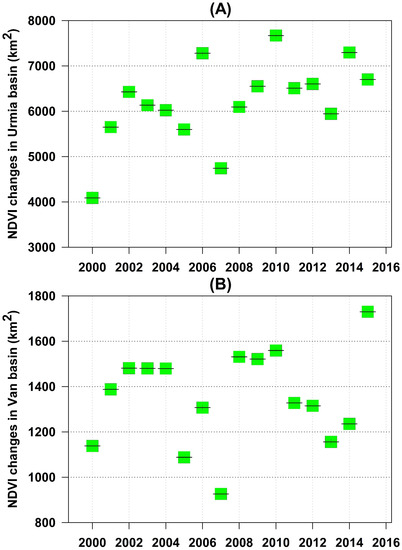
Figure 8.
NDVI changes and its trends in the basins of LU (A) and LV (B).
Nonetheless, NDVI levels in the LU basin stabilized from 2012 to 2013, in the LV basin from 2003 to 2005, and from 2009 to 2011. (Figure 8). Longer-term NDVI data revealed an increase in both basins, as well as in regions where land use had changed (for example, greater agricultural growth) (Figure 9).
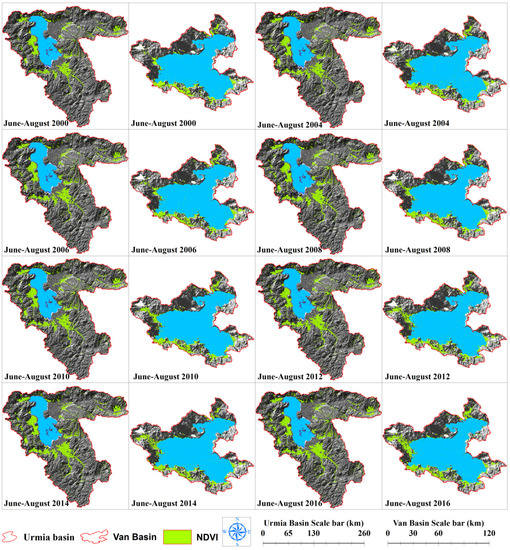
Figure 9.
Variations in NDVI values in LU and LV basins from June to August based on MODIS images.
3.3. Satellite-Derived Evapotranspiration (ET)
According to MODIS ET, the average ET in the LU and LV basins from 2000 to 2014 was roughly 300 and 294 mm/year, respectively (Figure 10). Maximum annual ET was calculated to be 346 (2012) and 338 (2011) mm/year, respectively. ET was higher in the eastern and western areas of the LU basin than in the center, northern, and southern regions, according to a spatial analysis of ET maps in the LU basin (Figure 11). Lower ET was recorded exclusively in the southern part of the LV basin. When comparing Figure 10 and Figure 11, it is clear that the difference in average annual precipitation between the two basins was greater than the difference in annual evapotranspiration. Accordingly, it can be concluded that evapotranspiration is not the main factor in shrinking the LU.
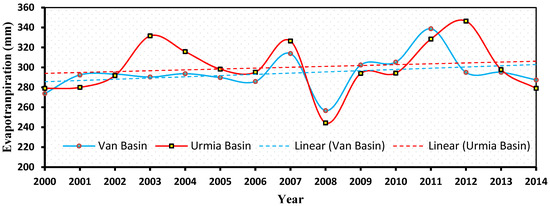
Figure 10.
Mean annual time series of ET in the LU and LV basins, based on MODIS data.
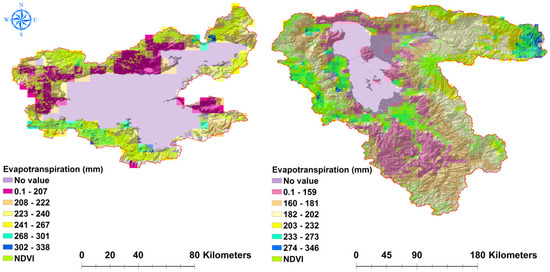
Figure 11.
Average long-term ET in the LU and LV basins, which is highly correlated with the NDVI.
ET revealed a slightly positive trend in the LU and LV basins (Figure 10), which was closely associated with other climate parameters such as precipitation and temperature in the basins. The ET was also correlated with the NDVI maps, so that areas with more vegetation cover in the basins have higher ET values (Figure 11). This was expected, given that the Leaf Area Index is the key factor used to calculate MODIS ET. According to ET and NDVI maps, most of the area in both basins (particularly the LU basin) is vegetated, implying that some of the water is lost by transpiration rather than solely evaporation from the open water bodies.
3.4. Spatial Distribution of Water Depth
Figure 12 shows the water depth for both lakes. LV is significantly deeper than LU. The maximum water depth in a considerable portion of LV is roughly 400 m, but the maximum water depth for LU only for restricted areas is approximately 9 m. In contrast, the mean depth of LU in 2000 was approximately 2.2 m, and approximately 172 m for LV. LU’s deepest and shallowest portions are located in the upper, inner islands, and peripheral areas. These sections of LV are located on the lake’s western and central sides, as well as its northern and peripheral zones. Notably, a large part of LU is shallow, while LV shows the opposite. Hence, the evaporation will be significantly different due to the difference in thermal classification in the lakes.
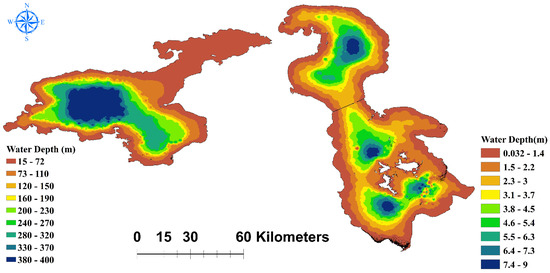
Figure 12.
Bathymetric maps of LU (right) and LV (left) in 2000.
3.5. Precipitation and Temperature
The results for precipitation (rain and snow) and temperature in the LU and LV basins are shown in Figure 13. From 2000 to 2016, the amount of snow in both basins showed a slightly negative trend, whereas rainfall showed a slightly positive trend. The temperature in the basins was shown to be associated with these developments. Furthermore, the LV basin receives more snowfall, rainfall, and total precipitation than the LU basin. Temperatures were higher in the LU basin (Figure 13), and both basins showed a somewhat positive trend.
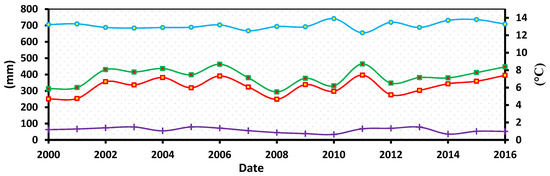
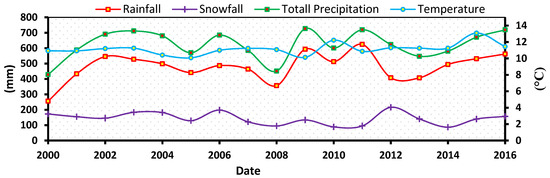
Figure 13.
Mean annual time series of snowfall, rainfall, air temperature, and total precipitation in the LU basin (top) and the LV basin (bottom).
Although the LV basin’s land-to-lake area ratio is lower than that of the LU basin, total precipitation in the LV basin exceeded that of the LU basin (Figure 14). Furthermore, the variability of precipitation in the LV basin was greater than in the LU basin. Average annual precipitation in the area of LV was 500 mm/year in the east of the basin, 580 mm/year in the south, 850 mm/year in the southwest, and 480 mm/year in the north. In contrast, the corresponding LU values were 410, 375, 340, and 353 mm/year, respectively.
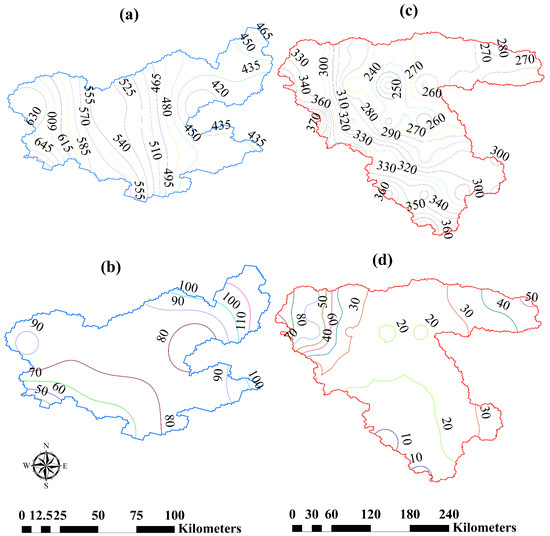
Figure 14.
Spatial distribution of rainfall and snowfall (mm) in the LV (a,b) and LU basin (c,d) respectively, based on [20].
3.6. Stream Flow and Dam Construction
A time series and trend analysis of the discharge of two major rivers (Zarineh-Roud and Simineh-Roud) that feed over 50% of the inflow volume into LU [33] was performed on the eight major rivers in the LU basin. Streamflow typically varies over a wide period and may respond to seasonal rainfall and upstream water management, such as dam and water diversion infrastructure. During the 30-year period (1985–2015), the months of peak river discharge aligned with the spring season due to snow melt (Figure 15), demonstrating that streamflow in the LU basin is mostly snowfall-driven, supporting the association between streamflow and snowfall.
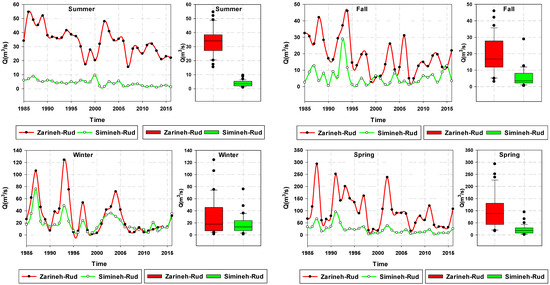
Figure 15.
Seasonal hydrographs of the Zarineh-Roud and Simineh-Roud in the LU basin during 1985–2015.
For the 30-year period from 1985 to 2015, a decreasing trend of streamflow was evident in both the Zarineh-Roud and Simineh-Roud rivers during the spring and summer seasons (Figure 15). The reason for this trend can be attributed to dam and water diversion infrastructure construction on these rivers. This result is consistent with the results of other studies on trends in streamflow in the LU basin [7,16], and dam and water diversion construction on the main rivers in the LU basin (Figure 16) may account, in part, for the decreasing water volume and surface area of LU.
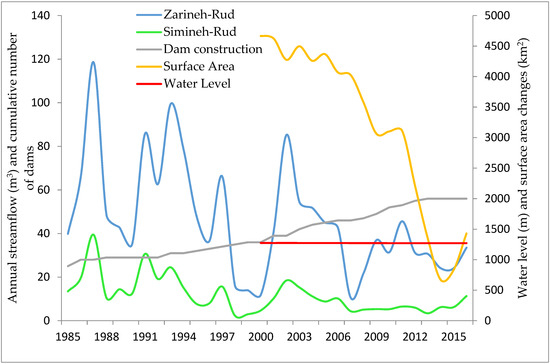
Figure 16.
Number of dams constructed and annual stream flow from 1985 to 2016 and surface area and water level changes from 2000 to 2016 in the LU basin.
According to the Iranian Ministry of Energy, about twenty dams were built on major rivers in the LU basin between 2000 and 2013 (Figure 16). However, as seen in the graph, the number of dams built and the annual streamflow for the two main rivers fell from 2000 to 2015 (analogous dam data were not available for the LV basin; however, the water level in LV remained relatively stable from 2000 to 2016).
4. Discussion
Because Lake Urmia’s water volume has declined significantly over the past 17 years, comparing its water volume fluctuations with those of another lake with similar climatic conditions but different policies for managing streamflow within the basins helps to investigate the underlying causes of this environmental disaster. Thus, this study compared meteorological indicators and anthropogenic activities in Iran’s Lake Urmia basin to those in Turkey’s Lake Van basin.
According to a preliminary examination of the Lake Urmia basin streamflow dataset, the peak streamflow occurred from 1990 to 1995, followed by a decreasing streamflow trend until 2016. Anthropogenic impacts can be associated with seasonal fluctuations in streamflow. This study’s streamflow data were used to measure downstream dams and water diversion structures.
During the 17-year period from 2000 to 2016, some parameters showed similar trends in the Lake Urmia and Lake Van basins. The NDVI index, for example, increased in both basins from 2006 to 2007 and declined in both from 2008 to 2009, with corresponding increases and declines in evapotranspiration in both basins from 2006 to 2007 and 2008 to 2009. The rainfall records from the 10 gauge stations in the Lake Urmia basin were analyzed, and there were no differences in annual and seasonal rainfall patterns across the gauge stations. These findings are consistent with the findings of earlier research that looked at precipitation patterns in the Lake Urmia basin [7,34,35]. Furthermore, a review of precipitation data from the EU-WATCH dataset revealed no climate variation between the Lake Urmia and Lake Van basins. Lake Urmia’s water level decreased from 2000 to 2016, although Lake Van’s remained relatively steady (unchanged). Because both basins experienced similar precipitation during these 17 years, the main factors causing the decreasing water level in Lake Urmia were not climatic, which concurs with the conclusion of dams [36].
Dam construction considerably impacted streamflow variability in the Lake Urmia basin. Although streamflow regulation data from dam operations were not available for this study, the presence of dams on major rivers has influenced the hydrological flow regime variability in the basin. This influence is partly attributed to dam runoff storage during the wet seasons. Reduced streamflow is evident during the wet seasons from 2000 to 2015 (Figure 15), when twenty dams were built on major rivers in the Lake Urmia basin (Figure 16). Reduced streamflow during the summer, on the other hand, can be attributed in part to water diversion for irrigation purposes.
Variance in yearly streamflow in the Zarineh-Rud and Simineh-Rud rivers from 1985 to 2016 was assumed to indicate water level variation in the other major rivers in the Lake Urmia basin. The results of the annual streamflow analysis in Zarineh-Rud and Simineh-Rud showed a decreasing trend during these 30 years. The average discharge in the first five years, compared to the average discharge in the last five years, decreased by 51% and 40% in Zarineh-Rud and Simineh-Roud, respectively. Some of this decrease in discharge would have been partly due to increased irrigation in both basins. Evaluation of historical changes in the number of irrigated farms based on MODIS (MOD13Q1) in both the Lake Urmia and Lake Van basins showed that while the number of irrigated farms in both basins had increased, the increase was greater in the Lake Urmia basin, in agreement with other studies in which trends in agricultural development were assessed [7,37,38,39].
Previous studies have shown a high correlation between increased vegetation due to the increased area of irrigated farmland and the increase in total evapotranspiration in the Lake Urmia basin [7,40]. The increased use of river water for farmland irrigation has negatively influenced input flow into Lake Urmia and water availability throughout the basin. Moreover, the construction of reservoirs to store water has decreased input flow to the lake relative to the situation before reservoir construction [16,41].
Water levels in Lake Urmia have decreased from 1985 to 2016, while those in Lake Van have remained essentially steady. According to the findings of this study, climatic differences in precipitation and temperature are not likely key drivers of the water level shift in Lake Urmia. Instead, the declining water level in Lake Urmia is most likely due to decreased input flow caused by building dams on the principal rivers in the Lake Urmia basin and water diversion from the rivers directly for irrigation of agriculture or diversion into reservoirs for further irrigation [35,42]. Although both lakes are terminal lakes with no considerable water outflow, Lake Urmia has experienced greater water level and surface area fluctuations than Lake Van because Lake Urmia is much shallower and has less water capacity. This study’s findings support previous research that identified cropland expansion and other anthropogenic influences, such as dam construction and water diversion channels, as the primary causes of LU shrinkage [7,18,43].
5. Conclusions
This study examined changes in water level and surface areas in LU and LV based on trend analyses and satellite image processing. The annual precipitation, evapotranspiration, air temperature, NDVI, water depth, water level, and surface area time series of both lakes for 2000–2016 and hydrometric data for 1985–2015 were analyzed. Since both lakes are terminal lakes with no significant water outflow, loss of water from the lakes occurs only by evaporation. The time series analysis of both LU and LV showed that water level and surface area only changed significantly in LU.
The decreasing trend of water level and surface area in LU was due to differences in climatic parameters (such as precipitation, temperature, and evaporation) or changes in input flow volume due to human activities. Since both the LU and LV basins experienced a relatively unchanged pattern in climate parameters from 2000 to 2016, it was concluded that these factors could not explain the decreasing trend in water level and surface area in LU. Furthermore, since 2000, dam construction and water diversion projects have drastically expanded in the LU basin. Moreover, an increase in the NDVI indicates the expansion of irrigated agriculture in the basin over the past two decades. These changes are the main factors responsible for reducing inflow into LU. Apart from these, regarding the shallow depth of most parts of LU compared to LV’s depth, a decrease in input flow volume into the lake would quickly result in an extensive decrease in the water surface area compared to LV.
To summarize, developing and implementing strategies and regulations in the LU basin are critical to limiting and minimizing future water level changes. For this purpose, district officials should employ appropriate measures such as rewarding rules and legislation, water transfer programs, changing farming patterns, novel irrigation systems, and greenhouse cultivation to reduce water consumption from the lake’s supplying rivers. Finally, due to some limitations, such as a lack of access to hydrological and climatic data and the difficulty in applying the same methods to a wide range of factors for both lakes, we encourage longer-term studies focusing on water resource management and agricultural policies using field observation data.
Author Contributions
S.K. wrote the paper and observed the scientific content of the paper; A.L. edited, acquired funding, and supervised the content of the paper; A.S. edited and observed the scientific content of the paper. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
S.K. was supported in part by a fellowship from the Integrated Modeling Program for Canada (https://gwf.usask.ca/impc/ (accessed on 23 January 2019)) at the University of Saskatchewan, Canada.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Saman Razavi Amin Haghnegahdar for supporting to add new ideas throughout the research, and also Shervan Gharari for providing the EU-WATCH dataset for the study areas.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Brown, L.C.; Duguay, C.R. The response and role of ice cover in lake-climate interactions. Prog. Phys. Geogr. 2010, 34, 671–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, M. The world’s vanishing lakes. Curr. Biol. 2017, 27, R43–R46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wurtsbaugh, W.A. Management of the Great Salt Lake Ecosystem: Water, Economic Values and Competing Interests. Watershed Sci. Fac. Publ. 2014, 26, 594. Available online: http://digitalcommons.usu.edu/wats_facpub/594 (accessed on 27 May 2020).
- Gao, H.; Bohn, T.J.; Podest, E.; McDonald, K.C.; Lettenmaier, D.P. On the causes of the shrinking of Lake Chad. Environ. Res. Lett. 2011, 6, 034021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wurtsbaugh, W.A.; Miller, C.; Null, S.E.; Derose, R.J.; Wilcock, P.; Hahnenberger, M.; Howe, F.; Moore, J. Decline of the world’s saline lakes. Nat. Geosci. 2017, 10, 816–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Wang, S.; Gao, G.; Fu, B.; Ye, Z.; Shen, Q. Exploring responses of lake area to river regulation and implications for lake restoration in arid regions. Ecol. Eng. 2019, 128, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khazaei, B.; Khatami, S.; Alemohammad, S.H.; Rashidi, L.; Wu, C.; Madani, K.; Kalantari, Z.; Destouni, G.; Aghakouchak, A. Climatic or regionally induced by humans? Tracing hydro-climatic and land-use changes to better understand the Lake Urmia tragedy. J. Hydrol. 2019, 569, 203–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilcox, D.A.; Thompson, T.A.; Booth, R.K.; Nicholas, J.R. Lake-level variability and water availability in the Great Lakes. U.S. Geol. Surv. Circ. 2007, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.A.; Yang, Z.F. A method to assess the alteration of water-level-fluctuation patterns in lakes. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2012, 13, 2427–2436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakahaji, H.; Banadaki, H.D.; Kakahaji, A.; Kakahaji, A. Prediction of Urmia Lake Water-Level Fluctuations by Using Analytical, Linear Statistic and Intelligent Methods. Water Resour. Manag. 2013, 27, 4469–4492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Valle, P.D.; Lakhan, V.C.; Trenhaile, A.S. Short term fluctuations of Lake Erie water levels and the El Niño/Southern Oscillation. Great Lakes Geogr. 2000, 7, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Ouarda, T.B.M.J.; Ehsanzadeh, E.; Saley, H.M.; Khaliq, N.; Seidou, O.; Charron, C.; Pietroniro, A.; Lee, D. Analysis of Changes in the Great Lakes Net Basin Supply (NBS) Components and Explanatory Variables. 2009, pp. 1–73. Available online: https://www.academia.edu/26609186/Analysis_of_Changes_in_the_Great_Lakes_Net_Basin_Supply_NBS_Components_and_Explanatory_Variables?from_sitemaps=true&version=2 (accessed on 27 May 2020).
- Sellinger, C.E.; Stow, C.A.; Lamon, E.C.; Qian, S.S. Recent water level declines in the Lake Michigan-Huron system. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 367–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ülgen, U.B.; Franz, S.O.; Biltekin, D.; Çagatay, M.N.; Roeser, P.A.; Doner, L.; Thein, J. Climatic and environmental evolution of Lake Iznik (NW Turkey) over the last ∼4700 years. Quat. Int. 2012, 274, 88–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalili, S.; Hamidi, S.A.; Morid, S.; Namdar Ghanbari, R. Comparative analysis of Lake Urmia and Lake Van water level time series. Arab. J. Geosci. 2016, 9, 644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shadkam, S.; Ludwig, F.; van Oel, P.; Kirmit, Ç.; Kabat, P. Impacts of climate change and water resources development on the declining inflow into Iran’s Urmia Lake. J. Great Lakes Res. 2016, 42, 942–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AghaKouchak, A.; Norouzi, H.; Madani, K.; Mirchi, A.; Azarderakhsh, M.; Nazemi, A.; Nasrollahi, N.; Farahmand, A.; Mehran, A.; Hasanzadeh, E. Aral Sea syndrome desiccates Lake Urmia: Call for action. J. Great Lakes Res. 2015, 41, 307–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barideh, R.; Nasimi, F. Investigating the changes in agricultural land use and actual evapotranspiration of the Urmia Lake basin based on FAO’s WaPOR database. Agric. Water Manag. 2022, 264, 107509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çimen, M.; Kisi, O. Comparison of two different data-driven techniques in modeling lake level fluctuations in Turkey. J. Hydrol. 2009, 378, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EU-WATCH. Available online: http://www.eu-watch.org (accessed on 27 May 2020).
- Weedon, G.P.; Gomes, S.; Viterbo, P.; Shuttleworth, W.J.; Blyth, E.; Österle, H.; Adam, J.C.; Bellouin, N.; Boucher, O.; Best, M. Creation of the WATCH forcing data and its use to assess global and regional reference crop evaporation over land during the twentieth century. J. Hydrometeorol. 2011, 12, 823–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stahl, K.; Tallaksen, L.M.; Gudmundsson, L.; Christensen, J.H. Streamflow data from small basins: A challenging test to high-resolution regional climate modeling. J. Hydrometeorol. 2011, 12, 900–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Muñoz, J.C. Correction to “A generalized single-channel method for retrieving land surface temperature from remote sensing data” by Juan C. Jiménez-Muñoz and José A. Sobrino. J. Geophys. Res. 2004, 109, 8112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, Q.; Lu, D.; Schubring, J. Estimation of land surface temperature-vegetation abundance relationship for urban heat island studies. Remote Sens. Environ. 2004, 89, 467–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theia. Available online: http://hydroweb.theia-land.fr/ (accessed on 27 May 2020).
- Zambrano-Bigiarini, M. Goodness-of-Fit Functions for Comparison of Simulated and Observed Hydrological Time Series. 2020, Volume 22. Available online: https://github.com/hzambran/hydroGOF (accessed on 27 May 2020).
- Park, E.; Lewis, Q.W.; Sanwlani, N. Large lake gauging using fractional imagery. J. Environ. Manage. 2019, 231, 687–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USGS. Available online: https://earthexplorer.usgs.gov/ (accessed on 27 May 2020).
- NASA Earth Data Search. Available online: https://search.earthdata.nasa.gov/search (accessed on 27 May 2020).
- Zhang, Z.; Teng, H. An inversion method of remote sensing water depth based on transmission bands ratio. In Proceedings of the 2011 Fourth International Joint Conference on Computational Sciences and Optimization, Kunming/Lijiang, China, 15–19 April 2011; pp. 1002–1006. [Google Scholar]
- Le, Y.; Hu, M.; Chen, Y.; Yan, Q.; Zhang, D.; Li, S.; Zhang, X.; Wang, L. Investigating the Shallow-Water Bathymetric Capability of Zhuhai-1 Spaceborne Hyperspectral Images Based on ICESat-2 Data and Empirical Approaches: A Case Study in the South China Sea. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nan, Y.; Jianhui, L.; Wenbo, M.; Wangjun, L.; Di, W.; Wanchao, G.; Changhao, S. Water depth retrieval models of East Dongting Lake, China, using GF-1 multi-spectral remote sensing images. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2020, 22, e01004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urmia Lake Restoration Program. 2015. Available online: http://ulrp.sharif.ir/en (accessed on 3 September 2016).
- Fathian, F.; Morid, S.; Kahya, E. Identification of trends in hydrological and climatic variables in Urmia Lake basin, Iran. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2015, 119, 443–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassanzadeh, E.; Zarghami, M.; Hassanzadeh, Y. Determining the Main Factors in Declining the Urmia Lake Level by Using System Dynamics Modeling. Water Resour. Manag. 2012, 26, 129–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalili, S.; Hamidi, S.A.; Namdar Ghanbari, R. Climate variability and anthropogenic effects on Lake Urmia water level fluctuations, northwestern Iran. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2016, 61, 1759–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhari, S.; Felfelani, F.; Shin, S.; Pokhrel, Y. Climate and anthropogenic contributions to the desiccation of the second largest saline lake in the twentieth century. J. Hydrol. 2018, 560, 342–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrian, M.R.; Hernandez, R.P.; Yavari, A.R.; Faryadi, S.; Salehi, E. Investigating the causality of changes in the landscape pattern of Lake Urmia basin, Iran using remote sensing and time series analysis. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2016, 188, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Shrestha, S.; Gilani, H.; Gumma, M.K.; Siddiqui, B.N.; Jain, A.K. Dynamics and drivers of land use and land cover changes in Bangladesh. Reg. Environ. Chang. 2020, 20, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orth, R.; Destouni, G. Drought reduces blue-water fluxes more strongly than green-water fluxes in Europe. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adam, J.C.; Haddeland, I.; Su, F.; Lettenmaier, D.P. Simulation of reservoir influences on annual and seasonal streamflow changes for the Lena, Yenisei, and Ob’ rivers. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2007, 112, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathian, F.; Dehghan, Z.; Eslamian, S. Analysis of water level changes in Lake Urmia based on data characteristics and non-parametric test. Int. J. Hydrol. Sci. Technol. 2014, 4, 18–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naboureh, A.; Li, A.; Ebrahimy, H.; Bian, J.; Azadbakht, M.; Amani, M.; Lei, G.; Nan, X. Assessing the effects of irrigated agricultural expansions on Lake Urmia using multi-decadal Landsat imagery and a sample migration technique within Google Earth Engine. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2021, 105, 102607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).