Comparative Analysis of Binhu and Cosmic-2 Radio Occultation Data
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Data and Methods Descriptions
2.1. Data Description
2.2. Methods Description
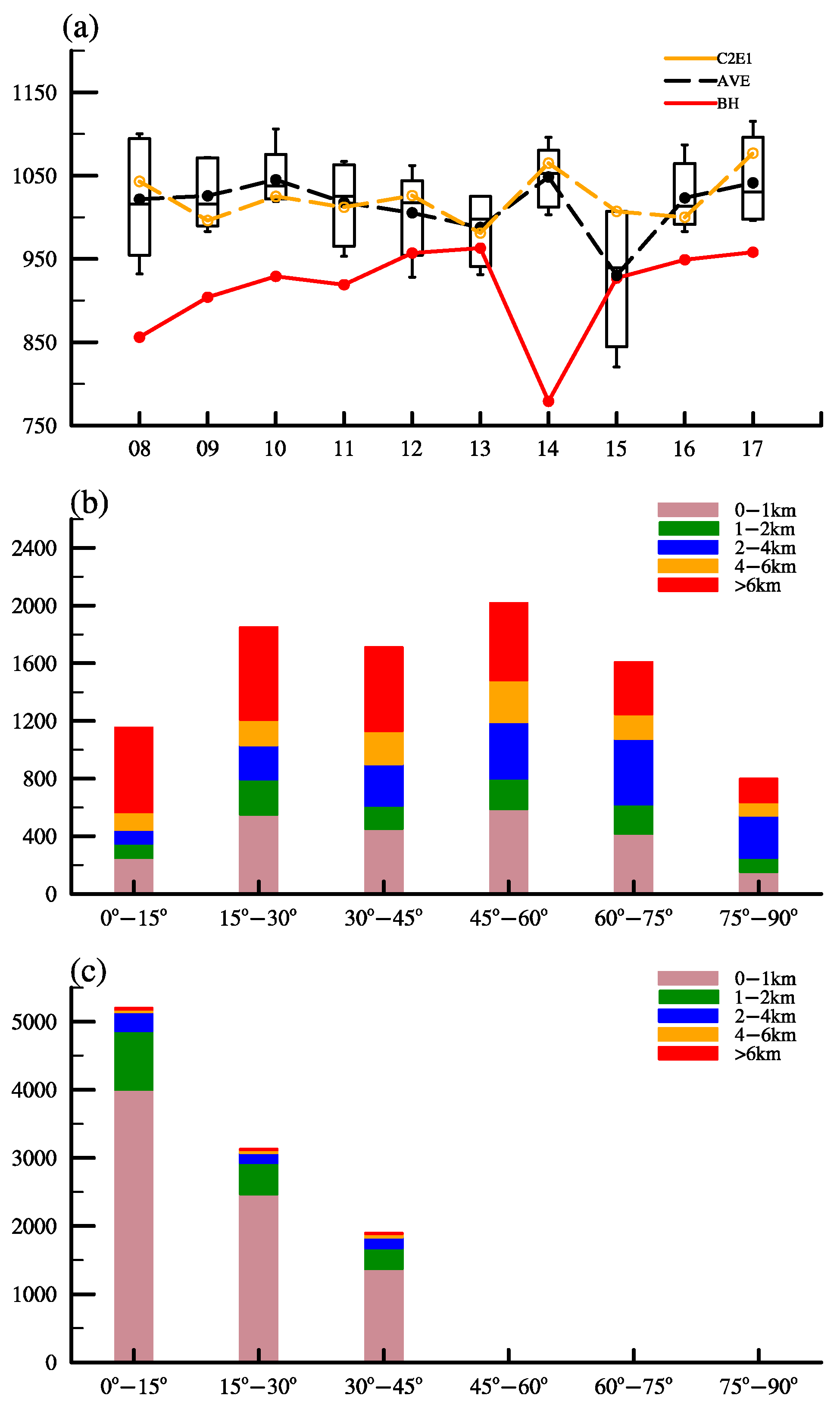
3. Temporal Characteristics of the RO Data
4. Comparative Analysis
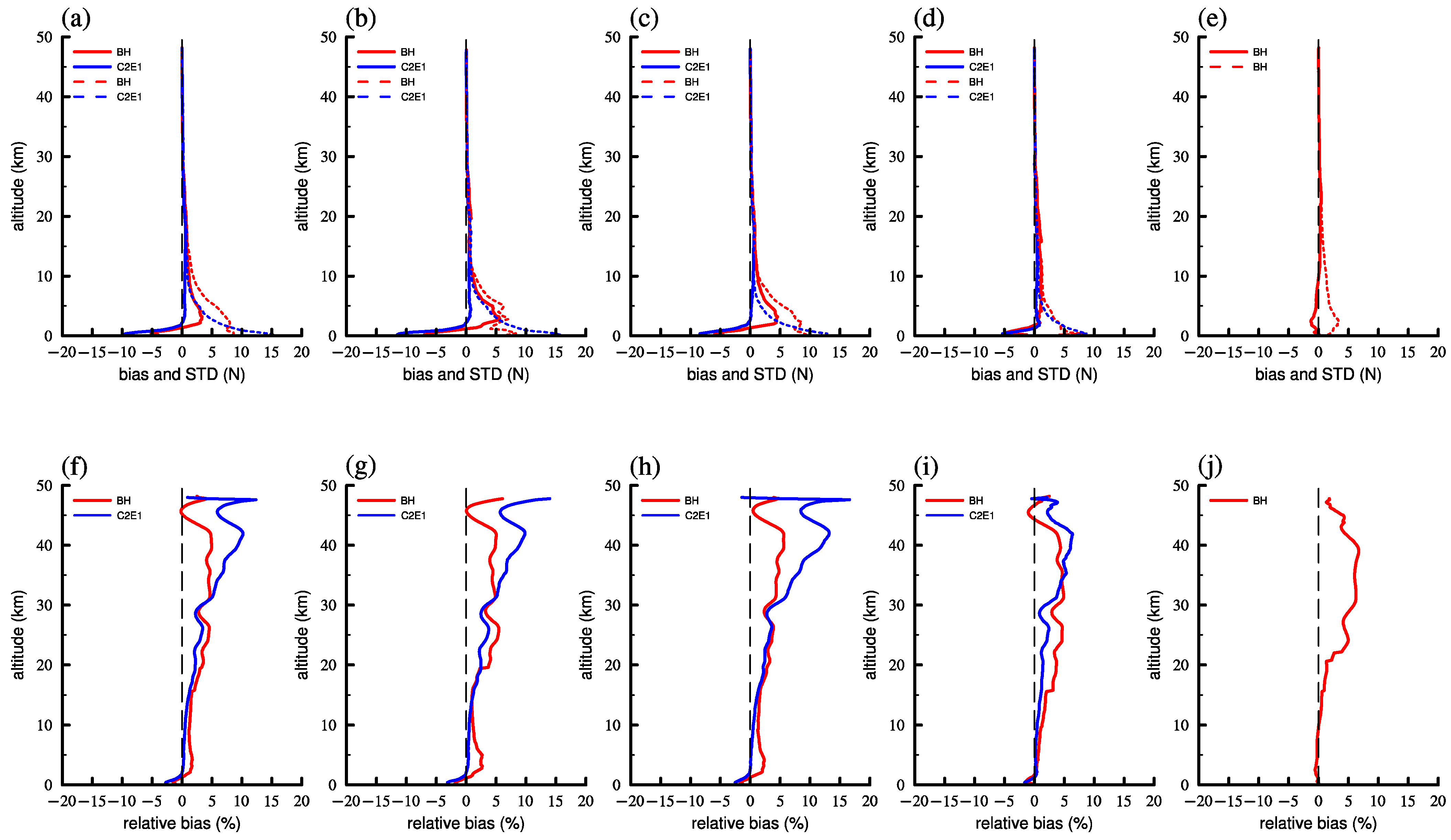
4.1. Refractivity Profile
4.2. Specific Humidity and Temperature Profile
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kliore, A.; Cain, D.L.; Levy, G.S.; Eshleman, V.R.; Fjeldbo, G.; Drake, F.D. Occultation experiment: Results of the first direct measurement of Mars’s atmosphere and ionosphere. Science 1965, 149, 1243–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fjeldbo, G.; Eshleman, V.R. The atmosphere of Mars analyzed by integral inversion of the Mariner IV occultation data. Planet. Space Sci. 1968, 16, 1035–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eshleman, V.R. The radio occultation method for the study of planetary atmospheres. Planet. Space Sci. 1973, 21, 1521–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yunck, T.P. An overview of atmospheric radio occultation. J. Glob. Posit. Syst. 2002, 1, 58–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ware, R.; Rocken, C.; Solheim, F.; Exner, M.; Kuo, Y.H. GPS sounding of the atmosphere from low Earth orbit: Preliminary results. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1996, 77, 19–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kursinski, E.R.; Hajj, G.A.; Bertiger, W.I.; Leroy, S.S.; Meehan, T.K.; Romans, L.J.; Schofield, J.T.; Mccleese, D.J.; Melbourne, W.G.; Thornton, C.L. Initial results of radio occultation observations of Earth’s atmosphere using the Global Positioning System. Science 1996, 271, 1107–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, D.D.; Herman, B.M. Remotely Sensing the Earth’s Atmosphere Using the Global Positioning System (GPS)—The GPS/MET Data Analysis. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 1999, 16, 989–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickert, J.; Reigber, C.; Beyerle, G.; Knig, R.; Hocke, K. Atmosphere sounding by GPS radio occultation: First results from CHAMP. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2001, 28, 3263–3266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anthes, R.A.; Ector, D.; Hunt, D.C.; Kuo, Y.H.; Rocken, C.; Schreiner, W.S.; Syndergaard, S.; Wee, T.K.; Zeng, Z. The COSMIC/FORMOSAT-3 mission: Early results. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2012, 89, 313–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, M.; Sun, L.; Yang, G.; Yue, X.; Tao, Y.; Cong, H.; Zeng, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J. First Ionospheric Radio-Occultation Measurements From GNSS Occultation Sounder on the Chinese Feng-Yun 3C Satellite. IEEE T. Geosci. Remote 2016, 54, 5044–5053. [Google Scholar]
- Luntama, J.P.; Kirchengast, G.; Borsche, M.; Foelsche, U.; Marquardt, C. Prospects of the EPS GRAS mission for operational atmospheric applications. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2008, 89, 1863–1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, P.G.; Berutti, B.; Blythe, P.; Callies, J.; Fransen, C.; Krutsch, R.; Lefebvre, A.R.; Loiselet, M.; Stricker, N. The MetOp satellite-Weather information from polar orbit. ESA Bull. 2006, 127, 8–17. [Google Scholar]
- Kursinski, E.R.; Hajj, G.A.; Schofield, J.T.; Linfield, R.P.; Hardy, K.R. Observing earth’s atmosphere with radio occultation measurements using the global positioning system. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1997, 102, 23429–23465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Healy, S.B. Smoothing radio occultation bending angles above 40 km. Ann. Geophys. 2001, 19, 459–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hajj, G.A.; Kursinski, E.R.; Romans, L.J.; Bertiger, W.I.; Leroy, S.S. A technical description of atmospheric sounding by GPS occultation. J. Atmos. Sol.-Terr. Phys. 2002, 64, 451–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, E.J.; Zhang, K.F.; Marion, K.Y.; Xu, X.H.; Marshall, J.; Rea, A.; Weymouth, G.; Kuleshov, Y. Assessing COSMIC GPS radio occultation derived atmospheric parameters using Australian radiosonde network data. Procedia Earth Planet. Sci. 2009, 1, 1054–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Ho, S.P.; Chen, H.; Zhou, X.; Hunt, D.; Kuo, Y.H. Assessment of radiosonde temperature measurements in the upper troposphere and lower stratosphere using COSMIC radio occultation data. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2009, 36, L17807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Reale, A.; Seidel, D.J.; Hunt, D.C. Comparing radiosonde and COSMIC atmospheric profile data to quantify differences among radiosonde types and the effects of imperfect collocation on comparison statistics. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2010, 115, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatanaka, Y.; Mannoji, N.; Naito, I.; Ichikawa, R.; Shimada, S.; Yabuki, T.; Tsuji, H.; Tanaka, T. Global positioning system project to improve Japanese weather, earthquake predictions. EOS Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 1998, 79, 301–311. [Google Scholar]
- Healy, S.B. Forecast impact experiment with a constellation of GPS radio occultation receivers. Atmos. Sci. Lett. 2008, 9, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poli, P.; Moll, P.; Puech, D.; Rabier, F.; Healy, S.B. Quality control, error analysis, and impact assessment of FORMOSAT3/COSMIC in numerical weather prediction. Terr. Atmos. Ocean. Sci. 2009, 20, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Rennie, M.P. The impact of GPS radio occultation assimilation at the Met Office. Q. J. Roy. Meteor. Soc. 2010, 136, 116–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cucurull, L. Assimilation of Global Positioning System Radio Occultation Observations into NCEP’s Global Data Assimilation System. Mon. Wea. Rev. 2010, 135, 3174–3193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Xue, J. Assimilation of GNSS radio occultation observations in GRAPES. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2014, 7, 7613–7639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, P.; Radnóti, G.; Healy, S.; Cardinali, C. GNSS Radio Occultation Constellation Observing System Experiments. Mon. Wea. Rev. 2014, 142, 555–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.Y.; Huang, C.Y.; Kuo, Y.H.; Guo, R.Y.; Sokolovskiy, S. Assimilation of GPS refractivity from FORMOSAT3/COSMIC using a nonlocal operator with WRF 3DVAR and its impact on the prediction of a typhoon event. Terr. Atmos. Ocean. Sci. 2009, 20, 133–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Kuo, Y.H.; Wang, B.; Wu, W.S.; Sokolovskiy, S. Comparison of local and nonlocal observation operators for the assimilation of GPS RO data with the NCEP GSI system: An OSSE study. Mon. Wea. Rev. 2009, 137, 3575–3587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kueh, M.T.; Huang, C.Y.; Chen, S.Y.; Chen, S.H.; Wang, C.J. Impact of GPS Radio Occultation Refractivity Soundings on a Simulation of Typhoon Bilis (2006) Upon Landfall. Terr. Atmos. Ocean. Sci. 2009, 20, 115–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Huang, C.Y.; Kuo, Y.H.; Chen, S.Y.; Terng, C.T.; Chien, F.C.; Lin, P.L.; Kueh, M.T.; Chen, S.H.; Yang, M.J.; Wang, C.J.; et al. Impact of GPS radio occultation data assimilation on regional weather predictions. GPS Solut. 2010, 14, 35–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunii, M.; Seko, H.; Ueno, M. Impact of Assimilation of GPS Radio Occultation Refractivity on the Forecast of Typhoon Usagi in 2007. J. Meteor. Soc. Jpn. 2012, 90, 255–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.C.; Hsieh, M.E.; Hsiao, L.F.; Kuo, Y.H.; Yang, M.J.; Huang, C.Y.; Lee, C.S. Systematic evaluation of the impacts of GPSRO data on the prediction of typhoons over the northwestern Pacific in 2008–2010. Atmos. Meas. Tech. Discuss. 2015, 8, 2531–2542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, M.J.; Kren, A.C.; Cucurull, L.; Casey, S.P.F.; Peevey, T.R. Impact of refractivity profiles from a proposed GNSS-RO constellation on tropical cyclone forecasts in a global modeling system. Mon. Wea. Rev. 2020, 148, 3037–3057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Zou, X.; Ray, P.S. Comparison of TC temperature and water vapor climatologies between the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans from GPS RO observations. J. Climate 2018, 31, 8557–8571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Anderson, J.E.; Kuo, Y.H. Improved Analyses and Forecasts of Hurricane Ernesto’s Genesis Using Radio Occultation Data in an Ensemble Filter Assimilation System. Mon. Wea. Rev. 2012, 140, 151–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.Y.; Kuo, Y.H.; Rao, A.; Chen, S.Y. The assimilation of GPS radio occultation data and its impact on rainfall prediction along the west coast of India during monsoon 2002. Pure Appl. Geophys. 2007, 164, 1577–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.C.; Chen, S.H.; Chen, S.Y.; Huang, C.Y.; Chen, C.S. Evaluating the impact of the COSMIC RO bending angle data on predicting the heavy precipitation episode on 16 June 2008 during SoWMEX-IOP8. Mon. Wea. Rev. 2014, 142, 4139–4163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, V.V.M.J.; Ratnam, M.V.; Santhi, Y.D.; Raman, M.R.; Rao, S.V.B. On the detection of onset and activity of the Indian summer monsoon using GPS RO refractivity profiles. Mon. Wea. Rev. 2013, 141, 2096–2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherllin-Pirscher, B.; Steiner, A.K.; Anthes, R.A.; Alexander, A.J.; Zeng, Z. Tropical Temperature Variability in the UTLS: New Insights from GPS Radio Occultation Observations. J. Climate 2020, 34, 2813–2838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neiman, P.J.; Ralph, F.M.; Wick, G.A.; Kuo, Y.H.; Wee, T.K.; Ma, Z.; Taylor, G.H.; Dettinger, M.D. Diagnosis of an intense atmospheric river impacting the Pacific Northwest: Storm summary and offshore vertical structure observed with COSMIC satellite retrievals. Mon. Wea. Rev. 2008, 136, 4398–4420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Zhao, N.; Kikuchi, K.; Nasuno, T.; Nakano, M.; Annamalai, H. Atmospheric Rivers over the Indo-Pacific and Its Associations with the Boreal Summer Intraseasonal Oscillation. J. Climate 2021, 34, 9711–9728. [Google Scholar]
- Harnisch, F.; Healy, S.B.; Bauer, P.; English, S.J. Scaling of GNSS Radio Occultation Impact with Observation Number Using an Ensemble of Data Assimilations. Mon. Wea. Rev. 2013, 141, 4395–4413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, E.K.; Weintraub, S. The constants in the equation for atmospheric refractive index at radio frequencies. Proc. IRE 1953, 41, 1035–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cucurull, L.; Casey, S.P.F. Improved Impacts in Observing System Simulation Experiments of Radio Occultation Observations as a Result of Model and Data Assimilation Changes. Mon. Wea. Rev. 2021, 149, 207–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreiner, W.S.; Weiss, J.P.; Anthes, R.A.; Braun, J.; Chu, V.; Fong, J.; Hunt, D.; Kuo, Y.-H.; Meehan, T.; Serafino, W.; et al. COSMIC-2 Radio Occultation Constellation-First Results. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2020, 47, e2019GL086841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
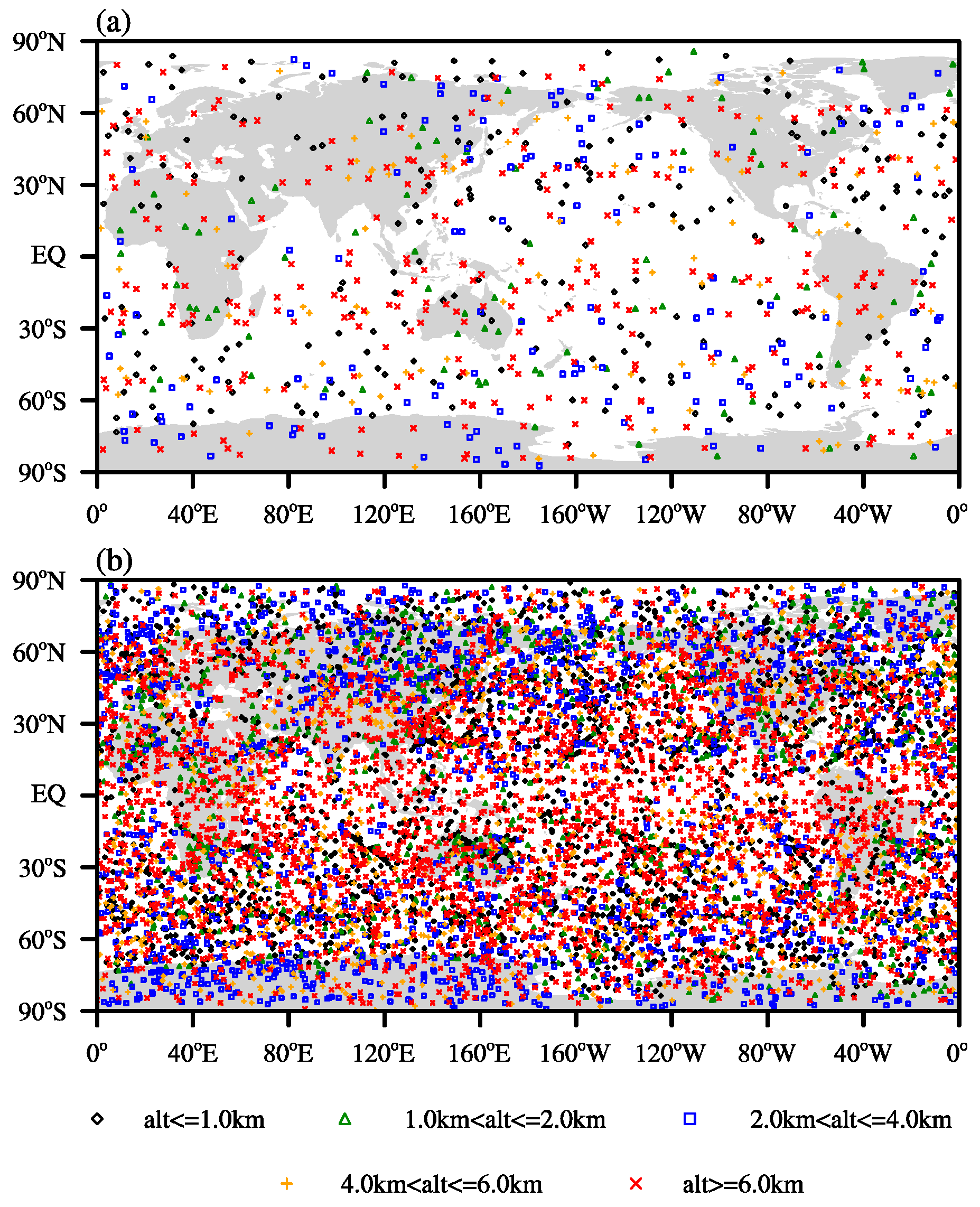
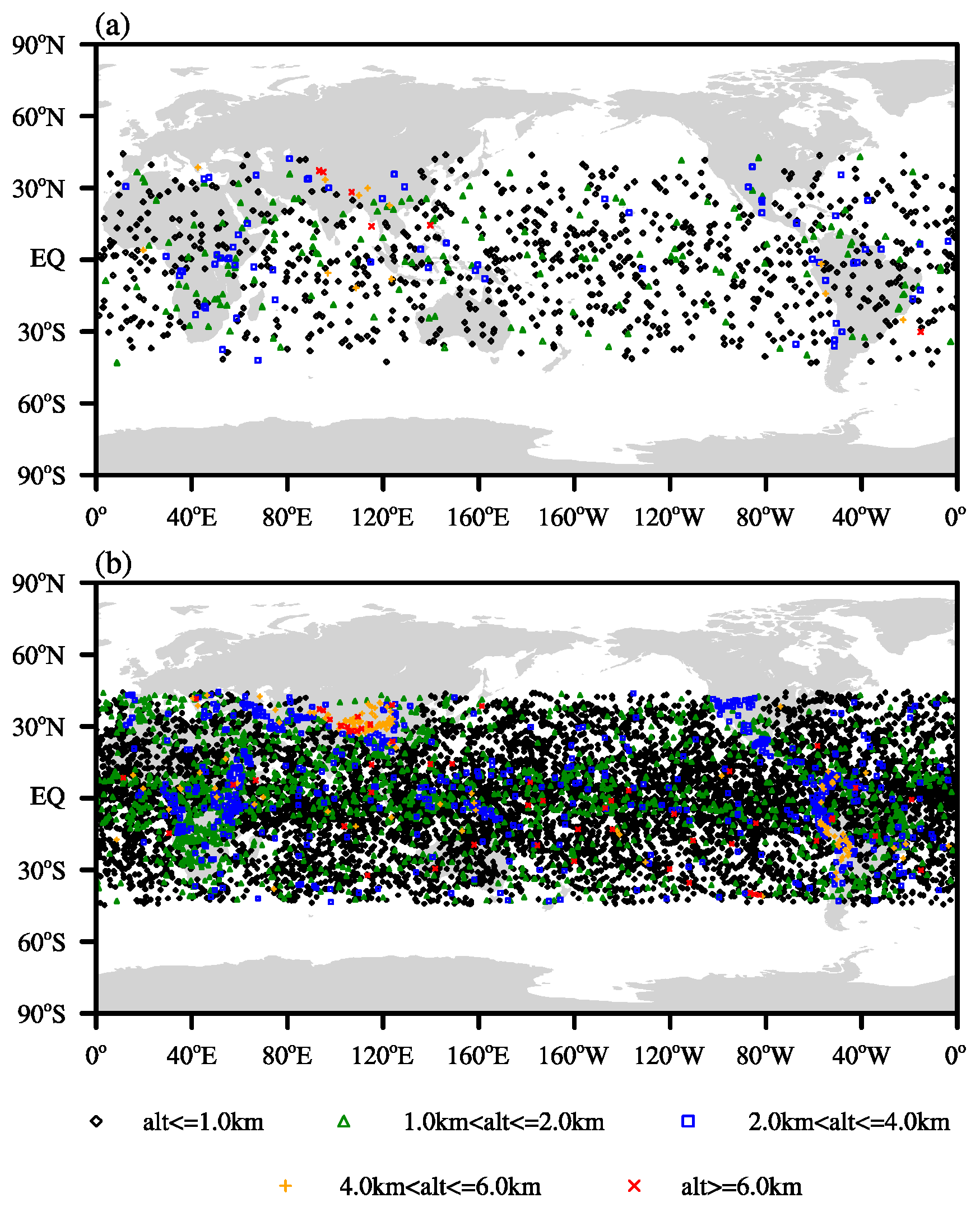

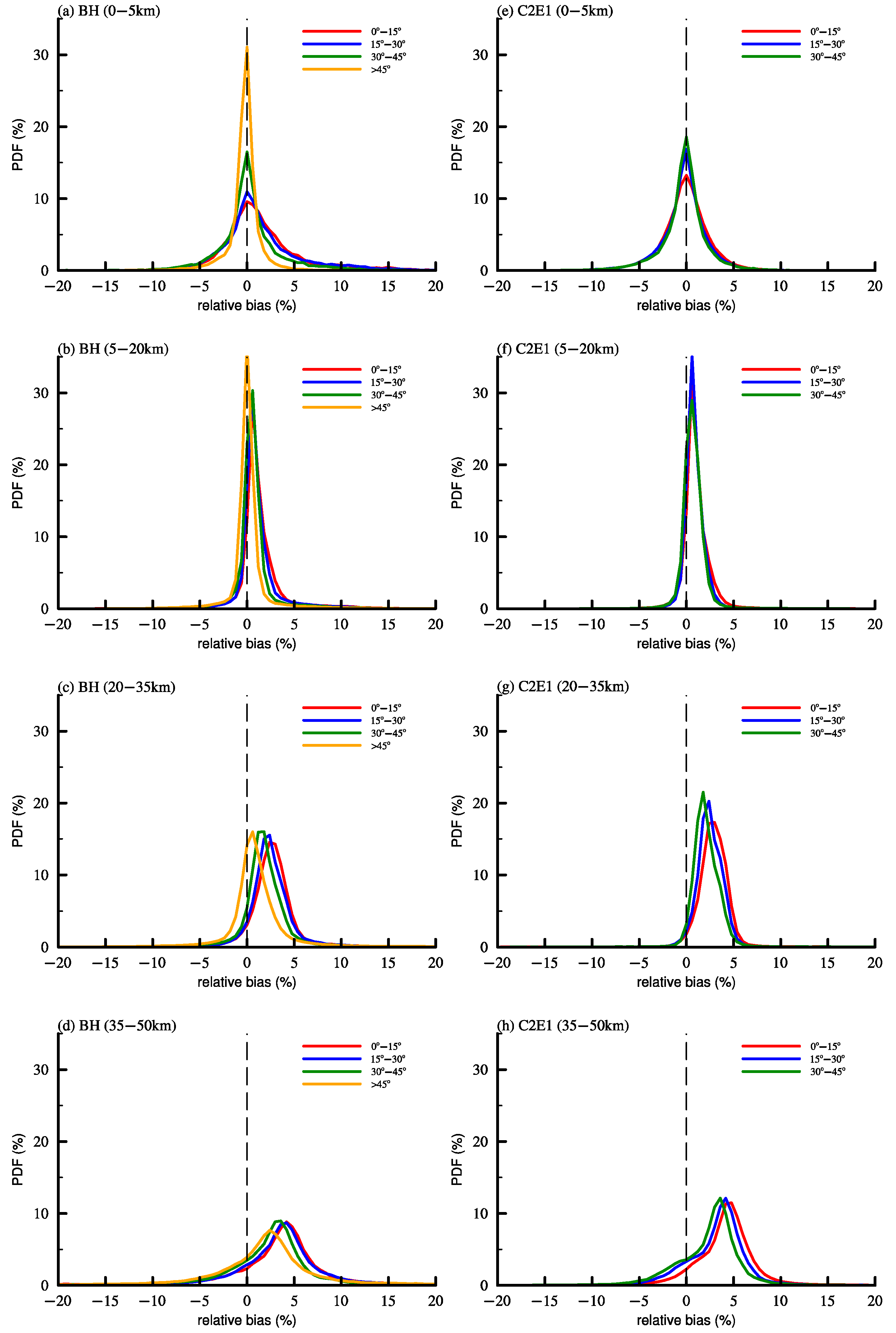
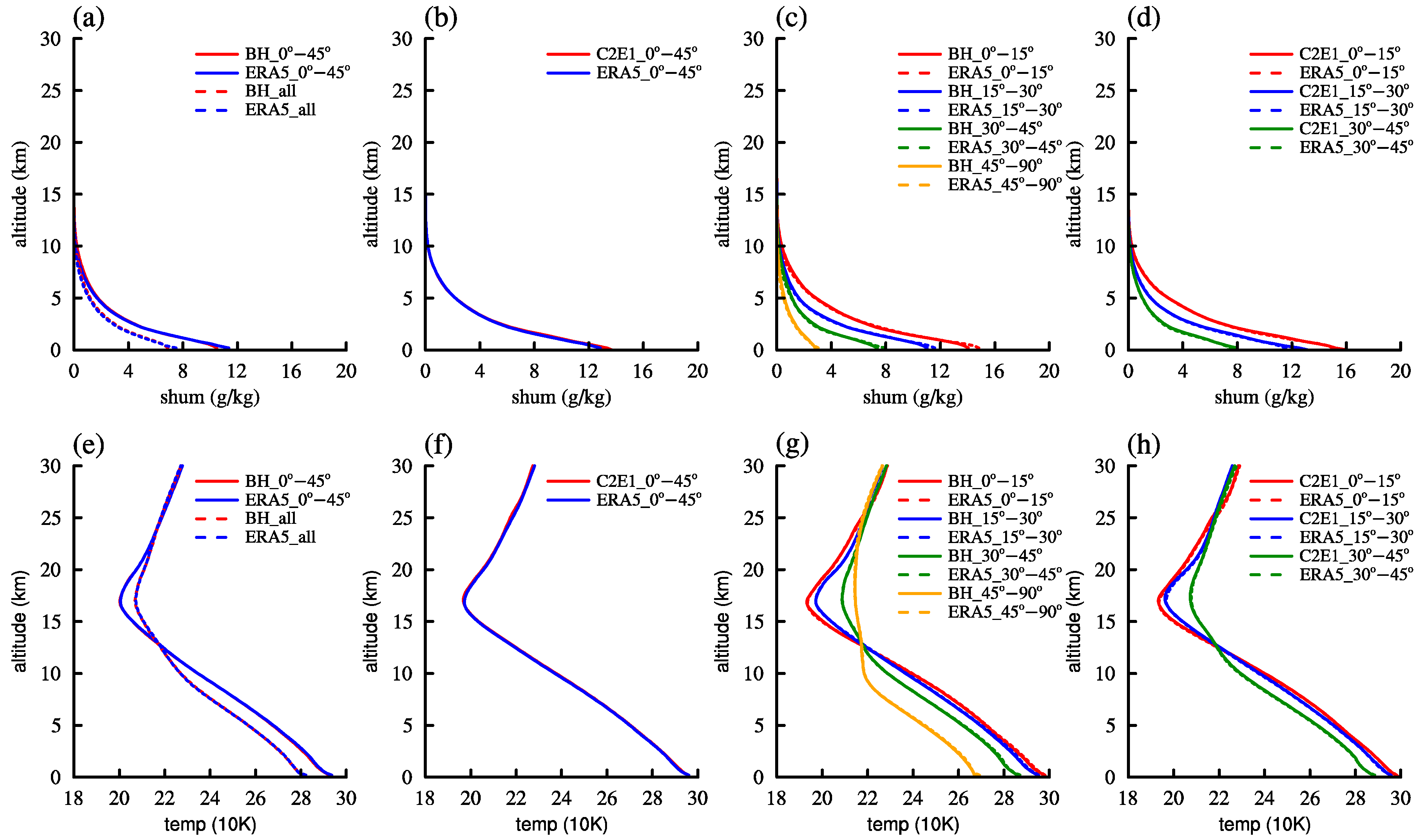
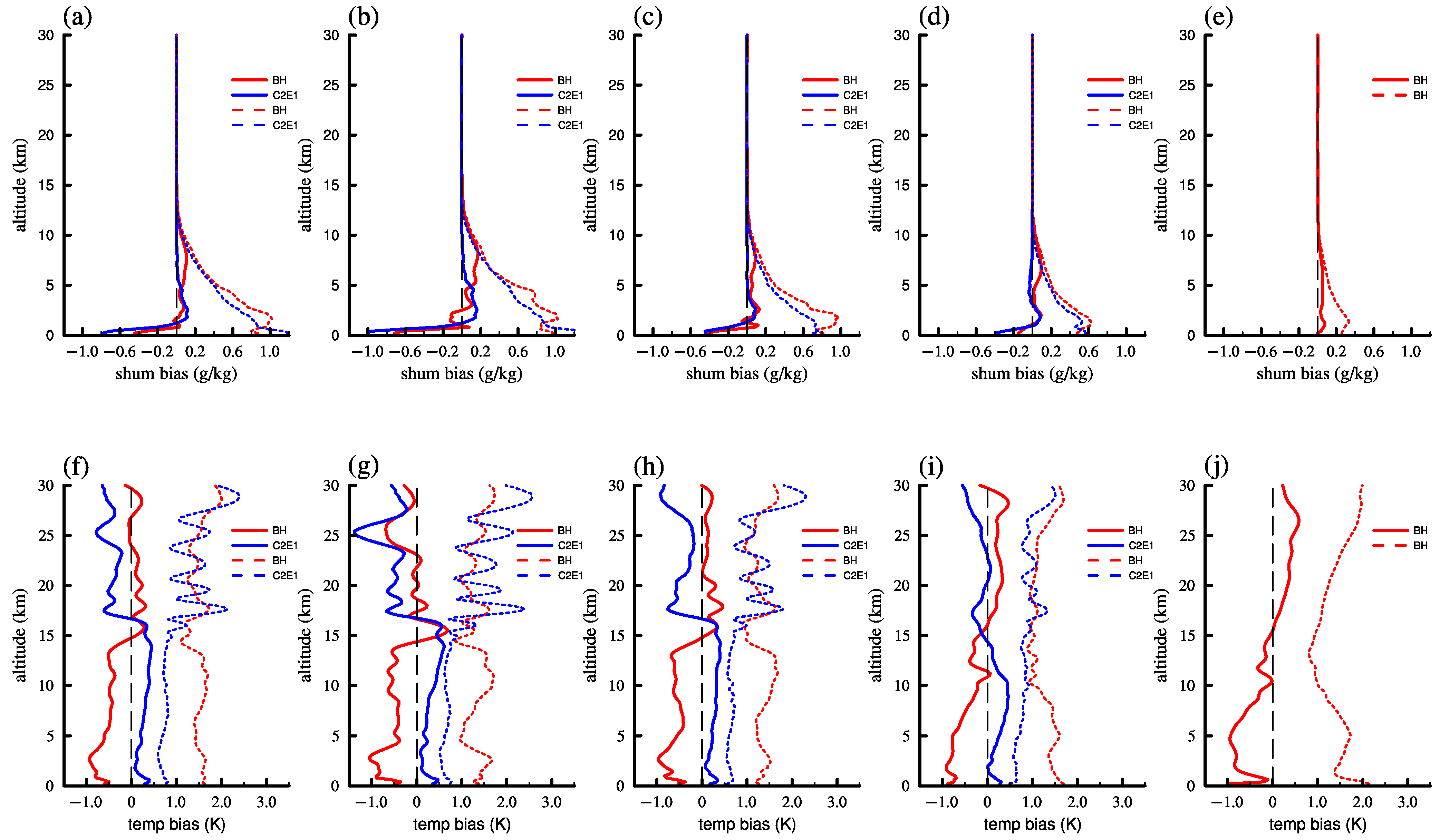
| Data | Latitude | Refractivity (N) | Temperature (K) | Specific Humidity (g/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BH | 0–45° | 0.73 (1.43) | 0.33 (1.52) | 0.030 (0.15) |
| 45–90° | 0.23 (0.72) | 0.41 (1.40) | 0.015 (0.04) | |
| C2E1 | 0–45° | 0.43 (1.12) | 0.37 (1.10) | 0.027 (0.13) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, H.; Huangfu, J.; Wang, X.; Chen, W.; Peng, W.; Tang, Q.; Chu, Y.; Xue, Z. Comparative Analysis of Binhu and Cosmic-2 Radio Occultation Data. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4958. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14194958
Zhang H, Huangfu J, Wang X, Chen W, Peng W, Tang Q, Chu Y, Xue Z. Comparative Analysis of Binhu and Cosmic-2 Radio Occultation Data. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(19):4958. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14194958
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Hongjie, Jingliang Huangfu, Xingbao Wang, Wen Chen, Wenwu Peng, Qi Tang, Yiqi Chu, and Ziyue Xue. 2022. "Comparative Analysis of Binhu and Cosmic-2 Radio Occultation Data" Remote Sensing 14, no. 19: 4958. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14194958
APA StyleZhang, H., Huangfu, J., Wang, X., Chen, W., Peng, W., Tang, Q., Chu, Y., & Xue, Z. (2022). Comparative Analysis of Binhu and Cosmic-2 Radio Occultation Data. Remote Sensing, 14(19), 4958. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14194958






