Enhanced Understanding of Groundwater Storage Changes under the Influence of River Basin Governance Using GRACE Data and Downscaling Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
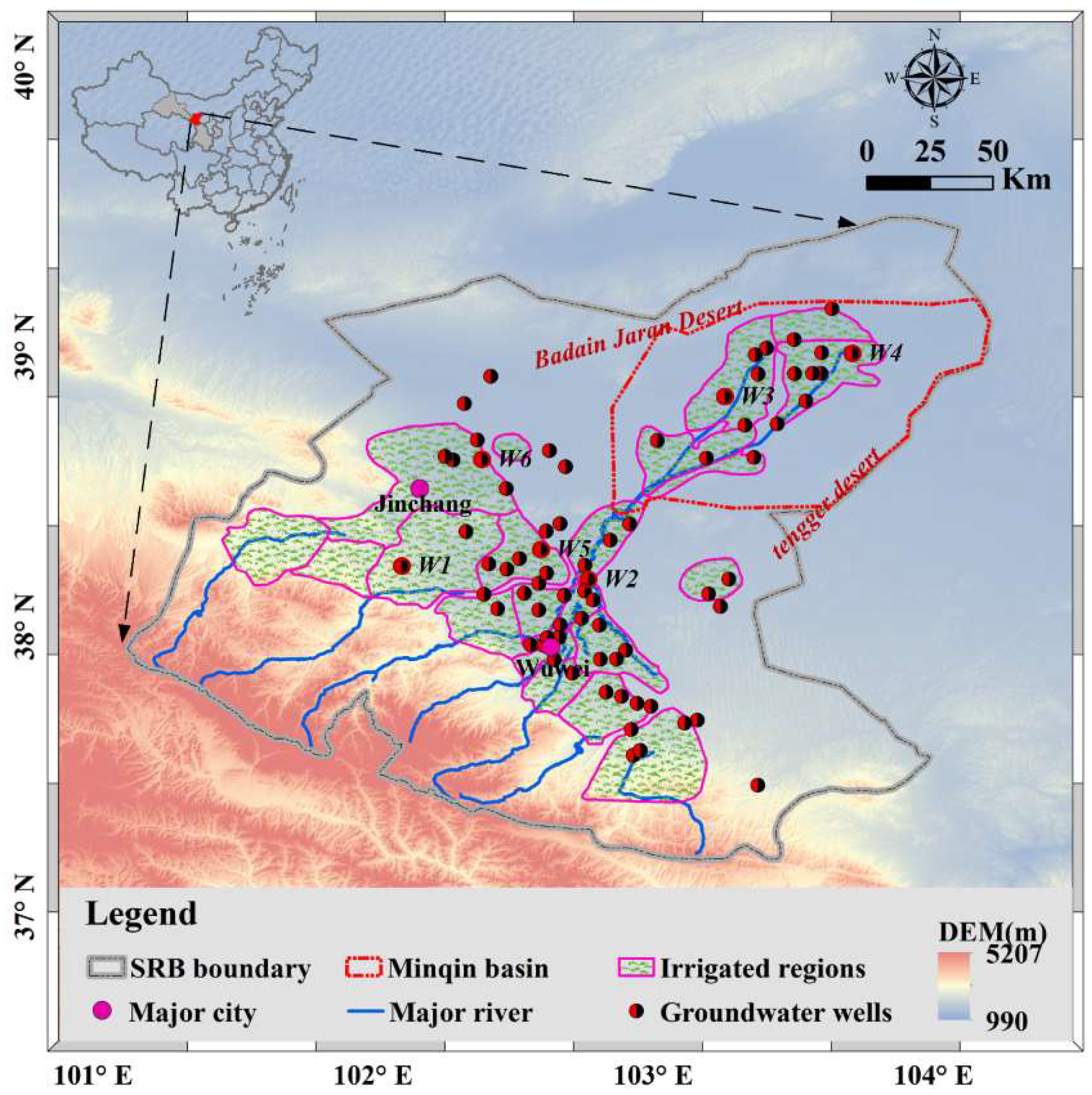
2. Study Area
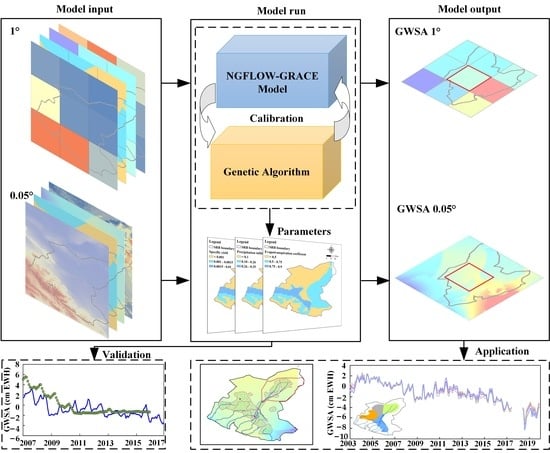
3. Methods and Data
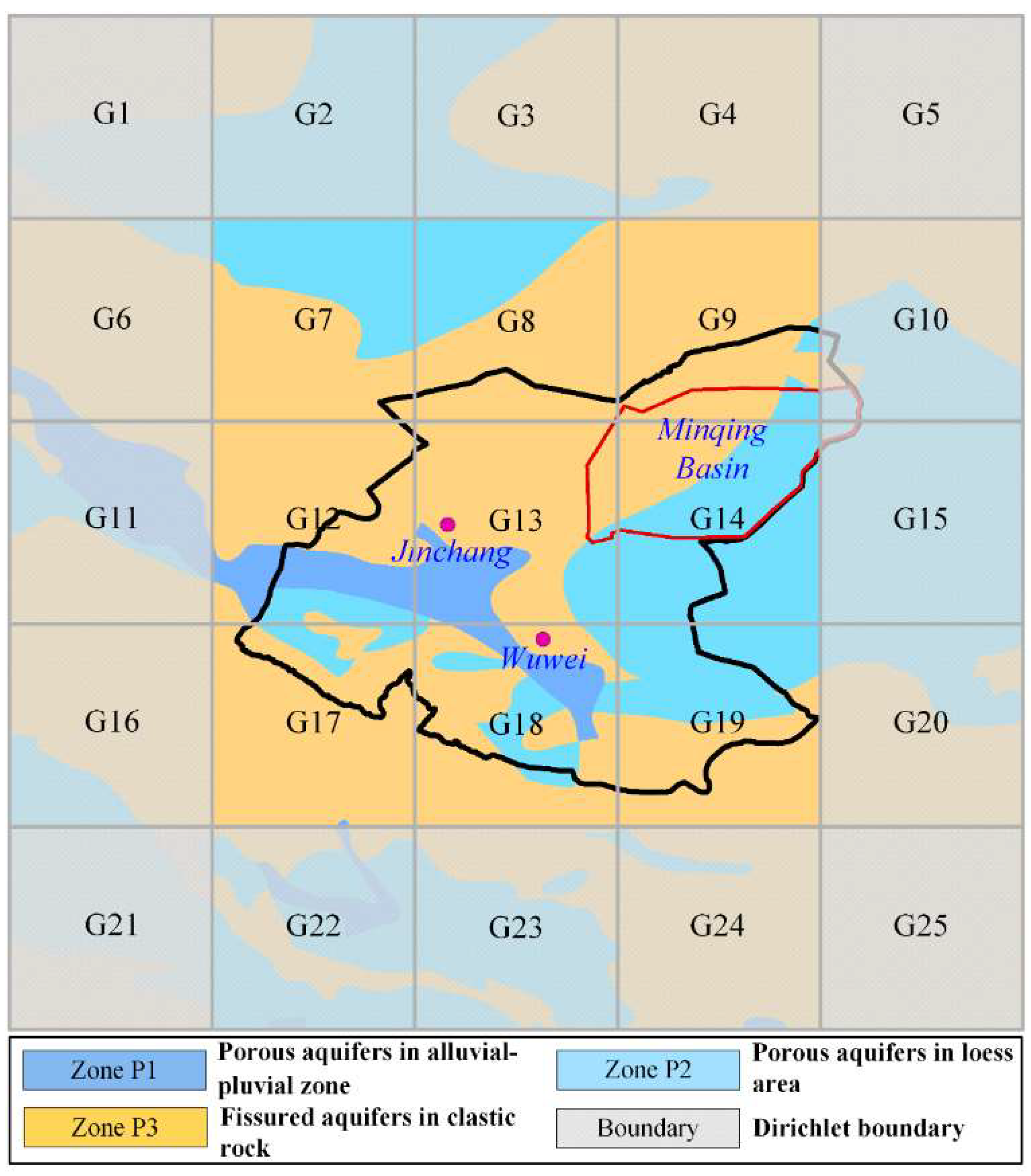
3.1. Governing Equations of the Numerical Model
3.2. Model Evaluation
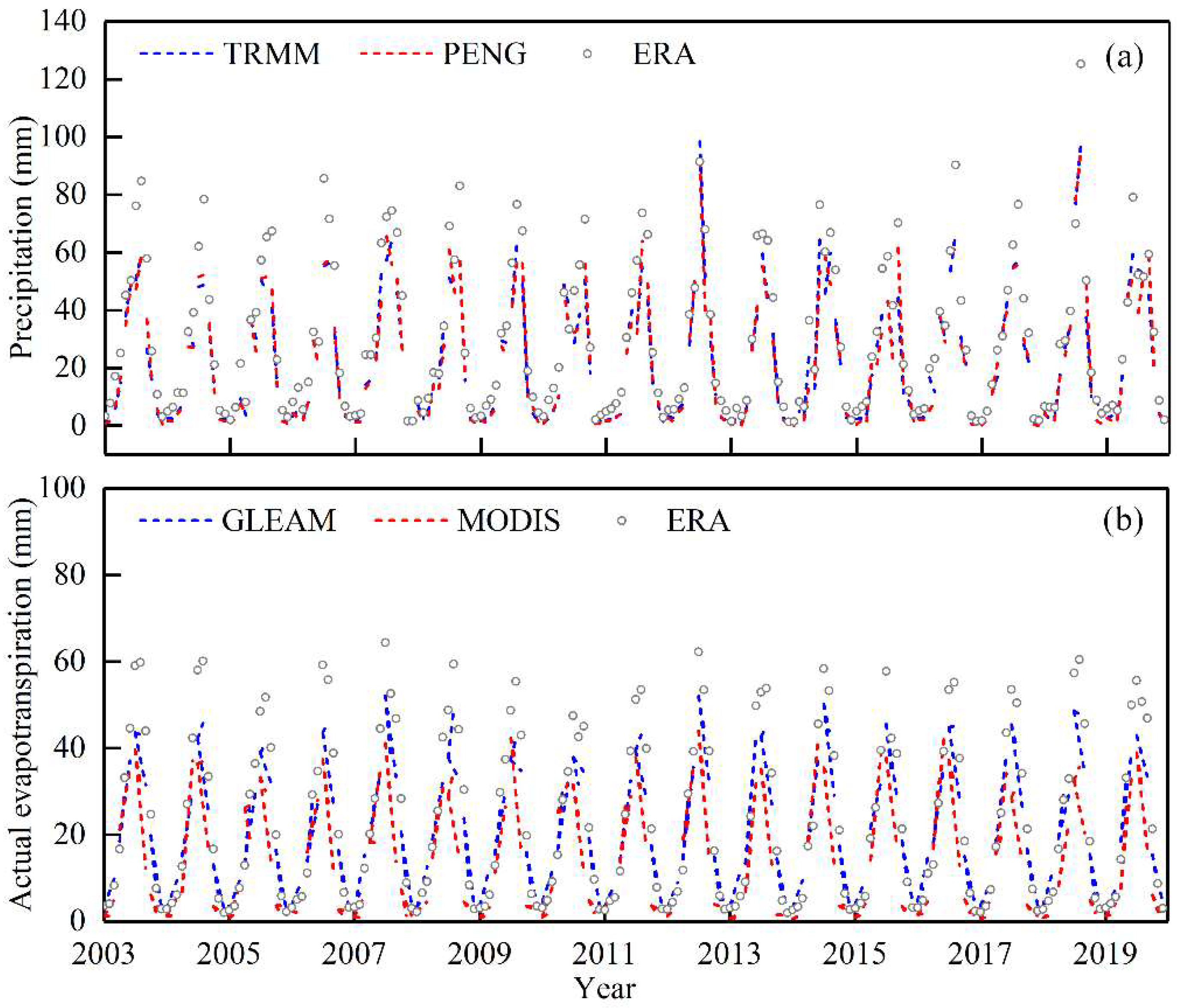
3.3. Data Preparation
3.3.1. Precipitation and Evapotranspiration Data
3.3.2. GRACE-Derived Data
3.3.3. In Situ Data
3.4. Model Development
4. Results
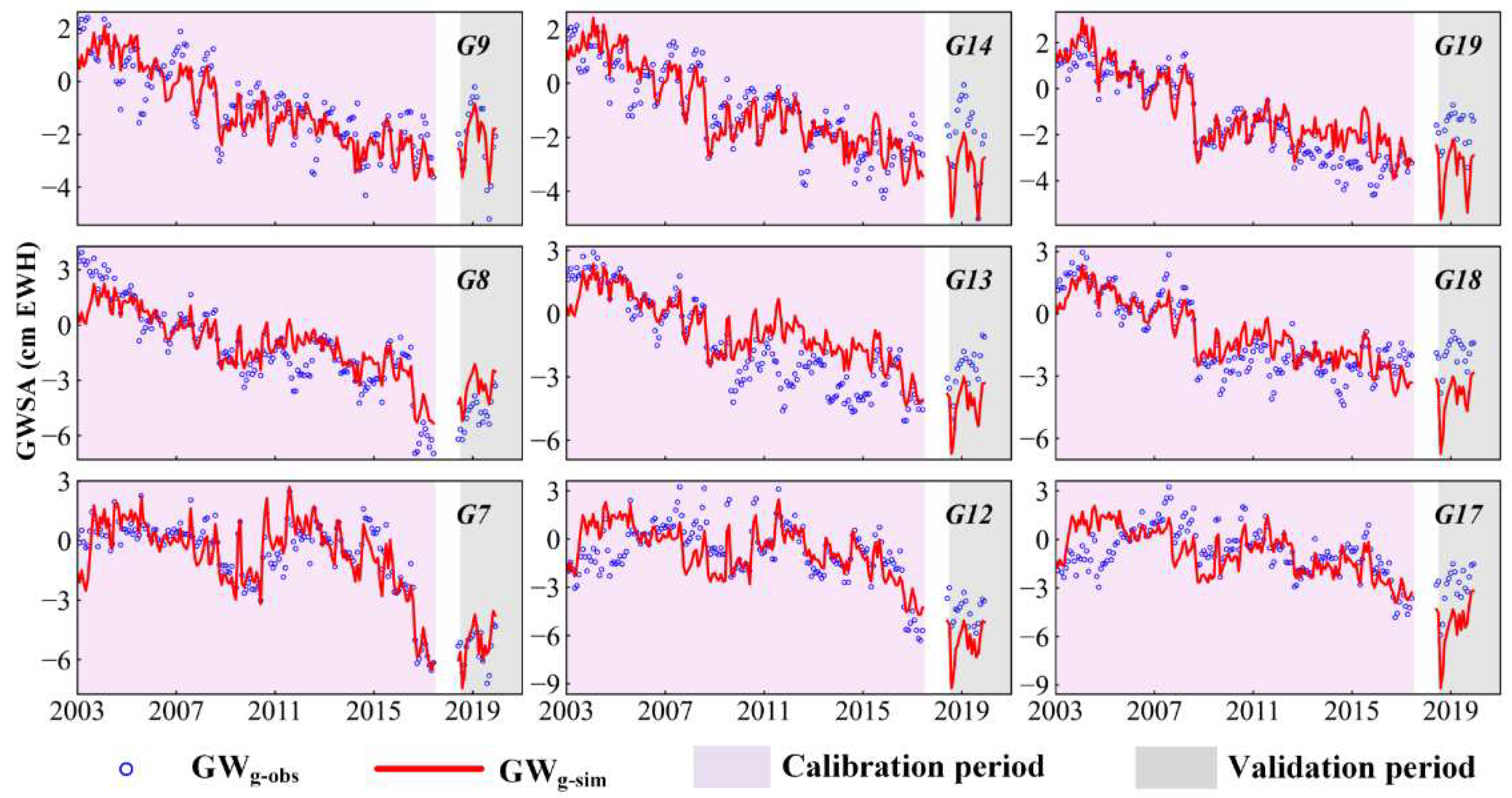
4.1. Model Calibration and Validation
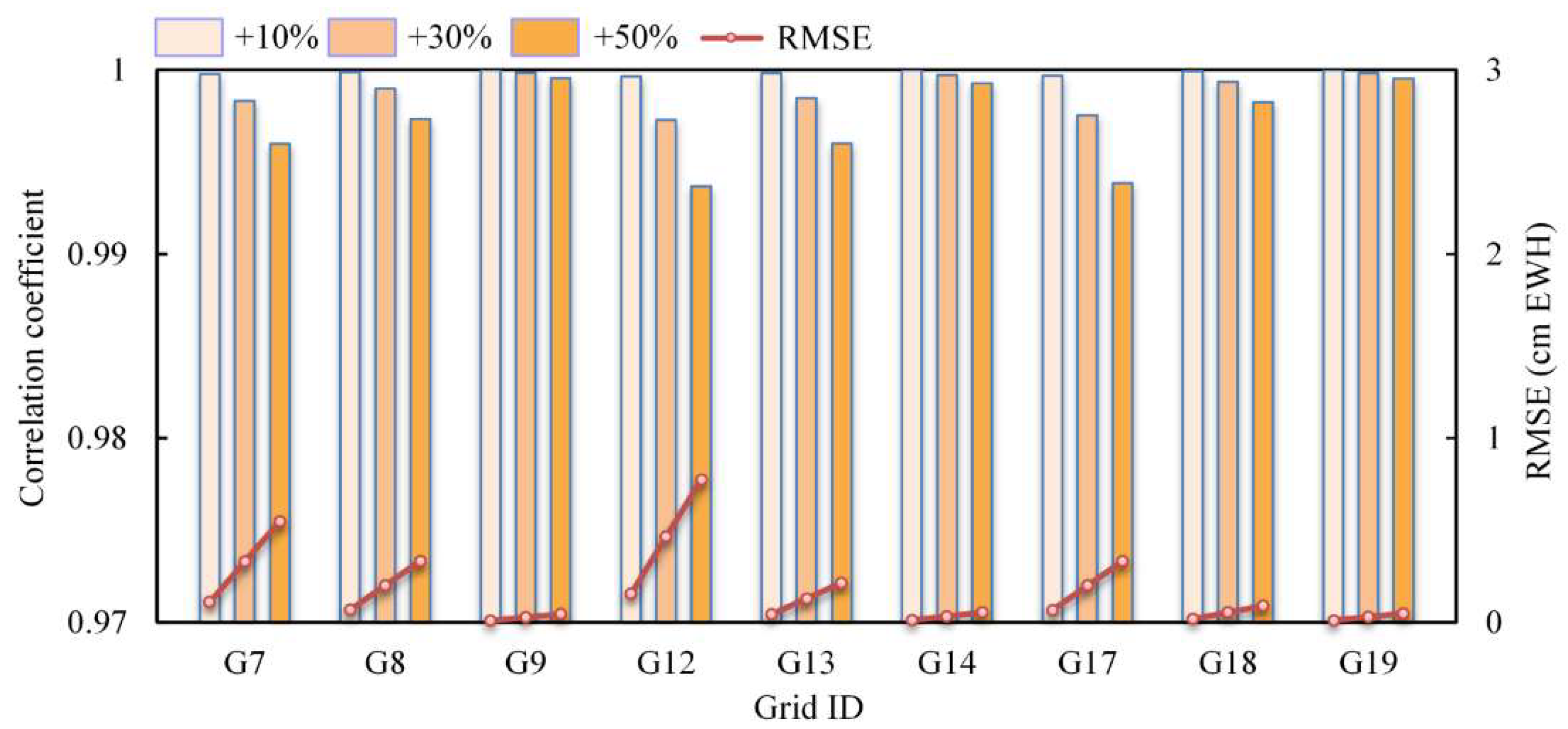
4.2. Model Uncertainty Analysis
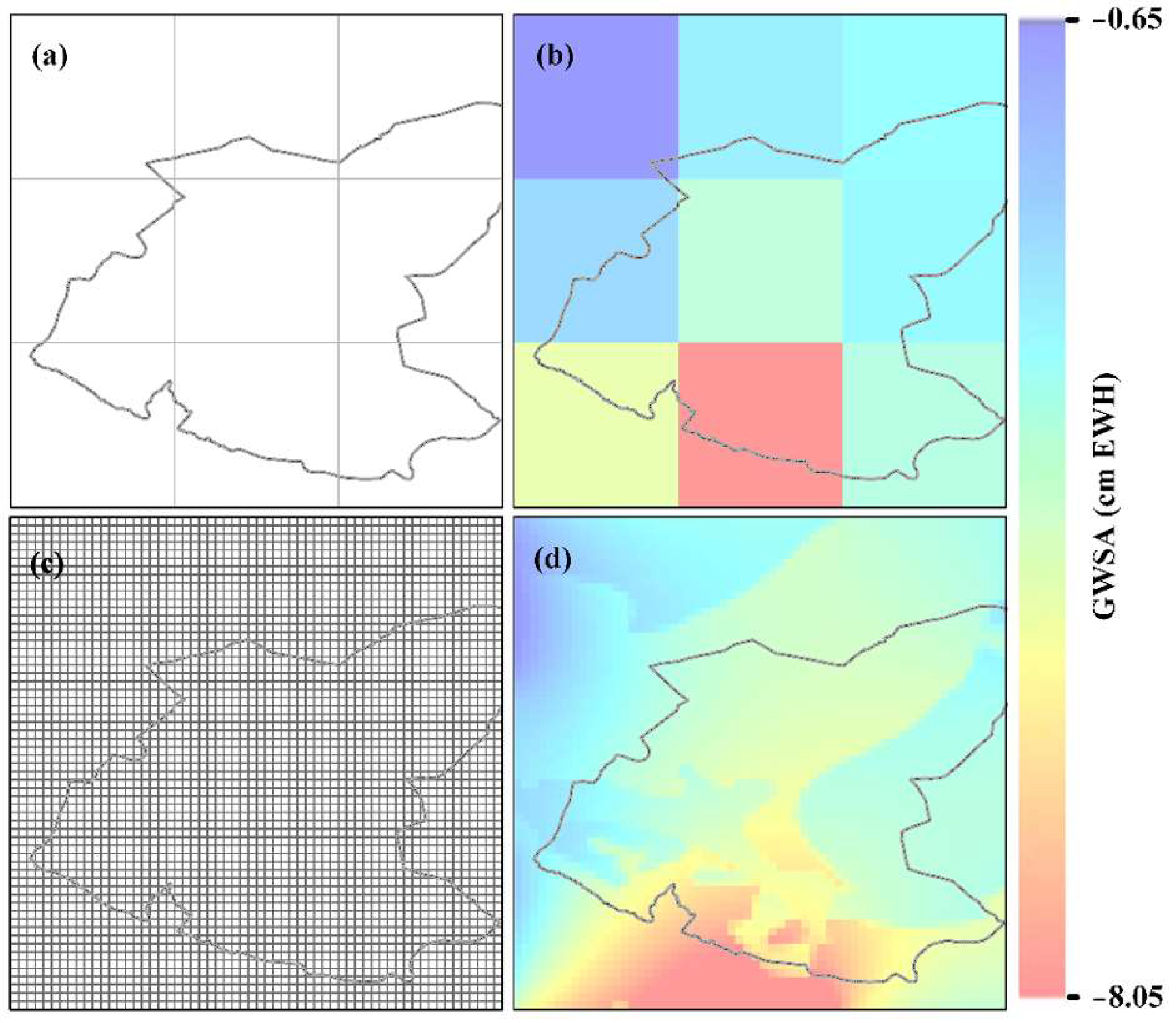
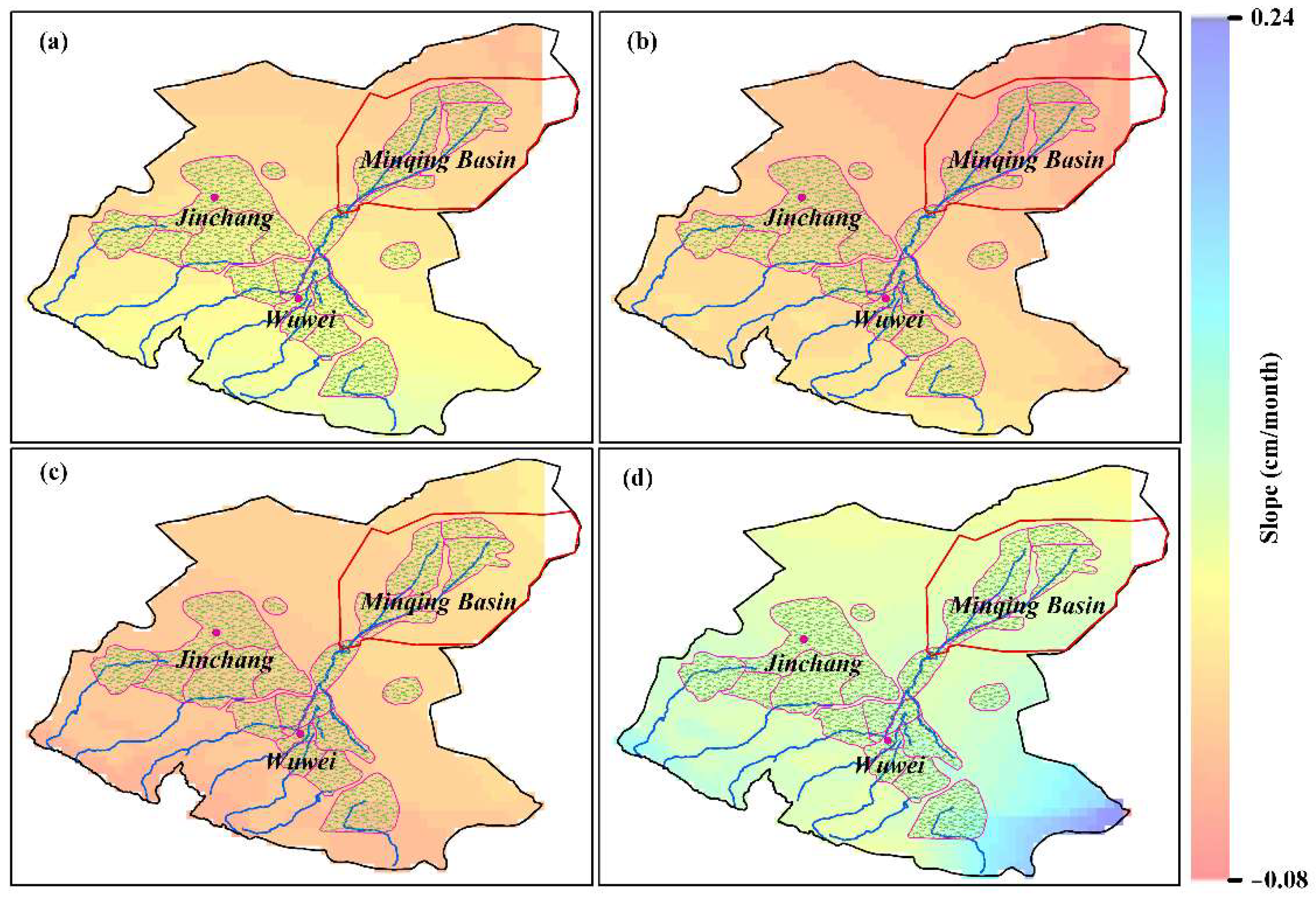
4.3. Downscaling of GWSA Data
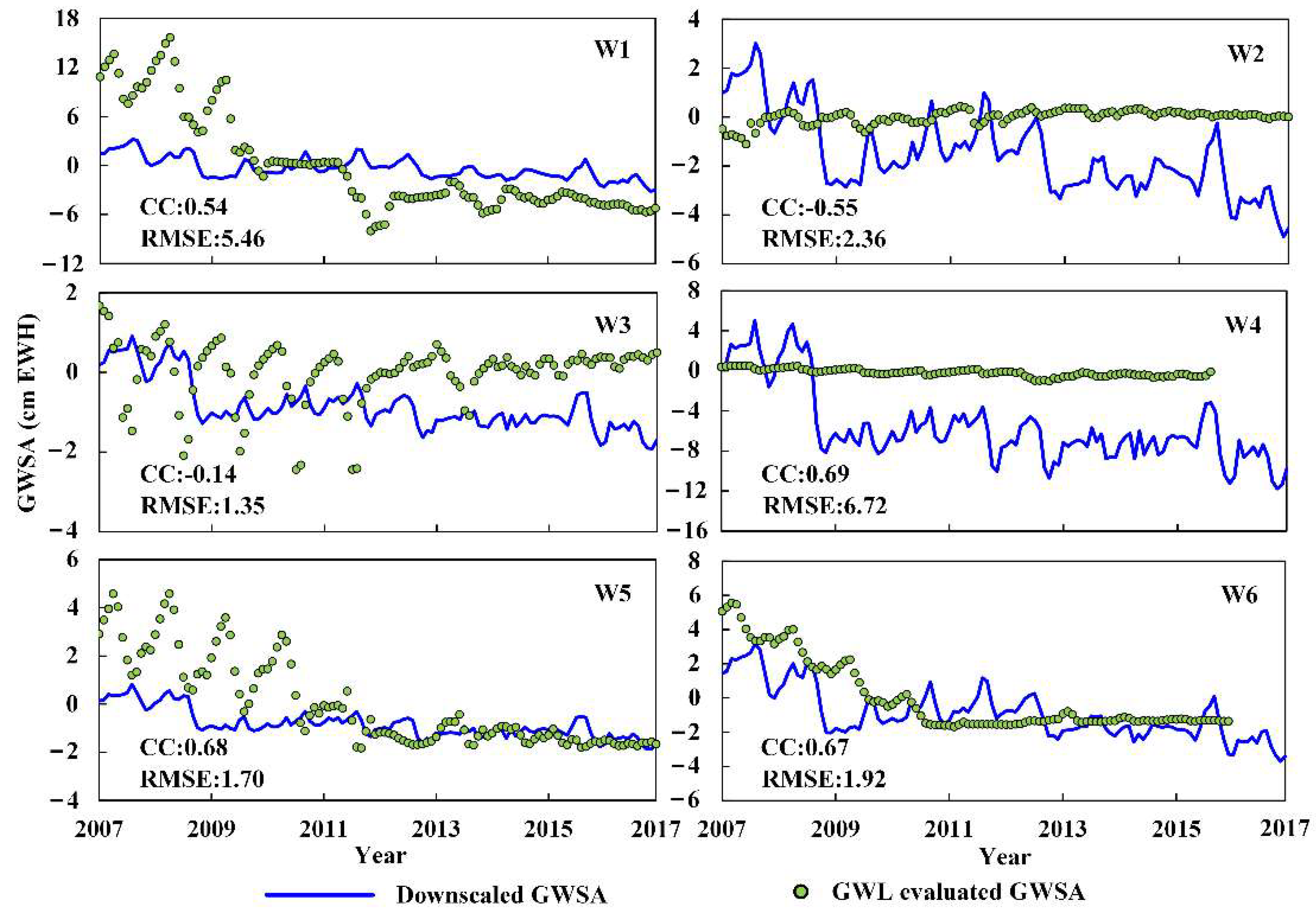
4.4. Validation of Downscaling Results
5. Discussion
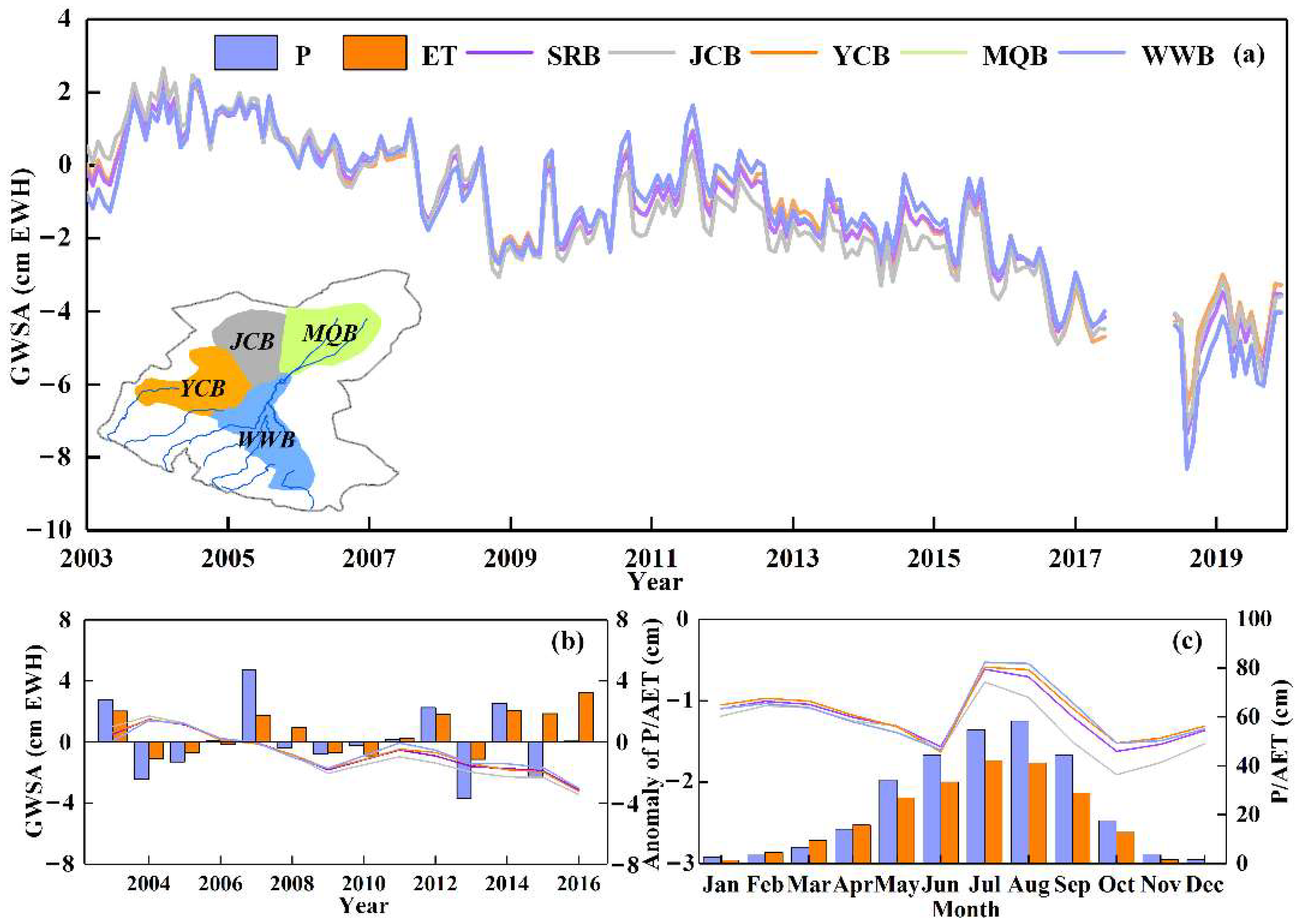
5.1. Basin-Scale Groundwater Storage Anomaly Changes
5.2. Subregion-Scale Groundwater Storage Anomaly Changes
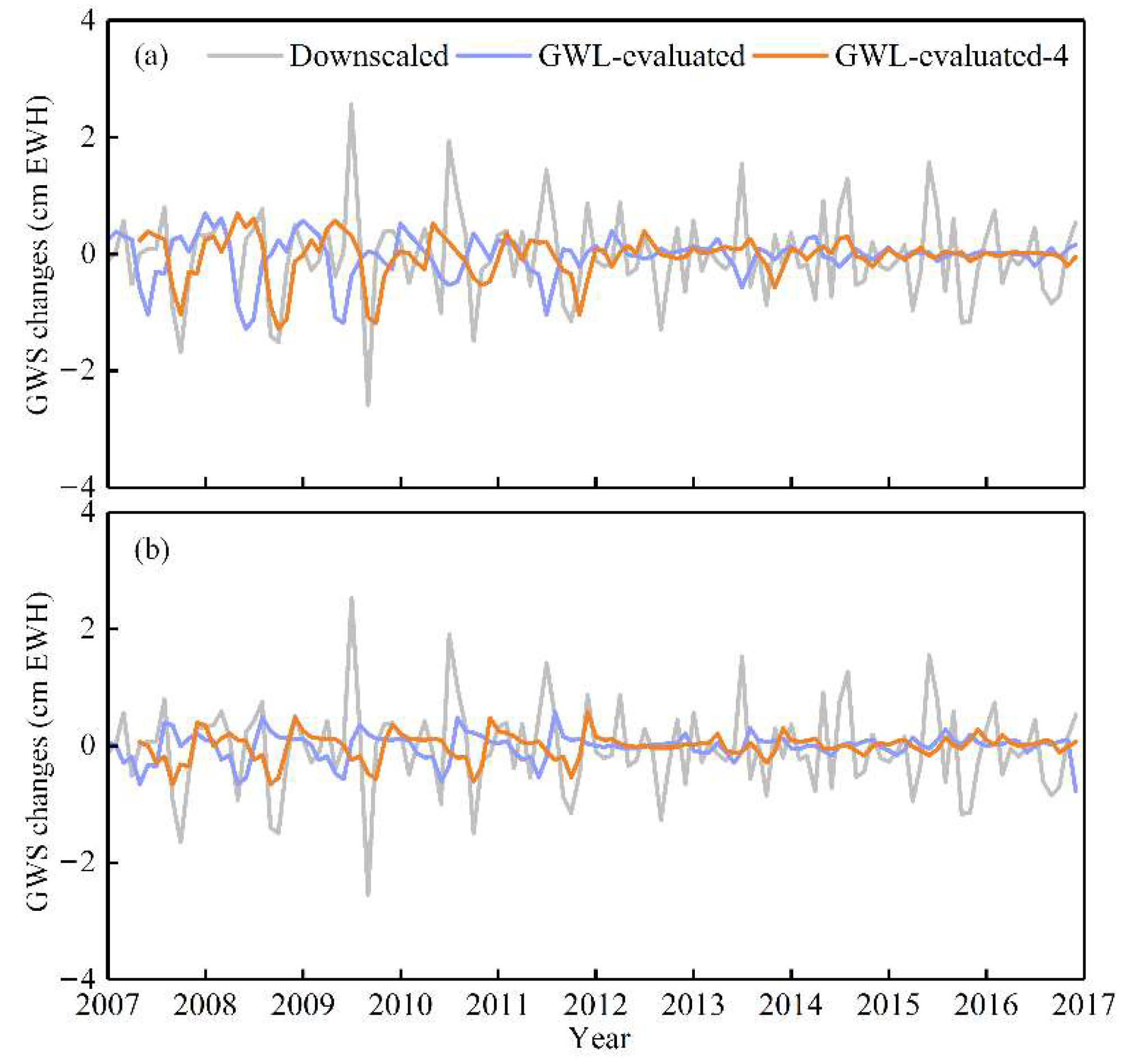
5.3. Comparison of GWS Changes from Downscaled and Field Observations
5.4. Limitations and Perspectives
6. Conclusions
- (1)
- The changes in the simulated groundwater storage anomalies fit well with the observed values, and the correlation coefficients between the simulated and observed values were generally over 0.6 in both the calibration and validation periods. The uncertainty analysis of the model showed that the boundary conditions had a greater impact on the model results, whereas the precipitation and evapotranspiration data from different sources had no obvious effect on the results. The sensitivity of the hydraulic gradient coefficient was significantly higher than that of the other parameters.
- (2)
- The downscaled GWSA maintains a spatial distribution and time-series changing patterns similar to those of the GRACE-derived GWSA, as well as capturing more fine groundwater storage features. The changing patterns of the downscaled GWSA were consistent with those from the observation well data.
- (3)
- The GWS generally showed a downward trend from 2003 to 2019. In the initial stage of groundwater governance implementation, the overall GWS decreased and only increased slightly from 2009 to 2011. After 2012, the downward trend in GWS did not slow down significantly. Since June 2018, the areas of GWS increase were mainly distributed in the southern piedmont area.
- (4)
- The annual decline rates of GWSA from 2003 to 2016 were 0.26 cm/year, 0.32 cm/year, 0.22 cm/year, 0.22 cm/year, and 0.28 cm/year in SRB, JCB, MQB, WWB, and YCB, respectively. The GWS changes in the MQB are mainly affected by the exploitation and utilization of water resources in the WWB, and the change trend of the GWS between the MQB and WWB is highly consistent. In addition, there was a four-month time lag between the field observations and downscaled GWSA changes.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Taylor, R.G.; Scanlon, B.; Döll, P.; Rodell, M.; Van Beek, R.; Wada, Y.; Longuevergne, L.; Leblanc, M.; Famiglietti, J.S.; Edmunds, M.; et al. Ground water and climate change. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2013, 3, 322–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasechko, S.; Perrone, D.; Befus, K.M.; Bayani Cardenas, M.; Ferguson, G.; Gleeson, T.; Luijendijk, E.; McDonnell, J.J.; Taylor, R.G.; Wada, Y.; et al. Global aquifers dominated by fossil groundwaters but wells vulnerable to modern contamination. Nat. Geosci. 2017, 10, 425–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalin, C.; Wada, Y.; Kastner, T.; Puma, M.J. Groundwater depletion embedded in international food trade. Nature 2017, 543, 700–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahamed, A.; Knight, R.; Alam, S.; Pauloo, R.; Melton, F. Assessing the utility of remote sensing data to accurately estimate changes in groundwater storage. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 807, 150635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodell, M.; Velicogna, I.; Famiglietti, J.S. Satellite-based estimates of groundwater depletion in India. Nature 2009, 460, 999–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapley, B.; Bettadpur, S.; Ries, J.; Thompson, P.; Watkins, M. GRACE measurements of mass variability in the Earth system. Science 2004, 305, 503–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Rodell, M.; Kumar, S.; Beaudoing, H.K.; Getirana, A.; Zaitchik, B.F.; de Goncalves, L.G.; Cossetin, C.; Bhanja, S.; Mukherjee, A.; et al. Global GRACE data assimilation for groundwater and drought monitoring: Advances and challenges. Water Resour. Res. 2019, 55, 7564–7586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, W.; Zhong, M.; Lemoine, J.M.; Biancale, R.; Hsu, H.T.; Xia, J. Evaluation of groundwater depletion in North China using the Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment (GRACE) data and ground-based measurements. Water Resour. Res. 2013, 49, 2110–2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swenson, S.; Yeh, P.J.F.; Wahr, J.; Famiglietti, J. A comparison of terrestrial water storage variations from GRACE with in situ measurements from Illinois. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33, 627–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Famiglietti, J.S.; Lo, M.; Ho, S.L.; Bethune, J.; Anderson, K.J.; Syed, T.H.; Rodell, M. Satellites measure recent rates of groundwater depletion in California’s Central Valley. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2011, 38, L16401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilby, R.L.; Wigley, T.M.L.; Conway, D.; Jones, P.D.; Hewitson, B.C.; Main, J.; Wilks, D.S. Statistical downscaling of general circulation model output: A comparison of methods. Water Resour. Res. 1998, 34, 2995–3008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vishwakarma, B.D.; Zhang, J.; Sneeuw, N. Downscaling GRACE total water storage change using partial least squares regression. Sci. Data. 2021, 8, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ning, S.W.; Ishidaira, H.; Wang, J. Statistical downscaling of GRACE-derived terrestrial water storage using satellite and GLDAS products. J. Jpn. Soc. Civ. Eng. 2014, 70, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, W.; Hu, L.; Zhang, M.; Wang, J.; Han, S.C. Statistical downscaling of GRACE-derived groundwater storage using ET data in the North China plain. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2018, 123, 5973–5987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miro, M.E.; Famiglietti, J.S. Downscaling GRACE remote sensing datasets to high-resolution groundwater storage change maps of California’s Central Valley. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; He, Q.; Liu, K.; Li, J.; Jing, C. Downscaling of GRACE-derived groundwater storage based on the random forest model. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyoum, W.M.; Kwon, D.; Milewski, A.M. Downscaling GRACE TWSA data into high-resolution groundwater level anomaly using machine learning-based models in a glacial aquifer system. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaitchik, B.F.; Rodell, M.; Reichle, R.H. Assimilation of GRACE terrestrial water storage data into a land surface model: Results for the Mississippi River Basin. J. Hydrometeorol. 2008, 9, 535–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, D.; Wang, S.; Li, J. A self-calibration variance-component model for spatial downscaling of GRACE observations using land surface model outputs. Water Resour. Res. 2021, 57, e2020WR028944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Jiao, J.J. Calibration of a large-scale groundwater flow model using GRACE data: A case study in the Qaidam Basin, China. Hydrogeol. J. 2015, 23, 1305–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, A.Y.; Green, R.; Swenson, S.; Rodell, M. Toward calibration of regional groundwater models using GRACE data. J. Hydrol. 2012, 422, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.T.; Wang, Z.J.; Tian, W.; Zhao, J.S. Coupled surface water-groundwater model and its application in the arid Shiyang River basin, China. Hydrol. Process. Int. J. 2009, 23, 2033–2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, D.; Yang, Y.; Wada, Y.; Hong, Y.; Liang, W.; Chen, Y.; Yong, B.; Hou, A.; Wei, J.; Chen, L. Deriving scaling factors using a global hydrological model to restore GRACE total water storage changes for China’s Yangtze River Basin. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 168, 177–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitley, D. A genetic algorithm tutorial. Stat. Comput. 1994, 4, 65–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Feng, Q. Geostatistical analysis of temporal and spatial variations in groundwater levels and quality in the Minqin oasis, Northwest China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2013, 70, 1367–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Xie, Y.; Ma, J.; Zhang, W. The critical role of local policy effects in arid watershed groundwater resources sustainability: A case study in the Minqin oasis, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 601, 1084–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.; Kang, S.; Huo, Z.; Chen, S.; Mao, X. Neural networks to simulate regional ground water levels affected by human activities. Groundwater 2018, 46, 80–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Bie, Q.; Lu, H.; He, L. Spatio-temporal changes of oases in the Hexi Corridor over the past 30 years. Sustainability 2018, 10, 4489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, D.; Li, X.; Song, D.; Yang, G. Temporal and spatial dynamical simulation of groundwater characteristics in Minqin Oasis. Sci. China Ser. D-Earth Sci. 2007, 50, 261–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aeschbach-Hertig, W.; Gleeson, T. Regional strategies for the accelerating global problem of groundwater depletion. Nat. Geosci. 2012, 5, 853–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Liu, H.; Yu, Y.; Zhao, W.; Yang, Q.; Liu, J. Evaluation of groundwater sustainability in the arid Hexi Corridor of Northwestern China, using GRACE, GLDAS and measured groundwater data products. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 705, 135829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Hu, L.; Sun, K.; Yang, Z.; Sun, J.; Yin, W. Improved understanding of groundwater storage changes under the influence of river basin governance in northwestern China using GRACE data. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aarnoudse, E.; Bluemling, B.; Qu, W.; Herzfeld, T. Groundwater regulation in case of overdraft: National groundwater policy implementation in north-west China. Int. J. Water Resour. D 2019, 35, 264–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abou Zaki, N.; Torabi Haghighi, A.; Rossi, P.M.; Tourian, M.J.; Klove, B. Monitoring groundwater storage depletion using gravity recovery and climate experiment (GRACE) data in the semi-arid catchments. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2018, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, B.F.; Famiglietti, J.S.; Landerer, F.W.; Wiese, D.N.; Molotch, N.P.; Argus, D.F. GRACE groundwater drought index: Evaluation of California Central Valley groundwater drought. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 198, 384–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Xu, C.; Wen, Y.; Li, W. Monitoring groundwater storage changes in the Loess Plateau using GRACE satellite gravity data, hydrological models and coal mining data. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, N.; Hossain, F.; Lee, H.; Akhter, G. Integrated groundwater resource management in Indus Basin using satellite gravimetry and physical modeling tools. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2017, 189, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Data Item | Source | Spatial Resolution | Time Resolution | Time Span (Year) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TWS | GRACE | 0.5° | Monthly | 2003–2019 |
| SM, SWE | GLDAS V2.1 | 1° | Monthly | 2003–2019 |
| Precipitation | TRMM 3B43 | 0.25° | Monthly | 2003–2019 |
| ERA5 | 0.25° | Monthly | 2003–2019 | |
| PENG | 0.05° | Monthly | 2003–2019 | |
| AET | GLEAM v3.5 | 0.25° | Monthly | 2003–2019 |
| MODIS | 0.05° | Monthly | 2003–2019 | |
| ERA5 | 0.25° | Monthly | 2003–2019 | |
| GWL | In situ observation | - | Daily | 2007–2018 |
| Cell ID | Calibration Period | Validation Period | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CC | RMSE | CC | RMSE | |
| G7 | 0.89 | 0.77 | 0.52 | 1.42 |
| G8 | 0.91 | 1.57 | 0.64 | 1.08 |
| G9 | 0.88 | 0.74 | 0.92 | 0.98 |
| G12 | 0.65 | 1.55 | 0.44 | 2.38 |
| G13 | 0.92 | 1.31 | 0.59 | 0.99 |
| G14 | 0.89 | 0.80 | 0.90 | 0.83 |
| G17 | 0.60 | 1.26 | 0.85 | 1.61 |
| G18 | 0.92 | 1.04 | 0.81 | 0.69 |
| G19 | 0.94 | 1.01 | 0.84 | 0.75 |
| Time Period | Rapid Decline | Decline | Slow Decline | Slow Rise | Rise | Rapid Rise |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2003–2006 | 1.3% | 27.9% | 37.2% | 27.6% | 6.0% | 0.0% |
| 2007–2010 | 24.0% | 50.5% | 25.5% | 0.0% | 0.0% | 0.0% |
| 2011–2017.6 | 14.2% | 72.7% | 13.1% | 0.0% | 0.0% | 0.0% |
| 2018.6–2019.12 | 0.0% | 0.0% | 0.0% | 5.1% | 23.6% | 71.3% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, J.; Hu, L.; Liu, X.; Sun, K. Enhanced Understanding of Groundwater Storage Changes under the Influence of River Basin Governance Using GRACE Data and Downscaling Model. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4719. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14194719
Sun J, Hu L, Liu X, Sun K. Enhanced Understanding of Groundwater Storage Changes under the Influence of River Basin Governance Using GRACE Data and Downscaling Model. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(19):4719. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14194719
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Jianchong, Litang Hu, Xin Liu, and Kangning Sun. 2022. "Enhanced Understanding of Groundwater Storage Changes under the Influence of River Basin Governance Using GRACE Data and Downscaling Model" Remote Sensing 14, no. 19: 4719. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14194719
APA StyleSun, J., Hu, L., Liu, X., & Sun, K. (2022). Enhanced Understanding of Groundwater Storage Changes under the Influence of River Basin Governance Using GRACE Data and Downscaling Model. Remote Sensing, 14(19), 4719. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14194719