Combined Radar Quality Index for Quantitative Precipitation Estimation of Heavy Rainfall Events
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
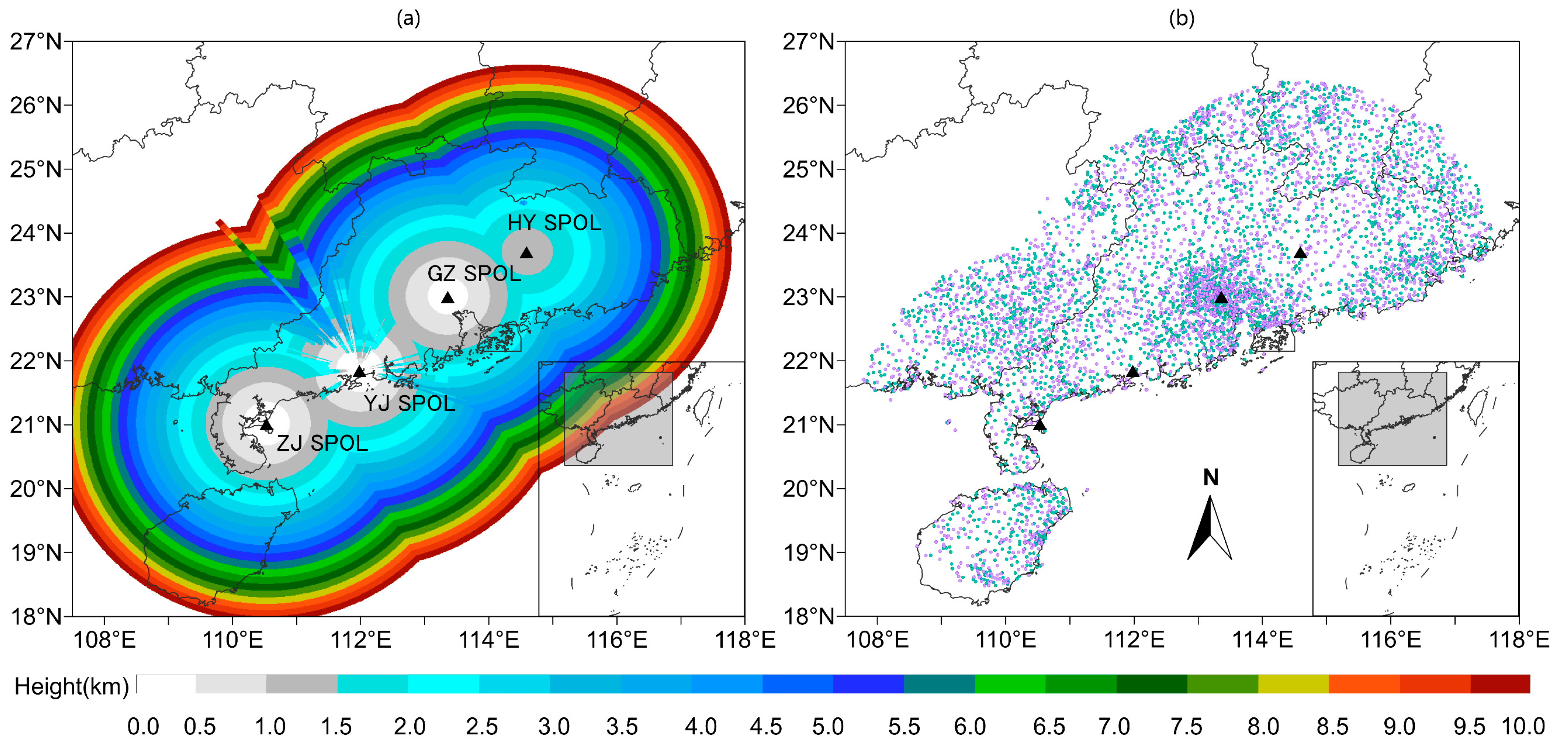
2.1. Polarimetric Radar Data and Quality Control
2.2. Rain Gauge Data and Quality Control
2.3. Polarimetric Radars and Rain Gauges Mosaic QPE Algorithm
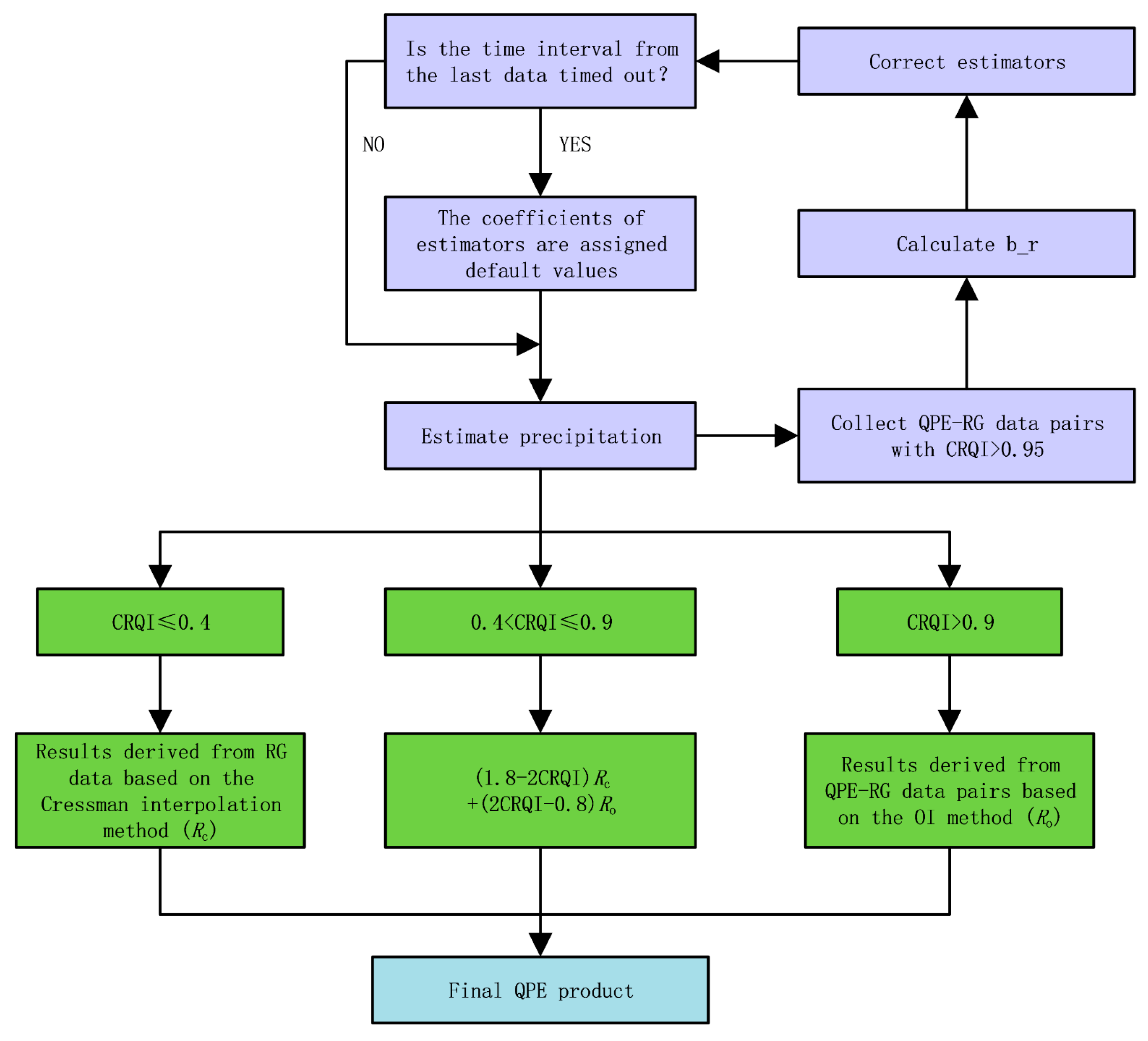
2.3.1. Algorithm Introduction
2.3.2. Contrast Tests
2.3.3. Evaluation Method for QPE Products
3. Results
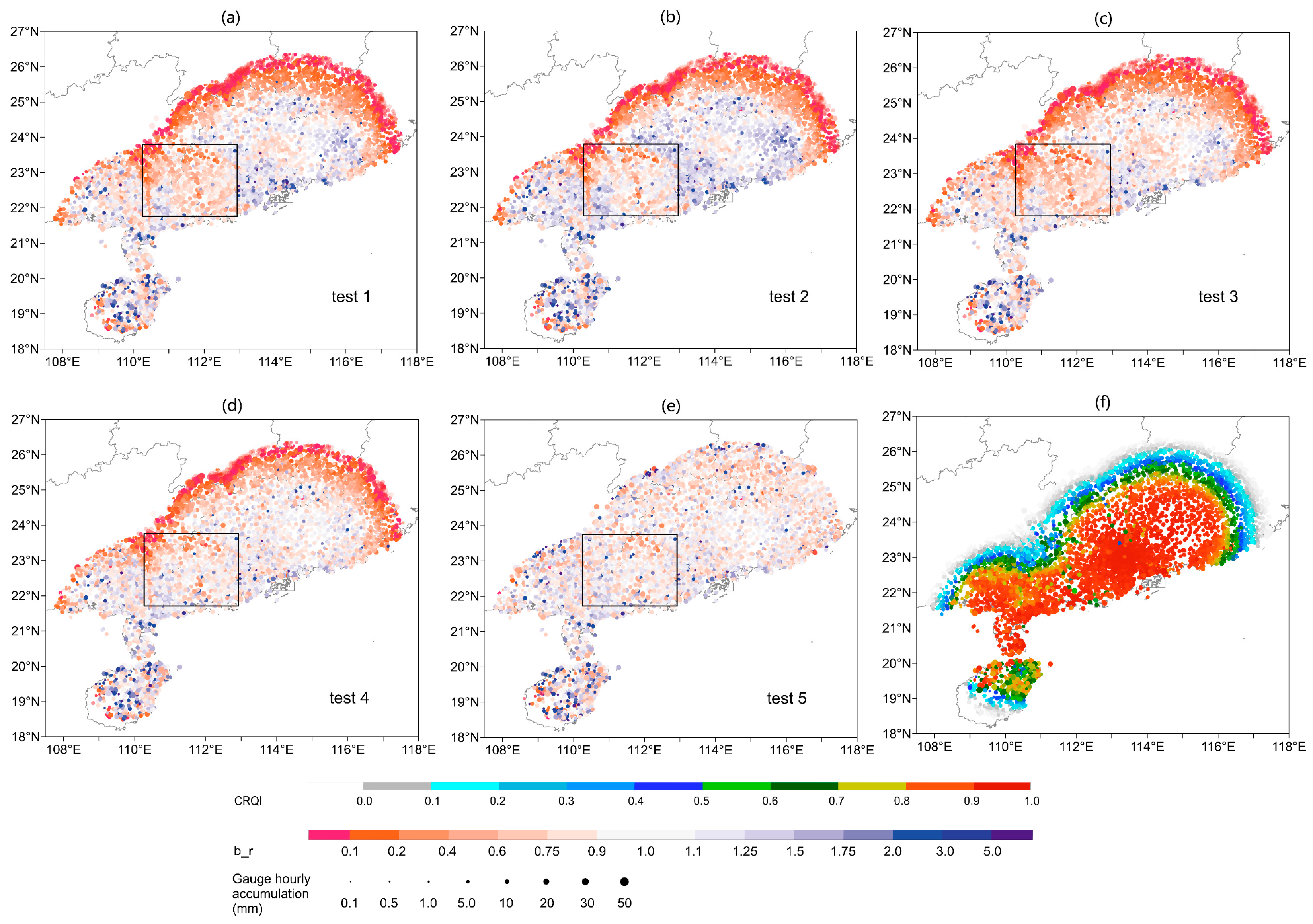
3.1. Spatial Distribution of B_rs
3.2. Evaluated Statistical Scores
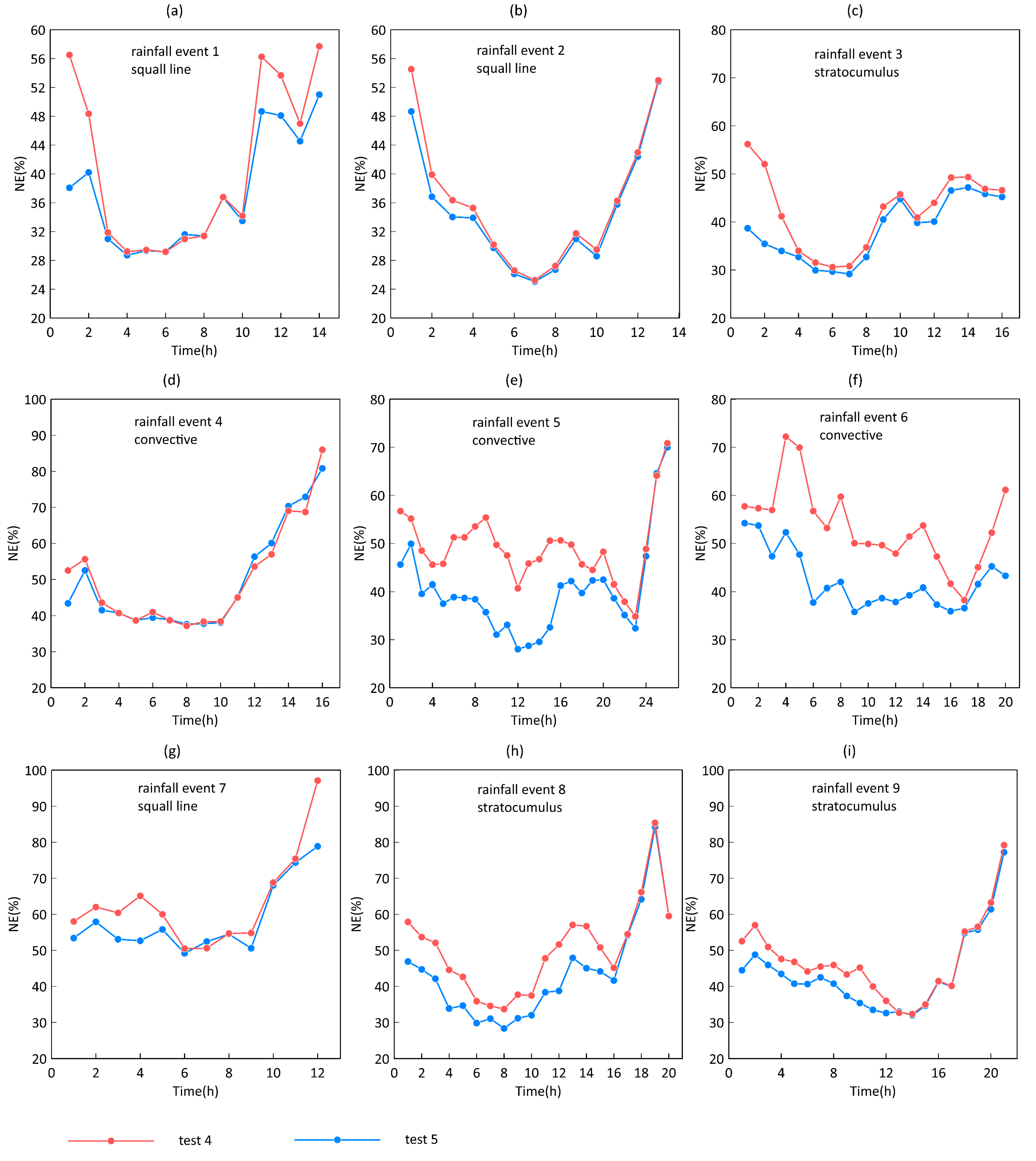
3.3. Evaluation Results over Time
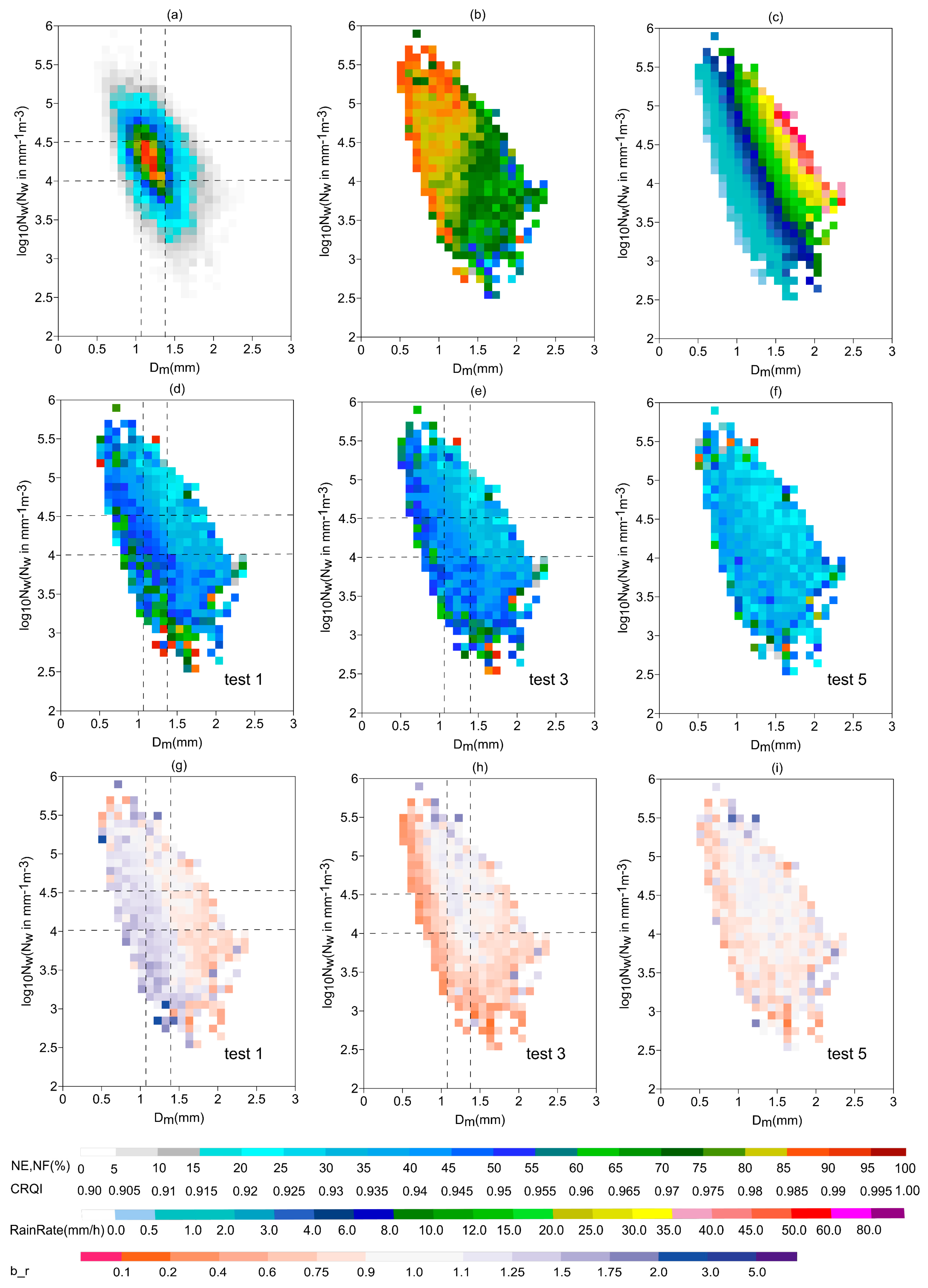
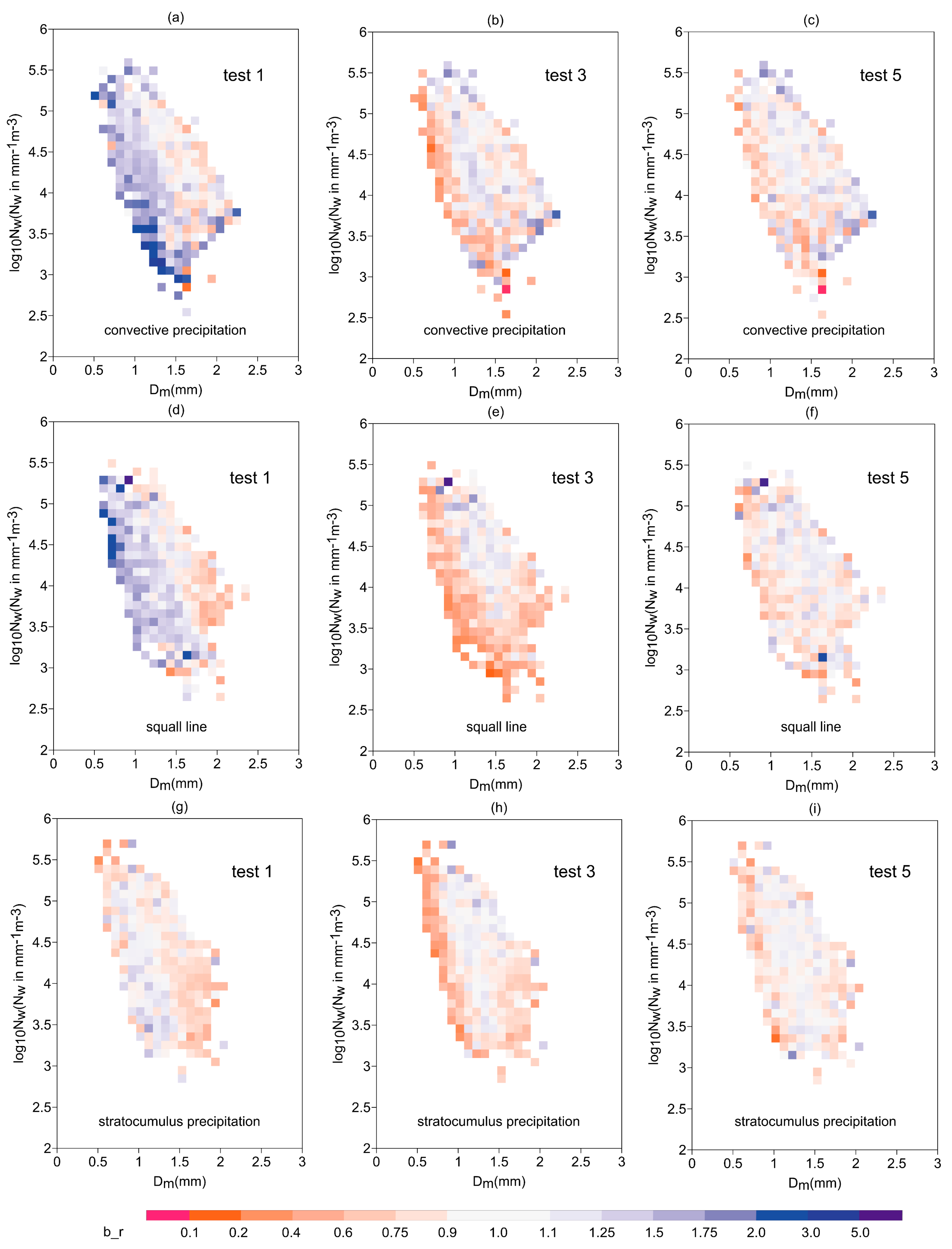
3.4. Biases Analysis Based on Microphysical Parameters
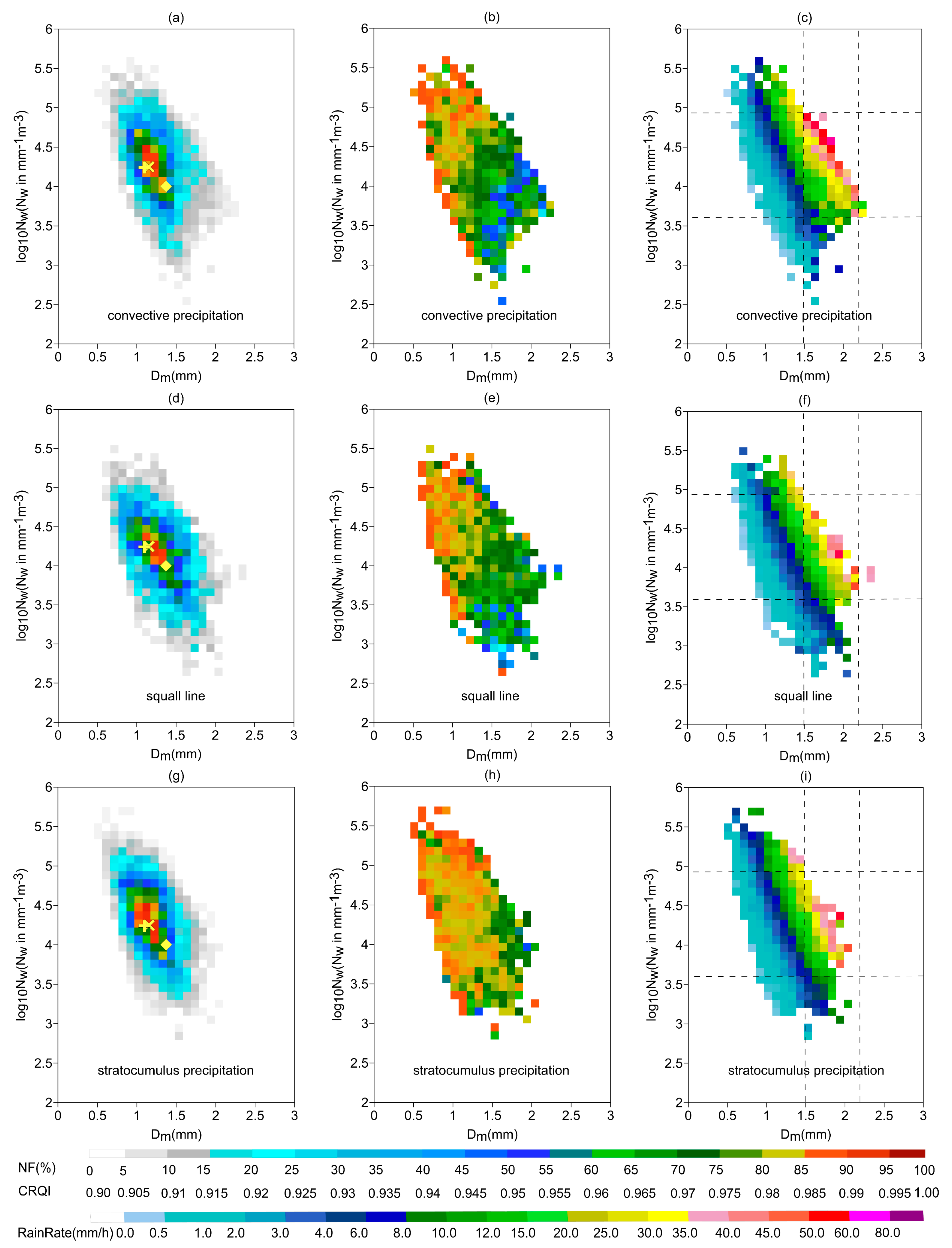
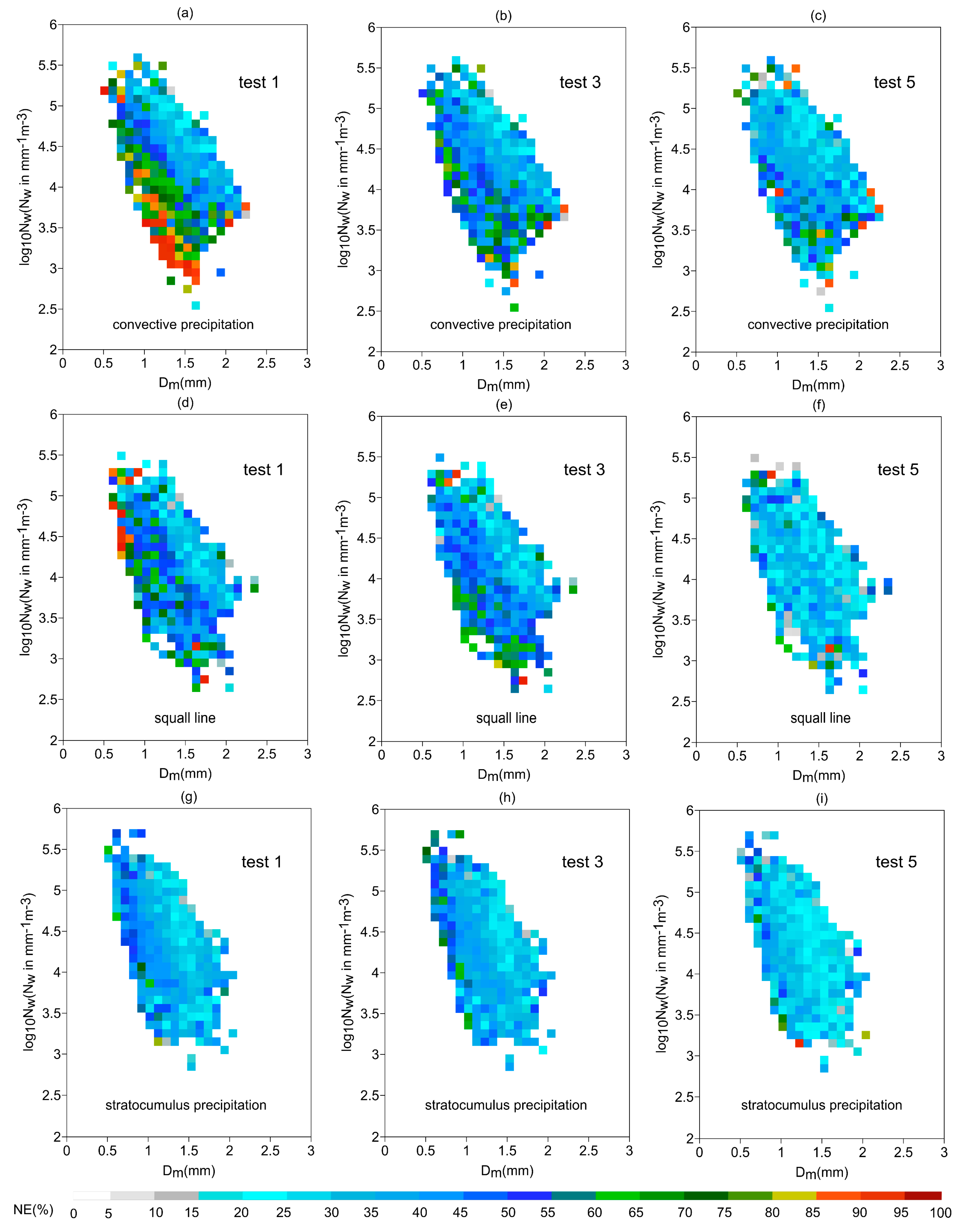
3.5. Microphysical Characteristics of Three Types of Precipitation
3.6. QPE Performances for Three Types of Precipitation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wilson, J.W.; Brandes, E.A. Radar measurement of rainfall—A summary. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1979, 60, 1048–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Germann, U.; Galli, G.; Boscacci, M.; Bolliger, M. Radar precipitation measurements in a mountainous region. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2006, 132, 1669–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciach, G.J.; Krajewski, W.F.; Villarini, G. Product-errordriven uncertainty model for probabilistic precipitation estimation with NEXRAD data. J. Hydrometeorol. 2007, 8, 1325–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goudenhoofdt, E.; Delobbe, L. Evaluation of radar–gauge merging methods for quantitative precipitation estimates. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2009, 13, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, L.; Wen, H. Performance of a Radar Mosaic Quantitative Precipitation Estimation Algorithm Based on a New Data Quality Index for the Chinese Polarimetric Radars. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Qi, Y.; Langston, C.; Kaney, B.; Howard, K. A Real-Time Algorithm for Merging Radar QPEs with Rain Gauge Observations and Orographic Precipitation Climatology. J. Hydrometeorol. 2013, 15, 1794–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, G.; Liu, L.; Ding, Y. Improvement of radar quantitative precipitation estimation based on real-time adjustments to Z–R relationships and inverse distance weighting correction schemes. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2012, 29, 575–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gou, Y.; Liu, L.; Yang, J.; Wu, C. Operational application and evaluation of the quantitative precipitation estimates algorithm based on the multi–radar mosaic. Act. Meteor. Sin. 2014, 72, 731–748. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Libertino, A.; Allamano, P.; Claps, P.; Cremonini, R.; Laio, F. Radar estimation of intense rainfall rates through adaptive calibration of the Z–R relation. Atmosphere 2015, 6, 1559–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y. Study on the Quantitative Precipitation Estimation Algorithm and Performance Evaluation with the Operational Dual-Polarization Radar Network and Automatic Stations. Ph.D. Thesis, Nanjing University of Information Science and Technology, Nanjing, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Fulton, R.A.; Breidenbach, J.P.; Seo, D.J.; Miller, D.A.; O’Bannon, T. The WSR-88D rainfall algorithm. Weather Forecast. 1998, 13, 377–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabary, P. The new French radar rainfall product. Part I: Methodology. Weather Forecast. 2007, 22, 393–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Howard, K.; Langston, C.; Vasiloff, S.; Kaney, B.; Arthur, A.; Van Cooten, S.; Kelleher, K.; Kitzmiller, D.; Ding, F.; et al. Coauthors: National Mosaic and Multi-Sensor QPE (NMQ) system: Description, results, and future plans. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2011, 92, 1321–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haberlandt, U. Geostatistical interpolation of hourly precipitation from rain gauges and radar for a large-scale extreme rainfall event. J. Hydrol. 2007, 332, 144–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velasco-Forero, C.A.; Sempere-Torres, D.; Cassiraga, E.F.; Gomez-Hernandez:, J.J. A non-parametric automatic blending methodology to estimate rainfall fields from rain gauge and radar data. Adv. Water Resour. 2009, 32, 986–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verworn, A.; Haberlandt:, U. Spatial interpolation of hourly rainfall—Effect of additional information, variogram inference and storm properties. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 15, 569–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sideris, I.V.; Gabella, M.; Erdin, R.; Germann:, U. Realtime radar–rain-gauge merging using spatio-temporal co-kriging with external drift in the alpine terrain of Switzerland. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2013, 140, 1097–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiemann, R.; Erdin, R.; Willi, M.; Frei, C.; Berenguer, M.; Sempere-Torres:, D. Geostatistical radar-raingauge combination with nonparametric correlograms: Methodological considerations and application in Switzerland. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 15, 1515–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Berndt, C.; Rabiei, E.; Haberlandt:, U. Geostatistical merging of rain gauge and radar data for high temporal resolutions and various station density scenarios. J. Hydrol. 2014, 508, 88–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, P. Optimum interpolation method used for measuring regional precipitation with weather radar. J. Oceanogr. Taiwan Strait 1996, 15, 255–259. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Yang, W.; Gou, L.; Chen, Z. A study of improving precision of measuring regional precipitation in optimum interpolation method. J. Atmos. Sci. 2000, 24, 263–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedrich, K.; Hagen, M.; Einfalt, T. A Quality Control Concept for Radar Reflectivity, Polarimetric Parameters, and Doppler Velocity. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2006, 23, 865–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vulpiani, G.; Montopoli, M.; Passeri, L.D.; Gioia, A.G.; Giordano, P.; Marzano, F.S. On the Use of Dual-Polarized C-Band Radar for Operational Rainfall Retrieval in Mountainous Areas. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2012, 51, 405–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Zhang, J. A Physically Based Two-Dimensional Seamless Reflectivity Mosaic for Radar QPE in the MRMS System. J. Hydrometeorol. 2017, 18, 1327–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Gourley, J.J.; Hong, Y.; Kirstetter, P.E.; Zhang, J.; Howard, K.; Flaming, Z.L.; Hu, J.; Qi, Y. Evaluation and uncertainty estimation of NOAA/NSSL next-generation National Mosaic QPE (Q2) over the continental United States. J. Hydrometeorol. 2013, 14, 1308–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Qi, Y.; Langston, C.; Kaney, B. Radar Quality Index (RQI)—A combined measure for beam blockage and VPR effects in a national network. In Proceedings of the Symposium Weather Radar and Hydrology, Exeter, UK, 18–21 April 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafer, M.A.; Fiebrich, C.A.; Arndt, D.S.; Fredrickson, S.E.; Hughes, T.W. Quality Assurance Procedures in the Oklahoma Mesonetwork. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2000, 17, 474–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eischeid, J.K.; Baker, C.B.; Karl, T.; Diaz, H.F. The quality control of long-term climatological data using objective data analysis. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1995, 34, 2787–2795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eischeid, J.K.; Pasteris, P.A.; Diaz, H.F.; Diaz, H.F.; Plantico, M.S.; Lott, N.J. Creating a Serially Complete, National Daily Time Series of Temperature and Precipitation for the Western United States. J. Appl. Meteorol. 2000, 39, 1580–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandin, L.S. Complex Quality Control of Meteorological Observations. Mon. Weather Rev. 1988, 116, 1137–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wade, C.G. A quality control program for surface meteorological data. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 1987, 4, 435–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroeder, J.L.; Burgett, W.S.; Haynie, K.B.; Sonmez, I.; Skwira, G.D.; Doggett, A.L.; Lipe, J.W. The West Texas Mesonet: A Technical Overview. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2005, 22, 211–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, L.; Wen, H.; Wu, C.; Zhang, Y. Evaluation of the Polarimetric-Radar Quantitative Precipitation Estimates of an Extremely Heavy Rainfall Event and Nine Common Rainfall Events in Guangzhou. Atmosphere 2018, 9, 330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huo, Z.; Ruan, Z.; Wei, M.; Ge, R.; Li, F.; Ruan, Y. Statistical characteristics of raindrop size distribution in south china summer based on the vertical structure derived from vpr-cfmcw. Atmos. Res. 2019, 222, 47–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Zhao, K.; Zhang, G.; Huang, H.; Liu, S.; Wen, L.; Yang, Z.; Yang, Z.; Xu, L.; Zhu, W. Improving polarimetric c-band radar rainfall estimation with two-dimensional video disdrometer observations in eastern china. J. Hydrometeorol. 2017, 18, 1375–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Parameter Type | Setting |
|---|---|
| Antenna diameter (m) | 8.54 |
| Antenna gain (dB) | 45.31 |
| Beam width (°) | <0.98 |
| First side lobe (dB) | <−30 |
| Wavelength (cm) | 10.3 |
| Operating mode | Simultaneous horizontal and |
| vertical transmission and reception | |
| Minimum detectable power (dBm) | −117.8 |
| Volume scan mode | VCP21 (9 tilts) |
| Range resolution (km) | 0.25 |
| Scan period (min) | 6 |
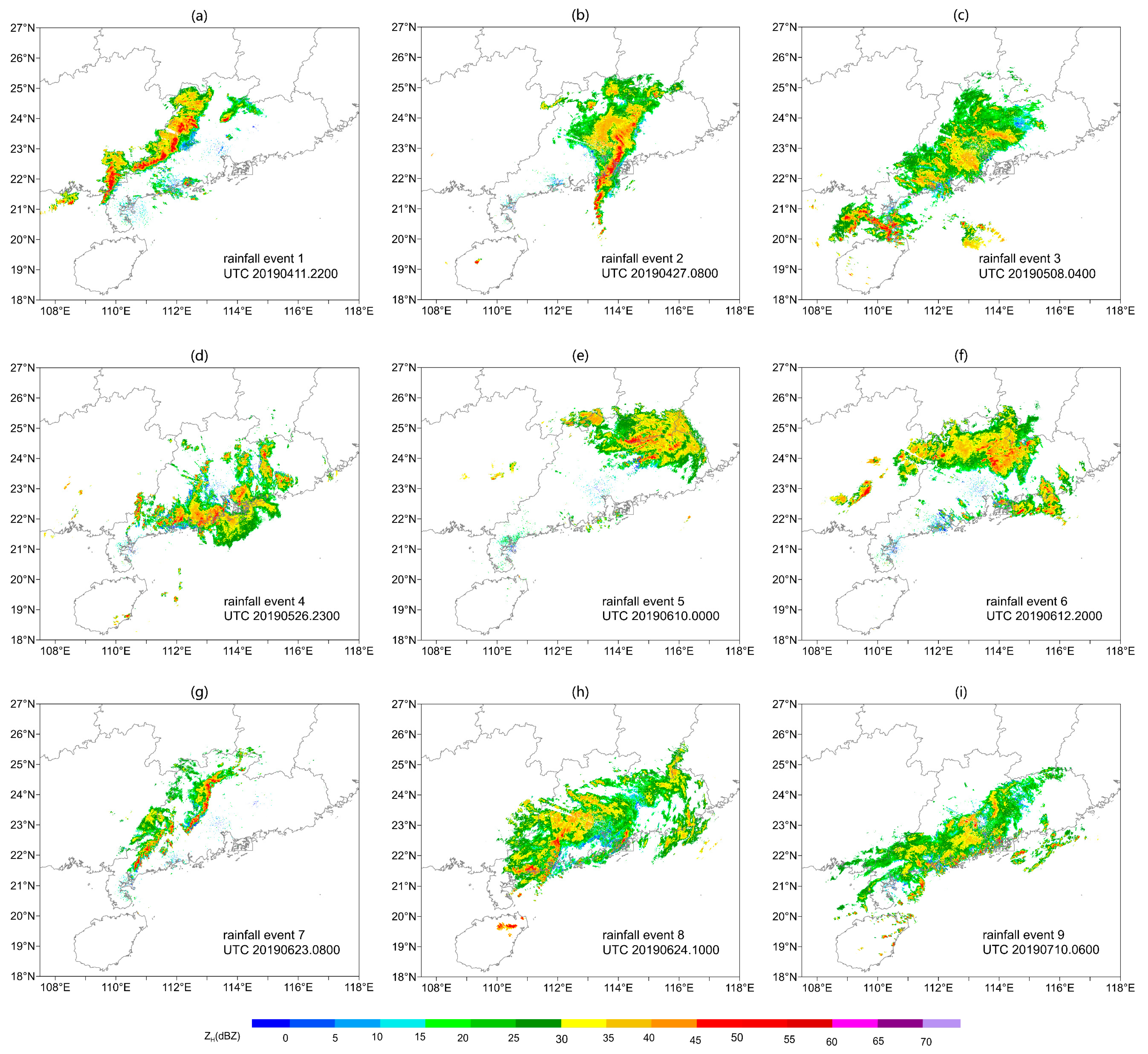
| # | Date (UTC) | Total Time (h) | No. of Valued Gauges | Mean Gauge Accumulation (mm) | Max Gauge Accumulation (mm) | Precipitation Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 11–12 April 2019 | 14 | 3873 | 16.66 | 144.7 | squall line |
| 2 | 27 April 2019 | 13 | 2996 | 22.08 | 189.2 | squall line |
| 3 | 7–8 May 2019 | 16 | 4114 | 17.42 | 237.6 | stratocumulus |
| 4 | 26–27 May 2019 | 16 | 3506 | 19.64 | 542.6 | convective |
| 5 | 9–10 June 2019 | 26 | 3684 | 35.53 | 297.6 | convective |
| 6 | 12–13 June 2019 | 20 | 3982 | 25.09 | 239.8 | convective |
| 7 | 23 June 2019 | 12 | 2905 | 9.14 | 75.6 | squall line |
| 8 | 23–24 June 2019 | 20 | 3182 | 40.44 | 211.6 | stratocumulus |
| 9 | 9–10 July 2019 | 21 | 3577 | 24.84 | 176.6 | stratocumulus |
| # | Estimators Correction Method | Spatial Correction Method |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | No correction for estimators | No spatial correction |
| 2 | Correct estimators with all data pairs | No spatial correction |
| 3 | Correct estimators with good-quality data pairs (CRQI > 0.95) | No spatial correction |
| 4 | Correct estimators with good-quality data pairs (CRQI > 0.95) | Spatial correction via the traditional OI method |
| 5 | Correct estimators with good-quality data pairs (CRQI > 0.95) | Spatial correction via the proposed algorithm |
| Test | CRQI | CC | NB (%) | NE (%) | RMSE (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | >0.9 | 0.87 | 1.22 | 40.18 | 3.68 |
| 2 | >0.9 | 0.87 | 10.84 | 43.00 | 3.83 |
| 3 | >0.9 | 0.87 | −2.96 | 39.31 | 3.66 |
| 4 | >0.9 | 0.89 | −0.45 | 34.78 | 3.41 |
| 5 | >0.9 | 0.89 | −0.44 | 34.79 | 3.41 |
| 1 | >0.0 | 0.78 | −15.67 | 50.67 | 4.40 |
| 4 | >0.0 | 0.81 | −14.93 | 45.04 | 4.18 |
| 5 | >0.0 | 0.86 | −2.57 | 38.89 | 3.63 |
| Type | Test | CC | NB (%) | NE (%) | RMSE (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| convective | 1 | 0.86 | 6.57 | 42.92 | 4.30 |
| convective | 3 | 0.86 | −1.38 | 41.15 | 4.28 |
| convective | 5 | 0.88 | 0.67 | 37.39 | 4.05 |
| squall line | 1 | 0.87 | 8.39 | 41.80 | 4.04 |
| squall line | 3 | 0.88 | 0.88 | 39.77 | 3.98 |
| squall line | 5 | 0.90 | 2.33 | 34.23 | 3.65 |
| stratocumulus | 1 | 0.88 | −7.43 | 37.01 | 3.00 |
| stratocumulus | 3 | 0.88 | −6.57 | 37.58 | 3.02 |
| stratocumulus | 5 | 0.90 | −3.03 | 33.08 | 2.79 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Liu, L.; Wen, H.; Yu, B.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Y. Combined Radar Quality Index for Quantitative Precipitation Estimation of Heavy Rainfall Events. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3154. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14133154
Zhang Y, Liu L, Wen H, Yu B, Wang H, Zhang Y. Combined Radar Quality Index for Quantitative Precipitation Estimation of Heavy Rainfall Events. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(13):3154. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14133154
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yang, Liping Liu, Hao Wen, Benchao Yu, Huiying Wang, and Yong Zhang. 2022. "Combined Radar Quality Index for Quantitative Precipitation Estimation of Heavy Rainfall Events" Remote Sensing 14, no. 13: 3154. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14133154
APA StyleZhang, Y., Liu, L., Wen, H., Yu, B., Wang, H., & Zhang, Y. (2022). Combined Radar Quality Index for Quantitative Precipitation Estimation of Heavy Rainfall Events. Remote Sensing, 14(13), 3154. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14133154





