Intercomparison of Resampling Algorithms for Advanced Technology Microwave Sounder (ATMS)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. ATMS Resampling Methodology
2.1. ATMS Instrument
2.2. Backus–Gilbert Inversion
2.3. AAPP Resampling Algorithm
2.4. Modified AAPP Resampling Algorithm
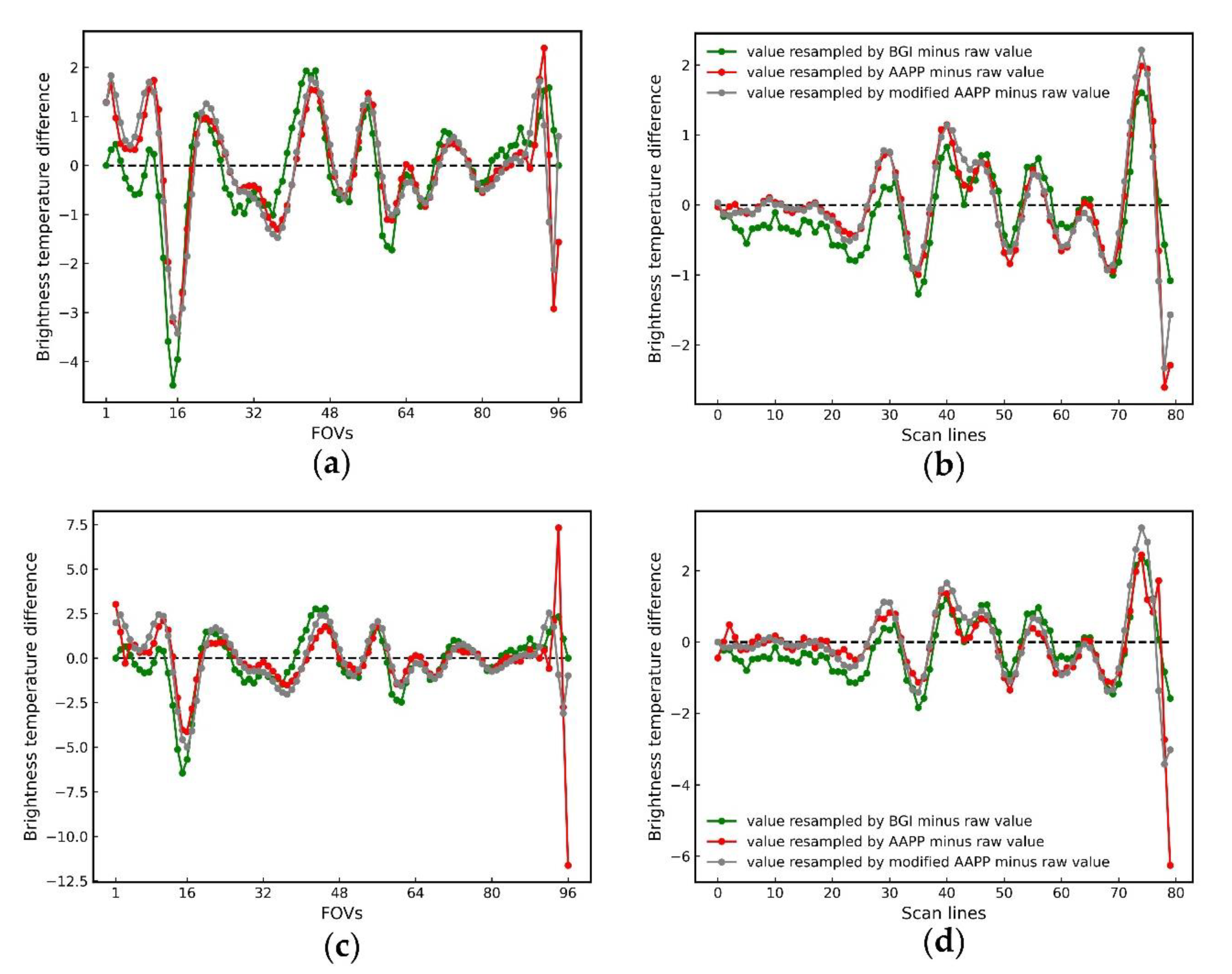
2.5. Algorithm Evaluation and Verification
- (1)
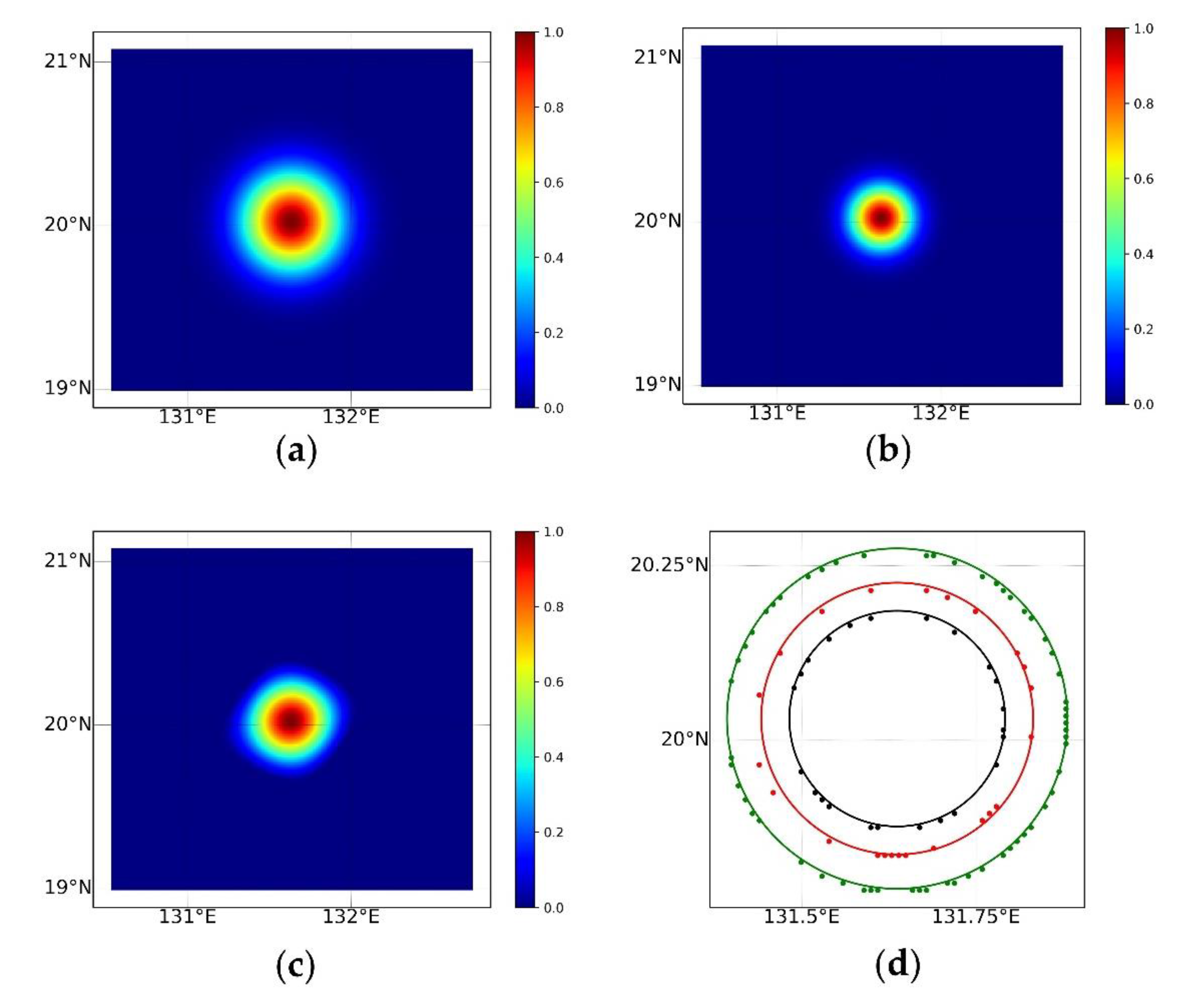
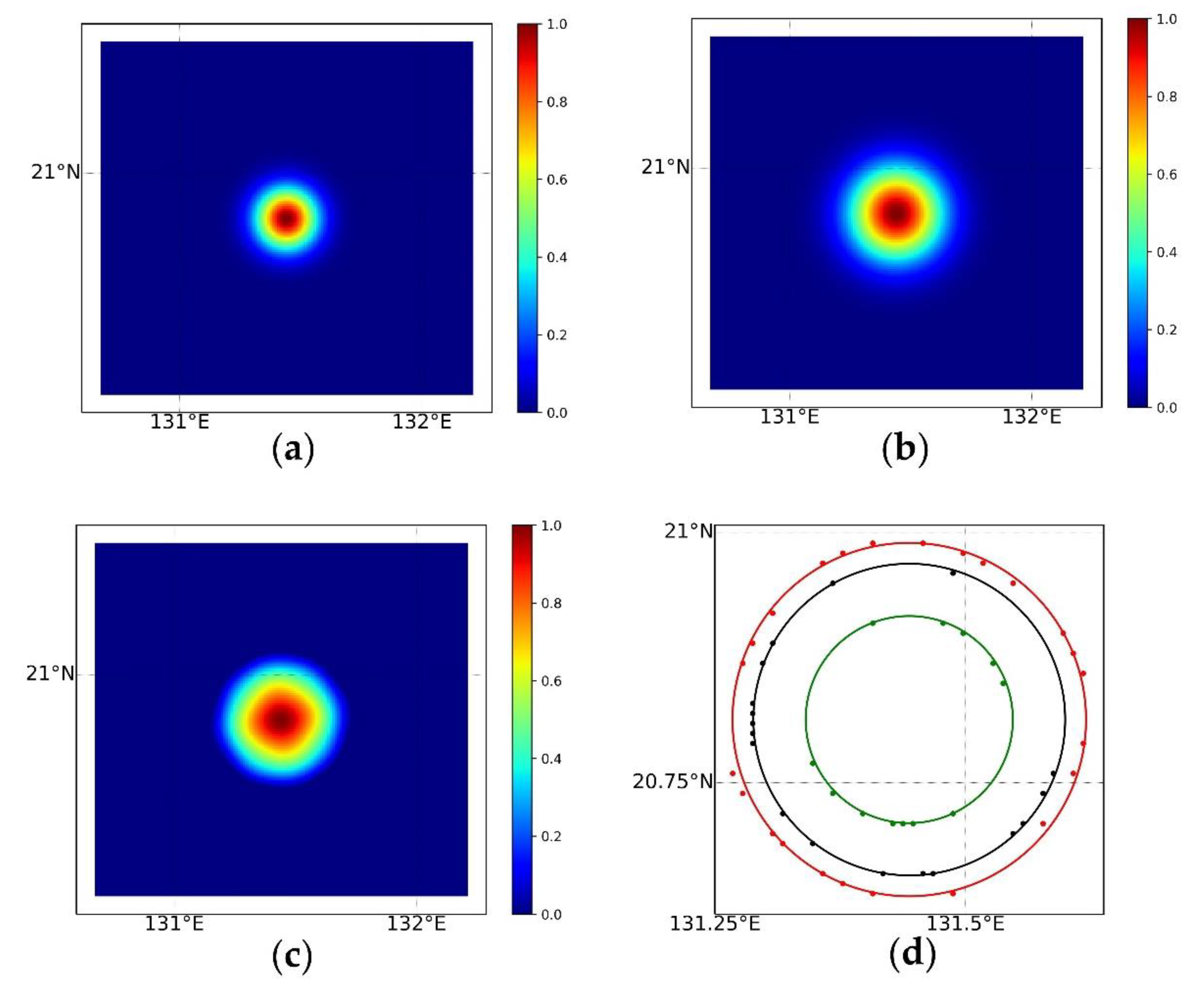
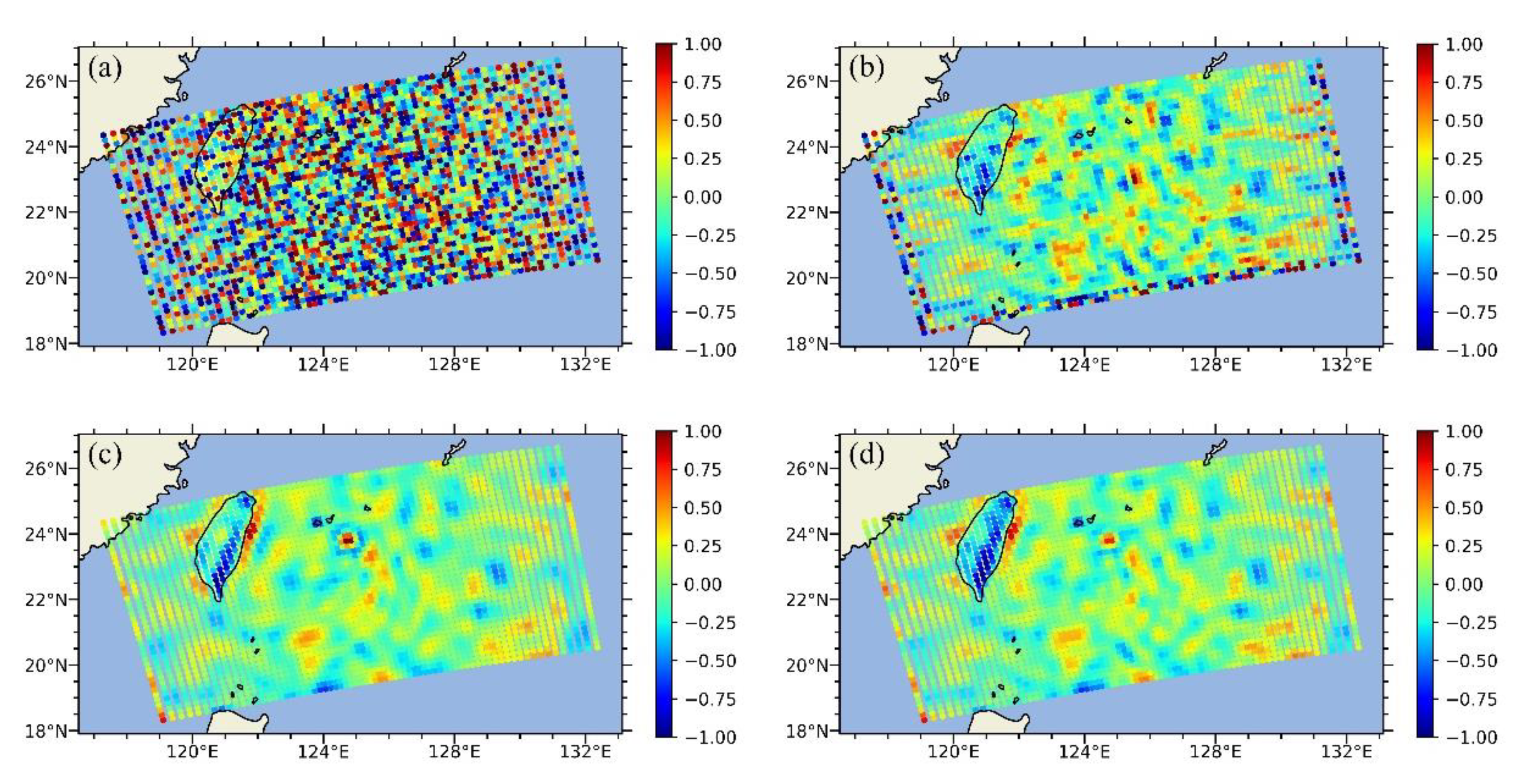
- For the BGI method, the antenna gain function (AGF) projected to the geographic coordinate system can be used for qualitative evaluations. However, this verification method does not work for frequency domain algorithms.
- (2)
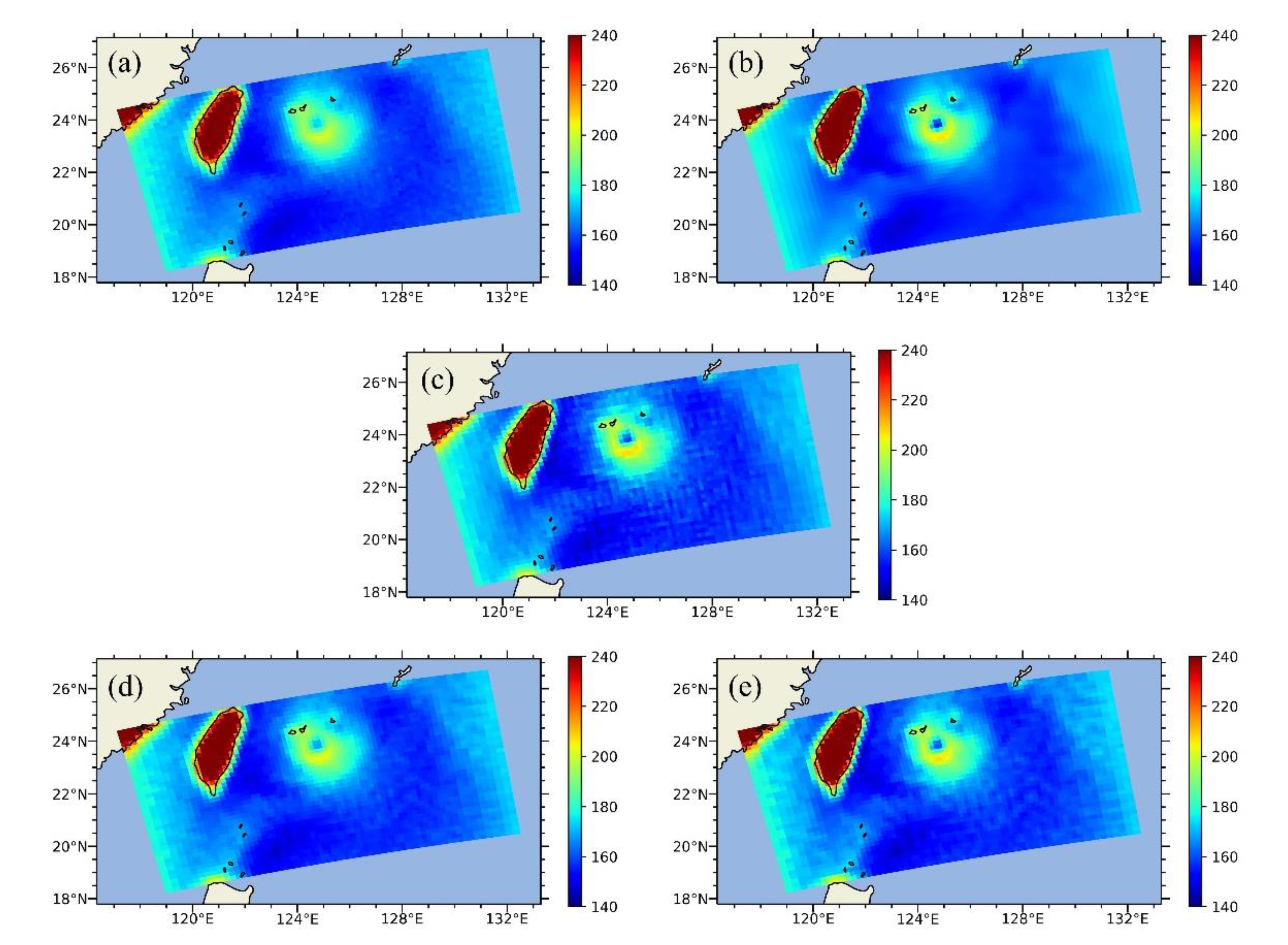
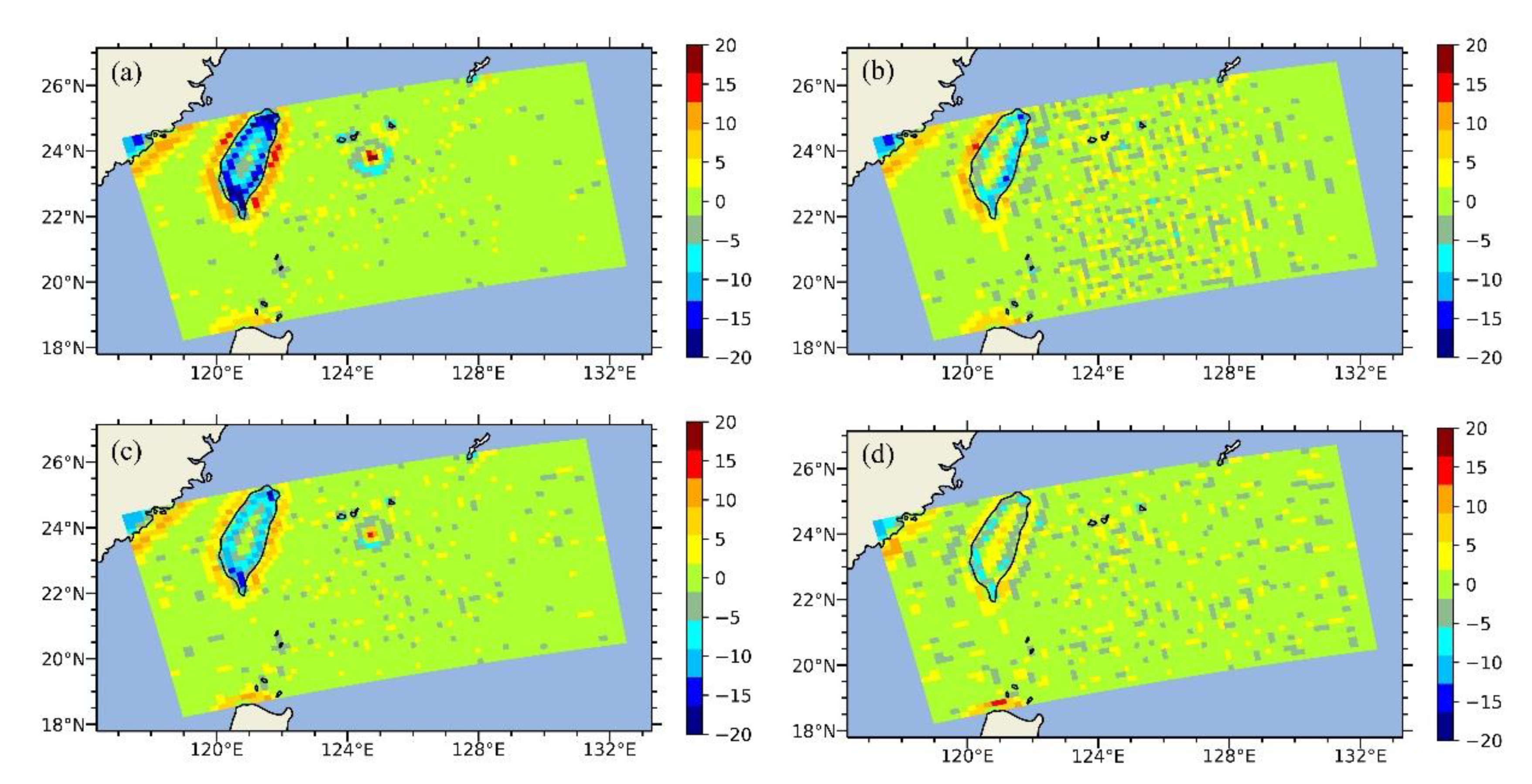
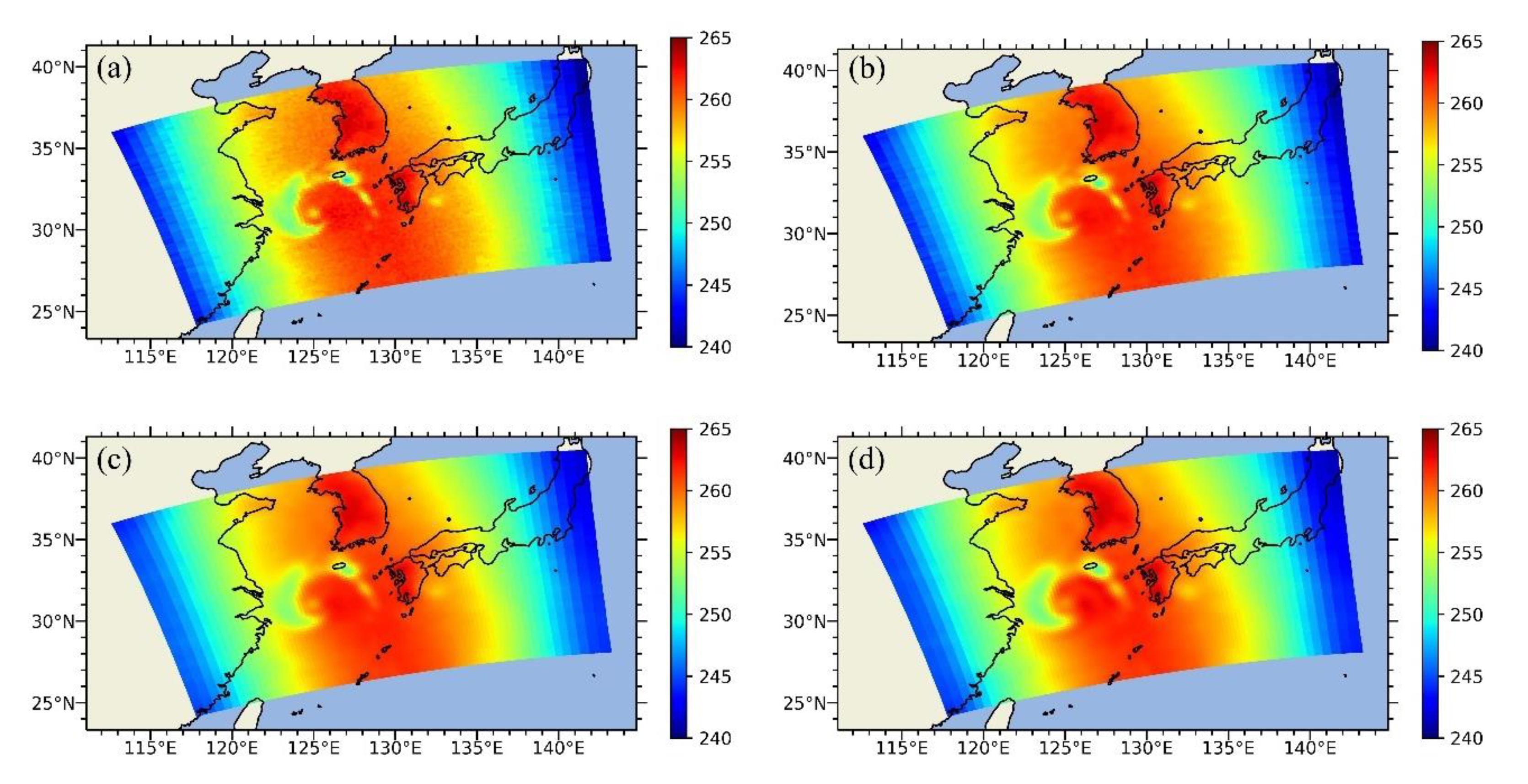
- Quantitative evaluations are performed using the radiative transfer model simulation results. First, the atmospheric and surface parameters of typhoon Lekima on 8 August 2019, are generated using the weather research and forecasting (WRF) model with a resolution of 3 km. Then, these outputs are used as inputs to the fast radiation transfer model ARMS (advanced radiative transfer modeling system) [28] to simulate the ATMS brightness temperatures at 22 channels. The brightness temperature fields are used to construct the actual scene brightness temperature . It is worth noting that when using ARMS to simulate the brightness temperature, the limb effect of ATMS is taken into account. Finally, the AGFs of different antenna sizes are convolved with to obtain the ATMS antenna temperature according to Equation (1). The antenna temperature with an AGF beam width of 3.3° simulated by the model can be used as the true value, so that the qualitative and quantitative evaluations of the BGI, AAPP, and modified AAPP resampling algorithms can be carried out.Using mean absolute error (MAE), root mean square error (RMSE), and BIAS for quantitative evaluation, the calculation formula is as follows:where is the true value simulated by the ARMS, and is the brightness temperatures from resampling algorithms.
- (3)
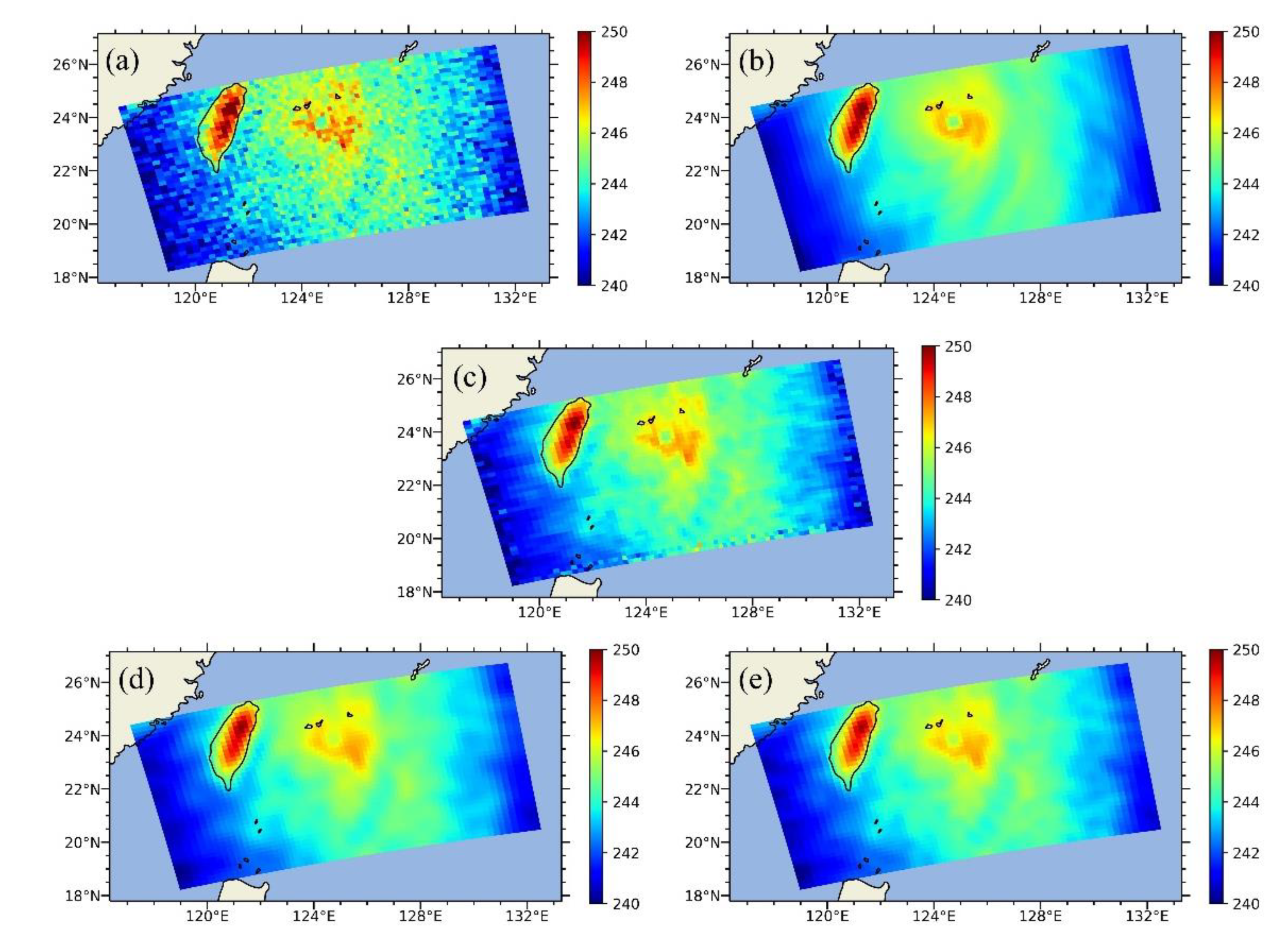
- Observed ATMS data from NOAA-20 satellites are also used for qualitative assessments.
3. Results
3.1. Antenna Gain Function Reconstructed by BGI
3.2. Experiments and Comparisons Using Simulated Brightness Temperatures
3.3. Experiments and Comparisons Using ATMS Observations
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Eyre, J.R.; Kelly, G.A.; McNally, A.P.; Andersson, E.; Persson, A. Assimilation of TOVS radiance information through one-dimensional variational analysis. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1993, 119, 1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Weng, F.; Lv, L.; Lu, N.; Liu, G.; Bai, M.; Qian, Q.; He, J.; Xu, H. The FengYun-3 microwave radiation imager on-orbit verification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 49, 4552–4560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, K.M.; Schwartz, C.S.; Liu, Z.; Shao, H.; Huang, X.-Y. Evaluating forecast impact of assimilating microwave humidity sounder (MHS) radiances with a regional ensemble Kalman filter data assimilation system. Weather Forecast. 2015, 30, 964–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangla, R.; Indu, J.; Chambon, P.; Mahfouf, J.-F. First steps towards an all-sky assimilation framework for tropical cyclone event over Bay of Bengal region: Evaluation and assessment of GMI radiances. Atmos. Res. 2021, 257, 105564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrar, M.R.; Smith, E.A. Spatial resolution enhancement of terrestrial features using deconvolved SSM/I microwave brightness temperatures. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1992, 30, 349–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Yang, H. Comparison of the resampling algorithms for the advanced technology microwave sounder (ATMS). Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stogryn, A. Estimates of brightness temperatures from scanning radiometer data. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 1978, 26, 720–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poe, G.A. Optimum interpolation of imaging microwave radiometer data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1990, 28, 800–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chakraborty, P.; Misra, A.; Misra, T.; Rana, S.S. Brightness temperature reconstruction using BGI. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2008, 46, 1768–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, T. Spatial resolution enhancement algorithm based on the Backus–Gilbert method and its application to GCOM-W AMSR2 data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 58, 2809–2816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, H.; England, A.W. AMSR-E data resampling with near-circular synthesized footprint shape and noise/resolution tradeoff study. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2007, 45, 3193–3203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, D.G.; Daum, D.L. Spatial resolution enhancement of SSM/I data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1998, 36, 407–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Long, D.G.; Hardin, P.J.; Whiting, P.T. Resolution enhancement of spaceborne scatterometer data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1993, 31, 700–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Long, D.G.; Brodzik, M.J. Optimum image formation for spaceborne microwave radiometer products. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 54, 2763–2779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Long, D.G.; Brodzik, M.J.; Hardman, M.A. Enhanced-resolution SMAP brightness temperature image products. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 4151–4163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sethmann, R.; Burns, B.A.; Heygster, G.C. Spatial resolution improvement of SSM/I data with image restoration techniques. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1994, 32, 1144–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawei, L.; Kai, L.; Changchun, L.; Jungang, M. Resolution enhancement of passive microwave images from geostationary Earth orbit via a projective sphere coordinate system. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2014, 8, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, W.; Li, Y.; Zhang, W.; Chen, S.; Lv, X.; Ligthart, L. Spatial resolution enhancement of satellite microwave radiometer data with deep residual convolutional neural network. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Hu, W.; Chen, S.; Zhang, W.; Guo, R.; He, J.; Ligthart, L. Spatial resolution matching of microwave radiometer data with convolutional neural network. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, H.; Zou, X. Optimal ATMS resampling algorithm for climate research. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 7290–7296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Yang, H. Noise suppression in ATMS spatial resolution enhancement using adaptive window method. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium IGARSS, Brussels, Belgium, 11–16 July 2021; pp. 7693–7695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, F.; Zou, X.; Wang, X.; Yang, S.; Goldberg, M.D. Introduction to Suomi national polar-orbiting partnership advanced technology microwave sounder for numerical weather prediction and tropical cyclone applications. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2012, 117, D19112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.; Lyu, C.-H.; Anderson, K.; Leslie, R.V.; Blackwell, W.J. S-NPP ATMS instrument prelaunch and onorbit performance evaluation. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 5653–5670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zou, C.-Z.; Wang, W. Intersatellite calibration of AMSU-A observations for weather and climate applications. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2011, 116, D23113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mears, C.A.; Wentz, F.J.; Thorne, P.; Bernie, D. Assessing uncertainty in estimates of atmospheric temperature changes from MSU and AMSU using a Monte-Carlo estimation technique. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2011, 116, D08112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piles, M.; Camps, A.; Vall-llossera, M.; Talone, M. Spatial-resolution enhancement of SMOS data: A deconvolution-based approach. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2009, 47, 2182–2192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, W.D.; Kummerow, C.; Olson, W.S. A technique for enhancing and matching the resolution of microwave measurements from the SSM/I instrument. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1992, 30, 419–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, F.; Yu, X.; Duan, Y.; Yang, J.; Wang, J. The advanced radiative transfer modeling system (ARMS)—A new generation of satellite observation operator developed for numerical weather prediction and remote sensing applications. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2020, 37, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
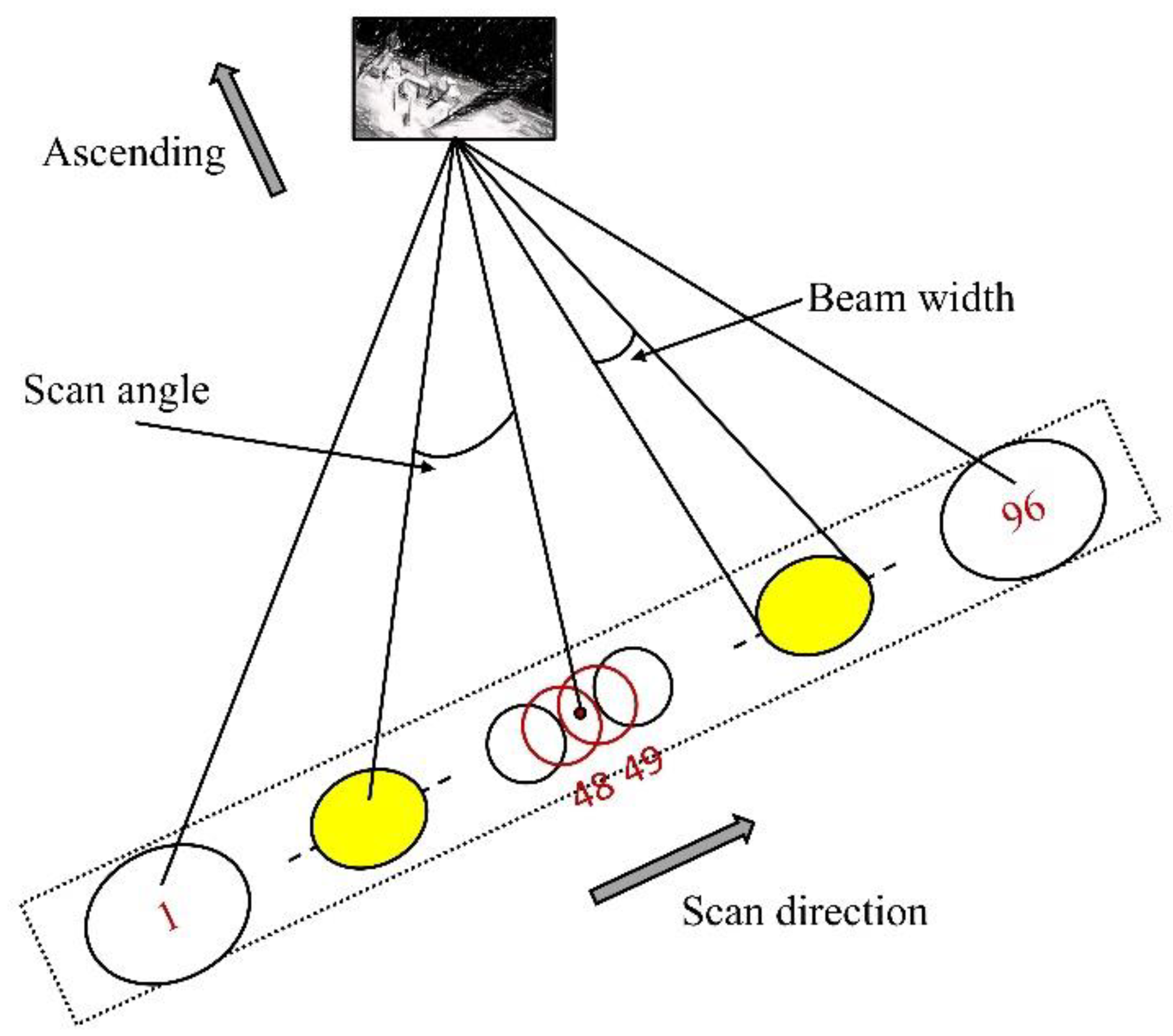
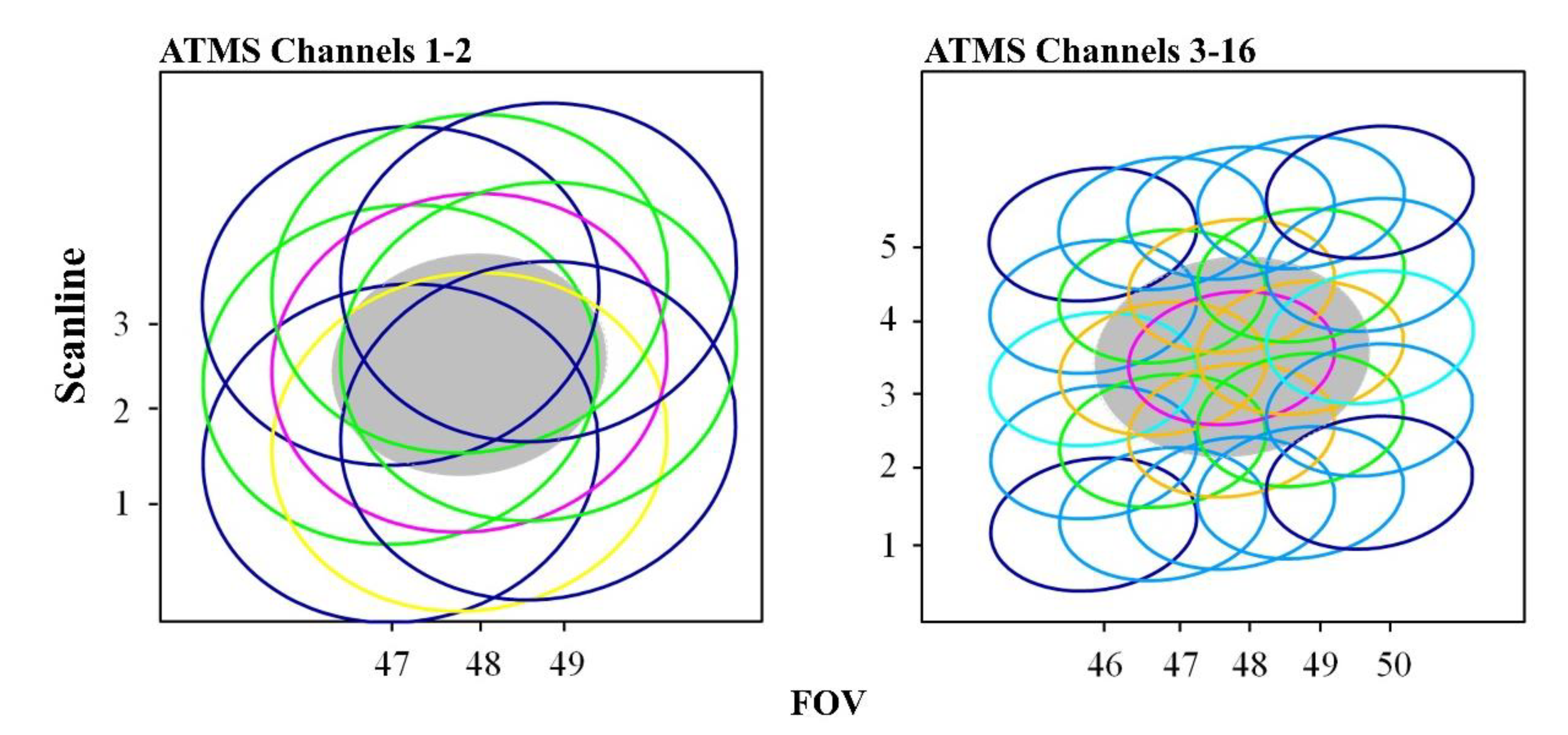


| Channel | Center Frequency (GHz) | NEDT(K) | Beam Width (degree) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 23.8 | 0.7 | 5.2 |
| 2 | 31.4 | 0.8 | 5.2 |
| 3 | 50.3 | 0.9 | 2.2 |
| 4 | 51.76 | 0.7 | 2.2 |
| 5 | 52.8 | 0.7 | 2.2 |
| 6 | 53.596 ± 0.115 | 0.7 | 2.2 |
| 7 | 54.4 | 0.7 | 2.2 |
| 8 | 54.94 | 0.7 | 2.2 |
| 9 | 55.5 | 0.7 | 2.2 |
| 10 | 57.290344 | 0.7 | 2.2 |
| 11 | 57.290344 ± 0.217 | 0.75 | 2.2 |
| 12 | 57.290344 ± 0.3222 ± 0.048 | 1.2 | 2.2 |
| 13 | 57.290344 ± 0.3222 ± 0.022 | 1.2 | 2.2 |
| 14 | 57.290344 ± 0.3222 ± 0.010 | 1.5 | 2.2 |
| 15 | 57.290344 ± 0.3222 ± 0.0045 | 2.4 | 2.2 |
| 16 | 88.2 | 3.5 | 2.2 |
| 17 | 165.5 | 0.5 | 1.1 |
| 18 | 183.31 ± 7 | 0.6 | 1.1 |
| 19 | 183.31 ± 4.5 | 0.8 | 1.1 |
| 20 | 183.31 ± 3 | 0.8 | 1.1 |
| 21 | 183.31 ± 1.8 | 0.8 | 1.1 |
| 22 | 183.31 ± 1 | 0.9 | 1.1 |
| Channel | Algorithm | BIAS (K) | MAE (K) | RMSE (K) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | None | 0.0947 | 1.8436 | 3.7254 |
| BGI | −0.1353 | 1.6522 | 2.5355 | |
| AAPP | −0.0556 | 1.5443 | 2.7039 | |
| Modified AAPP | −0.0215 | 1.3354 | 2.0239 | |
| 2 | None | 0.0709 | 1.8115 | 3.5291 |
| BGI | −0.1361 | 1.7288 | 2.5616 | |
| AAPP | −0.0411 | 1.4988 | 2.6123 | |
| Modified AAPP | −0.0086 | 1.377 | 2.0413 | |
| 3 | None | −0.0197 | 1.0947 | 1.6852 |
| BGI | −0.0001 | 0.4958 | 0.8902 | |
| AAPP | 0.0006 | 0.4187 | 0.6336 | |
| Modified AAPP | −0.0018 | 0.4273 | 0.6411 | |
| 4 | None | −0.0189 | 0.7585 | 1.0934 |
| BGI | −0.0086 | 0.3377 | 0.5562 | |
| AAPP | 0.003 | 0.2998 | 0.4421 | |
| Modified AAPP | 0.0067 | 0.2994 | 0.4419 | |
| 5 | None | −0.0094 | 0.6162 | 0.7925 |
| BGI | −0.0064 | 0.2677 | 0.3753 | |
| AAPP | 0.0077 | 0.2363 | 0.3217 | |
| Modified AAPP | 0.0076 | 0.2307 | 0.3162 | |
| 6 | None | 0.0128 | 0.5637 | 0.7052 |
| BGI | 0.0088 | 0.2415 | 0.3364 | |
| AAPP | −0.0152 | 0.1621 | 0.2074 | |
| Modified AAPP | −0.0146 | 0.1591 | 0.2048 | |
| 7 | None | −0.0041 | 0.5727 | 0.7153 |
| BGI | −0.0074 | 0.2474 | 0.3397 | |
| AAPP | 0.0054 | 0.1338 | 0.2111 | |
| Modified AAPP | 0.0063 | 0.1604 | 0.2323 | |
| 8 | None | 0.0183 | 0.5620 | 0.7044 |
| BGI | 0.0163 | 0.2419 | 0.3340 | |
| AAPP | −0.0158 | 0.1170 | 0.2074 | |
| Modified AAPP | −0.0138 | 0.1123 | 0.2050 | |
| 9 | None | 0.0014 | 0.5603 | 0.7001 |
| BGI | 0.0004 | 0.2452 | 0.3334 | |
| AAPP | 0.0019 | 0.1599 | 0.2264 | |
| Modified AAPP | 0.0021 | 0.1529 | 0.2178 | |
| 10 | None | 0.0037 | 0.5543 | 0.6972 |
| BGI | 0.0031 | 0.2396 | 0.3309 | |
| AAPP | −0.0013 | 0.1578 | 0.2308 | |
| Modified AAPP | 0.0023 | 0.1701 | 0.2422 | |
| 11 | None | 0.0184 | 0.5995 | 0.7843 |
| BGI | 0.0163 | 0.2539 | 0.3502 | |
| AAPP | −0.0168 | 0.1646 | 0.2422 | |
| Modified AAPP | −0.0189 | 0.1701 | 0.2451 | |
| 12 | None | −0.0038 | 0.9684 | 1.2103 |
| BGI | −0.0028 | 0.4241 | 0.5748 | |
| AAPP | 0.0027 | 0.2746 | 0.3892 | |
| Modified AAPP | 0.0029 | 0.2758 | 0.3899 | |
| 13 | None | 0.0080 | 0.9697 | 1.2165 |
| BGI | 0.0110 | 0.4125 | 0.5681 | |
| AAPP | −0.0146 | 0.2658 | 0.3933 | |
| Modified AAPP | −0.0166 | 0.2701 | 0.3988 | |
| 14 | None | 0.0170 | 1.2092 | 1.5156 |
| BGI | 0.0194 | 0.5394 | 0.7388 | |
| AAPP | −0.0240 | 0.3581 | 0.5211 | |
| Modified AAPP | −0.0245 | 0.3602 | 0.5297 | |
| 15 | None | 0.0266 | 1.9125 | 2.4030 |
| BGI | 0.0230 | 0.8394 | 1.1569 | |
| AAPP | −0.0301 | 0.5537 | 0.8132 | |
| Modified AAPP | −0.0295 | 0.5501 | 0.8089 | |
| 16 | None | −0.0768 | 3.1231 | 4.0295 |
| BGI | −0.0377 | 1.3640 | 1.9480 | |
| AAPP | 0.0488 | 1.2000 | 1.6611 | |
| Modified AAPP | 0.0464 | 1.1892 | 1.6429 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xie, Y.; Weng, F. Intercomparison of Resampling Algorithms for Advanced Technology Microwave Sounder (ATMS). Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2781. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14122781
Xie Y, Weng F. Intercomparison of Resampling Algorithms for Advanced Technology Microwave Sounder (ATMS). Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(12):2781. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14122781
Chicago/Turabian StyleXie, Yuchen, and Fuzhong Weng. 2022. "Intercomparison of Resampling Algorithms for Advanced Technology Microwave Sounder (ATMS)" Remote Sensing 14, no. 12: 2781. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14122781
APA StyleXie, Y., & Weng, F. (2022). Intercomparison of Resampling Algorithms for Advanced Technology Microwave Sounder (ATMS). Remote Sensing, 14(12), 2781. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14122781






