Optimization and Evaluation of SO2 Emissions Based on WRF-Chem and 3DVAR Data Assimilation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Data and Methodology
2.1. Observational Data and a Priori Emission Data
2.2. WRF-Chem Forecast Model and the 3DVAR DA System
2.3. The Methodology Used for Optimizing the SO2 Emission Inventory
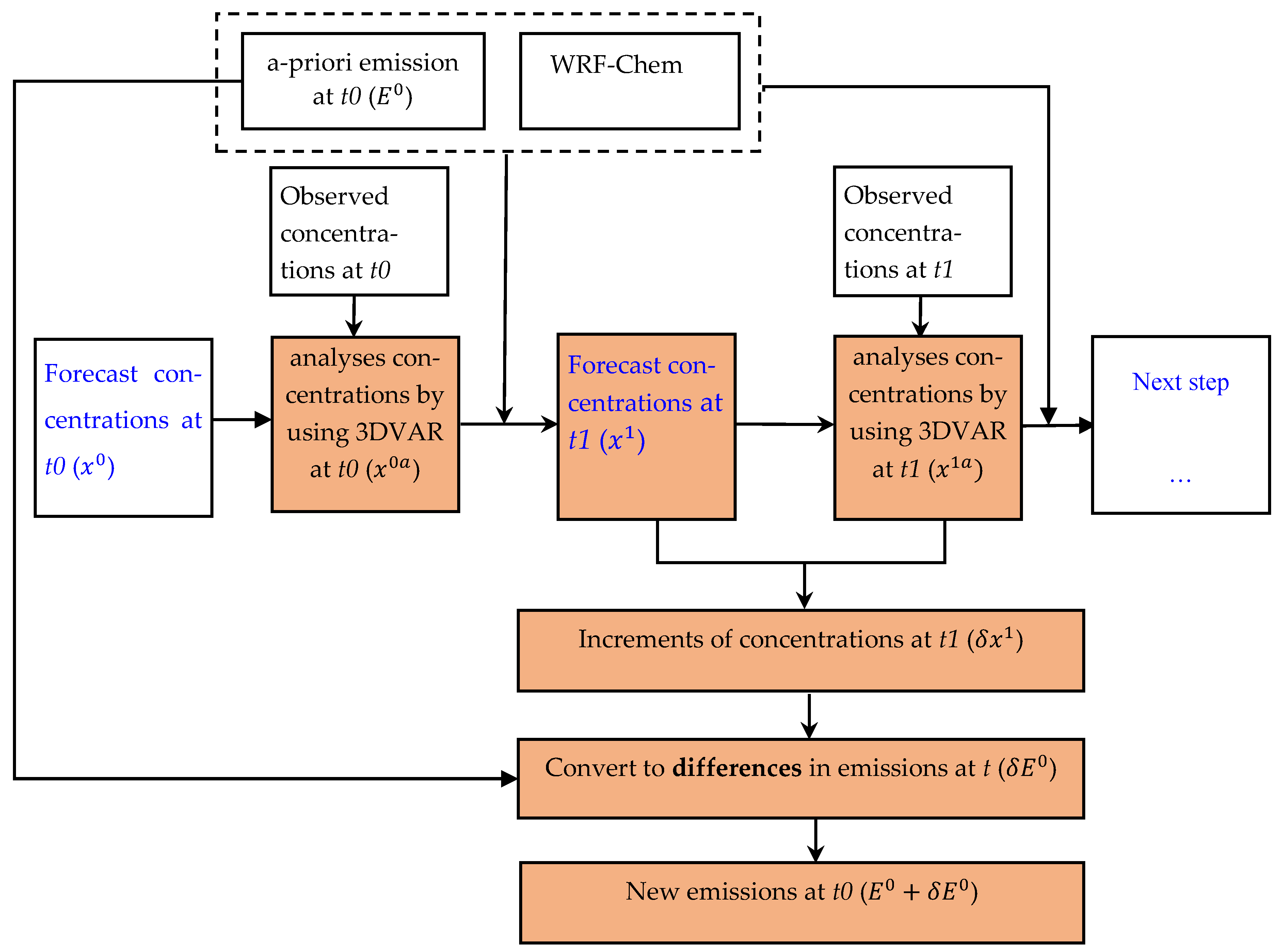
2.3.1. The Assumptions and Procedure to Optimize the Emissions
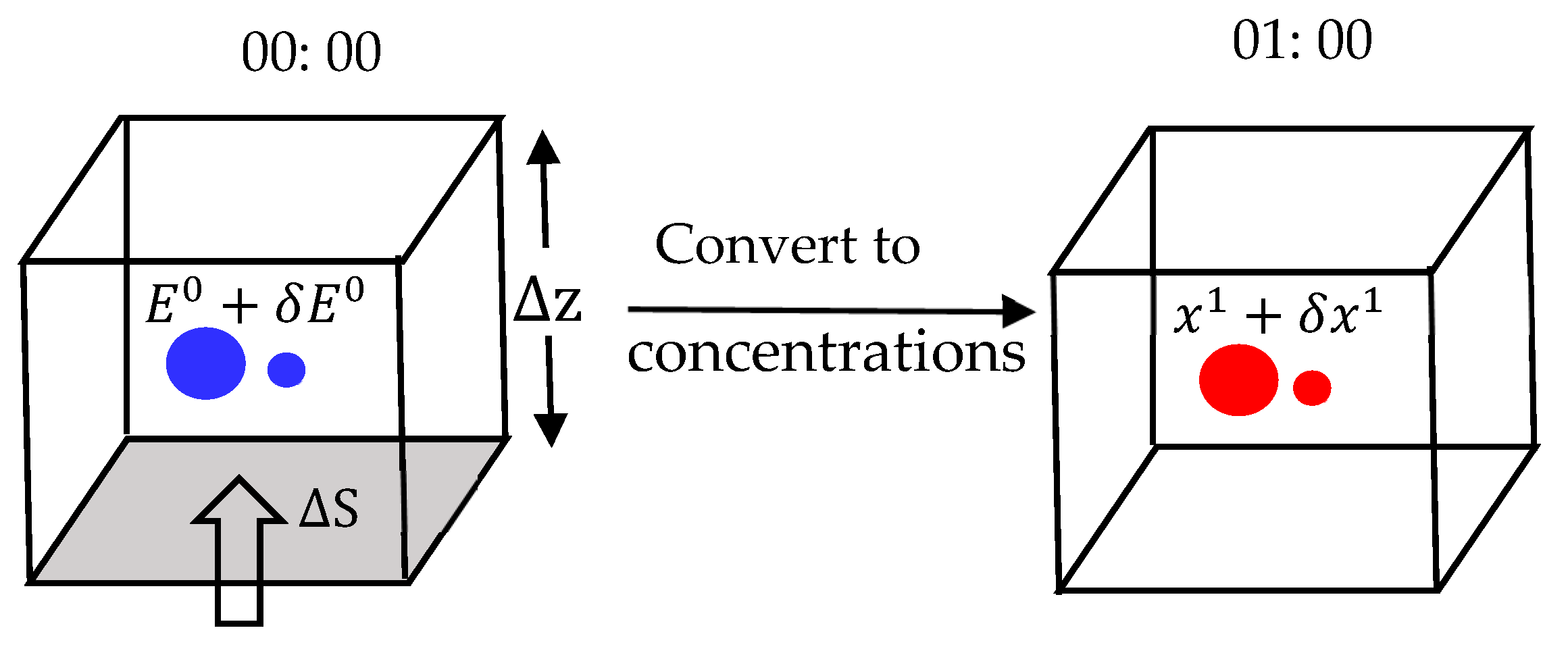
2.3.2. Conversion from Forecast Error to Emission Error
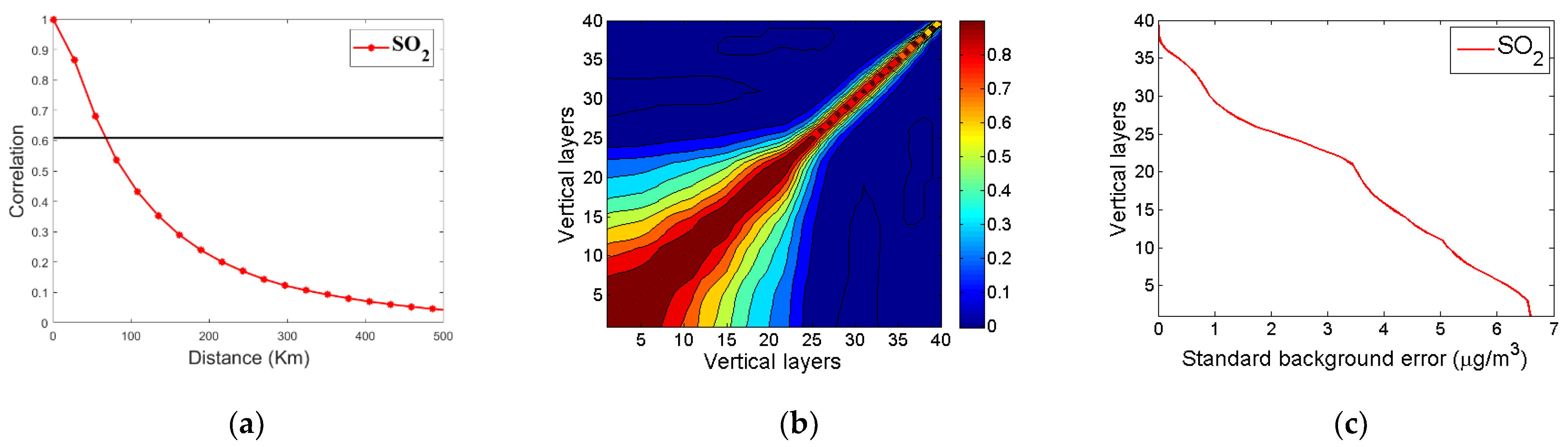
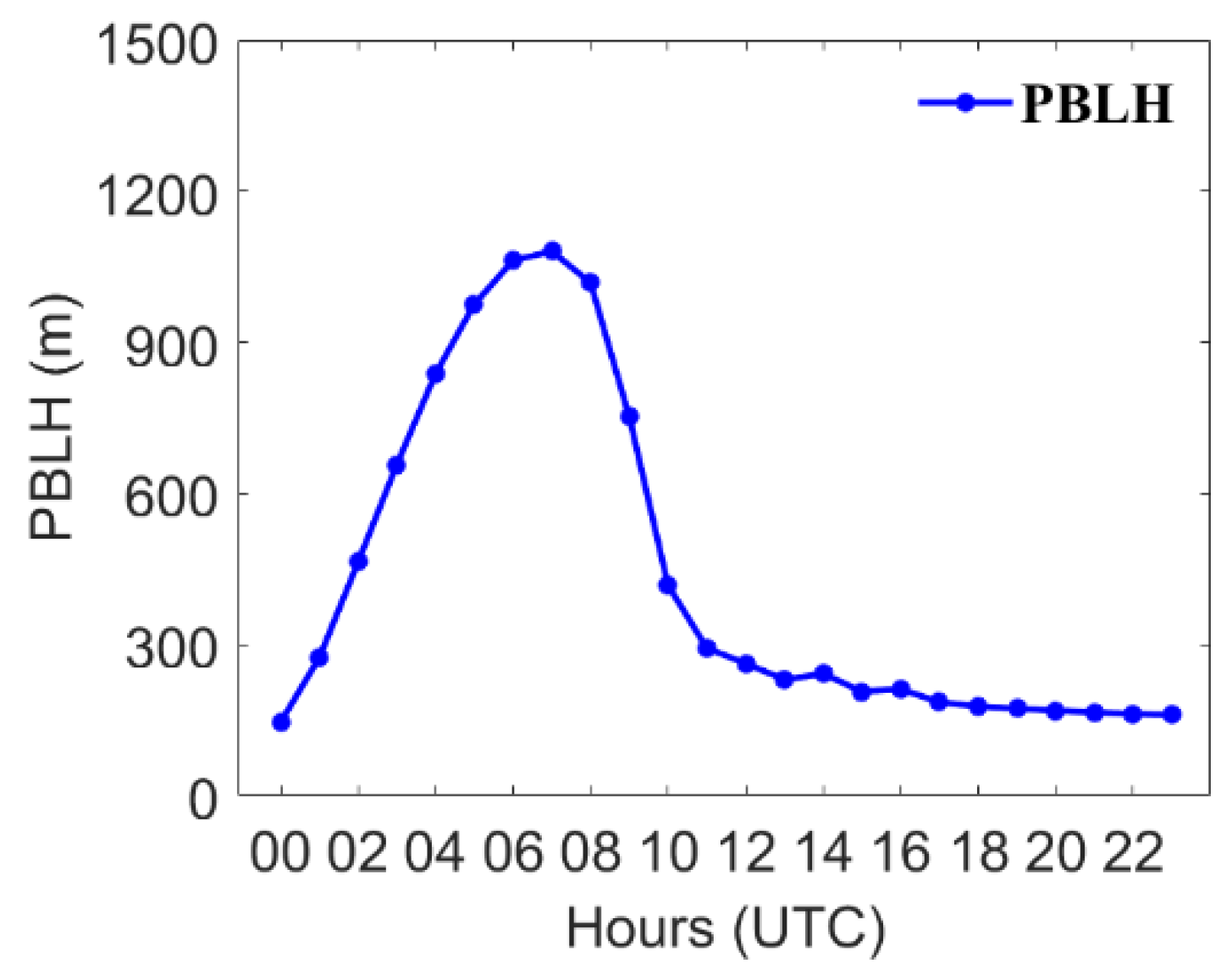
2.3.3. The Operational Consideration for Emission Optimization
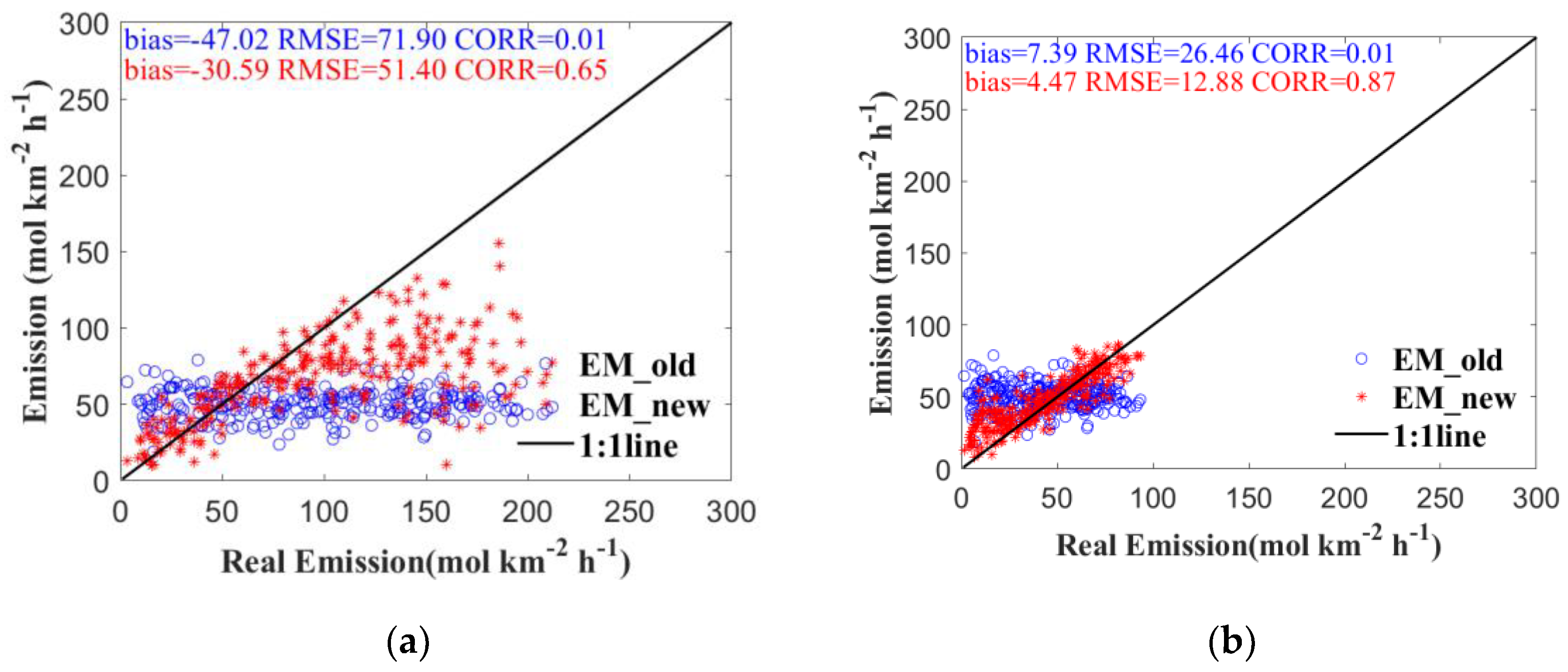
2.4. Observing Systems Simulation Experiment
2.5. Experimental Design
3. Results
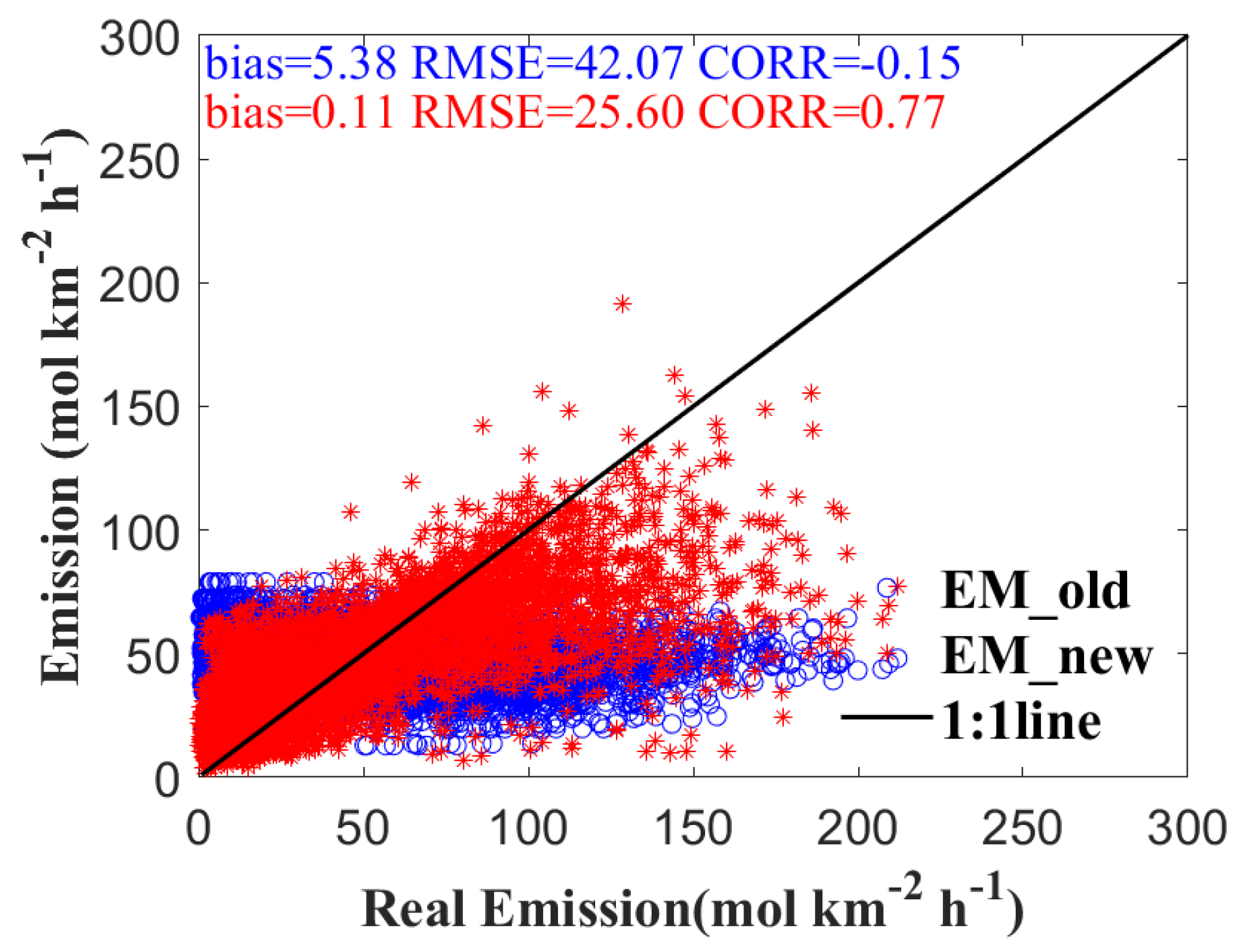
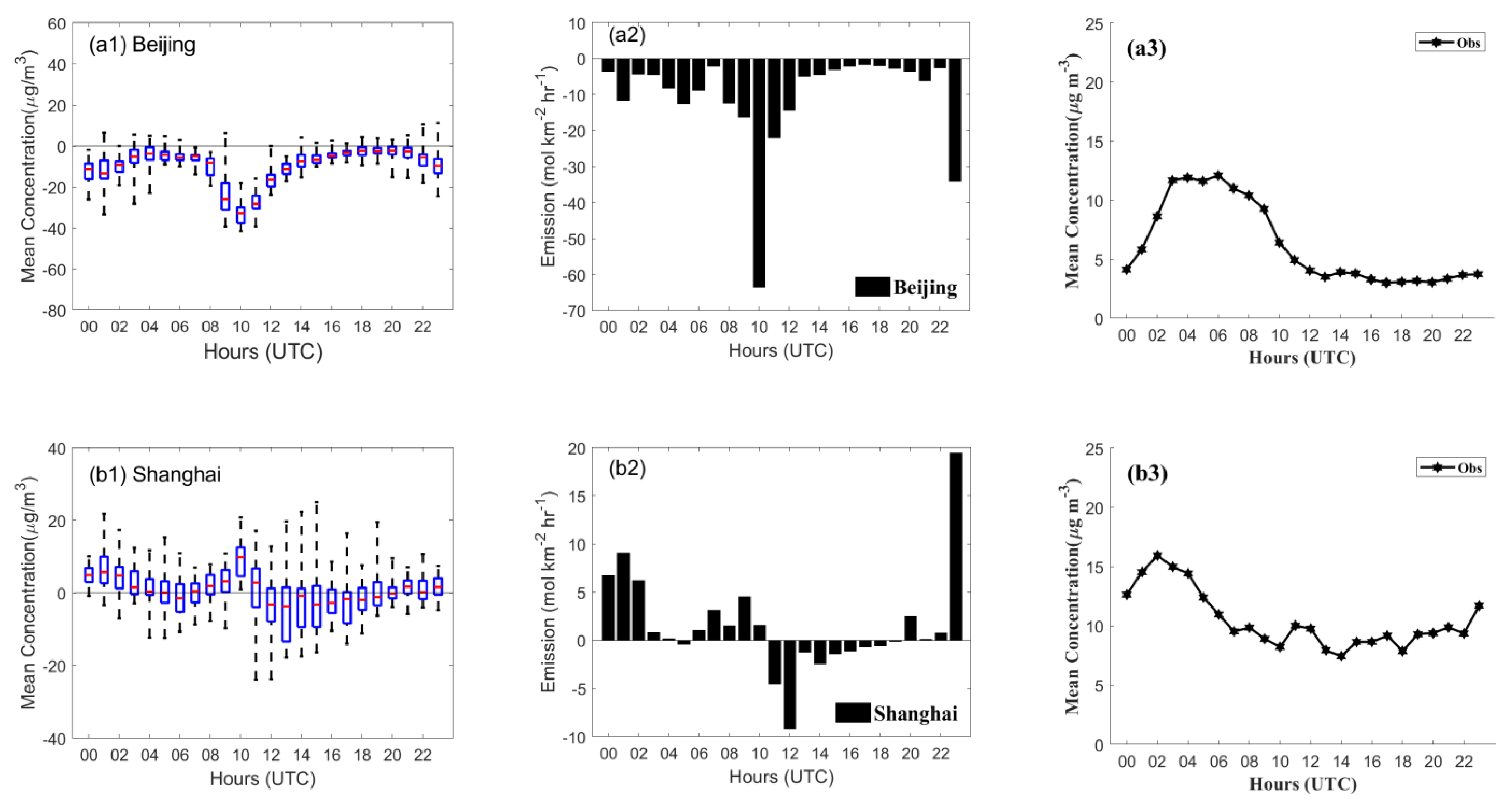
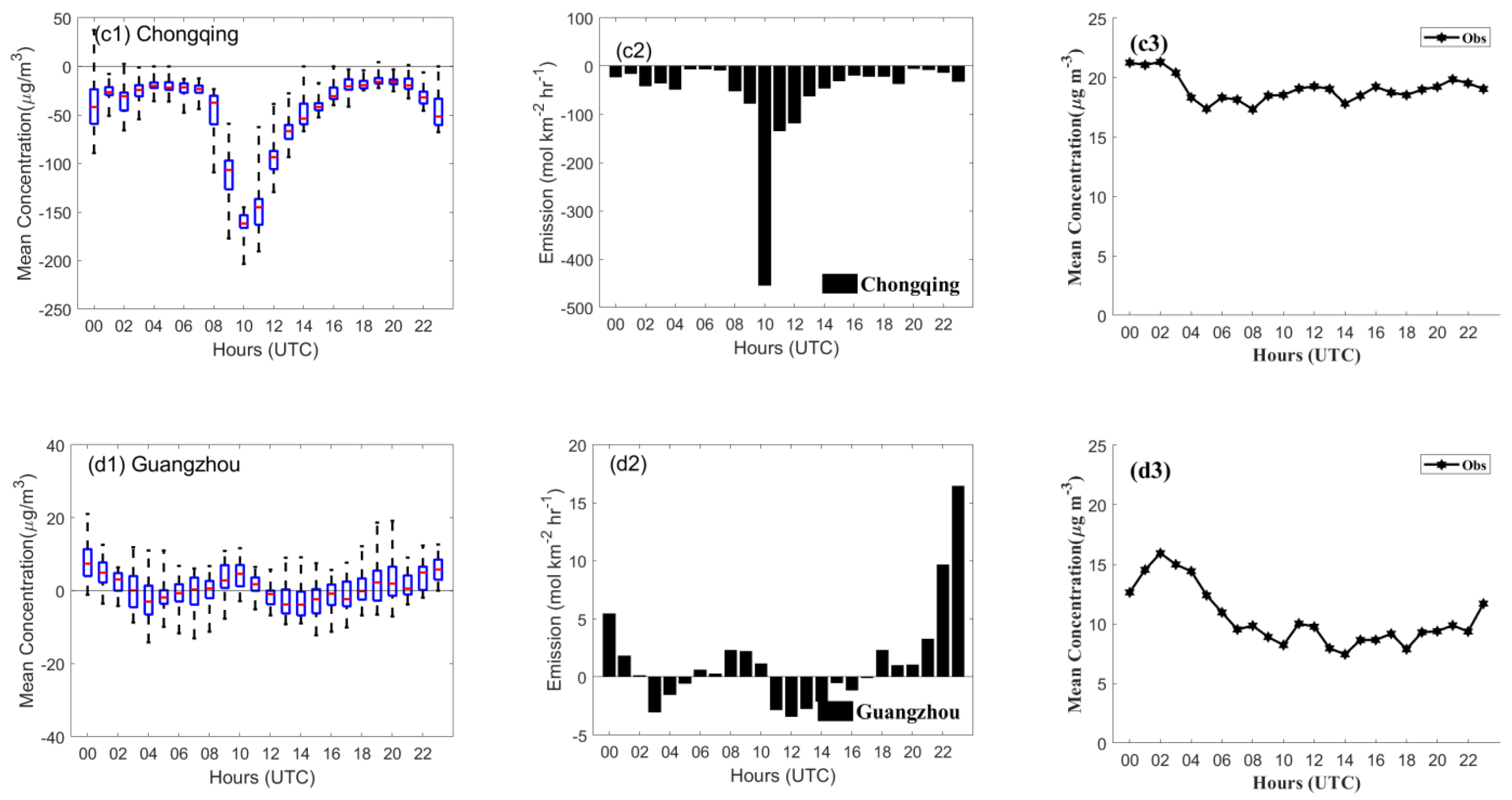
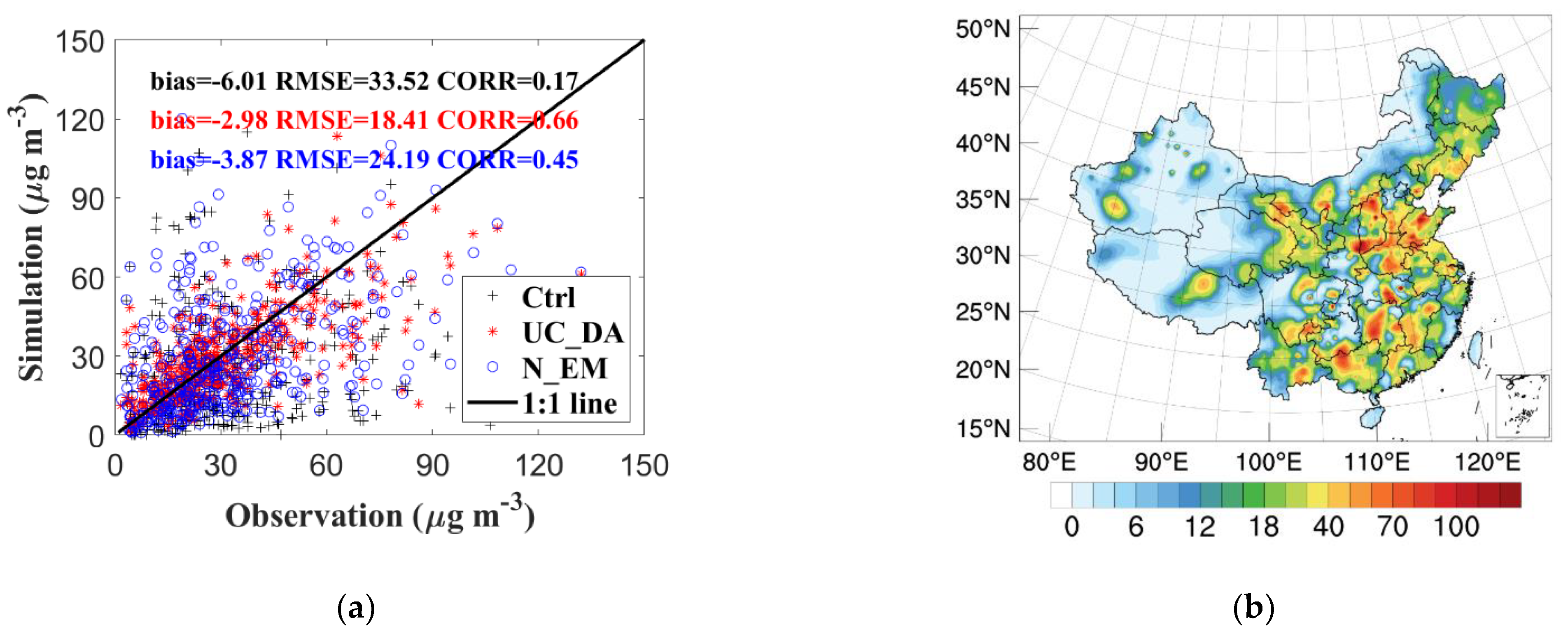
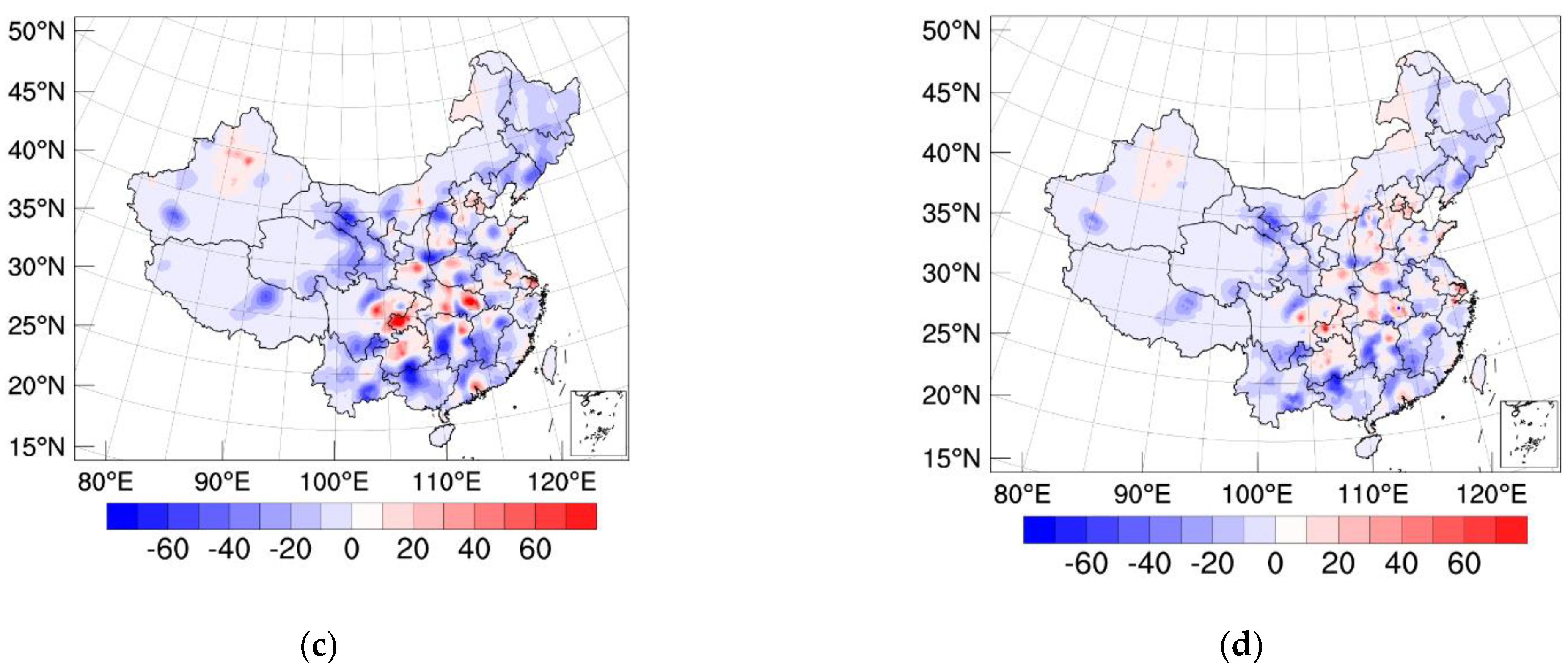
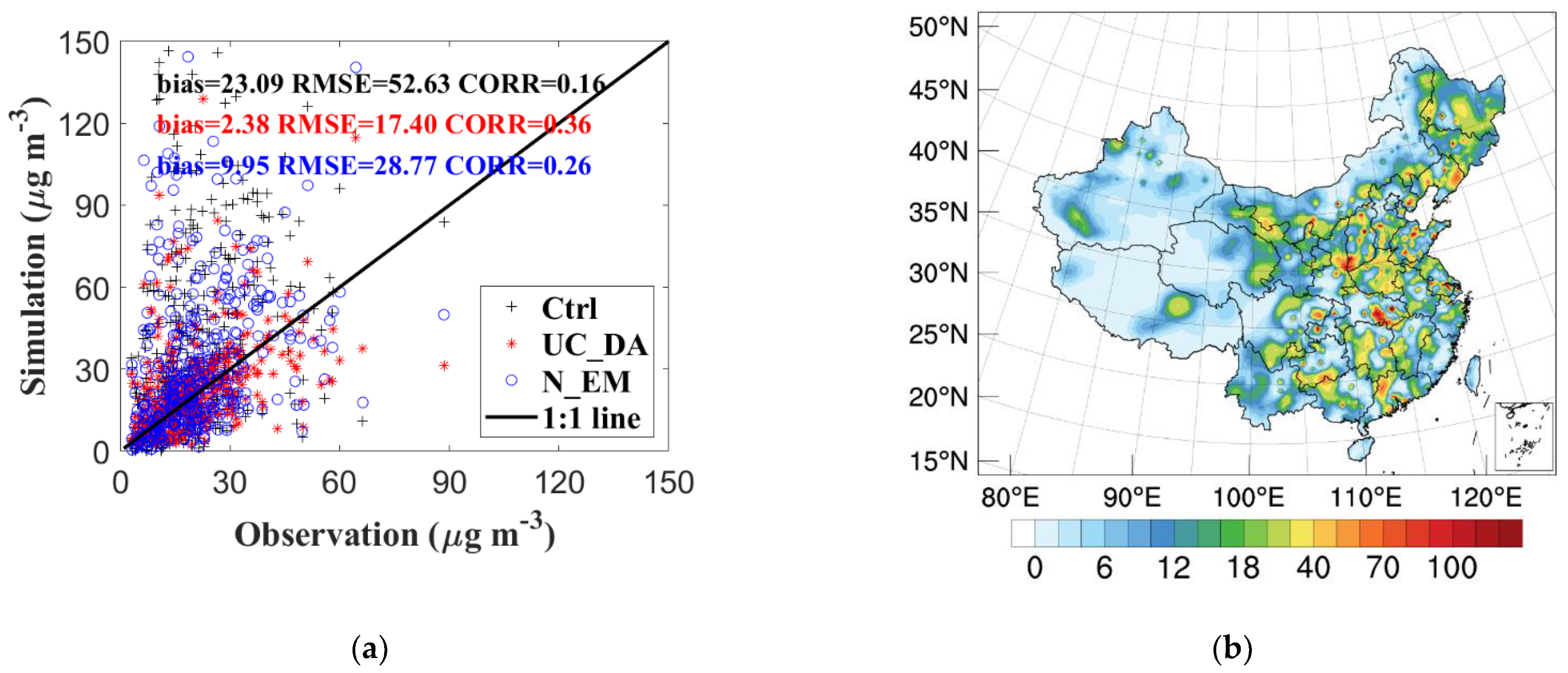
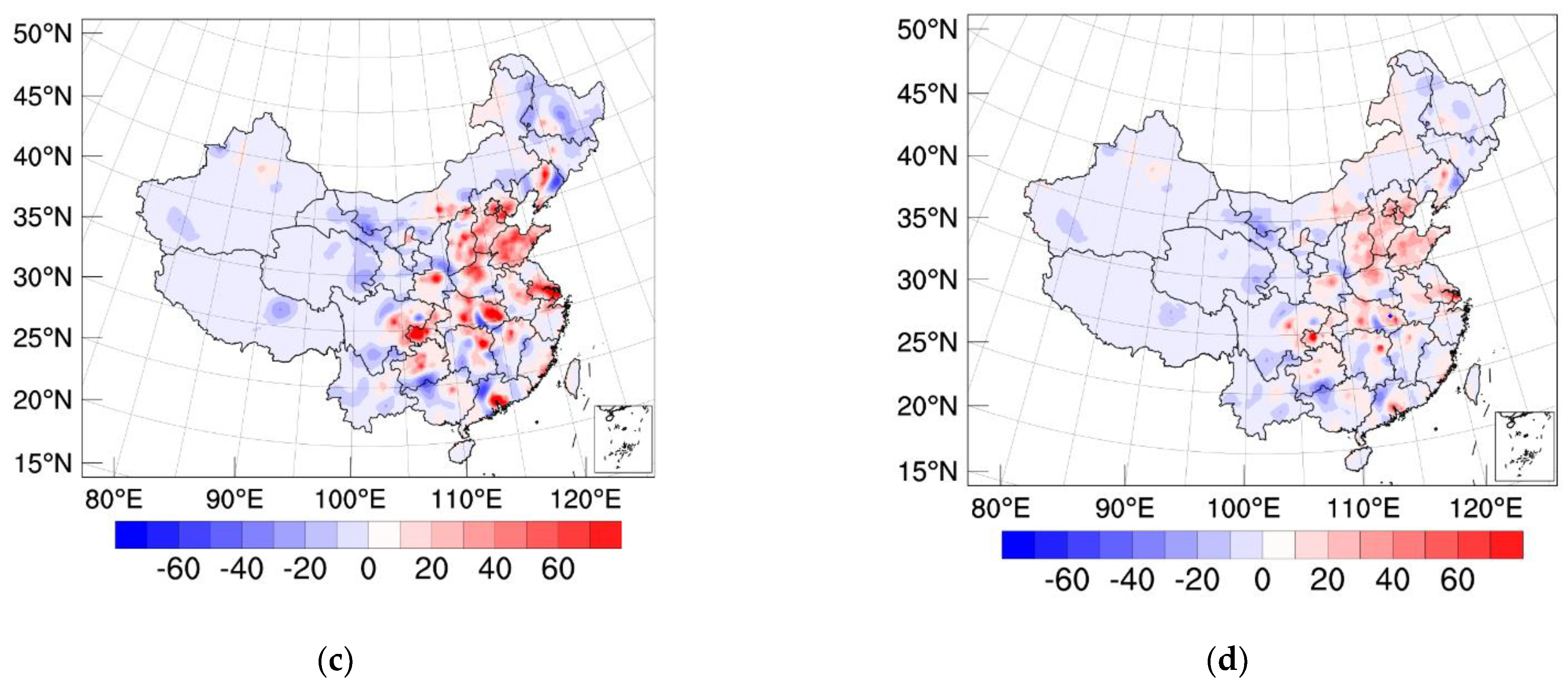
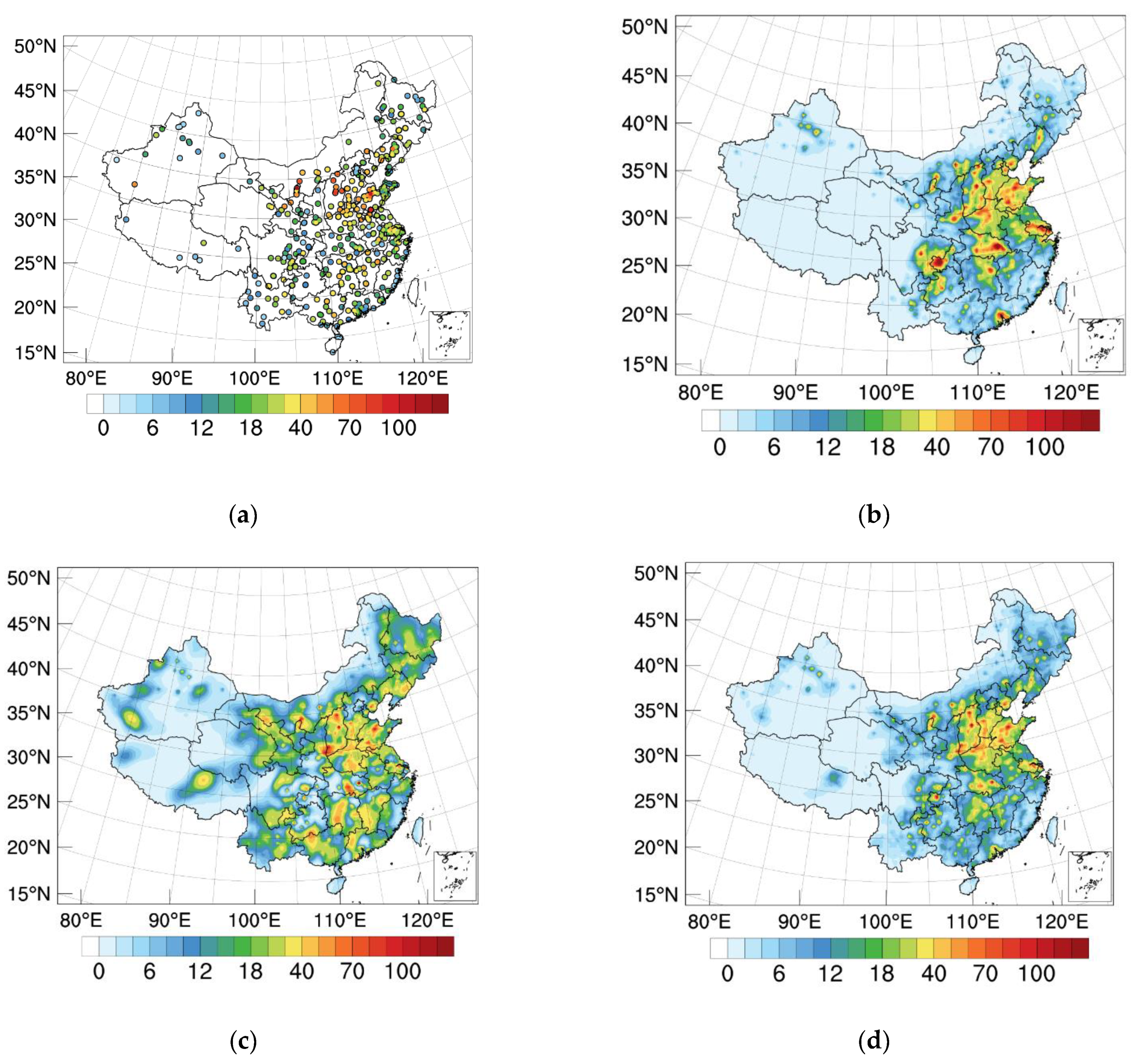
3.1. Increments of SO2 Concentration and Optimized Emissions
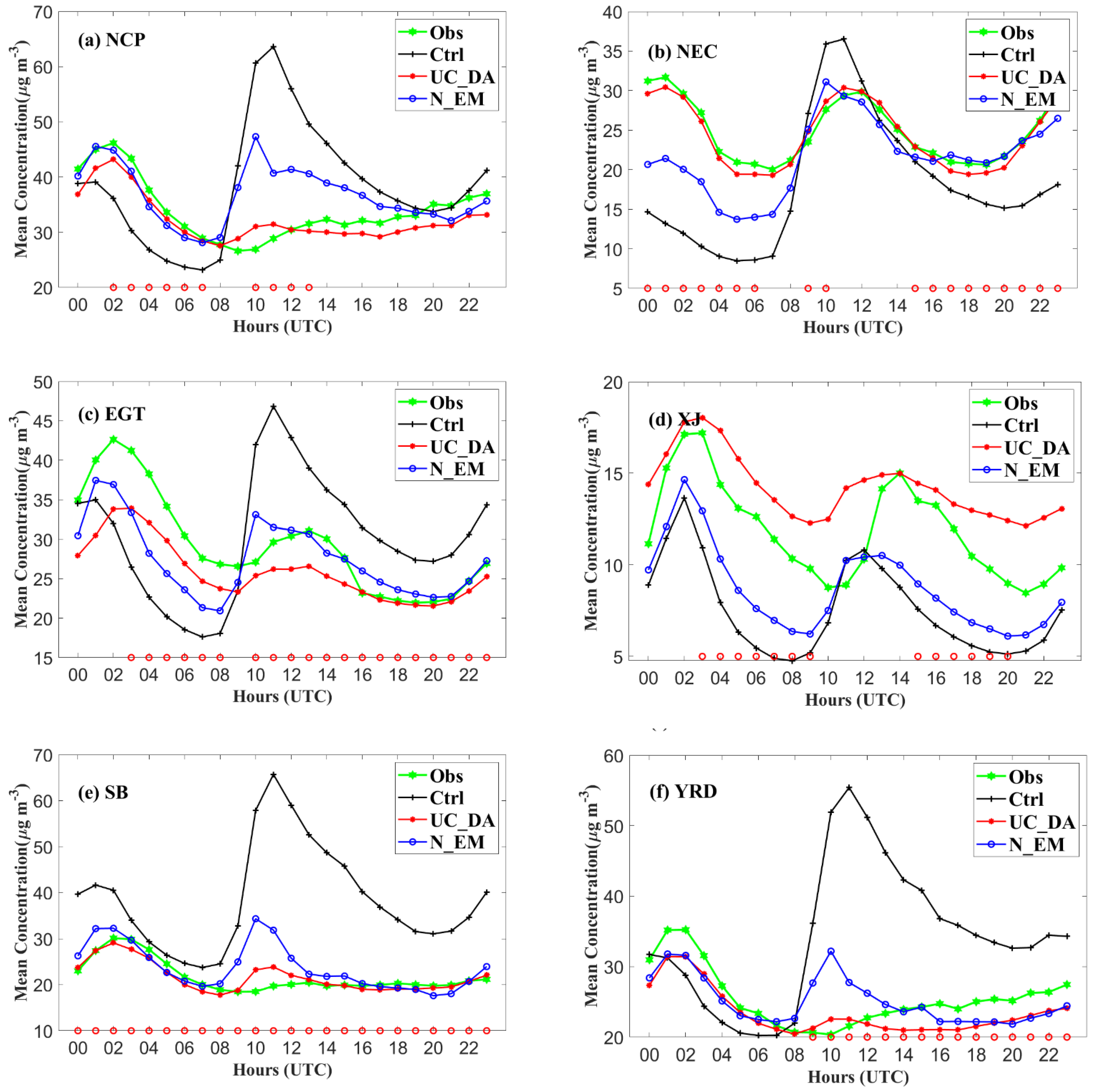
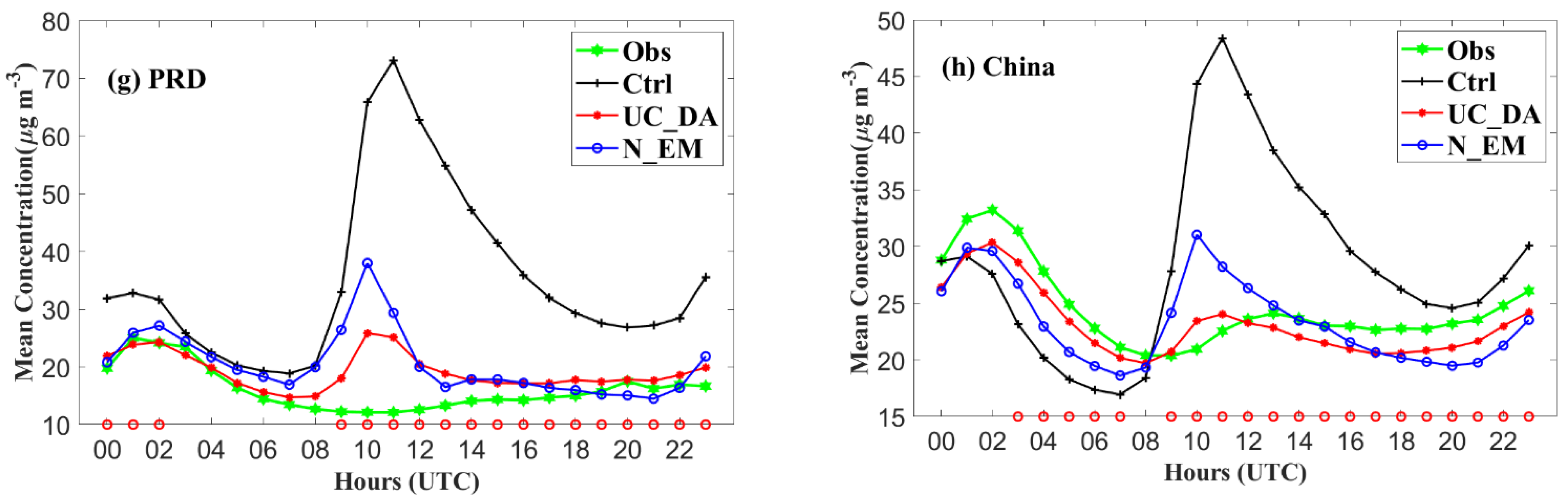
3.2. Forecast Performance
3.2.1. Improvement in Hourly SO2 Simulations
3.2.2. Spatial Distribution of SO2 Concentrations
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Koukouli, M.E.; Balis, D.S.; Theys, N.; Hedelt, P.; Richter, A.; Krotkov, N.; Li, C.; Taylor, M. Anthropogenic sulphur dioxide load over China as observed from different satellite sensors. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 145, 45–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Henze, D.K.; Zhu, L.; Song, Y.; Paulot, F.; Liu, X.; Pan, Y.; Lin, Y.; et al. Agricultural ammonia emissions in China: Reconciling bottom-up and top-down estimates. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 339–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Mclinden, C.; Fioletov, V.; Krotkov, N.; Carn, S.; Joiner, J.; Streets, D.; He, H.; Ren, X.; Li, Z. India Is Overtaking China as the World’s Largest Emitter of Anthropogenic Sulfur Dioxide. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 14304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, B.; Tong, D.; Li, M.; Liu, F.; Hong, C.; Geng, G.; Li, H.; Li, X.; Peng, L.; Qi, J.; et al. Trends in China’s anthropogenic emissions since 2010 as the consequence of clean air actions. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 14095–14111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, W.; Zhong, Q.; Yun, X.; Zhu, X.; Huang, T.; Shen, H.; Chen, H.; Zhou, F.; Liu, J.; Wang, X.; et al. Improvement of a Global High-Resolution Ammonia Emission Inventory for Combustion and Industrial Sources with New Data from the Residential and Transportation Sectors. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 2821–2829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, J.; Zheng, B.; Li, M.; Yu, F.; Chen, C.; Liu, F.; Zhou, X.; Yuan, J.; Zhang, Q.; He, K. A high-resolution air pollutants emission inventory in 2013 for the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region, China. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 170, 156–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bocquet, M.; Elbern, H.; Eskes, H.; Hirtl, M.; Žabkar, R.; Carmichael, G.R.; Flemming, J.; Inness, A.; Pagowski, M.; Pérez Camaño, J.L.; et al. Data assimilation in atmospheric chemistry models: Current status and future prospects for coupled chemistry meteorology models. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 5325–5358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calkins, C.; Ge, C.; Wang, J.; Anderson, M.; Yang, K. Effects of meteorological conditions on sulfur dioxide air pollution in the North China plain during winters of 2006–2015. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 147, 296–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Gong, S.; Yu, Y.; Yu, L.; Wu, L.; Mao, H.; Song, C.; Zhao, S.; Liu, H.; Li, X.; et al. Air pollution characteristics and their relation to meteorological conditions during 2014–2015 in major Chinese cities. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 223, 484–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubin, J.I.; Reid, J.S.; Hansen, J.A.; Anderson, J.L.; Holben, B.N.; Xian, P.; Weatphal, D.L.; Zhang, J. Assimilation of AERONET and MODIS AOT observations using variational and ensemble data assimilation methods and its impact on aerosol forecasting skill. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2017, 122, 4967–4992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Pagowski, M.; Chai, T.; Pan, L.; Lee, P.; Barry, B.; Rajesh, K.; Luca, D.M.; Daniel, T.; Hyun-Cheol, K. A case study of aerosol data assimilation with the Community Multi-scale Air Quality Model over the contiguous United States using 3D-Var and optimal interpolation methods. Geosci. Model Dev. 2017, 10, 4743–4758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Liu, Z.; Ban, J.; Chen, M. The 2015 and 2016 winter-time air pollution in China: SO2 emission changes derived from a WRF-Chem/EnKF coupled data assimilation system. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 8619–8650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.; Han, Z.; Liu, Z.; Li, M.; Xin, J.; Tao, Z.; Li, J.; Kang, J.E.; Huang, K.; Dong, X.; et al. Air quality and climate change, Topic 3 of the Model Inter-Comparison Study for Asia Phase III (MICS-Asia III)—Part 1: Overview and model evaluation. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 4859–4884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sha, T.; Ma, X.; Jia, H.; Ding, J.; Zhang, Y.; Chang, Y. Exploring the influence of two inventories on simulated air pollutants during winter over the Yangtze River Delta. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 206, 170–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sha, T.; Ma, X.; Zhang, H.; Janechek, N.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Castro, G.L.; Jenerette, G.D.; Wang, J. Impacts of Soil NOx Emission on O3 Air Quality in Rural California. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 7113–7122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, Z.; Larson, S.M.; Williams, A.; Caughey, M.; Wuebbles, D.J. Sensitivity of regional ozone concentrations to temporal distribution of emissions. Atmos. Environ. 2004, 38, 6279–6285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Liang, X.; Jiang, W.; Tao, Z.; Wang, X.L.J.; Liu, H.; Han, Z.; Liu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Grell, G.A.; et al. WRF-Chem simulation of East Asian air quality: Sensitivity to temporal and vertical emissions distributions. Atmos. Environ. 2010, 44, 660–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zhang, Q.; Kurokawa, J.I.; Woo, J.H.; He, K.; Lu, Z.; Ohara, T.; Song, Y.; Streets, D.G.; Carmichael, G.R.; et al. MIX: A mosaic Asian anthropogenic emission inventory under the international collaboration framework of the MICS-Asia and HTAP. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 935–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Fu, H.; Cui, L.; Li, J.; Wu, Y.; Meng, Y.; Wang, Y.; Chen, J. The spatiotemporal variation and key factors of SO2 in 336 cities across China. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 210, 602–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Streets, D.G.; Carmichael, G.R.; He, K.B.; Huo, H.; Kannari, A.; Klimont, Z.; Park, I.S.; Reddy, S.; Fu, J.S.; et al. Asian emissions in 2006 for the NASA INTEX-B mission. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2009, 9, 5131–5153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Hua, S.; Wang, K.; Qiu, P.; Wu, B.; Shao, P.; Liu, X.; Wu, Y.; Xue, Y.; Hao, Y.; et al. Spatial-temporal variation characteristics of air pollution in Henan of China: Localized emission inventory, WRF/Chem simulations and potential source contribution analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 624, 396–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, D.T. Methane emissions from natural gas production and use: Reconciling bottom-up and top-down measurements. Curr. Opin. Chem. Eng. 2014, 5, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Nakatani, J.; Shan, Y.; Moriguchi, Y. Inter-regional spillover of China’s sulfur dioxide (SO2) pollution across the supply chains. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 207, 418–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granier, C.; Bessagnet, B.; Bond, T.; D’Angiola, A.; Denier van der Gon, H.; Frost, G.J.; Heil, A.; Kaiser, J.W.; Kinne, S.; Klimont, Z.; et al. Evolution of anthropogenic and biomass burning emissions of air pollutants at global and regional scales during the 1980–2010 period. Clim. Change 2011, 109, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Nielsen, C.P.; Lei, Y.; McElroy, M.B.; Hao, J. Quantifying the uncertainties of a bottom-up emission inventory of anthropogenic atmospheric pollutants in China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 2295–2308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, M.; Fu, J.S.; Zhu, J.; Liao, H.; Li, J.; Huang, K.; Ge, B.; Wang, X.; et al. MICS-Asia III: Multi-model comparison and evaluation of aerosol over East Asia. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 11911–11937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guenther, A.B.; Jiang, X.; Heald, C.L.; Sakulyanontvittaya, T.; Duhl, T.; Emmons, L.K.; Wang, X. The Model of Emissions of Gases and Aerosols from Nature Version 2.1 (MEGAN2.1): An Extended and Updated Framework for Modeling Biogenic Emissions. Geosci. Model Dev. 2012, 5, 1471–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crippa, M.; Guizzardi, D.; Muntean, M.; Schaaf, E.; Dentener, F.; van Aardenne, J.A.; Monni, S.; Doering, U.; Olivier, J.G.J.; Pagliari, V.; et al. Gridded emissions of air pollutants for the period 1970–2012 within EDGAR v4.3.2. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2018, 10, 1987–2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssens-Maenhout, G.; Crippa, M.; Guizzardi, D.; Dentener, F.; Muntean, M.; Pouliot, G.; Keating, T.; Zhang, Q.; Kurokawa, J.; Wankmüller, R.; et al. HTAP_v2.2: A mosaic of regional and global emission grid maps for 2008 and 2010 to study hemispheric transport of air pollution. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 11411–11432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Sha, T.; Wang, J.; Jia, H.; Tian, R. Investigating impact of emission inventories on PM2.5 simulations over North China Plain by WRF-Chem. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 195, 125–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; He, J.; Liu, H.; Miao, Y.; Liu, H.; Zhai, P. Impact of various emission control schemes on air quality using WRF-Chem during APEC China 2014. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 140, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houyoux, M.R.; Vukovich, J.M.; Coats, C.J., Jr.; Wheeler, N.J.M.; Kasibhatla, P.S. Emission inventory development and processing for the Seasonal Model for Regional Air Quality (SMRAQ) project. J. Geophys. Res. 2000, 105, 9079–9090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byun, D.; Schere, K.L. Review of the Governing Equations, Computational Algorithms, and Other Components of the Models-3 Community Multiscale Air Quality (CMAQ) Modeling System. Appl. Mech. Rev. 2006, 59, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, K.; Pham, T.; Ho, B.; Nguyen, T.; Nguyen, H. Air emission inventory and application TAPM-AERMOD models to study air quality from 34 ports in Ho Chi Minh City. Sci. Technol. Dev. J. Sci. Earth Environ. 2018, 2, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhou, G.; Xu, J.; Xie, Y.; Chang, L.; Gao, W.; Gu, Y.; Zhou, J. Numerical air quality forecasting over eastern China: An operational application of WRF-Chem. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 153, 94–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der A, R.J.; Mijling, B.; Ding, J.; Koukouli, M.E.; Liu, F.; Li, Q.; Mao, H.; Theys, N. Cleaning up the air: Effectiveness of air quality policy for SO2 and NOx emissions in China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 1775–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Mijling, B.; Levelt, P.F.; Hao, N. NOx emission estimates during the 2014 Youth Olympic Games in Nanjing. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 9399–9412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Eskes, H.; Ding, J.; Mijling, B. Evaluation of modeling NO2 concentrations driven by satellite-derived and bottom-up emission inventories using in situ measurements over China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 4171–4186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Mijling, B.; Jalkanen, J.-P.; Johansson, L.; Levelt, P.F. Maritime NOx emissions over Chinese seas derived from satellite observations. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2018, 45, 2031–2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.; Martin, R.V.; van Donkelaar, A.; Lee, H.; Dickerson, R.R.; Hains, J.C.; Krotkov, N.; Richter, A.; Vinnikov, K.; Schwab, J.J. SO2 emissions and lifetimes: Estimates from inverse modeling using in situ and global, space-based (SCIAMACHY and OMI) observations. J. Geophys. Res. 2011, 116, D06304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazaki, K.; Eskes, H.J.; Sudo, K.; Zhang, C. Global lightning NOx production estimated by an assimilation of multiple satellite data sets. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 3277–3305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Zhu, J.; Wang, Z.F.; Gbaguidi, A.; Lin, C.Y.; Xin, J.Y.; Song, T.; Hu, B. Limitations of ozone data assimilation with adjustment of NOx emissions: Mixed effects on NO2 forecasts over Beijing and surrounding areas. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 6395–6405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yumimoto, K.; Uno, I. Adjoint inverse modeling of CO emissions over Eastern Asia using four-dimensional variational data assimilation. Atmos. Environ. 2006, 40, 6836–6845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yumimoto, K.; Uno, I.; Sugimoto, N.; Shimizu, A.; Satake, S. Adjoint inverse modeling of dust emission and transport over East Asia. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34, L08806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koukouli, M.E.; Theys, N.; Ding, J.; Zyrichidou, I.; Mijling, B.; Balis, D. Updated SO2 emission estimates over China using OMI/Aura observations. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2018, 11, 1817–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fioletov, V.E.; McLinden, C.A.; Krotkov, N.; Li, C. Lifetimes and emissions of SO2 from point sources estimated from OMI. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2015, 42, 1969–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Xu, X.; Henze, D.K.; Qu, Z.; Yang, K. Inverse modeling of SO2 and NOx emissions over China using multisensor satellite data—Part 1: Formulation and sensitivity analysis. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 6631–6650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhou, M.; Henze, D.K.; Ge, C.; Wang, W. Inverse modeling of SO2 and NOx emissions over China using multisensor satellite data—Part 2: Downscaling techniques for air quality analysis and forecasts. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 6651–6670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Tang, K.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Feng, W.; Zhang, H.; Liao, H.; Hu, J.; Long, X.; Shi, C.; et al. Is the efficacy of satellite-based inversion of SO2 emission model dependent? Environ. Res. Lett. 2021, 16, 035018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, T.; Cheng, Y.; Goto, D.; Li, Y.; Tang, X.; Shi, G.; Nakajima, T. Revealing the sulfur dioxide emission reductions in China by assimilating surface observations in WRF-Chem. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2021, 21, 4357–4379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K. Multi-resolution emission Inventory for China (MEIC): Model framework and 1990–2010 anthropogenic emissions. In Proceedings of the International Global Atmospheric Chemistry Conference, Beijing, China, 17–21 September 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, F.; Yang, X.; Ji, C.; Li, Y.; Deng, F.; Dong, M. Establishment and assessment of hourly high-resolution gridded air temperature data sets in Zhejiang, China. Meteorol. Appl. 2019, 26, 396–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, Q.; Fu, W.; Liu, Y.; Li, T.; Shi, K.; Sivakumar, B. Evaluation of Quantitative Precipitation Predictions by ECMWF, CMA, and UKMO for Flood Forecasting: Application to Two Basins in China. Nat. Hazards Rev. 2018, 19, 05018003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gustafson, W.I., Jr.; Chapman, E.G.; Ghan, S.J.; Easter, R.C.; Fast, J.D. Impact on modeled cloud characteristics due to simplified treatment of uniform cloud condensation nuclei during NEAQS 2004. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34, L19809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mlawer, E.J.; Taubman, S.J.; Brown, P.D.; Iacono, M.J.; Clough, S.A. Radiative transfer for inhomogeneous atmospheres: RRTM, a validated correlated-k model for the longwave. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1997, 102, 16663–16682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, M.-D.; Suarez, M.J. An Efficient Thermal Infrared Radiation Parameterization for Use in General Circulation Models; NASA Goddard Space Flight Center: Greenbelt, MD, USA, 1994; Volume 3, p. 25.
- Hong, S.Y.; Noh, Y.; Dudhia, J. A new vertical diffusion package with an explicit treatment of entrainment processes. Mon. Weather Rev. 2006, 134, 2318–2341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Yang, K.; Zhou, D.; Qin, J.; Guo, X. Improving the Noah land surface model in arid regions with an appropriate parameterization of the thermal roughness length. J. Hydrometeorol. 2010, 11, 995–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaveri, R.A.; Easter, R.C.; Fast, J.D.; Peters, L.K. Model for Simulating Aerosol Interactions and Chemistry (MOSAIC). J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2008, 113, D13204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaveri, R.A.; Peters, L.K. A new lumped structure photochemical mechanism for large-scale applications. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1999, 104, 30387–30415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zang, Z.; Li, Q.B.; Chao, Y.; Chen, D.; Ye, Z.; Liu, Y.; Liou, K.N. A three-dimensional variational data assimilation system for multiple aerosol species with WRF/Chem and an application to PM2.5 prediction. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 4265–4278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, Z.; Hao, Z.; Li, Y.; Pan, X.; You, W.; Li, Z.; Chen, D. Background error covariance with balance constraints for aerosol species and applications in variational data assimilation. Geosci. Model Dev. 2016, 9, 2623–2638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, Z.; Li, Z.; Pan, X.; Hao, Z.; You, W. Aerosol data assimilation and forecasting experiments using aircraft and surface observations during CalNex. Tellus B Chem. Phys. Meteorol. 2016, 68, 29812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garland, J.A.; Branson, J.R. The mixing height and mass balance of SO2 in the atmosphere above Great Britain. Atmos. Environ. 1967, 10, 353–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuesta-Mosquera, A.P.; Wahl, M.; Acosta-López, J.G.; García-Reynoso, J.A.; Aristizábal-Zuluaga, B.H. Mixing layer height and slope wind oscillation: Factors that control ambient air SO2 in a tropical mountain city. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2020, 52, 101852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattioli, F. Spectral analysis of wind and SO2 concentration in the Venice area. Atmos. Environ. 1977, 11, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, P. Effect of winds on SO2 and SPM concentrations in Delhi. Atmos. Environ. 2002, 36, 2925–2930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dana, M.T. SO2 versus sulfate wet deposition in the eastern United States. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 1980, 85, 4475–4480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Zang, Z.; Liu, D.; Yan, P.; Hu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; You, W. Development of a three-dimensional variational assimilation system for lidar profile data based on a size-resolved aerosol model in WRF–Chem model v3.9.1 and its application in PM2.5 forecasts across China. Geosci. Model Dev. 2020, 13, 6285–6301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Physical or Chemical Process | Option |
|---|---|
| Microphysics | Lin microphysics scheme [54] |
| Long-wave radiation | Rapid Radiative Transfer Model [55] |
| Shortwave radiation | Goddard Space Flight Center shortwave radiation scheme [56] |
| Boundary layer scheme | Yonsei University [57] |
| Land surface model | Noah land surface model [58] |
| Cumulus parameterization | Grell 3-D scheme [59] |
| Aerosol scheme | Model for Simulating Aerosol Interactions and Chemistry (MOSAIC-4 bin) [60] |
| Gas scheme | Carbon Bond Mechanism-Z [61] |
| Initial condition for chemical species | 10 d spin-up |
| Experiment Name | Emissions | Data for DA | Cycle DA |
|---|---|---|---|
| Control (Ctrl) | MEIC_2010 | / | / |
| Update Cycle DA (UC_DA) | MEIC_2010 | Surface observations of SO2 concentration | hourly |
| New Emission (N_EM) | 2015 optimized emissions | / | / |
| N Data | Mean Concentration | Bias | RMSE | CORR | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Obs | Ctrl | UC_DA | N_EM | Ctrl | UC_DA | N_EM | Ctrl | UC_DA | N_EM | Ctrl | UC_DA | N_EM | ||
| China | 241,023 | 23.41 | 28.95 | 22.96 | 23.16 | 5.54 | −0.45 | −0.25 | 33.81 | 19.56 | 25.04 | 0.18 | 0.51 | 0.27 |
| NCP | 36,866 | 33.81 | 38.42 | 32.19 | 36.78 | 4.61 | −1.62 | 2.97 | 39.10 | 23.91 | 32.96 | 0.24 | 0.70 | 0.40 |
| NEC | 29,939 | 24.77 | 18.12 | 24.24 | 19.91 | −6.65 | −0.53 | −4.86 | 28.67 | 22.11 | 25.51 | 0.17 | 0.55 | 0.31 |
| EGT | 43,683 | 30.84 | 30.09 | 25.83 | 27.34 | −0.74 | −5.01 | −3.49 | 36.42 | 24.42 | 30.64 | 0.14 | 0.56 | 0.28 |
| XJ | 16,819 | 11.59 | 6.99 | 13.93 | 8.21 | −4.60 | 2.34 | −3.37 | 17.09 | 13.25 | 14.87 | 0.16 | 0.37 | 0.21 |
| SB | 58,012 | 21.79 | 38.21 | 21.56 | 23.64 | 16.42 | −0.23 | 1.85 | 41.80 | 18.49 | 25.10 | 0.16 | 0.42 | 0.22 |
| YRD | 42,964 | 25.03 | 35.60 | 23.82 | 25.64 | 10.56 | −1.21 | 0.61 | 35.22 | 19.24 | 25.01 | 0.25 | 0.52 | 0.31 |
| PRD | 12,740 | 16.05 | 35.23 | 19.14 | 20.56 | 19.17 | 3.08 | 4.51 | 38.39 | 15.52 | 21.23 | 0.13 | 0.43 | 0.20 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, Y.; Zang, Z.; Chen, D.; Ma, X.; Liang, Y.; You, W.; Pan, X.; Wang, L.; Wang, D.; Zhang, Z. Optimization and Evaluation of SO2 Emissions Based on WRF-Chem and 3DVAR Data Assimilation. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 220. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14010220
Hu Y, Zang Z, Chen D, Ma X, Liang Y, You W, Pan X, Wang L, Wang D, Zhang Z. Optimization and Evaluation of SO2 Emissions Based on WRF-Chem and 3DVAR Data Assimilation. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(1):220. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14010220
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Yiwen, Zengliang Zang, Dan Chen, Xiaoyan Ma, Yanfei Liang, Wei You, Xiaobin Pan, Liqiong Wang, Daichun Wang, and Zhendong Zhang. 2022. "Optimization and Evaluation of SO2 Emissions Based on WRF-Chem and 3DVAR Data Assimilation" Remote Sensing 14, no. 1: 220. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14010220
APA StyleHu, Y., Zang, Z., Chen, D., Ma, X., Liang, Y., You, W., Pan, X., Wang, L., Wang, D., & Zhang, Z. (2022). Optimization and Evaluation of SO2 Emissions Based on WRF-Chem and 3DVAR Data Assimilation. Remote Sensing, 14(1), 220. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14010220







