An Observing System Simulation Experiment Framework for Air Quality Forecasts in Northeast Asia: A Case Study Utilizing Virtual Geostationary Environment Monitoring Spectrometer and Surface Monitored Aerosol Data
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
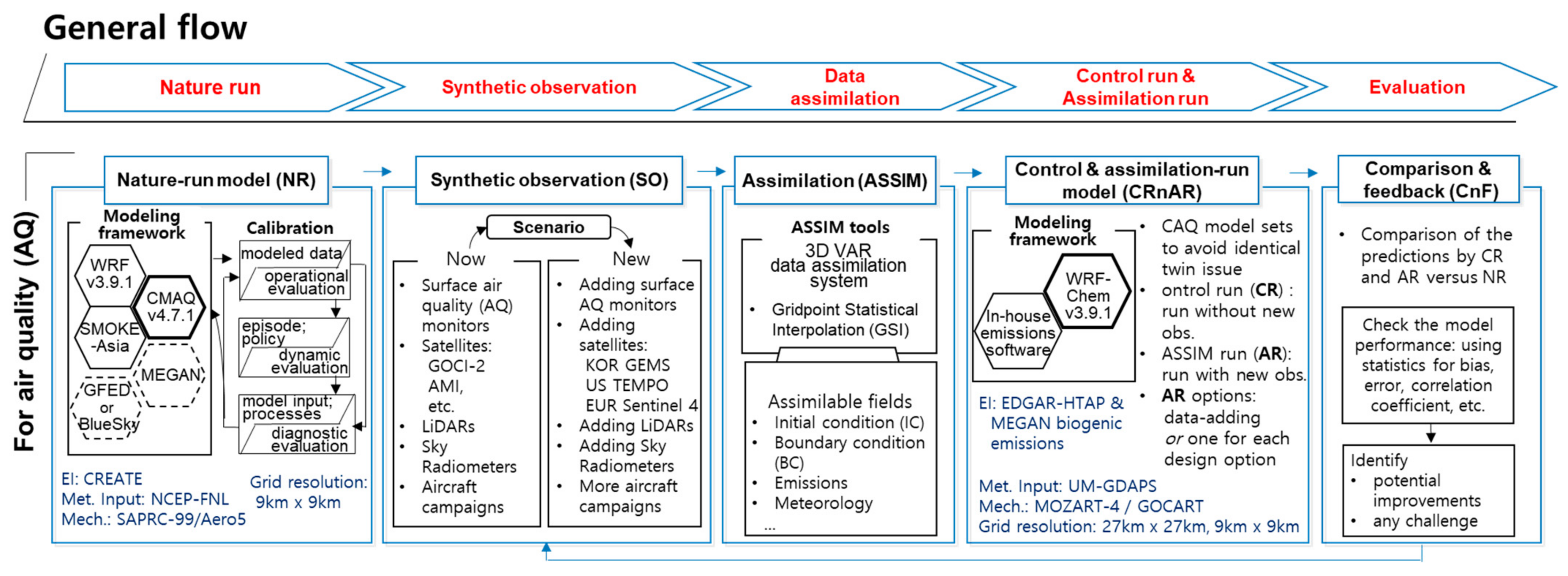
2.1. OSSE Framework for Regional Air Quality Forecasting
2.1.1. Nature Run Module
2.1.2. Synthetic Observation Module
2.1.3. Assimilation Module
2.1.4. Control Run and Assimilation Run Module
2.1.5. Comparison and Feedback Module
2.2. Implementation of PM2.5 Forecasting
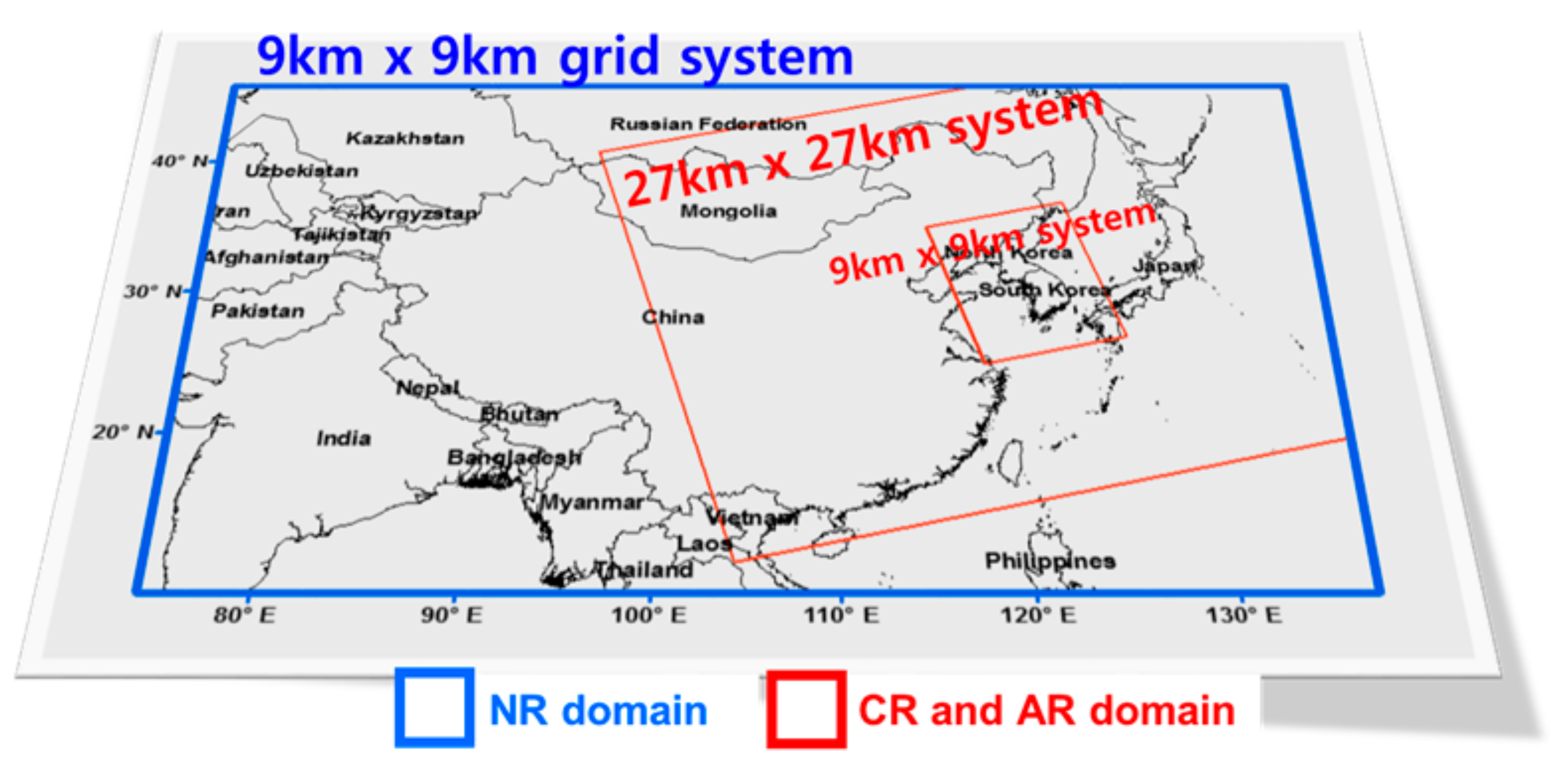
2.2.1. Spatial and Temporal Scope
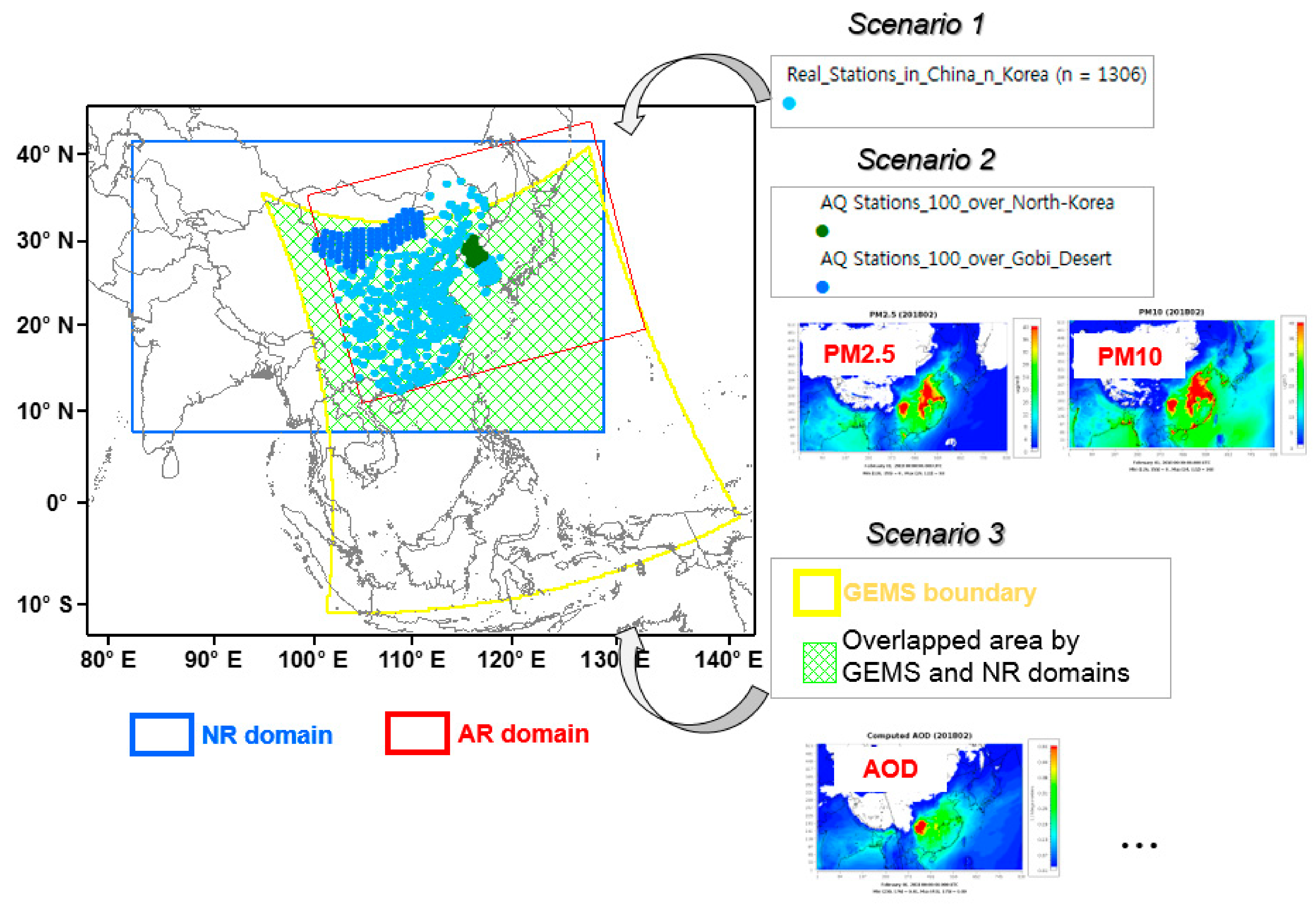
2.2.2. Scenarios and Data Reconstruction
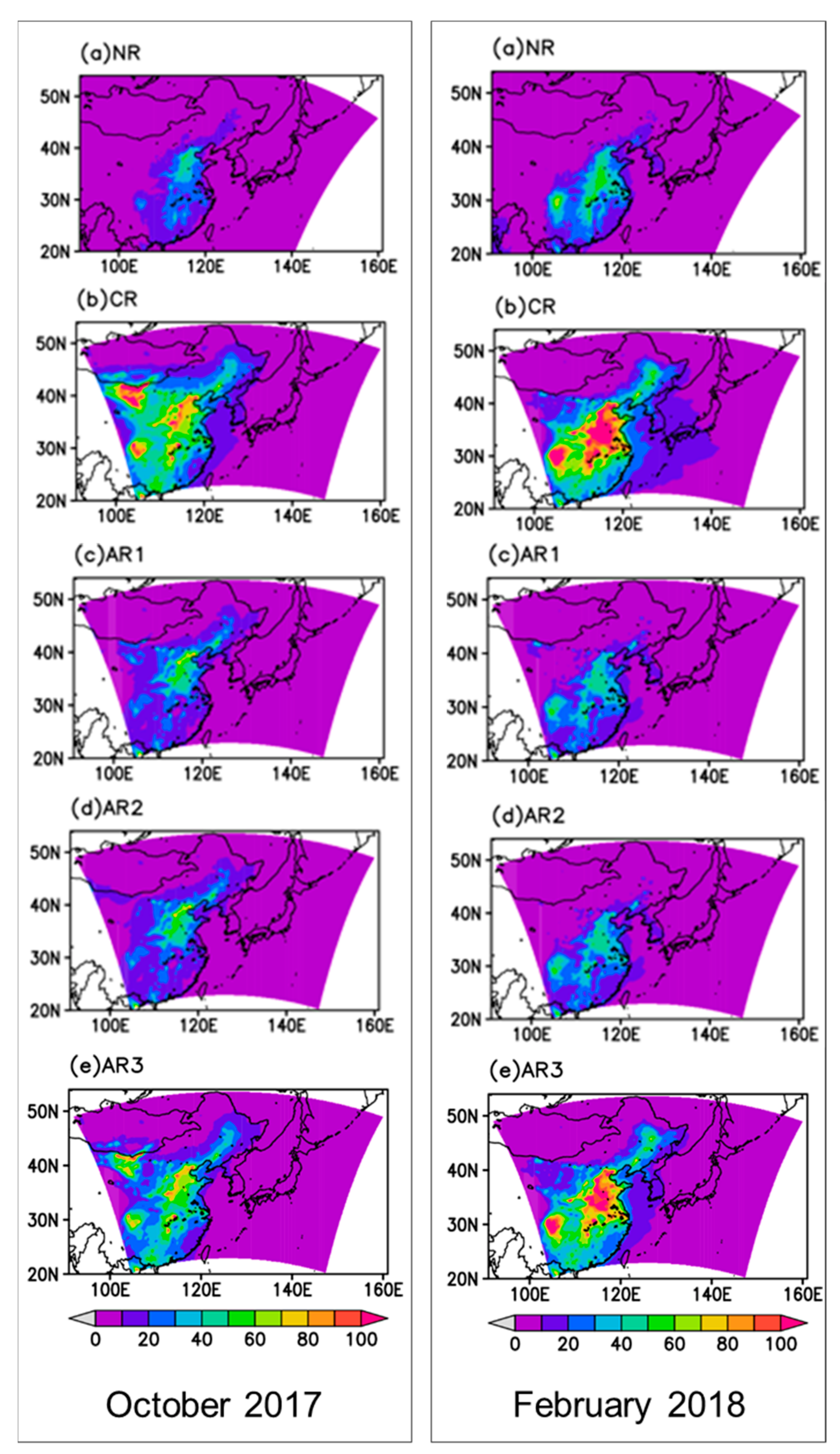
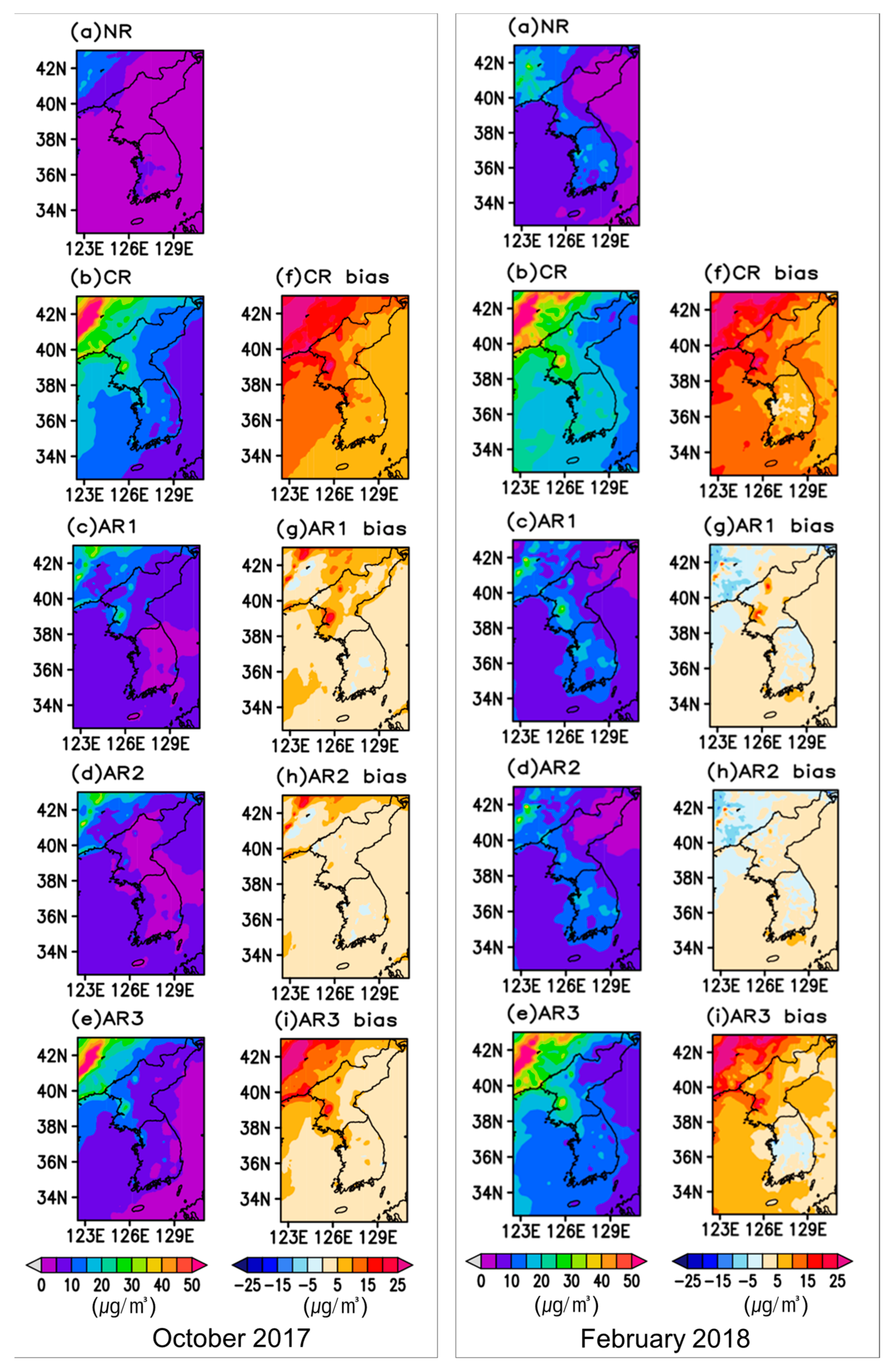
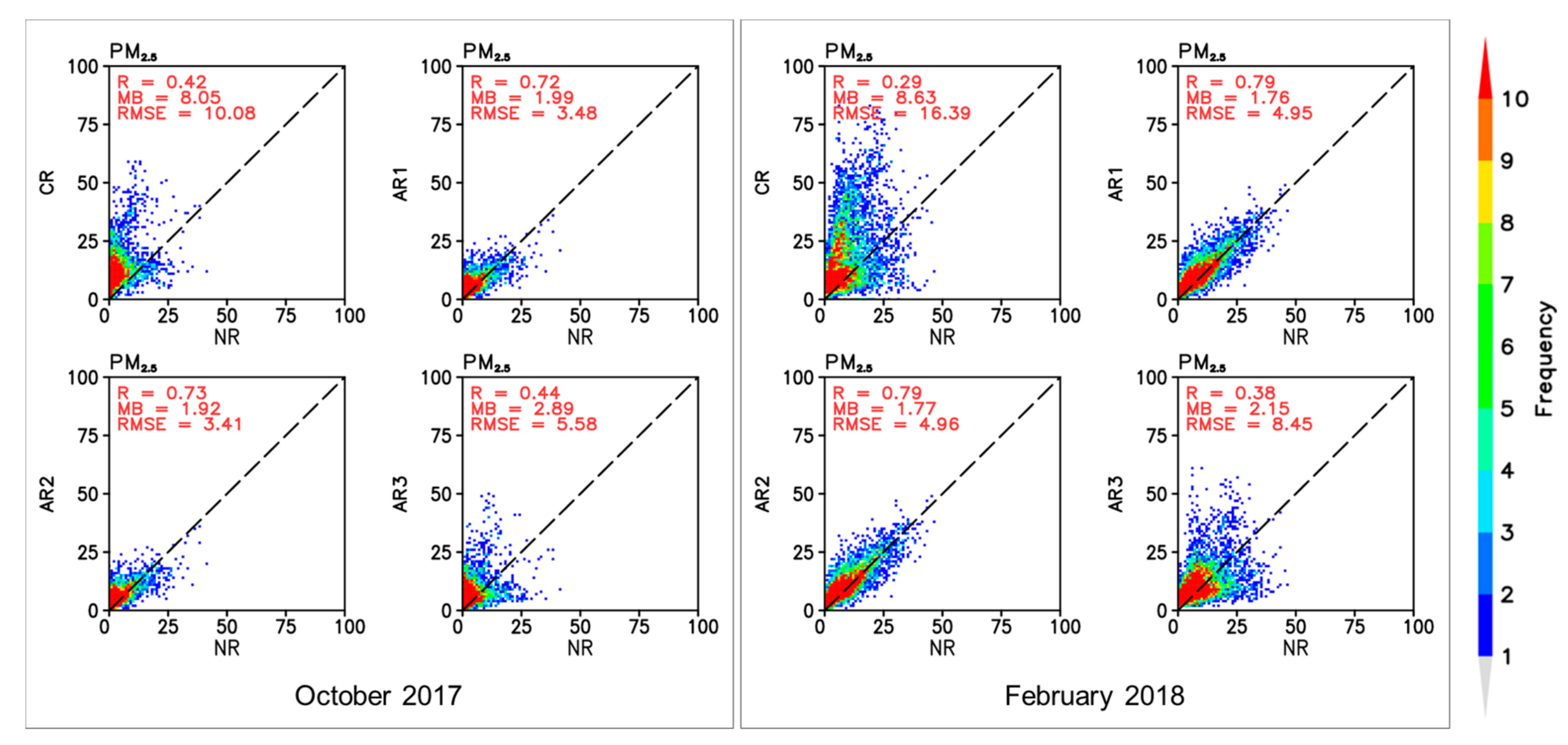
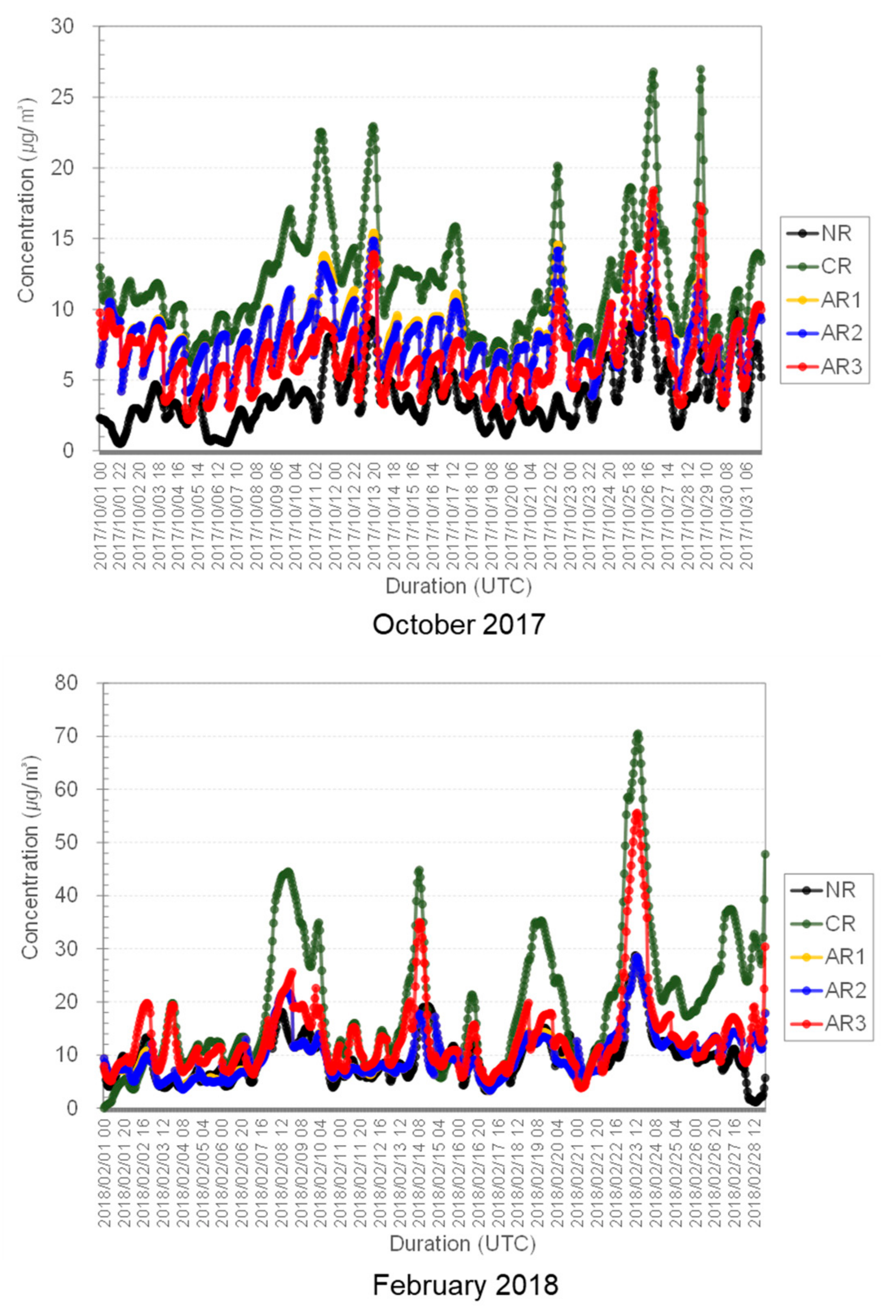
3. Results
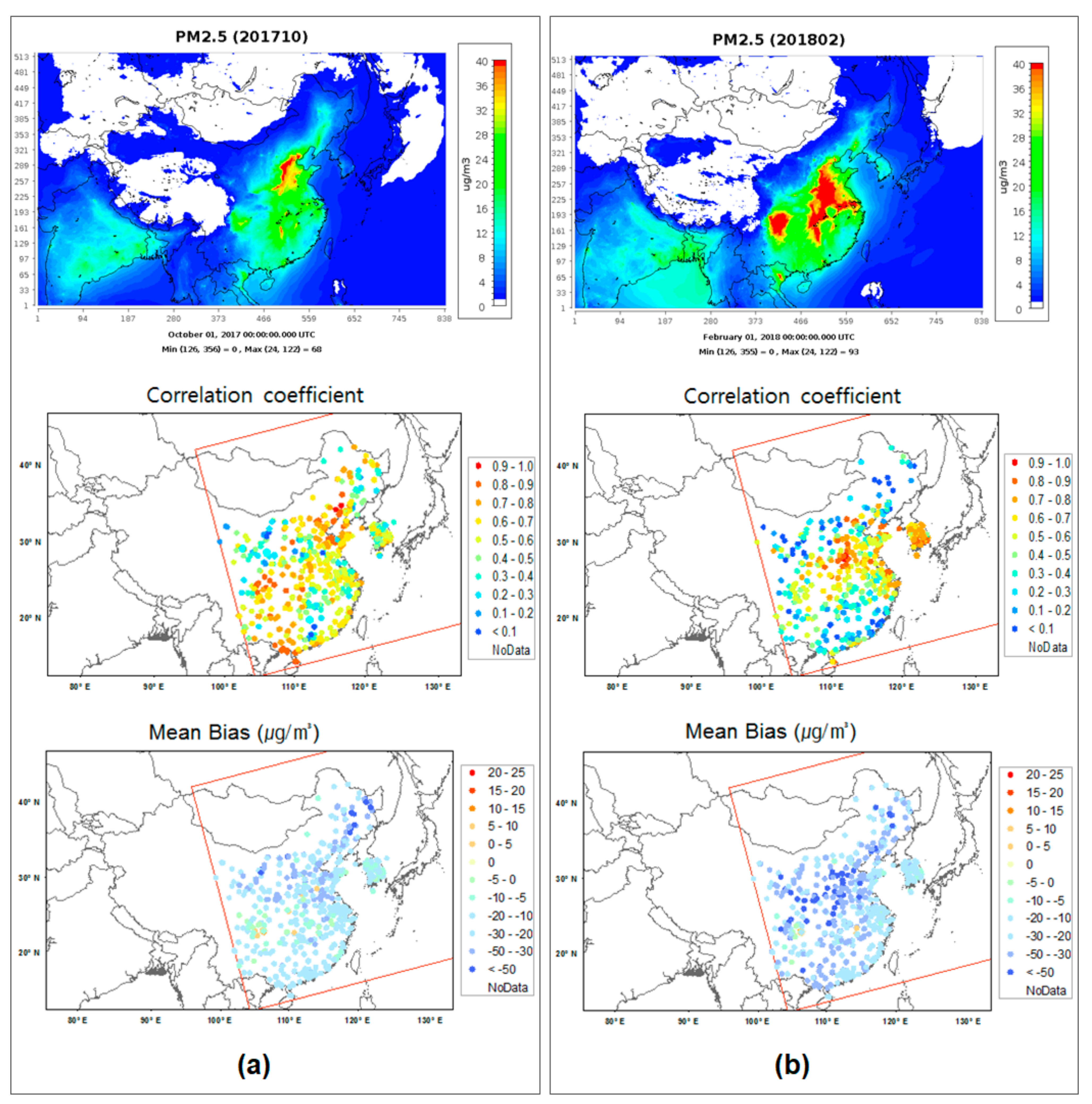
3.1. Performance of the Nature Run
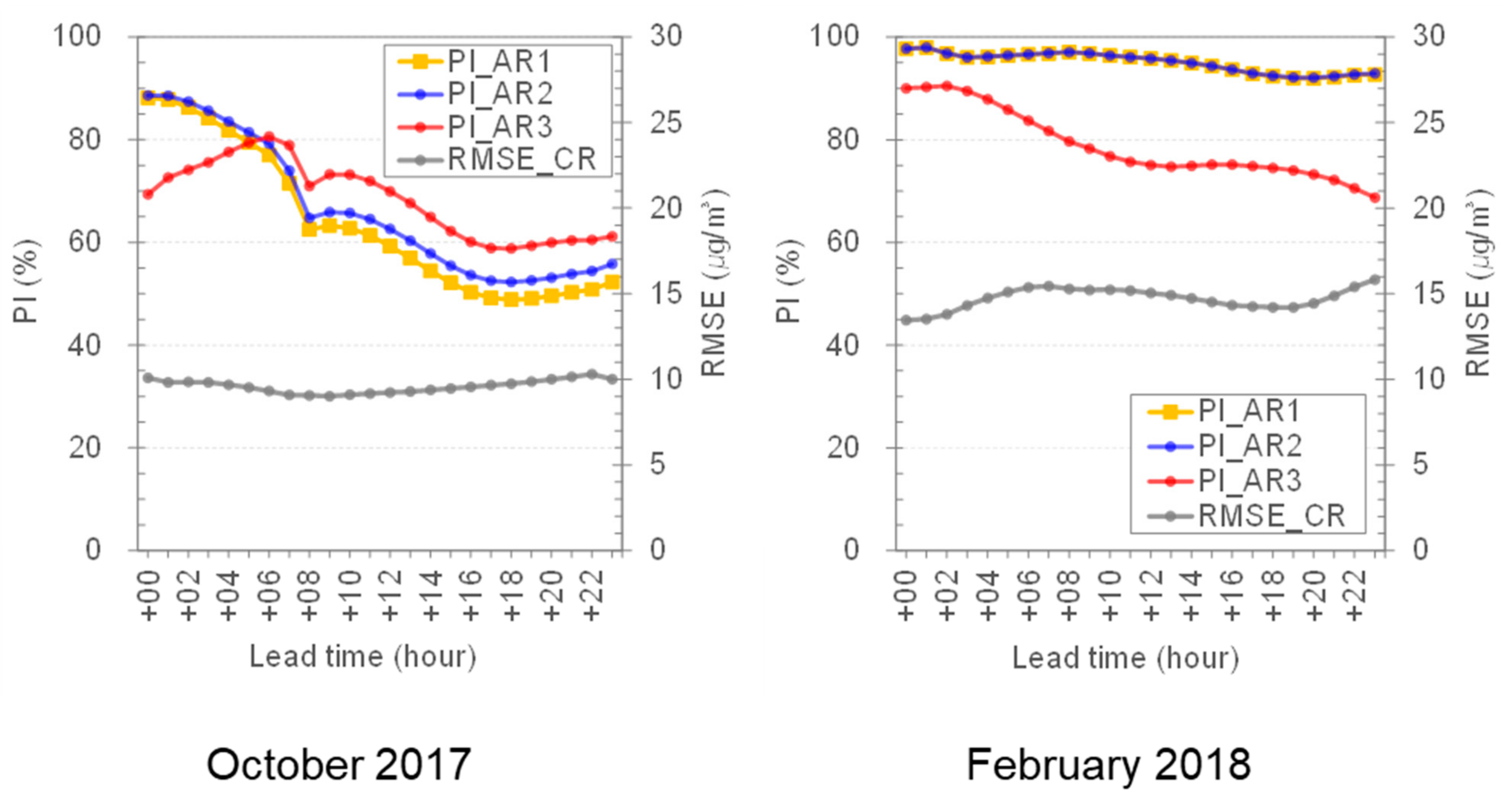
3.2. Potential Effects of New Observation Data
4. Discussion
4.1. Nature Run Module
4.2. Data Scenario
4.3. Assimilation Run Module
4.4. Data Assimilation System
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization Regional Office for Europe. Review of Evidence on Health Aspects of Air Pollution: REVIHAAP Project: Technical Report; World Health Organization; Regional Office for Europe: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Carmichael, G.R.; Sandu, A.; Chai, T.; Daescu, D.N.; Constantinescu, E.M.; Tang, Y. Predicting air quality: Improvements through advanced methods to integrate models and measurements. J. Comput. Phys. 2008, 227, 3540–3571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Jeong, U.; Ahn, M.-H.; Kim, J.H.; Park, R.J.; Lee, H.; Song, C.H.; Choi, Y.-S.; Lee, K.-H.; Yoo, J.-M.; et al. New Era of Air Quality Monitoring from Space: Geostationary Environment Monitoring Spectrometer (GEMS). Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2020, 101, E1–E22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Timmermans, R.; Lahoz, W.; Attié, J.-L.; Peuch, V.-H.; Edwards, D.; Eskes, H.; Builtjes, P. Observing System Simulation Experiments (OSSEs) for Air Quality Applications; Steyn, D.G., Chaumerliac, N., Eds.; Air Pollution Modeling and its Application XXIV; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 581–585. [Google Scholar]
- Masutani, M.; Schlatter, T.W.; Errico, R.M.; Stoffelen, A.; Andersson, E.; Lahoz, W.; Woollen, J.S.; Emmitt, G.D.; Riishøjgaard, L.-P.; Lord, S.J. Observing System Simulation Experiments. In Data Assimilation: Making Sense of Observations; Lahoz, W., Khattatov, B., Menard, R., Eds.; Springer Berlin Heidelberg: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 647–679. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, I.S.; Lee, J.Y.; Wee, D.; Kim, Y.P. Estimation of the contribution of biomass fuel burning activities in North Korea to the air quality in Seoul, South Korea: Application of the 3D-PSCF method. Atmos. Res. 2019, 230, 104628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, M.-I.; Son, S.-W.; Kim, H.C.; Kim, S.-W.; Park, R.J.; Chen, D. Contrasting synoptic weather patterns between non-dust high particulate matter events and Asian dust events in Seoul, South Korea. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 214, 116864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filonchyk, M. Characteristics of the severe March 2021 Gobi Desert dust storm and its impact on air pollution in China. Chemosphere 2022, 287, 132219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byun, D.; Schere, K.L. Review of the Governing Equations, Computational Algorithms, and Other Components of the Models-3 Community Multiscale Air Quality (CMAQ) Modeling System. Appl. Mech. Rev. 2006, 59, 51–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foley, K.M.; Roselle, S.J.; Appel, K.W.; Bhave, P.V.; Pleim, J.E.; Otte, T.L.; Mathur, R.; Sarwar, G.; Young, J.O.; Gilliam, R.C.; et al. Incremental testing of the Community Multiscale Air Quality (CMAQ) modeling system version 4.7. Geosci. Model Dev. 2010, 3, 205–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chang, L.-S.; Cho, A.; Park, H.; Nam, K.; Kim, D.; Hong, J.-H.; Song, C.-K. Human-model hybrid Korean air quality forecasting system. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2016, 66, 896–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, J.-J.; Lee, J.-B.; Kim, O.; Heo, G.; Lee, H.; Lee, D.; Kim, D.-G.; Lee, S.-D. Crop Residue Burning in Northeast China and Its Impact on PM2.5 Concentrations in South Korea. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, J.-H.; Choi, K.-C.; Kim, H.K.; Baek, B.H.; Jang, M.; Eum, J.-H.; Song, C.H.; Ma, Y.-I.; Sunwoo, Y.; Chang, L.-S.; et al. Development of an anthropogenic emissions processing system for Asia using SMOKE. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 58, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, J.-H.; Kim, Y.; Kim, H.-K.; Choi, K.-C.; Eum, J.-H.; Lee, J.-B.; Lim, J.-H.; Kim, J.; Seong, M. Development of the CREATE Inventory in Support of Integrated Climate and Air Quality Modeling for Asia. Sustainability 2020, 12, 7930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guenther, A.; Karl, T.; Harley, P.; Wiedinmyer, C.; Palmer, P.I.; Geron, C. Estimates of global terrestrial isoprene emissions using MEGAN (Model of Emissions of Gases and Aerosols from Nature). Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2006, 6, 3181–3210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Larkin, N.K.; O’Neill, S.M.; Solomon, R.; Raffuse, S.; Strand, T.; Sullivan, D.C.; Krull, C.; Rorig, M.; Peterson, J.; Ferguson, S.A. The BlueSky smoke modeling framework. Int. J. Wildland Fire 2009, 18, 906–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van der Werf, G.R.; Randerson, J.T.; Giglio, L.; van Leeuwen, T.T.; Chen, Y.; Rogers, B.M.; Mu, M.; van Marle, M.J.E.; Morton, D.C.; Collatz, G.J.; et al. Global fire emissions estimates during 1997–2016. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2017, 9, 697–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Timmermans, R.M.A.; Lahoz, W.A.; Attié, J.L.; Peuch, V.H.; Curier, R.L.; Edwards, D.P.; Eskes, H.J.; Builtjes, P.J.H. Observing System Simulation Experiments for air quality. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 115, 199–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, M.; Rood, R.B.; Lin, S.-J.; Müller, J.-F.; Thompson, A.M. Atmospheric sulfur cycle simulated in the global model GOCART: Model description and global properties. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2000, 105, 24671–24687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purser, R.J.; Wu, W.-S.; Parrish, D.F.; Roberts, N.M. Numerical Aspects of the Application of Recursive Filters to Variational Statistical Analysis. Part I: Spatially Homogeneous and Isotropic Gaussian Covariances. Mon. Weather Rev. 2003, 131, 1524–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purser, R.J.; Wu, W.-S.; Parrish, D.F.; Roberts, N.M. Numerical Aspects of the Application of Recursive Filters to Variational Statistical Analysis. Part II: Spatially Inhomogeneous and Anisotropic General Covariances. Mon. Weather Rev. 2003, 131, 1536–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.-S.; Purser, R.J.; Parrish, D.F. Three-Dimensional Variational Analysis with Spatially Inhomogeneous Covariances. Mon. Weather Rev. 2002, 130, 2905–2916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, Z.; Liu, Z.; Wang, T.; Schwartz, C.S.; Lin, H.-C.; Jiang, F. Probing into the impact of 3DVAR assimilation of surface PM10 observations over China using process analysis. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 6738–6749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Liu, Q.; Lin, H.-C.; Schwartz, C.S.; Lee, Y.-H.; Wang, T. Three-dimensional variational assimilation of MODIS aerosol optical depth: Implementation and application to a dust storm over East Asia. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2011, 116, 399–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pagowski, M.; Liu, Z.; Grell, G.A.; Hu, M.; Lin, H.C.; Schwartz, C.S. Implementation of aerosol assimilation in Gridpoint Statistical Interpolation (v. 3.2) and WRF-Chem (v. 3.4.1). Geosci. Model Dev. 2014, 7, 1621–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parrish, D.F.; Derber, J.C. The National Meteorological Center’s Spectral Statistical-Interpolation Analysis System. Mon. Weather Rev. 1992, 120, 1747–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbern, H.; Strunk, A.; Schmidt, H.; Talagrand, O. Emission rate and chemical state estimation by 4-dimensional variational inversion. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2007, 7, 3749–3769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schwartz, C.S.; Liu, Z.; Lin, H.-C.; McKeen, S.A. Simultaneous three-dimensional variational assimilation of surface fine particulate matter and MODIS aerosol optical depth. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2012, 117, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, M.; Kim, J.; Lee, J.; Kim, M.; Park, Y.J.; Holben, B.; Eck, T.F.; Li, Z.; Song, C.H. GOCI Yonsei aerosol retrieval version 2 products: An improved algorithm and error analysis with uncertainty estimation from 5-year validation over East Asia. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2018, 11, 385–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, G.; Lee, S.; Im, J.; Song, C.-K.; Kim, J.; Lee, M.-i. Aerosol data assimilation and forecast using Geostationary Ocean Color Imager aerosol optical depth and in-situ observations during the KORUS-AQ observing period. GIScience Remote Sens. 2021, 58, 1175–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grell, G.A.; Peckham, S.E.; Schmitz, R.; McKeen, S.A.; Frost, G.; Skamarock, W.C.; Eder, B. Fully coupled “online” chemistry within the WRF model. Atmos. Environ. 2005, 39, 6957–6975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssens-Maenhout, G.; Dentener, F.; Van Aardenne, J.; Monni, S.; Pagliari, V.; Orlandini, L.; Klimont, Z.; Kurokawa, J.; Akimoto, H.; Ohara, T.; et al. EDGAR-HTAP: A harmonized Gridded Air Pollution Emission Dataset Based on National Inventories; European Commission, Joint Research Centre, Institute for Environment and Sustainability: Luxemburg, 2012; pp. 1–40. Available online: https://publications.jrc.ec.europa.eu/repository/handle/JRC68434 (accessed on 15 October 2020).
- Hand, J.L.; Copeland, S.A.; Day, D.E.; Dillner, A.M.; Indresand, H.; Malm, W.C.; McDade, C.E.; Moore, C.T.; Pitchford, M.L.; Schichtel, B.A.; et al. IMPROVE (Interagency Monitoring of Protected Visual Environments): Spatial and Seasonal Patterns and Temporal Variability of Haze and Its Constituents in the United States; 2011. Available online: http://vista.cira.colostate.edu/Improve/spatial-and-seasonal-patterns-and-temporal-variability-of-haze-and-its-constituents-in-the-united-states-report-v-june-2011/ (accessed on 29 January 2019).
- Carter, W.P. Implementation of the SAPRC-99 Chemical Mechanism into the Models-3 Framework; United States Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2000; pp. 1–101. Available online: https://intra.cert.ucr.edu/~carter/pubs/s99mod3.pdf (accessed on 30 January 2021).
- Rio, M.H.; Santoleri, R. Improved global surface currents from the merging of altimetry and Sea Surface Temperature data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 216, 770–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, C.P.; Dey, C.H. Observing-Systems Simulation Experiments: Past, Present, and Future. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1986, 67, 687–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boylan, J.W.; Russell, A.G. PM and light extinction model performance metrics, goals, and criteria for three-dimensional air quality models. Atmos. Environ. 2006, 40, 4946–4959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, N.K.; Kim, I.S.; Song, I.H.; Park, S.M.; Lim, H.B.; Kim, Y.P.; Shin, H.J.; Lee, J.Y. Temporal variation of sulfate concentration in PM2.5 and major factors enhancing sulfate concentration in the atmosphere of Seoul, Korea. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2021, 14, 985–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Sartelet, K.N.; Bocquet, M.; Chazette, P.; Sicard, M.; D’Amico, G.; Léon, J.F.; Alados-Arboledas, L.; Amodeo, A.; Augustin, P.; et al. Assimilation of lidar signals: Application to aerosol forecasting in the western Mediterranean basin. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 12031–12053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Werner, M.; Kryza, M.; Guzikowski, J. Can Data Assimilation of Surface PM2.5 and Satellite AOD Improve WRF-Chem Forecasting? A Case Study for Two Scenarios of Particulate Air Pollution Episodes in Poland. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Russell, A.; Dennis, R. NARSTO critical review of photochemical models and modeling. Atmos. Environ. 2000, 34, 2283–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyat Appel, K.; Napelenok, S.; Hogrefe, C.; Pouliot, G.; Foley, K.M.; Roselle, S.J.; Pleim, J.E.; Bash, J.; Pye, H.O.T.; Heath, N.; et al. Overview and Evaluation of the Community Multiscale Air Quality (CMAQ) Modeling System Version 5.2; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 69–73. [Google Scholar]
| Air Quality Model Setting | Input Observation for DA | |
|---|---|---|
| NR | CMAQ version 4.7.1 with
| Not used |
| CR | WRF–Chem version 3.9.1 model with
| Not used |
| AR 1 | Same as CR but for 6-hourly data assimilation
| PM10 and PM2.5 from NR at real station location (1306 sites) |
| AR 2 | Same as AR1 and AR3 but for the input observation for DA | PM10 and PM2.5 from NR at the locations of the real monitoring sites and 100 sites over the Gobi Desert area and 100 sites over the North Korean non-forest area (1506 sites) |
| AR 3 | Same as AR1 and AR2 but for the input observation for DA | AOD from NR consistent with time and spatial resolution of the GEMS satellite (746,115 locations) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, H.-K.; Lee, S.; Bae, K.-H.; Jeon, K.; Lee, M.-I.; Song, C.-K. An Observing System Simulation Experiment Framework for Air Quality Forecasts in Northeast Asia: A Case Study Utilizing Virtual Geostationary Environment Monitoring Spectrometer and Surface Monitored Aerosol Data. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 389. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14020389
Kim H-K, Lee S, Bae K-H, Jeon K, Lee M-I, Song C-K. An Observing System Simulation Experiment Framework for Air Quality Forecasts in Northeast Asia: A Case Study Utilizing Virtual Geostationary Environment Monitoring Spectrometer and Surface Monitored Aerosol Data. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(2):389. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14020389
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Hyeon-Kook, Seunghee Lee, Kang-Ho Bae, Kwonho Jeon, Myong-In Lee, and Chang-Keun Song. 2022. "An Observing System Simulation Experiment Framework for Air Quality Forecasts in Northeast Asia: A Case Study Utilizing Virtual Geostationary Environment Monitoring Spectrometer and Surface Monitored Aerosol Data" Remote Sensing 14, no. 2: 389. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14020389
APA StyleKim, H.-K., Lee, S., Bae, K.-H., Jeon, K., Lee, M.-I., & Song, C.-K. (2022). An Observing System Simulation Experiment Framework for Air Quality Forecasts in Northeast Asia: A Case Study Utilizing Virtual Geostationary Environment Monitoring Spectrometer and Surface Monitored Aerosol Data. Remote Sensing, 14(2), 389. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14020389







