Ionospheric Disturbances Observed Following the Ridgecrest Earthquake of 4 July 2019 in California, USA
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
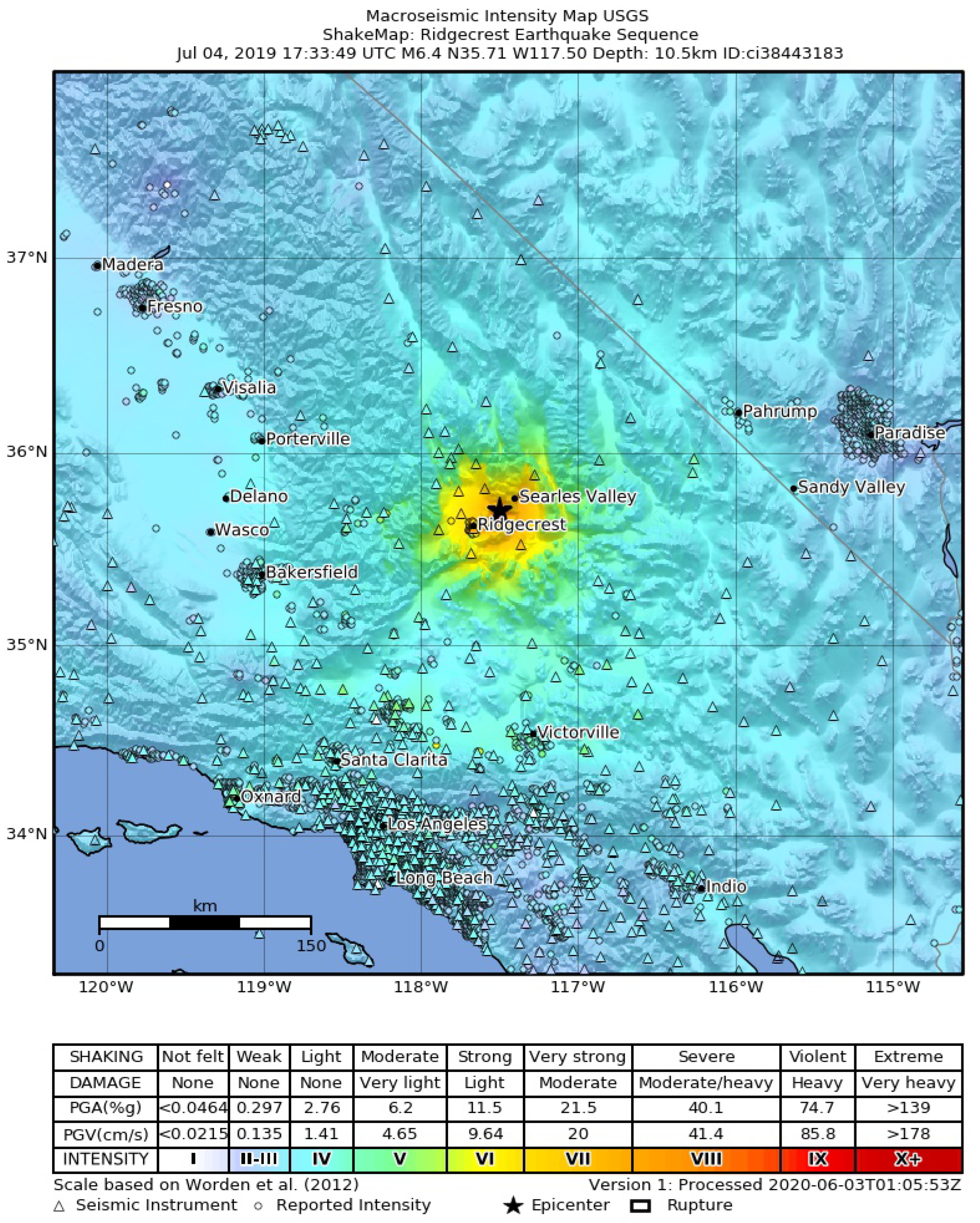
2.1. The 4 July 2019 Ridgecrest Earthquakes
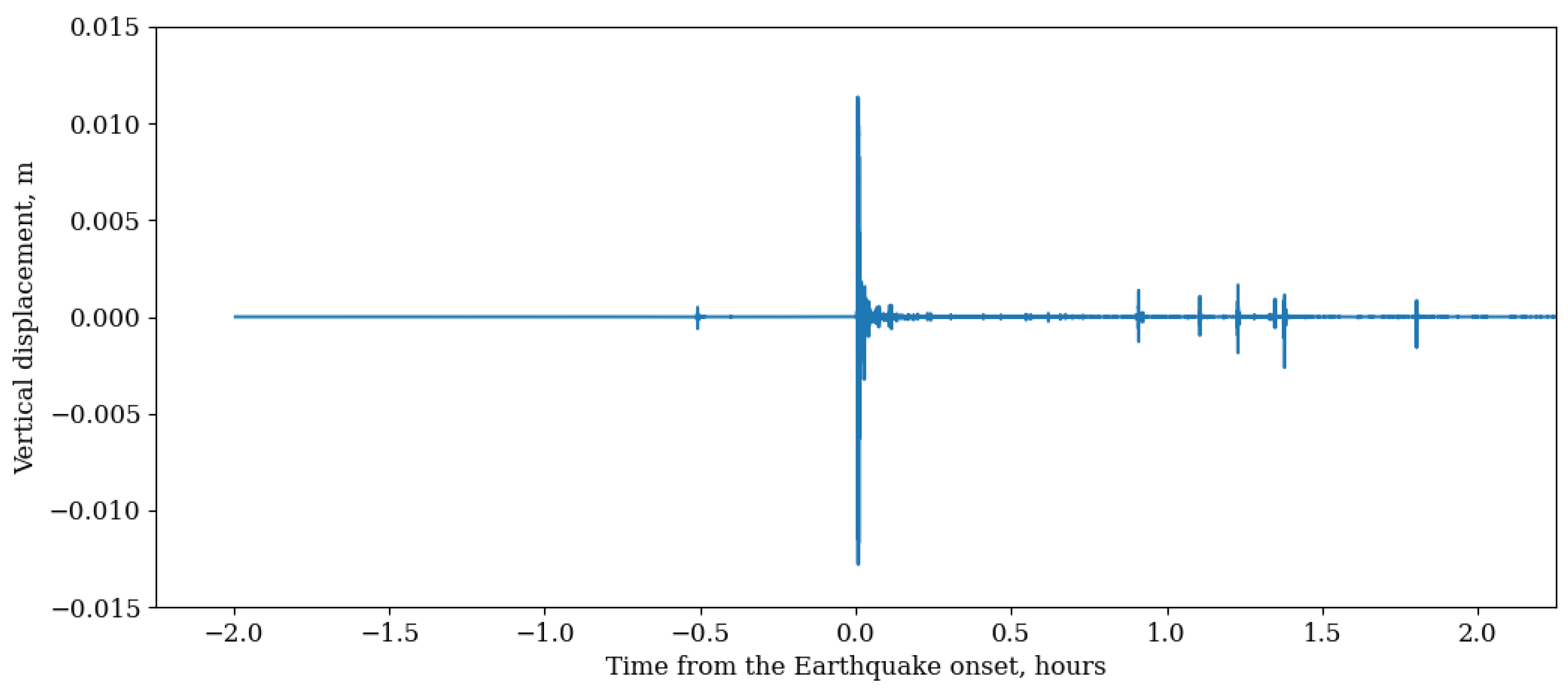
2.2. GNSS and Seismometer Data
2.3. Estimations of TEC and TEC Disturbance (ΔTEC)
2.4. Estimation of Ground Vertical Velocity and Displacement from Recorded Ground Motion
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Ionoquakes during a Mainshock of 6.4
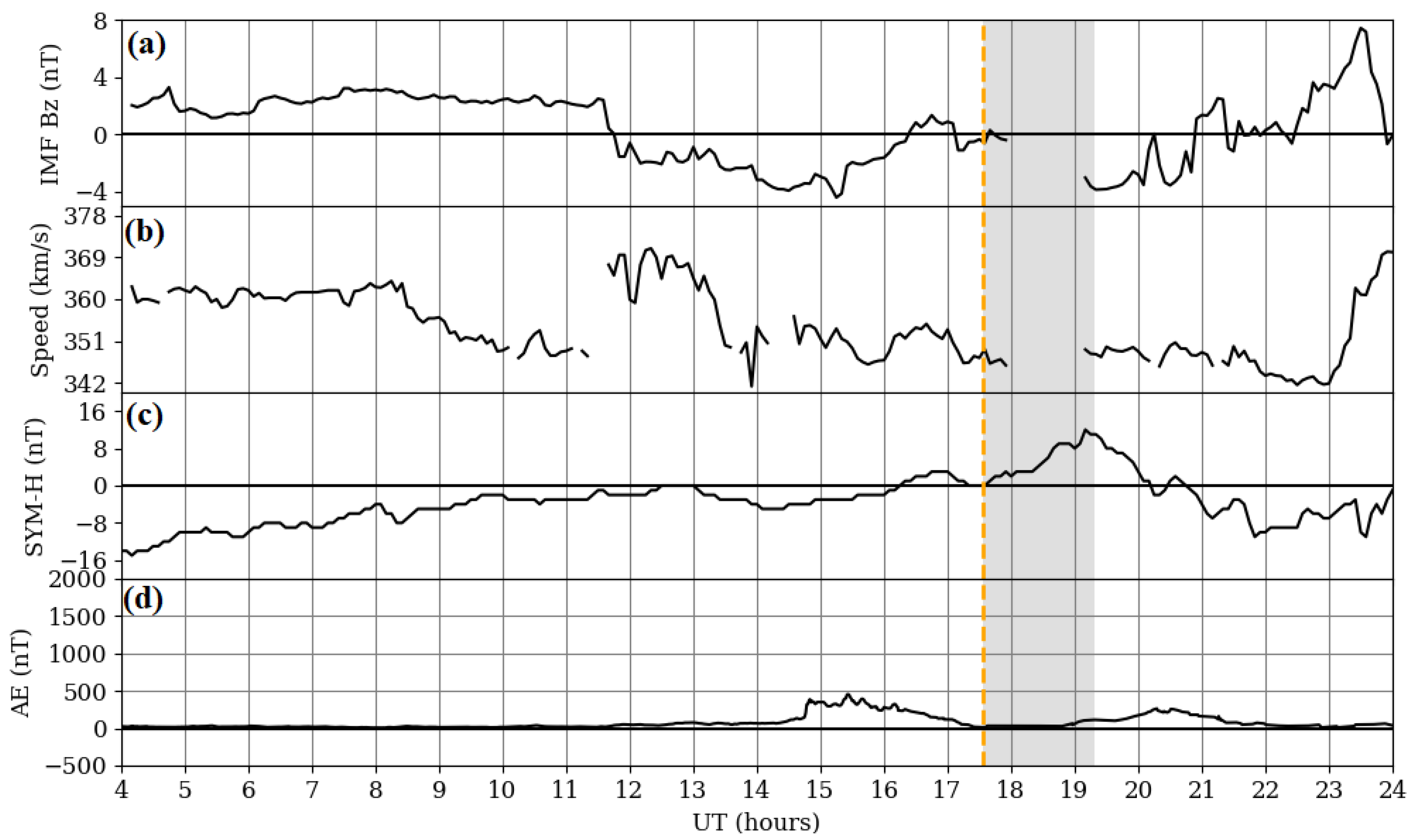
3.2. Solar and Geomagnetic Activity during the Ionoquakes
3.3. Ionoquakes and Co-Seismic Crustal Displacements
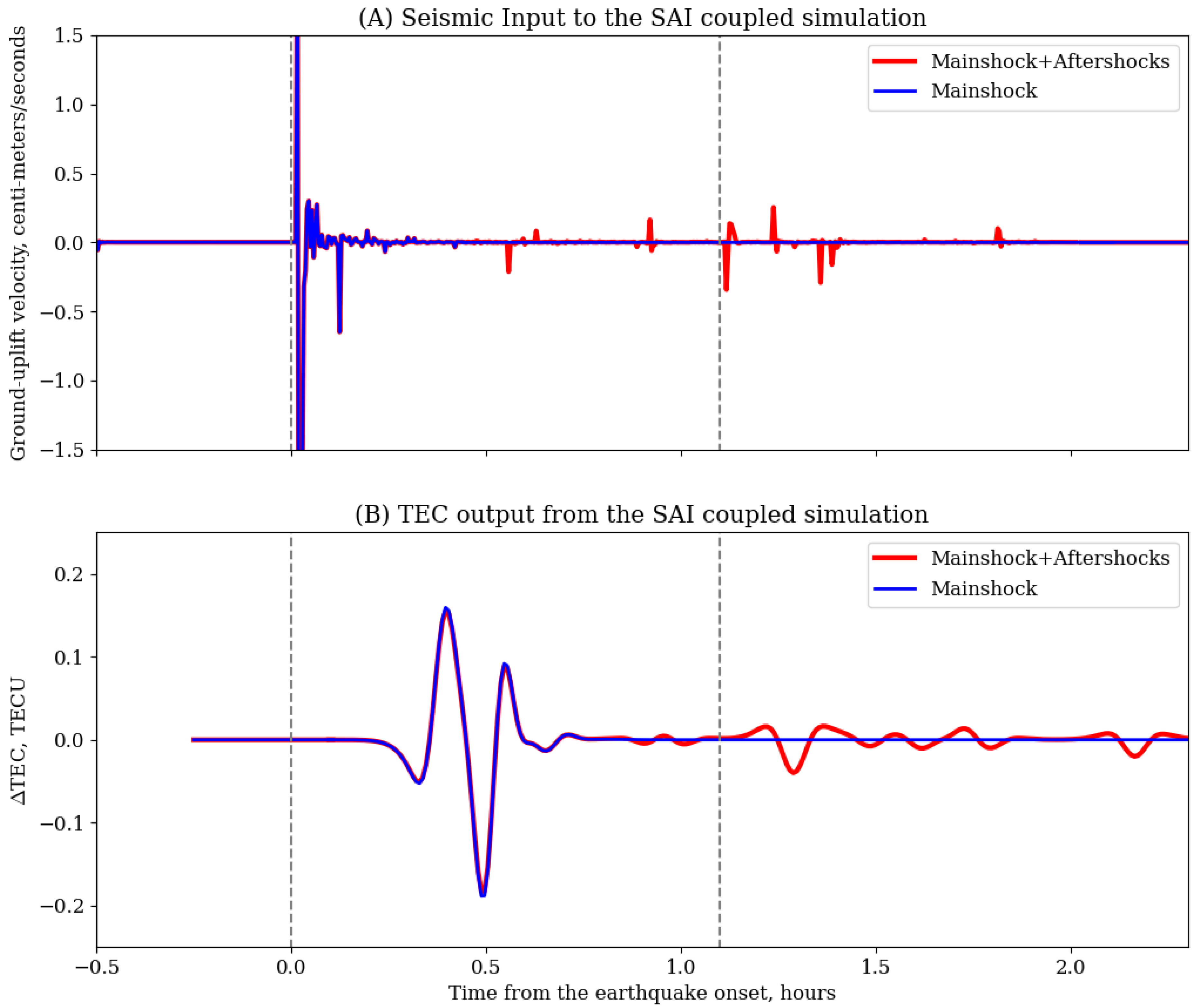
3.4. Ionoquake Simulation
4. Summary
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| GNSS | Global Navigation Satellite Systems |
| TEC | Total electron content |
| IPP | Ionospheric piercing point |
| TIDs | Traveling ionospheric disturbances |
| MSTIDs | Medium-scale traveling ionospheric disturbances |
| AGWs | Acoustic Gravity Waves |
| SAI | Seismo–atmosphere–ionosphere |
Appendix A
References
- Calais, E.; Minster, J.B. GPS, earthquakes, the ionosphere, and the Space Shuttle. Phys. Earth Planet. Inter. 1998, 105, 167–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artru, J.; Farges, T.; Lognonné, P. Acoustic waves generated from seismic surface waves: Propagation properties determined from Doppler sounding observations and normal-mode modelling. Geophys. J. Int. 2004, 158, 1067–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heki, K.; Ping, J. Directivity and apparent velocity of the coseismic ionospheric disturbances observed with a dense GPS array. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2005, 236, 845–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, J.Y.; Tsai, Y.B.; Chen, S.W.; Lee, C.P.; Chen, Y.C.; Yen, H.Y.; Chang, W.Y.; Liu, C. Giant ionospheric disturbances excited by the M9.3 Sumatra earthquake of 26 December 2004. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 23, L02103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lognonné, P. Seismic waves from atmospheric sources and atmospheric/ionospheric signatures of seismic waves. In Infrasound Monitoring for Atmospheric Studies; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 281–308. [Google Scholar]
- Astafyeva, E.; Heki, K. Two-mode long-distance propagation of coseismic ionosphere disturbances. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2009, 114, A10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chum, J.; Hruska, F.; Zednik, J.; Lastovicka, J. Ionospheric disturbances (infrasound waves) over the Czech Republic excited by the 2011 Tohoku earthquake. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2012, 117, A8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Occhipinti, G.; Rolland, L.; Lognonné, P.; Watada, S. From Sumatra 2004 to Tohoku-Oki 2011: The systematic GPS detection of the ionospheric signature induced by tsunamigenic earthquakes. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2013, 118, 3626–3636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afraimovich, E.L.; Astafyeva, E.I.; Demyanov, V.V.; Edemskiy, I.K.; Gavrilyuk, N.S.; Ishin, A.B.; Kosogorov, A.B.; Leonovich, E.A.; Lesyuta, L.A.; Lesyuta, O.S.; et al. A review of GPS/GLONASS studies of the ionospheric response to natural and anthropogenic processes and phenomena. J. Space Weather Space Clim. 2013, 3, A27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Astafyeva, E. Ionospheric detection of natural hazards. Rev. Geophys. 2019, 57, 1265–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Vergados, P.; Komjathy, A.; Verkhoglyadova, O. Upper atmospheric responses to surface disturbances: An observational perspective. Radio Sci. 2019, 54, 1076–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heki, K. Ionospheric disturbances related to earthquakes. In Ionosphere Dynamics and Applications; Huang, C., Lu, G., Zhang, Y., Paxton, L.J., Eds.; American Geophysical Union: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 511–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, S.; Bagiya, M.S.; Maurya, S.; Hazarika, N.K.; Kumar, A.S.S.; Prasad, D.S.V.V.D.; Ramesh, D.S. Terrestrial resonant oscillations during the 11 April 2012 Sumatra doublet earthquake. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2021, e2021JA029169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kherani, E.A.; Abdu, M.A.; de Paula, E.R.; Fritts, D.C.; Sobral, J.H.; de Meneses, F.C., Jr. The impact of gravity waves rising from convection in the lower atmosphere on the generation and nonlinear evolution of equatorial bubble. Ann. Geophys. 2009, 27, 657–1668. [Google Scholar]
- Chum, J.; Liu, J.Y.; Laštovička, J.; Fišer, J.; Mošna, Z.; Baše, J.; Sun, Y.Y. Ionospheric signatures of the 25 April 2015 Nepal earthquake and the relative role of compression and advection for Doppler sounding of infrasound in the ionosphere. Earth Planets Space 2016, 68, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ducic, V.; Artru, J.; Philippe, L. Ionospheric remote sensing of the Denali Earthquake Rayleigh surface waves. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2003, 30, 1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astafyeva, E.; Heki, K. Dependence of waveform of near-field coseismic ionospheric disturbances on focal mechanisms. Earth Planets Space 2009, 61, 939–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, J.Y.; Tsai, H.F.; Lin, C.H.; Kamogawa, M.; Chen, Y.I.; Lin, C.H.; Huang, B.S.; Yu, S.B.; Yeh, Y.H. Coseismic ionospheric disturbances triggered by the Chi-Chi earthquake. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2010, 115, A08303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolland, L.M.; Lognonné, P.; Astafyeva, E.; Kherani, E.A.; Kobayashi, N.; Mann, M.; Munekane, H. The resonant response of the ionosphere imaged after the 2011 off the Pacific coast of Tohoku Earthquake. Earth Planets Space 2011, 63, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Komjathy, A.; Galvan, D.A.; Stephens, P.; Butala, M.D.; Akopian, V.; Wilson, B.; Verkhoglyadova, O.; Mannucci, A.J.; Hickey, M. Detecting ionospheric TEC perturbations caused by natural hazards using a global network of GPS receivers: The Tohoku case study. Earth Planets Space 2012, 64, 1287–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Komjathy, A.; Yang, Y.M.; Meng, X.; Verkhoglyadova, O.; Mannucci, A.J.; Langley, R.B. Review and perspectives: Understanding natural-hazards-generated ionospheric perturbations using GPS measurements and coupled modeling. Radio Sci. 2016, 51, 951–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagiya, M.S.; Sunil, P.S.; Sunil, A.S.; Ramesh, D.S. Coseismic Contortion and Coupled Nocturnal Ionospheric Perturbations During 2016 Kaikoura, Mw 7.8 New Zealand Earthquake. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2018, 123, 1477–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, C.T.; Oluwadare, S.T.; Le, N.T.; Alizadeh, M.; Wickert, J.; Schuh, H. Spatial and Temporal Distributions of Ionospheric Irregularities Derived from Regional and Global ROTI Maps. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Ou, J. Auto-covariance estimation of variable samples (ACEVS) and its application for monitoring random ionospheric disturbances using GPS. J. Geod. 2001, 75, 438–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astafyeva, E.; Shults, K. Ionospheric GNSS imagery of seismic source: Possibilities, difficulties, and challenges. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2019, 124, 534–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maletckii, B.; Astafyeva, E. Determining spatio-temporal characteristics of Coseismic Travelling Ionospheric Disturbances (CTID) in near real-time. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 20783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zedek, F.; Rolland, L.M.; Dylan Mikesell, T.; Sladen, A.; Delouis, B.; Twardzik, C.; Coïsson, P. Locating surface deformation induced by earthquakes using GPS, GLONASS and Galileo ionospheric sounding from a single station. Adv. Space Res. 2021, 68, 3403–3416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perevalova, N.P.; Sankov, V.A.; Astafyeva, E.I.; Zhupityaeva, A.S. Threshold magnitude for ionospheric TEC response to earthquakes. J. Atmos. Sol.-Terr. Phys. 2014, 108, 77–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cahyadi, M.N.; Heki, K. Coseismic ionospheric disturbance of the large strike-slip earthquakes in North Sumatra in 2012: Mw dependence of the disturbance amplitudes. Geophys. J. Int. 2015, 200, 116–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Farges, T.; Artru, J.; Lognonné, P.; Le Pichon, A. Effets des séismes sur l’ionosphère; Chocs, 26; CEA-DAM Île-de-France: Arpajon, France, 2002; pp. 7–18. [Google Scholar]
- Ross, Z.E.; Idini, B.; Jia, Z.; Stephenson, O.L.; Zhong, M.; Wang, X.; Zhan, Z.; Simons, M.; Fielding, E.J.; Jung, S. Hierarchical interlocked orthogonal faulting in the 2019 Ridgecrest earthquake sequence. Science 2019, 366, 5346–5351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bernhard, H.-W.; Herbert, L.; Elmar, W. GNSS-Global Navigation Satellite Systems; Springer: Vienna, Austria, 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Coster, A.; Williams, J.; Weatherwax, A.; Rideout, W.; Herne, D. Accuracy of GPS total electron content: GPS receiver bias temperature dependence. Radio Sci. 2013, 48, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poularikas, A.D. Transforms and Applications Handbook, 3rd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA; London, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krischer, L.; Megies, T.; Barsch, R.; Beyreuther, M.; Lecoc, T.; Caudron, C.; Wassermann, J. ObsPy: A bridge for seismology into the scientific Python ecosystem. Comput. Sci. Discov. 2015, 8, 014003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astafyeva, E.; Heki, K. Vertical TEC over seismically active region during low solar activity. J. Atm. Solar-Terr. Physics 2011, 73, 1643–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cai, X.; Burns, A.G.; Wang, W.; Qian, L.; Pedatella, N.; Coster, A.; Zhang, S.; Solomon, S.C.; Eastes, R.W.; Daniell, R.E.; et al. Variations in thermosphere composition and ionosphere total electron content under “geomagnetically quiet” conditions at solar-minimum. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2021, 48, 2021GL093300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, B.J. Statistical studies of Pc 3-5 pulsations and their relevance for possible source mechanisms of ULF waves. Ann. Geophys. 1993, 11, 128–143. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.; Lay, T.; Brodsky, E.E.; Dascher-Cousineau, K.; Xiong, X. Coseismic Rupture Process of the Large 2019 Ridgecrest Earthquakes From Joint Inversion of Geodetic and Seismological Observations. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2019, 46, 11820–11829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kherani, E.A.; Rolland, L.; Lognonne, P.H.; Sladen, A.; Klausner, V.; de Paula, E.R. Traveling ionospheric disturbances propagating ahead of the Tohoku-Oki tsunami: A case study. Geophys. J. Int. 2016, 204, 148–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kherani, E.A.; Abdu, M.A.; Fritts, D.C.; de Paula, E.R. The acoustic gravity wave induced disturbances in the equatorial Ionosphere. In Aeronomy of the Earth’s Atmosphere and Ionosphere; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands; Heidelberg, Germany; London, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2011; pp. 141–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobolev, G. Seismic Quiescence and Activation; Encyclopedia of Solid Earth Geophysics; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2011; pp. 1178–1184. [Google Scholar]
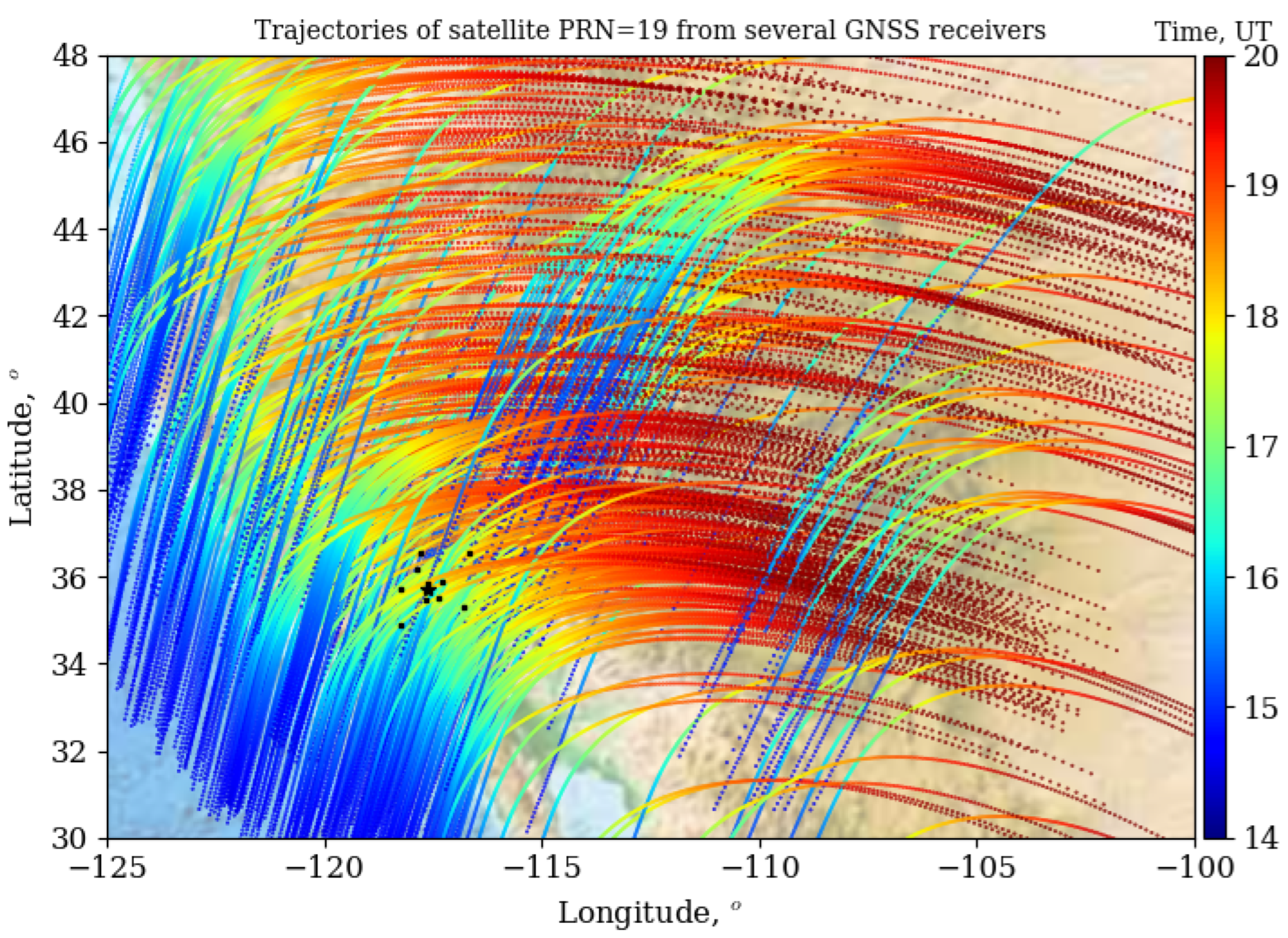
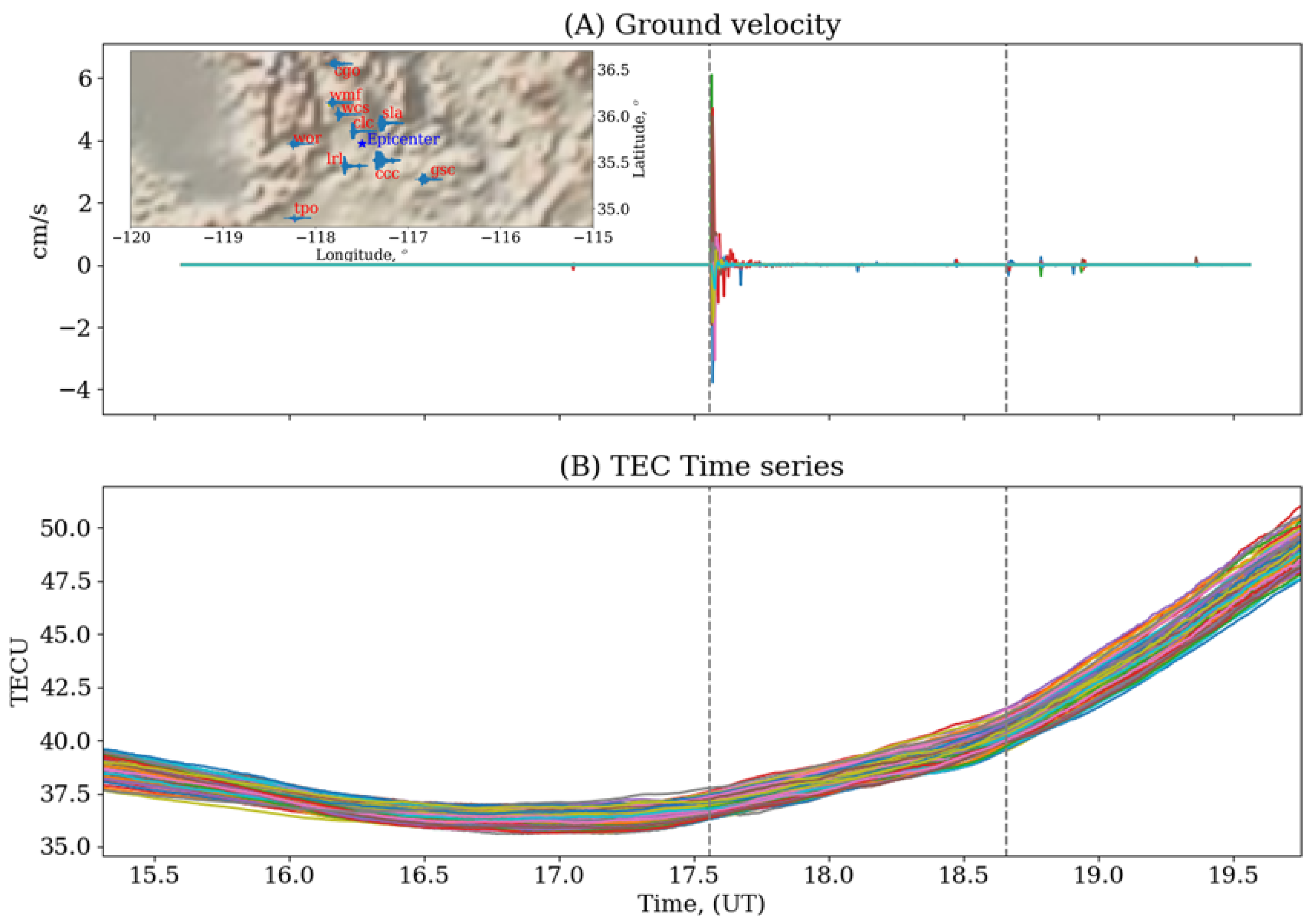
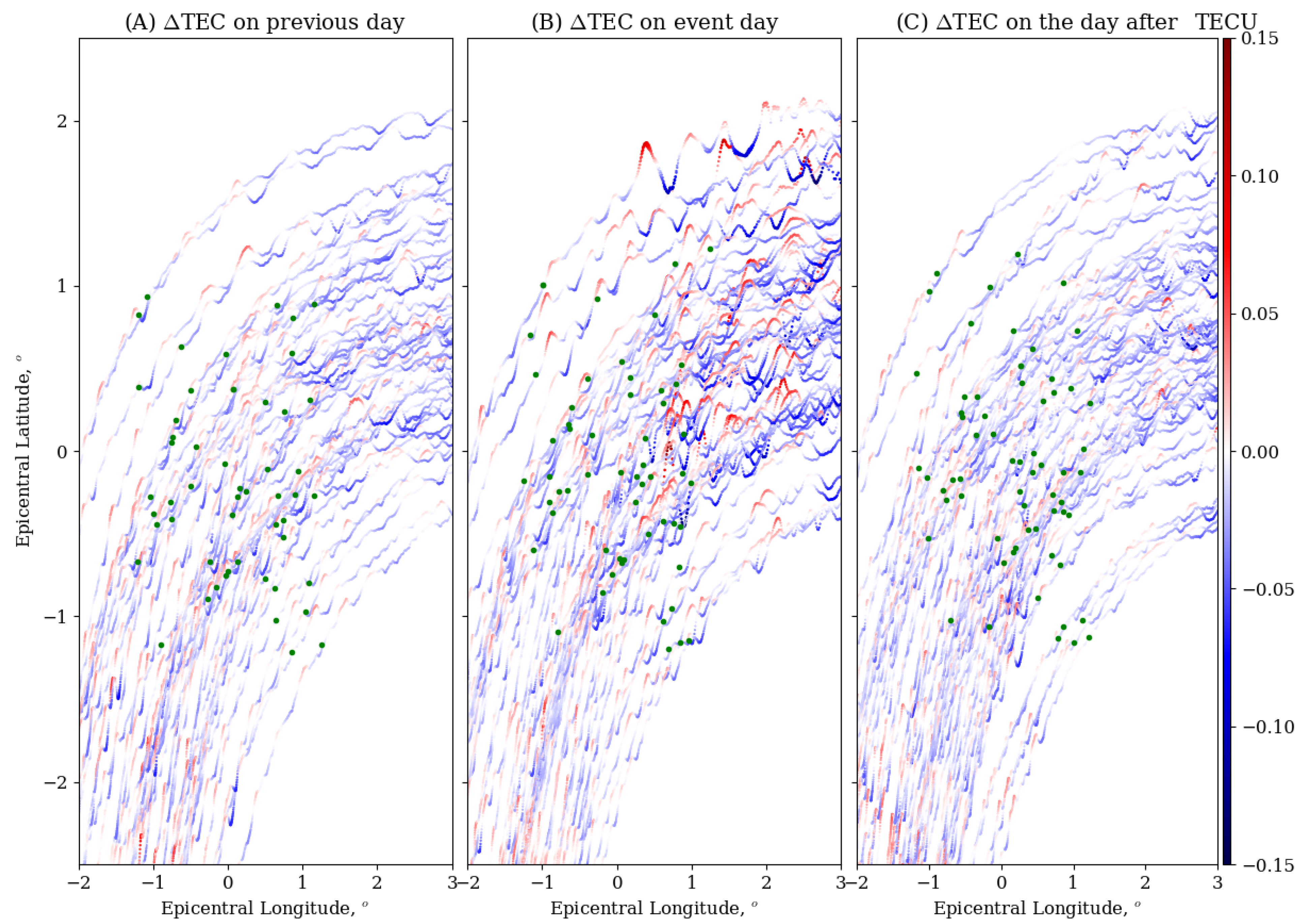
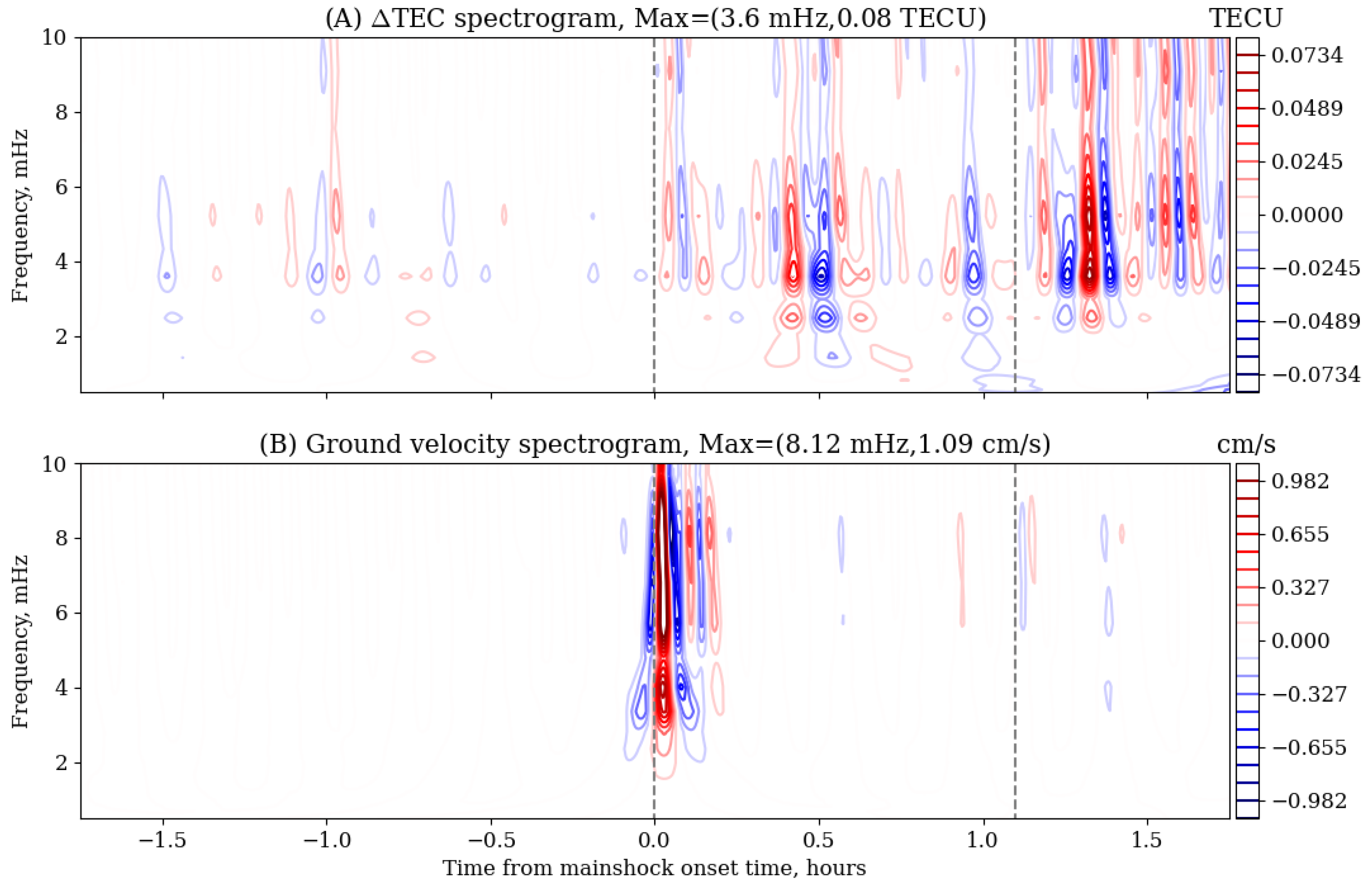

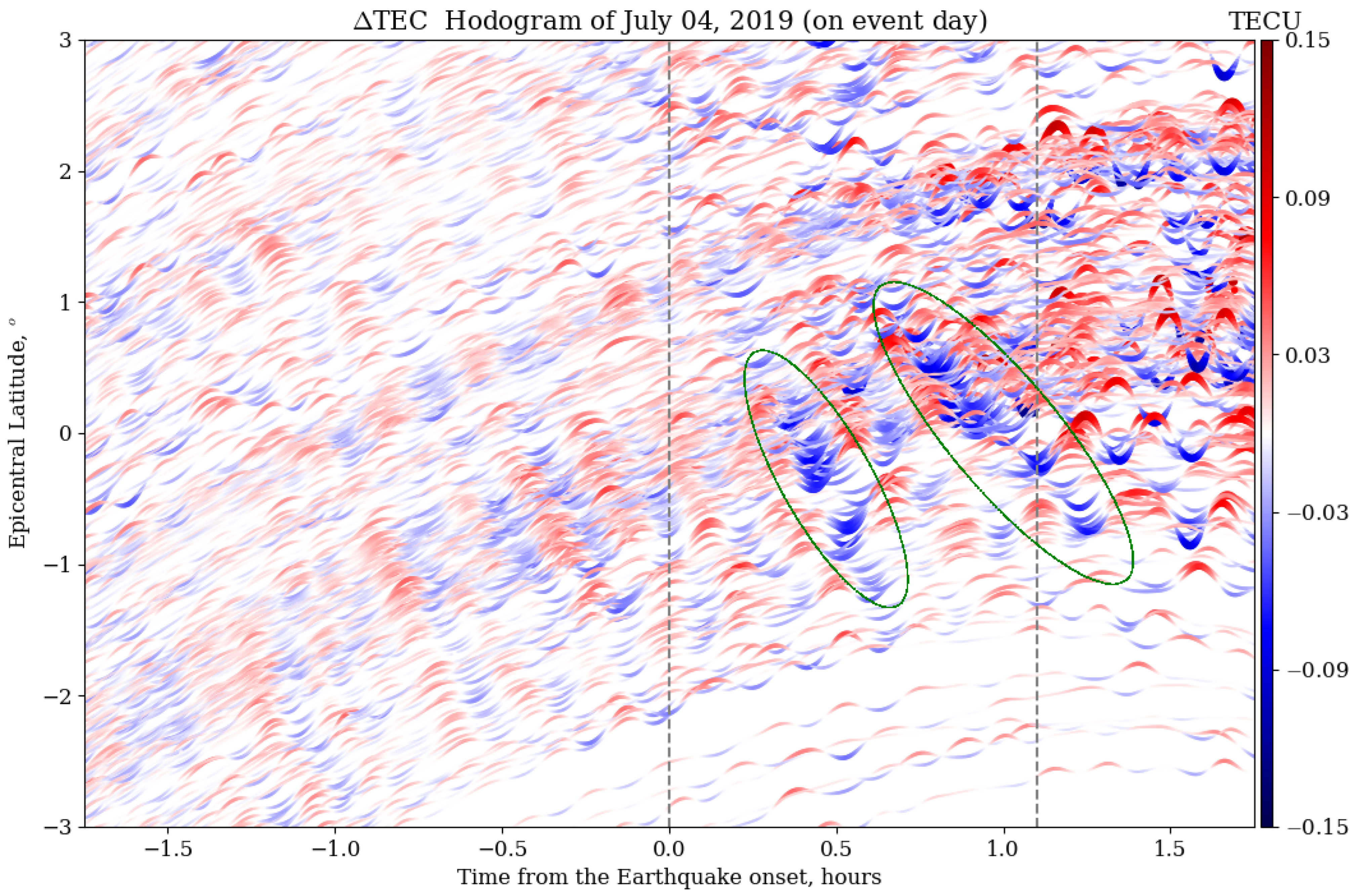
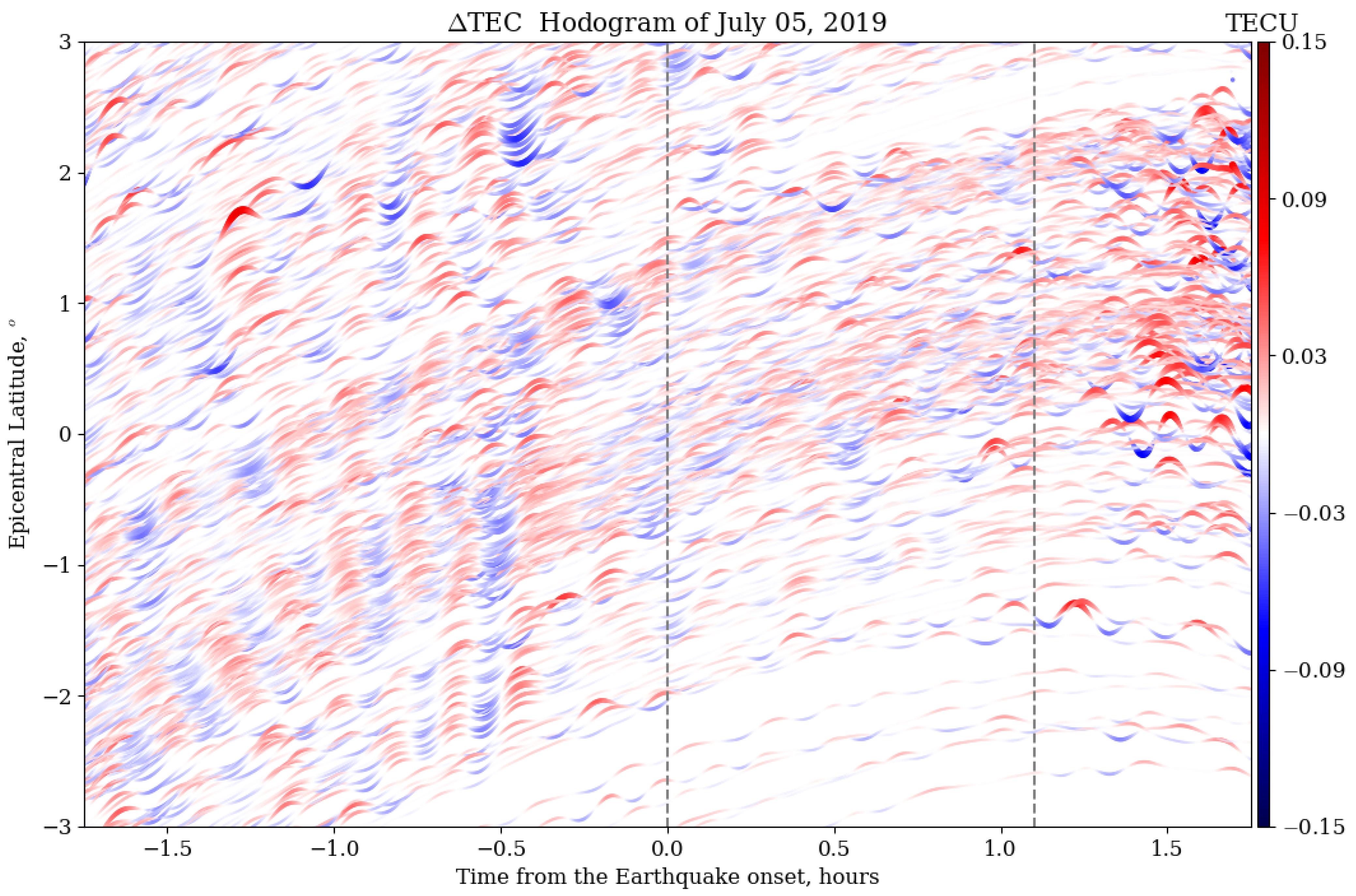
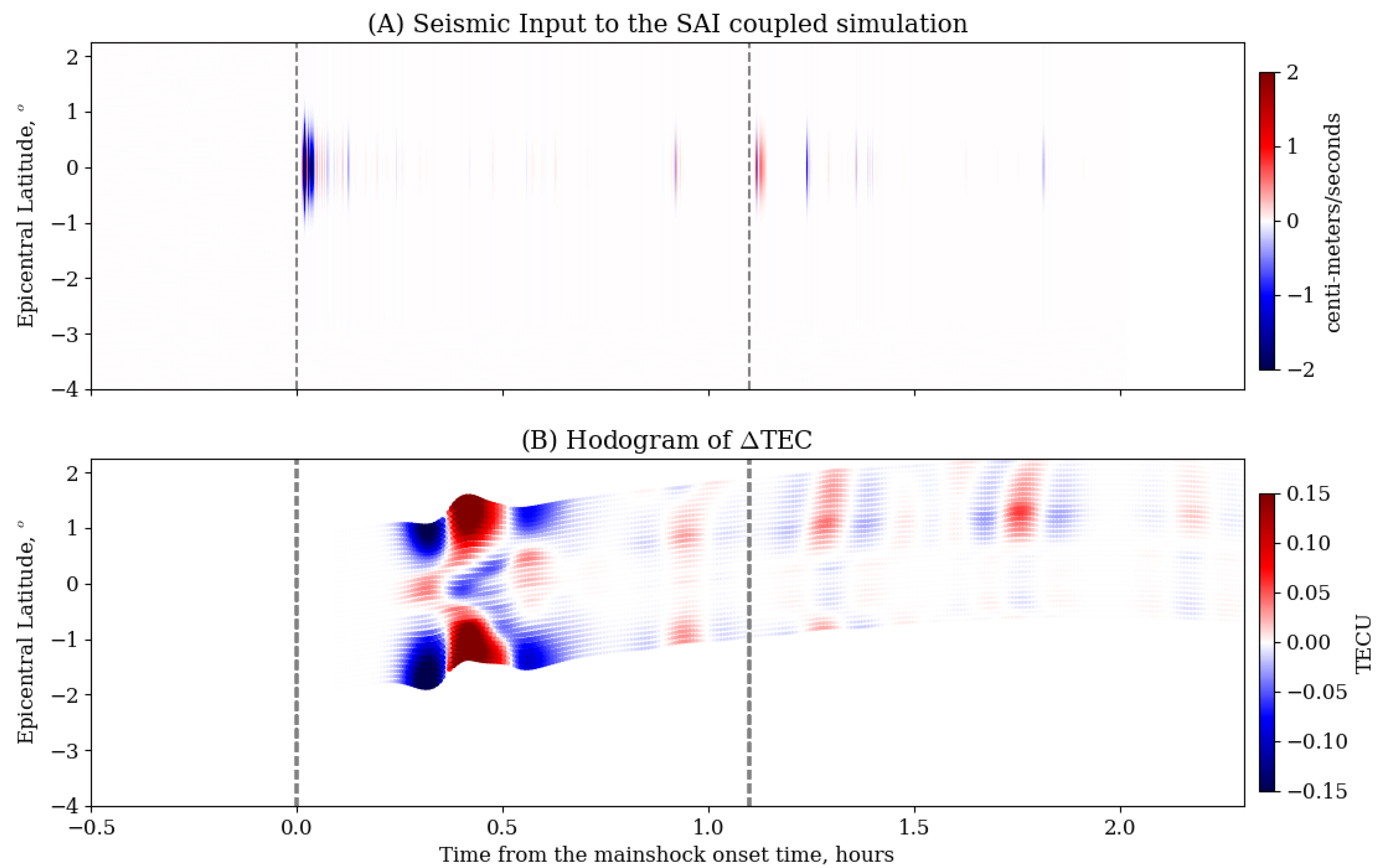
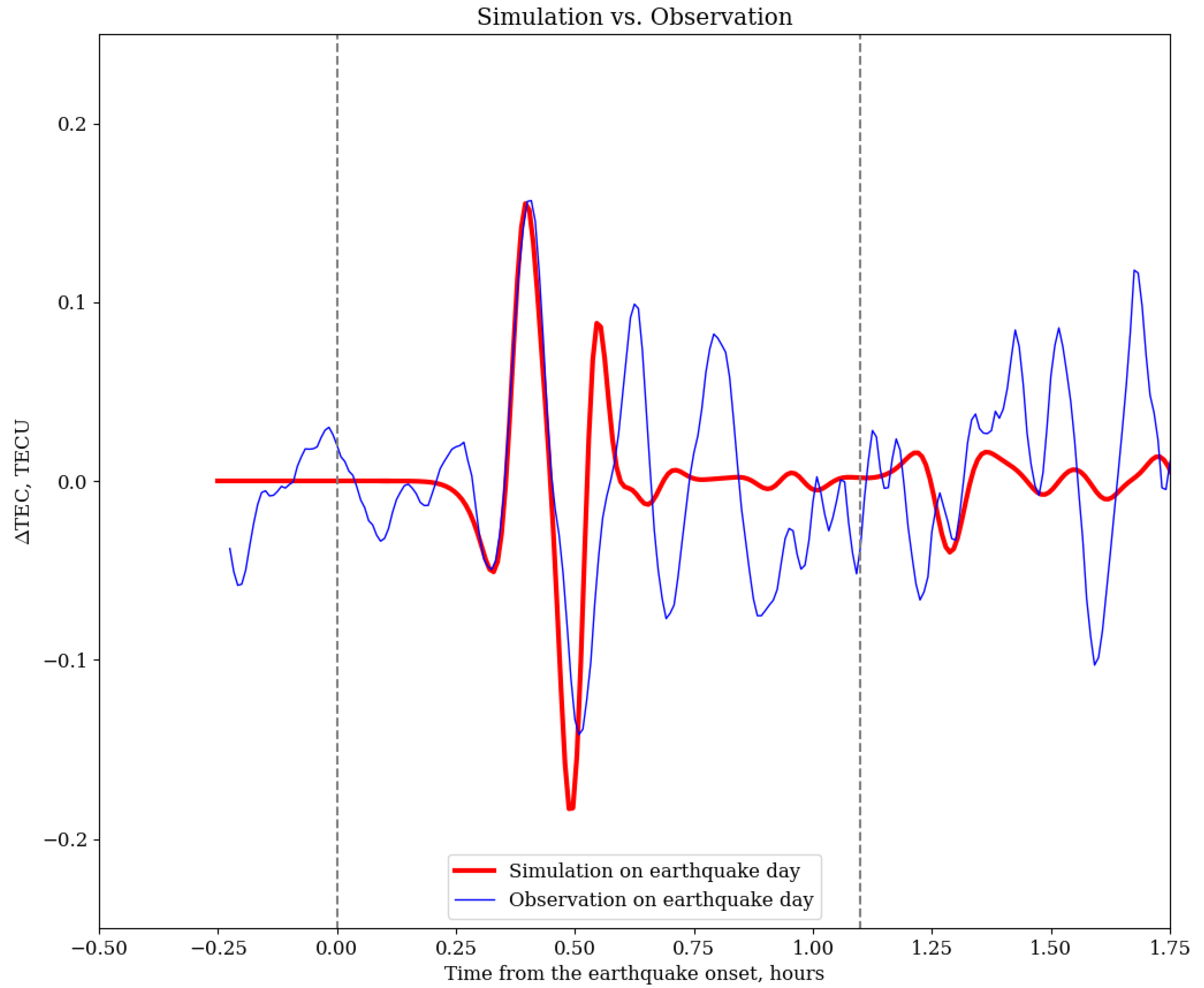
| No. | Time (UT) | Lat, Lon (Degrees) | Depth (km) | Magnitude | Location |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 17:33:49 | 35.71, −117.50 | 10.50 | 6.40 | Ridgecrest Earthquake Sequence |
| 2 | 18:08:45 | 35.71, 35.71 | 117.47 | 3.55 | 9 km SW of Searles Vallay |
| 3 | 18:27:59 | 35.75, −117.55 | 6.64 | 4.23 | 14 km W of Searles Valley |
| 4 | 18:39:44 | 35.60, −117.60 | 2.81 | 4.59 | 7 km ESE of Ridgecrest |
| 5 | 18:47:06 | 35.67, −117.49 | 8.53 | 4.34 | 13 km SW of Searles Valley |
| 6 | 18:54:13 | 35.60, −117.60 | 5.33 | 4.07 | 7 km ESE of Ridgecrest |
| 7 | 18:56:06 | 35.72, −117.56 | 1.92 | 4.58 | 15 km NE of Ridgecrest |
| 8 | 18:56:22 | 35.71, −117.55 | 1.16 | 4.21 | 15 km NE of Ridgecrest |
| 9 | 19:21:32 | 35.67, −117.49 | 5.16 | 4.50 | 13 km SSW of Searles Valley |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sanchez, S.A.; Kherani, E.A.; Astafyeva, E.; de Paula, E.R. Ionospheric Disturbances Observed Following the Ridgecrest Earthquake of 4 July 2019 in California, USA. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 188. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14010188
Sanchez SA, Kherani EA, Astafyeva E, de Paula ER. Ionospheric Disturbances Observed Following the Ridgecrest Earthquake of 4 July 2019 in California, USA. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(1):188. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14010188
Chicago/Turabian StyleSanchez, Saul A., Esfhan A. Kherani, Elvira Astafyeva, and Eurico R. de Paula. 2022. "Ionospheric Disturbances Observed Following the Ridgecrest Earthquake of 4 July 2019 in California, USA" Remote Sensing 14, no. 1: 188. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14010188
APA StyleSanchez, S. A., Kherani, E. A., Astafyeva, E., & de Paula, E. R. (2022). Ionospheric Disturbances Observed Following the Ridgecrest Earthquake of 4 July 2019 in California, USA. Remote Sensing, 14(1), 188. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14010188







