Multiple Effects of Topographic Factors on Spatio-Temporal Variations of Vegetation Patterns in the Three Parallel Rivers Region, Southeast Qinghai-Tibet Plateau
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Sources and Preprocessing
2.2.1. Remote Sensing Data
2.2.2. DEM Data
2.2.3. Vegetation Type Data
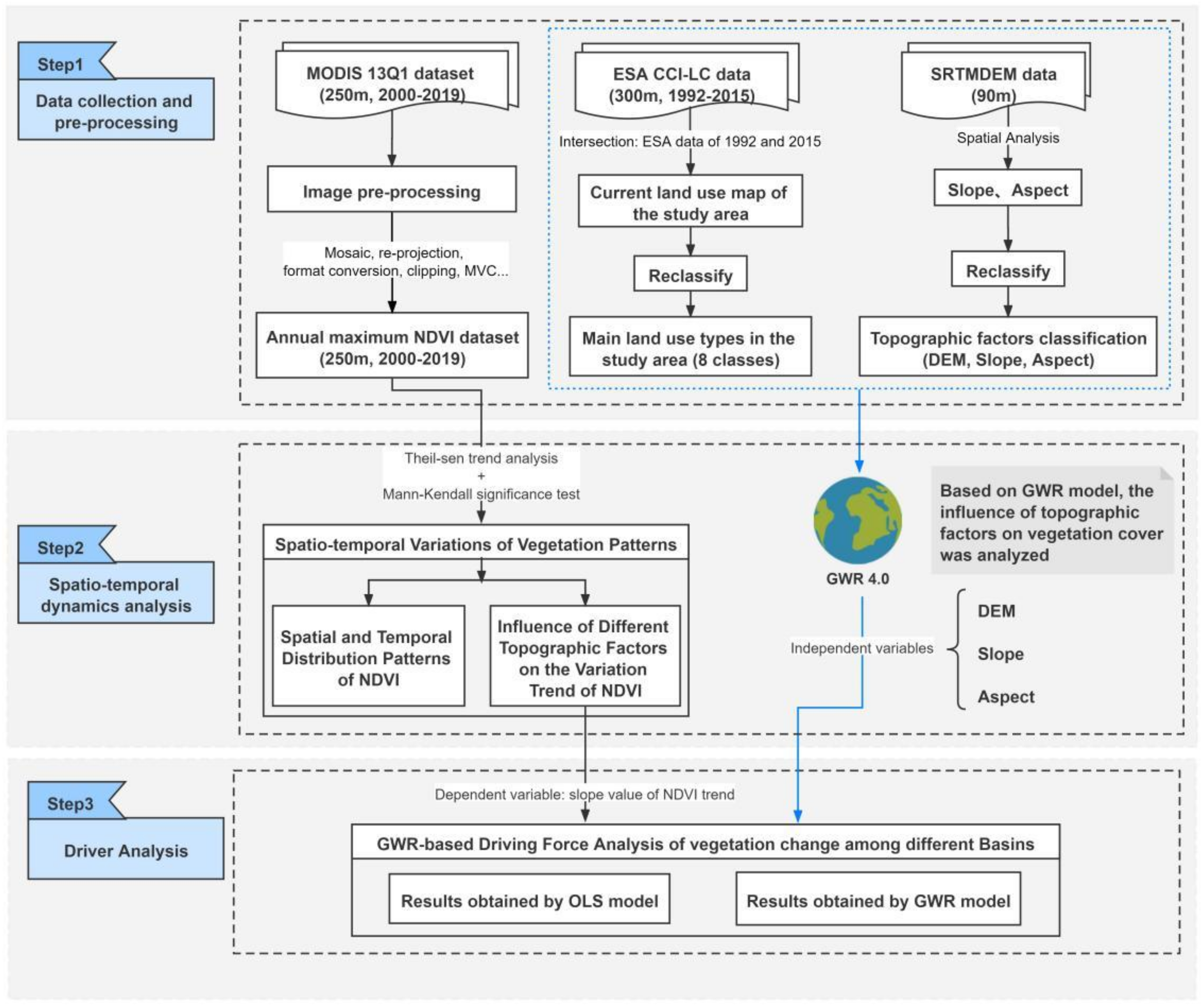
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. Trend Analysis and Significance Test
2.3.2. Geographically Weighted Regression Model
3. Results
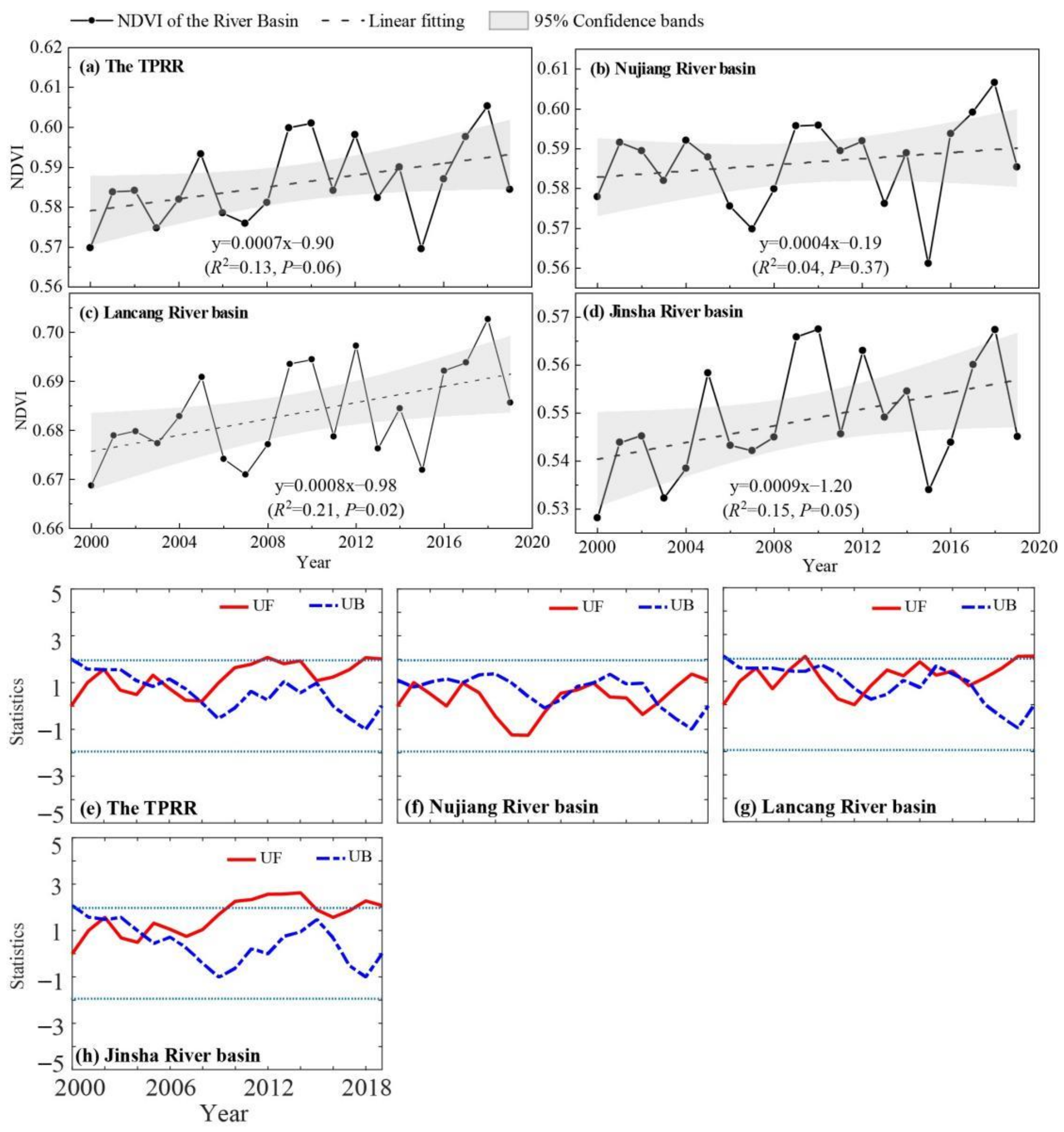
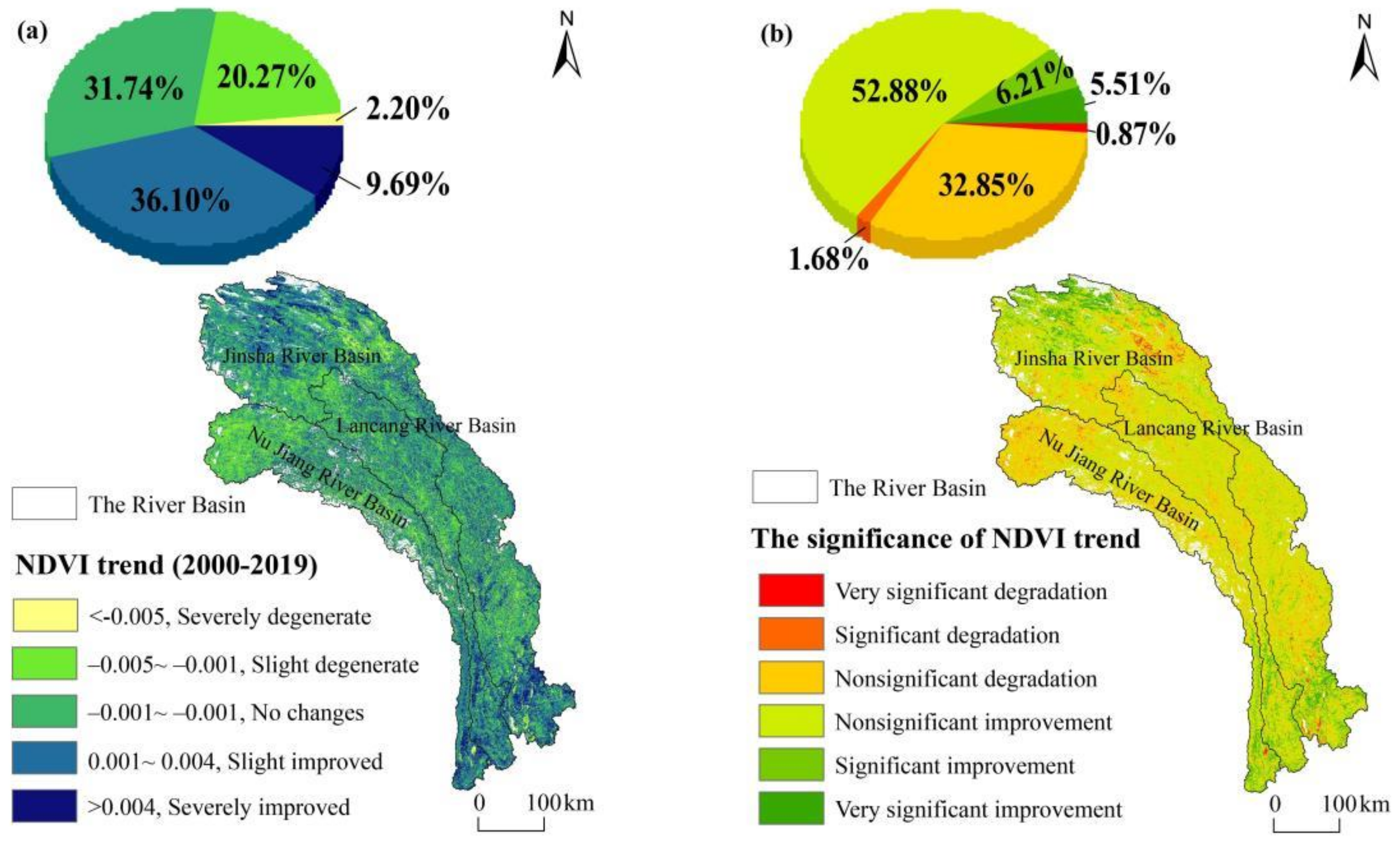
3.1. Spatial and Temporal Distribution Patterns of NDVI
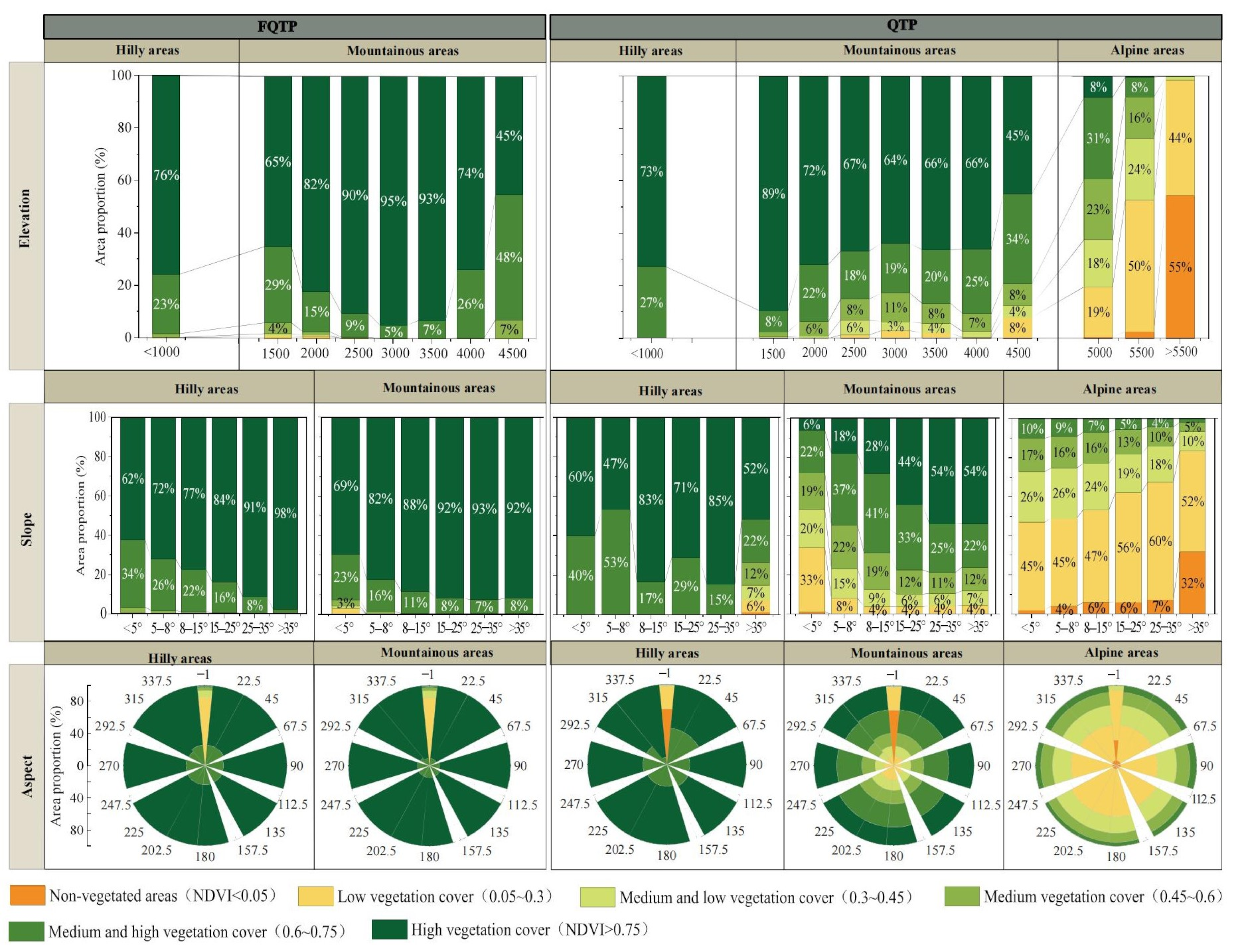
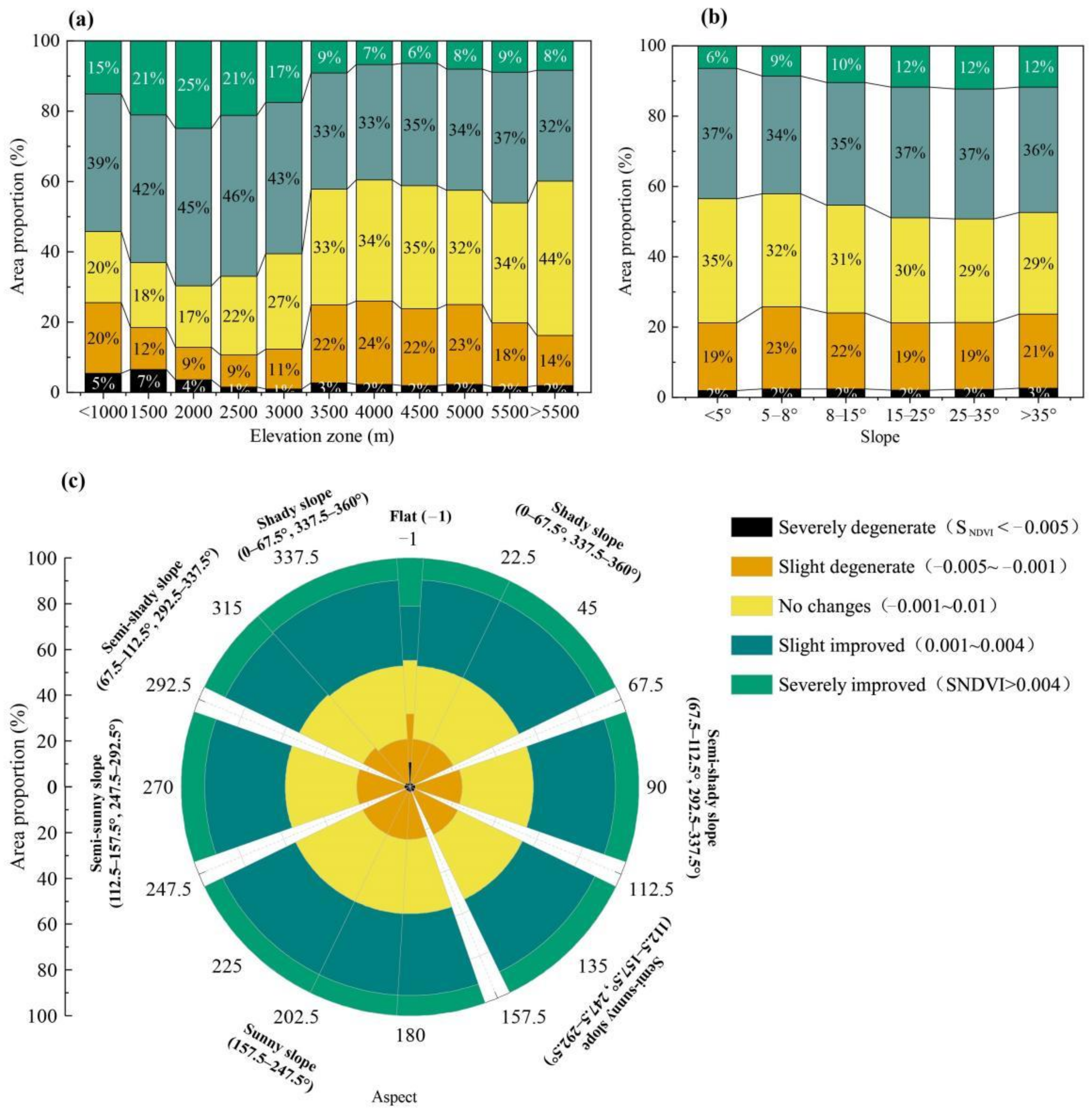
3.2. Influence of Different Topographic Factors on the Variation Trend of NDVI
3.3. GWR-Based Driving Force Analysis of Vegetation Change among Different Basins
4. Discussion
4.1. Temporal and Spatial Distribution of Vegetation Patterns
4.2. Spatial Heterogeneity of Topographic Factors on Vegetation
4.3. Analysis of the Other Drivers Influencing Changes in Vegetation Dynamics
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wen, Z.F.; Wu, S.J.; Chen, J.L.; Lu, M.Q. NDVI indicated long-term interannual changes in vegetation activities and their responses to climatic and anthropogenic factors in the Three Gorges Reservoir Region, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 574, 947–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.P.; Cai, Y.P.; Yang, W.; Yi, Y.J.; Yang, Z.F.; Fu, Q. Contributions of climatic and anthropogenic drivers to vegetation dynamics indicated by NDVI in a large dam-reservoir-river system. J. Clean Prod. 2020, 256, 120477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, S.; Wang, L.C.; Lin, A.W.; Zhu, H.J.; Yuan, M.X. What drives the vegetation restoration in Yangtze River basin, China: Climate change or anthropogenic factors? Ecol. Indic. 2018, 90, 438–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julio Camarero, J.; Manzanedo, R.D.; Sanchez-Salguero, R.; Navarro-Cerrillo, R.M. Growth response to climate and drought change along an aridity gradient in the southernmost Pinus nigra relict forests. Ann. For. Sci. 2013, 70, 769–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palombo, C.; Marchetti, M.; Tognetti, R. Mountain vegetation at risk: Current perspectives and research reeds. Plant Biosyst. 2014, 148, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Xu, Y.; Huang, A.; Liu, C.; Marcos-Martinez, R.; Huang, L. Influences of Topographic Factors on Outcomes of Forest Programs and Policies in a Mountain Region of China: A Case Study. Mt. Res. Dev. 2020, 40, R48–R60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Ma, L.; Jia, Y.; Liu, M. Integrating the effects of latitude and altitude on the spatial differentiation of plant community diversity in a mountainous ecosystem in China. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0176866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grytnes, J.-A.; Kapfer, J.; Jurasinski, G.; Birks, H.H.; Henriksen, H.; Klanderud, K.; Odland, A.; Ohlson, M.; Wipf, S.; Birks, H.J.B. Identifying the driving factors behind observed elevational range shifts on European mountains. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2014, 23, 876–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, G.P. Extrinsic regime shifts drive abrupt changes in regeneration dynamics at upper treeline in the Rocky Mountains, USA. Ecology 2012, 93, 1614–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moyes, A.B.; Germino, M.J.; Kueppers, L.M. Moisture rivals temperature in limiting photosynthesis by trees establishing beyond their cold-edge range limit under ambient and warmed conditions. New Phytol. 2015, 207, 1005–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbutt, C.; Edwards, T.J. Reconciling ecological and phytogeographical spatial boundaries to clarify the limits of the montane and alpine regions of sub-Sahelian Africa. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2015, 98, 64–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemp, A. Climate change-driven forest fires marginalize the impact of ice cap wasting on Kilimanjaro. Glob. Change Biol. 2005, 11, 1013–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hertel, D.; Wesche, K. Tropical moist Polylepis stands at the treeline in East Bolivia: The effect of elevation on stand microclimate, above- and below-ground structure, and regeneration. Trees Struct. Funct. 2008, 22, 303–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, J.A.F.; Hiltbrunner, E.; Koerner, C. Functional morphology and microclimate of Festuca orthophylla, the dominant tall tussock grass in the Andean Altiplano. Flora 2011, 206, 387–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klimes, L.; Dolezal, J. An experimental assessment of the upper elevational limit of flowering plants in the western Himalayas. Ecography 2010, 33, 590–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koerner, C. Global Statistics of “Mountain” and “Alpine” Research. Mt. Res. Dev. 2009, 29, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Körner, C. Alpine Plant Life: Functional Plant Ecology of High Mountain Ecosystems, 3rd ed.; Springer Nature Switzerland AG: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 53–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.H.; Lv, C.H.; Lv, T.T.; Yang, A.Q.; Liu, C. Regional differentiation of vegetation change in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Prog. Geog. 2009, 28, 391–397. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, D.; Zhang, H.Y.; Hou, G.L.; Zhao, J.J.; Liu, D.Y.; Guo, X.Y. Topographic controls on alpine treeline patterns on Changbai Mountain, China. J. Mt. Sci. Engl. 2014, 11, 429–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.F.; Zhang, J.S.; Zhu, X.F.; Pan, Y.Z.; Liu, Y.X.; Zhang, D.H.; Lin, Z.H. Spatiotemporal changes in vegetation coverage and its driving factors in the Three-River Headwaters Region during 2000–2011. J. Geogr. Sci. 2014, 24, 288–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Xu, G.; Li, P.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Jia, L.; Zhang, J. Vegetation dynamics and their relationships with climatic factors in the Qinling Mountains of China. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 108, 105719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoungrana, B.J.B.; Conrad, C.; Thiel, M.; Amekudzi, L.K.; Da, E.D. MODIS NDVI trends and fractional land cover change for improved assessments of vegetation degradation in Burkina Faso, West Africa. J. Arid. Environ. 2018, 153, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Li, Y.; Tian, L.; Liu, Y.X.; Wang, Y.L. Vegetation Dynamics and Associated Driving Forces in Eastern China during 1999–2008. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 13641–13663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Li, X.; Liu, M.; Shi, Y.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, B.; Yan, J. Spatial variation patterns of plant herbaceous community response to warming along latitudinal and altitudinal gradients in mountainous forests of the Loess Plateau, China. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2020, 172, 103983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Liu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Wu, J.; Han, Y. Trend analysis of vegetation dynamics in Qinghai–Tibet Plateau using Hurst Exponent. Ecol. Indic. 2012, 14, 28–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Qi, Y.; Huang, C.; Li, X.; Deng, X.; Zhang, J. Analysis of vegetation changes and dominant factors on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, China. Sci. Cold Arid. Reg. 2019, 11, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yirdaw, E.; Starr, M.; Negash, M.; Yimer, F. Influence of topographic aspect on floristic diversity, structure and treeline of afromontane cloud forests in the Bale Mountains, Ethiopia. J. For. Res. 2015, 26, 919–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohapatra, J.; Singh, C.P.; Tripathi, O.P.; Pandya, H.A. Remote sensing of alpine treeline ecotone dynamics and phenology in Arunachal Pradesh Himalaya. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2019, 40, 7986–8009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacquin, A.; Sheeren, D.; Lacombe, J.-P. Vegetation cover degradation assessment in Madagascar savanna based on trend analysis of MODIS NDVI time series. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2010, 12, S3–S10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q.Z.; Li, Y.; Wan, Y.F.; Zhang, W.N.; Borjigdai, A. Challenges in disentangling the influence of climatic and socio-economic factors on alpine grassland ecosystems in the source area of Asian major rivers. Quatern. Int. 2013, 304, 126–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.L.; Yang, Y.L.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.L. Assessing vegetation dynamics and their relationships with climatic variability in northern China. Phys. Chem. Earth 2015, 87–88, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zewdie, W.; Csaplovics, E.; Inostroza, L. Monitoring ecosystem dynamics in northwestern Ethiopia using NDVI and climate variables to assess long term trends in dryland vegetation variability. Appl. Geogr 2017, 79, 167–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Lu, Y.; Fu, B.; Comber, A.; Li, T.; Hu, J. Driving Factors of Land Change in China’s Loess Plateau: Quantification Using Geographically Weighted Regression and Management Implications. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunsdon, C.; Fotheringham, A.S.; Charlton, M.E. Geographically Weighted Regression: A Method for Exploring Spatial Nonstationarity. Geogr. Anal. 1996, 28, 281–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dullinger, S.; Dirnbock, T.; Grabherr, G. Modelling climate change-driven treeline shifts: Relative effects of temperature increase, dispersal and invasibility. J. Ecol. 2004, 92, 241–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diao, Y.X.; Wang, J.J.; Yang, F.L.; Wu, W.; Zhou, J.; Wu, R.D. Identifying optimized on-the-ground priority areas for species conservation in a global biodiversity hotspot. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 290, 112630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, J.; Liu, Y.; Ying, L.; Li, P.; Xu, Y.; Shen, Z. Road impacts on spatial patterns of land use and landscape fragmentation in three parallel rivers region, Yunnan Province, China. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2014, 24, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, X.; Replumaz, A.; van der Beek, P. Contrasting exhumation histories and relief development within the Three Rivers Region (south-east Tibet). Solid Earth 2021, 12, 563–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Körner, C.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, R.; Geng, Y.; Shi, W.; Ou, X. No slope exposure effect on alpine treeline position in the Three Parallel Rivers Region, SW China. Alp. Bot. 2013, 123, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhao, K.; Zhu, X.; Yang, S. Protecting and using of ecotourism resource of moon mountain scenic spot in Three Parallel River Area. Ecol. Econ. 2008, 5, 75–80. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y.; Yang, F.; Wang, J.; Wu, R. Assessment of the tourism and recreation cultural ecosystem services in Three Parallel Rivers Region. Acta Ecol. 2020, 40, 4351–4361. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y.; Wu, R.; Yang, F.; Wang, J. The spatial patterns of scenic spots in Three Parallel Rivers Region. J. Yunnan Univ. 2020, 42, 992–1003. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, X.; Wu, X.; Shen, Y.; Liu, F.; Zhang, C. Responses of Vegetation Coverage Changes to Climate Factors in the Source Regions of Three Parallel Rivers. Mt. Res. 2015, 33, 218–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, C.; Zhang, W. Spatiotemporal distribution and the characteristics of the air temperature of a river source region of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Environ. Monit. Assess 2018, 190, 368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.; Li, Y.F.; Liu, G.H.; Zhang, H.L.; Liu, Q.S. Recent climate variability and its impact on precipitation, temperature, and vegetation dynamics in the Lancang River headwater area of China. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2014, 35, 2822–2834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.P.; Dong, S.K.; Peng, M.C.; Li, X.Y.; Liu, S.L. Vegetation distribution pattern in the dam areas along middle-low reach of Lancang-Mekong River in Yunnan Province, China. Front. Earth Sci. 2012, 6, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.J.; Weng, C.Y.; Guo, J.Q.; Dai, L.; Zhou, Z.Z. Vegetation responses to late Quaternary climate change in a biodiversity hotspot, the Three Parallel Rivers region in southwestern China. Palaeogeogr. Palaeocl. 2018, 491, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.; Deng, J.; Liu, X.; Zhou, Z.; Yao, J.; Dai, F.; Ren, K.; Li, L. Primary Recognition of Active Landslides and Development Rule Analysis for Pan Three-river-parallel Territory of Tibet Plateau. Adv. Eng. Sci. 2020, 52, 16–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Zhao, S.; Deng, J. Developing Law of Damming Landslide and Challenges for Disaster Prevention and Mitigation in the Three-river-parallel Territory in the Tibetan Plateau. Adv. Eng. Sci. 2020, 52, 50–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers, N.; Mittermeier, R.A.; Mittermeier, C.G.; da Fonseca, G.A.B.; Kent, J. Biodiversity hotspots for conservation priorities. Nature 2000, 403, 853–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, T.; Duan, Q.; Hua, S.; Shi, D.; Xu, C.; Tong, W.; Ning, D.; Lu, S.; Qin, B.; Yu, J.; et al. Ministry of Water Resources the People’s Republic of China. Standards for Classification and Gradation of Soil Erosion; China Water & Power Press: Beijing, China, 2008; pp. 8–9. (In Chinese)
- He, W.; Ye, C.; Sun, J.; Xiong, J.; Wang, J.; Zhou, T. Dynamics and Drivers of the Alpine Timberline on Gongga Mountain of Tibetan Plateau-Adopted from the Otsu Method on Google Earth Engine. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.G.; Liu, X.N.; Feng, Z.M. Remote sensing identification and spatial pattern analysis of the alpine timberline in the three parallel rivers region. Resour. Sci. 2014, 36, 259–266. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.K.; Xiao, P.F.; Feng, X.Z.; Li, H.X. Accuracy assessment of seven global land cover datasets over China. ISPRS J. Photogramm. 2017, 125, 156–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuppel, S.; Fan, Y.; Jobbagy, E.G. Seasonal hydrologic buffer on continents: Patterns, drivers and ecological benefits. Adv. Water Resour. 2017, 102, 178–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gang, C.C.; Zhao, W.; Zhao, T.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, X.R.; Wen, Z.M. The impacts of land conversion and management measures on the grassland net primary productivity over the Loess Plateau, Northern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 645, 827–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bontemps, S.; Boettcher, M.; Brockmann, C.; Kirches, G.; Lamarche, C.; Radoux, J.; Santoro, M.; Vanbogaert, E.; Wegmüller, U.; Herold, M.; et al. Multi-year global land cover mapping at 300 m and characterization for climate modelling: Achievements of the Land Cover component of the ESA Climate Change Initiative. ISPRS Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2015, XL-7/W3, 323–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregory, D.; Josh, H.; Alessandro, C. A dataset mapping the potential biophysical effects of vegetation cover change. Sci. Data 2018, 5, 180014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wen, Z.; Gang, C. Normalized difference vegetation index of different vegetation cover types and its responses to climate change in the Loess Plateau. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2020, 40, 678–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Xie, M.; Wang, H.; Li, S.; Xu, M. Spatial Heterogeneity of Vegetation Response to Mining Activities in Resource Regions of Northwestern China. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhi, Y.; Shan, L.; Ke, L.; Yang, R. Analysis of Land Surface Temperature Driving Factors and Spatial Heterogeneity Research Based on Geographically Weighted Regression Model. Complexity 2020, 2020, 2862917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comber, A.J.; Brunsdon, C.; Radburn, R. A spatial analysis of variations in health access: Linking geography, socio-economic status and access perceptions. Int. J. Health Geogr. 2011, 10, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; Li, R.; Sha, Z. Exploring the Dynamics of Urban Greenness Space and Their Driving Factors Using Geographically Weighted Regression: A Case Study in Wuhan Metropolis, China. Land 2020, 9, 500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Yao, M.; Yang, L.; Qi, H.; Meng, X.; Zhou, F. Using geographically weighted regression to predict the spatial distribution of frozen ground temperature: A case in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Environ. Res. Lett. 2021, 16, 024003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakaya, T. GWR4.09 User Manual. WWW Document. Available online: https://raw.githubusercontent.com/gwrtools/gwr4/master/GWR4manual_409.pdf (accessed on 16 May 2021).
- Zhang, D.; Jia, Q.; Wang, P.; Zhang, J.; Hou, X.; Li, X.; Li, W. Analysis of spatial variability in factors contributing to vegetation restoration in Yan’an, China. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 113, 106278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, R.; Yu, X.; Li, D.; Ye, X. Using geographically weighted regression to explore the effects of environmental heterogeneity on the space use by giant pandas in Qinling Mountains. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2020, 40, 2647–2654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, S.A. The Problem of Pattern and Scale in Ecology: The Robert H. MacArthur Award Lecture. Ecology 1992, 73, 1943–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.J.; Liu, L.; Song, K.C.; Li, X.D.; Wang, Y.D.; Tang, Y.; Jiang, H.R. Remote sensing the orographic effects of dry-hot valley on vegetation distribution in the southeast Tibetan Plateau. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2019, 40, 8589–8607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grytnes, J.A. Species-richness patterns of vascular plants along seven altitudinal transects in Norway. Ecography 2003, 26, 291–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenoir, J.; Graae, B.J.; Aarrestad, P.A.; Alsos, I.G.; Armbruster, W.S.; Austrheim, G.; Bergendorff, C.; Birks, H.J.B.; Brathen, K.A.; Brunet, J.; et al. Local temperatures inferred from plant communities suggest strong spatial buffering of climate warming across Northern Europe. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2013, 19, 1470–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, A.B.; Kumar, P.; Tcheng, D. A data mining approach for understanding topographic control on climate-induced inter-annual vegetation variability over the United States. Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 98, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, L.; Li, Z.; Xu, G.; Ren, Z.; Li, P.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, B.; Zhang, J.; Yu, S. Dynamic change of vegetation and its response to climate and topographic factors in the Xijiang River basin, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 11637–11648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moeslund, J.E.; Arge, L.; Bocher, P.K.; Dalgaard, T.; Odgaard, M.V.; Nygaard, B.; Svenning, J.C. Topographically controlled soil moisture is the primary driver of local vegetation patterns across a lowland region. Ecosphere 2013, 4, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, M.M.; Szyska, B.; Kessler, M. Microhabitat partitioning promotes plant diversity in a tropical montane forest. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2011, 20, 558–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.S.; Li, X.Y.; Chen, L.; Xie, G.D.; Liu, C.L.; Pei, S. Effects of Topographical and Edaphic Factors on Tree Community Structure and Diversity of Subtropical Mountain Forests in the Lower Lancang River Basin. Forests 2016, 7, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jobbágy, E.G.; Sala, O.E.; Paruelo, J.M. Patterns and Controls of Primary Production in the Patagonian Steppe: A Remote Sensing Approach. Ecology 2002, 83, 307–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mou, X.; Yu, Y.; Li, X.; Degen, A. Presence frequency of plant species can predict spatial patterns of the species in small patches on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2020, 21, e00888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Cheng, G.W.; Li, W.P. Meta-analysis of relationships between environmental factors and aboveground biomass in the alpine grassland on the Tibetan Plateau. Biogeosciences 2013, 10, 1707–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Feng, X.; Zeng, Y.; Fu, B.; Yao, X.; Li, J.; Wu, B. Recent ecological transitions in China: Greening, browning, and influential factors. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, J.; Adamowski, J.F.; Deo, R.C.; Xu, X.; Gong, Y.; Feng, Q. Grassland Degradation on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau: Reevaluation of Causative Factors. Rangel. Ecol. Manag. 2019, 72, 988–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, S.; Sun, Y.; Li, M.; An, Y.; Shi, F. Spatial differentiation of the NPP and NDVI and its influencing factors vary with grassland type on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2021, 193, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Ganjurjav, H.; Liang, Y.; Gao, Q.; Wan, Y.; Li, Y.; Baima, Y.; Xirao, Z. Effect of a grazing ban on restoring the degraded alpine meadows of Northern Tibet, China. Rangel. J. 2015, 37, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fayiah, M.; Dong, S.; Li, Y.; Xu, Y.; Gao, X.; Li, S.; Shen, H.; Xiao, J.; Yang, Y.; Wessell, K. The relationships between plant diversity, plant cover, plant biomass and soil fertility vary with grassland type on Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2019, 286, 106659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


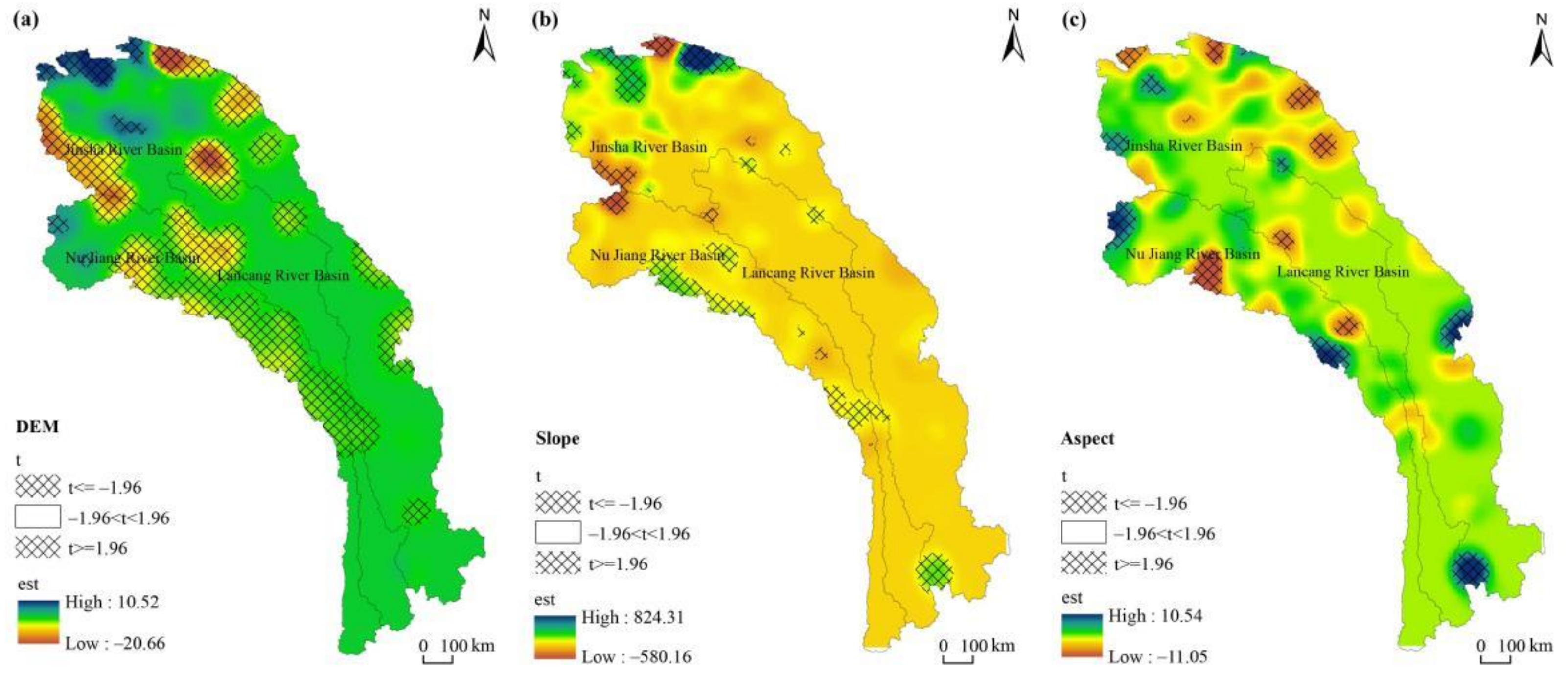
| Variable | Mean | Min | Max | Lwr Quartile | Median | Upr Quartile | SD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DEM | −1.13 | −20.66 | 10. 52 | −1.97 | −0.16 | 0.00 | 2.98 |
| Slope | 21.67 | −580.16 | 824. 38 | −0.00 | 1.15 | 30.08 | 81.37 |
| Aspect | 0.04 | −11.05 | 10. 54 | −0.55 | 0.00 | 0.53 | 2.35 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, C.; Wang, J.; Naudiyal, N.; Wu, N.; Cui, X.; Wei, Y.; Chen, Q. Multiple Effects of Topographic Factors on Spatio-Temporal Variations of Vegetation Patterns in the Three Parallel Rivers Region, Southeast Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 151. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14010151
Wang C, Wang J, Naudiyal N, Wu N, Cui X, Wei Y, Chen Q. Multiple Effects of Topographic Factors on Spatio-Temporal Variations of Vegetation Patterns in the Three Parallel Rivers Region, Southeast Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(1):151. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14010151
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Chunya, Jinniu Wang, Niyati Naudiyal, Ning Wu, Xia Cui, Yanqiang Wei, and Qingtao Chen. 2022. "Multiple Effects of Topographic Factors on Spatio-Temporal Variations of Vegetation Patterns in the Three Parallel Rivers Region, Southeast Qinghai-Tibet Plateau" Remote Sensing 14, no. 1: 151. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14010151
APA StyleWang, C., Wang, J., Naudiyal, N., Wu, N., Cui, X., Wei, Y., & Chen, Q. (2022). Multiple Effects of Topographic Factors on Spatio-Temporal Variations of Vegetation Patterns in the Three Parallel Rivers Region, Southeast Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Remote Sensing, 14(1), 151. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14010151







