Abstract
Discrete phreatophytic vegetation associated with organic mound springs is present in several places in the semi-arid Walyarta Conservation Park (Park) in northern Western Australia. The mound springs are heritage listed, having significant cultural and environmental significance. Increased industrial (mining and agriculture) development in the region, coupled with a growing demand for groundwater to support these developments, requires an enhanced understanding of how the springs operate and the source of water that sustains their presence. The springs are broadly believed to be situated on geological faults and receive groundwater from artesian sources. However, their association with deeper geological structures and aquifer systems, the focus of this study, is not well understood. This study employed regional- and finer-scale airborne geophysical data, including electromagnetics (AEM) and magnetics, to constrain the sub-basin-scale hydrogeology of the West Canning Basin in Western Australia and to detail tectonic deformation, sedimentological and hydrological processes. The AEM data were inverted using 1- and 2D methods to better define structural discontinuities in the Park, and the results identified the location of faults and other geological structures that were coincident with spring locations. A complementary analysis of spatiotemporal patterns of green vegetation was undertaken using remote sensing data. A model for the extent of green vegetation (in percent), calculated using a constrained linear spectral unmixing algorithm and applied to a select Landsat Thematic Mapper ™ image archive, showed the persistence of green vegetation aligned with interpreted fault systems through extended dry periods. These geophysical and remotely sensed datasets demonstrate that in the Park, the sedimentary aquifers and landscapes are highly compartmentalized and that this constrains aquifer distribution, groundwater quality and the location of wetlands and phreatophytic vegetation. Integrating key information from these datasets allows for the construction of a three-dimensional model that predicts the nature and extent of the critical zone which sustains perennial groundwater discharge within mound springs, drainages and wetlands and provides a framework to assess discharge rates, mixing and, ultimately, sensitivity to changed water availability.
1. Introduction
Globally, satellite and airborne remote sensing methods are critical in the mapping and monitoring of wetlands and springs (see, for example, [1,2]). These methods are particularly relevant in remote areas of north Western Australia where the climate is semi-arid and water bodies are generally ephemeral and difficult to access. In this region, numerous small, isolated permanent freshwater springs and waterholes occur in inland and along coastal areas. They are often coincident with geomorphic and geological discontinuities. Where present, the springs tend to be densely vegetated and have high environmental and heritage values for Australia’s indigenous people. Due to these sensitivities and their remoteness, non-invasive techniques such as remote sensing and airborne geophysics are important tools for investigating spring geology and hydrology.
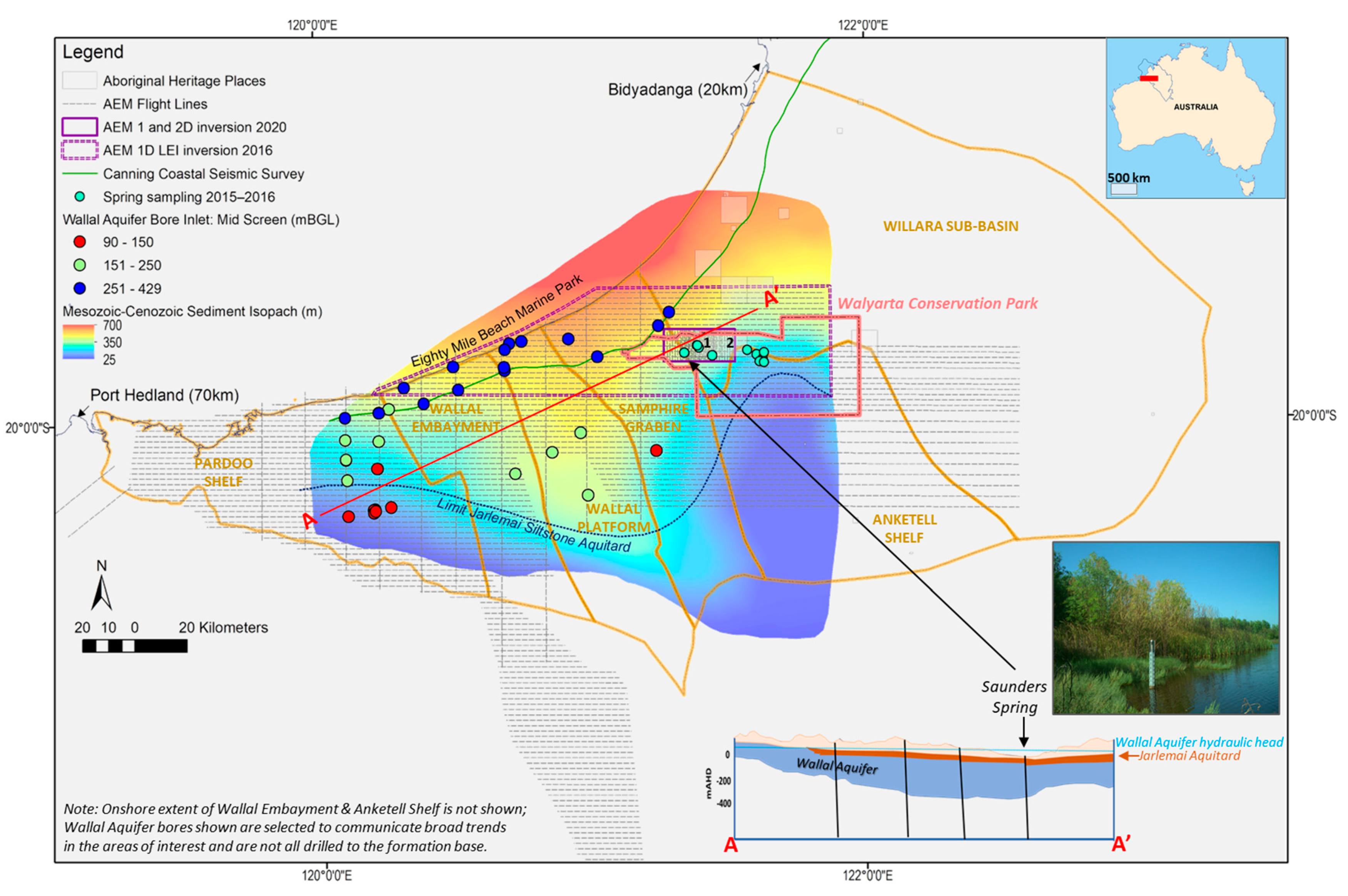
Several perennial organic mound springs occur in the study area, the Walyarta Conservation Park (Park), located in the semi-arid zone of Western Australia’s Canning Basin (Figure 1). Management of the Park is jointly vested between the Department of Biodiversity, Conservation and Attractions (DBCA) and traditional owners (TOs) [3]. The mound springs are located within a heritage listed area that is important for ceremonial purposes (Figure 1). These springs also form part of the Eighty-Mile Beach Ramsar site and are important refugia for birds, as they support small moats containing invertebrates [4,5]. The Park is remote, sparsely vegetated and large in area (~2300 km2), which makes it difficult to investigate and sample all spring sites. Surveyed springs range in size from tens to a few hundreds of meters in diameter, are generally densely vegetated and include species that thrive under mesic conditions [6,7,8]. Carbon dating of spring peat substrates confirms they developed thousands of years ago [9] and are similar in age to spring water discharge [10].
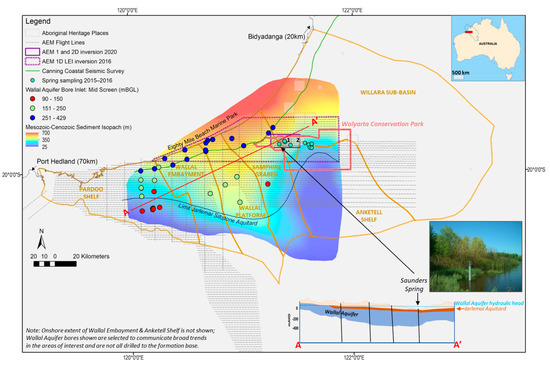
Figure 1.
Location of Walyarta Conservation Park study area showing tectonic elements of the West Canning Basin (WCB) and the broad-scale distribution of the combined Mesozoic to Cenozoic sediments that host the Wallal Sandstone aquifer. Note: Aboriginal Heritage Places marked 1 and 2 are registered sites 14478 and 14479 (Aboriginal Heritage Places (DPLH-001)–Datasets, Available online: https://www.dplh.wa.gov.au/information-and-services/aboriginal-heritage/aboriginal-heritage-search, accessed on 24 March 2021); the inset map of Australia has the full extent of the Canning Basin, with the WCB in red.
The generally accepted conceptual model for the West Canning Basin mound springs is that they receive groundwater from the confined Wallal aquifer which discharges via geological faults [11,12]. Faults provide a viable mechanism to deliver artesian groundwater to springs systems (e.g., [13,14]), and several studies have described the deployment of surface hydrogeophysical methods to identify controlling structures and their association with spring development (e.g., [15,16]). Where spring complexes are spatially dispersed and access is difficult, alternative approaches to ground investigations need to be considered, including airborne geophysics and remote sensing.
Satellite-based remote sensing methods have demonstrated value in monitoring the spatiotemporal stability of vegetation. They are particularly useful for understanding the persistence of mesic vegetation in relation to changes in water availability [17]. A normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) has proven effective in monitoring the decline in vegetation coverage associated with drying climates across large catchments and climatic zones in Asia and northern hemisphere permafrost regions [18,19]. In sparsely vegetated semi-arid to arid regions, surface water forms a mappable contrast with surface soils, which provides the opportunity to map the changing extents of lakes and springs [20,21], while the monthly frequency of satellite data acquisition allows for seasonal interrogation of vegetation at a global scale (e.g., [22]). The authors of [2] illustrate how temporal multispectral remote sensing can contribute to understanding spring discharge and the extent of vegetation associated with these systems. They do not touch on geological structural constraints.
Despite the effectiveness of ground geophysical, particularly electrical, techniques for resolving structures that constrain the presence of spring complexes, relatively few studies have explored the application of airborne electromagnetic (AEM) methods for undertaking such investigations. In environmental water research, inverted AEM data provide a three-dimensional framework to assess and predict the continuity of groundwater delivery. In [23], researchers have described the role of a heliborne time domain EM survey to help conceptualize constraints on spring systems identified in the Galapagos Islands, demonstrating their value for exploratory hydrogeological studies in geologically complex, poorly known environments. Spatial information on aquifers and groundwater quality sourced from AEM data helps to assess the size and resilience of groundwater flow systems. Where this groundwater supports vegetation, this also increases knowledge of vegetation hydrological tolerances. AEM data are most valuable where targets are resolved through electrical conductivity contrasts, such as land salinization and saltwater interface and freshwater lens mapping (e.g., [24,25,26]). Another common application of AEM data is the production of regolith and aquifer thickness maps, where bedrock and aquitards form conductivity contrasts (e.g., [27,28]).
Here, the application of multi-scale, fixed-wing time domain electromagnetics is assessed for mapping confined and unconfined aquifers and for their effectiveness in resolving geological faults and structures that could form groundwater flow conduits supporting organic mound springs. This is considered in a sedimentary basin setting where other airborne geophysical methods, such as potential field technologies, may be less effective, either because we are dealing with non-magnetic sediment sequences or resolution is limited. The focus for the study is organic mound springs located in the Walyarta Conservation Park, where finer-scaled AEM data were acquired. The interpretation of aquifer geometry and fault systems is reviewed against temporal Landsat Thematic Mapper (TM) satellite remote sensing data, data that have been acquired in times of prolonged drought. The rationale is to identify areas of persistent vegetation that are spatially linked to geological structures that source water from artesian aquifers at depth.
2. Background
The Walyarta Conservation Park study area is located in the Canning Basin (Figure 1), which is the largest sedimentary basin in Western Australia [29]. The basin contains thick sequences of mainly Ordovician- to Permian-aged sediments overlying Archaean- and Proterozoic-aged basement, with Mesozoic to Recent sediments located on the onshore basin margin, generally around 100 km from the current coastline (e.g., [29,30]. The basin is prospective for hydrocarbons, iron ore and base metals, and exploration for these commodities has provided information on the tectonic element boundaries and broad-scale distribution of geological formations (e.g., [29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38]).
2.1. Hydrogeological Setting
The basin also contains large supplies of potable groundwater, and these resources are suitable for human use, mining and agricultural activities including stock, horticulture and irrigated pasture (e.g., [11,39,40,41,42,43]). The main aquifer of interest in the Park is the Jurassic-aged Wallal Sandstone aquifer, which is mainly confined by the Jarlemai Siltstone aquitard and characterized by hydraulic heads of over forty meters within thirty kilometers from the coast [43] (Figure 1). Minor unconfined aquifers exist in the overlying Cretaceous Broome Sandstone and Cenozoic cover and the direction of groundwater flow in both the confined and unconfined aquifers is towards the coast. Groundwater recharge to the Wallal aquifer occurs from rainfall via Cenozoic formations and the Jarlemai aquitard, particularly where the aquitard is thin or absent, and the hydraulic head allows for the vertical movement of groundwater.
Cenozoic cover is mainly unsaturated, and inland, the cover is dominated by mainly thin evaporites in low-lying areas and fixed seif dunes that range in thickness from around 10 to 40 m. Dune sands mainly contain poorly sorted iron-stained quartz sand and ~1% heavy minerals, and this low maturity confirms the longevity of local-scale erosional and depositional processes [44]. The dunes are laterally continuous over long distances (e.g., over 50 km), and together with their elevation, they spatially constrain surface water flows and groundwater recharge.
Following cyclonic rainfall, many dune-controlled catchments deliver brackish water to inland playa lakes that have evaporite crusts. This describes the hydrological function of the Ramsar ephemeral lakes located in the Park valley floor. The climate in the Park is classified as semi-arid, with an annual average rainfall of around 377 mm (Figure 2) [45,46]. Rainfall mainly occurs in the wet season, which is generally between the months of December and May. Average annual rainfall since the late 1970’s has increased by approximately 23% due to the increased frequency of wet-season cyclones.
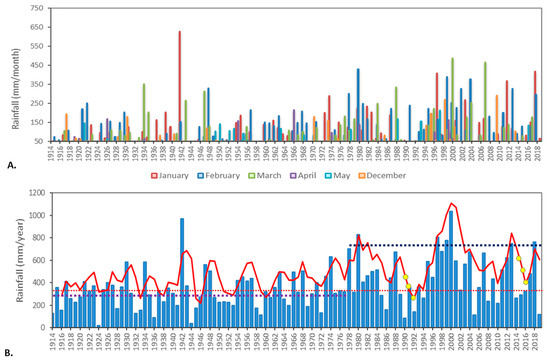
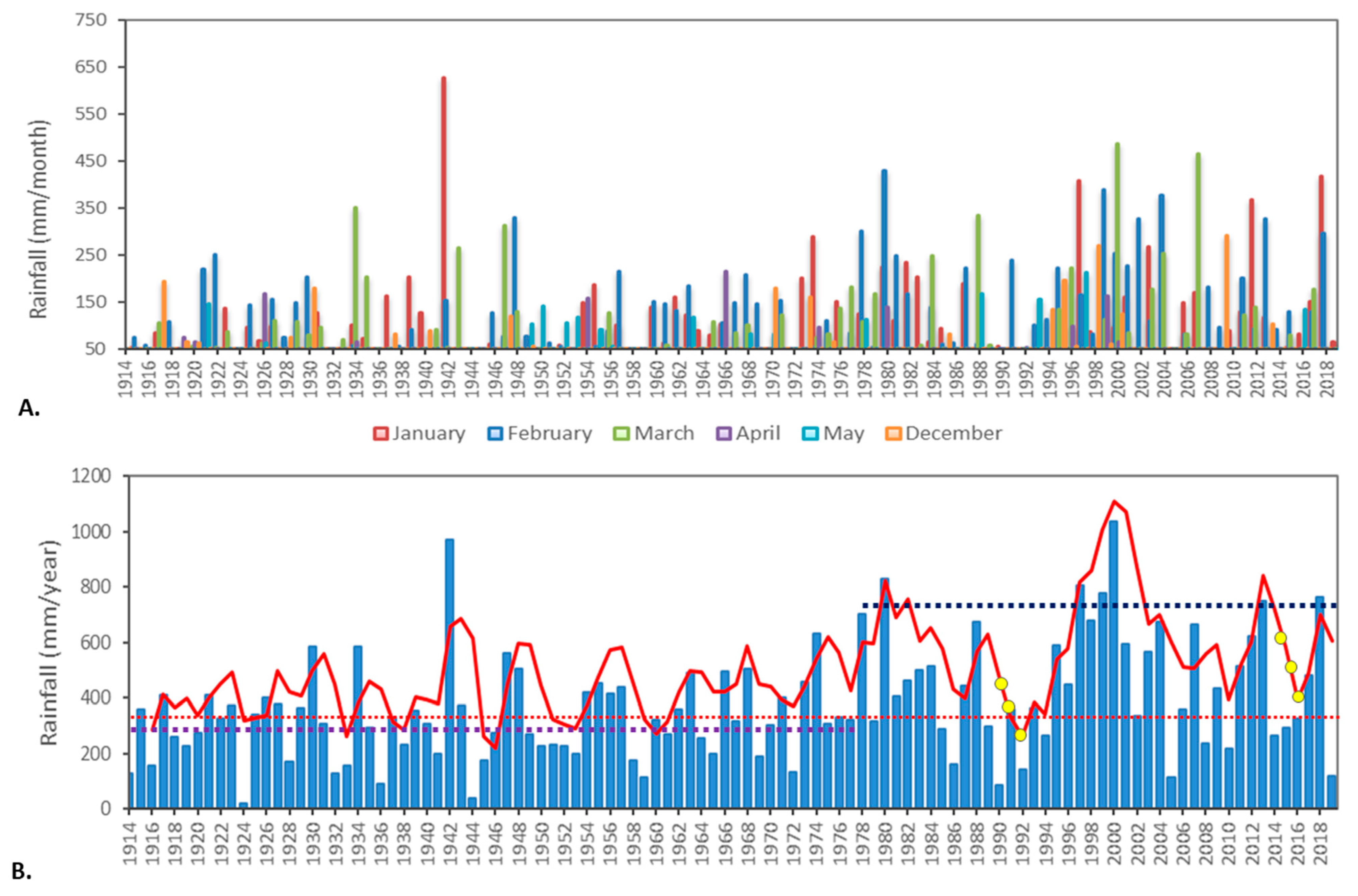
Figure 2.
Climate data from Mandora Bureau of Meteorology Station (BOM) No. 0419 (http://www.bom.gov.au/climate/data accessed on: 24 March 2021): (A). Bar graph of monthly wet season rainfall (1914 to 2019); (B). Bar graph of annual rainfall (1914 to 2019), with three-point moving average shown as a red solid line; mean annual rainfall for different periods (1914–2019: red dashed line @ ~377 mm; 1914–1977: purple dashed line @ ~320 mm; 1978–2019: blue dashed line @ ~463 mm) and yellow dots represent decreasing average rainfall trends at the end of the two climate cycles that are examined in this study.
Extreme rainfall events are important in sustaining habitat and biodiversity through the generation of surface water flows that inundate ephemeral lakes and wetlands. They also recharge aquifers that support groundwater-dependent vegetation, which, in the Park valley floor, comprises Typha within brackish pools and mangroves located along saline creek reaches. Halophytes, predominantly samphires (Tecticornia spp.), are more common in downgradient ephemeral lake beds and on coastal salt flats. Upgradient, different landforms are characterized by a varying composition of Sesbania formosa/Melaleuca woodlands, Acacia and Melaleuca alsophila shrublands, Triodia hummock grasslands and samphires [7,47]. Broad-scale vegetation consists of mainly sandplain shrublands (Acacia), grasslands and spinifex, with major deeper-rooted phreatophytic vegetation restricted to perennial springs, dune swales and river and creek beds. Perennial mound springs have a characteristic organic, carbon-rich substrate and small ephemeral moats which, together, support a restricted vegetation assemblage of tall Sesbania formosa/Melaleuca leucadendron woodlands and a mangrove fern (Acrostichum speciosum) understory.
Vegetation coverage over the Park is sparse, reflecting the low average rainfall and high temperatures. Due to its remoteness and mainly low water requirements, the native vegetation is stable unless it is subject to pressure from fire, flooding, land clearing and overgrazing from introduced animals, such as camels and cattle [7].
Vegetation monitoring in the Canning Basin and the Park is carried out using satellite remote sensing techniques, together with on-ground verification. NDVI methods have been employed by researchers at a basin-wide scale to assess changes in climate, groundwater storage and discharge (evapotranspiration) [45]. At the Park scale, remote sensing data from two different satellites Landsat TM and Advanced Spaceborne Thermal Emission and Reflection Radiometer (ASTER) have mapped the spatiotemporal distribution of perennial green vegetation [48,49]. Results showing perennial (riparian) vegetation patterns are generally constrained by localized geological and geomorphological features, including breakaways and faults.
Spatial variation in the groundwater recharge and flow in the Wallal and Broome aquifers has been more recently researched in the Pardoo Shelf and Wallal Embayment using hydrogeochemical and environmental tracer methods [50]. Results of that study show that Wallal aquifer recharge is restricted to inland areas where the Jarlemai aquitard is largely absent. Compared with the Broome aquifer, there is considerable aging of Wallal aquifer groundwater along a ~25 km groundwater flow path, with an average modeled Carbon-14 age at the coast of thousands of years [50].
The sampling of Park spring discharge water in 2015 and 2016 yielded similar Carbon-14 ages to the coastal Wallal aquifer results [49], indicating that mound spring groundwater is likely to be sourced from this aquifer and has evolved over a groundwater flow path of similar length. As drilling in the Park is limited to a small number of shallow bores, this research sought to use the existing airborne EM data to better map the hydrogeology and assess the viability of different stratigraphic and structural models to explain the evolution of mound spring discharge.
2.2. AEM Data Acquisition, Inversion and Analysis
Regional-scale TEMPEST AEM data (a fixed-wing time domain electromagnetic system; Appendix A; Figure A1) were acquired over the West Canning Basin between 2014 and 2015 [51] by State Government agencies to improve understanding of the geology and groundwater resources. The TEMPEST AEM system was developed in 1998 by CRC-AMET (Australian Mineral Exploration Technologies) established by the Australian government’s Cooperative Research Centres (CRC) program [52,53]. Mounted on a fixed-wing aircraft (a CASA 212), the transmitter loop is draped around the wingtips, tail and nose of the aircraft, while the receiver coils are hosted in a bird, which is towed nominally 120 m behind and 40 m below the aircraft. The system has been widely used in Australia for prospect-scale surveys, catchment management [52] and groundwater mapping [54]. It has also been deployed for surveys covering large regional areas, including, for example, the Paterson Range in Western Australia (WA), Pine Creek in the Northern Territory, the Frome Embayment in South Australia and the La Grange region of WA [55,56,57,58]. More recently, a variant of the TEMPEST system is being used to survey a significant part of the Australian sub-continent (see [59]).
The extent of the coverage, which included the Walyarta Conservation Park, is shown in Figure 1. Initial inversion and analyses of these data were reported by [60]. They showed that AEM resolved sediment electrical conductivity to depths of up to 700 m below ground level, with depth of investigation (DOI) decreasing in areas of thick evaporites or saltwater intrusion.
A stratigraphic interpretation based on AEM-derived geo-electrical responses and lithological information from drilling was completed for the full survey area [60]. Mapping of stratigraphic horizons where drilling was absent was complicated as both the Wallal and Broome Sandstone aquifers have a similar geo-electrical response (e.g., resistive, with a median electrical conductivity (EC) of ~20 mS/m) [60]. The thickness of individual aquifers was resolved where they were able to be separated by an electrically conductive Jarlemai Siltstone aquitard. This was an effective mapping technique closer to the coast, where the aquitard was thicker, but it was less effective further inland, where the aquitard was eroded [31,50] and, consequently, its conductance was lower [60].
A subset of the regional broadscale AEM dataset (Figure 1) was subsequently re-inverted to better understand the hydrogeology within the Park. This inversion used a laterally constrained smooth model 1D layered earth inversion (LEI) employing the AarhusInv 1D inversion code [61,62]. The spatial constraints, which are defined for adjacent soundings, allow prior information (e.g., the expected geological variability of the area) to migrate along the flight lines. The use of constraints along lines enhances the connection of layer parameters between adjacent soundings.
In the context of the Walyarta area, this approach encouraged the definition of laterally continuous conductive layers, which is an aid to target definition and geological interpretation (see [63] for details). This inversion was carried out to optimize the extraction of near-surface information required for environmental water investigations in the Park (Figure 1). A relationship between AEM and groundwater quality data was developed for the bores closest to the Park using groundwater laboratory analyses (total dissolved solids (TDS) reported in mg/L) and averaged modeled TEMPEST AEM conductivity for depths where bores were screened. Results confirmed that conductivity responses were primarily determined by aquifer solutes, which, in the Park valley floor, were high [49]. This complicated the definition of stratigraphic units as drilling data are sparse and the depth of investigation was significantly reduced due to high near-surface conductivities, as indicated in the conductivity depth intervals (Figure 3B–E) associated with tidal flat and ephemeral lake sediments. Sufficient information was retrieved from the AEM to produce a coarse-scale isopach of the Jarlemai Siltstone aquitard and interpret the spatial extent of confined and unconfined aquifers within the Park [49]. However, there was uncertainty associated with this interpretation where the Jarlemai aquitard was thin and less conductive. This was important in the Park as it indicated that the aquitard had been eroded and its effectiveness to confine groundwater was reduced. The study [49] recommended further investigations be undertaken to map the Jarlemai sedimentary unit and assess its integrity as an aquitard to ensure that this was considered in environmental water accounting.
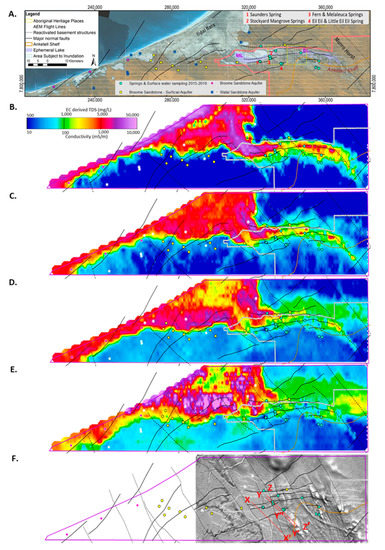
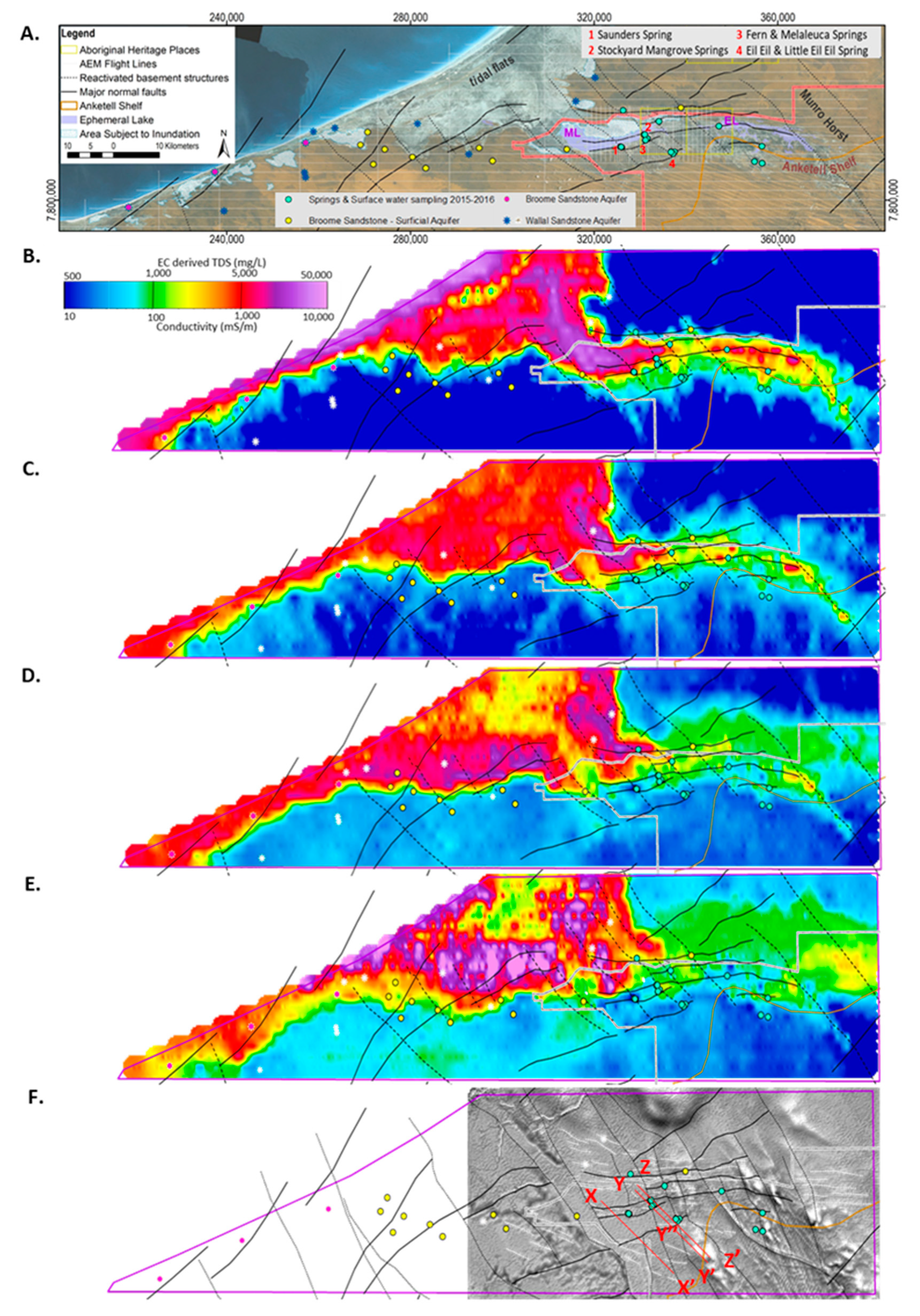
Figure 3.
TEMPEST airborne electromagnetic (AEM) 1D layered earth inversion (LEI) (2016): (A). Study area superimposed on SPOT 5 Imagery (2009) showing AEM flight lines, the location of major geological and physiographic features including Mandora Lake (ML) and East Lake (EL) and the Walyarta Conservation Park boundary (in red) (Note: previous Park boundary fell within the 2016 AEM inversion area); pseudo-colored interval conductivity images (CDI) for the following: (B). 0–10 m below ground level (BGL); (C). 30–40 m BGL; (D). 60–70 m BGL; (E). 100–110 m BGL; (F). Airborne magnetic first vertical derivative (1VD) greyscale image displaying deeper north–northwest structures (black linework) and strandlines (white dashed linework); see subsequent figures for explanations on X-X’, Y-Y”-Y’ and Z-Z’. Note: see Section 2.2 for the AEM conductivity and groundwater quality (TDS; mg/L) relationship presented in the key.
Conductivity depth interval images also revealed compartmentalized electrical conductivity responses that are, in places, associated with basement faults defined in airborne magnetics (Figure 3). These structures have been interpreted to control the presence and thickness of the Jarlemai aquitard [49]. Two dominant trends were apparent in the AEM, one being coarse-scale northwest trending reactivated faults that are known to be associated with neotectonics and were mappable in digital elevation models [64], and the other being east-west and southwest trending structures that were spatially aligned with hydrological features, such as ephemeral drainages and lake extents (Figure 3). The most obvious fault was the Munro Horst, which extends to the southeast and forms the eastern margin, the ephemeral wetland system in the Walyarta Conservation Park (Figure 3A).
2.3. Geological and Hydrogeological Interpretation of Geophysical Datasets
Regional-scale geological structures and structural styles have been interpreted in the West Canning Basin, including the study area, using airborne magnetics and surface gravity (e.g., [29,32] and, more recently, [33]). In [29], the major stress–strain relationships that influence northern Australian structural trends and the development of sedimentary basins are summarized, including northwest to southeast extension in the Late Carboniferous to Early Permian period (306–268 Ma) producing northeast trending normal faults and northwest relay zones; North-south compression in the Late Triassic period (220–210 Ma) which reactivated faults, resulting in the formation of dextral transpressional and sinistral wrench zones, accompanied by new north-south trending normal faults and east-west trending folds; complex reactivation of normal faults taking place in the Miocene to Recent (21–5 Ma) period, in response to the collision of southeast Asia microcontinental fragments with north-western Australia.
Recent interpretations of deep regional reflection seismic data have mapped the larger structural elements in the West Canning Basin and Park. They also resolve the transpression unconformity, which forms the base of the Mesozoic formations (Figure 1) [37,38]. Transpressional (e.g., combined strike-slip and shortening) movement is identified to be responsible for differential erosion. Importantly, retrogradation through combined depositional thinning and erosion results in thin Permian to Cenozoic sediment cover on the Anketell Shelf. Less of the section is missing, marginal to the gravity anomaly that defines the Anketell Shelf boundary [37]. Uncertainty in delineating and correlating faults was noted to be high due to the coarseness of the existing seismic grid [38]. Major north-westerly striking faults have been interpreted to terminate deep in the profile, at the base of the Permian formations, while the majority of younger, east- to northeast-oriented faults are thought to terminate at depths below Mesozoic sediments.
The propagation of structures to the ground surface has been a subject of much research and conjecture in the West Canning Basin. Investigations focusing on resource estimation and operations, as well as earthquake and tsunami risk, confirm that faulting through near-surface sediments occurs, and fault scarps exist at the land surface (e.g., [64,65]).
At a local scale, geological information in airborne magnetic data was reviewed to support AEM interpretations. Airborne magnetic data record variations in the Earth’s magnetic field, which are determined by variations in the magnetic susceptibility of the sub-surface. These data provide information on the structure and composition of the rocks present. The most relevant information provided by magnetic data is the structural fabric of the sub-surface, which is interpreted from consistent discontinuities and/or pattern breaks in the regional magnetic fabric.
The magnetic data used for this study were from the Geological Survey of Western Australia 80 m magnetic first vertical derivative (1VD) merged grid version 1 [66]. Although a variety of enhancement techniques are available for structural enhancement, a first vertical derivative (1VD) was employed to map near-surface intra-basinal features as it suppresses the effects of regional anomalies and enhances or amplifies higher-frequency contrasts in the magnetics field.
The structures evident in the available airborne magnetic data are broadly consistent with AEM conductivity discontinuities (Figure 3F). The main structural style in the magnetics, apparent as lateral discontinuities in the conductivity depth interval images (Figure 3), is north–northwest trending transfer faults that break up the geology into a series of fault blocks. When reactivated, these faults look to produce mainly right lateral strike-slip structures, with associated normal faulting and fractures. In the Park, east-west–southwest trending reverse normal faults have been defined through stratigraphic offsets. They are interpreted to form boundaries of relay zones, and most of the Park mound springs are in close proximity to these (Figure 3). Similar structures are observed at depth in the Fitzroy Basin, located within the northern Canning Basin [29] and this is used as the basis to conceptualize the fault structures shown in (Figure 4). Many east-west–northeast trending features apparent in the AEM are also resolved as high-frequency (shallow–near-surface) and spatially discrete magnetic responses. These are interpreted to belong to younger beach/slope deposits and strandlines, deposited during the last major sea-level highstand in the Pleistocene–Holocene period [31,67] (Figure 3F). High-amplitude and high-wavelength magnetic responses of the Anketell Shelf indicate a shallow depth to magnetic source, suggesting that Mesozoic and Cenozoic cover thins to the south of East Lake (Figure 3A). This conceptualization of the Anketell Shelf is reported in [37,49].
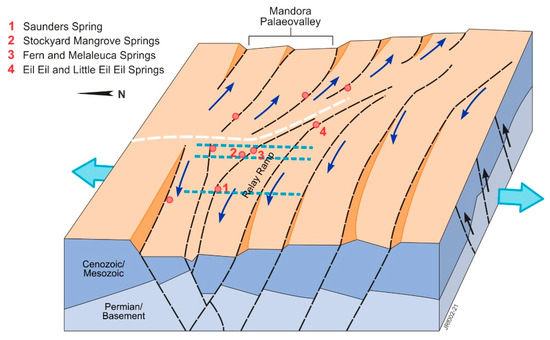
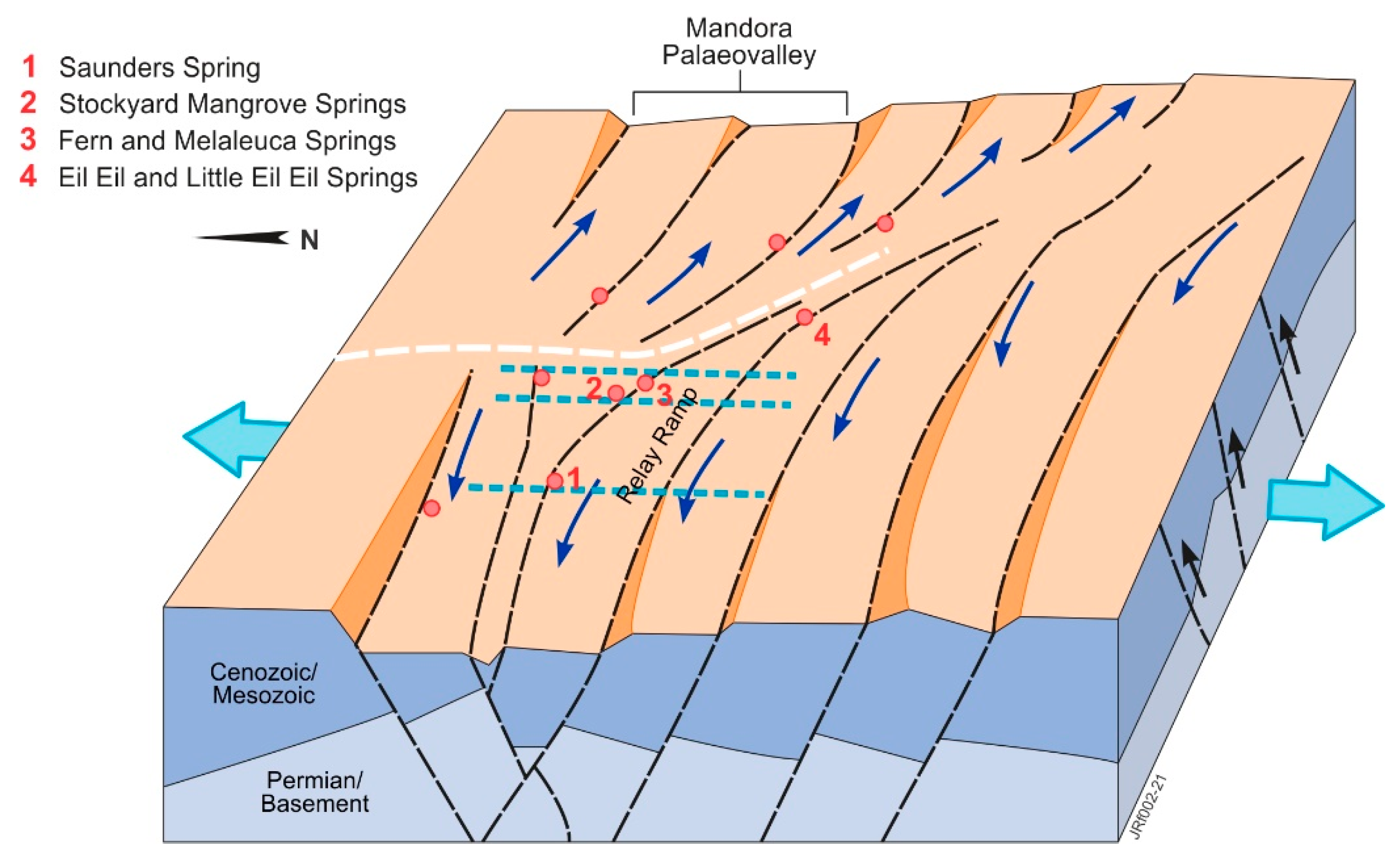
Figure 4.
Conceptualization of fault structures in the 2016 AEM 1D LEI Inversion area (adapted from [29,49]); AEM flight lines L40015, L40026 and L40027 (west to east) are blue dashed lines; spring sampling locations are in red; black arrows depict uplift in the Anketell Shelf area and relay fault movement is denoted by blue arrows, with the connecting fault (accommodation zone) in white.
To understand how structures influence aquifer geometry, connectivity and discharge within the Park, a 3D geological model was constructed using the Leapfrog Geo™ software program [49]. The 3D model covers the area defined as the AEM 1D LEI inversion 2016 in Figure 1 and Figure 3, with major stratigraphic horizons interpreted from 2-km-spaced east–west AEM flight lines and information from drilling, where it was available. The vertical extent of the model covered the average AEM DOI, which equated to 500 m Australian Height Datum (AHD). Information from previous geological mapping was employed as a starting model (e.g., [31]). The inverted AEM and airborne magnetic data were used to support the location of major structures that form fault block boundaries where the blocks are characterized by major changes in depositional and erosional conditions.
Following the interpretation of deep seismic data across the Park, an isopach for the combined thickness of Cenozoic and Mesozoic sediments was produced using the data presented in [37,38] (see Figure 1). Results for this combined sediment package were comparable with the 3D geological model produced from the 2-km-spaced AEM data, which increases confidence that AEM data were useful in this geo-electrical setting [49]. In both interpretations, the sedimentary package thins near the Park mound springs, on the southern margin of the Mandora Palaeovalley and Anketell Shelf boundary (Figure 3 and Figure 4). The thinning indicates that erosion has been an important process in the past. Other surface information discussed here (e.g., geomorphology and floristics) indicates that erosion is likely to be exacerbated locally by uplift along geological structures.
Questions remained on the suitability and reliability of the modeled AEM data to assess the Jarlemai aquitard’s integrity through mapping both geological structures and the sedimentary unit where its thickness is reduced. This is important for accounting for environmental water requirements, as artesian conditions are understood to sustain the Park mound springs [68].
Hydrogeological information in closer AEM line spaced data (e.g., AEM 1- and 2D inversion 2020, Figure 1) was yet to be tested, thus providing an opportunity to research this problem in this paper. Integrating the results with satellite remote sensing data allowed us to verify the findings and develop new approaches to map and quantify spring discharge.
3. Park-Scale Spring Source Assessment: Methodology
3.1. Geophysics—Time Domain Airborne Electromagnetics
Airborne electromagnetic (AEM) technologies are increasingly being deployed to assist geological and hydrogeological interpretation (see, for example, [26,69]). As mentioned previously, time domain EM systems, whether heliborne or fixed-wing, have proven to be a very effective, non-invasive technique for mapping sub-surface variations in electrical conductivity to depths of more than 500 m (depending on the ground conductivity).
As with the regional-scale study, the finer-scale investigation (Fine Scale AEM) discussed here used closely spaced lines acquired over the Conservation Park in a north-south orientation by the TEMPEST 25-Hz time domain airborne electromagnetic system. In total, 45 lines oriented N-S, covering 562 line kilometers, were examined for their ability to resolve controlling structures on the spring mounds. Line spacing varied between 250, 500 and 1000 m (Figure 1). The mode of operation of the TEMPEST system is discussed in Appendix A. Both inline (Z) and vertical (X) components [52] were measured. The deconvolved ground response was converted to a 100% duty cycle square-wave B-field response to yield better resolution of the near-surface detail in the ground conductivity structure. The response was then binned into fifteen windows. The vertical resolution varied between a few meters and tens of meters, while the lateral resolution (along lines) could be of the order of hundreds of meters, which is determined by the system footprint, sampling interval and flying height [70]. Off-line lateral resolution was governed to a large degree by line spacing. System type and footprint (Fixed-wing Time Domain Electromagnetic (TDEM) and 100+ m, respectively) are relevant in the context of this study given the need to resolve vertical to sub-vertical faults, although this becomes less of an issue if the lateral conductivity contrasts associated with these structures are significant. More detailed system and acquisition specifications can be found in the acquisition and logistics report provided in [51].
AEM Data Inversion
The data subsets processed and inverted for this work are highlighted in Figure 1. Two approaches were used. These included 1- and 2D inversions, with the aim, in both cases, of resolving sub-surface conductivity structures, particularly lateral contrasts in conductivity that may be indicative of fault systems. Although the study area is characterized by variably conductive sub-horizontal sedimentary systems, which would lend them to being defined by a 1D layered earth inversion, sharp changes in conductivity associated with steeply dipping faults, which may also be defined by steeply dipping conductors, have the potential to be better modeled by 2D approaches.
The 1D inversion scheme AarhusInv [62] was used in Aarhus Workbench to process and invert the TEMPEST data. The study [51] provided height, pitch and geometry roll (hprg)-corrected and raw or uncorrected data. The raw data were used here, and each line was processed manually to remove noise. The AarhusInv algorithm inverts soundings for a set of 1D models connected through constraints. In this study, we used the spatially constrained inversion (SCI) described by [71,72]. SCI uses a Delaunay triangulation to connect soundings both along lines and across lines through constraints. Obtaining models that honor information from along and across lines can result in the conductivity distribution appearing to vary smoothly laterally as well as vertically. The constraints in the Delaunay triangulation are given a weight according to their distance, so that soundings closer together are more tightly constrained and soundings far from each other are not linked at all. The inversion requires a data file as well as a model input definition file containing information on the starting model, regularization constraints as well as any prior information. For the purposes of this study, a 30-layer model was used for the inversion employing X and Z component data, specifically Bfield in fT (units of Femtoteslas). The first layer thickness was chosen to be 5 m with logarithmically increasing thickness to a depth of 500 m, which is the depth of the last layer boundary. The starting model for the inversion was a homogenous half-space with a resistivity of 10 ohm m. In order to obtain a robust conductivity distribution of the half-space, the AarhusInv algorithm also solved for the system geometry, the transmitter tilt and the altitude. The algorithm tried to fit both X and Z component data, considering the starting model, and after a specific number of iterations, it started to move the altitude and the transmitter angle values. A depth of investigation (DOI) was also defined using the method of [73]; two different DOIs were calculated, a standard one and another more conservative one.
A 2D inversion of the TEMPEST data was performed using the Moksha 2.5D code [74,75]. This is a re-engineered version of ArjunAir [76] incorporating a 2D inversion solver with adaptive regularization, which allows the incorporation of a misfit to the reference model and the model smoothness function. The regularization parameter is chosen automatically and changes adaptively at each iteration, as the model, the sensitivity and the roughness matrices change [75]. Estimation of the regularization parameter requires calculation of only one forward model and sensitivity matrix at each iteration and is controlled by the Relative Singular Value Truncation (RSVT) parameter. In this study, both X and Z component data were inverted with a 40-m (lateral dimension) mesh and a 5-m mesh at the surface, increasing with depth down to 450 m with 27 layers. The starting model for the inversion was a homogenous half-space with a resistivity of 250 ohm m. An estimate of system noise was made by analysis of an area of low signal using late time data. The noise estimate was calculated for each time gate, or channel, for both X and Z components and was used in the inversion.
For the 2D inversion, initial analysis of the data indicated that there appeared to be calibration and geometry problems with the X and Z components attributed to the high surface conductivities. As a result, it proved impossible to jointly fit the two components in the 2D inversion without scaling the Z component data by 25%. The best misfits and coherence were obtained using the variable pitch of the transmitter loop (Tx Pitch) and the mean system geometry, where the horizontal transmitter–receiver (Tx–Rx) separation was 112.6 m and vertical TX–Rx separation was 46.6 m. For this survey, the 2D inversion root mean squared (RMS) misfits were generally < 20% (range between 4.1 and 19.6), which is typical for towed bird systems. Interval conductivity images and conductivity-depth sections were generated as products from the inversion.
3.2. Remote Sensing Data
One of the objectives of this study was to examine the persistence of vegetation through periods of below-average rainfall, which, under current rainfall patterns, occurs at the end of a 4–5-year climate cycle (Figure 2B). As an independent indicator of potential controls on spring water sources, we sought to use remote sensing data, where accurate retrieval of the vegetation cover and change was not hindered by variations in the measured radiance, which is a function of atmospheric conditions, topography, sensor orientation and sun elevation.
To assist this spatiotemporal assessment, a subset of the seasonal fractional coverage for the Australian continent (http://auscover.org.au/purl/landsat-seasonal-fractional-cover) was extracted. This Australia-wide coverage has been generated from an analysis of Landsat TM, ETM+ and OLI data, sourced from the USGS EarthExplorer website as level L1T imagery data (dating back to 1986), which has a spatial resolution of approximately 30 m. These data have been corrected for atmospheric effects, bi-directional reflectance and topographic effects, using the methods described by [77]. Their approach involves atmospheric correction to compute surface-leaving radiance and bi-directional reflectance modeling to remove the effects of topography and angular variation in reflectance. While the bi-directional reflectance model was parameterized for eastern Australia, the approach has been applied across Australia. The image product generated is surface reflectance, standardized to a fixed viewing and illumination geometry [77].
Fractional Cover Model
A model for the extent of green vegetation (in percent) was calculated using a constrained linear spectral unmixing algorithm applied to the Landsat TM image archive, including imagery for the study area. The procedure is described in [78]. Three spectral endmembers—bare soil, green vegetation and non-green vegetation—were calculated using models linked to an extensive field sampling program covering a wide variety of vegetation, soil and climate types over 1500 sites. The unmixing applied to the image archive, including imagery for the study area, using the derived endmembers had an overall model root mean squared error (RMSE) of 11.6%. Overstory and ground cover were measured as part of this sampling program. Although the unmixing model generated fractions of bare ground, green vegetation and non-green vegetation, we opted to use only the green vegetation fraction and report that as percentage cover. The scope of this study limited our assessment of green vegetation persistence at the end of two climate cycles. The beginning and end of the cycles were characterized by above- and below-average rainfall, respectively (Figure 2b). The representative periods cover an extended dry period (low annual rainfall between 1990 and 1992) and a dry period following an extended wet period (higher annual rainfall between 2014 and 2016) (see Figure 2).
We generated color composites of the annual mean fractional cover of green vegetation across the Park for the two periods to highlight areas of persistent vegetation cover.
4. Results
In defining the controlling structural framework for the Walyarta Conservation Park mound spring complexes, an initial assessment of the finer-scale interpretation of the AEM was considered against the regional-scale geological model. This was undertaken to ensure that there was consistency in the geological/structural framework regardless of scale.
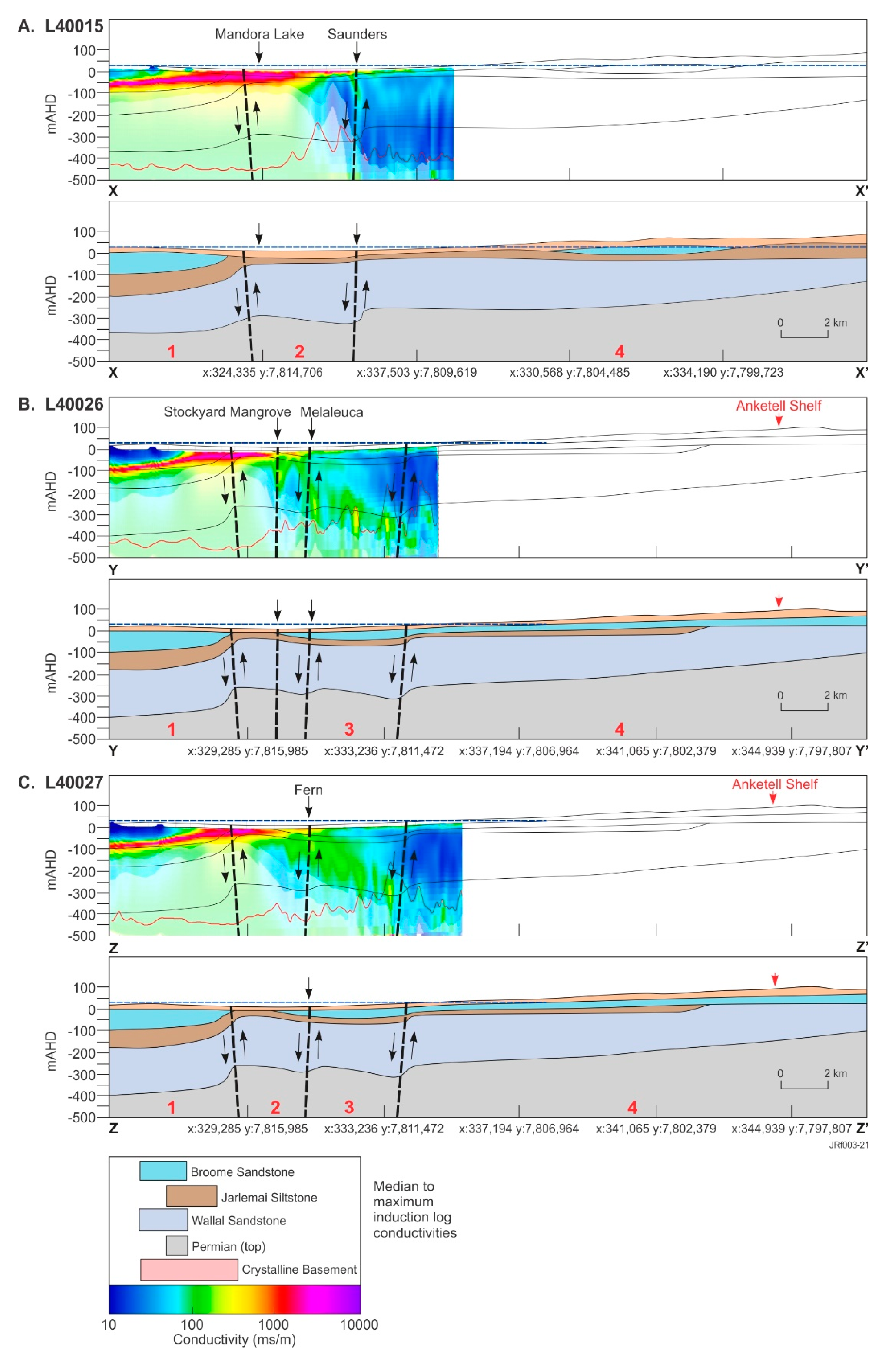
Three 28-km-long northwest to southeast trending geological cross-sections (see Figure 3F for location) were extracted from the regional-scale 3D geological model to show the relationship between stratigraphy and structure (Figure 5). One-dimensional conductivity depth sections for three flight lines (lines 40015, 40026 and 40027) were projected onto these sections, providing insight into the relationship between the modeled conductivity structure, its association with Mandora Lake and four mound springs: Saunders, Melaleuca, Fern and Stockyard Mangrove (Figure 3 and Figure 5), the interpreted stratigraphy and reactivated/near-surface faulting. The three conductivity sections are from the 1D SCI of the fine-scale TEMPEST dataset over the Park.
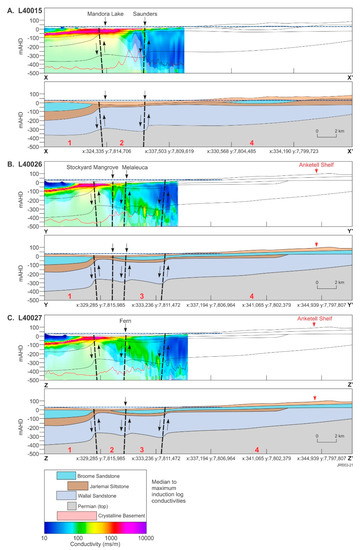
Figure 5.
TEMPEST AEM 1D spatially constrained inversion (SCI) pseudo-colored conductivity depth sections (2020) for flight lines (A) L40015, (B) L40026 and (C) L40027 (west to east; see Figure 4 for location) (grey shading represents depth of investigation (DOI), and red linework, the 1D AEM inversion error; to the left, conductivity depth sections are superimposed on respective northwest trending geological cross-sections (X-X’, Y-Y’ and Z-Z’; see Figure 3F), extracted from a 3D geological model and presented in greyscale; geological faults are displayed as black dashed lines with arrows denoting the direction of movement; numbers in red on geological sections represent major interpretation domains discussed in the text; blue dashed lines show the estimated Wallal Sandstone aquifer hydraulic head and the geology key is shown in relation to the AEM SCI scale (Note: Conductivity key induction log conductivities are from [60], the Callawa Fm. (Cretaceous) is not shown but is coeval with the Broome Sandstone and displays a similar data range).
4.1. D Fine Scale AEM Inversion
The geological cross-sections in Figure 5 are displayed west to east and provide an interpreted geology to depths of 500 m AHD. The conductivity depth sections only cover part of the derived geological model sections. They were fitted to geological cross-sections based on distances to common surface features, such as the locations of springs and lake boundaries. The geological model resolves stratigraphic variation from the northwest to the southeast, with three and four different mappable geological changes evident in sections X-X’, Y-Y’ and Z-Z’. The following discussion refers to the three cross-sections presented in Figure 5.
The geology in the northernmost geological domain is similar in all cross-sections and is constrained by drilling, which suggests that the sedimentary sequence is relatively flat-lying with the tops of the Jarlemai Siltstone aquitard and Wallal Sandstone aquifer at around −100 and −200 m AHD, respectively. Above, the Broome Sandstone aquifer is around ~100 m thick, with Cenozoic sediments increasing in thickness (between 10 and 40 m) to the southeast. Modeled conductivities resolve a resistive Cenozoic cover to the north in all cross-sections. This occurs within mainly unsaturated dunes and sandplains upgradient of the ephemeral Mandora Lake (Walyarta) (Figure 5).
Close to the lake, the salinities increase significantly with an accompanying increase in conductivity to over 1000 mS/m. High conductivities extend from the surface to over 50 m below ground level, with the conductive unit being laterally continuous, extending northward from Mandora Lake into the lower part of the Broome Sandstone aquifer. Whether this indicates that the extent of Mandora Lake may have been larger in the past and that it has decreased in size due to sedimentation, including dune migration, remains undetermined. Stratigraphic boundaries in the underlying Mesozoic and Permian formations are difficult to resolve in the AEM and have been constrained in the 3D geological model by lithological logs. The conductivities range from around 100 to 200 mS/m, although uncertainty here is high as the modeled DOI comes closer to the surface (~100 to 200 m AHD in Figure 5).
The second geological domain (Figure 5) is located approximately 4 to 5 km south of the northern extent of the finer-scale TEMPEST data and is coincident with an interpreted major east-west trending thrust or reverse normal fault (Figure 5). Faulting appears high-angled and produces a vertical displacement in the geology, with the throw in the southern fault block ranging from ~50 to ~100 m in sections X-X’ and Y-Y’/Z-Z’, respectively. This occurs on reactivated structures which have also been identified in the contemporary topography, indicating that re-activation is likely to have been a slow, long-lived and continuing process. The uplift of strata in the southern fault blocks has resulted in depositional thinning and erosion of the Mesozoic sediment package. Near-surface electrical conductivities in this domain remain high, mainly to the north, and exceed 1000 mS/m. These near-surface conductors appear coincident with the uplifted Jarlemai Siltstone aquitard, which also marks the central to southern extent of Mandora Lake. The Jarlemai Siltstone is at depths of around 10 to 20 m BGL (e.g., ~0 m AHD) and ranges in thickness from around 50 m in sections Y-Y’ and Z-Z’ to 30 m in the west (section X-X’).
Mapping stratigraphic boundaries from electrical responses is challenging in this domain as conductive responses and contrasts decrease to the south. Misfits in the 1D SCI increase to the south—associated with a zone of more complex faulting—interpreted as being east-west trending thrust faults that correspond to the locations of mound springs within the Park boundary (Figure 5).
The DOI also increases as nearer surface conductivities decrease (Figure 5). The faults show localized increases in modeled conductivity in the 1D sections, ranging from ~100 to 300 mS/m (e.g., ~1000 to 2000 mg/L; Figure 3). The magnitude of these variations aligns with the salinity of spring water sampled [49].
Further south in the third geological domain (Figure 5B,C), an additional east-west to northeast trending fault block has been identified in the easternmost geological sections (Y-Y’ and Z-Z’). Elevated near-surface conductivities in this area appear to form in response to evapotranspiration and are discrete and slightly higher (~100 mS/m) than those of the underlying cover sequences. This is also apparent in the areas around the mound springs to the north. The conductivity structure in these sections differs from the western geological section (X-X’) (Figure 5A). The most obvious difference is the ~50-m-thick discrete and laterally continuous conductor (~100 mS/m), the base of which is located at around -100 m AHD. This is interpreted to be the Jarlemai Siltstone aquitard. Similar to observations in domain 2, the error in the 1D AEM inversion appears higher in fault zones, which, in Figure 5B, occur within and south of Melaleuca Spring. Conductive responses in the easternmost geological section display less heterogeneity with depth (Figure 5C). This area is aligned to Fern Spring and is close to an intersection with a major northwest fault, and this is likely to influence the elevated (~100 mS/m) and uniform AEM response.
The most southerly geological domain (domain 4) is defined by a resistive (<50 mS/m) sedimentary substrate, apart from near-surface conductivity produced by evapotranspiration, which is noticeably higher in the western section, upgradient of the Saunders spring (Figure 5). The DOI increases to around 400 m AHD, but the conductivity structure is less revealing with respect to mapping stratigraphic boundaries. The interpreted geology depicted in the sections shows the gradual thinning of the combined Mesozoic and Cenozoic sediments, an interpretation defined from the 1D laterally constrained inversion (LCI) of the AEM dataset.
Defining stratigraphic boundaries in the AEM data proved challenging as lithological data from drilling were scarce, the DOI was limited and higher-salinity groundwater in the valley floor aquifers overprints formation-related geoelectrical contrasts. However, the data proved to be at an appropriate scale to map finer-scale features (e.g., faults) and identify near-surface hydrological processes (e.g., evapotranspiration).
4.2. Two-Dimensional Fine-Scale AEM Inversion
Results from the 2D inversion of the finer-scale TEMPEST data, particularly the conductivity depth interval images, defined a variable and complex sub-surface conductivity structure. These images and these data were particularly effective and are shown as conductivity depth images in Figure 6. The selected depths below ground level (BGL) are similar to those for the 2016 AEM inversion presented in Figure 3 (e.g., 7.6, 33.4, 69.7 and 106.2 m BGL). Structures in the 2D conductivity depth images were interpreted primarily from the 60.7 m BGL image and then projected onto the other conductivity depth images (Figure 6). This confirmed that the interpreted geological structures propagate from depths of greater than 100 m to the ground surface and that these faults compartmentalize the modeled conductivity responses. The structural styles are similar to trends evident in the regional-scale 1D LCI AEM inversion but provide more detail, while also revealing the complexity.
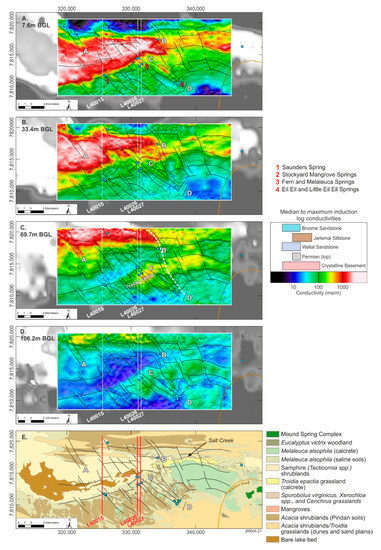
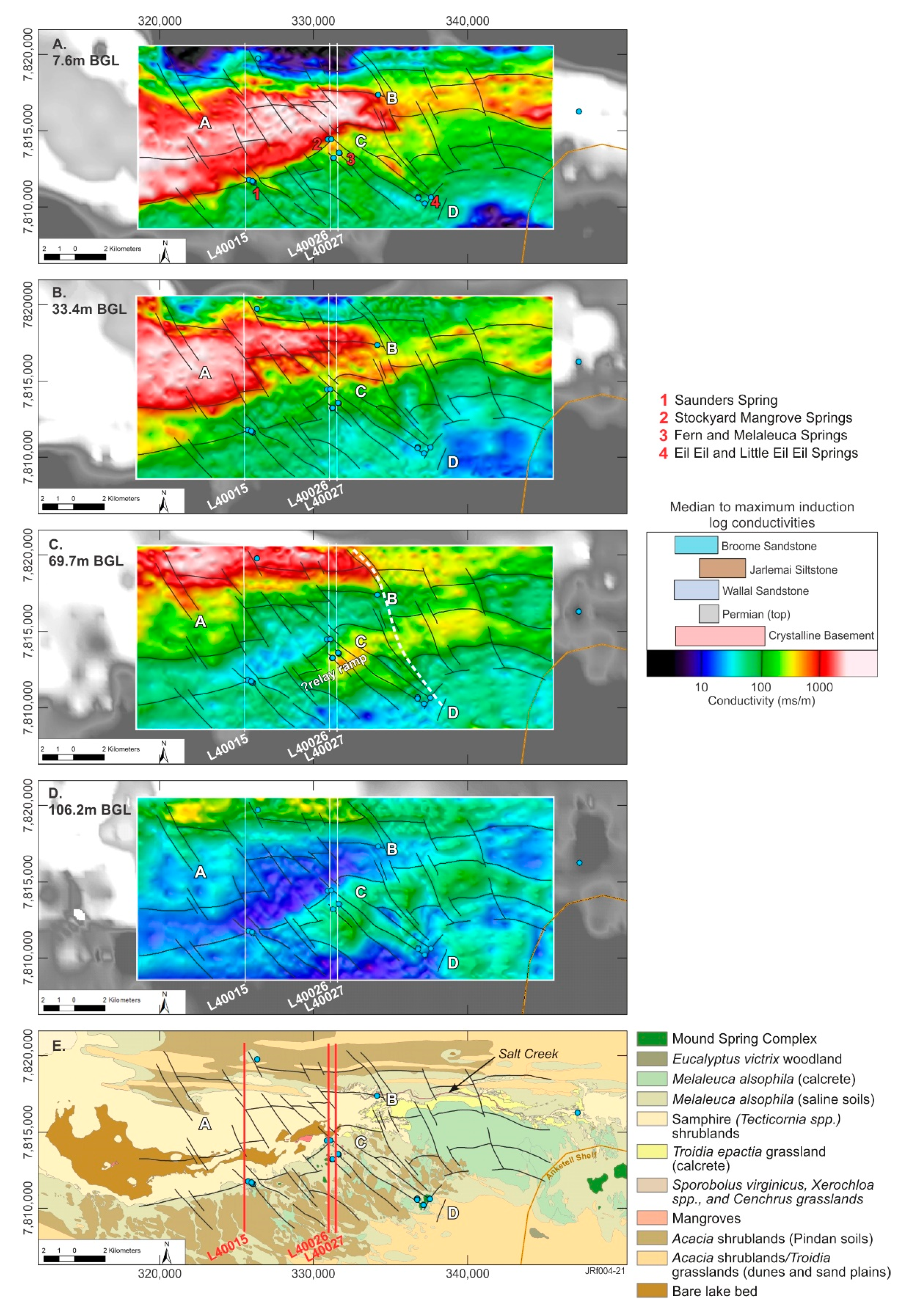
Figure 6.
TEMPEST AEM 2D inversion (2020) overlain on greyscale images of CDIs presented in Figure 3; pseudo-colored interval conductivity images (CDIs) for depths of (A) 7.6 m BGL; (B) 33.4 m BGL; (C) 69.7 m BGL and (D) 106.2 m BGL and a (E) vegetation map [47]. Spring sampling locations are blue dots; AEM flight lines L40015, L40026 and L40027 are white lines, geological faults are black lines; within maps, numbers A to D represent major interpretation domains discussed in the text. Note: connecting fault is shown as a white dashed line in C and conductivity key induction log conductivities are from [60] the Callawa Fm. (Cretaceous) is not shown but is coeval with the Broome Sandstone and displays a similar data range.
Several key interpretation sites were identified along the electrical conductivity boundaries defined in the 2D interval conductivity images. These were chosen to link the four main mound spring sites with changes in mapped vegetation assemblages (see sites 1 to 4 and A to D; Figure 6A,E). These sites represent areas where there might be changed water availability due to disruptions in the hydrogeology (structure and stratigraphy). They are discussed in relation to their floristics as reported by [47] (Figure 6). Note that full descriptions of floristics over a broader area are available in [47].
Site A represents an area associated with electrically conductive near-surface sediments within Mandora Lake. These conductive sediments (~10 m thick) extend northward beneath the northern dune system (Figure 5) and are characterized by lake bed and salt-tolerant flora, including samphire and mangroves that occur in a discrete area in the lake as well as along a perennial saline creek line (Salt Creek; Site B) (Figure 6E).
Conductivity depth images from the 2D inversion show that the conductor at site A dips to the north, with the steepest gradients evident to the east, located at Site B, which is coincident with a faster flowing reach within Salt Creek (Figure 6E). Salt Creek is a relatively narrow (tens of meters) and steeply incised perennial drainage that extends for ~10 km, connecting East Lake (EL) and Mandora Lake (ML) (Figure 3A). The mangrove-lined creek is incised into Triodia hummock grasslands, which have structurally controlled extents (colored yellow in Figure 6E) that appear to be influenced by the proximity of the northern boundary of the Anketell Shelf.
Sites C and D are aligned with a northwestern reactivated fault, also evident in the digital elevation model (DEM) (see section Y-Y’ in Figure 3f). Site C is located close to Fern Spring, which is within Melaleuca alsophila and Acacia ampliceps shrublands. Mound spring vegetation and Melaleuca alsophila shrublands are understood to have the greater groundwater dependency. Site D is in sandplain and located upgradient of the Eil Eil spring complex (Figure 6A,E).
The 2D AEM inversion resolves a northwest, curvilinear, trending structure that controls the floristics and connects Sites B and D. Sections of this fault are present in the topography and interpretations of seismic data by [38]. The authors of [33] identify this as a major deep structure that propagates through the underlying geology (e.g., Permian and older formations). At depths of over 60 m BGL, this fault truncates conductivity structures and appears to form a connecting fault to a southwest trending relay ramp (e.g., structural style hypothesized in Figure 4), with the relay ramp being a ~4-km-wide curvilinear, southwest trending block of sediments whose northern boundary is coincident with Saunders and Stockyard Mangrove springs (Figure 6C). In Figure 6, the conductivities of the fault block sediments are indicative of the Jarlemai Siltstone aquitard or crystalline basement. The Jarlemai Siltstone aquitard interpreted in this area in the 1D AEM SCI (e.g., cross-sections in Figure 5).
Immediately west of the connecting fault (north and south of Site C), persistent deformation is observed in sediments between the two faults (e.g., faults B to D and C to D). These faults connect in the south at Site D, near the Eil Eil spring complex, where they appear to terminate at structures that mimic the Anketell Shelf boundary. The curvilinear structure north of Site C marks the floristic boundary between samphire and Melaleuca alsophila shrublands, which also represents an important change in phreatophyte vegetation water demand (e.g., water volume and quality).
Similar curvilinear structures on the valley floor margin host mound springs. These are the northernmost normal reverse faults in the cross-sections presented in Figure 5 and trend southwest and include the Saunders spring and Stockyard Mangrove Complex (e.g., nos. 1 and 3, Figure 6A). The Fern and Melaleuca springs appear to be associated with stacked northwest trending faults (e.g., no. 2 Figure 6A) in the 2D AEM conductivity-depth intervals.
Above the valley floor, Melaleuca alsophila shrublands occur across the Park, particularly south of the ephemeral lakes. In the interpreted relay ramp area (Figure 6C), west of Sites B and D, Melaleuca alsophila is interspersed with Acacia ampliceps shrublands, with Acacia ampliceps understood to be less tolerant to prolonged periods of waterlogging [50]. The average conductivity in the uppermost 10 m, in both the 1D and 2D inversions, shows that the near surface is relatively resistive in areas of Melaleuca (e.g., averaging 100 mS/m or ~1000 mg/L).
These conductivities are similar to laboratory analyses of mound spring organic sediments (e.g., average 150 mS/m; average 2500 mg/L), where solute storages are slightly higher and perennial groundwater discharge tends to keep pace with transpiration [79].
4.3. Fractional Cover Model
In the Park, vegetation assemblages together with low near-surface electrical conductivities upgradient of Mandora Lake indicate that groundwater discharge from unconfined aquifers is not widespread or perennial. The development of shallow, seasonal aquifers and water bodies occurs following cyclonic rainfall run-off [46]. Discrete perennial discharge is more likely to be sourced from artesian groundwater and support vegetation assemblages with organic substrates, such as those within the mound springs. This was tested by examining spatiotemporal trends of evapotranspiration, represented by greenness of vegetation cover in fractional unmixing models in Figure 7 and Figure 8.
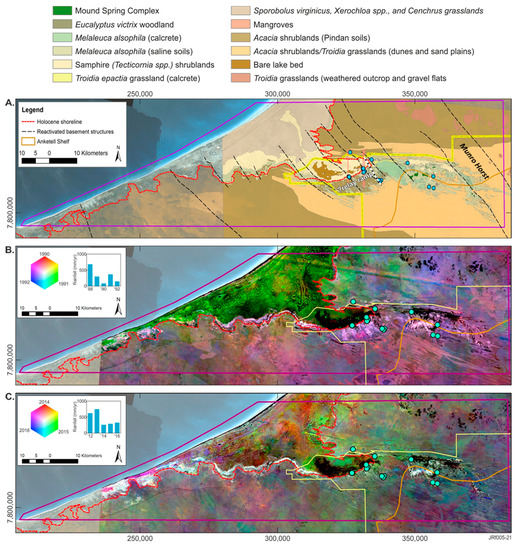
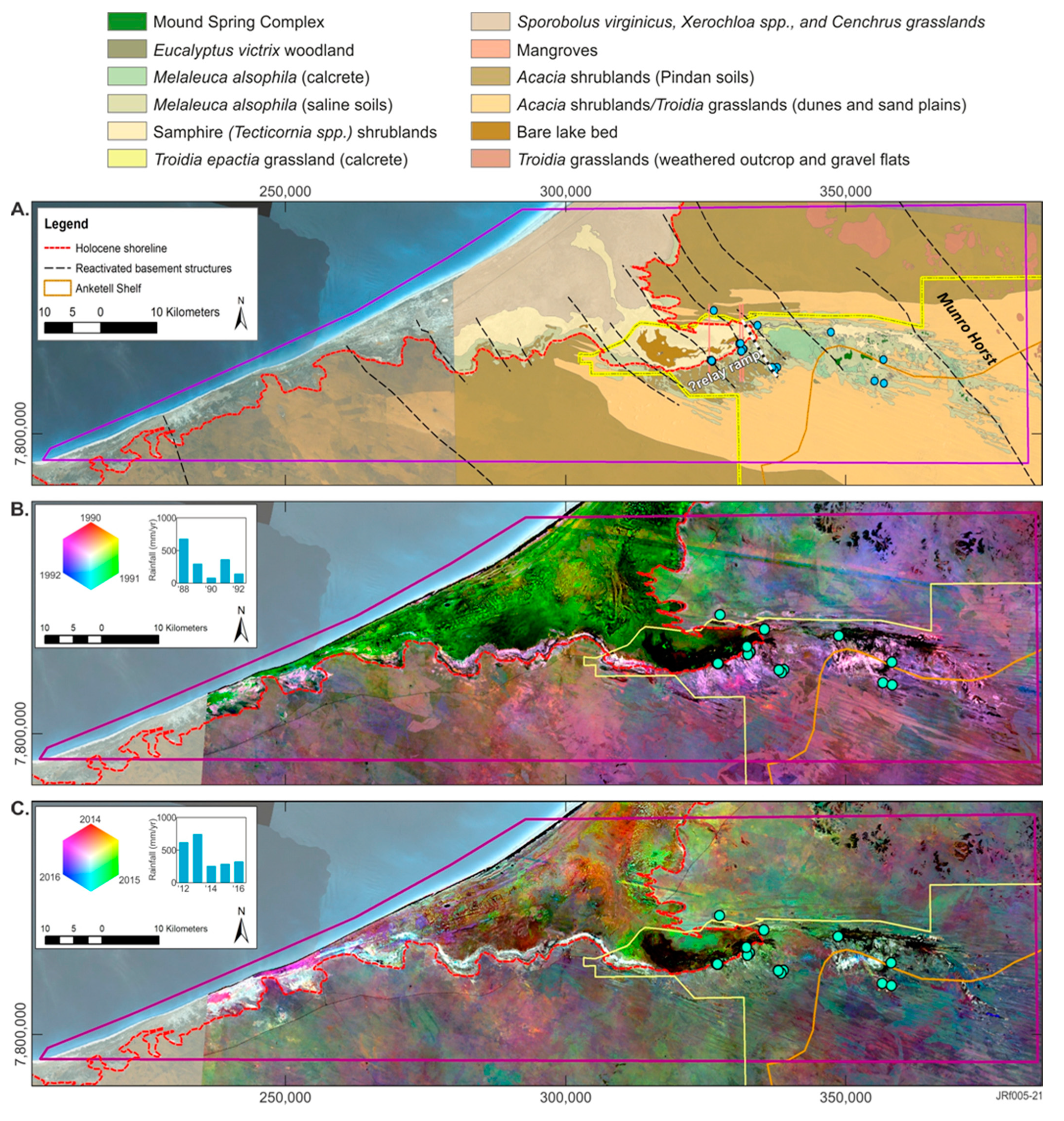
Figure 7.
Sub-regional-scale fractional cover models with Park spring sampling locations (blue dots) and the Walyarta Conservation Park boundary (yellow linework): (A) Vegetation map [47] with broad-scale physiographic constraints (e.g., Munro Horst and connecting fault (white dashed line) and approximate location of relay ramp (see Figure 6); (B) Fractional cover model displayed as composite image of average annual vegetation for years 1990, 1991 and 1992. Bar graph displays annual rainfall for 1988 to 1992; (C) Fractional cover model displayed as composite image of average annual vegetation for years 2014, 2015 and 2016. Bar graph displays annual rainfall for 2012 to 2016.
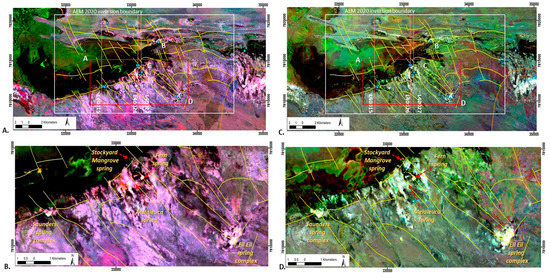
Figure 8.
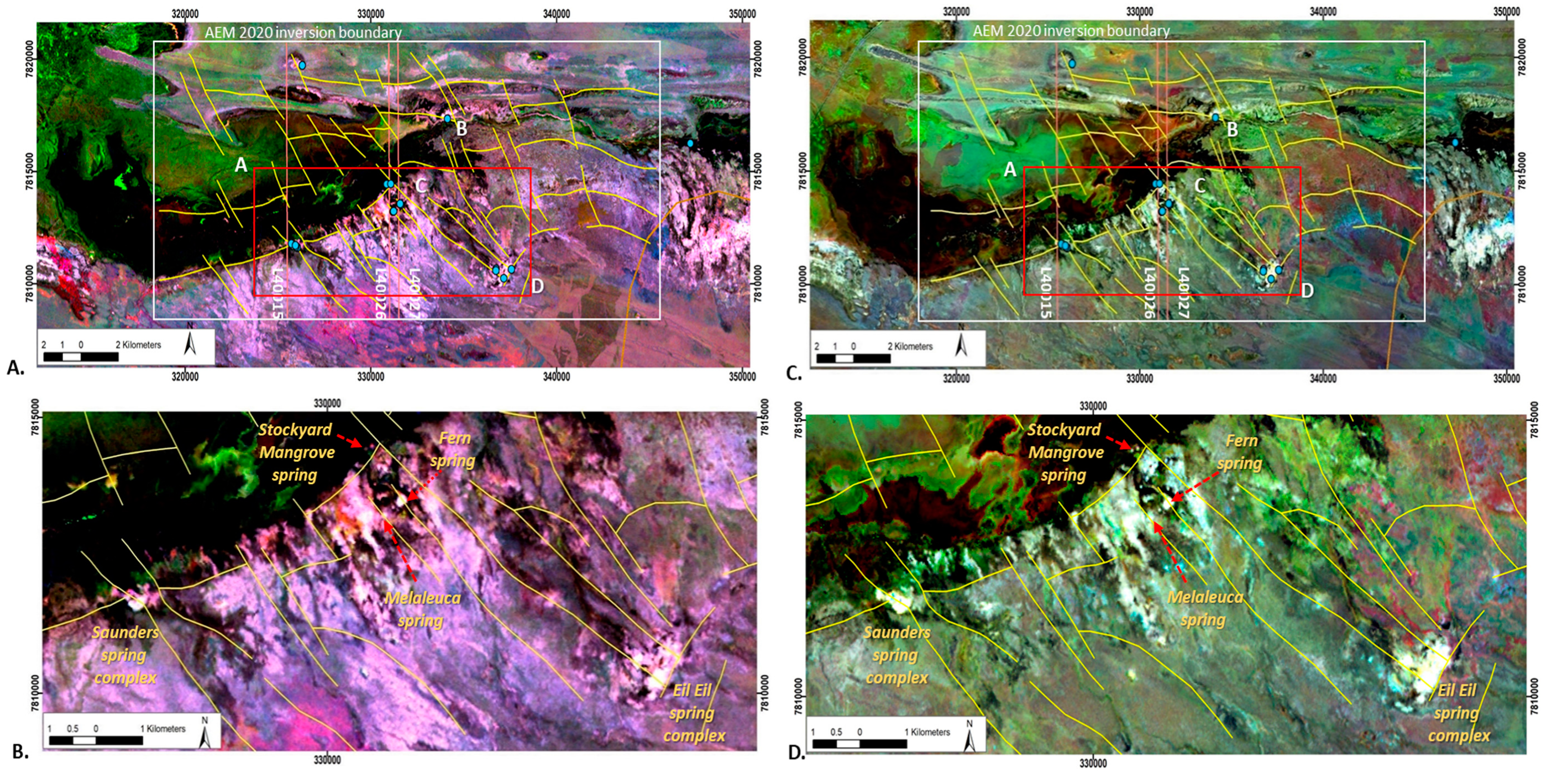
Fractional cover models, fine-scale interpretation of Figure 7: (A) Fractional cover model composite image of average annual vegetation for years 1990, 1991 and 1992; spring sampling locations (blue dots); geological faults are yellow lines; flight lines L40015, L40026 and L40027 are orange lines and numbers within maps and A to D represent major interpretation domains discussed in the text. (B) Detail within red rectangle in Figure 8A; (C) Fractional cover model composite image of average annual vegetation for years 2014, 2015 and 2016, detail as per Figure 8A and (D) detail within red rectangle in Figure 8C.
Persistent green vegetation in the Park was resolved by remotely sensed data using an approach that assessed spatial variation in green vegetation vigor in the driest eight years since data acquisition commenced with Landsat TM satellites [48]. The study [45] reviewed results of remotely sensed groundwater storages in the Canning Basin in relation to rainfall cycles since the 1950s. Both studies are cognizant of the need to incorporate climatic data in research design and interpretations. However, determining what constitutes a climate cycle in an environment where irregular cyclonic rainfall interrupts otherwise semi-arid conditions is challenging.
In the West Canning Basin, ninety percent of rainfall is received in the wet season between the months of December and May, with most rain (>70%) derived from cyclonic fronts from January to March (Figure 2A). Descriptive statistical analysis of rainfall data from BoM No. 04019 indicates there has been an approximate 23% increase in average rainfall since the late 1970s (see Figure 2). The increase in rainfall is due to the increased frequency of cyclonic events in the wet season. In [46], a moving average (7-point/month) data filter was applied to a 105-year annual rainfall record to resolve seven- to ten-year cycles that have occurred from the mid–late 1970s to 2011, noting that that dry climate cycles since the 1970s often experience very low average rainfall years compared to the older rainfall records.
In this study, we employed a three-year moving average across a 105-year rainfall record (see Figure 2) and selected two four- to five-year climate cycles to investigate and compare vegetation resilience from the middle to the end of each cycle. Very high rainfall in the early 2000s influences average rainfall statistics. This was addressed by choosing a climate cycle before and after the extreme rainfall events of the 2000s, 1988 to 1992 and 2012 to 2016, respectively (Figure 7). Both climate cycles are characterized by above-average rainfall at the beginning of the cycle and annual rainfall below the long-term average for the final three years. Data from the mean green fractional vegetation cover were produced for the 2016 AEM inversion area and the results were interpreted in relation to floristic maps (Figure 7A).
The mean green fractional cover is represented as a percentage for the years 1990, 1991 and 1992 in Figure 7B. Data were linearly scaled between 0 and 255 for display (with 100% cover as 255), and the scaled image for each year was then combined in a color composite with 1990 in red, 1991 in green and 1992 in blue (Figure 7B). The color variations displayed indicate the relative percent changes in green cover for the different years. White colors in the composite indicate persistent green cover over the three years with other primary (red, green and blue) colors, and mixes of those indicate annual variations in the persistence of that cover.
The tidal flats in Figure 7B appear predominantly green and this is likely to be the result of higher rainfall in 1991 compared to the other years represented in the composite. Local rainfall run-off increasing shallow root-depth vegetation is mapped in these areas (e.g., salt-tolerant couch (Sporobolus virginicus) and samphire (Tecticornia spp.) in Figure 7A).
As mentioned above, of most interest are those localities with persistent, dense green vegetation cover across all three years. These responses are interpreted to be related to deeper-rooted vegetation that is sustained by groundwater discharge, which is, therefore, less sensitive to reductions in average annual rainfall.
A similar color composite image was generated for the years 2014, 2015 and 2016, represented as red, green and blue, respectively (Figure 7C). As with Figure 7B, parts of the image with persistent green vegetation cover (year on year) are displayed as bright white areas. These areas display relatively consistent patterning across both the 1990s and 2010s composite images. Outside and west of the Park, areas with persistent vegetation are coincident with mapped Melaleuca alsophila shrublands that fringe the tidal flats. These areas occur downgradient of an erosional boundary that marks the interpreted Holocene shoreline (~10 m AHD) reported in [31] (Figure 7). Persistent vegetation within the western area of the Park occurs upgradient of the Holocene shoreline boundary and, in contrast, covers only small areas mapped as Melaleuca shrublands, particularly in the 2014–2016 color composite image. Further east, the Munro Horst and the Anketell Shelf boundaries constrain persistent vegetation patterns within the Park boundary (Figure 7A–C).
The western area of the Park is the main area of interest and this is shown at a finer scale in Figure 8. Spatial patterns of persistent vegetation within the finer-scale AEM survey area occur at the intersection of major relay ramp structures and are associated with mound spring complexes (see Figure 6, Figure 7 and Figure 8). These structures bound the relay ramp and comprise Sites B to D, C to D and the southeast trending fault system that connects the Saunders and Stockyard Mangrove springs (Figure 6 and Figure 8). Subsidiary northwest trending structures are interpreted as a series of stacked normal faults, particularly in the vicinity of Fern and Melaleuca springs, where they are also characterized by persistent vegetation responses in the satellite imagery.
Similar patterning is apparent in the images for both climate cycles examined, which confirms that hydrological processes are consistent. The 2014–2016 composite indicates that the green cover is more discrete in extent (see Figure 8C,D) compared with previous years (Figure 8A,B), particularly around the spring complexes. This is examined in more detail for the Saunders spring complex (Figure 9). Several groundwater discharge points are evident in this spring complex, with at least one appearing to have been enhanced through human excavations. Sampling and analysis of environmental tracers at the northern- and southernmost sampling points in the 2015 dry season confirmed that the percentage of modern carbon was consistently low, and therefore, groundwater was potentially thousands of years old across this complex [49].
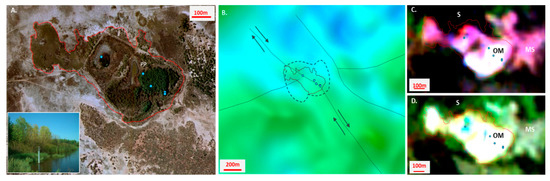
Figure 9.
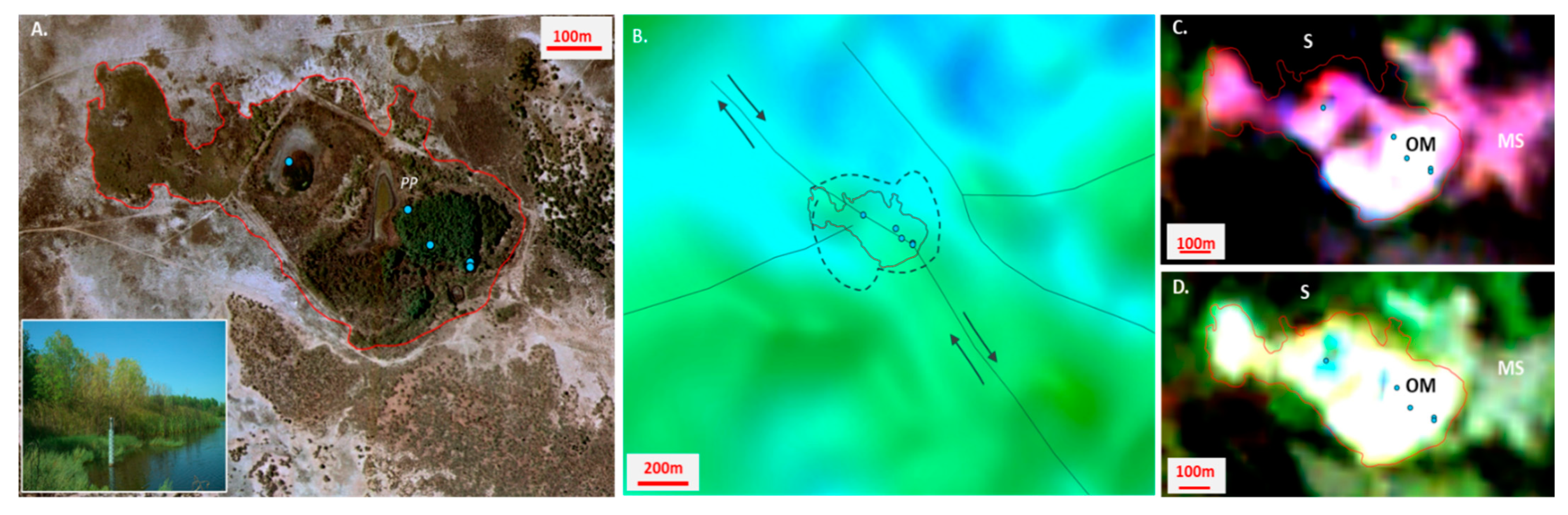
Structural interpretation of the Saunders spring complex: (A) Aerial photo (2010) interpretation of the Saunders spring complex boundary (red linework). Spring sampling locations are in blue; the inset photo is from a Reconyx camera installed near photo point PP to photograph the spring moat depth gauge. (B) AEM 2D inversion CDI image for depth interval 60–70 m BGL; spring complex extent in red; geological structures from Figure 6 are shown as solid black lines (arrows showing the direction of movement), with dashed black lines representing fault breakdown regions of concentrated stress (adapted from [80]). (C) Fractional cover model for years 1990, 1991 and 1992 and (D) fractional cover model for years 2014, 2015 and 2016. Abbreviations: OM (organic mound); MS (Melaleuca shrublands); S (samphire shrublands).
Viewed at this fine scale, the active discharge points and broader vegetation patterns in the Saunders complex are observed to trend to the northwest (Figure 9A), which is the same orientation as reactivated faults (see Figure 3). The complex occurs at the intersection of northwest- and southwest-oriented fault systems, which is acknowledged to increase stress. Over time, this is also likely to generate a broader fault breakdown region characterized by higher permeabilities that enables groundwater discharge from deeper, confined aquifers (e.g., [80,81,82]). Right lateral strike-slip movement on the northwest fault is interpreted to result in oblique shearing (transpression), with shortening to the southwest producing the resultant extent, or shape, of the groundwater discharge area that forms the Saunders spring complex, shown in red in Figure 9.
Faults are resolved in the 2D AEM inversion conductivity-depth interval (for 69.7 m BGL), including the offset in the northwest trending fault (Figure 9B). The color composite satellite data show persistent green vegetation cover extending across the structurally controlled spring complex boundary and provide a mappable response (bright white color) for both climate cycles modeled (Figure 9C,D). There is also a mappable distinction between vegetation within and outside the spring complex boundary, including samphire (S), Melaleuca alsophila and Acacia ampliceps shrublands (MS) and the organic mound (OM) located on the eastern margin of the spring complex (Figure 9C,D).
The 1990–1992 data appear to resolve more detail within the spring complex, with greater separation between the spring discharge points. The vegetation condition varies across the spring complex and this has been influenced by past grazing pressures by domestic and feral animals, as well as the fencing of the central and eastern sections of the spring complex [7]. The separation of the discharge bodies in the 1990–1992 data shows that vegetation persistence increases from west to east, and this is most likely to reflect the current distribution and density of phreatophyte vegetation within the Saunders spring complex.
5. Discussion
In areas challenged by the paucity of information on hydrogeology and processes, the integration of airborne geophysical (AEM) and remote sensing data demonstrably adds value and understanding. While earlier studies employing these data types were trialed over the Walyarta Conservation Park in the mid-2000s, restricted options regarding available inversion approaches, particularly with the AEM data, limited the definition on the finer-scale structural framework present. However, the regional conceptual 3D geological model developed this time did assist our understanding of the hydrological function of mound springs at a coarser scale.
Employing a combination of 1- and 2D inversion techniques with the finer-scale TEMPEST coverage over the Park allowed for refining boundaries associated with the Jarlemai Siltstone aquitard and resolved geological structures that have influenced its geometry. The inverted products also help define the location of geological structures that propagate through this formation through the definition of sharp lateral changes in the conductivity structure.
Increased confidence in AEM interpretations occurs south of ephemeral lakes where high-salinity groundwater does not overprint the formation-related electrical structure. In this area, conductivity depth sections from the 1D inversion resolve conductivity distributions to the DOI, which is up to 400 m BGL. Conductivity depth sections aligned with mound springs show laterally discrete linear conductivity patterns that connect near-surface conductors to others below the mapped extent of the Jarlemai aquitard. Although uncertainty exists with respect to the deeper sub-vertical conductivity structures in the 1D inversion as they maybe artefacts.
The structures identified in the conductivity depth sections conform with lateral conductivity pattern breaks in the regional-scale 1D LCI AEM inversion; breaks that coincide with the interpreted uplift and erosion of Mesozoic sediments reported in [38]. Information on the deeper conductor (e.g., Permian or Basement, at around 400 to 500 m AHD) is also resolved. This is important as the juxtaposition between the Jarlemai aquitard and the deeper conductor informs our understanding of the evolution of the sedimentary sequence and associated deep structures.
Conductivity depth images from the 2D AEM inversion further improve confidence in the resolution of lateral conductivity changes or breaks to depths of around 100 m below ground level. As mentioned above, the deeper conductivity structures remain untested. These images show the possible location and inclination of faults that have influenced where the Jarlemai aquitard has been deposited and where it might be preferentially preserved. Their interpretation also resolves the geometry of the southwest trending relay ramp where the Jarlemai aquitard is uplifted, but preserved, displaying minor thinning from the northeast to the southwest (Figure 6).
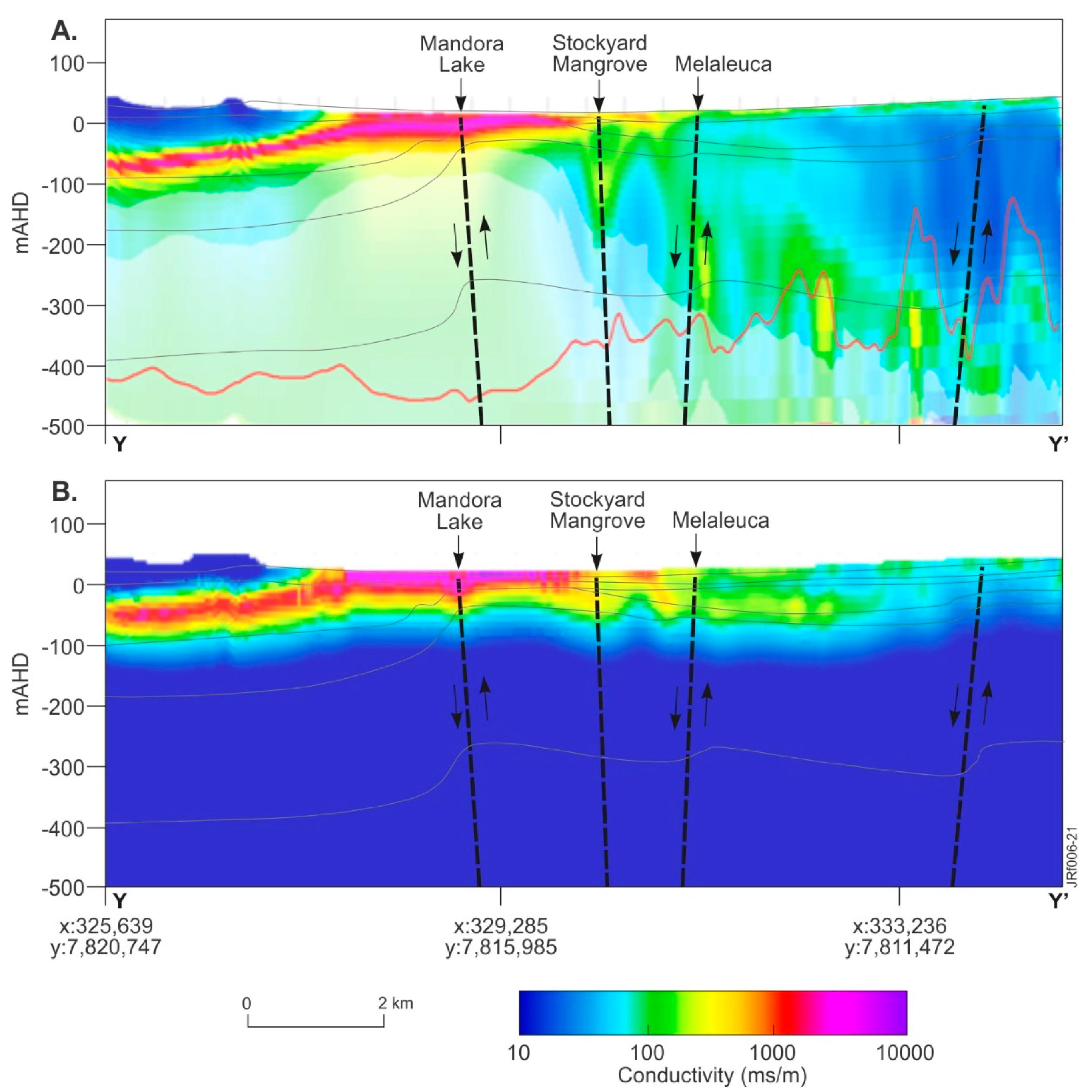
The upper and lower bounds of the Jarlemai Siltstone aquitard are defined in areas south of the Park’s ephemeral lakes. This is apparent in conductivity depth sections produced from both the 1D and 2D AEM inversions. A comparison of geological information provided by these inversions is shown in Figure 10. The conductivity sections are projected onto an interpreted geological section extracted from the 3D geological model, and the conductivity structure correlates with the Jarlemai surfaces (top and base) produced using the regional 1D LCI AEM inversion. The Jarlemai Siltstone aquitard bounds (e.g., ~0 to -50 m AHD/~15 to 65 m BGL) are resolved in flight line L40026 for both the 1D inversion (Figure 10A) and 2D inversion (Figure 10B), although its more southerly extent, south of Mandora Lake, appears better defined in the 2D model. In both models, subvertical structures are noted to disrupt the conductivity structure of the Jarlemai aquitard and appear to propagate through the aquitard from depth to the ground surface (Figure 10A,B).
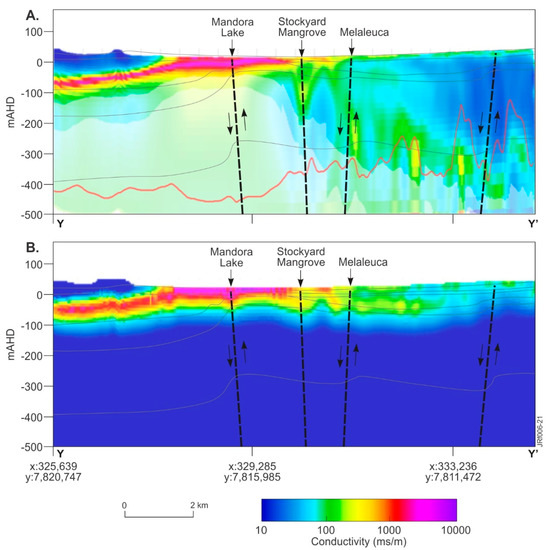
Figure 10.
TEMPEST AEM pseudo-colored conductivity depth sections for flight line L40026: (A) 1D SCI (2020); (B) 2D inversion (2020). Conductivity depth sections are superimposed on northwest trending geological cross-sections Y-Y’’ (see Figure 3F); geological faults are interpreted from the 3D geological model and displayed as dashed linework, with arrows denoting the direction of movement.
From a hydrogeological perspective, both the 1D and 2D AEM inversion results provide near-surface geological information in three dimensions. The Jarlemai Siltstone aquitard is mapped where it provides a conductivity contrast, and this helps define boundaries where the underlying Wallal Sandstone aquifer is confined and has potential to contribute groundwater to the Park’s mound springs.
The spring complexes within the Park maintain a high percentage of green vegetation cover at the end of a four- to five-year dry climate cycle (Figure 7 and Figure 8). The benefits of compositing in this manner with time series imagery, capturing seasonal variability, minimizes the problem of missing data and challenges associated with contamination sometimes encountered with single-date images [83].
The color composite satellite images also define areas of persistent vegetation that are coincident with fault structures interpreted from the 1D and 2D AEM inversions. They also assist in being able to differentiate between springs that may be supported by confined and unconfined aquifers. Groundwater discharge that supports phreatophyte vegetation does so under different geological constraints, within and outside the Park.
Break of slope discharge at the margin of the tidal flats and coastline is significant and more likely to be supported by groundwater from unconfined aquifers that discharge under the influence of gravity. In [49], it was observed that these systems, located west of the Park, were characterized by a different electrical conductivity response compared with the other spring systems further to the east. Specifically, they appeared to be associated with local thinning in the underlying Jarlemai Siltstone aquitard, indicating they may have been eroded and are associated with remnants of a palaeodrainage system. The spatial patterning in the color composite satellite images is different to that linked with springs sustained by the vertical movement of artesian groundwater (ascending springs), which are the prime focus of the research reported here.
Gaining a full understanding of gravity versus ascending springs requires the development of a physical model which describes spatial and temporal variations in the vertical and lateral movements of groundwater. Numerical modeling of the mound springs has been trialed. Results confirmed that vertical leakage of groundwater in faults that extend through the sediment package is a viable conceptual model [84]. More data are needed to verify the results, but for fault-controlled ascending springs, this includes measuring the mappable contrast that the fault represents, relative to its surrounds. Unfortunately, the fault breakdown region, or damage zone, and the processes that encourage fault conduits to remain open are difficult to investigate (e.g., [80,82]).
Most hydrogeological methods are too coarse to advise on the dynamics of fault zones (e.g., [85]). Exceptions include heat and some environmental tracers. For example, in thermal springs where temperature is a mappable contrast, [86] collected and gridded over 1500 fine-scale (55 × 36 m) on-ground temperature measurements from one spring and successfully resolved areas of increased groundwater flow. A coarser-scale study by [87] sampled temperature and environmental tracers from thirteen springs along a ~300-m drainage line and observed that considerable variation in spring water geochemistry exists over this small area. In [88], the investigation scale was increased to study natural soil carbon dioxide fluxes along springs and faults, with a collection of data from over 400 sites used to map travertine springs as well as diffuse leakage around a fault damage zone.
More successful research outcomes in the mapping of fault damage zones seem to be linked to high-resolution data collection. We considered this by examining spatial patterns observed in the persistent green vegetation cover from the remote sensing data at the individual spring scale. Around the Saunders spring, the limits of a fault damage zone—a hydrological process boundary (e.g., groundwater discharge)—were mapped by the observed extent of persistent phreatophyte vegetation. Longer-term and higher spatial resolution data might assist in refining that understanding.
Data from AEM inversions provide a coarser-scale geological and hydrogeological context on structure and processes that occur below the ground surface. However, it is worth noting that neither geophysical nor remote sensing data will advise on the hydraulic conductivity distribution, including fault damage zones, below the mound springs.
The four major fault systems interpreted to sustain the ascending springs in the Park can now be investigated to resolve the presence and geometry of fault damage zones with depth. Such knowledge would be important for the optimal siting of monitoring installations, such as groundwater bores, as a means of understanding aquifer hydraulic head gradients in the Park, but it would require significant investment.
6. Conclusions
The combined application and interpretation of remote sensing and fine-scale airborne geophysical (electromagnetic) methods has allowed the definition of a relatively detailed geological and structural framework for the Walyarta Conservation Park organic spring complexes. The inverted AEM data, through the definition of sharp lateral discontinuities in conductivity from surface to depth, suggest that sub-vertical fault systems propagate from the Wallal Sandstone aquifer up through the confining Jarlemai Siltstone aquitard and express themselves at the surface. The temporal fractional cover composite imagery shows persistent green vegetation associated with the spatially limited areas of discharge that are coincident with some of the identified faults, supporting the argument that they are ascending springs.
The inverted AEM data resolved structural styles and related-sedimentation models which have significance for resource exploration; notably, the deep northwest trending transfer faults and associated east-west to southwest trending normal faults. It is relevant to note that the lateral discontinuities resolved in the finer-scale conductivity images emphasize the importance of the considered image processing, including decorrugation, gridding and shading to enhance structurally related spatial detail not apparent in other geophysical datasets. It also places emphasis on the acquisition of airborne data at scales relevant to the targets of interest. The structural framework for the Park area investigated here would not have been determined as effectively with a flight line spacing exceeding 500 m. It is recommended that the definition of detailed structural frameworks would most likely benefit from line spacing between 200 and 250 m with fixed-wing AEM systems. Both the 1- and 2D inversion methods employed helped conceptualize the hydrogeology underpinning the presence of artesian and gravity-fed spring complexes in the area.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.R., methodology, J.R., T.M. and A.M., validation, J.R., T.M. and A.M.; formal analysis, J.R., T.I., T.M., A.M., A.V., A.R. and R.P., investigation, J.R. and A.M., resources J.R., T.M. and A.M., writing—original draft preparation, J.R., T.I., T.M., A.M., A.V., A.R. and R.P., writing—review and editing, J.R., T.M. and A.M., visualization, J.R., T.I., T.M., A.M., A.V., A.R. and R.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
BHP is acknowledged for funding this work through the Eighty-Mile Beach and Walyarta Conservation Program 2014–2017.
Data Availability Statement
Remote sensing and airborne electromagnetic (AEM) data are available in the following publicly accessible repositories; (http://auscover.org.au/purl/landsat-seasonal-fractional-cover, accessed on 24 March 2021) and Airborne Geophysics Index (MAGIX) (dmp.wa.gov.au, accessed on 24 March 2021).
Acknowledgments
The following are acknowledged for their assistance at various stages during this project. We respectively acknowledge the Nyangumarta and Karajarri as the traditional owners of the land on which the spring survey was conducted. We are grateful to you for imparting your cultural knowledge, for introducing us to the springs and wetlands of Walyarta and for assistance in the 2015 and 2016 field surveys. DBCA Kensington staff Val English for requesting the investigation, Adrian Pinder for supporting the project, Lindsay Bourke for managing the 2015 hydrological field program and Bart Huntley for providing remote sensing advice and carrying out the initial pilot study. DBCA staff of the Kimberley Region for invaluable advice and assistance in coordinating the field programs; Tracy Sonneman and Naomi Findlay (2015–2016) and Bruce Greatwich and Nicole Godfrey (2019–2020). Glenn Harrington is thanked for undertaking the 2015–2016 sampling and reporting preliminary results. Angelo Vartesi is thanked for drafting and improving on many figures presented here. The editor and three anonymous reviewers are thanked for their constructive comments that have helped us improve this manuscript. The Department of Water and Environmental Regulation (DWER) and the Department of Primary Industries and Rural Development (DPIRD) for sharing data collected across the Canning Basin. The authors would also like to thank CSIRO’s Deep Earth Imaging Future Science Platform for supporting this work.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare there is no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Appendix A. Fixed-Wing AEM System
A fixed-wing time domain airborne electromagnetic system (AEM) system, such as TEMPEST (see [52]), consists of a transmitter loop suspended around the fixed wings of an aircraft with receiver coils housed in a “bird” deployed via a cable behind and below the aircraft [89]. The transmitter coil carries a current which generates a magnetic field—the primary field in the surrounding ground and air. When the current is turned off abruptly, the changing magnetic field induces eddy currents in the ground that move in circular horizontal paths. It also induces a secondary magnetic field (the secondary field). Initially, this is equal to the primary magnetic field but is rapidly weakened by the electrical resistivity of the ground, and it then dissipates or decays. The decaying secondary magnetic field is measured by the receiver coils positioned in the “bird” deployed behind and below the aircraft (Figure A1). While dissipating, the current diffuses downwards and outwards, occupying an increasing volume of the sub-surface. Shortly after turn-off, the current is concentrated in the near-surface, and therefore, the measured signal will reflect the conductivities of near-surface layers. With later times, the current propagates deeper into the ground and the measured signal contains information on the conductivity of these deeper layers (note that there is an inverse relationship between conductivity and resistivity; i.e., a high conductivity is equivalent to a low resistivity and vice versa).
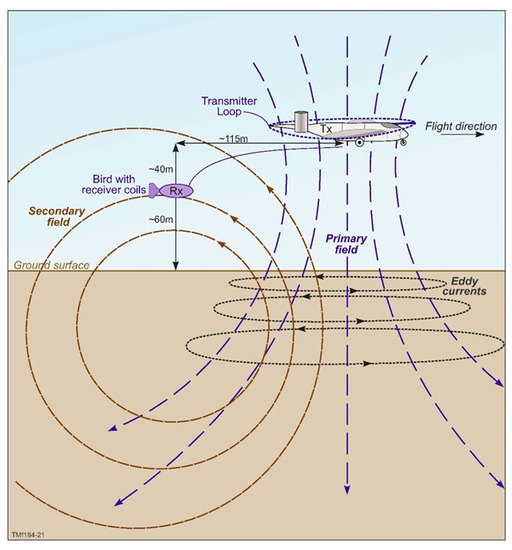
Figure A1.
Principles of time domain EM data acquisition for a fixed-wing time domain EM system, such as the TEMPEST AEM system.
Figure A1.
Principles of time domain EM data acquisition for a fixed-wing time domain EM system, such as the TEMPEST AEM system.
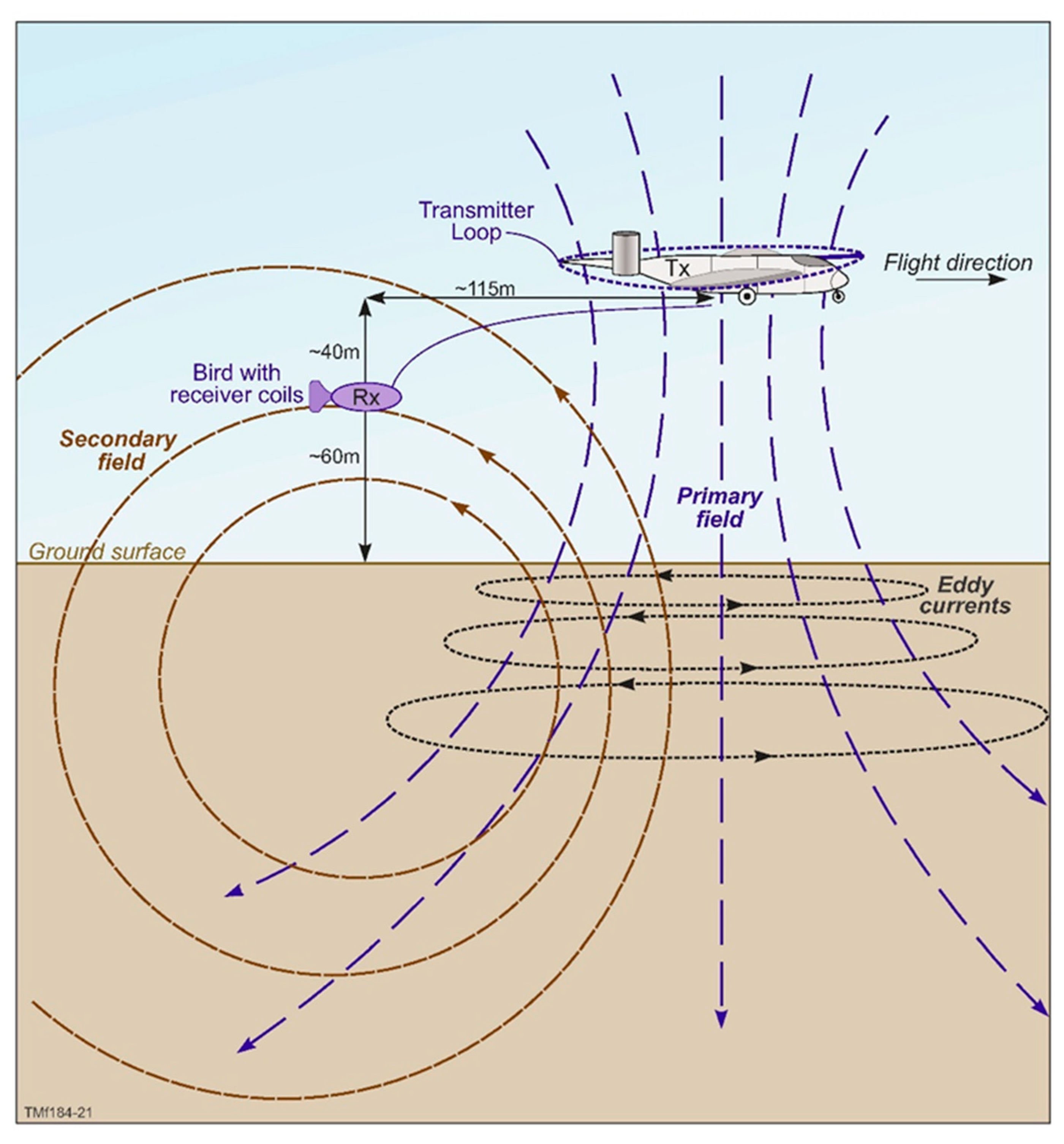
References
- Guo, M.; Li, J.; Sheng, C.; Xu, J.; Wu, L. A Review of Wetland Remote Sensing. Sensors 2017, 17, 777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, D.C.; Lewis, M.M. A new approach to monitoring spatial distribution and dynamics of wetlands and associated flows of Australian Great Artesian Basin springs using QuickBird satellite imagery. J. Hydrol. 2011, 408, 140–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Department of Parks and Wildlife (DPaW). Parks and Reserves of the South-West Kimberley and North-West Pilbara—Draft Joint Management Plan 2016; Department of Parks and Wildlife: Perth, Australia, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Storey, A.W.; Halse, S.A.; Shield, R.J.; Creagh, S. Aquatic fauna and water chemistry of the mound springs and wetlands of Mandora Marsh, north-western Australia. J. R. Soc. West. Austr. 2011, 94, 419–437. [Google Scholar]
- Quinlan, K.; Pinder, A.; Lewis, L. Aquatic Fauna Survey at Mandora Marsh (Walyarta) in September 2015: Pre-pared for Parks and Wildlife’s Kimberley Region; Department of Parks and Wildlife: Kensington, Australia, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Department of Conservation and Land Management (CALM). A Land Management Assessment of Mandora Marsh and its Immediate Surrounds; Graham, G., Ed.; Unpublished Report; Department of Conservation and Land Management: Perth, WA, Australia, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- English, V.; Luu, R.; Coote, M. Survey of Mandora Mound Springs and Salt Creek, Walyarta; Department of Parks and Wildlife: Kensington, WA, Australia, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Markey, A. Mandora Marsh / Walyarta Flora and Floristic Vegetation Survey: 2015. Progress Report; Department of Parks and Wildlife: Kenisngton, WA, Australia, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Wyrwoll, H.; McKenzie, N.L.; Pederson, B.J.; Tapley, I.J. The Great Sandy Desert of northwestern Australia: The last 7000 years. Search 1986, 17, 208–210. [Google Scholar]
- Harrington, G.A.; Harrington, N.M. Hydrochemistry of Peat Mound Springs within Mandora Marsh, West Canning Basin, WA; A Report Prepared for Department of Parks and Wildlife, Western Australia by Innovative Groundwater Solutions; Innovative Groundwater Solutions: Wayville, SA, Australia, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Leech, R.E.J. Geology and Groundwater Resources of the Southwestern Canning Basin, Western Australia; Geological Survey of Western Australia; Record 1979/9; Department of Mines, Industry Regulation and Safety: Perth, WA, Australia, 1979; ISBN 072448034X. [Google Scholar]
- Aquaterra. West Canning Basin Modelling Project; Report to the Western Australian Department of Water by Aqua-terra Consulting Pty Ltd.: Kenisngton, WA, Australia, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Aldam, R.; Kuang, K. An Investigation of Structures Controlling Discharge of Spring Waters in the South Western Great Artesian Basin; Adelaide SA: Report Book 88/4; Department of Mines and Energy: Adelaide, SA, Australia, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Krieg, G.W.; Rogers, P.A.; Callen, R.A.; Freeman, P.J.; Alley, N.F.; Forbes, B.G. Curdimurka, South Australia. Explanatory notes. 1:250,000 Geological Series—Sheet SH 53-8; Geological Survey of South Australia: Adelaide, Australia, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Inverarity, K.; Heinson, G.; Hatch, M. Groundwater flow underneath mound spring tufas from geophysical surveys in the southwestern Great Artesian Basin, Australia. Aust. J. Earth Sci. 2016, 63, 857–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halihan, T.; Love, A.; Keppel, M.; Dailey, M.K.M.; Berens, V.; Wohling, D. Evidence for groundwater mixing at Freeling Spring Group, South Australia. Hydrogeol. J. 2019, 28, 313–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, M.W. Potential for Satellite Remote Sensing of Ground Water. Ground Water 2006, 44, 306–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pastick, N.J.; Jorgenson, M.T.; Wylie, B.K.; Minsley, B.J.; Ji, L.; Walvoord, M.A.; Smith, B.D.; Abraham, J.D.; Rose, J.R. Extending Airborne Electromagnetic Surveys for Regional Active Layer and Permafrost Mapping with Remote Sensing and Ancillary Data, Yukon Flats Ecoregion, Central Alaska. Permafr. Periglac. Process. 2013, 24, 184–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhu, X.; Zhu, W.; Pan, Y.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, D. Changes in Spring Phenology in the Three-Rivers Headwater Region from 1999 to 2013. Remote. Sens. 2014, 6, 9130–9144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albano, C.M.; McGwire, K.C.; Hausner, M.B.; McEvoy, D.J.; Morton, C.G.; Huntington, J.L. Drought Sensitivity and Trends of Riparian Vegetation Vigor in Nevada, USA (1985–2018). Remote. Sens. 2020, 12, 1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshehri, F.; Sultan, M.; Karki, S.; Alwagdani, E.; Alsefry, S.; Alharbi, H.; Sahour, H.; Sturchio, N. Mapping the Distribution of Shallow Groundwater Occurrences Using Remote Sensing-Based Statistical Modeling over Southwest Saudi Arabia. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munier, S.; Carrer, D.; Planque, C.; Camacho, F.; Albergel, C.; Calvet, J.-C. Satellite Leaf Area Index: Global Scale Analysis of the Tendencies Per Vegetation Type Over the Last 17 Years. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pryet, A.; D’Ozouville, N.; Violette, S.; Deffontaines, B.; Auken, E. Hydrogeological settings of a volcanic island (San Cristóbal, Galapagos) from joint interpretation of airborne electromagnetics and geomorphological observations. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2012, 16, 4571–4579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goebel, M.; Knight, R.; Halkjær, M. Mapping saltwater intrusion with an airborne electromagnetic method in the offshore coastal environment, Monterey Bay, California. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2019, 23, 100602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paine, J.G. Determining salinization extent, identifying salinity sources, and estimating chloride mass using surface, borehole, and airborne electromagnetic induction methods. Water Resour. Res. 2003, 39, 1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siemon, B.; Vest Christiansen, A.; Auken, E. A review of helicopter-borne electromagnetic methods for groundwater exploration. Near Surf. Geophys. 2009, 7, 629–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickinson, J.E.; Pool, D.R.; Groom, R.W.; Davis, L.J. Inference of lithologic distributions in an alluvial aquifer using airborne transient electromagnetic surveys. Geophysics 2010, 75, WA149–WA161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oldenborger, G.; Logan, C.; Hinton, M.; Pugin, A.-M.; Sapia, V.; Sharpe, D.; Russell, H. Bedrock mapping of buried valley networks using seismic reflection and airborne electromagnetic data. J. Appl. Geophys. 2016, 128, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parra-García, M.; Sanchez, G.; Dentith, M.C.; George, A.D. Regional Structural and Stratigraphic Study of the Canning Basin; Report; Geological Survey of Western Australia: Perth, WA, Australia, 2014; Volume 140, 215p. [Google Scholar]
- Geological Survey of Western Australia (GSWA). Prospectivity of State Acreage Release Areas L12-8 and L12-9, Canning Basin; Geological Survey of Western Australia: Perth, WA, Australia, 2012; p. 10. [Google Scholar]
- Forman, D.J.; Wales, D.W. Geological Evolution of the Canning Basin, Western Australia, Bulletin 210 Bureau of Mineral Resources, Geology and Geophysics; Australian Government Publishing Service: Canberra, Australia, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- FrOG Tech 2005. OZ SEEBASETM v1 2005. Structural GIS. Available online: http://www.frogtech.com.au/seebase-range/ (accessed on 27 March 2021).
- Frogtech Geoscience. Canning Basin SEEBASE Study and GIS Data Package: Geological Survey of Western Australia; Report 182; Geology and Geophysics and Geological Survey of Western Australia: Perth, WA, Australia, 2017; p. 297. [Google Scholar]
- Towner, R.R. 1:250 000 Geological Series—Explanatory Notes: Mandora Western Australia Sheet SE/51-13 Interna-tional Index; Bureau of Mineral Resources, Geology and Geophysics and Geological Survey of Western Australia: Perth, WA, Australia, 1982; p. 22. [Google Scholar]
- Towner, R.R. 1:250 000 Geological Series—Explanatory Notes: Munro Western Australia Sheet SE/51-14 International Index; Bureau of Mineral Resources, Geology and Geophysics and Geological Survey of Western Australia: Perth, WA, Australia, 1982; p. 22. [Google Scholar]
- Towner, R.R.; Gibson, D.L. Geology of the onshore Canning Basin, Western Australia: Bureau of Mineral Resources, Geology and Geophysics. Bulletin 1983, 215, 51. [Google Scholar]
- Zhan, Y. A Seismic Interpretation of the Southwestern Canning Basin, Western Australia: Geological Survey of Western Australia; Report 178; Department of Mines, Industry Regulation and Safety: Perth, WA, Australia, 2018; p. 36. [Google Scholar]
- Zhan, Y. A Seismic Interpretation of the Broome Platform, Willara Sub-Basin and Munro Arch of the Canning Basin, Western Australia: Geological Survey of Western Australia; Report 193; Department of Mines, Industry Regulation and Safety: Perth, WA, Australia, 2019; p. 43. [Google Scholar]
- Department of Water (DoW). La Grange Groundwater Allocation Plan; Department of Water, Water Resource Allocation and Planning Report Series Report no. 25; The Department of Water and Environmental Regulation: Perth, WA, Australia, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Department of Water (DoW). West Canning Basin Groundwater Allocation Limit Report—Background Information and Method Used to Set an Allocation Limit for Aquifers in the West Canning Basin. Department of Water, Water Resource Allocation and Planning Report Series Report no. 52; The Department of Water and Environmental Regulation: Perth, WA, Australia, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- NTEC Environmental Technology (NTEC). West Canning Basin Groundwater Model: Northstar Magnetite Project; Report for Fortescue Metals Group (FMG) Ltd. EPA Western Australia: Joondalup, WA, Australia, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Paul, R.J.; George, R.J.; Gardiner, P.S. A Review of the Broome Sandstone Aquifer in the La Grange Area, Resource Management Technical Report 387; Department of Agriculture and Food: Perth, Australia, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Pells Sullivan Meynink (PSM). West Canning Basin Groundwater Model Report, A Report to Department of Water and Environmental Regulation Perth Western Australia; The Department of Water and Environmental Regulation: Perth, WA, Australia, 2017; p. 394. [Google Scholar]
- Traves, D.M.; Casey, J.N.; Wells, A.T. The Geology of the South-Western Canning Basin, Western Australia. Commonwealth of Australia, Department of National Development, The Bureau of Mineral Resources, Geology and Geophysics; Report no 29; BMR; The Bureau of Mineral Resources, Geology and Geophysics: Canberra, ACT, Australia, 1956. [Google Scholar]
- Munier, S.; Maisongrande, P.; Becker, M.; Cazenave, A. Using GRACE to detect groundwater storage variations: The cases of Canning Basin and Guarani aquifer system. Int. Water Technol. J. 2012, 2, 2–13. [Google Scholar]
- Rutherford, J.; Greatwich, B.; Godfrey, N.; Rings, C.; Hunter, N.; McDonald, J. Seasonal Groundwater and Surface Water Interactions in the Walyarta Mound Springs and Mandora Lake: 2019–2020; Department of Biodiversity, Conservation and Attractions: Kensington, Australia, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Markey, A.; Dillion, S. Draft Vegetation Map of the Walyarta Conservation Park: February 2019; Prepared for DBCAs Parks and Wildlife Services West Kimberley Region; Department of Biodiversity, Conservation and Attractions: Kensington, WA, Australia, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Huntley, B. Walyarta-Preliminary Remote Sensing Report; Department of Parks and Wildlife: Perth, WA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Rutherford, J.L.; Cendón, D.I.; Søerensen, C.; Batty, S.; Huntley, B.; Bourke, L.; Pinder, A.; Quinlan, K.; English, V.; Coote, M. Hydrological Conceptualisation of the Walyarta Mound Springs; Department of Biodiversity, Conservation and At-tractions, Wetlands Conservation Program: Perth, Australia, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Meredith, K.; Han, L.; Cendón, D.; Crawford, J.; Hankin, S.; Peterson, M.; Hollins, S. Evolution of dissolved inorganic carbon in groundwater recharged by cyclones and groundwater age estimations using the 14C statistical approach. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2018, 220, 483–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CGG. Department of Water TEMPEST Geophysical Survey West Canning Basin Survey, Western Australia: Logistics and Processing Report; Project Number: 2474; Bureau of Mineral Resources, Geology and Geophysics and Geological Survey of Western Australia: Perth, WA, Australia, 2016; p. 58. [Google Scholar]
- Lane, R.; Green, A.; Golding, C.; Owers, M.; Pik, P.; Plunkett, C.; Sattel, D.; Thorn, B. An example of 3D conductivity mapping using the TEMPEST airborne electromagnetic system. Explor. Geophys. 2000, 31, 162–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lane, R.; Pracilio, G. Visualisation of Sub-Surface Conductivity Derived from Airborne EM. In Proceedings of the Symposium on the Application of Geophysics to Engineering and Environmental Problems 2000, Arlington, VA, USA, 20–24 February 2000; pp. 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sattel, D.; Kgotlhang, L. Groundwater Exploration with Aem in the Boteti Area, Botswana. Explor. Geophys. 2004, 35, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roach, I.C. (Ed.) Geological and Energy Implications of the Paterson Province Airborne Electromagnetic (AEM) Survey, Western Australia; Record 2010/12; Geoscience Australia: Canberra, Australia, 2010; Record 2010/12. [Google Scholar]
- Roach, I.C.; Jaireth, S.; Costelloe, M.T. Applying regional airborne electromagnetic (AEM) surveying to understand the architecture of sandstone-hosted uranium mineral systems in the Callabonna Sub-basin, Lake Frome region, South Australia. Aust. J. Earth Sci. 2014, 61, 659–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, M.A. (Ed.) Geological and Energy Implications of the Pine Creek Region Airborne Electromagnetic (AEM) Survey; Northern Territory, Australia. Record 2011/18, 292; Geoscience Australia: Canberra, Australia, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Annetts, D.; Munday, T.; George, R.; Wright, N.; Raper, G.P.; Cahill, K. The Application of AEM to Mapping the Aquifer and Groundwater Characteristics of the La Grange Groundwater Area; WA: Final Report, Report EP165299; CSIRO: Perth, Australia, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Ley-Cooper, A.Y.; Brodie, R.C.; Richardson, M. AusAEM: Australia’s airborne electromagnetic continental-scale acquisition program. Explor. Geophys. 2019, 51, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mira Geoscience. Inversion and Preliminary Interpretation of Airborne Electromagnetic Data from the West Canning Basin—Sandfire TEMPEST Survey; A Report Prepared for the Government of Western Australia, The Department of Water and Environmental Regulation: Perth, WA, Australia, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Auken, E.; Vest Christiansen, A. Layered and laterally constrained 2D inversion of resistivity data. Geophysics 2004, 69, 752–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auken, E.; Vest Christiansen, A.; Kirkegaard, C.; Fiandaca, G.; Schamper, C.; Behroozmand, A.A.; Binley, A.; Nielsen, E.; Effersø, F.; Christensen, N.B.; et al. An overview of a highly versatile forward and stable inverse algorithm for airborne, ground-based and borehole electromagnetic and electric data. Explor. Geophys. 2015, 46, 223–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sørensen, C.C.; Munday, T.J.; Rutherford, J.L.; Cahill, K. Processing and Inversion of Mandora Marsh AEM Data: Enhanced TEMPEST Data Processing and Interpretation; CSIRO Technical Report EP 178999; CSIRO: Kensington, WA, Australia, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Clark, D.; McPherson, A.; Collins, C.D.N. Australia’s Seismogenic Neotectonic Record: A Case for Heterogeneous Intraplate Deformation; Record 2011/11; Geoscience Australia: Canberra, Australia, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Bailey, A.; Henson, P. Mapping Northern Australia’s Present Day Stress Field: The Canning Basin. ASEG Ext. Abstr. 2018, 2018, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brett, J.W. 80 m Magnetic 1VD Merged Grid of Western Australia 2020 Version 1: Geological Survey of Western Australia; Department of Mines, Industry Regulation and Safety: Perth, WA, Australia, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- V&C Semeniuk Research Group. Wetlands of the North-Western Great Sandy Desert; Unpublished; V&C Semeniuk Research Group: Perth, WA, Australia, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Haig, T. The Pilbara Coast Water Study. Government of Western Australia, Department of Water Hydrogeological Record Series; Report no. HG34; Government of Western Australia; Wayville, SA, Australia, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Knight, R.; Smith, R.; Asch, T.; Abraham, J.; Cannia, J.; Viezzoli, A.; Fogg, G. Mapping Aquifer Systems with Airborne Electromagnetics in the Central Valley of California. Ground Water 2018, 56, 893–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, J.E.; Vrbancich, J. A comparison of the inductive-limit footprints of airborne electromagnetic configurations. Geophysics 2004, 69, 1229–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viezzoli, A.; Auken, E.; Munday, T. Spatially constrained inversion for quasi 3D modelling of airborne electromagnetic data—An application for environmental assessment in the Lower Murray Region of South Australia. Explor. Geophys. 2009, 40, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viezzoli, A.; Vest Christiansen, A.; Auken, E.; So̸rensen, K. Quasi-3D modeling of airborne TEM data by spatially constrained inversion. Geophysics 2008, 73, F105–F113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vest Christiansen, A.; Auken, E. A global measure for depth of investigation. Geophysics 2012, 77, WB171–WB177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paterson, R.; Silic, J.; Fitzgerald, D. Improved Structural Mapping and Conductive Targeting Delivered by a new 2.5D AEM Inversion Solver. ASEG Ext. Abstr. 2016, 2016, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silic, J.; Paterson, R.; FitzGerald, D.; Archer, T. Comparing 1D and 2.5D AEM inversions in 3D geological mapping using a new adaptive inversion solver. In Proceedings of the 14th International Congress of the Brazilian Geophysical Society & EXPOGEF, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 3–6 August 2015; Society of Exploration Geophysicists: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, G.; Raiche, A.; Sugeng, F. 2.5D inversion of airborne electromagnetic data. Explor. Geophys. 2006, 37, 363–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flood, N.; Danaher, T.; Gill, T.; Gillingham, S. An Operational Scheme for Deriving Standardised Surface Reflectance from Landsat TM/ETM+ and SPOT HRG Imagery for Eastern Australia. Remote. Sens. 2013, 5, 83–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muir, J.; Schmidt, M.; Tindall, D.; Trevithick, R.; Scarth, P.; Stewart, J. Guidelines for Field Measurement of Fractional Ground Cover: A Technical Handbook Supporting the Australian Collaborative Land Use and Management Program; Tech. Rep.; Queensland Department of Environment and Resource Management for the Australian Bureau of Agricultural and Resource Economics and Sciences: Canberra, Australia, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Rutherford, J.; Cendón, D.I.; Madden, R.; Greatwich, B.; Godfrey, N.; Ibrahimi, T. (in prep) Hydrogeochemical and Mineralogical Evidence of Long-Term Groundwater Discharge in Organic Mound Springs in Semi-Arid North Western Australia.
- Curewitz, D.; A Karson, J. Structural settings of hydrothermal outflow: Fracture permeability maintained by fault propagation and interaction. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 1997, 79, 149–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gudmundsson, A. Active fault zones and groundwater flow. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2000, 27, 2993–2996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faulkner, D.; Jackson, C.; Lunn, R.; Schlische, R.; Shipton, Z.; Wibberley, C.; Withjack, M. A review of recent developments concerning the structure, mechanics and fluid flow properties of fault zones. J. Struct. Geol. 2010, 32, 1557–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flood, N. Seasonal Composite Landsat TM/ETM+ Images Using the Medoid (a Multi-Dimensional Median). Remote. Sens. 2013, 5, 6481–6500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CyMod Systems Pty. Ltd. Local Scale Solute Transport Modelling of Walyarta Conservation Park Using WCAMS V1.3; Report to Department of Biodiversity, Conservation and Attractions; CyMod Systems Pty. Ltd.: Bedfordale, WA, Australia, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Bense, V.; Gleeson, T.; Loveless, S.; Bour, O.; Scibek, J. Fault zone hydrogeology. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2013, 127, 171–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, T.R.; Fairley, J.P. Relating permeability to the structural setting of a fault-controlled hydrothermal system in southeast Oregon, USA. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2008, 113, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowland, J.C.; Manga, M.; Rose, T.P. The influence of poorly interconnected fault zone flow paths on spring geochemistry. Geofluids 2008, 8, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, N.-H.; Han, W.S.; Watson, Z.; Graham, J.P.; Kim, K.-Y. Fault-controlled CO2 leakage from natural reservoirs in the Colorado Plateau, East-Central Utah. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2014, 403, 358–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palacky, G. Use of airborne electromagnetic methods for resource mapping. Adv. Space Res. 1993, 13, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).