S-NPP VIIRS Day Night Band On-Board Solar Diffuser Calibration Validation Using the Scheduled Lunar Collections
Abstract
1. Introduction
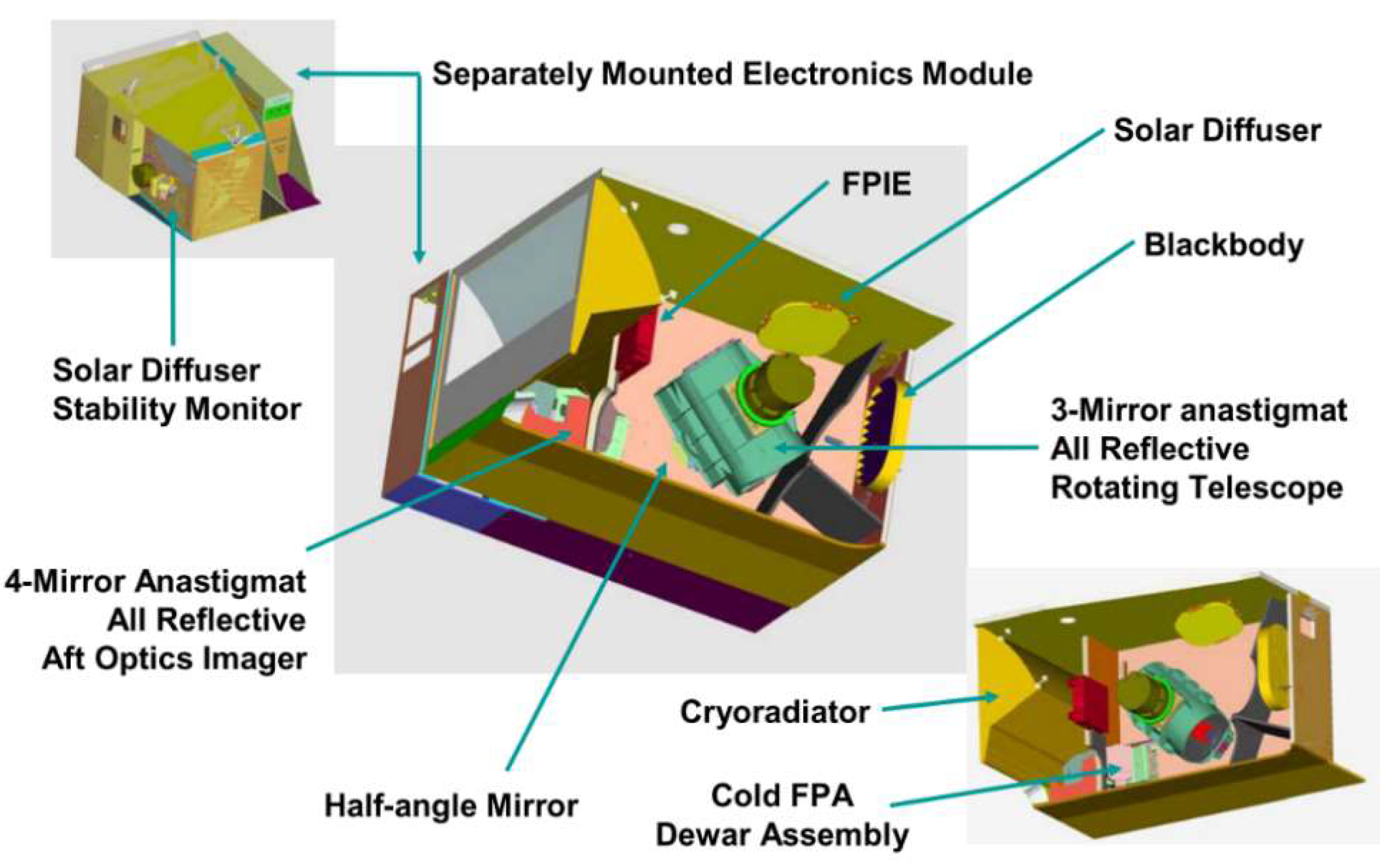
2. On-orbit DNB Calibration
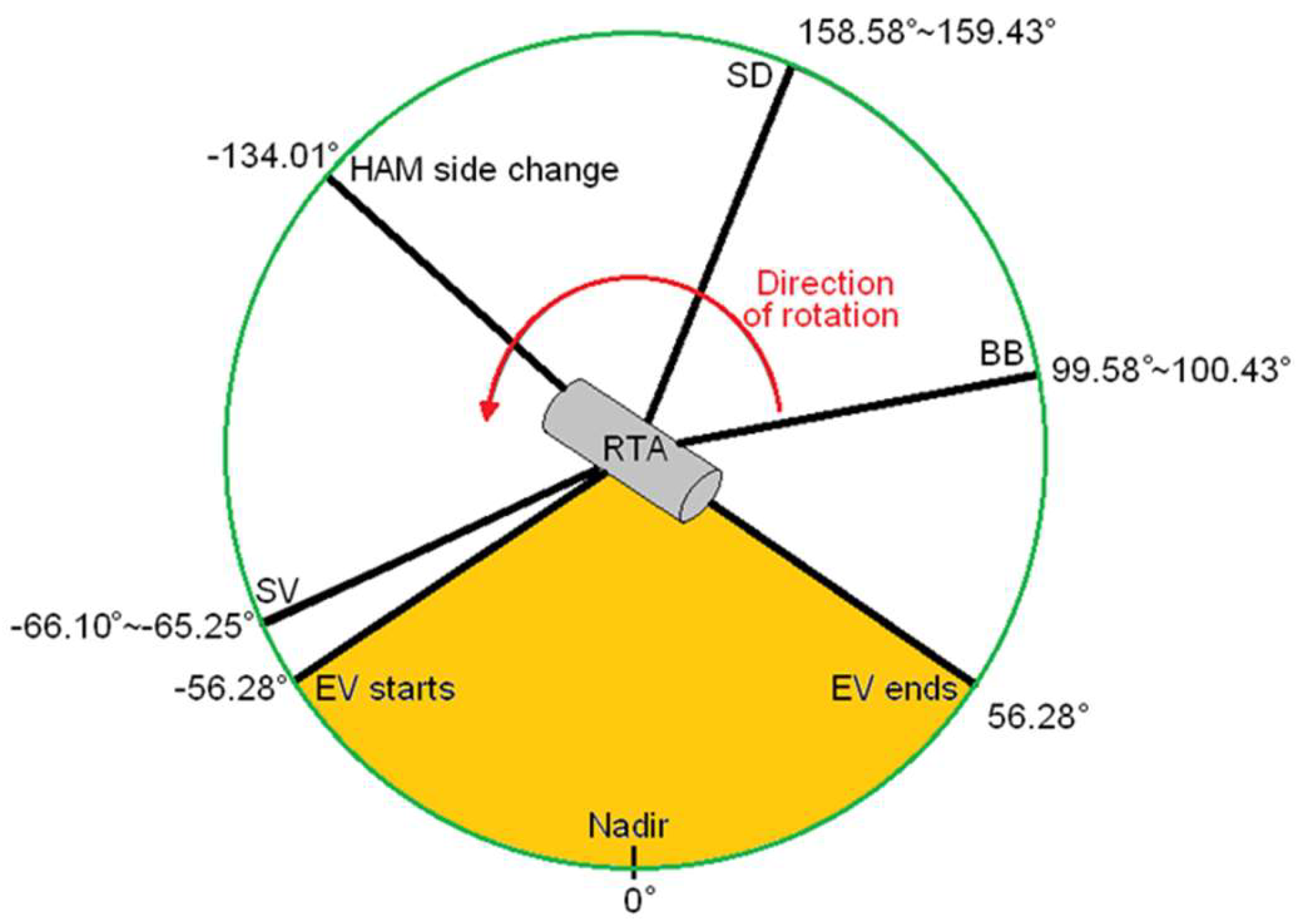
2.1. Primary On-Orbit DNB Calibration Using SD
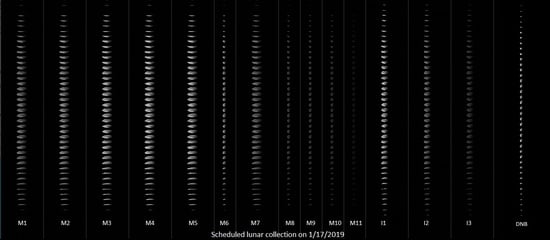
2.2. Scheduled Lunar Collection
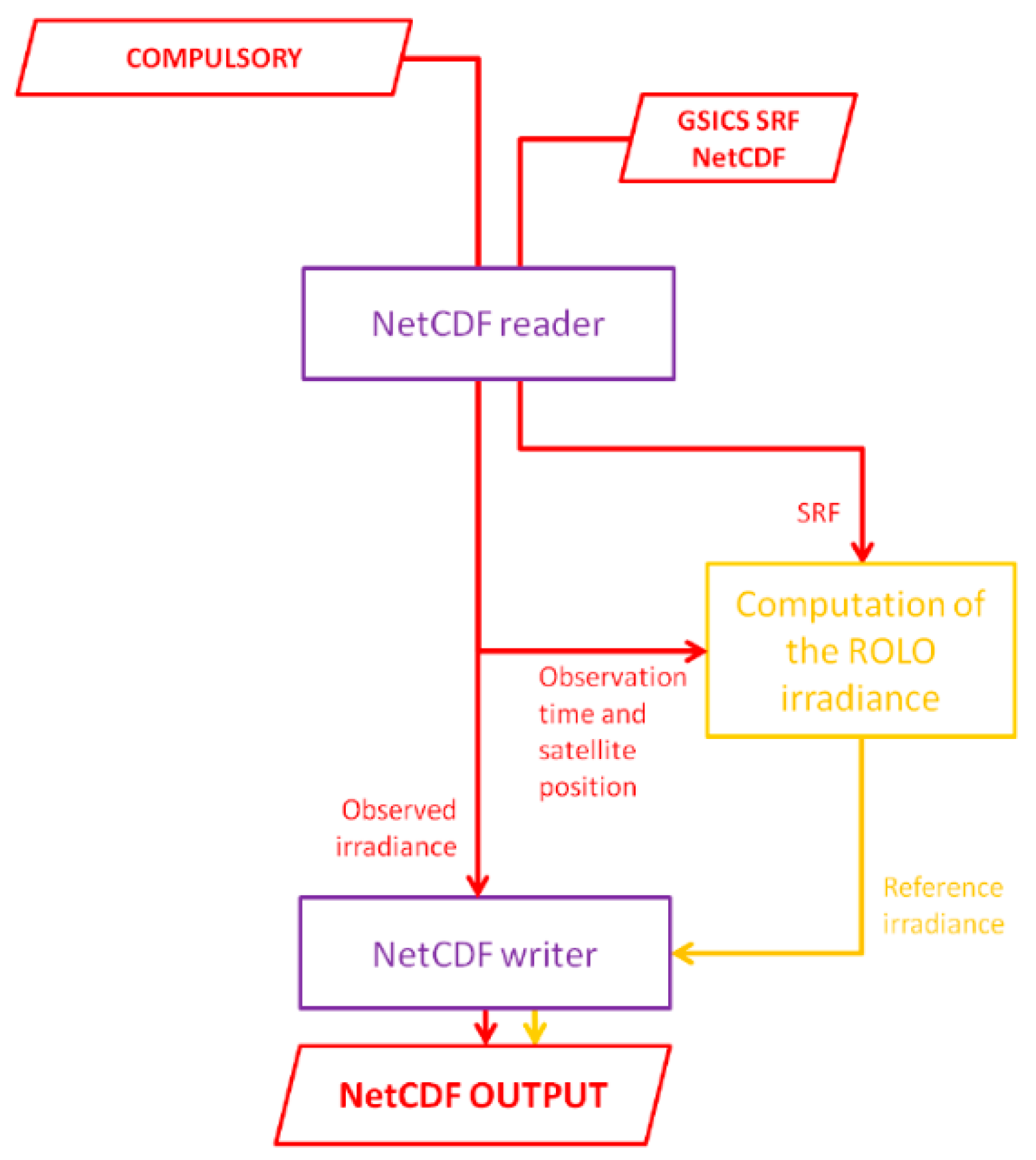
2.3. Lunar Radiance and Irradaince Calculation
2.4. Lunar Irradiance from the GIRO and Lunar F-Factor
3. Results
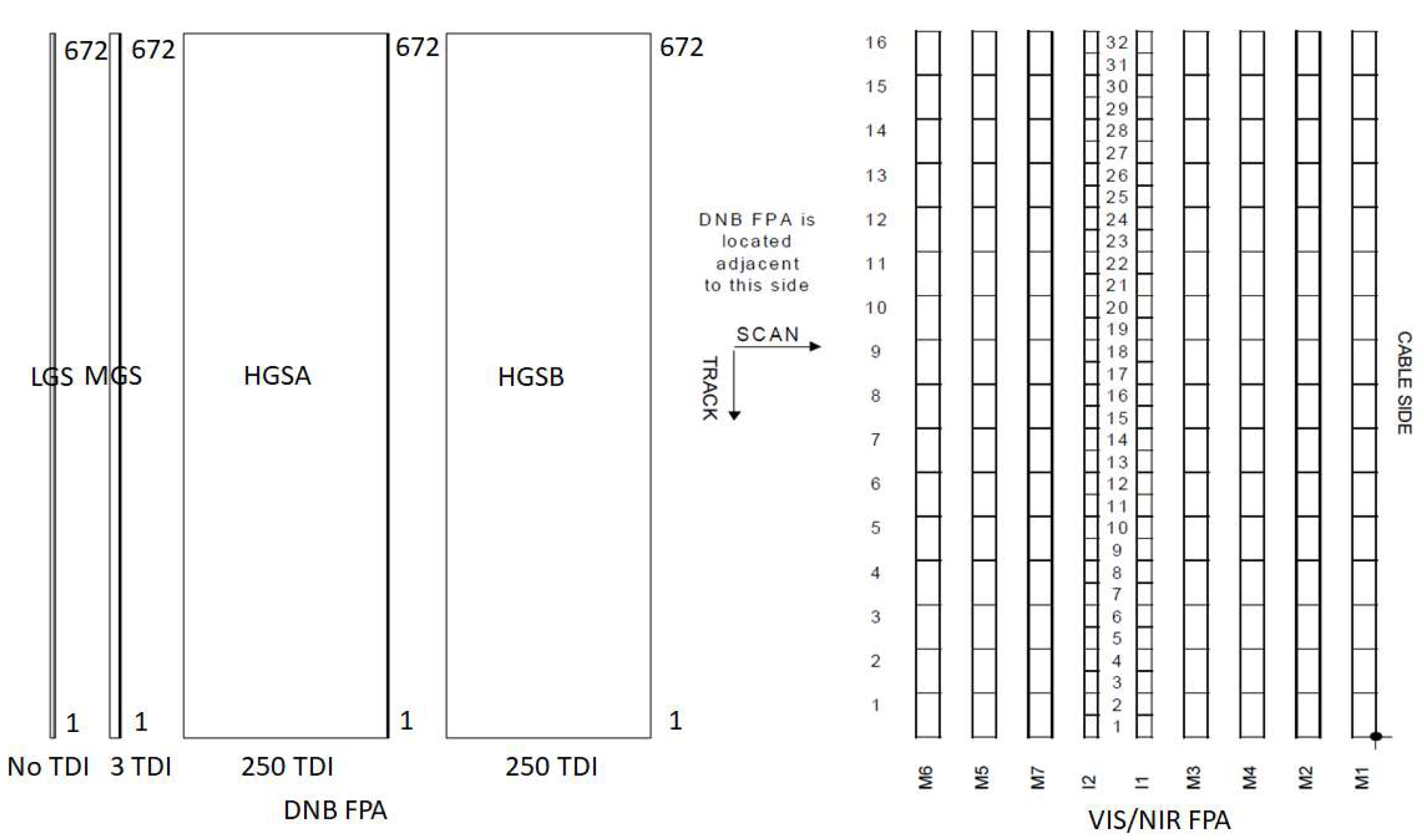
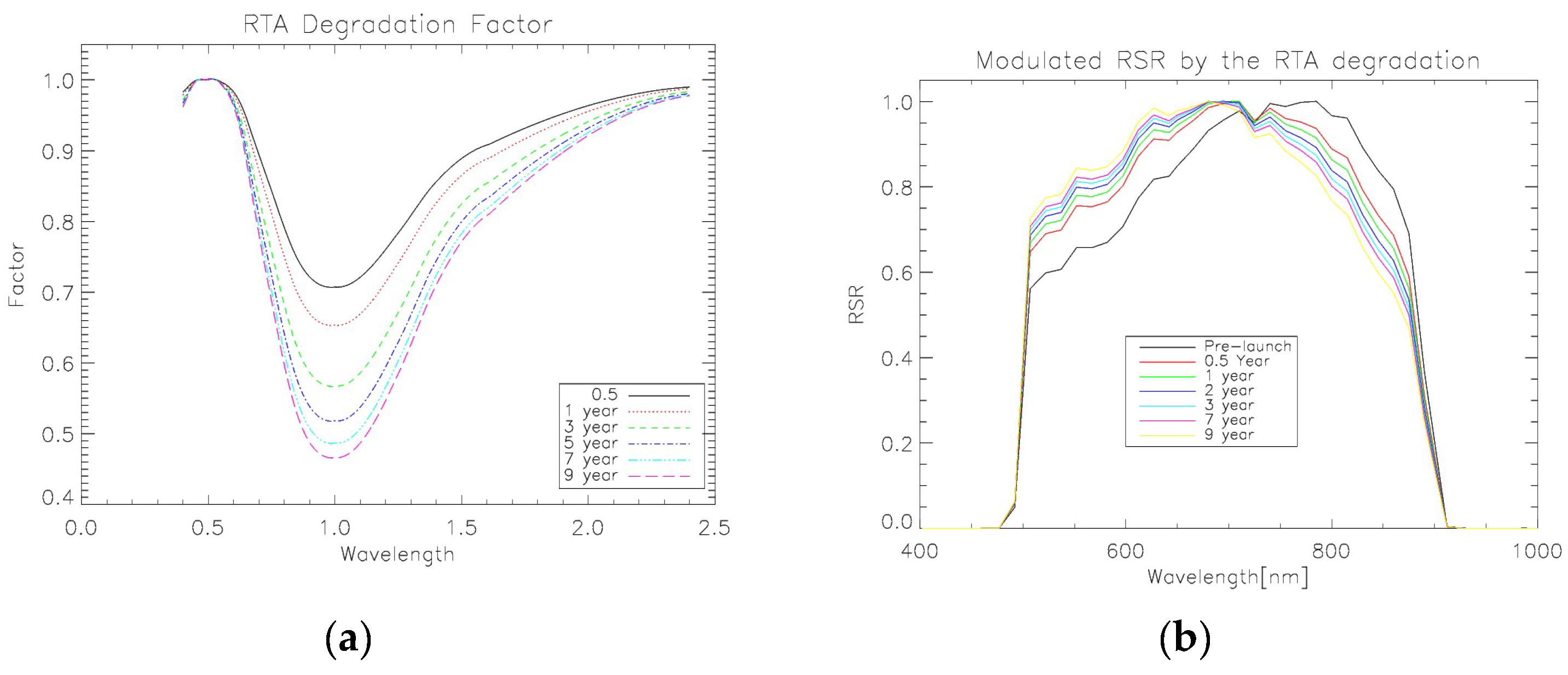
3.1. The S-NPP VIIRS DNB RSR
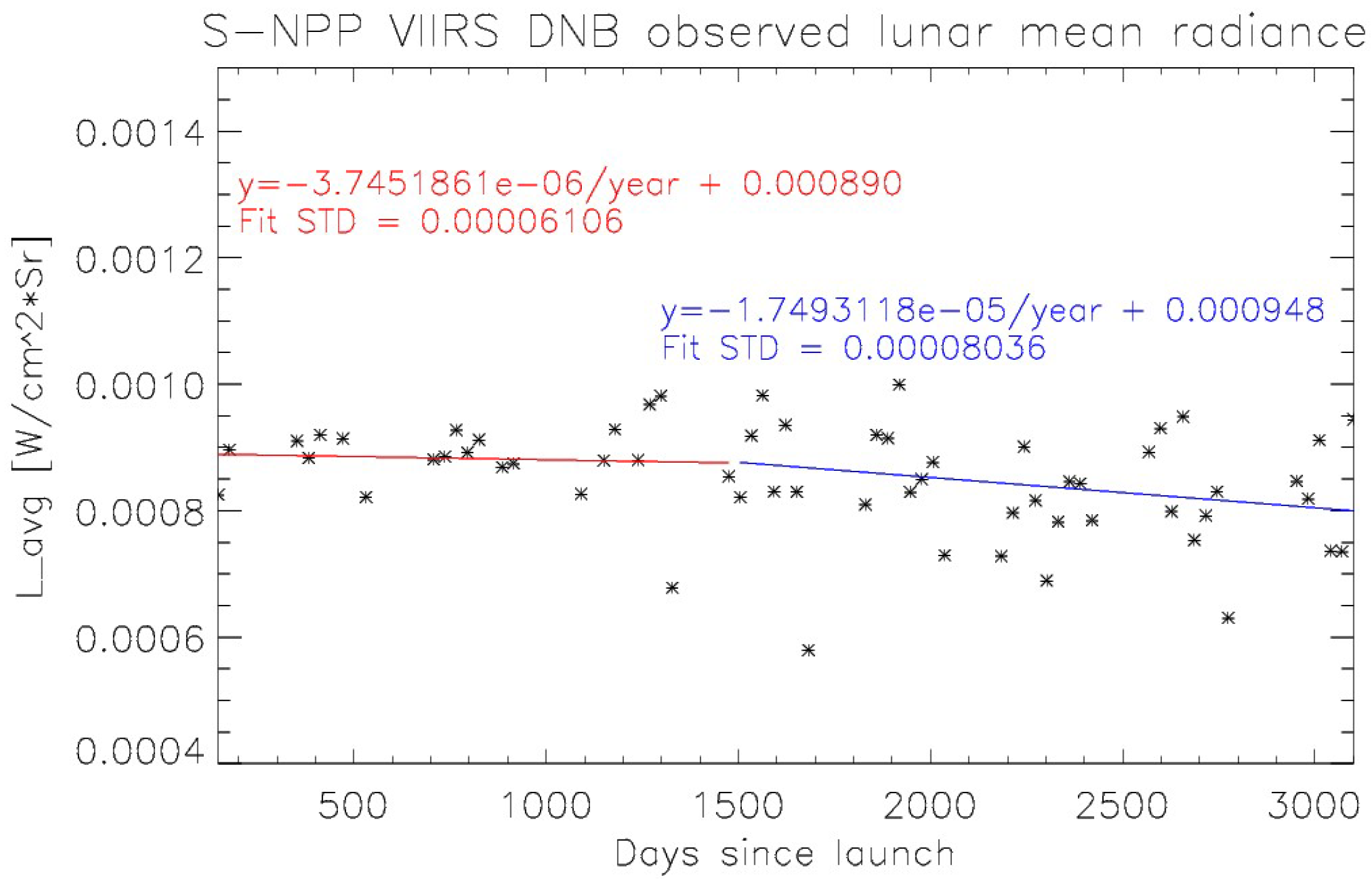
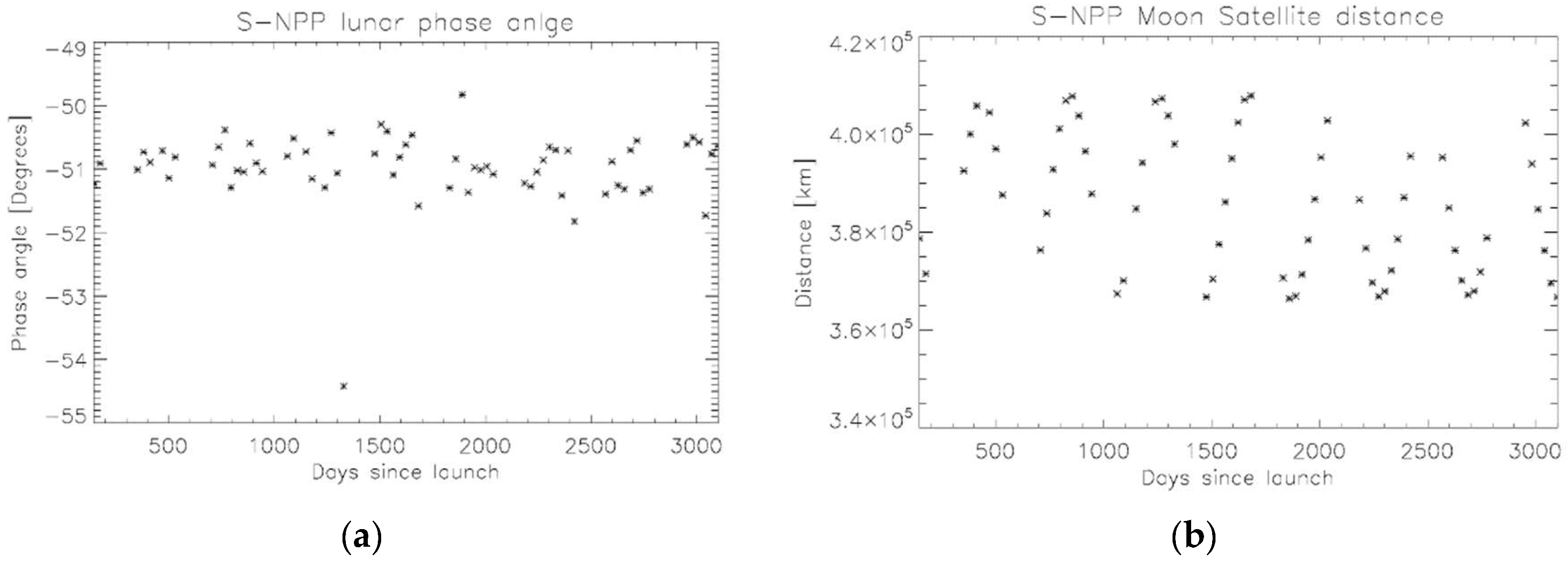
3.2. VIIRS Observed Lunar Radiance
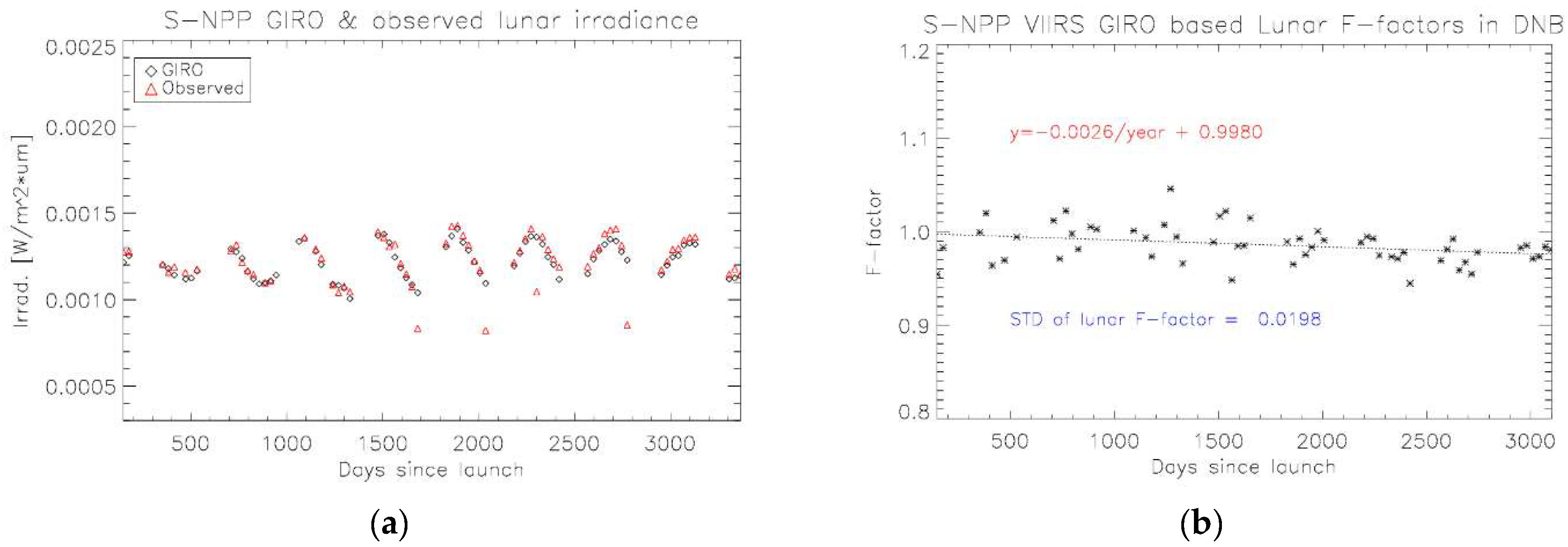
3.3. VIIRS Observed Lunar Irradiance and Lunar F-Factor
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Disclaimer
References
- Cao, C.; Xiong, J.; Blonski, S.; Liu, Q.; Uprety, S.; Shao, X.; Bai, Y.; Weng, F. Suomi NPP VIIRS sensor data record verification, validation, and long-term performance monitoring. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 664–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, C.; De Luccia, F.J.; Xiong, X.; Wolfe, R.; Weng, F. Early On-Orbit Performance of the Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite Onboard the Suomi National Polar-Orbiting Partnership (S-NPP) Satellite. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 1142–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, N.; Kilcoyne, H. Joint Polar Satellite System (JPSS) VIIRS Radiometric Calibration Algorithm Theoretical Basis Document (ATBD); NASA: Greenbelt, MD, USA, 2011.
- Choi, T.; Shao, X.; Cao, C. On-orbit radiometric calibration of Suomi NPP VIIRS reflective solar bands using the Moon and solar diffuser. Appl. Opt. 2018, 57, 9533–9542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, T.; Shao, X.; Cao, C.; Weng, F. Radiometric Stability Monitoring of the Suomi NPP Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite (VIIRS) Reflective Solar Bands Using the Moon. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Chiang, K.; Xiong, X.; Sun, C.; Anderson, S. The S-NPP VIIRS Day-Night Band On-Orbit Calibration/Characterization and Current State of SDR Products. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 12427–12446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrie, J.D.; Xiong, X.; Fuqua, P.D.; Meshishnek, M.J.; Gu, X.; Ciofalo, M.R.; Chu, C.T.; Chaney, J.A.; Moision, R.M.; Graziani, L. Root cause determination of on-orbit degradation of the VIIRS rotating telescope assembly. In Proceedings of the Earth Observing Systems XVII, San Diego, CA, USA, 15 October 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, N.; Wang, Z.; Guenther, B.; Xiong, X.; Gleason, J. Modeling the detector radiometric response gains of the Suomi NPP VIIRS reflective solar bands. SPIE Remote Sens. 2012, 8533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Xiong, J.; Eplee, J.R.E.; Xiong, X.; Stone, T.; Meister, G.; McClain, C.R. MODIS and Seawifs on-Orbit Lunar Calibration. In Proceedings of the Earth Observing Systems XIII, San Diego, CA, USA, 11–13 August 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, J.-Q.; Xiong, X.; Barnes, W.L.; Guenther, B. MODIS Reflective Solar Bands On-Orbit Lunar Calibration. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2007, 45, 2383–2393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, X.; Sun, J.; Barnes, W. Intercomparison of On-Orbit Calibration Consistency Between Terra and Aqua MODIS Reflective Solar Bands Using the Moon. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2008, 5, 778–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morfitt, R.; Barsi, J.; Levy, R.; Markham, B.; Micijevic, E.; Ong, L.; Scaramuzza, P.; Vanderwerff, K. Landsat-8 Operational Land Imager (OLI) Radiometric Performance On-Orbit. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 2208–2237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Stone, T.C.; Yu, F.; Han, D. Vicarious calibration of GOES Imager visible channel using the Moon. SPIE Opt. Photonics 2006, 6296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, T.; Cao, C.; Weng, F. Radiometric Stability Monitoring of the S-Npp Viirs Ocean Color Bands Using the Moon. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Remote Sensing (ISRS), Jeju, Korea, 20 April 2016; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Cao, C.; Ignatov, A.; Liang, X.; Li, Z.; Wang, L.; Zhang, B.; Blonski, S.; Li, J. Improving the Calibration of Suomi NPP VIIRS Thermal Emissive Bands During Blackbody Warm-Up/Cool-Down. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 1977–1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taeyoung, C.; Junqiang, S.; Zhang, B.; Wang, Z.; Cao, C.; Weng, F.; Wang, M. Suomi-NPP VIIRS Initial Reprocessing Improvements and Validations in the Reflective Solar Bands. SPIE Opt. Eng. Appl. 2017, 10402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, T.; Cao, C. S-NPP VIIRS On-Orbit Calibration Coefficient Improvements with Yaw Maneuver Reanalysis. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 7460–7465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, X.; Liu, T.-C.; Xiong, X.; Cao, C.; Choi, T.; Angal, A. Surface Roughness-Induced Spectral Degradation of Multi-Spaceborne Solar Diffusers Due to Space Radiation Exposure. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, X.; Cao, C.; Liu, T.-C. Spectral Dependent Degradation of the Solar Diffuser on Suomi-NPP VIIRS Due to Surface Roughness-Induced Rayleigh Scattering. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, N.; Guenther, B.; Wang, Z.; Xiong, X.; Xiong, X. Modeling SNPP VIIRS reflective solar bands optical throughput degradation and its impacts on the relative spectral response. SPIE Opt. Eng. Appl. 2013, 8866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Xiong, X.; Fulbright, J.P. Suomi-NPP VIIRS unscheduled lunar observations. SPIE Remote Sens. 2016, 1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patt, F.S.; Butler, J.J.; Eplee, R.E.; Barnes, R.A.; Meister, G.; Butler, J.J. Use of the moon as a calibration reference for NPP VIIRS. Opt. Photonics 2005, 5882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blonski, S.; Cao, C. Suomi NPP VIIRS Reflective Solar Bands Operational Calibration Reprocessing. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 16131–16149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geis, J.; Florio, C.; Moyer, D.; Gu, X.; Rausch, K.; De Luccia, F.J. VIIRS day-night band gain and offset determination and performance. SPIE Opt. Eng. Appl. 2012, 8510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, L.B.; Weiss, S.; Mills, S.; Hauss, B. Suomi NPP VIIRS day-night band on-orbit performance. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 705–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Uprety, S.; Blonski, S.; Zhang, B.; Cao, C. Improved algorithm for determining the Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite Day/Night Band high-gain stage dark offset free from light contamination. Appl. Opt. 2019, 58, 1400–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kieffer, H.H.; Stone, T. The Spectral Irradiance of the Moon. Astron. J. 2005, 129, 2887–2901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hapke, B. A Theoretical Photometric Function for the Lunar Surface. J. Geophys. Res. 1963, 68, 4571–4586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, T.; Kieffer, H.H. Absolute irradiance of the moon for on-orbit calibration. In Proceedings of the SPIE—The International Society for Optical Engineering, Seattle, WA, USA, 7–10 July 2002; pp. 211–221. [Google Scholar]
- Kieffer, H.H. Photometric Stability of the Lunar Surface-annotated. ICARUS 1997, 130, 323–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, X.; Geng, X.; Angal, A.; Sun, J.; Barnes, W. Using the Moon to track MODIS reflective solar bands calibration stability. SPIE Remote Sens. 2011, 8176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eplee, J.R.E.; Xiong, X.; Sun, J.-Q.; Meister, G.; McClain, C.R. The cross calibration of SeaWiFS and MODIS using on-orbit observations of the Moon. Appl. Opt. 2011, 50, 120–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, N.; Xiong, X.; Guenther, B. Modeling the Detector Radiometric Gains of the Suomi NPP VIIRS Reflective Solar Bands. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2015, 53, 1565–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, T.C.; Kieffer, H.H. Assessment of uncertainty in ROLO lunar irradiance for on-orbit calibration. In Proceedings of the Optical Science and Technology, the SPIE 49th Annual Meeting, Denver, CO, USA, 2–6 August 2004. [Google Scholar]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Choi, T.; Cao, C. S-NPP VIIRS Day Night Band On-Board Solar Diffuser Calibration Validation Using the Scheduled Lunar Collections. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1093. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13061093
Choi T, Cao C. S-NPP VIIRS Day Night Band On-Board Solar Diffuser Calibration Validation Using the Scheduled Lunar Collections. Remote Sensing. 2021; 13(6):1093. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13061093
Chicago/Turabian StyleChoi, Taeyoung, and Changyong Cao. 2021. "S-NPP VIIRS Day Night Band On-Board Solar Diffuser Calibration Validation Using the Scheduled Lunar Collections" Remote Sensing 13, no. 6: 1093. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13061093
APA StyleChoi, T., & Cao, C. (2021). S-NPP VIIRS Day Night Band On-Board Solar Diffuser Calibration Validation Using the Scheduled Lunar Collections. Remote Sensing, 13(6), 1093. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13061093