Abstract
Under the transformation from over-cultivation to ecological protection in China’s karst, how human activities affect ecosystem services should be studied. This study combined satellite imagery and ecosystem models (Carnegie-Ames-Stanford Approach (CASA), Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE) and Integrated Valuation of Ecosystem Services and Trade-offs (InVEST)) to evaluate primary ecosystem services (net ecosystem productivity (NEP), soil conservation and water yield) in a typical karst region (Huanjiang County). The relationships between human activities and ecosystem services were also examined. NEP increased from 441.7 g C/m2/yr in 2005 to 582.19 g C/m2/yr in 2015. Soil conservation also increased from 4.7 ton/ha to 5.5 ton/ha. Vegetation recovery and the conversion of farmland to forest, driven largely by restoration programs, contributed to this change. A positive relationship between increases in NEP, soil conservation and rural-urban migration (r = 0.62 and 0.53, P < 0.01, respectively) indicated decreasing human dependence on land reclamation and naturally regenerated vegetation. However, declining water yield from 784.3 to 724.5 mm highlights the trade-off between carbon sequestration and water yield should be considered. Our study suggests that conservation is critical to vegetation recovery in this region and that easing human pressure on land will play an important role.
1. Introduction
Ecosystem services, the benefits that humans receive from ecosystems, are significant to supply products, system regulation and service support to human populations [1]. About 60% of ecosystem services worldwide are degraded because of anthropogenic activities, such as population growth and unsustainable economic development [2]. Carbon sequestration, soil conservation and water regulation in the degraded karst area are particularly important for regional sustainable development [3,4]. Unlike other karst regions in the world where the population is relatively sparse, high population density (about 195 people/km2) and limited arable land resources in the karst region of southwest China has caused a sharp disconnect between the human population and the landbase that should sustain them [5]. Centuries of traditional farming practices have enforced dependencies on cultivated land [6]. Unsustainable farming activities destroyed the surface vegetation and accelerated soil erosion during the 1950s to 1980s, causing ecosystem degradation including low vegetation cover and landscapes of exposed bedrock [7,8]. The fragile ecosystems (e.g., shallow soils and intense anthropogenic disturbances) in China’s karst regions have prevented natural recovery and contributed to ecosystem service degradation.
Human activities primarily affect ecosystem service function by changing land-use patterns [3,4,9,10]. Major anthropogenic activities in the karst region of southwest China include farming, logging and urban expansion [11]. Since 1998, Chinese governments have implemented a series of large-scale ecological restoration projects to recover degraded land (including the karst regions). Monitoring results using satellite images showed that China was revegetating [12,13], especially in the karst region of southwest China. However, such results from large-scale research are contentious and limited by the coarse resolution of satellite images. Many previous studies have focused on vegetation change [14,15], yet it remains to be determined if vegetation growth improves ecosystem services and the precise impact of anthropogenic activities on ecosystem services at a regional scale.
Satellite imagery is an important data source for ecosystem service assessment [14,16,17]. Images have been used to monitor land cover change, vegetation carbon sequestration, biodiversity and soil and water-related ecosystem services. Surrogate information extracted from satellite imagery (e.g., plant and soil characteristics) is used to measure spatially explicit parameters of ecosystem processes that are related to ecosystem services [3,5]. Along with other data sources, information from satellite image classification feeds ecosystem models though which ecosystem services are measured [6,16].
Analytical methods to determine ecosystem service value and physical status are in wide use [18,19]. Many studies have been conducted to assess ecosystem services using comprehensive models where the fundamentals of these services are considered [13,20,21]. Net ecosystem productivity (NEP) is a direct reflection of the carbon accumulation ability of an ecosystem [22]. NEP is the remainder of net primary productivity (NPP), once autotrophic respiration is deducted. NPP is commonly calculated using the Carnegie–Ames–Stanford Approach (CASA) model [23], and is widely used in vegetation productivity assessment. The geological origin of carbonate rocks determines the dual structure (surface runoff and vertical water loss) in hydrologic processes of karst areas. This affects the process of soil erosion and its assessment [24]. A modified Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE) was used to evaluate soil conservation and had been shown to be suitable for karst areas [25,26]. The Integrated Valuation of Ecosystem Services and Trade-offs (InVEST) model includes a module for evaluating the water yield and has been applied in many studies [27].
Along with ecosystem services evaluation, exploring ecosystem health and its potential for ecosystem services and recovery in the karst region requires more study. The fragility of the karst ecosystem and its shallow soils result in slow vegetation recovery [28,29]. Although the implementation of the ecological restoration projects improved vegetation growth, the karst ecosystem still lacks stability [30,31]. Therefore, understanding the current state of the ecosystem and its development potential might contribute to improved ecosystem services through sustainable human activities.
This research used the CASA, modified RUSLE and InVEST models to simulate and evaluate ecosystem NEP, soil conservation and water yield in a typical karst region (Huanjiang, Guangxi, China). We further analyzed the spatial–temporal changes of these three types of ecosystem services and explored their relationships with human activities. Results from this study are intended to guide ecosystem services improvement.
2. Study Area
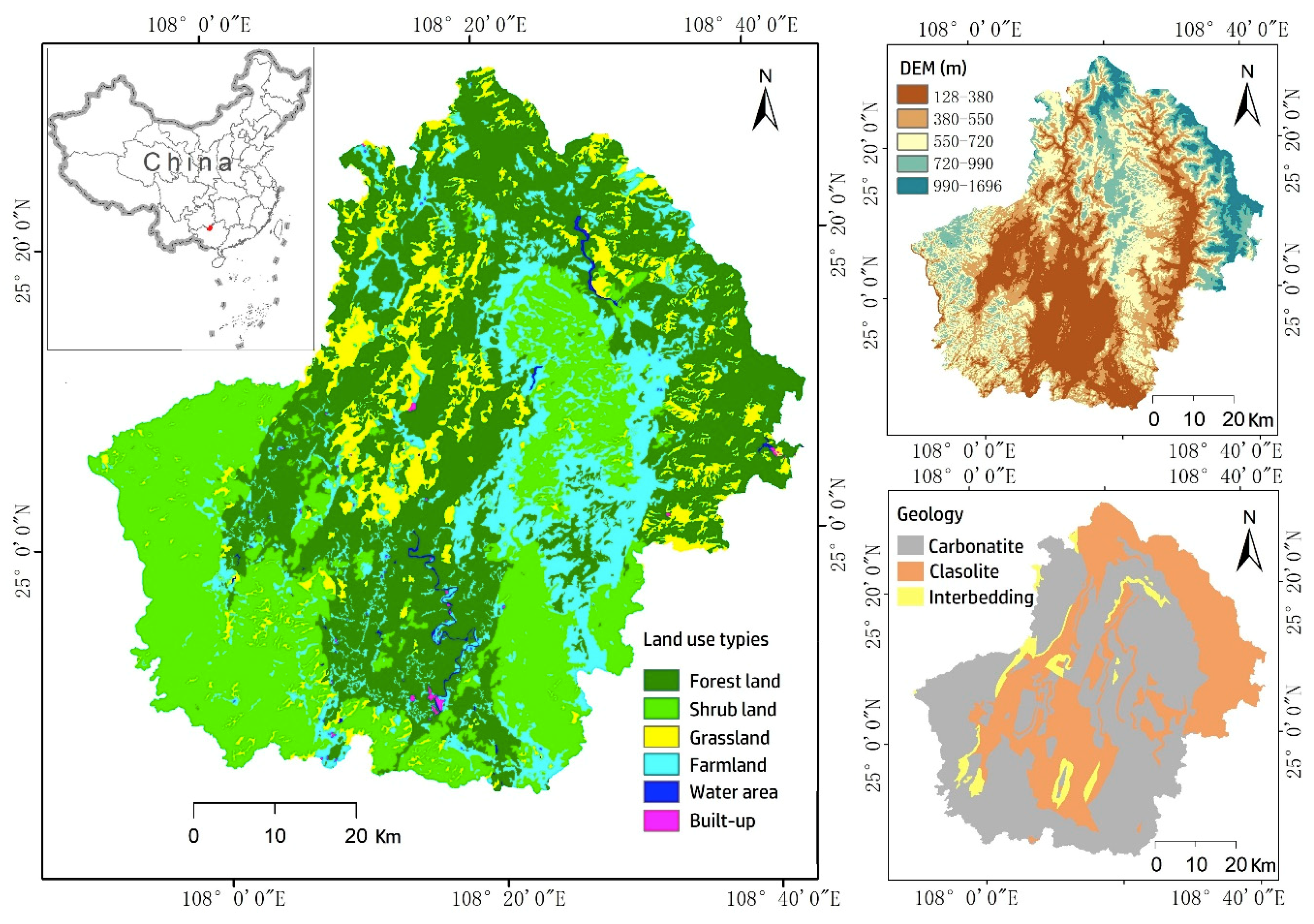
The study area, Huanjiang County, (107°51’–108°43’E, 24°44’–25°33’N) is located in the karst region of Guangxi Province, southwest China (Figure 1). The county is 4572 km2 with an elevation range of 128 to 1696 m. About half of the study area is overlain with carbonate rock, where typical landforms are depressions and tower karsts. About 60% of this area has slope angles steeper than 25°. The other half of the Huanjiang County has a clastic landform with relatively gentle hills. The climate is warm-moist subtropical, with a mean annual temperature of 19.9 °C and a mean annual precipitation of 1389 mm. Subtropical evergreen forest is the climatic vegetation community climax of this area.
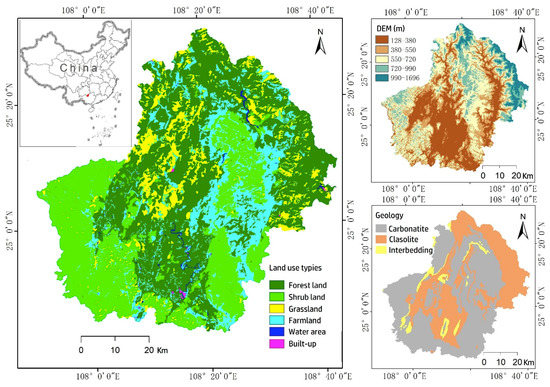
Figure 1.
Location of the study area (Huanjiang County) and its land use and cover in 2015. Elevation and geology are in the image background.
Historically, intense human disturbance on slopes has led to serious vegetation degradation. Relatively high population density (about 81 people per km2) and extensive farming on the slopes have caused the disappearance of the climax communities in this region. By the 1990s, large areas were dominated by grasses and shrubs. Vegetation change has caused serious ecological degradation including water and soil erosion and resulted in outcrops of exposed bedrock.
A series of ecosystem restoration programs were implemented beginning in the late 1990s, with the aim to rebuild the damaged ecological environment. The Green for Grain program was implemented in carbonate dominated regions, where shrubs had replaced treed, intended to convert sloped farmland to forests and reduce soil erosion. In the clastic region, programs encouraged converting grasslands to plantations and farming due to their relatively good soil condition.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Research Data
Meteorological station data from 2005 to 2015 for 64 meteorological stations in and around the study area were obtained from China Meteorological Data Network (http://data.cma.cn/ (accessed on 25 January 2021)). Weather parameters available included, but were not limited to rainfall, temperature, humidity, wind speed, air pressure and radiation. ANUSPLIN interpolation was adopted to interpolate climate parameters from regional maps. The maps were clipped using the study area boundary to obtain meteorological data in this study. DEM data were acquired from the geospatial data cloud (http://www.resdc.cn/ (accessed on 25 January 2021)) with a 30 × 30 m resolution. Landsat 5 and 8 series images in 2005 and 2015 were downloaded from the Data-sharing Network of Earth System Science, China (http://www.geodata.cn (accessed on 25 January 2021)) to extract land use data for ecosystem service assessment.
Many sources of field data from these two years were used to facilitate modeling, validation and assessment of ecosystem research. Land use data from Huanjiang County in 2005 and 2015 were extracted from Landsat series images using ERDAS IMAGINE 9.1 Software (Leica). Land use types include forest, shrub, grassland, farming land, water and built-up (Table 1). A widely used maximum likelihood classifier was applied for land use and land cover classification. Training samples on forest, shrub, grassland and agriculture land were collected based on long-term positioning observation sample sites that were established in Huanjiang County from 2002 to 2004. Training samples for water and built cover were determined based on historical landcover maps, and information from interviews with local residents was also used to confirm the land used types in 2005 and 2015. Spectral curves from training points were checked, and the separability (Jeffries-Matusita parameter) of training points of each land-use types was calculated to determine dependable training points. Finally, a total of 136 training samples (31, 40, 29, 13, 10 and 13 training points for forest, shrub, grassland, farming land, water and built, respectively) in 2005 and 147 training samples (34, 40, 31, 14, 12 and 16 training points for forest, shrub, grassland, farming land, water and built, respectively) in 2015 were determined from Landsat image classification. The combination of inverse Minimum Noise Fraction Rotation (MNF) image, Normalized Difference Moisture Index (NDMI) and Moisture Stress Index (MSI) was also used to reduce topographic effects and improve classification accuracy [32]. Testing points for accuracy assessment were generated using a stratified random approach. Class labels from 112 testing points (29, 36, 18, 13, 6 and 10 testing points for forest, shrub, grassland, farming land, water and built-up, respectively) in 2005 were determined by visual interpretation of high spatial resolution IKONOS and Spot-5 images in 2004 and 2005. Historical land cover information was also collected from interviews with local people. A total of 132 testing points (39, 46, 21, 13, 5 and 8 testing points for forest, shrub, grassland, farming land, water and built-up, respectively) in 2015 were determined using field surveys throughout Huanjiang County in 2015. Accuracy assessments were conducted using error matrices and the kappa coefficient. The overall accuracy of the land cover classification was 86.6% in 2005 and 87.9% in 2015 with respective Kappa coefficients of 0.83 and 0.84.

Table 1.
Study area classification systems.
3.2. NEP Calculation
NEP is the net primary productivity (NPP) minus the photosynthetic products consumed by heterotrophic respiration (RH):
where NPP is calculated by referring to literature sources [14], RH is calculated empirically using relevant landscapes in China [33], R is precipitation, and T is temperature.
3.3. Soil Conservation
The revised universal soil erosion model (RUSLE) is applied to simulate soil conservation [25]. It is calculated by subtracting the potential of soil erosion (assuming soil erosion on bare land), vegetation cover factor (C) and soil and water conservation factor (P) defined as the actual soil erosion (soil loss under vegetation cover; ton/ha):
where A is the average annual soil loss (ton/ha), R is the factor for annual rainfall erosivity (MJ·mm·ha−1·h−1·yr−1) [34], R is the annual rainfall duration that can be fitted based on the observed long-term rainfall data. K is the soil corrosion factor (t·ha−1·yr−1), LS is a dimensionless factor for slope, C and P are dimensionless factors related to land cover and soil conservation, which can be defined with literature values [35].
3.4. Water Yield Modeling
The evaluation of water yield was calculated using the water yield module in the InVEST model. The module is based on the water-thermal coupling equilibrium hypothesis of Budyko and the of annual average precipitation data [36]. The annual water yield Y(x) of each grid unit x (mm) in the study area was determined using Equation (4):
where Y(x) is annual water quantity (mm) in grid x, P(x) is the average annual precipitation (mm) in grid x, E(x) is the potential evapotranspiration in grid x (mm), ∆ is the slope of saturation vapor pressure and temperature (kPa·°C−1), γ is the dry-wet table constant (kPa·°C−1), Rn is net radiation, G is soil heat flux, λ is the latent heat of vaporization, U2 is wind speed, Rh is relative humidity, Es is saturation vapor pressure, is the nonphysical parameter of natural climate–soil property [24], lat is latitude, and CTI is the terrain index.
3.5. Ecosystem Health Assessment
The ecosystem health assessment of Huanjiang County is based on the pressure-state-response (PSR) framework [30,37]. This framework is the combination of the pressure (P), the state (S) and the response (R)) [38]. Human pressure can be described using indices such as landscape fragmentation and population density. PSR assesses human pressure (e.g., fragmentation, population growth), which changes the environmental conditions (i.e., the state) of the ecosystem. The state of the karst ecosystem was represented using values from the Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI), landscape diversity, average patch area, ecological service value and ecological resilience. Each index was weighted based on the analytic hierarchy process (AHP) [39], then all indices were combined into an ecosystem health (ESH) index. We used the standardized indices as input to calculate ESH:
where n is the number of indices, Wi is the weight of index i, Vi is the value of index i after standardization.
3.6. Potential Vegetation Restoration Prediction
A relatively undisturbed protected area was selected as a baseline vegetation reference point. The regression equation between vegetation and meteorological factors is established at the state when only the impact of climate change is considered. The potential NDVI of the area is calculated using this regression equation. Through comparison with real NDVI calculated by satellite images, the difference value represents the potential of vegetation restoration of the region.
Correlation analysis was conducted between monthly NDVI and climate factors from the first N (N = 0, 1, 2, 3, 4) months; we found that monthly NDVI was most significantly correlated with rainfall and average temperature in the first 0–2 months (correlation coefficient > 0.65), and most significantly correlated with average temperature in the first 0–1 months (correlation coefficient > 0.7). Both rainfall and temperature have a hysteresis effect, with rainfall lagging by about 2 months and temperature lagging by about 1 month. Therefore, rainfall in the first 2 months and average temperature in the first 1 month of the year were used as input factors in the potential NDVI model in the simulation of potential vegetation growth. The regression equation between the pixel-based NDVI and climate factor combination (rainfall and temperature) is determined as:
where Yndvi is the monthly NDVI value, P is the rainfall and in the first months, T is the average temperature in the first 1 month and a, b and c are the fitting coefficients.
4. Results
4.1. Ecosystem Services Evaluation
4.1.1. NEP and Its Change
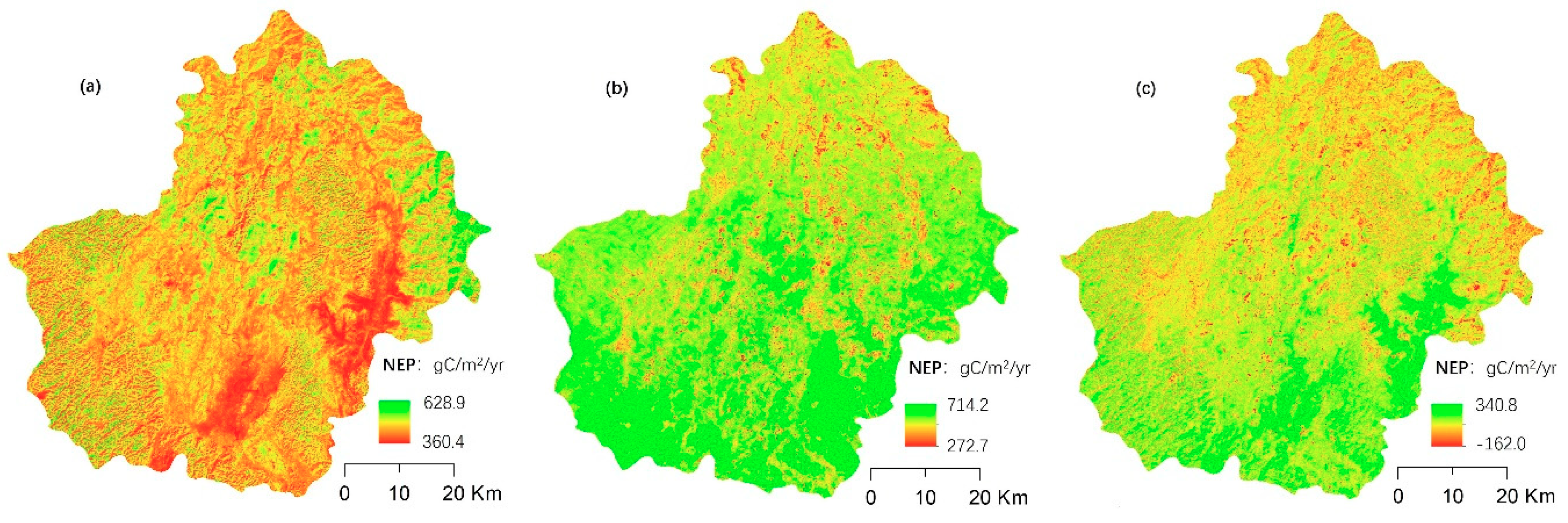
NEP increased from 2005 to 2015 (Figure 2). The mean accumulation rate of ecosystem carbon was 441.7 and 582.19 g C/m2/yr in 2005 and 2015, respectively, increasing by 12.77 g C/m2/yr during the study period. The spatial distribution of NEP was higher in the east of the study area in 2005, where patches of water conservation forest, that had been protected by the government since the 1980s, was located. In contrast, NEP was lower in two areas near the southeast of the study region where there was a relatively large area of cropland and forest plantation (Figure 1). The distribution of NEP changed in 2015, with most areas increasing significantly, especially in the south of the study area.
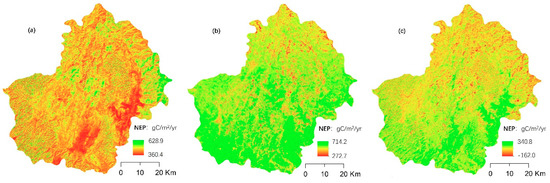
Figure 2.
Spatial distribution of net ecosystem productivity (NEP) and its change in Huanjiang County. (a) The distribution of NEP in 2005; (b) the distribution of NEP in 2015; (c) the changes of NEP from 2005 to 2015.
From 2005 to 2015, NEP significantly increased in the southeast and southwest portions of the study region. Increasing vegetated land cover in the southeast, which contributed to the NEP increase, appeared to have been caused by a reduction in intensive agriculture or farming practice changes. In the southeast, large mountains with exposed rock and shrubs are found and vegetation may have recovered naturally during this period. NEP decreased to some extent in the north and central areas. However, the area of decreased NEP only accounted for 2.8% of the whole study area.
4.1.2. Soil Conservation and Its Change
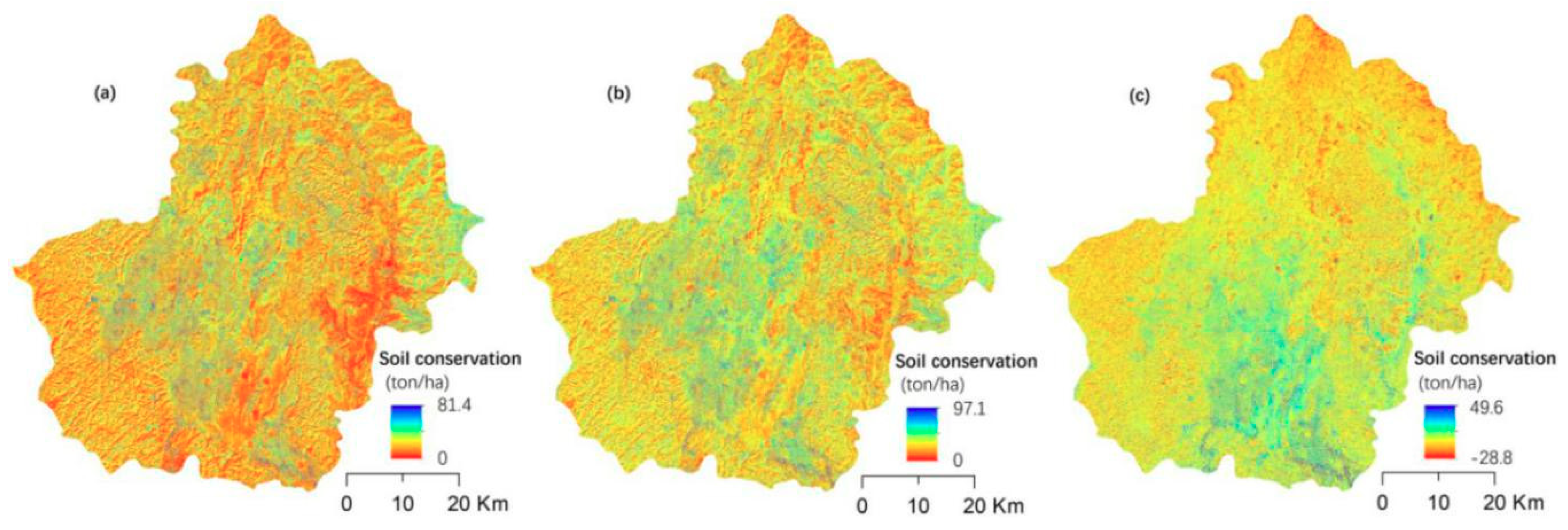
The average annual soil conservation in Huanjiang County increased from 4.7 ton/ha in 2005 to 5.5 ton/ha in 2015, while the value of average annual soil conservation increased by 0.8 ton/ha from 2005 to 2015 (Figure 3). Regions with higher soil conservation were mainly located in the center of the study area during both study periods. The apparent reason for this is that the center of the study area is hilly with gradual slopes and thicker soil, thus tending towards soil recovery. In comparison, rugged mountains with exposed rock are in the southwest of Huanjiang County. Changes in soil conservation showed that areas with increased soil retention amount accounted for 81.92% of the study area, and only 18.08% of the study area remained unchanged or showed a small decline. Regions with improved soil conservation were mainly located in the central regions. Another improvement occurred in two regions in the southeast of the study area where about half of sugarcane and corn fields were converted to fruit and mulberry fields during the study period.
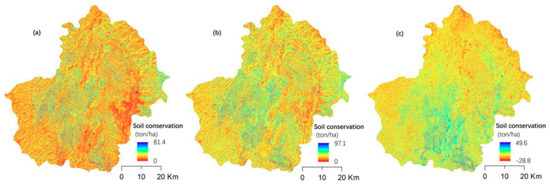
Figure 3.
Spatial distribution of soil conservation and its change in Huanjiang County. (a) The distribution of soil conservation in 2005; (b) The distribution of soil conservation in 2015; (c) the changes of soil conservation from 2005 to 2015.
4.1.3. Water Yield and Its Change
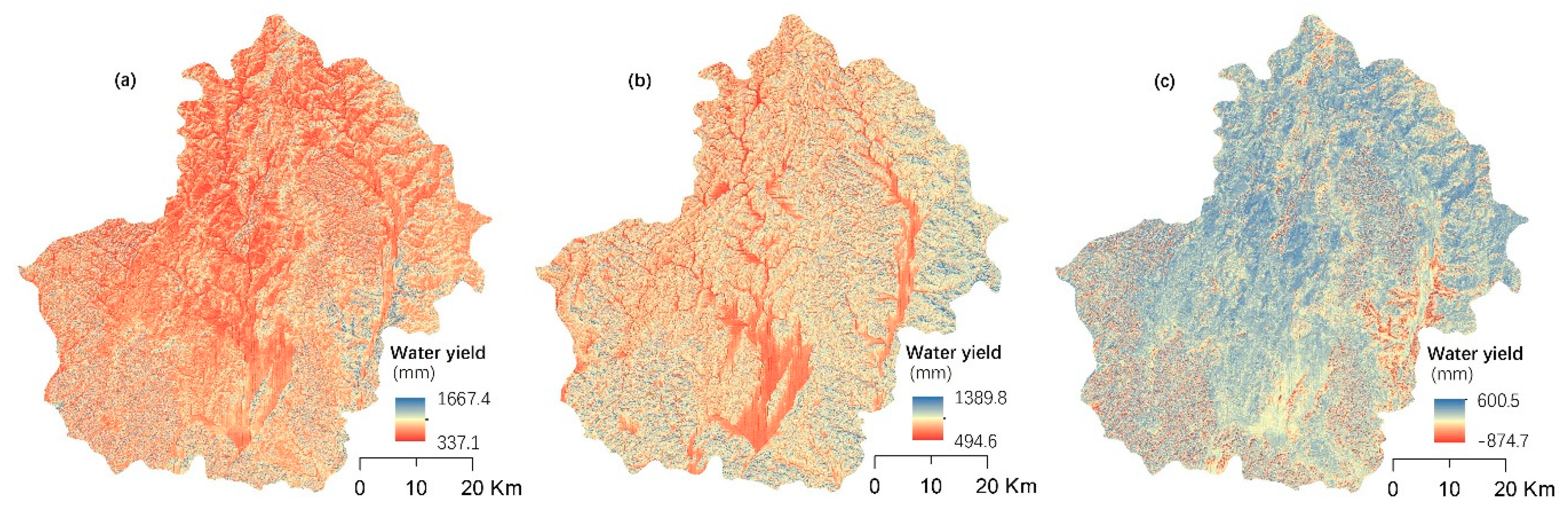
There was a downward trend in water yield from 2005 to 2015 in the study area (Figure 4) with an average annual water yield of 784.3 mm in 2005 and 724.5 mm in 2015. The spatial distribution of water yield in the study area are basically consistent between 2005 and 2015. Areas with higher water yield were mainly concentrated in the southeast and southwest of the study area, where rugged mountains are located. This suggests that high slopes may be favorable for water yield. The regions with poor water yield are mainly the central and northwest of the research areas where the slopes are gentle and where most of the forest plantation, cropland and grassland were found in 2005 and 2015. However, changes in water yield showed that the capacity of water yield increased in the central and north of the study area from 2005 to 2015. In contrast, water yield in the southeast and southwest of the study region decreased during this period.
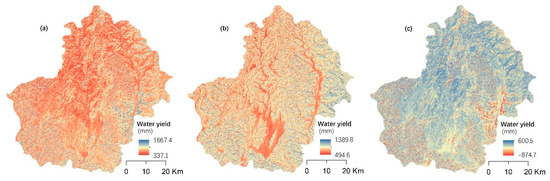
Figure 4.
Spatial distribution of water yield and its change in Huanjiang County. (a) The distribution of water yield in 2005; (b) the distribution of water yield in 2015; (c) the changes of water yield from 2005 to 2015.
4.2. Ecosystem Health in Huanjiang County
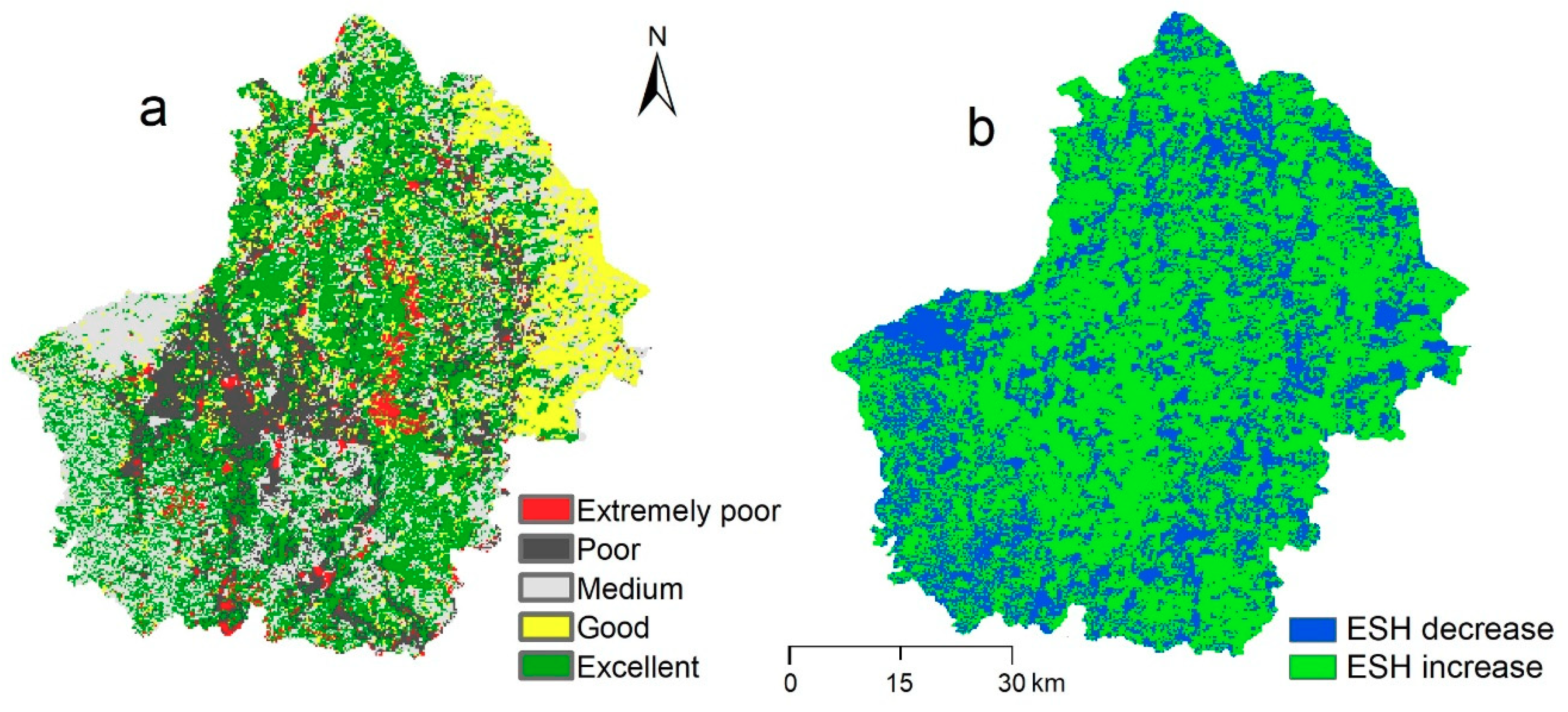
The areas with poor ESH are scattered and mainly distributed in the center of the study area (Figure 5a). The proportions of areas with high ESH (greater than 0.7) increased by 3% from 2005 to 2015 (from 71.06% to 74.32%) during the 11-year period. The area with low ESH (less than 0.2) decreased by about 4% (from 10.89% to 7.12%) (Figure 5b). Overall, 66.72% of the pixels showed an increase in ESH, and 33.28% of the total area had a decreasing ESH.
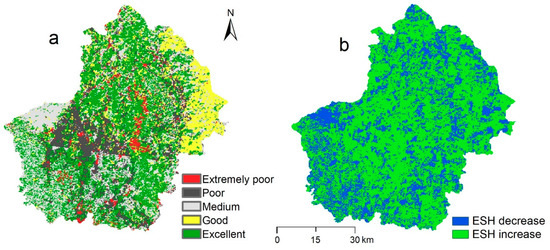
Figure 5.
ESH assessment for the study area. (a) is the ESH index for 2005; (b) is the changes in ESH between 2005 and 2015.
4.3. Potential for Vegetation Recovery
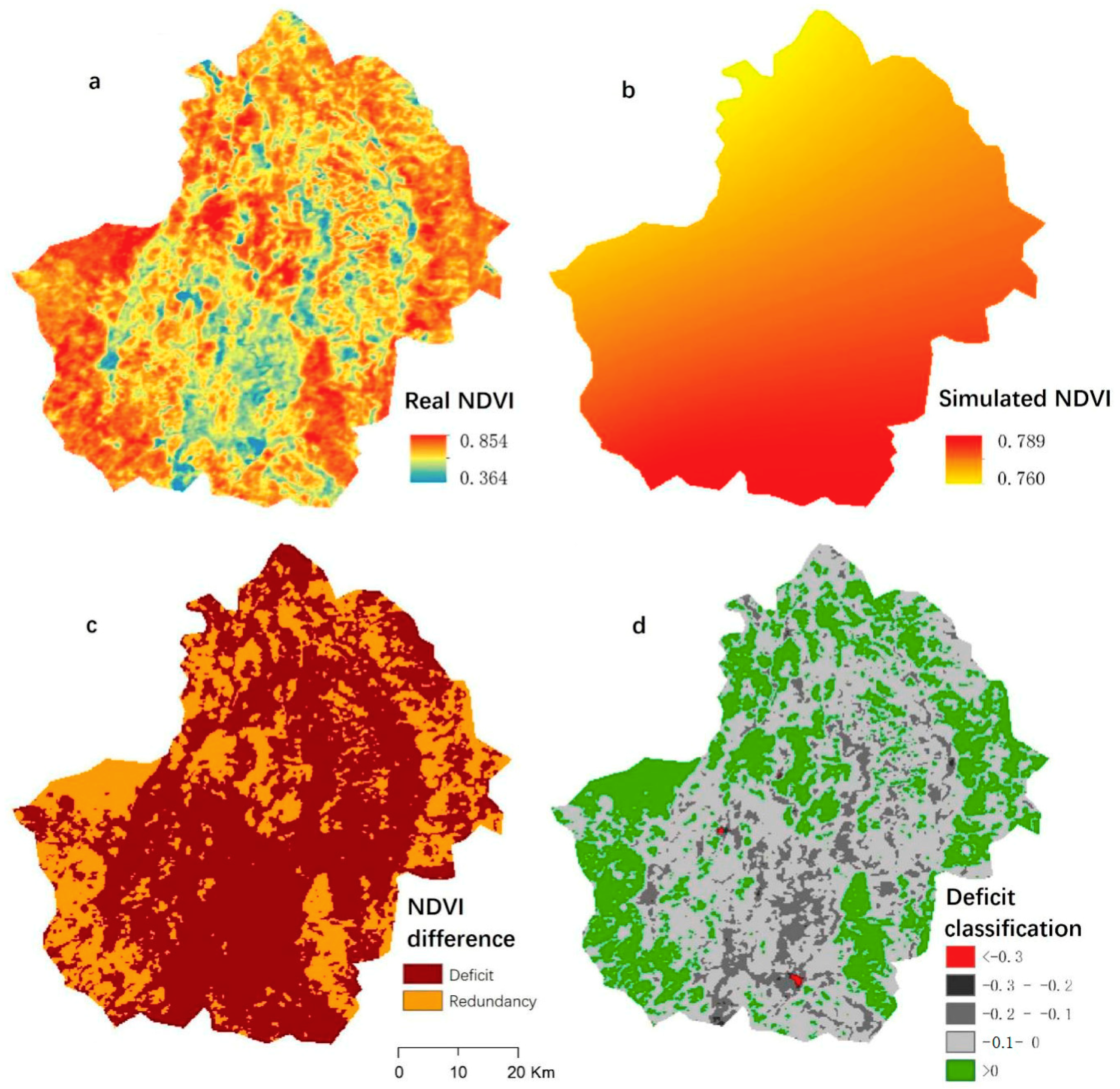
Throughout the study area, 75.29% had a vegetation deficit to varying degrees (NDVIdifference < 0) (Figure 6d). Of the area with vegetation deficit, 0.27% had an extremely serious vegetation deficit (NDVIdifference < −0.3); mostly around towns and cities. Across the study area, 1.41% had a relatively serious vegetation deficit (−0.3 < NDVIdifference < −0.1) (Figure 6). Of these areas, 58.20% had a relatively small vegetation deficit (−0.1 < NDVIdifference < 0) (Figure 6d) that were mainly distributed in the south-center of the study area. Generally, most of the vegetation deficits occurred in and around towns, indicating that human activities in high-density population areas continued to significantly affect vegetation restoration. In contrast, vegetation recovery was mainly located in the southwest of the study area, indicating successful vegetation protection.
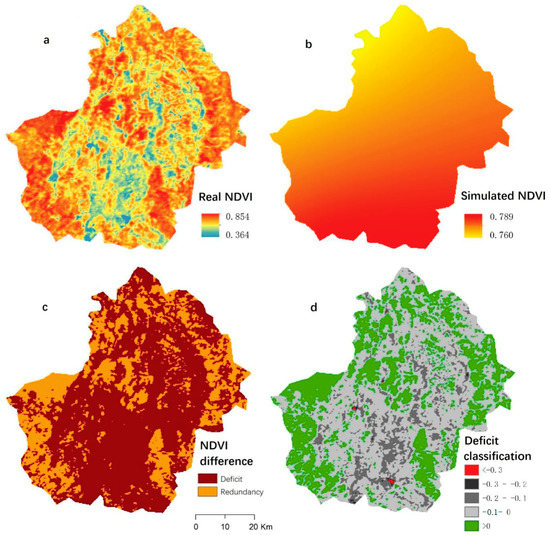
Figure 6.
Spatial distribution of potential vegetation. (a) is the real vegetational NDVI in 2015; (b) is the simulated vegetational NDVI; (c) is the differences between (a) and (b); (d) is the classification of vegetation deficit.
5. Discussion
5.1. Increased Ecosystem Services via Ecological Restoration Programs
As a link between human populations and nature, ecosystem services and their changes show strong feedback loops with human activities (land-use changes) and natural conditions [11,40,41]. The improvement in NEP and soil conservation appeared to be the result of vegetation recovery in the study area as land-use changed (Table 2). Shrub covered land was dominant, taking up about half (49.42%) of the study area in 2005. A positive vegetational succession occurred from 2005 to 2015, and grassland and shrubs were largely converted into shrub and forested land, respectively. Grassland decreased by 202.3 km2 (38.69%), and the forests increased by 347.77 km2 (33.55%). Positive vegetation succession always increased vegetation biomass, soil carbon accumulation, water and soil retention [28,29]. At the same time farmland area decreased by 165.72 km2 (23.18%), with most being converted into forest plantations.

Table 2.
Land-use changes in Huanjiang County from 2005 to 2015.
The implementation of an ecological conservation program could explain the significant vegetation recovery that improved ecosystem carbon sequestration and soil conservation in this typical karst region. Due to the fragility of the ecological environment and intense human activities, serious vegetation degradation occurred in this karst region during 1950s to 1990s. The government enforced policy of closing mountains to development which prohibited deforestation, forest burning and agricultural activities for vegetation recovery appeared to have been successful [42]. Local residents who violated the ban were fined. Despite initial resistance from villagers, the promotion of environmental protection awareness and enforcement led to gradual compliance. In addition, the local government invested money into a biogas generation system that improved the power grid for residents, reducing demand for fuel wood and lowering vegetation disturbance [32]. The results of land-use changes indicated that about one third of vegetated area in the study area recovered from 2005 to 2015.
The Grain to Green program was also active in the karst region that promoted the conversion of crops on steep slopes into forests since 1999 [14,32]. The cultivation of slopes has caused serious vegetation degradation and soil erosion [3]. To prevent further environmental deterioration, local farmers were required to abandon sloped field, replaced by grain and financial subsidies from the government. The local government spent 0.8–1.3 million Yuan (6.6 Yuan equals 1 Dollar) annually as subsidies to implement this program [14]. Reforestation of the abandoned slopes in our study resulted in about a quarter of farmland being converted into forests.
Although NEP and soil conservation have improved in the study area, a simultaneous decline of water yield occurred in this period. A field-based study showed that soil conservation and water yield in the karst region in southwest China gradually increased due to vegetation growth [43]. However, studies focused on large-scale afforestation indicated that an increase in forest plantation cover in southwest China significantly promoted land-surface evapotranspiration resulting in the decrease in regional soil moisture [44,45]. It is possible that the rapid growth of plantations (i.e., Eucalyptus and Masson’s Pine) in this karst region consumed and transpired more water [31]. The increase in NEP was strongly correlated with vegetation recovery, soil carbon sequestration and soil conservation suggesting a trade-off between NEP, soil conservation and water yield. Therefore, the promotion of ecosystem services and its trade-off should be considered simultaneously.
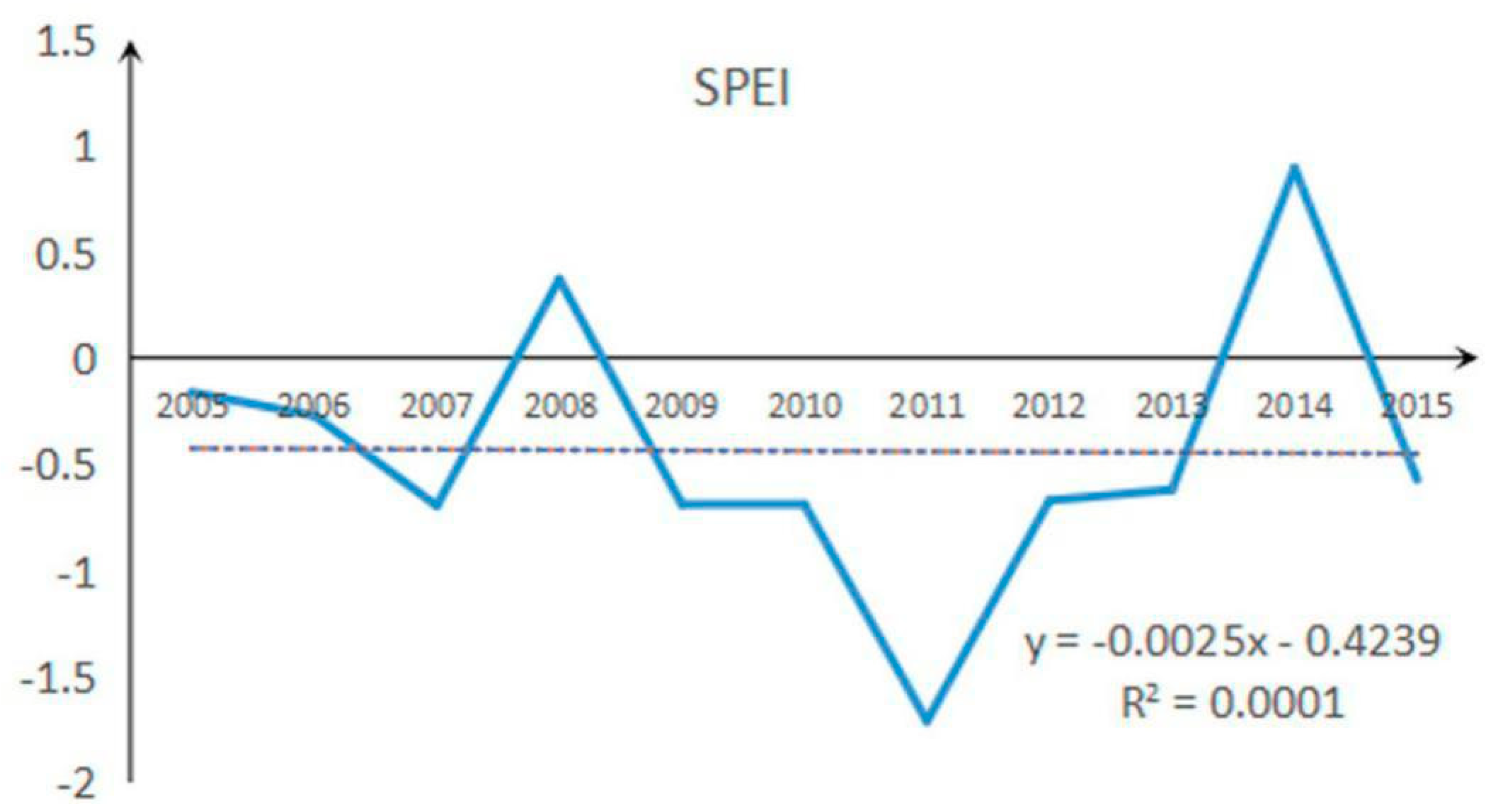
Compared with the implementation of ecological conservation programs, climate conditions did not significantly favor vegetation growth in the study area. The Standardized Precipitation Evapotranspiration Index in the study area had a negative trend from 2005 to 2015. Indeed, most of its values were negative (Figure 7), indicating adverse climatic conditions in the study area and is consistent with conditions in previous studies [21,46]. This further demonstrates that ecological engineering significantly promoted better vegetation recovery (NEP and soil conservation) under adverse climatic conditions in the karst areas of southwest China. However, irrespective of whether the climate in the karst region will limit vegetation, active restoration methods should be considered in future research.
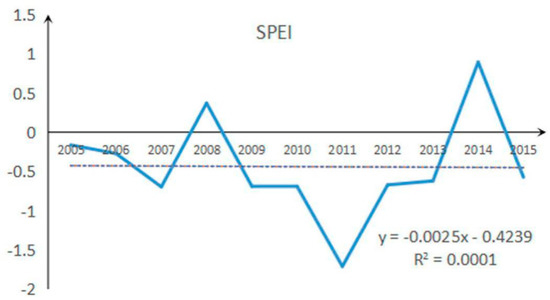
Figure 7.
Standardized Precipitation Evapotranspiration Index (SPEI) and its changes during the study period.
One possible deficiency of our study is that the distribution and variation of hydrology in the karst region was not specifically included in the design. Because of the highly fragile karst landscape and the dual hydrologic structure above- and belowground in the karst region, surface water may flow through underground pipes, magnifying errors or uncertainties of water yield estimation [47]. Hence, more long-term observations of water use efficiency of plants, underground vertical drainage and soil moisture should be conducted to better understand the water yield in this karst region.
5.2. Ongoing Outmigration Reduced Ecosystem Disturbance
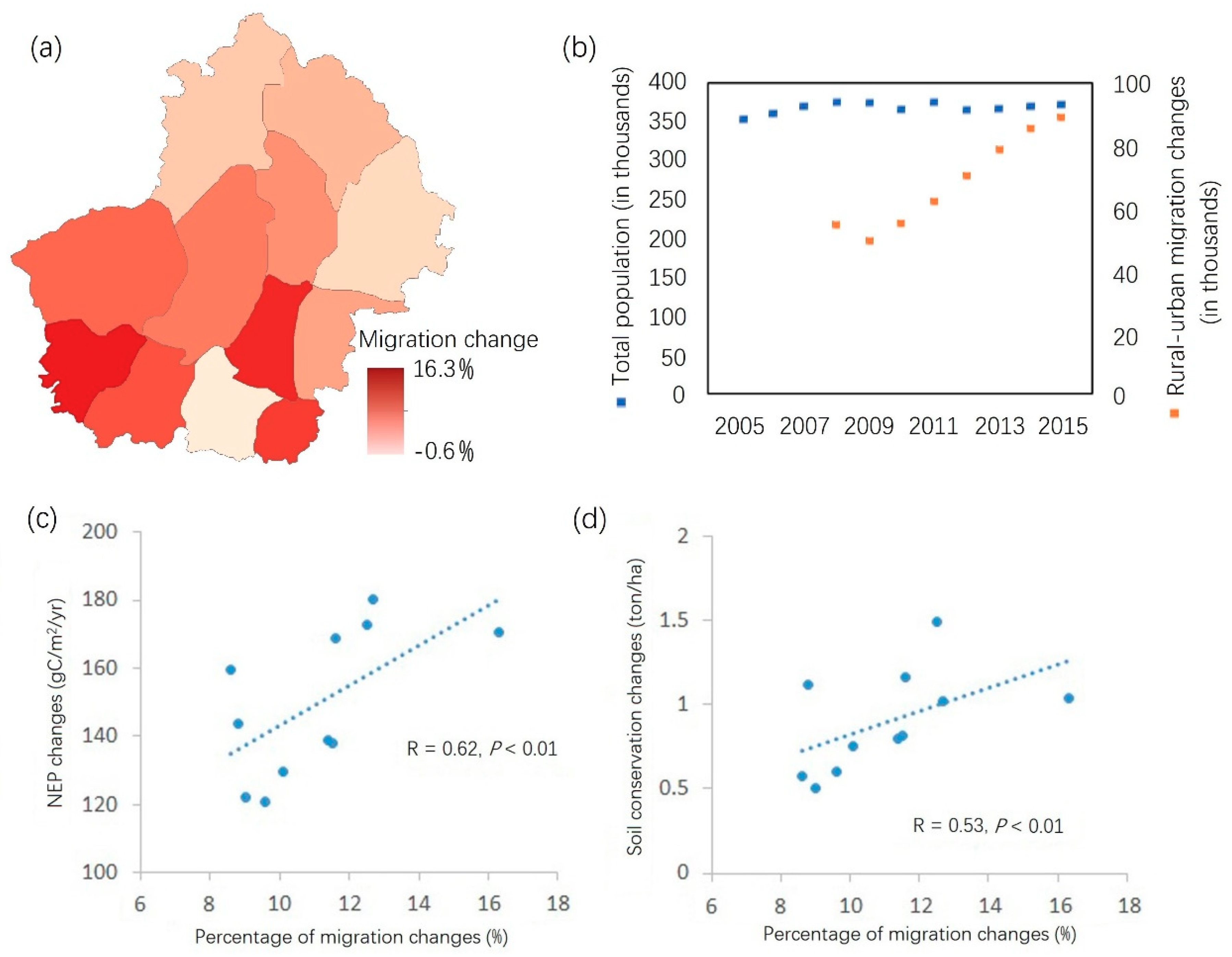
The outmigration of residents from rural to urban areas for work opportunities greatly reduced the human pressure on our study area’s natural landscapes and influenced the changes we observed in ecosystem services. The implementation of ecological projects promoted by the government, enabled the voluntary movements of rural residents; the numbers of outmigrants increased from 2008 to 2015 (Figure 8b). The percentage of migrants out the total population, accounting for 13.1% in 2008, increased to 21.6% in 2015. In fact, the real number of migrants is likely larger because this statistic only shows the number of people who spent more than half of the year working outside the home. Some people only went to city to work a few months each year.
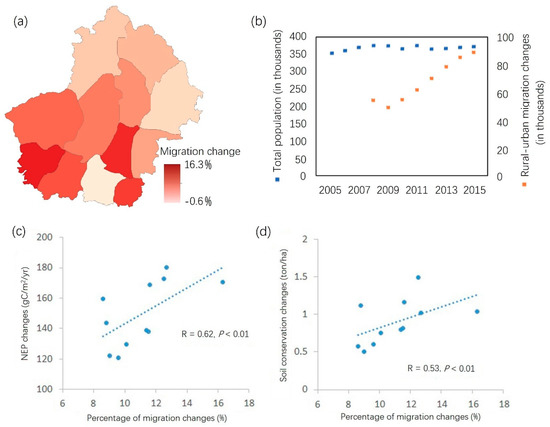
Figure 8.
Changes in rural–urban migration from 2005 to 2015 and its correlation with ecosystem services in the Huanjiang County. (a) The distribution of the percentage of rural-urban migration changes from 2005 to 2015; (b) comparison of total population and rural–urban migration; (c,d) correlations between the percentage of rural-urban migration changes and ecosystem services.
In Huanjiang County, the percentage of outmigration out of the total population increased from 8.8% to 16.3% from 2005 to 2015 in eleven townships. The exception was in the town where the county government is seated (−0.6%). This significant relationship nevertheless shows that NEP (correlation index = 0.62) and soil conservation (correlation index = 0.53) was positively correlated with rural–urban migration (Figure 8c,d). This showed that townships with higher percentages of migrants had reduced human pressures on the natural environment. Those who moved to the city for work opportunities improved their earning potential and living conditions over that possible by relying on farming for a living [42]. Consequently, high rates of soil erosion on slopes in rural areas was reduced as rural residents gave up farming entirely to work in the city year-round.
Some cultivated land was converted into forest plantations by farmers, effectively reducing crop rotations and allowing time for rural residents to travel for work. This change is demonstrated by the decreasing area of cropland in the study area. Deceasing farming activities ultimately reduced soil disturbance and facilitated soil carbon sequestration. water and soil conservation in this karst region [26,29]. Regions in the southwest of the study area have a typical karst environment (rugged terrain, shallow soil and fragile ecosystem) that is extremely sensitive to disturbance [48]. However, as with our study, the relatively high rural–urban migration in this region contributed to fewer disturbances and significantly improved ecosystem services (Figure 2, Figure 3 and Figure 8a).
5.3. Ecosystem Services Improvement through Vegetation Recovery
Vegetation recovery likely played a critical role in the improvement of NEP, water and soil conservation. Although land-use changes reflected a positive vegetation succession (vegetation recovery) in the study area, 75.29% appear vegetation-deficient. The characteristics of shallow soils, rapid hydrological drainage and fragile ecosystems in the karst region of southwest China slowed vegetation recovery [6]. That 33.28% of total areas had decreasing ESH contributed to ongoing ecosystem degradation; the majority of the local residents are still highly dependent on farming activities for a living. Centuries of traditional farming practices cannot be overturned in 11 years [4]. However, our study may help focus environmental managers’ attention to key problematic areas with decreasing ESH. In karst regions, minimizing soil disturbances is critical for soil conservation, vegetation restoration and sustainable agricultural development [5,6]. Converting annual crops to perennial forage grass, mulberry or natural vegetation reduce soil disturbance frequency and are the most effective methods to prevent water and soil erosion [29]. The value generated from forage grass and mulberry has the potential to increase income and improve the supply of services to residents of karst ecosystems.
6. Conclusions
The implementation of ecological restoration programs led by Chinese governments and the trend of outmigration effectively changed land use and land cover. This led to increased forested land and decreased cropped and grassland areas in the karst region of southwest China. This contributed to improved carbon sequestration and soil conservation.
Huanjiang County was a carbon sink from 2005 to 2015, as the average annual NEP increased from 441.7 g C/m2/yr in 2005 to 582.19 g C/m2/yr in 2015. Soil conservation also increased from 4.7 ton/ha to 5.5 ton/ha during the study period. However, water yield decreased from 784.3 mm to 724.5 mm at the same time. The NEP and soil conservation are in a synergic relationship. The increase in NEP was highly correlated with vegetation recovery, soil carbon sequestration and soil conservation. A trade-off relationship exists between NEP, soil conservation and water yield. The rapid growth of planted forest may increase demand on water sources, causing declining water yield in the karst region. An increment of NEP and soil conservation decreased quantitative water yield.
An ecological health assessment showed that though vegetation recovered during the last 11 years, EHS of 33.28% over the total study area decreased, signifying the existence of overexploitation in this region. The ongoing dominance of shrub cover indicates the low stability of the karst ecosystem yet a significant potential for vegetation recovery.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, X.Q., Y.Y. C.Z. and K.W.; Formal analysis, X.Q. and M.Z.; Funding acquisition, X.Q. and Y.Y.; Methodology, Q.L., L.Z., X.Z. and C.L.; writing—original draft, X.Q.; writing—review and editing, X.Q., Y.Y., C.Z. and Y.X. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Key Research and Development Program (2016YFC0502400, 2016YFC0502501, 2018YFD1100103, 2017YFC0505606), the Strategic Priority Research Program of Chinese Academy of Sciences (XDA19050502), and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41930652, U20A2048, 41501206).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
We appreciate the constructive comments and suggestions from the reviewers that helped improve the quality of this manuscript. We also would like to offer our sincere thanks to those who participated in the data processing and manuscript revisions.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Cord, A.F.; Seppelt, R.; Turner, W. Sustainable development goals:monitor ecosystem services from space. Nature 2015, 33, 525–533. [Google Scholar]
- Joppa, L.N.; Boyd, J.W.; Duke, C.S.; Hampton, S.; Jackson, S.T.; Jacobs, K.L.; Kassam, K.A.S.; Mooney, H.A.; Ogden, L.A.; Ruckelshaus, M.; et al. Government: Plan for ecosystem services. Science 2016, 351, 1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.C.; Wang, S.J.; Bai, X.Y.; Luo, G.J.; Xu, Y. Trade-offs among ecosystem services in a typical karst watershed, SW China. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 566–567, 1297–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.Y.; Wang, K.L.; Liu, H.Y.; Zhang, C.H.; Yue, Y.M.; Qi, X.K. Effect of ecological engineering projects on ecosystem services in a karst region: A case study of northwest guangxi, china. J. Clean Prod. 2018, 183, 831–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.C.; Lian, Y.Q.; Qin, X.Q. Rocky desertification in Southwest China: Impacts, causes, and restoration. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2014, 132, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Y.M.; Wang, K.L.; Zhang, B.; Jiao, Q.J.; Liu, B.; Zhang, M.Y. Remote sensing of fractional cover of vegetation and exposed bedrock for karst rocky desertification assessment. Proc. Environ. Sci. 2012, 13, 847–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.H.; Qi, X.K.; Wang, K.L.; Zhang, M.Y.; Yue, Y.M. The application of geospatial techniques in monitoring karst vegetation recovery in southwest China: A review. Prog. Phys. Geogr. 2017, 41, 450–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.L.; Zhang, C.H.; Chen, H.S.; Yue, Y.M.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, M.Y.; Qi, X.K.; Fu, Z.Y. Karst landscapes of China: Patterns, ecosystem processes and services. Landsc. Ecol. 2019, 34, 2743–2763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, Z.Y.; Zheng, H.; Xiao, Y.; Polasky, S.; Liu, J.G.; Xu, W.H.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, L.; Xiao, Y.; Rao, E.M.; et al. Improvements in ecosystem services from investments in natural capital. Science 2016, 352, 1455–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterling, S.M.; Ducharne, A.; Polcher, J. The impact of global land-cover change on the terrestrial water cycle. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2012, 3, 35–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, L.; Song, T.; Du, H.; Wang, K.; Peng, W.; Zeng, F.; Zeng, Z.; He, T. The succession charactersitcs and its driving mechanism of plant community in karst region, southwest China. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2015, 35, 5822–5833, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Tong, X.W.; Brandt, M.; Yue, Y.M.; Horion, S.; Wang, K.L.; Wanda, D.K.; Tian, F.; Schurgers, G.; Xiao, X.M.; Luo, Y.Q.; et al. Increased vegetation growth and carbon stock in China karst via ecological engineering. Nat. Sustain. 2018, 1, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marc, M.F. Satellite images show China going green. Nature 2018, 553, 411–413. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Wang, K.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, C. Impacts of climate change and human activities on vegetation cover in hilly southern China. Ecol. Eng. 2015, 81, 451–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, X.K.; Wang, K.L.; Zhang, C.H. Comparing Remote Sensing Methods for Monitoring Karst Rocky Desertification at Sub-pixel Scales in a Highly Heterogeneous Karst Region. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, H.; Zuo, L. Identification of Dominant Factors Affecting Soil Erosion and Water Yield within Ecological Red Line Areas. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, D.; Shi, Y.; Wu, Q.; Fang, R. Multidimensional Assessment of Food Provisioning Ecosystem Services Using Remote Sensing and Agricultural Statistics. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharps, K.; Masante, D.; Thomas, A.R.C.; Jackson, B.M.; Cosby, B.J.; Emmet, B.A.; Jones, L. Comparing strengths and weaknesses of three ecosystem services modelling tools in a diverse UK river catchment. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 584, 118–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.J.; Wu, T.; Li, Y.Z.; Xie, S.L.; Han, B.L.; Zheng, H.; Ouyang, Z.Y. Urbanization impacts on natural habitat and ecosystem services in the guangdong-hong kong-macao “megacity”. Sustainability 2020, 12, 6675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costanza, R.; d’Arge, R.; deGroot, R.; Farber, S.; Grasso, M.; Hannon, B.; Limburg, K.; Naeem, S.; O’Neil, R.V.; Paruelo, J. The value of the world’s ecosystem services and natural capital. Nature 1997, 387, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.Y.; Wang, K.L.; Liu, H.Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, C.H.; Yue, Y.M.; Qi, X.K. Spatio-Temporal variation and impact factors for vegetation carbon sequestration and oxygen production based on rocky desertifification control in the karst region of Southwest China. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imhoff, M.L.; Bounoua, L.; Ricketts, T.; Loucks, C.; Harriss, R.; Lawrence, W.T. Global patterns in human consumption of net primary production. Nature 2004, 249, 870–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potter, C.S.; Randerson, J.T.; Field, C.B.; Matson, P.A.; Vitousek, P.M.; Mooney, H.A.; Klooster, S.A. Terrestrial ecosystem production: A process model based on global satellite and surface data. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycle 1993, 7, 811–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.L.; Liu, W.; Scanlon, B.R.; Zhang, L.; Pan, M. Local and global factors controlling water-energy balances within the Budyko framework. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2013, 40, 6123–6129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.M.; Fu, B.J.; Lu, N.; Zeng, Y.; Wu, B.F. How ecological restoration alters ecosystem services:an analysis of carbon sequestration in China’s Loess Plateau. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 2846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.S.; Hu, K.; Nie, Y.P.; Wang, K.L. Analysis of soil water movement inside a footslope and a depression in a karst catchment, Southwest China. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 2544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawler, J.J.; Lewis, D.J.; Nelson, E.; Plantinga, A.J.; Polasky, S.; Withey, J.C.; Helmers, D.P.; Martinuzzi, S.; Pennington, D.; Radeloff, V.R. Projected land-use change impacts on ecosystem services in the United States. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 7492–7497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, H.; Hu, F.; Zeng, F.P.; Wang, K.L.; Peng, W.X.; Zhang, H.; Zeng, Z.X.; Zhang, F.; Song, T.Q. Spatial distribution of tree species in evergreen-deciduous broadleaf karst forests in southwest china. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 15664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, P.L.; Liu, S.J.; Ye, Y.Y.; Zhang, W.; Wang, K.L.; Su, Y.R. Effects of environmental factors on soil organic carbon under natural or managed vegetation restoration. Land Degrad. Dev. 2018, 29, 387–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, C.J.; Yue, Y.M.; Wang, K.L.; Fensholt, R.; Tong, W.X.; Brandt, M. Ecological restoration enhances ecosystem health in the karst regions of southwest china. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 90, 416–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, X.W.; Brandt, M.; Yue, Y.M.; Ciais, P.; Fensholt, R. Forest management in southern China generates short term extensive carbon sequestration. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, X.K.; Wang, K.L.; Zhang, C.H. Effectiveness of ecological restoration projects in a karst region of southwest china assessed using vegetation succession mapping. Ecol. Eng. 2013, 54, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Jiang, Y.; Li, Z.Y.; Zhang, N.; Hu, M. Estimation of vegetation net primary productivity and carbon sink in western Jilin province based on CASA model. J. Arid Land Resour. Environ. 2013, 27, 1–7, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Wischmeier, W.H. Predicting rainfall erosion losses-a guide to conservation planning. In Agriculture Handbook; US Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 1978; p. 537. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.M.; Peng, J.; Shao, X.M. Assessment of soil erosion using rusle and gis: A case study of the maotiao river watershed, guizhou province, hina. Environ. Geol. 2009, 72, 2217–2217. [Google Scholar]
- Hamel, P.; Guswa, A.J. Uncertainty analysis of a spatially explicit annual water-balance model: Case study of the Cape Fear basin, North Carolina. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2015, 19, 839–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walz, R. Development of environmental indicator systems:experiences from Germany. Environ. Manag. 2000, 25, 613–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neri, A.C.; Dupin, P.; Sánchez, L.E. A pressure-state-response approach to cumulative impact assessment. J. Clean Prod. 2016, 126, 288–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.T.; Lin, W.P.; Chen, G.S.; Guo, P.P.; Zeng, Y. Wetland ecosystem health assessment through integrating remote sensing and inventory data with an assessment model for the Hangzhou Bay, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 566, 627–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costanza, R.; de Groot, R.; Braat, L.; Kubiszewski, L.; Fioramonti, L.; Sutton, P.; Farber, S.; Grasso, M. Twenty years of ecosystem services: How far have we come and how far do we still need to go? Ecosyst. Serv. 2017, 28, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, C.H.; Fu, B.J.; He, C.S.; Lü, Y.H. Variation of ecosystem services and human activities: A case study in the Yanhe watershed of China. Acta Oecol. 2012, 44, 46–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.Y.; Wang, K.L.; Liu, H.Y.; Zhang, C.H.; Wang, K.L.; Yue, Y.M.; Qi, X.K. How ecological restoration alters ecosystem services: An analysis of vegetation carbon sequestration in the karst area of northwest Guangxi, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 74, 5307–5317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, Y.P.; Chen, H.S.; Wang, K.L.; Yang, J. Water source utilization by woody plants growing on dolomite outcrops and nearby soils during dry seasons in karst region of Southwest China. J. Hydrol. 2012, 420, 264–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, H.; Yang, X.; Wang, K.; Xiao, L. Is forest restoration in the southwest china karst promoted mainly by climate change or human-induced factors? Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 9895–9910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Piao, S.L.; Li, L.Z.X.; Chen, A.P.; Wang, X.H.; Ciais, P.; Huang, L.; Lian, X.; Peng, S.S.; Zeng, Z.Z.; et al. Divergent hydrological response to large-scale afforestation and vegetation greening in China. Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, eaar4182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, X.W.; Wang, K.L.; Yue, Y.M.; Brandt, M.; Liu, B.; Zhang, C.H.; Liao, C.J.; Fensholt, R. Quantifying the effectiveness of ecological restoration projects on long-term vegetation dynamics in the karst regions of Southwest China. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2017, 54, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Wei, H.; Liang, S.L.; Zhou, T.; He, B.; Tang, B.J.; Wu, D.H. Responses of natural vegetation to different stages of extreme drought during 2009–2010 in southwestern China. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 14039–14054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, W.; Wu, M.; Ye, Y.; Wang, K.; Li, D. Changes in soil nitrogen stocks following vegetation restoration in a typical karst catchment. Land Degrad. Dev. 2019, 30, 60–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).